Apologia Advanced Biology Module 1 Study Guide for Test
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Gross anatomy
The study of the parts of the body we can see
Microscopic anatomy
The study of structures so small that they require a microscope to be seen
Physiology
The study of how the body's parts function and work together to make the human body the wonder it is
Histology
The study of tissues
Organ
A group of tissues specialized for a particular function
Tissues
A group of cells forming various building materials of the body
Homeostasis
A state of dynamic equilibrium in the body with respect to its internal environment and functions
Effector
A structure in the body that can change the value of a variable in response to a signal from the control center
Selective permeability
The ability to let certain materials in or out while restricting others
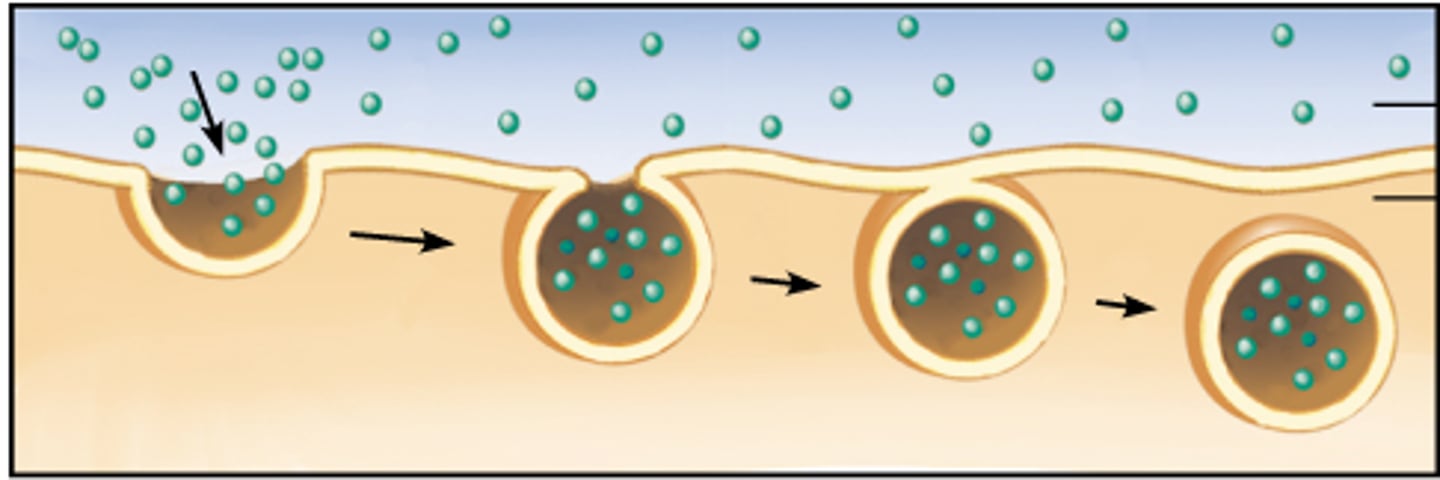
Endocytosis
Taking large molecules into the cell
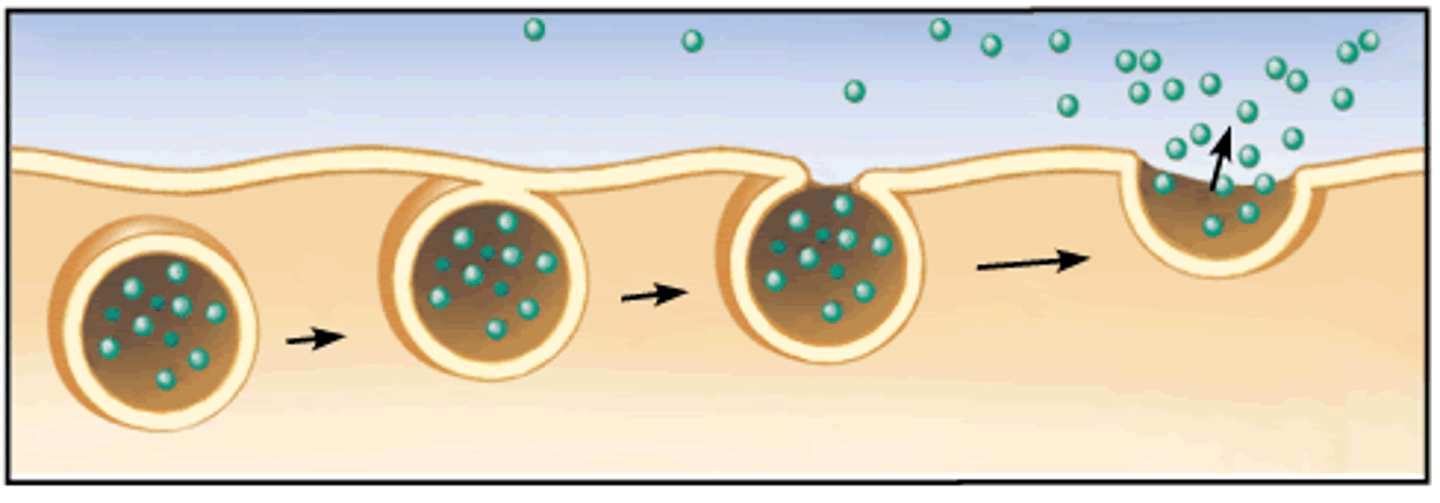
Exocytosis
Transportation of material from inside the cell to outside the cell using vesicles; also called secretion
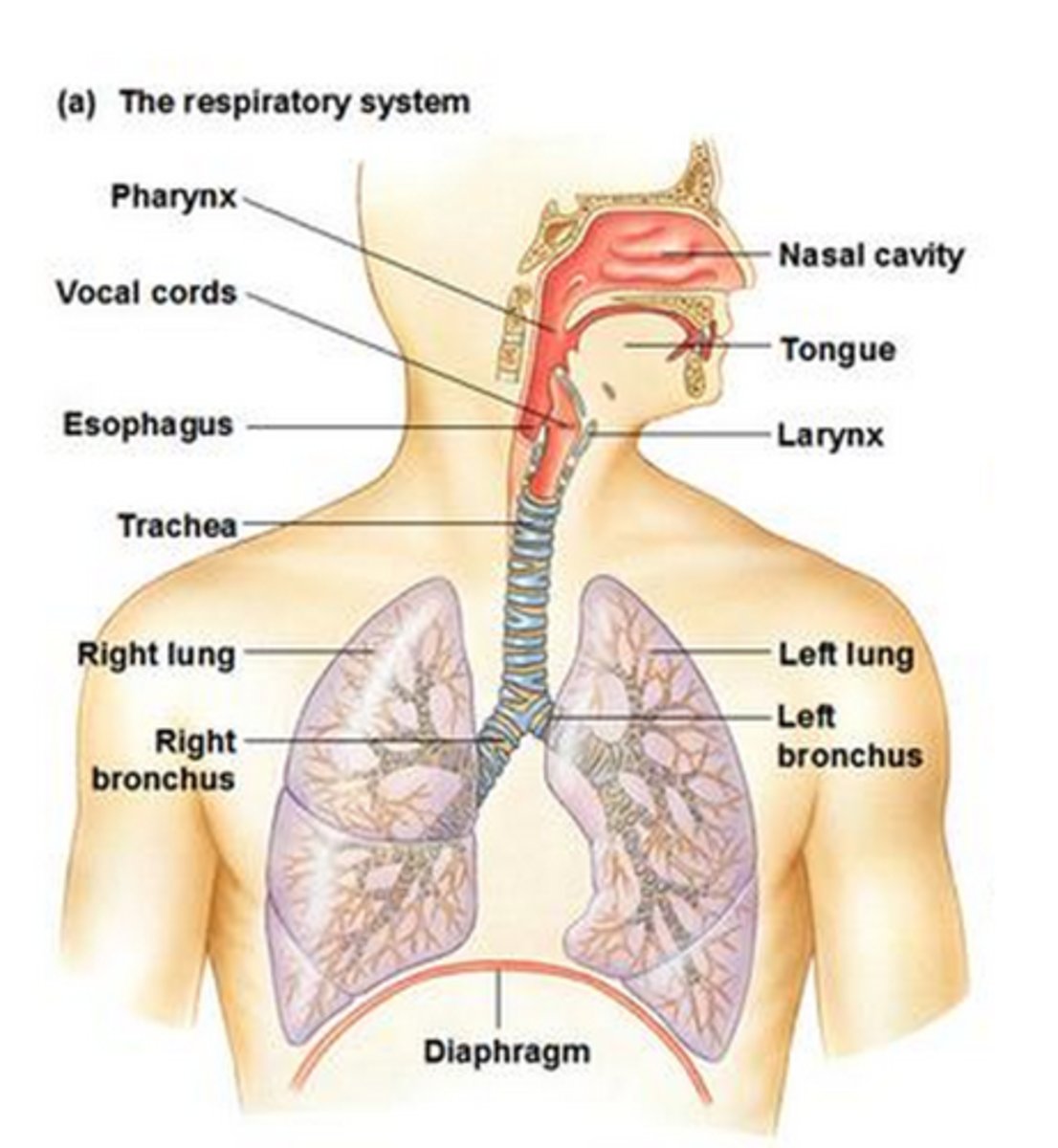
Anatomy course
The name of each organ and where it is in the body
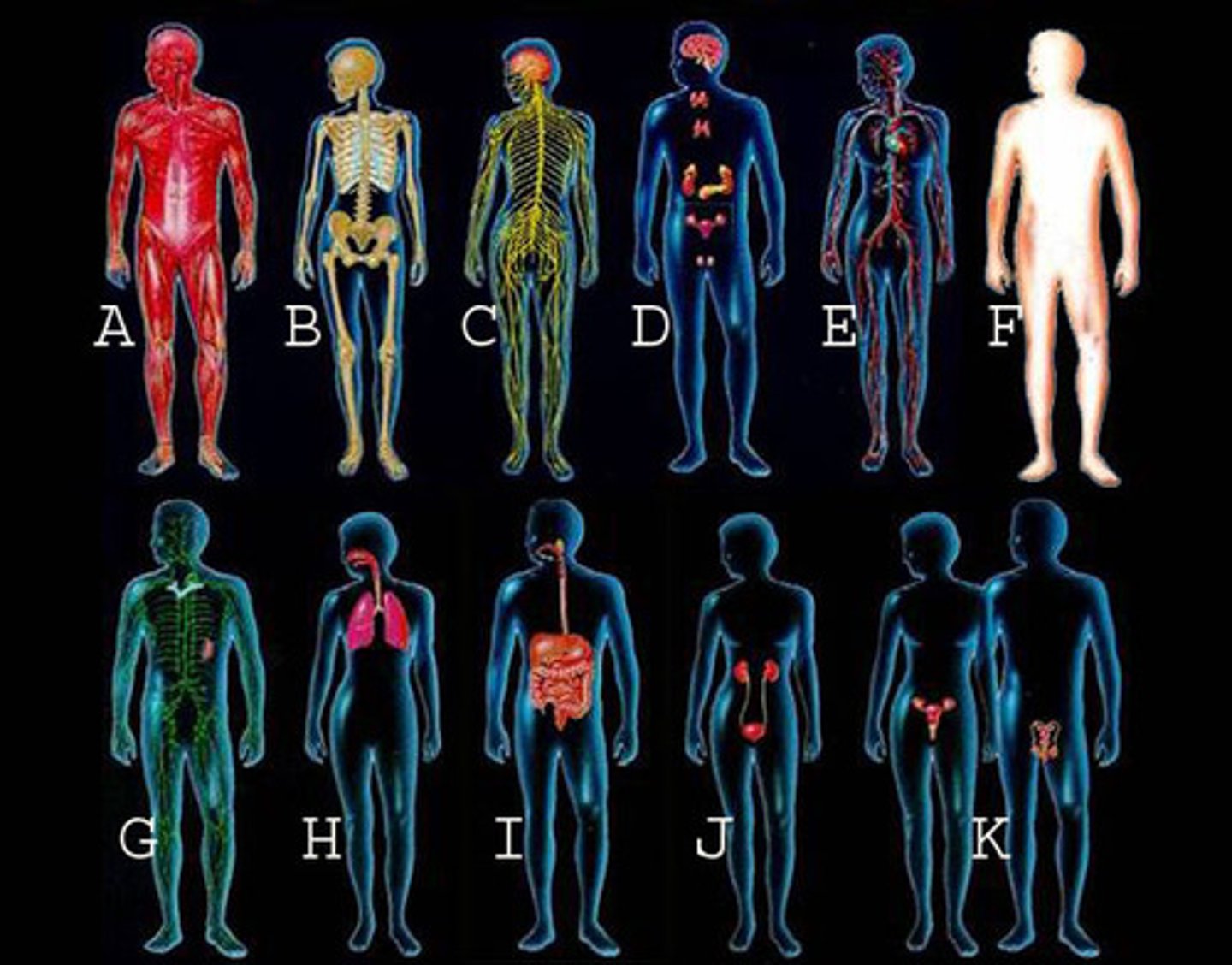
Whole organism,
The first levels of organization in a living organism
organ systems
second level of organization in an organism
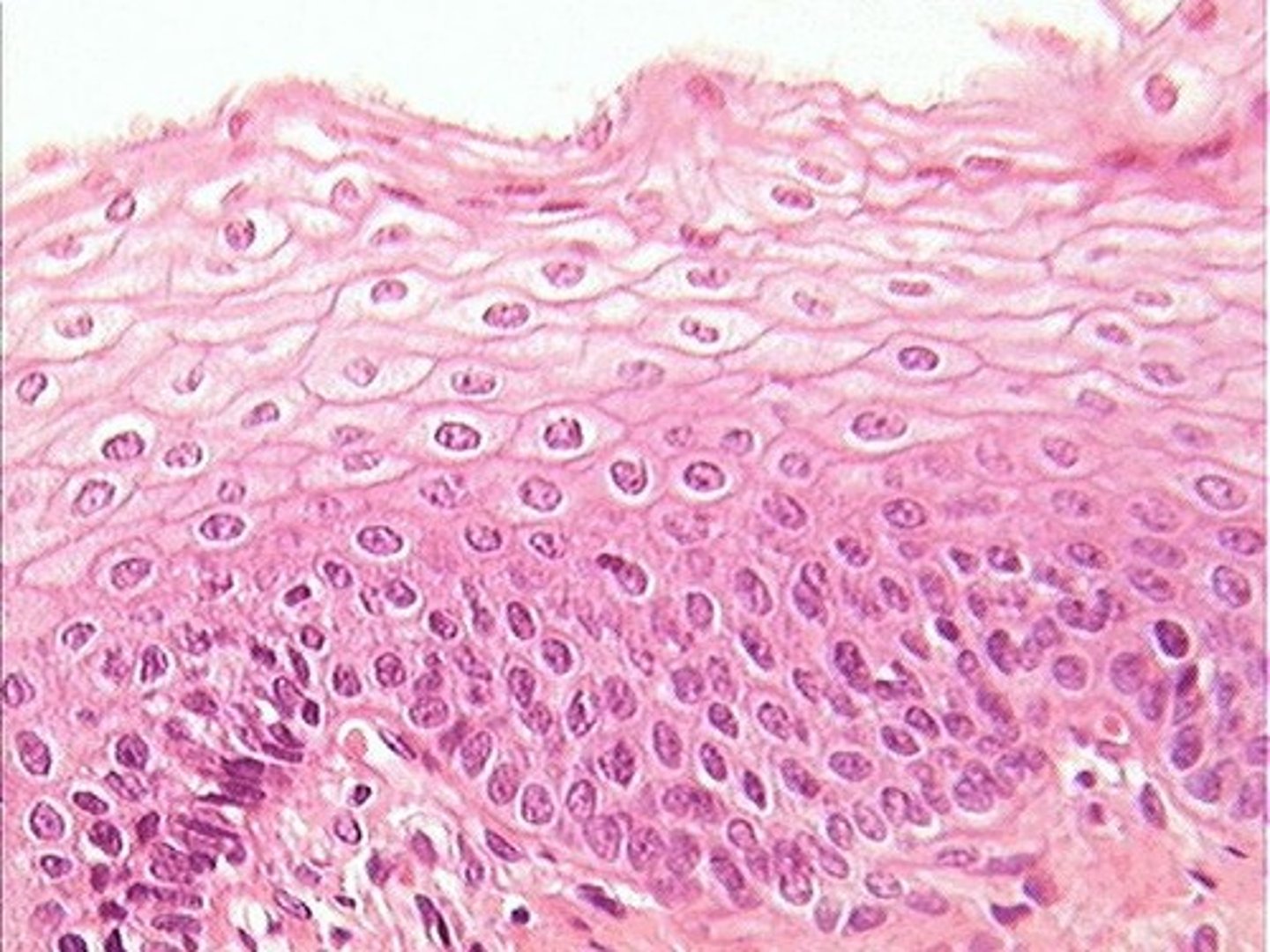
Epithelial
The type of tissue that makes up your skin, inner lining of respritory passages, and other passages and tracts in your body.
