Lecture 32 -- acid base balance
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
what does our survival depend on?
v tight regulation between acid and bases in the blood
what is acid and bases in blood measured with? what’s the equation?
pH scale
pH of 7.37 -7.42 = normal
pH of 6.8 - 8.-00 = survival limits
pH = -log[H+]
what do buffer systems do?
help minimize the change in free H+ concentration (=minimize pH changes)
what is the main sources of H+ production in the body?
constantly produced by normal metabolism
two principle sources:
volatile acid = ~12,000-20,000 mmolday of CO2 (carbonic acid H2CO3)
byproduct of oxidative metabolism
lungs eliminate CO2
fixed (non-volatile) acid: ~50 mmol/day of inorganic and organic acid
cannot be eliminated by lungs
what are the 3 lines of defense against fixed acid-induced acidification of body fluids?
physiochemical buffering
seconds-min
respiratory compensation (CO2 elimination)
min-hour
renal compensation (H+ excretion; generation of HCO3)
hrs-days
what is physiochemical buffering? major systems?
fastest line of defense against H+ accumulation
3 major buffering systems in body fluid:
proteins
prosphate
bicarbonate/carbonic acid
most plentiful buffer in the body

what is respiratory compensation?
regulates blood levels of carbonic acid (H2CO3)
CO2 will readily form carbonic acid in the blood through reaction with water
high CO2 in blood = more H2CO3
more H2CO3 = lower blood pH (acidic)
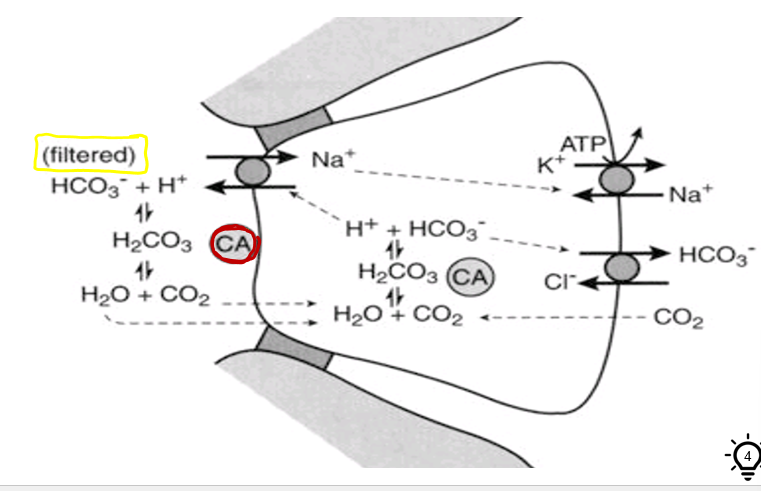
what is renal compensation?
the kidneys control levels of bicarbonate (HCO3-) in the blood
nephron NOT permeable to HCO3-
how do you get around the fact the nephron is not permeable to bicarbonate?
through indirect reabsorption of bicarbonate
CA = carbonic anhydrase