2.1b Perception: Perceptual Organization and Interpretation
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
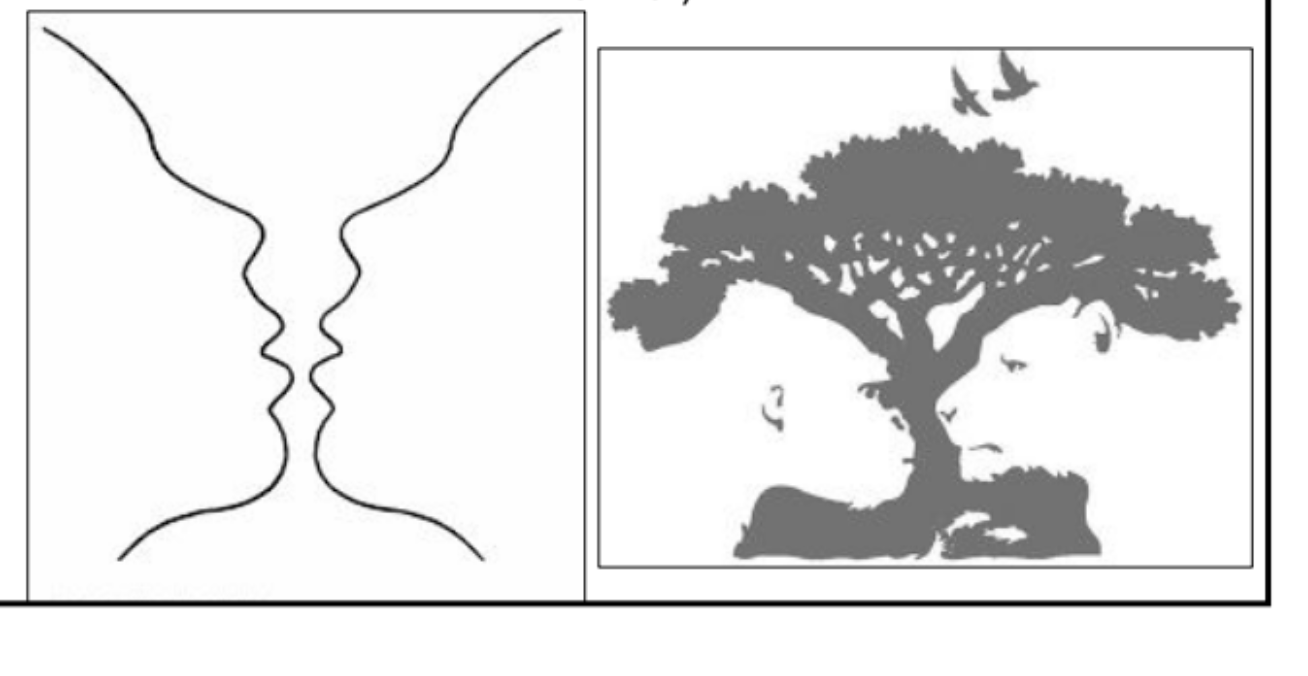
(form perception) Figure-Ground is
is your mind organizing between an
object (the object in forefront) that stand out from its
surrounding (the background in which the object is in
front of).
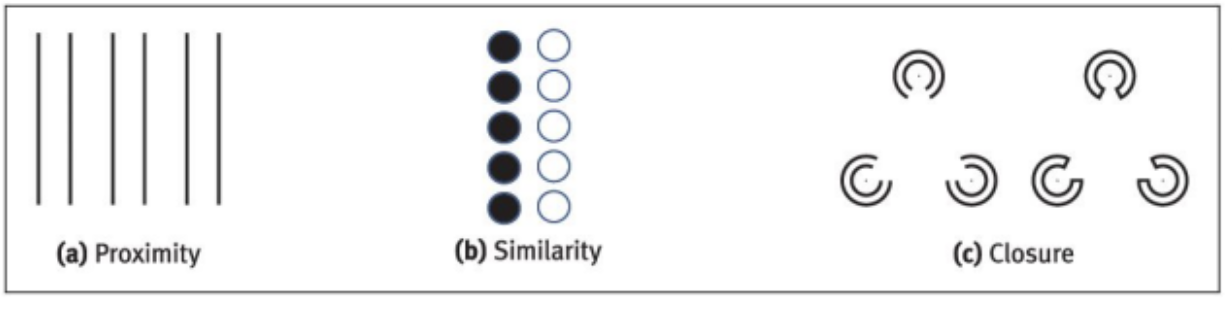
Grouping
is a perceptual tendency of our
brain to organize things into logical groups.
Gestalt Law of Proximity
states that individual elements that are placed close to each other percieved as belonging together.

Gestalt Law of Similarity
elements that look simillar to each other are grouped together in the mind
Closure Gestalt Principle
human mind seeks to create coherence. will gap in missing images to make a completed image.
Depth perception
ability to see in 3D and allows us to
judge distance.
Visual Cliff
to test depth perception in infants and
young animals. This device lets
us know that depth perception
is innate!
Binocular cues
are depth cues that requires the use
of BOTH eyes. We use binocular cues to judge the
distance of nearby objects.
Retinal disparity
is another binocular cue that comes from the slight difference between the images each of your eyes
see.
Monocular cues
depth cues detected with ONE eye
Motion Perception
brain’s ability to understand when
objects are moving and in which direction.
Stroboscopic movement
an illusion of continuous
movement (as in a motion picture) experienced when
viewing a rapid series of slightly varying still images.
Phi phenomenon
is an illusion of movement created when
a sequence of lights blinks on & off.
Perceptual constancy
is top down process of perceiving
objects as UNCHANGING even as retinal images change.
Color constancy
perceiving familiar objects as having
consistent color, even if changing illumination alters the
wavelengths reflected by the object.
Brightness (lightness) constancy
perceiving an object as having a constant brightness even while its
illumination varies.
Shape constancy
the perception that familiar objects stays constant even when our retinas
receive changing images of them.
Size constancy
the perception that objects have a constant size, even when our distance from them
varies.
Perceptual Interpretation
Our experience guides our perceptual interpretations.
What you’ve never experienced,
you can’t interpret.
perceptual adaptation
is your brain’s ability to adjust to an
artificially displaced or even
inverted visual field.