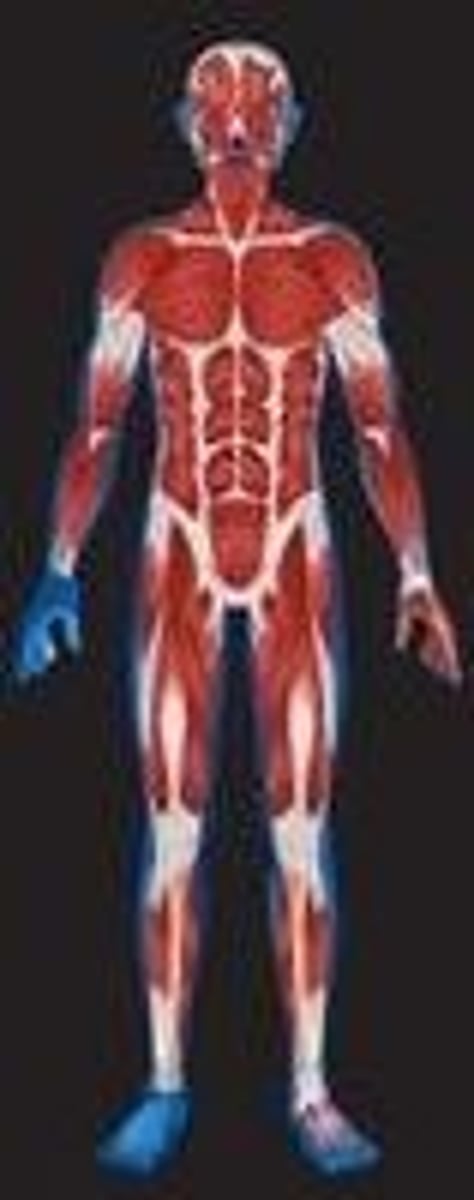
Muscular
The type of tissue that makes up the muscle
Connective
The type of tissue that makes up the cartilage in your joints, bones, the deeper layer of skin, and the bindings or connectors around and between organs.
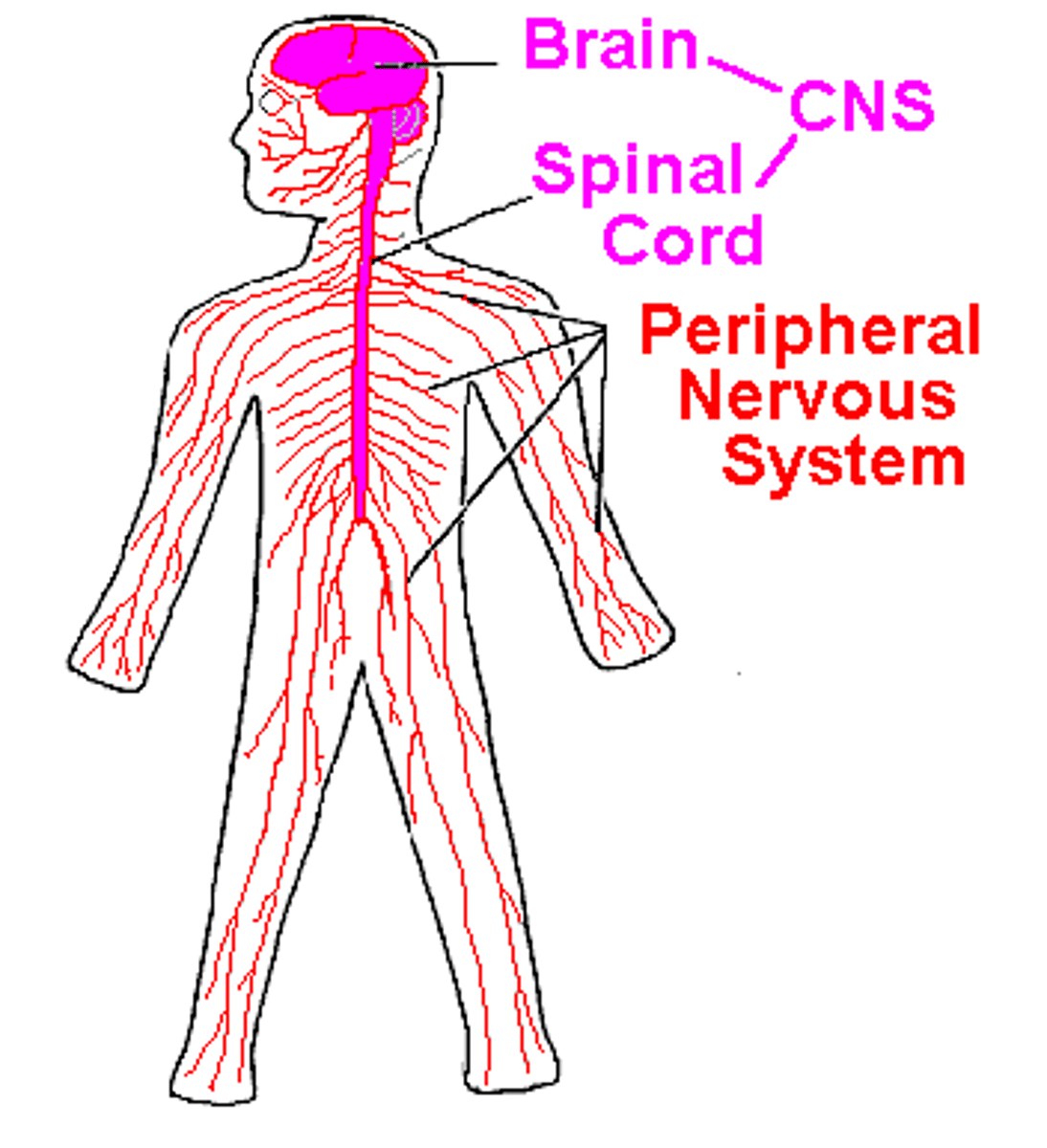
Nervous
makes up brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
Stress
The general term for the processes in the environment that threaten homeostasis
negative feedback system
a process that results in a response that reverses the original stimulus to regulate organ systems and mantain homeostasis
Endocrine and nervous systems
