Patient Evaluation, Risk Assessment, Diagnostic Process
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Intro
▪ Practice of dentistry today is far different from that of only a decade or two ago-advances in medical science=people living longer
▪ The dentist must remain knowledgeable about a wide range of medical conditions
▪ 6 in 10 adults have a chronic disease, 4 in 10 have 2 or more
▪ Failure to make appropriate treatment modifications may have serious clinical consequences
▪ Key to successful dental management of a medically compromised patient is a thorough evaluation followed by assessment of risk to determine if a planned procedure can be safely tolerated
▪ Does the benefit of dental treatment outweigh the risk of a medical complication occurring during or as a result of treatment?
▪ If uncontrolled condition, do not treat!
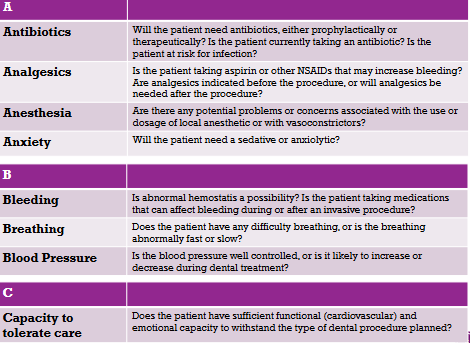
Checklist for Evaluation, Risk Assessment, Dental Management Modification considerations
PREOPERATIVE RISK ASSESSMENT
R: Recognize risks
Be aware of adverse events that may occur
P: Patient evaluation
Review medical history and discuss with patient
Identify all meds and drugs taken (or supposed to be taken)
Examine for signs and symptoms of disease, obtain vitals
Review or obtain recent lab tests/imaging as applicable
Ex) Diabetics, Peeps who take blood thinners, other diseases
Obtain a medical consultation if poorly controlled or undiagnosed or if health status is uncertain
Medical History
▪ Must be taken for every patient who is to receive dental treatment
▪ Use of a questionnaire that the patient fills out is the most common approach in dental offices
▪ MUST be reviewed by dialogue with the patient!
▪ Clarify and determine the significance of any finding that might impact dental treatment
Heart Failure
▪A clinical syndrome complex that results from an underlying cardiovascular problem
▪Increased risk and generally are not candidates for elective dental treatment
▪Chair position may influence ability to breathe
Can’t lay patients back
▪Vasoconstrictors should be avoided
Heart Attack (MI)
Within the recent past (30 days) may preclude elective dental care
Patients are at increased risk for reinfarctions, arrhythmias, and heart failure
Medications being taken may alter the dental management of patients
Potential interactions with vasoconstrictors in LA
Angina Pectoris
Brief substernal pain resulting from myocardial ischemia--a common, significant symptom of coronary heart disease
▪ Commonly provoked by physical activity or emotional stress
▪ Increased risk for arrhythmias, MI, and sudden death
▪ Not a candidate for elective dental care if unstable or progressive
High blood pressure
Should be identified by history and the diagnosis confirmed by measurement
▪ Some antihypertensive medications may require caution in the use of vasoconstrictors
▪ Co-administration of calcium channel blockers with macrolide antibiotics can result in excessive hypotension
▪ Stress and anxiety reduction measures may be appropriate
▪ Elective dental care should be deferred for patients with severe hypertension (BP ≥180/110mm Hg) until controlled
Heart murmur
▪ Caused by turbulence of blood flow that produces vibratory sounds during the beating of the heart
▪ May be an indication of underlying heart disease
▪ antibiotic prophylaxis not needed
Mitral valve prolapse
the leaflets of the mitral valve “prolapse” or balloon back into the left atrium during systole
▪ Can cause backflow of blood (regurgitation) into the atrium
▪ Antibiotic prophylaxis not needed for invasive dental procedures to prevent infective endocarditis
Rheumatic fever
An autoimmune condition that can follow upper respiratory hemolytic streptococcal infection and may lead to damage of the heart valves (rheumatic heart disease)
Congenital heart disease
▪ Patients with some forms of severe congenital heart disease are at increased risk for infective endocarditis (potentially fatal inflammation of heart valves’ lining and sometimes heart chambers’ lining)
Some might need prophylaxis premeds
Artificial heart valve
▪ Associated with high risk for development of infective endocarditis, with significant morbidity and mortality
▪ *AHA recommends prophylactic antibiotics before most dental procedures
May be on anticoagulants to prevent blood clots associated with the valve
Excessive bleeding may be encountered with surgical procedures
level of anticoagulation must be determined before any invasive procedure
Arrhythmias
▪ Frequently related to heart failure or ischemic heart disease
▪ Stress, anxiety, physical activity, drugs, and hypoxia may precipitate
▪ Vasoconstrictors in local anesthetics should be used cautiously
▪ Stress reduction measures may be appropriate
▪ Antiarrhythmic drugs may cause oral changes or other side effects
▪ Patients with atrial fibrillation also may be on anticoagulant or antiplatelet medication
Peeps with this may require a pacemaker or a d-fib to regulate or pace heart rhythm
Caution advised with the use of certain types of electric equipment in patients with these
Coronary artery bypass graft/angioplasty/stent
