3.2.1 Enthalpy changes
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
enthaly change
is the heat energy transferred in a reaction at constant ressure ∆H
standard conditions for enthaly changes
100kPa
298K
ΔH°
standard states
hysical states of reactants under standard conditions
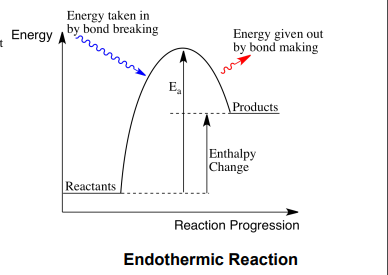
endthermic reaction
when energy is taken in from the surroundings so roducts have more energy than reactants heat taken in
endothermic enthaly change
ositive
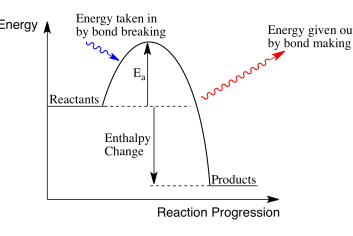
exothermic reaction
when energy is released to surroundings roducts have less energy than reactants heat is given out
enthaly change of exothermic reaction
negative
overall enthaly change equation
energy needed to break bonds(reactants - energy released making bonds (roducts
activation energy
minimimum amiunt of energy for a chemical reaction to tak lave
activation energy on enthaly rofile diagrm
difference btween reactants and to of hum
exothermic enthaly rofile diagram
endothermic enthaly rofile diagram
standard enthaly change of reaction
∆r H
enthaly change when a reaction occurs in the molar quantities shown in the chemical equation under standard conditions with all reactants and roducts in their standard states
standard enthaly change of fromation
∆f H
enthaly change when 1 mole of a comound is formed from its elements in their standard states under standard conditions
standard enthaly change of combustion
∆c H
enthaly change when 1 mole of a substance is comletely burned in oxygen under standard conditions with all reactants and roducts in their standard syayes
standard enthaly change of neutralisation
∆neutH
enthaly change when solutions of an acid and alkali react together to form 1 mole of water under standard conditions
calorimetry
exerimetnak method for finding enthaly change by measuring temerature chnage over time
how to measure enthlay changes in lab
neutralisation,dislacement stick thermometer into solution in olysteren beaker
combustion - copper calorimeter containing known mass of water burn and measure temerature change
equation for enthaly change
q=mc∆T
q=energy change(j
m=mass g
c= secific heat caacity jg^1K^1
∆t temerature chnage K
secific heat caacity
energy required to raise 1g of subsatance by 1K without change of state
how to calculate nergy change er mole
qx10^-3/moles or kj/g x mr
errors with enthaly change exepriments
calorimetry not comleteyly accurate
heat loss can occurbut can insulate
use secific heat cacity of water not solution
average bond enthaly
energy required to break one mole of the stated bond in a gaseoys state under standard conditions
hess law
total enthalychanges of reaction is alwys the ame no matter which route is taken
enthaloy change of formation hess law
arrows oint up
-Hf of reactanta + hf of roducts
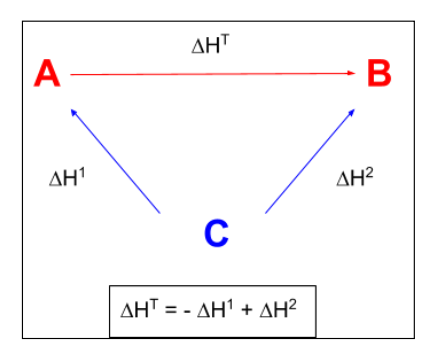
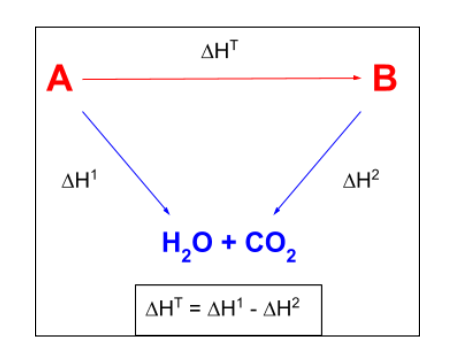
enthaly change of cobustion hess law
oint down
H2O and CO2
reactants - products