Which two organ systems are most involved in controlling the negative-feedback systems of the body?
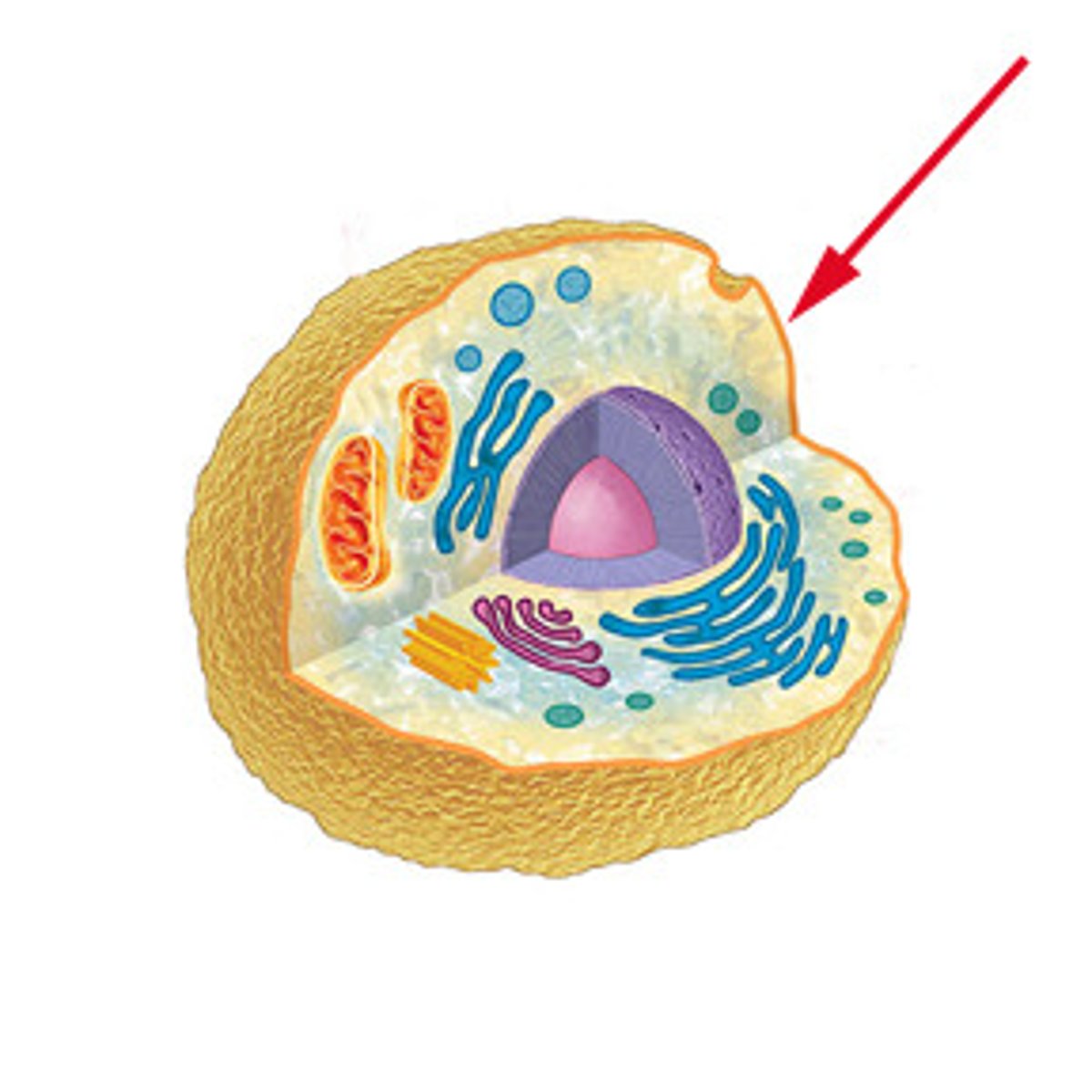
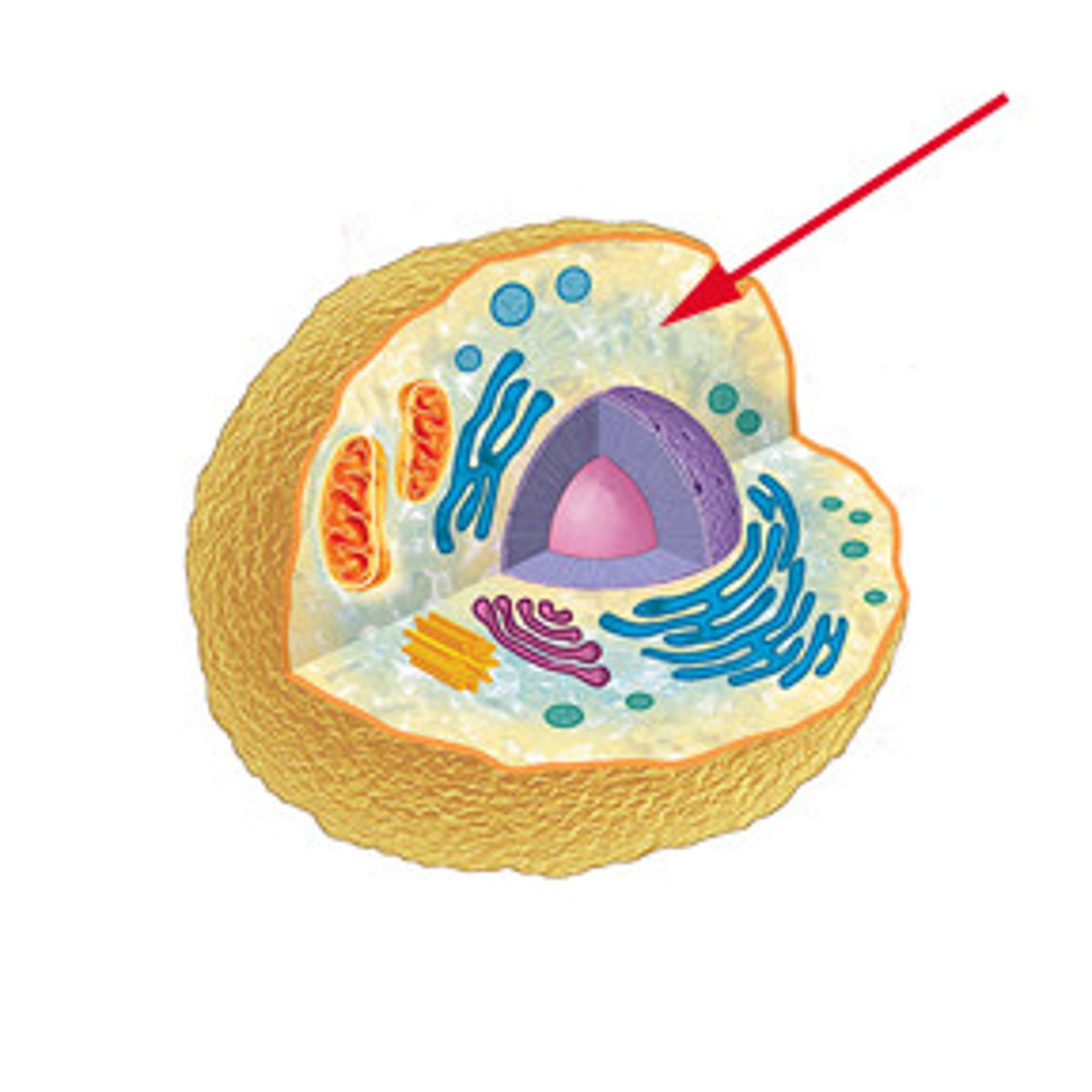
Plasma membrane
Holds the cell together & controls what comes in and goes out
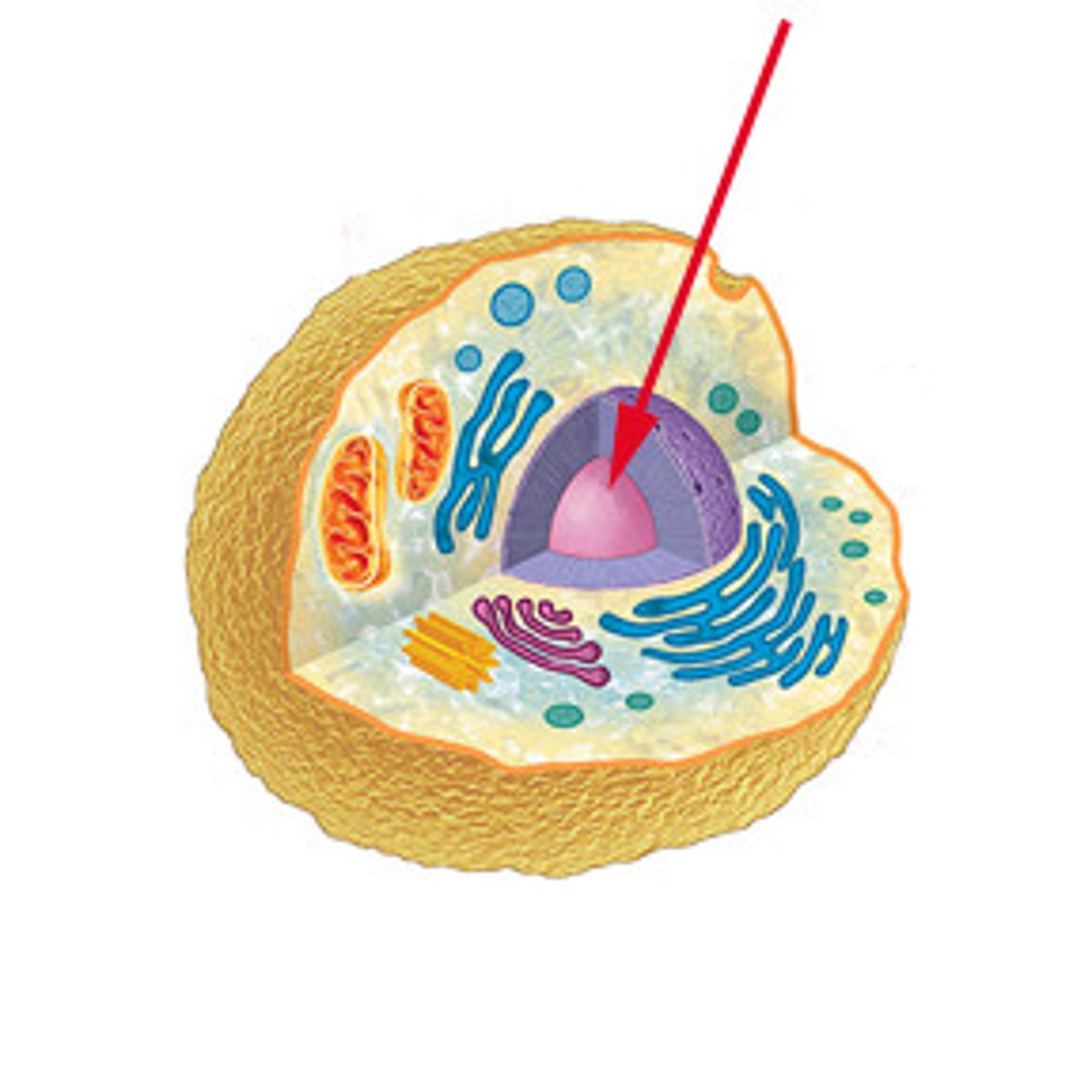
Nucleus
Spreads out the DNA it contains
Cytoplasm
Has cytosol
Ribosomes
Synthesize proteins, which determine the cell's function
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Intracellular transport, produces lipids and carbohydrates
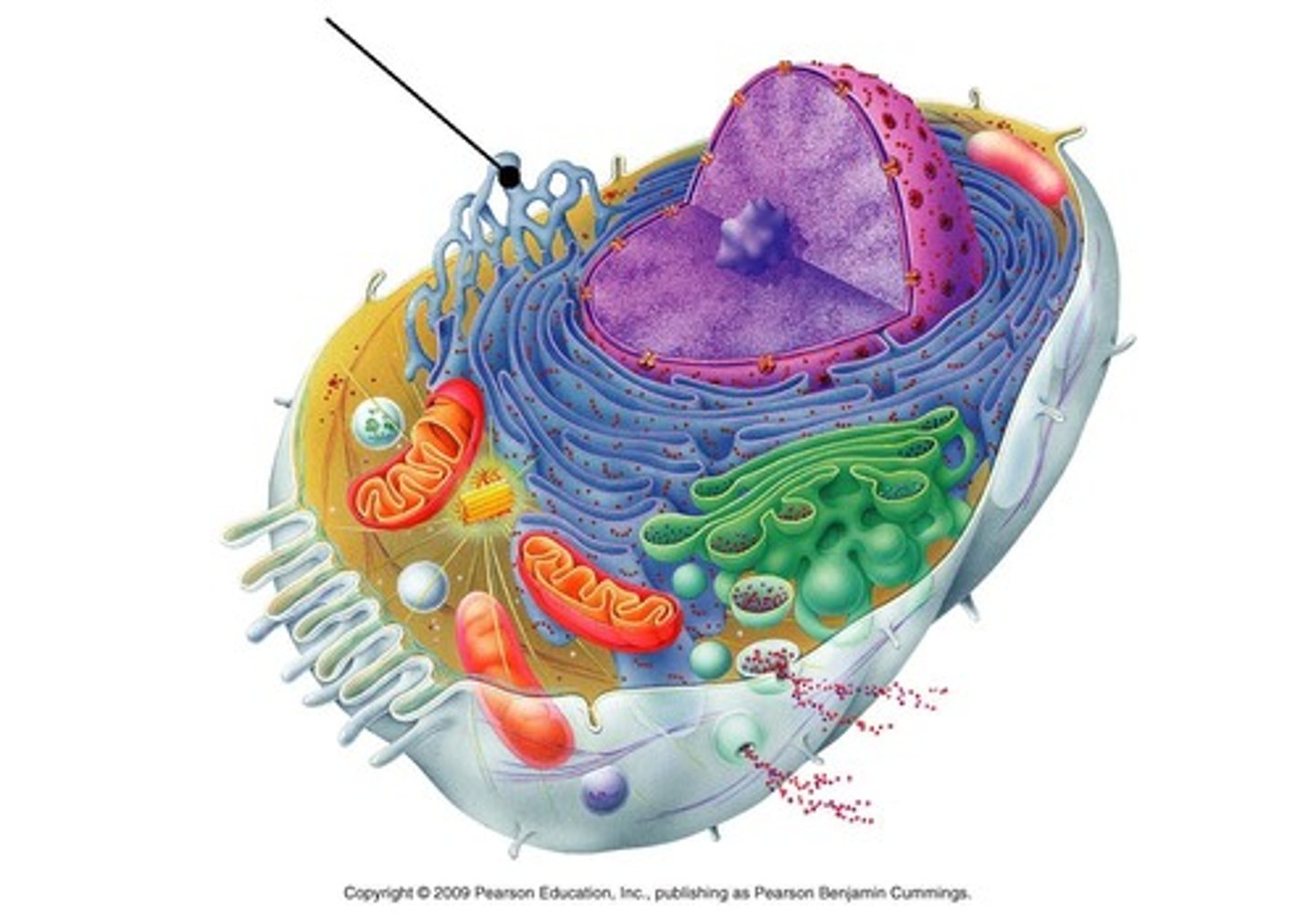
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Intracellular transport, synthesizes proteins