▪ Performed in patients with coronary heart disease to restore patency to blocked coronary arteries
▪ The grafted artery bypasses the occluded portion of the artery
▪ The balloon catheter is inserted into the partially blocked artery; the balloon is then inflated, which compresses the atheromatous plaque against the vessel wall
Hemophilia or inherited bleeding disorder
▪ Patients are at risk for severe bleeding after any type of dental treatment that causes bleeding, including scaling and root planing
▪ These patients must be identified and managed in cooperation with their physician or hematologist
▪ Patients with severe factor deficiency may require factor replacement before invasive treatment, as well as aggressive postoperative measures to maintain hemostasis
Blood transfusion
The underlying problem that necessitated this must be identified, and alterations in the delivery of dental treatment may have to be made
These patients also may be carriers of hepatitis B or C or may have become infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and must be identified
Laboratory screening or medical consultation may be appropriate to determine the status of liver function
Anemia
▪ May result from an underlying pathologic process such as chronic blood loss, decreased production of red blood cells, or hemolysis
▪ Oral lesions, infections, delayed wound healing, and adverse responses to hypoxia all are potential matters of concern
Leukemia/lymphoma
Depending on the type of leukemia or lymphoma, status of the disease, and type of treatment, some patients may have oral manifestations (gingival enlargement), bleeding problems or delayed healing, or may be prone to infection
Blood thinner use
tendency to bleed longer than normal
Information about an episode of unexplained bleeding should be obtained and evaluated
Many reports of unexplained bleeding are more apparent than real
Patients taking anticoagulant or antiplatelet medication will need to be evaluated to determine the risk for postoperative bleedin
Stroke
▪ Disorders that predispose this, like hypertension and diabetes, must be identified to allow for appropriate management alterations
▪ Avoid elective treatment in the immediate poststroke period (increased risk for subsequent)
▪ Caution using vasoconstrictors
▪ Possible paralysis, speech impairment, or other physical impairments that require special care
Calcifications may be seen in carotid arteries on Pano
May be risk factor for this
Refer to physician
Epilepsy, seizures, and convulsions
▪ A history of epilepsy or grand mal seizures should be identified, and the degree of seizure control should be determined
▪ Patients may discontinue the use of anticonvulsant medication without their doctor’s knowledge and thus may be susceptible to seizures during dental treatment
Important to ask about regularity of taking meds!
Behavioral disorders and psychiatric treatment
▪ Patients with a history of a behavioral disorder or psychiatric illness, as well as the nature of that disorder or illness need to be identified
▪ May help explain unusual or unexpected behavior
▪ May require stress reduction measures
▪ Some psychiatric drugs could interact adversely with vasoconstrictors in LA or produce adverse oral effects
Xerostomia, increased caries risk
Stomach or intestinal ulcers, gastritis, and colitis
Should not be given drugs that are directly irritating to the gastrointestinal tract
Aspirin and NSAIDs
Patients with colitis or a history of colitis may not be able to take certain antibiotics
Some drugs used to treat gastric or duodenal ulcers may cause dry mouth
Hepatitis, liver disease, jaundice, and cirrhosis
▪ Patients who have a history of viral hepatitis may be asymptomatic carriers of the disease and can transmit it unknowingly to dental personnel or other patients
▪ Patients also may have chronic hepatitis (B or C) or cirrhosis, with associated impairment of liver function
▪ Can result in prolonged bleeding
Can result in less efficient metabolism of drugs like LA and analgesics
Allergies or hives
From antibiotics, analgesics
▪ Latex allergy also is common, and in patients so affected, alternative materials, such as vinyl or powderless gloves, and latex-free rubber dams, can be used to prevent an adverse reaction
▪ True allergy to amide local anesthetics is uncommon
▪ Dentists should procure a history regarding allergy by specifically asking patients how they react to a particular substance
▪ Symptoms and signs include
itching, urticaria (hives), rash, swelling, wheezing, angioedema, runny nose, and tearing eyes
▪ Isolated signs and symptoms
nausea, vomiting, heart palpitations, and fainting
generally are not of an allergic origin but rather are manifestations of drug intolerance, adverse side effects, or psychogenic reactions
Asthma
▪ The type should be identified, as should the drugs taken and any precipitating factors or triggers
▪ Patient who uses an albuterol inhaler for treatment of acute attacks should bring it to their appointment
Emphysema/chronic bronchitis
▪ Chair position-some patients may not be able to tolerate a supine position
▪ Most commonly caused by cigarette smoking
▪ Smoking cessation counseling may be indicated
