Lecture 6 - thrombosis, embolism and infarction
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
define haemostasis
blood stopping
orchestrated process involving platelets, clotting factors. and endothelium that occurs at the site of vascular injury
also maintains blood in a fluid state in normal vessels
thrombus vs clot
thrombus - a solid mass of coagulated blood formed within the CVS
clot - a solid mass of coagulated blood that firms outside the CVS or post-mortem
very similar
thrombosis
the formation of a thrombus
embolism
an obstruction in a blood vessel due to material that gets stuck whilst traveling through the bloodstream
can be composed of thrombus, air, fat, amniotic fluid but are most commonly thromboelboli
what are the four stages of haemostasis
vasoconstriction
primary haemostasis
secondary haemostasis
thrombotic and anti-thrombotic events
transient vasoconstriction
neurohormonal vasoconstriction - endothelin from endothelial cells
temporarily slows bleeding, helps platelets and factors come into contact with each other
primary haemostasis
subendothelial ECM epxosed (to blood)
subendothelial components are high thrombogenic (von Willebrand factor)
platelets adhere, activate and release granules that recruit more platelets to form a platelet plug
secondary haemostasis
tissue factor released - glycoprotein from endothelial cells, initiates coagulation cascade
throbin is generated (from circulating prothrombin) - recruits and activates more platelets, converts fibrinogen to fibrin
fibrin polymerises - acts like a net, stabilising platelet plug and trapping other cells
thrombotic and anti-thrombotic events
counter-regulatory mechanisms
limit the plug to the site of injury
what causes of thrombosis are asosciated with arteries
endothelial injury
abnormal blood flow - turbulence
less associated with hypercoagulability (platelets)
what causes of thrombosis are asosciated with veins
less endothelial injury
abnormal blood flow - stasis
hypercoagulability - coagulation
risk factors for arterial thrombosis
dyslipidaemia
diabetes mellitus
hypertension
risk factors for venous thrombosis
trauma
surgery
cancer
previous venous thrombosembolism
pregnancy
thrombophilia
common risk factors fro thrombosis
age
obesit
smoking
estrogens
hyperhomocysteinemia
what is an aneurysm
a sac filled with thrombus
very dangerous if burst
can be repaired surgically
what is the blue in this image
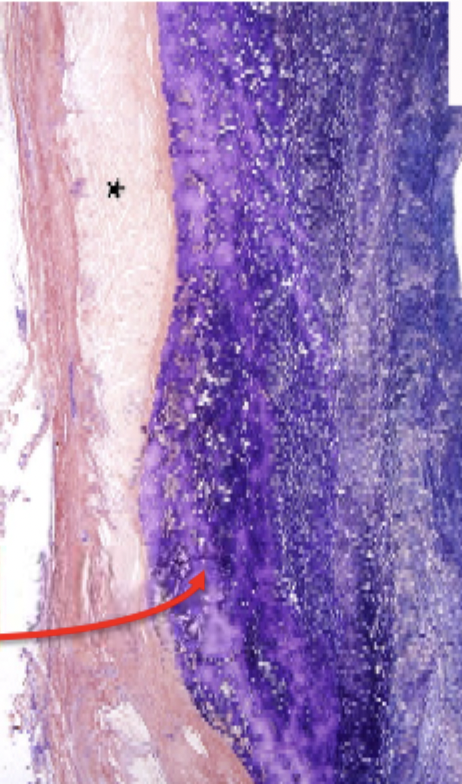
fibrin
lines of zahn
alternating layers of platelets and blood cells
only form when the blood is moving quickly - arterial not venous thrombi
canaliculi
perpendicular to lines of zahn
allow more porous parts to drain through the thrombus
important for fibrolytic zone - allows fibrolytic zone to drain down
fibrinolytic zone
fibrin turns from a darker blue to a lighter colour
what are the possible fates of the thrombus
resolution
organisation and recanalisation
propagation
embolisation
resolution
fibrinolysis, blood flow re-established, most likely when thrombi are small
organisation and recanalisation
epithelium can grow over the thombosis and incorporate it into the wall (organisation)
can grow epithelial cells through the middle - create a new lumen to bypass the thrombus (recanulize)
propagation
the thrombus gets longer
the end that is growing can form a tail which can break off and form an emboli
embolisation
part of the thrombus breaks off and travels through the bloodstream
lodges at distant site
systemic veins → lungs (pulmonary thrombi)
left heart (mural thrombus) → aorta → renal, mesenteric, femoral and other arteries
carotid arteries → brain
abdominal aorta → arteries of the leg
pulmonary embolism
95% arise from DVT in the leg
contributes to ~10% acute adult hospital deaths
usually in predisposed patients - underlying disorder, immobilised, hypercoaguable
may result in pulmonary infarction, pulmonary hypertension, right ventricular failure
other types of embolism
air
amniotic fluid
nitrogen
fat
tumour cells
infarction
a form of ischaemic necrosis caused by the occlusion of arterial or venous vessels
myocardial, cerebral, pulmonary, bowel, skin
99% due to thrombosis, mostly arterial occlusion
other causes include vasospasm, external pressure, trauma, twisting of organs, oedema
infarct development depends on
nature of blood supply - red from dual blood supply or venous occlusion, white from end arterial occlusion
rate of occlusion - gradual from atherosclerosis of coronary arteries, acute from pulmonary embolism from DVT
white infarcts
arterial insufficiency
AND
single blood supply (end artery)
AND not reperfused
red infarcts
venous occlusion OR dual blood supply OR reperfused