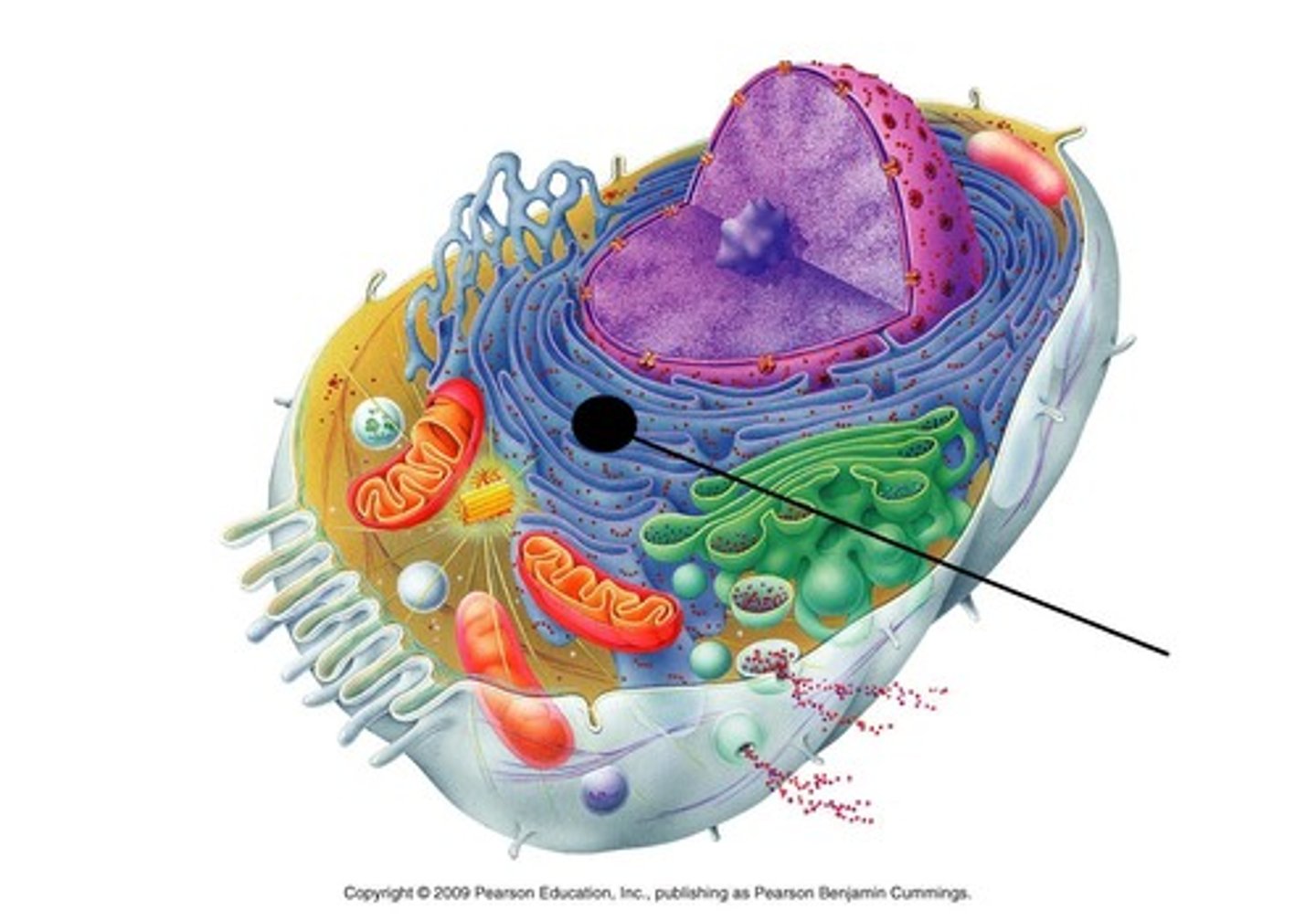
Golgi apparatus
Packages various chemicals for secretion
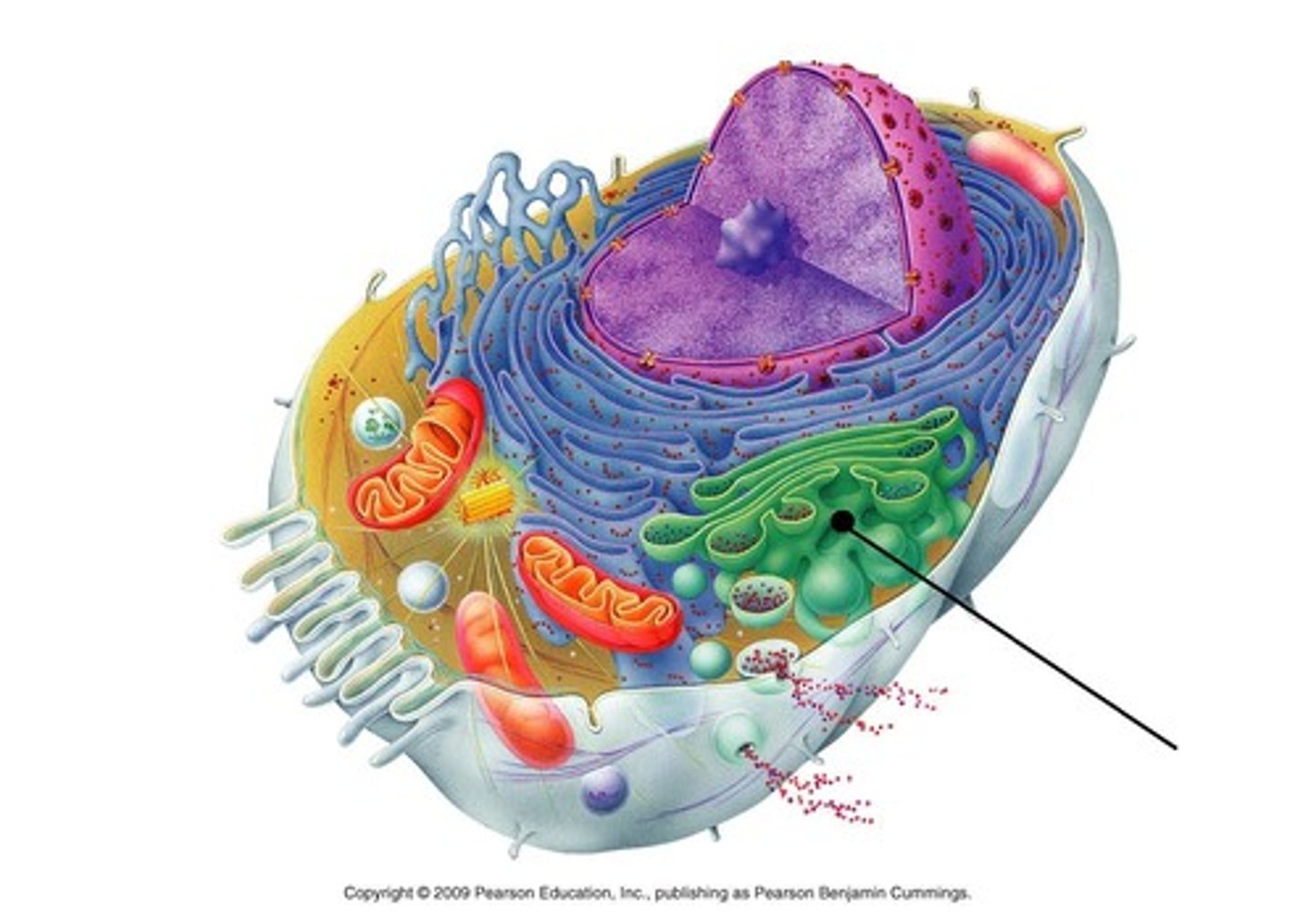
Secretory vesicle
Releases a chemical when it gets a signal from the cell
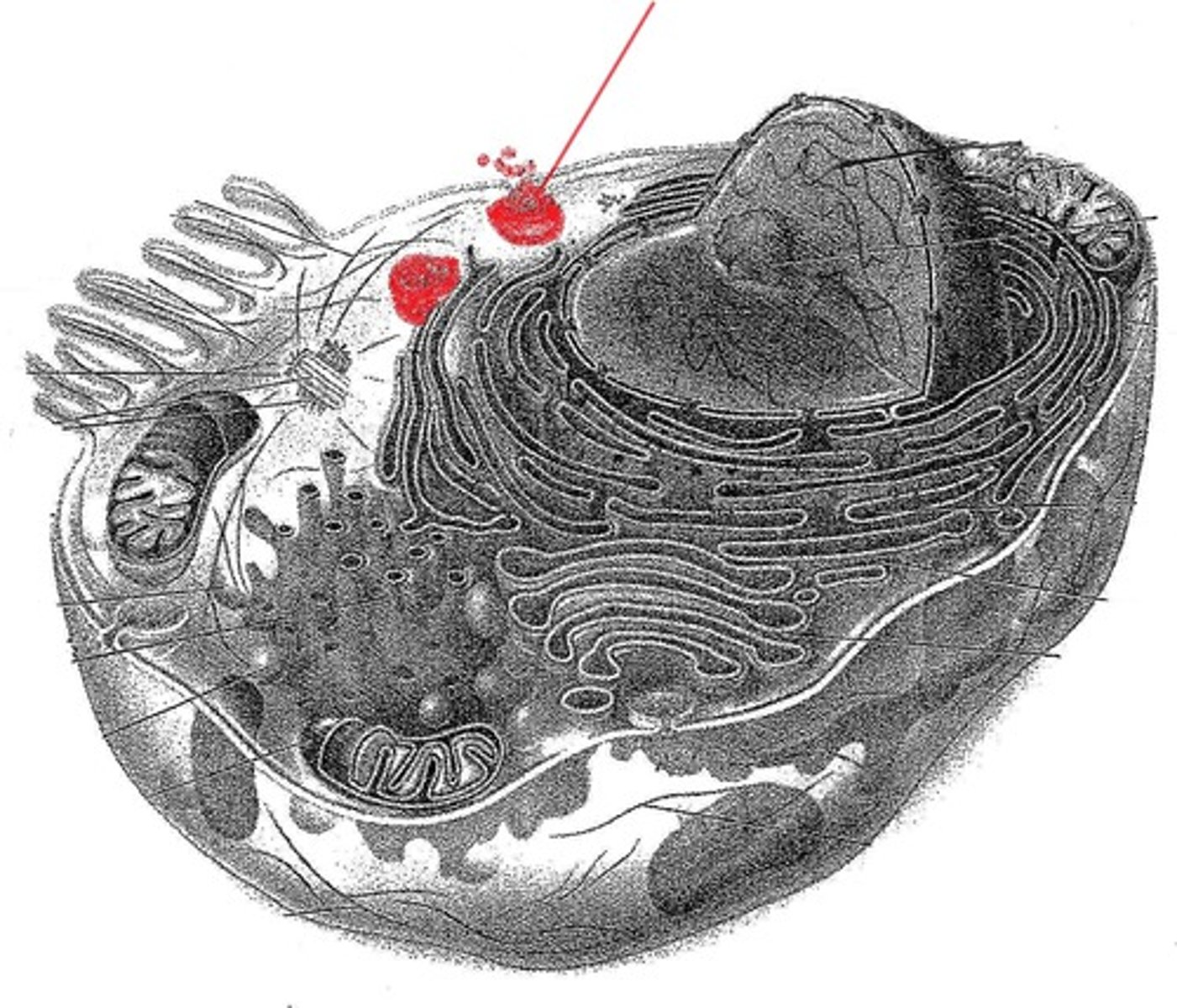
Lysosome
Breaks down lipids, proteins, polysaccharides, carbs, and nucleic acids (suicide sack)
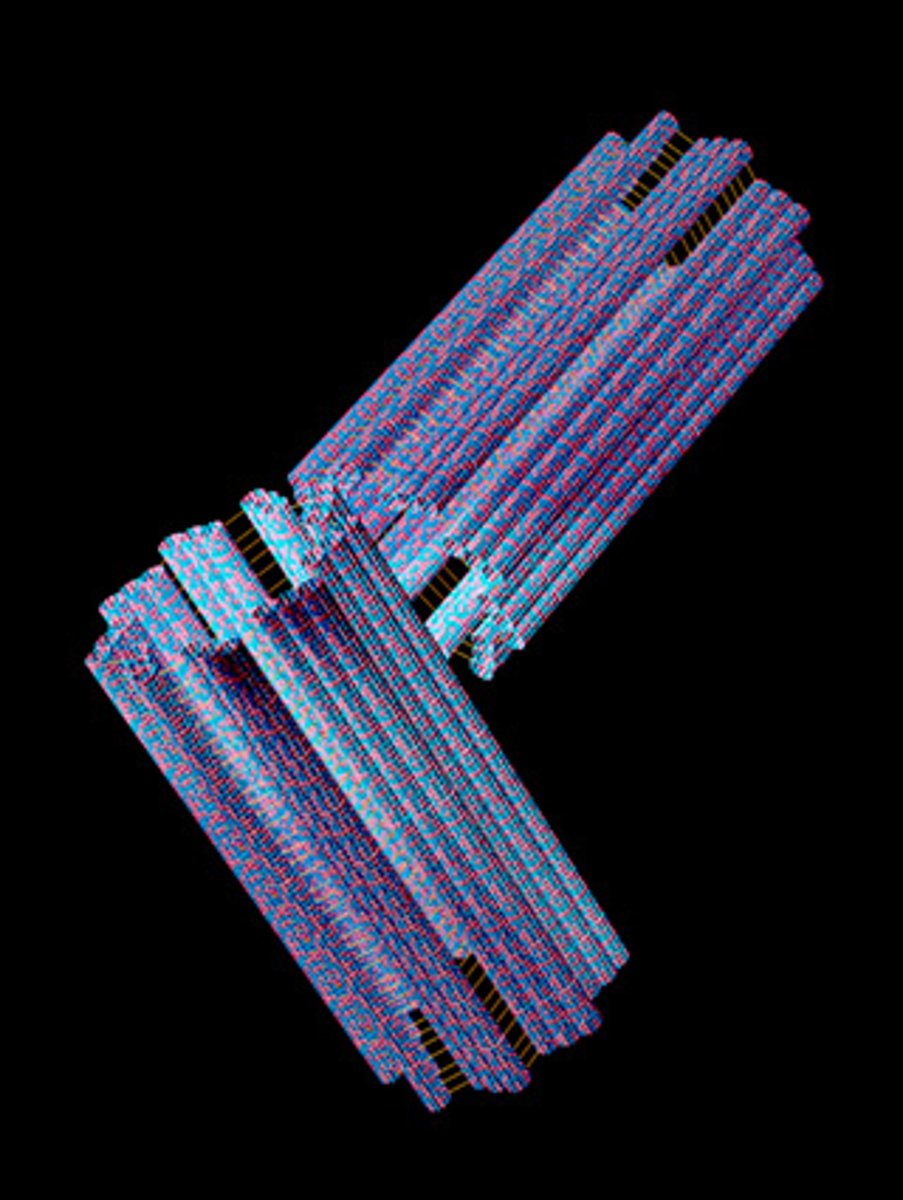
Centrioles
Necessary for cellular reproduction and spindle formation
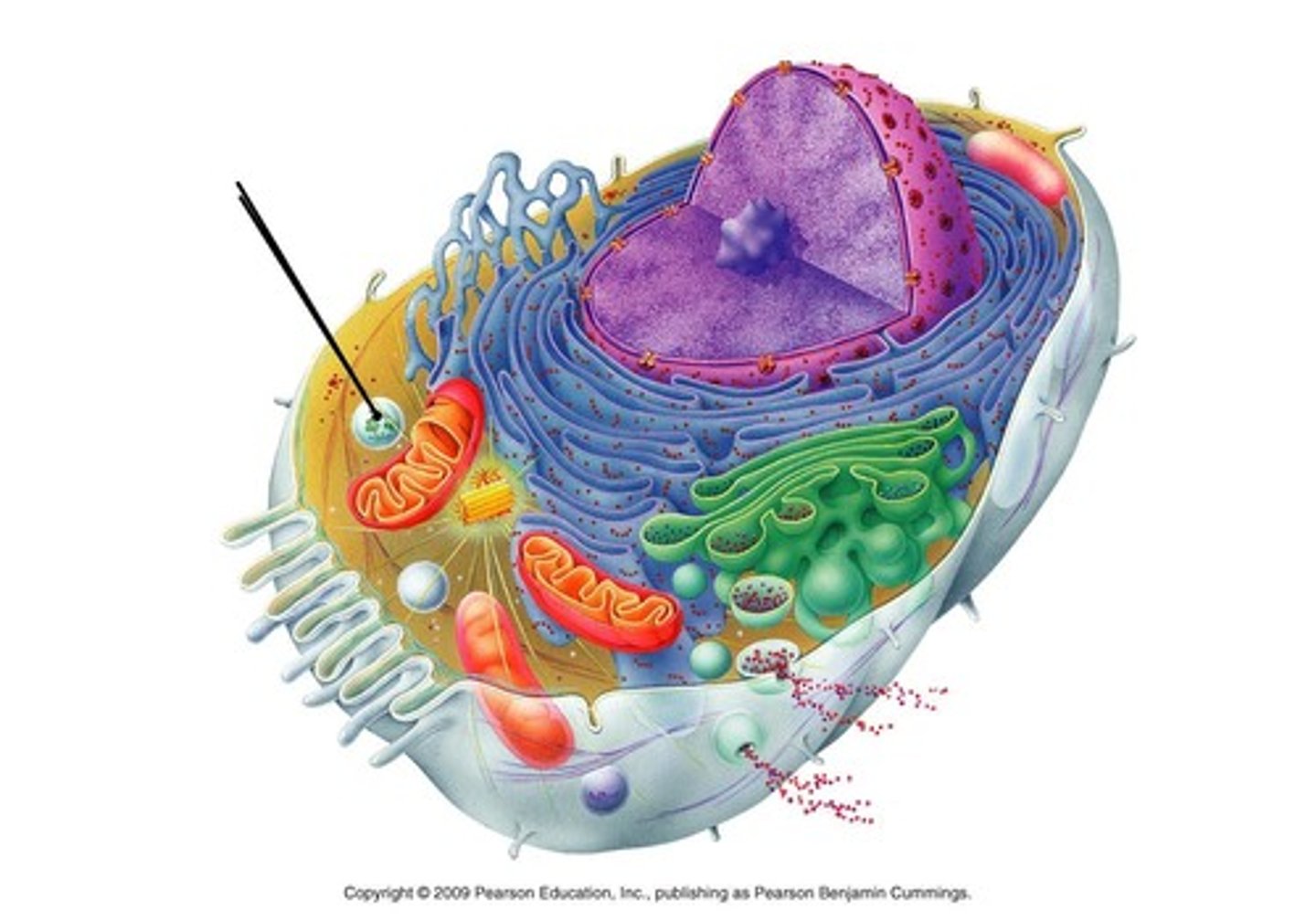
Cilia
Tiny hairs that get rid of junk and provide for movement of molecules