Contagious respiratory infections
▪ Examples: influenza, COVID-19, TB
▪ Patients must be identified and information about the infectivity status, testing, and treatment must be sought
▪ Dental treatment must be delayed until active disease is effectively treated
▪ Providers should be familiar with stages and symptoms of these infections
Sleep apnea/snoring
increased risk for hypertension, MI, stroke, diabetes, and car crashes, and should receive treatment for the disorder
▪ Signs and symptoms: loud snoring, excessive daytime sleepiness, and witnessed breathing cessation during sleep
▪ Refer to a sleep physician specialist for evaluation
Arthritis
▪ Most common types are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis
▪ Patients with Sjӧgrensyndrome, which may occur with rheumatoid arthritis or independently of that, have a dry mouth that can be very problematic
▪ May have problems with manual dexterity that impact oral hygiene
▪ Could involve the temporomandibular joints
Prosthetic joints
▪ Some patients thought to be at increased risk for infection of the prosthesis subsequent to dental treatment
▪ Current guidelines do not recommend that prophylactic antibiotics be provided before any treatment likely to produce bacteremia
Diabetes
▪ Patients must be identified to determine the type, how it is being treated, and how well controlled it is
▪ Type 1 are of greater concern regarding management
▪ Symptoms and signs suggestive include
dry mouth, excessive thirst and hunger, frequent urination, weight loss, poor wound healing, and frequent infections
Odontogenic infections, oral candidiasis, periodontal disease
▪ Patients who take insulin are at risk for episodes of hypoglycemia in the dental office if meals are skipped or if stress or infection is present
Thyroid disease
▪ Patients with uncontrolled hyperthyroidism are potentially hypersensitive to stress and α1 -adrenergic effects of sympathomimetics, so the use of vasoconstrictors generally is contraindicated
▪ These patients also may be easily upset emotionally and intolerant of heat, and they may exhibit tremors
▪ Palpation of thyroid gland is important!
▪ Exophthalmos may be present
Kidney failure
▪ Patients with chronic kidney disease or a kidney transplant must be identified
▪ Potential for abnormal drug metabolism, immunosuppressive drug therapy, bleeding problems, hepatitis, infection, high BP, concurrent diabetes, and heart failure
Sexually transmitted diseases
▪ A variety of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), such as syphilis, gonorrhea, and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, can have manifestations in the oral cavity because of oral-genital contact or secondary to hematogenous dissemination in the blood or immune suppression
▪ Dental professional may be the first to identify these conditions
▪ Risk of oropharynx cancer
Tobacco and alcohol use
▪ The use of tobacco products is a risk factor that is associated with cancer, cardiovascular disease, pulmonary disease, and periodontal disease
▪ Excessive use of alcohol is a risk factor for periodontal disease, malignancy, and heart disease, and may lead to liver disease
▪ Ask about quantity, duration, and whether they would like to quit/encourage them to do so
Drug addiction and substance use disorder
▪ Patients who have a history of intravenous drug use are at increased risk for infectious diseases such as hepatitis B or C, AIDS, and infective endocarditis
▪ Vasoconstrictors should be avoided in patients who are cocaine or methamphetamine users because these agents may precipitate arrhythmias, MI, or severe hypertension
Tumors and cancer
▪ Patients who have had cancer are at risk for recurrence, so they should be closely monitored
▪ Cancer treatment regimens including chemotherapy, targeted biologic agents, immunotherapy, or radiation therapy may result in infection, gingival bleeding, oral ulcerations, dry mouth, mucositis, and impaired healing after invasive dental treatment, all of which represent significant management considerations
Therapy for head and neck cancers
Patients who had previous surgery may have severe oral function deficits
Patients with previous radiation treatment to the head, neck, or jaw must be carefully evaluated
Destroys blood supply to the jaws, mucositis and irreversible damage to salivary glands, fibrosis of masticatory muscles
Chemotherapy can produce many undesirable adverse effects, most commonly a severe mucositis
Resolve after therapy is complete
Steroids
▪ Used in treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases
▪ Cortisone and prednisone are examples of steroids that are used in treatment of many diseases
Operations or hospitalizations
▪ A history of hospitalization can provide a record of past serious illnesses that may have current significance
▪ Information about hospitalizations should include diagnosis, treatment, and complications
Pregnancy
▪ Women who are or may be pregnant may need special consideration in dental management
▪ Caution in administration of drugs, timing of dental treatment, and chair position
▪ Stress the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene during pregnancy!