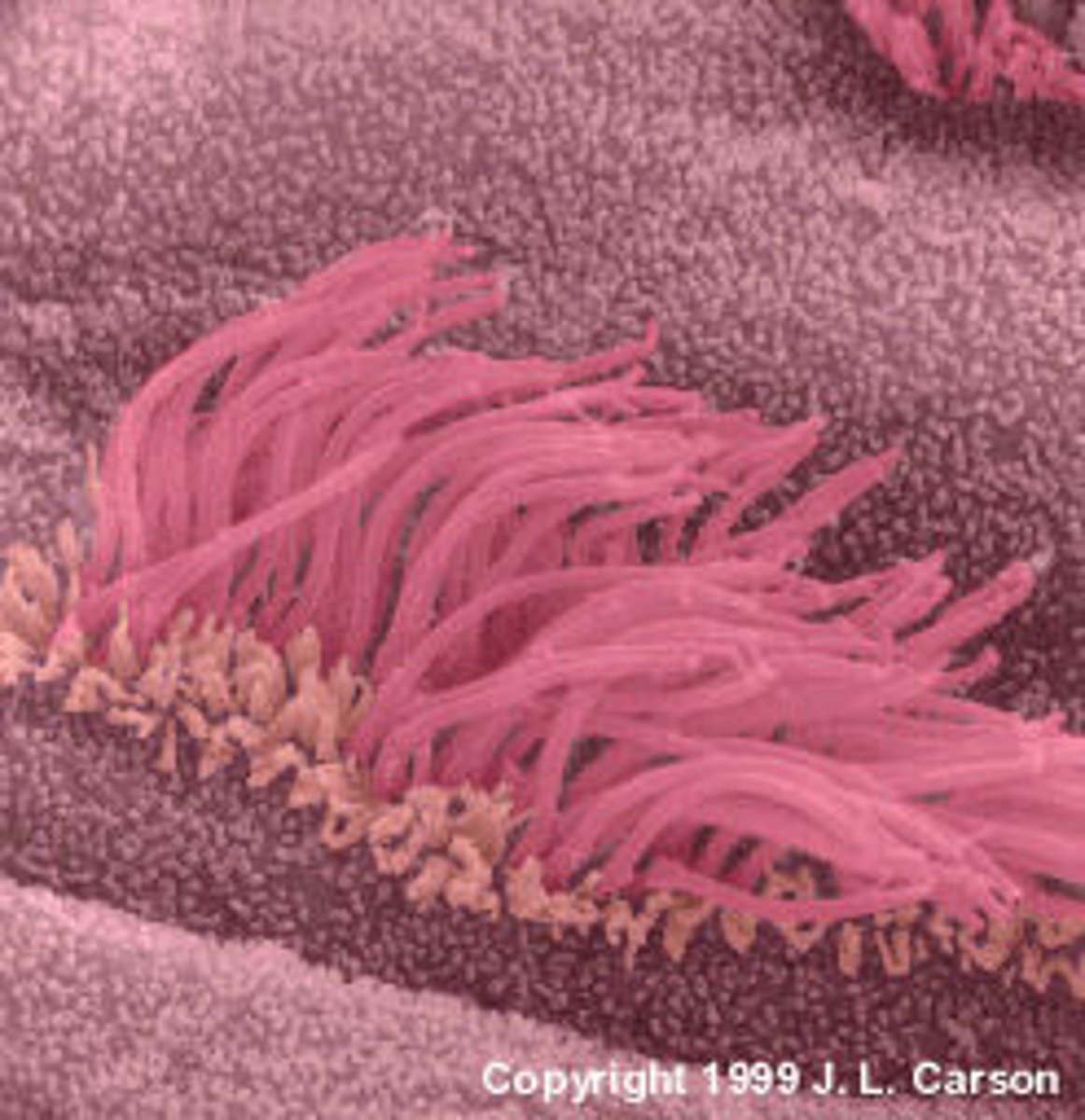
Microfilaments
Enable certain cells to contract or maintain their shape
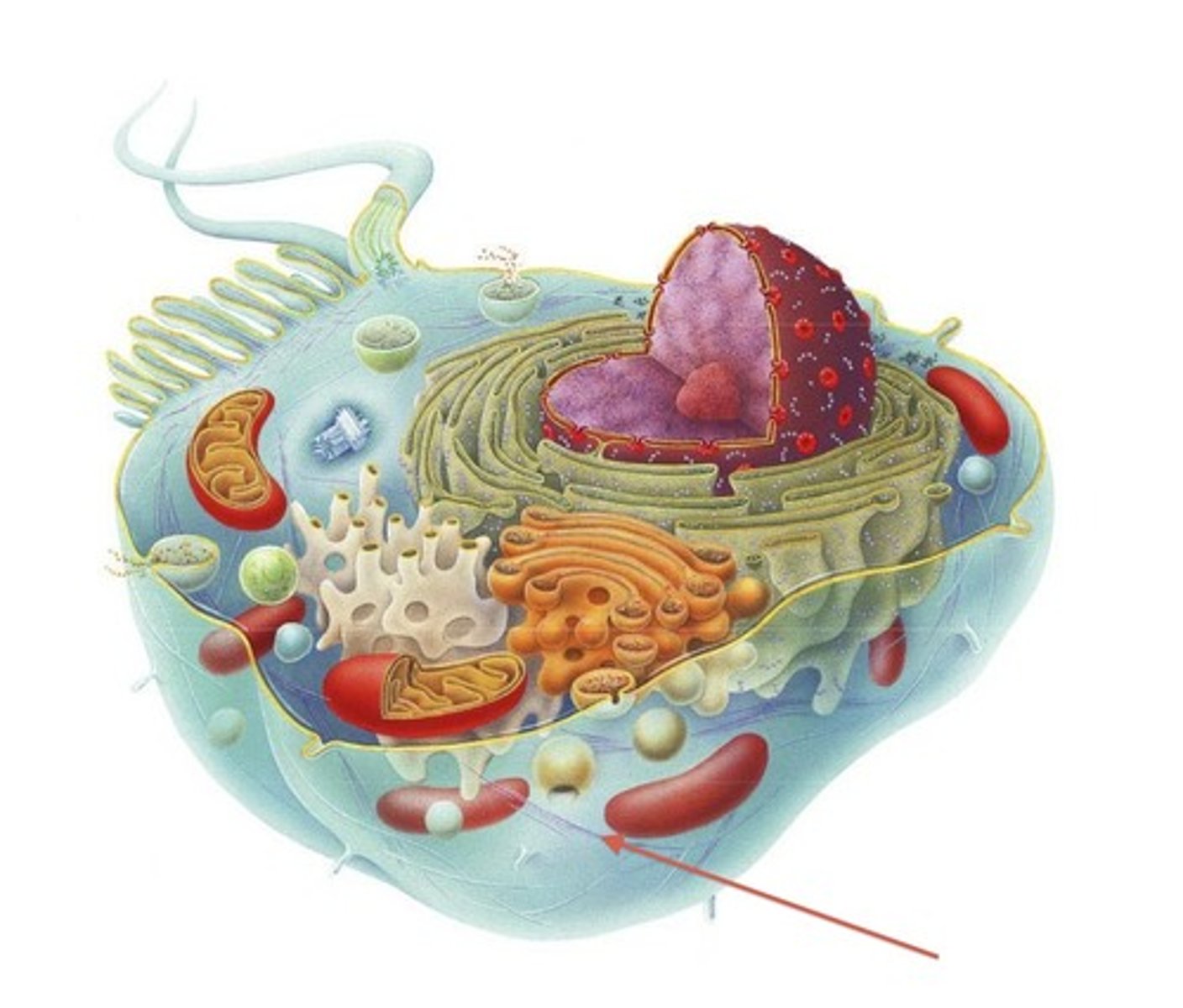
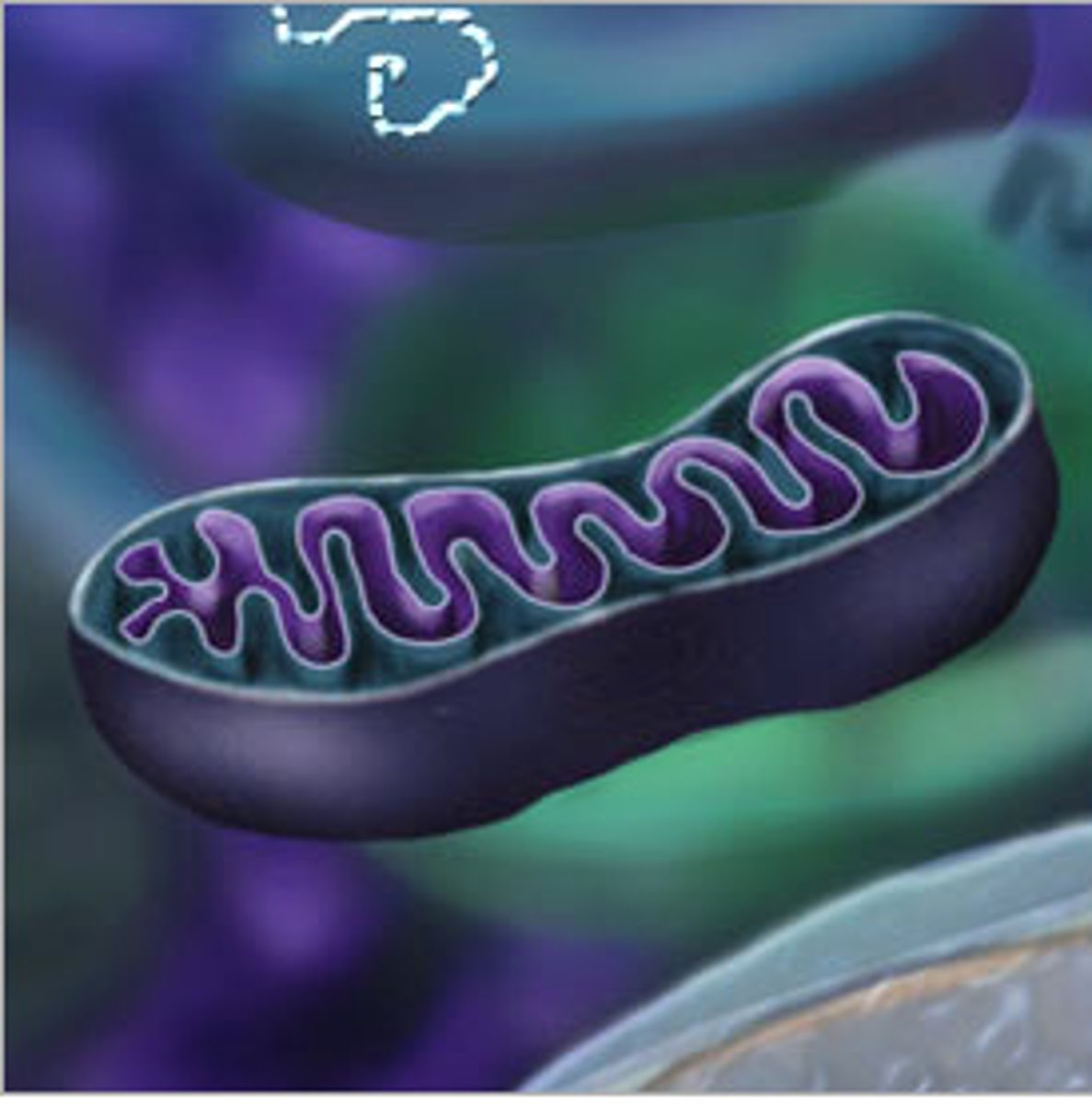
Mitochondria
Produces most of the cell's cellular energy
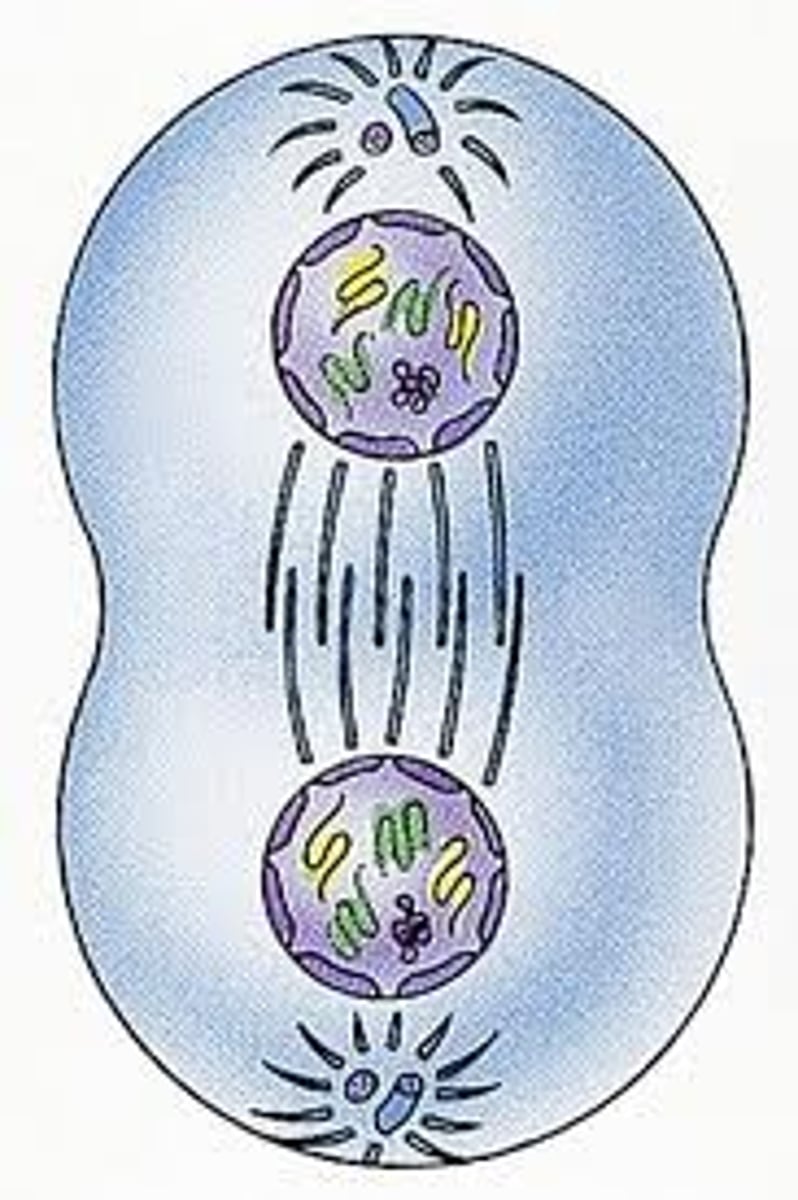
Prophase, ,
first and longest phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate and take up positions on the opposite sides of the nucleus

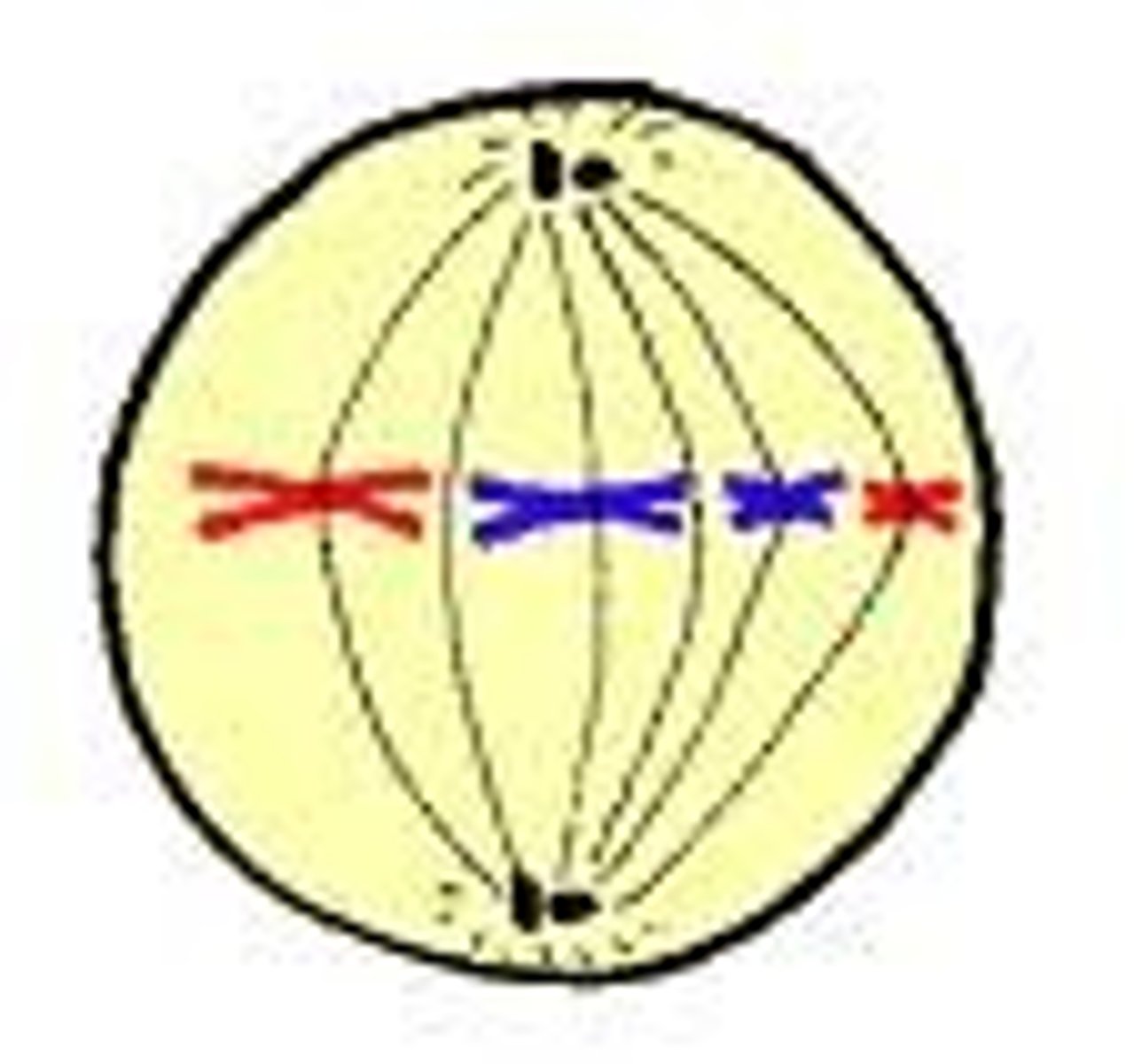
metaphase
second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
Polarity
the property of phospholipids gives the plasma membrane the ability to automatically reassemble.
the function of a glycoprotein in the plasma membrane
allowing cells to recognize eachother
the function of a receptor protein in the plasma membrane
Recieving messages from other cells
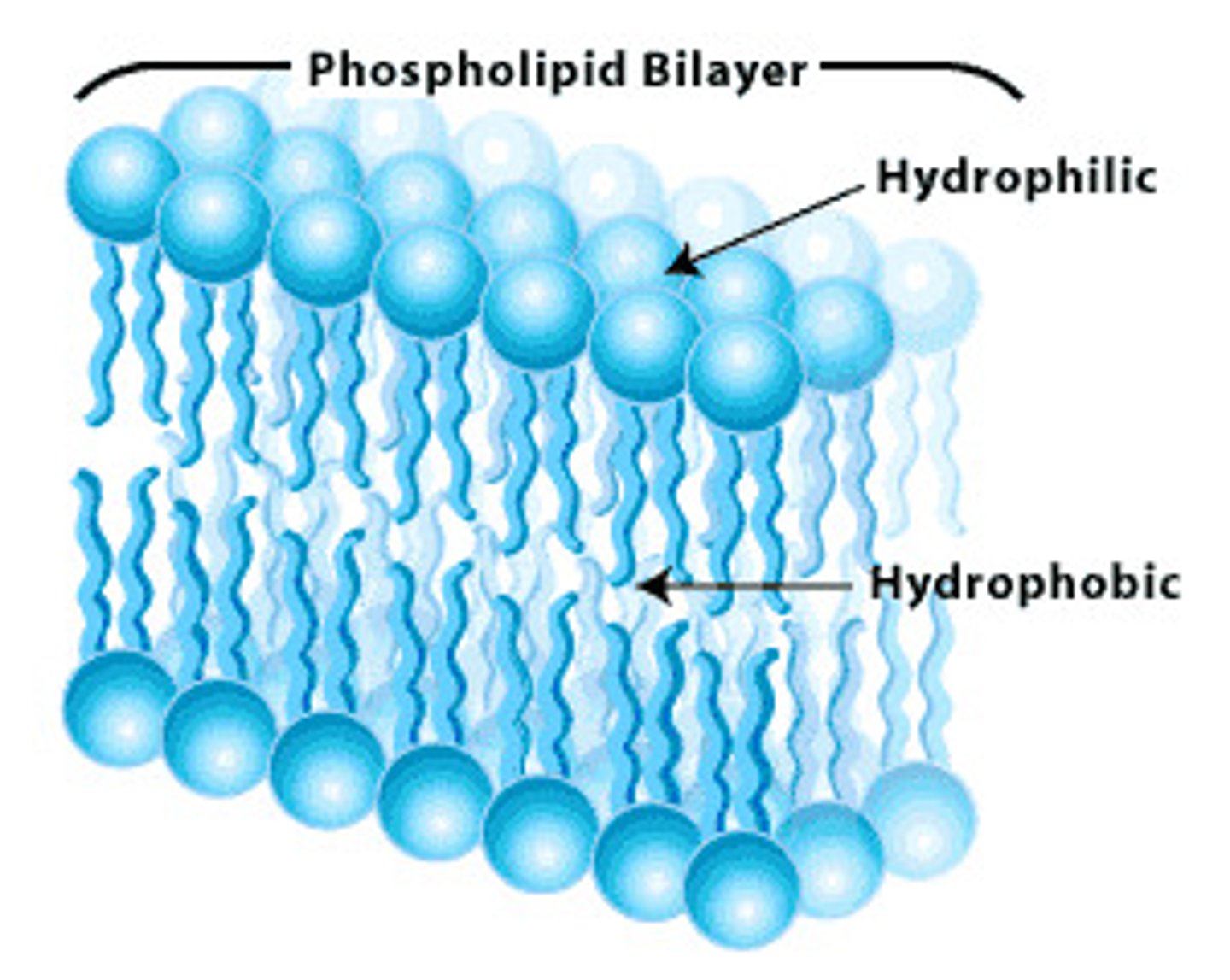
Phospholipids are
the "fluid" in fluid mosaic?
All the different proteins floating there
the "mosaic" in fluid mosaic?
Endocytosis, pinocytosis, phagocytosis, channel proteins, carrier proteins, phospholipids
The six ways a substance can get through the plasma membrane
Channel proteins
How does water get through the plasma membrane?
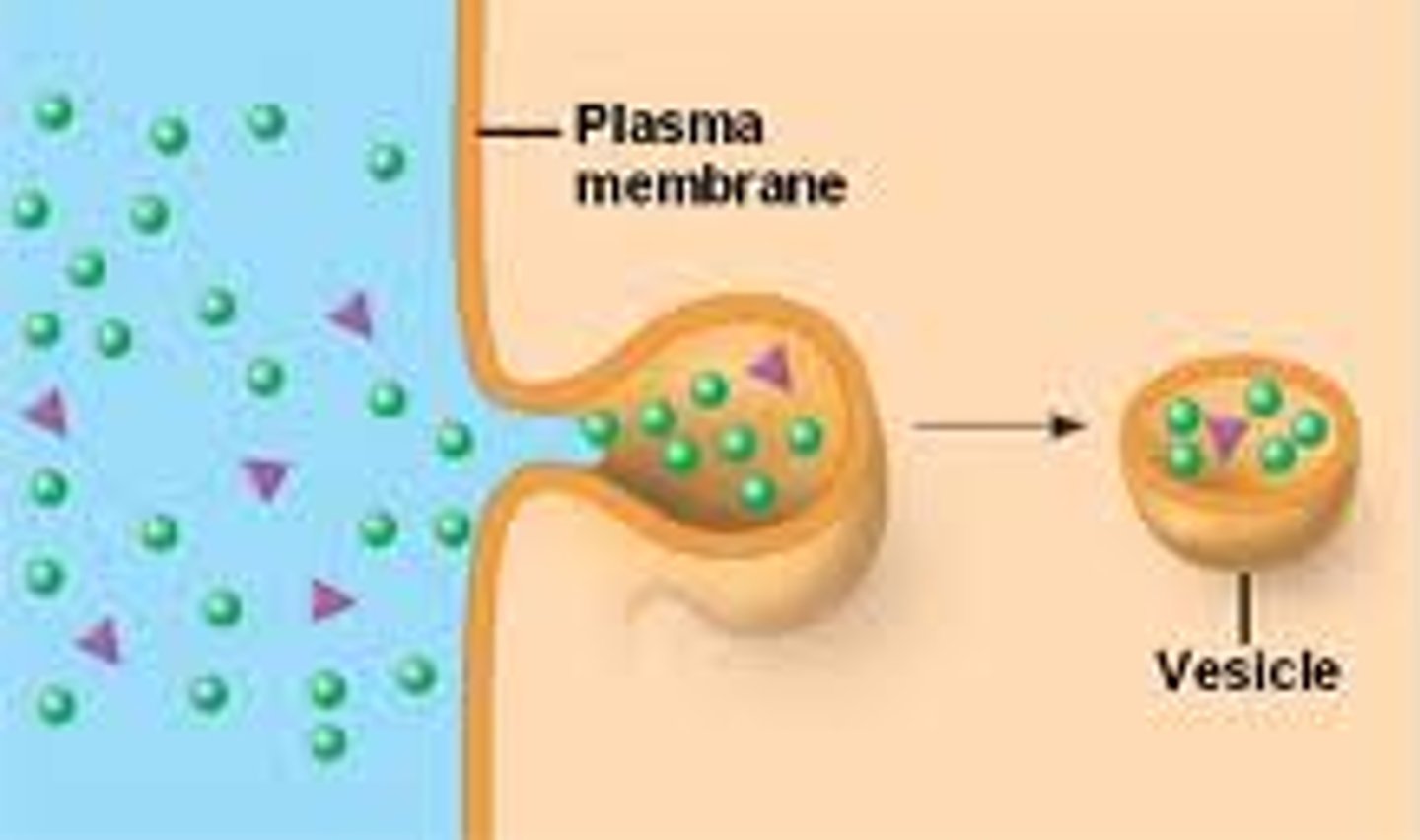
Pinocytosis
How does a protein get through the plasma membrane?
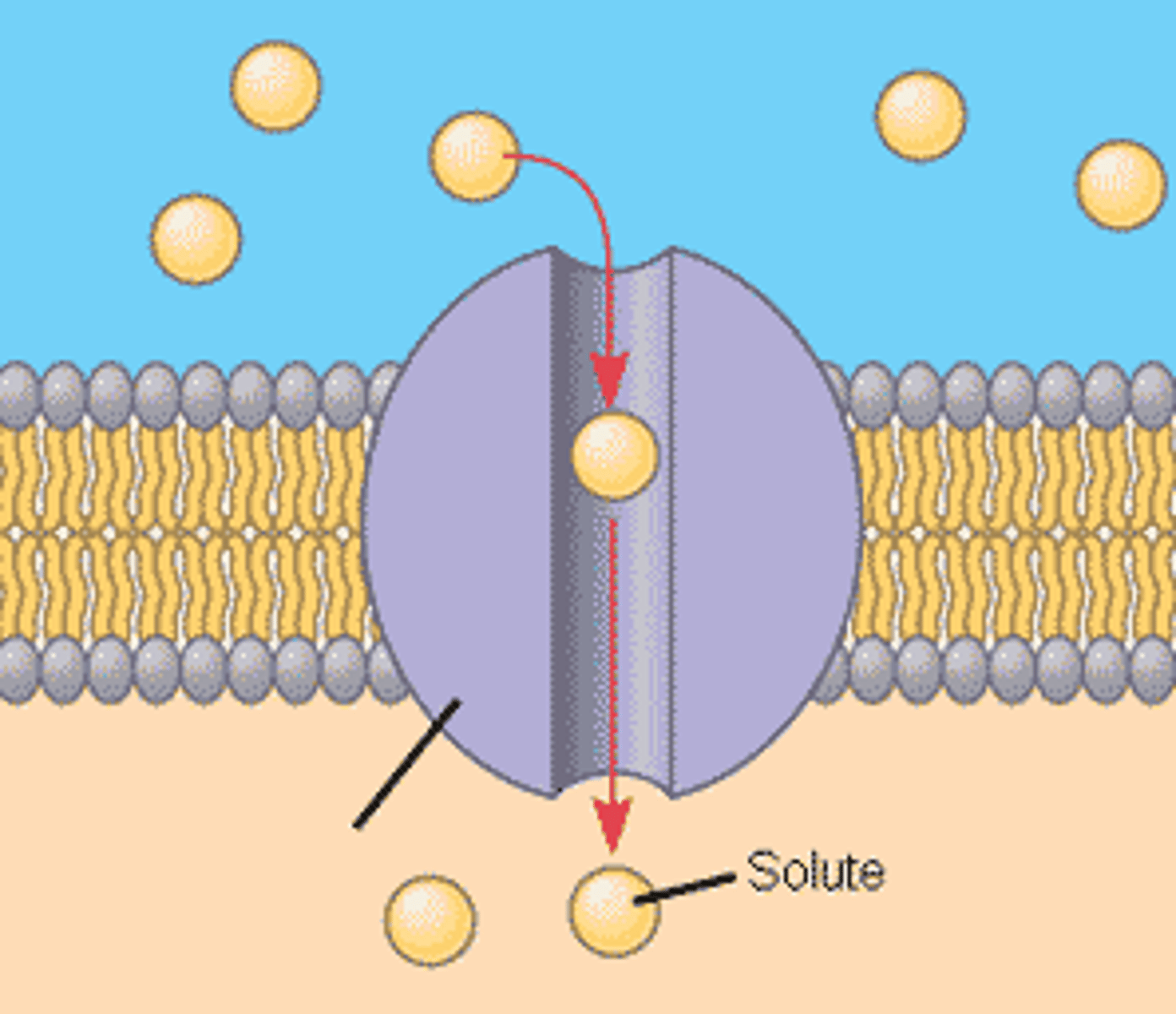
Charged channel proteins
How does a Mg2+ ion get through the plasma membrane?