Current physician
▪ Information should be sought regarding the identity of the patient’s physician, why the patient is under medical care, diagnoses, and treatment received
▪ A patient who does not have a physician may require a more cautious approach than a patient who sees a doctor regularly
Drugs, medicines, or pills
▪ All drugs, medicines, supplements, or pills that a person is taking, or is supposed to be taking, should be identified and investigated for actions, adverse side effects, and potential drug interactions
▪ The dentist should have a reliable, up-to-date, comprehensive source for drug information, in print format or through an online database
▪ The patient's list of medications (“drug history”) may provide the only clues to presence of an unreported medical disorder
Functional capacity
▪ It is important to ask some screening questions regarding the ability of the patient to engage in normal physical activity (functional capacity)
▪ A patient who reports an inability to walk up a flight of stairs without shortness of breath, fatigue, or chest pain may be at increased risk for medical complications during dental treatment, especially when such limitation is combined with other risk factors and the patient is under stress
Physical exam
▪ Skin and nails
▪ Face
▪ Eyes
▪ Ears
▪ Neck
▪ Pulse
▪ Rate
▪ Rhythm
▪ Blood pressure
▪ Respiration
▪ Oxygen saturation
▪ Temperature
▪ Height
▪ Weight
General appearance
Careful observation can lead to awareness and recognition of abnormal or unusual features or medical conditions that may exist and may influence the provision of dental care
Consists of an assessment of the general appearance of the patient and inspection of exposed body areas
The patient's outward appearance and movement can give an indication of her or his general state of health and well-being
Skin and nails
▪ Changes associated with systemic disease
▪ Alterations in the fingernails, such as clubbing, white discoloration, yellowing, and splinter hemorrhages, usually are caused by chronic disorders
▪ Dorsal surfaces of the hands are common sites for actinic keratosis and basal cell carcinomas
▪ A raised, darkly pigmented lesion with irregular borders may be a melanoma
Face
▪ The shape and symmetry of the face are abnormal in a variety of syndromes and conditions
▪ Acromegaly, Cushing (hyperthyroidism), Bell palsy
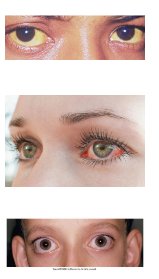
Eyes
▪ Sensitive indicators of systemic disease and should be closely inspected
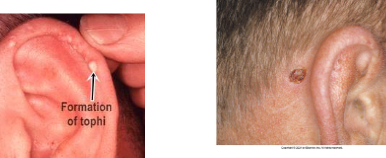
Ears
▪ The ears should be inspected for gouty tophi in the helix or antihelix
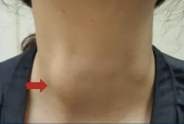
Neck
▪ The neck should be inspected for enlargement and asymmetry
▪ Lymph nodes evaluated for size, location, tenderness, and whether movable or fixed
▪ Bilateral palpation of the thyroid gland should be performed
Vital signs
Consist of blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate, temperature, height, and weight
▪ Not always done in private practice.. educate!