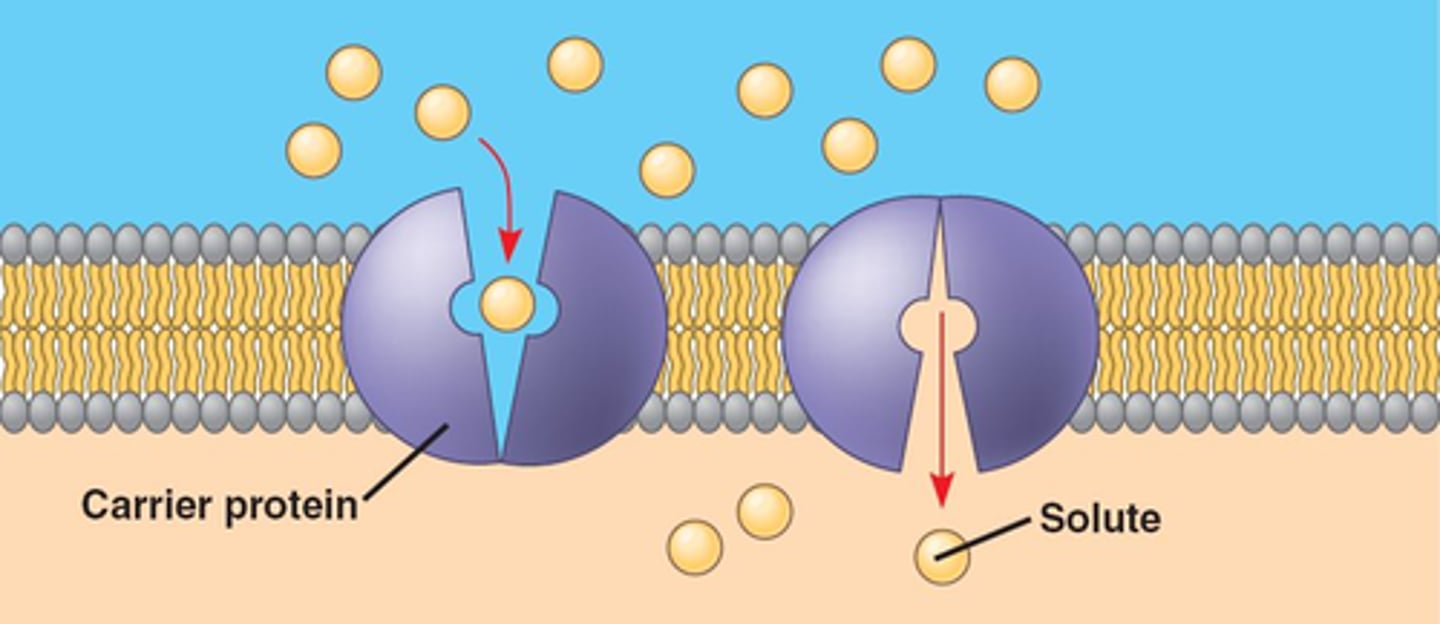
Carrier proteins
How does a monosaccharide (simple sugar) get through the plasma membrane?
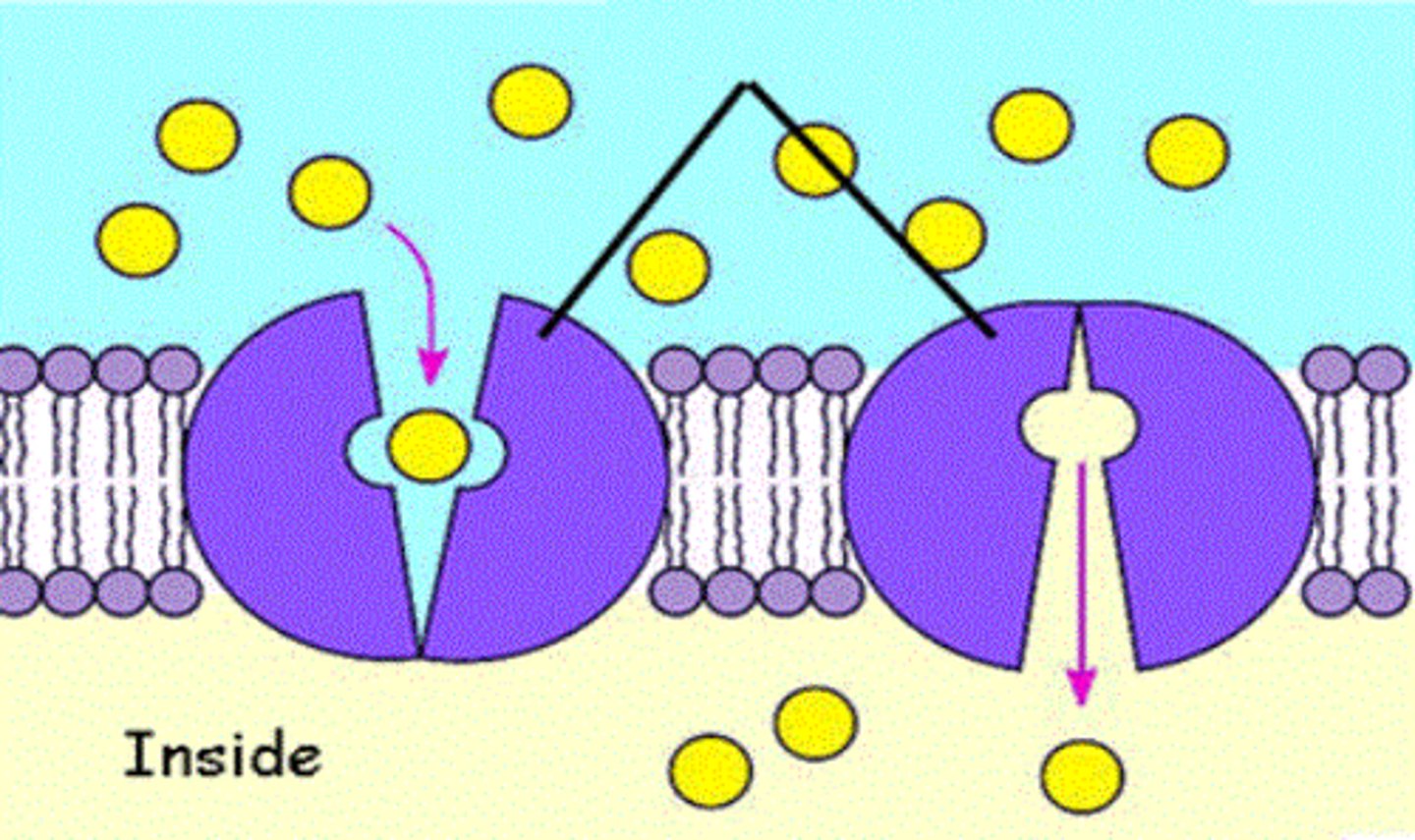
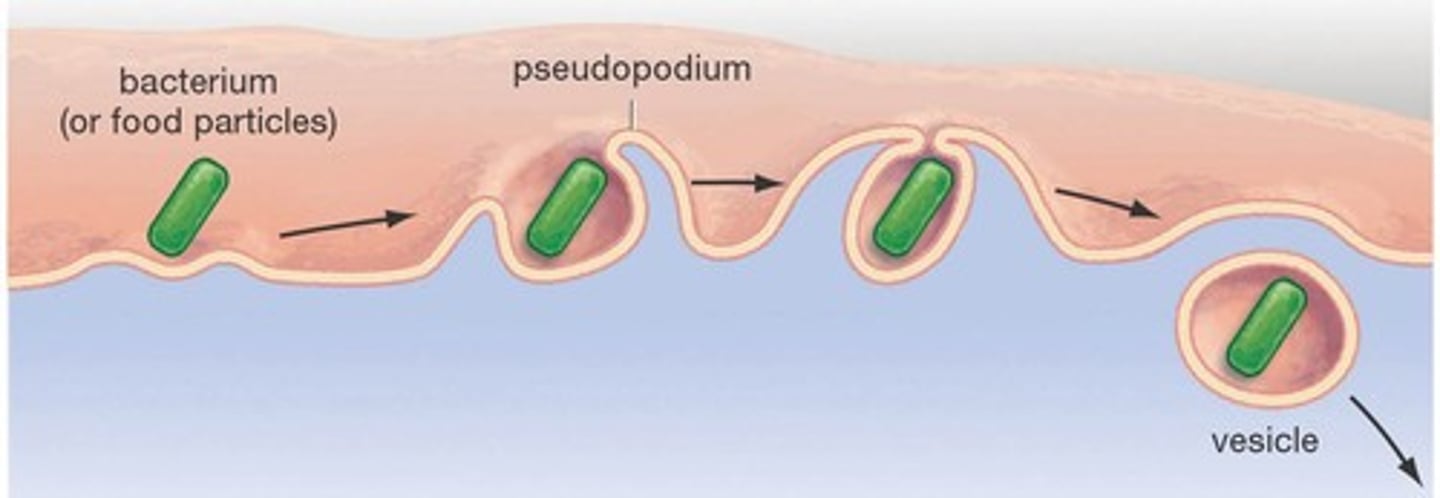
Phagocytosis
How does an invading bacterium get through the plasma membrane?
Phospholipids
How does a lipid get through the plasma membrane?
Active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
No
When a glucose molecule enters a cell and the concentration of glucose inside the cell is lower than the concentration of glucose outside the cell, did the cell use ATP to get the glucose inside?