▪ Establishment of baseline normal values ensures a standard of comparison in the event of a medical emergency during treatment
▪ The purpose of this examination is merely detection of abnormality--not diagnosis
▪ Discuss abnormalities with pt and refer to physician for further evaluation
Pulse
▪ Can be determined by palpating carotid artery at the side of the trachea or the radial artery on the thumb side of the wrist
▪ Pulse should be palpated for 1 minute
Rate
▪ The average pulse rate in normal adults is 60 to 100 beats/minute
▪ Abnormal pulse rate may be a sign of cardiovascular disorder, but the pulse also may be influenced by anemia, exercise, conditioning, anxiety, drugs, or fever
Rhythm
▪ The normal pulse is a series of rhythmic beats that occur at regular intervals
Blood pressure
▪Determined by indirect measurement in the upper extremities with a blood pressure cuff and stethoscope
▪A cuff that is too small yields falsely elevated values, whereas a cuff that is too large yields falsely low values
Normal systolic pressure ranges between 90 and 120mm; normal
diastolic pressure ranges between 60 and 80 mm
Respiration
▪ The rate and depth of respiration should be noted through careful observation of movement of the chest and abdomen in the quietly breathing patient
▪ Make note of patients with labored breathing, rapid breathing, or irregular breathing patterns
▪ A common finding in apprehensive patients is hyperventilation (rapid, prolonged, deep breathing or sighing), which may result in lowered carbon dioxide levels and cause disturbing symptoms and signs
Oxygen saturation
▪ Determined with a pulse oximeter placed on pad of index finger
▪ Levels should be 98% or higher
▪ Levels below 92% suggest supplemental oxygenation and evaluation
Temp
not usually recorded during a routine dental examination but rather is determined when a patient has febrile signs or symptoms such as might be found with an abscessed tooth, a mucosal or gingival lesion, or a fascial space infection
▪ Normal oral temperature is 98.6°F (37°C) but may vary by as much as ±1°F over 24h and usually is highest in the afternoon
Height
should be determined so insight into growth and development as well as conditions such as osteoporosis can be assessed
Weight
▪ Patients should be questioned about any recent unintentional gain or loss of weight
▪ Rapid loss could indicate malignancy, diabetes, TB, or other wasting disease
▪ Rapid gain could indicate heart failure, edema, hypothyroidism, or neoplasm
▪ Obesity (BMI of 30 or higher) is a risk factor for many health problems including heart disease and diabetes
Head and neck exam
may vary in its comprehensiveness but should include inspection and palpation of the soft tissues of the oral cavity, maxillofacial region, and neck, as well as evaluation of cranial nerve function
Diagnostic tests
▪ An important part of the evaluation of a patient’s health status
▪ Indications for clinical laboratory testing in dentistry
▪ Aiding in detection of suspected disease (diabetes, infection, bleeding disorders, malignancy)
▪ Screening at-risk patients for diabetes, HIV, chronic kidney disease, hepatitis B or C
▪ Establishing normal baseline values before treatment (anticoagulant status, WBCs, platelets)
▪ Assessing risk for bleeding
Physician referral and consultation
▪ Contacting the physician for consultation or referral purposes may be warranted if any concerns on patient’s general health
▪ Conversation and all communications must be recorded in the progress notes
Problem list and diagnoses
▪ Once all information is collected, a problem list with diagnoses should be constructed. The list should be comprehensive and include final conclusions regarding abnormalities detected after assessment of the chief complaint
Risk assessment
▪ Recommended prior to dental treatment
▪ “ABC” checklist offers an assessment as to whether a patient can safely undergo planned dental treatment.
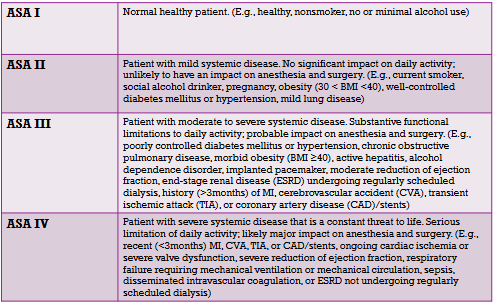
▪ American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) Physical Classification System- method of assessing medical risk
▪ As classification level increases, so does the risk
▪ Each situation requires consideration to determine whether the benefits of having dental treatment outweigh the potential risks to the patient
Age
▪ Young patients may have behavioral and cognitive issues that make it difficult to sit still or take instruction
▪ Elderly patients may suffer from multiple comorbid conditions of variable degree
▪ Tend to have more medical problems and take more medications
▪ ½ of older adults report having 2 or more chronic illnesses, 1/3 of all prescription meds are taken by older adults
Treatment modifications
▪ The goal is to provide methods to evaluate and reduce risk as much as possible, including the possibility of urgencies or emergencies that can arise in the dental office
▪ Simple modifications in the delivery of dental treatment can be made in an effort to reduce risk to the patient
▪ Antibiotic prophylaxis or anxiolytic drug
▪ Adjustment of chair position
▪ Monitoring of vitals
Stress and anxiety reduction
important to control to help reduce risk
establish good rapport and trust