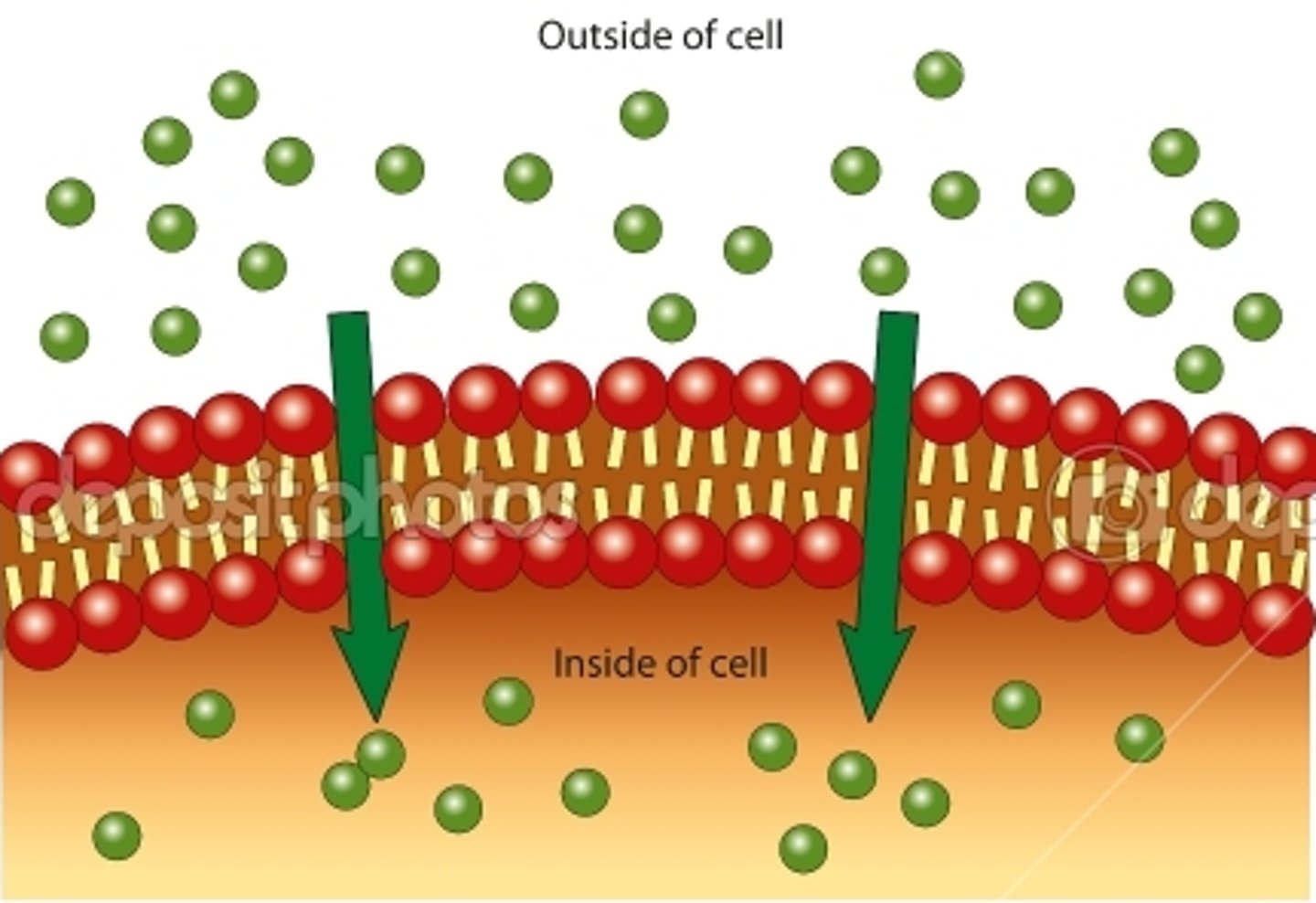
passive transport
The movement of materials through a cell membrane without using energy
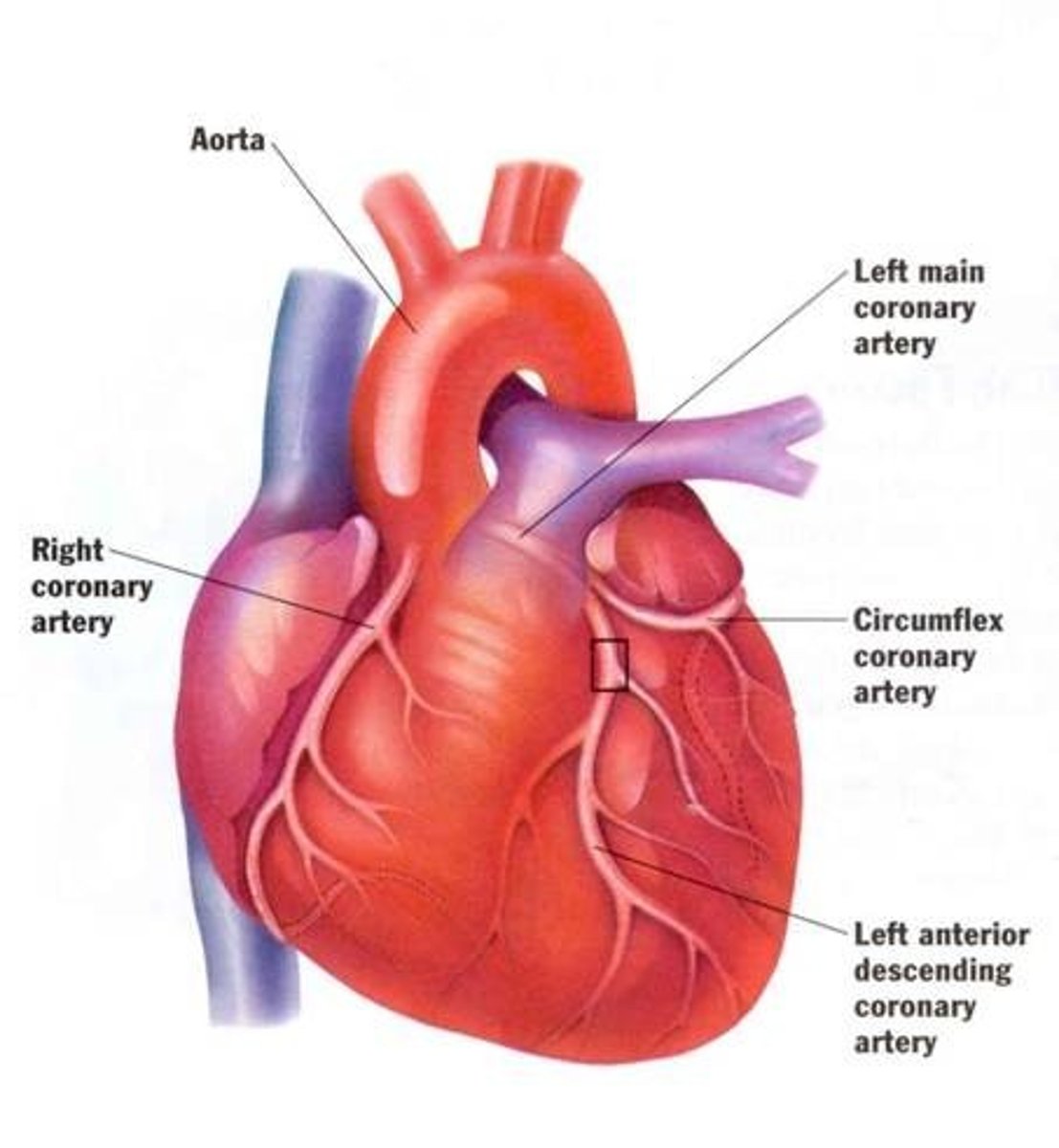
Organ
third level of organization in an organism
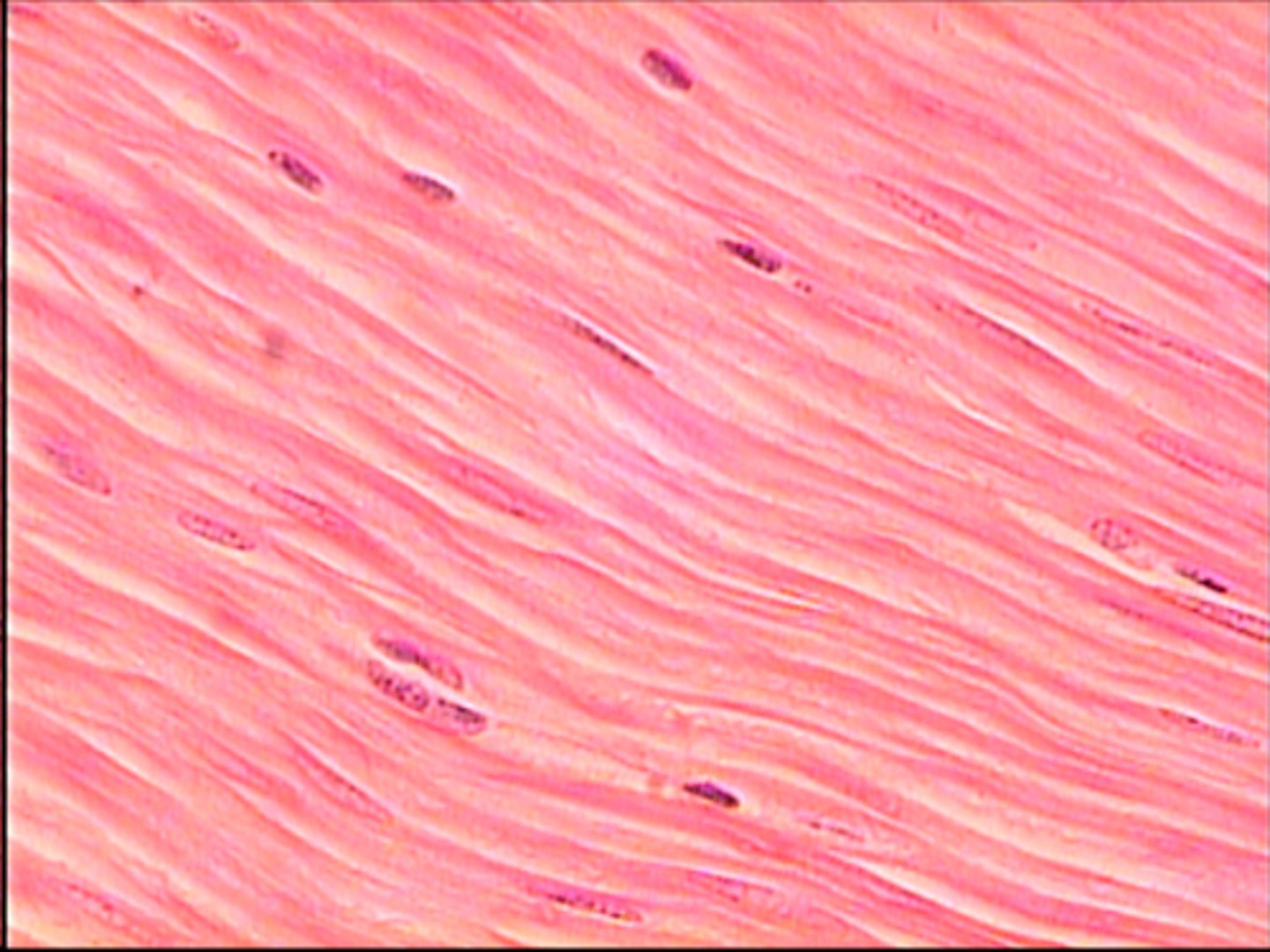
tissues
fourth level of organization in an organism
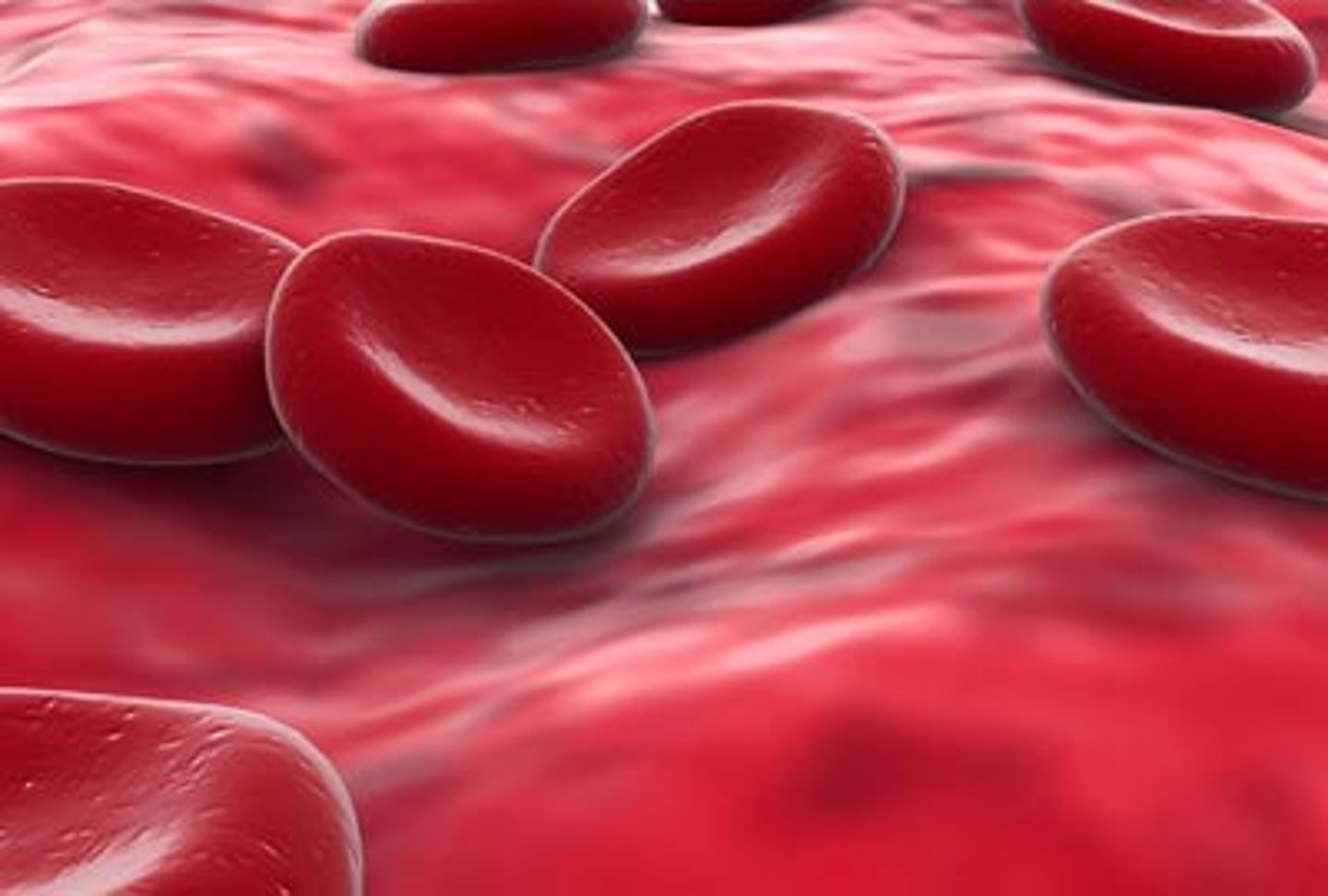
cells
fith level of organization in an organism
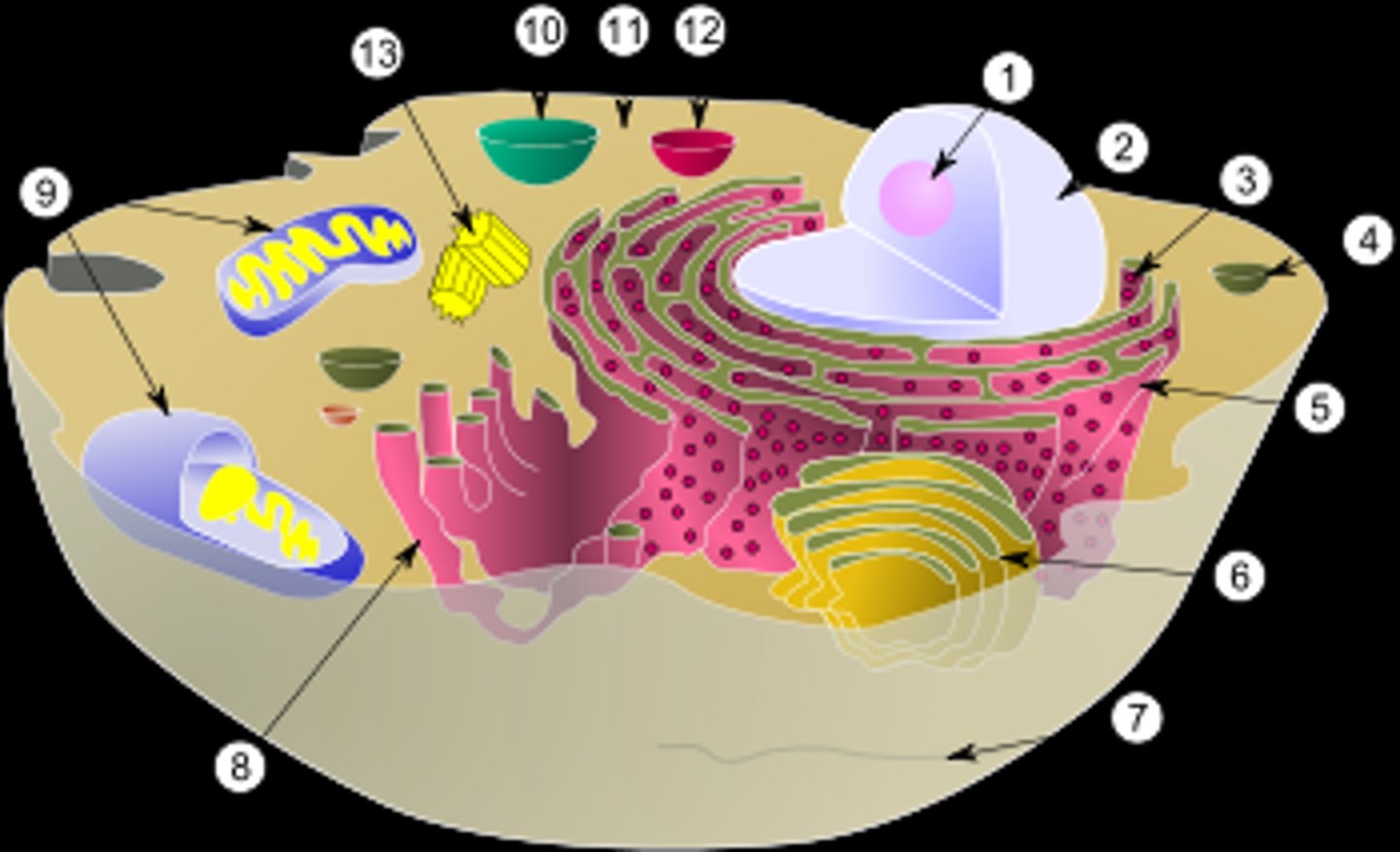
organelles
sixth level of organization in an organism
molecules
seventh level of organization in an organism
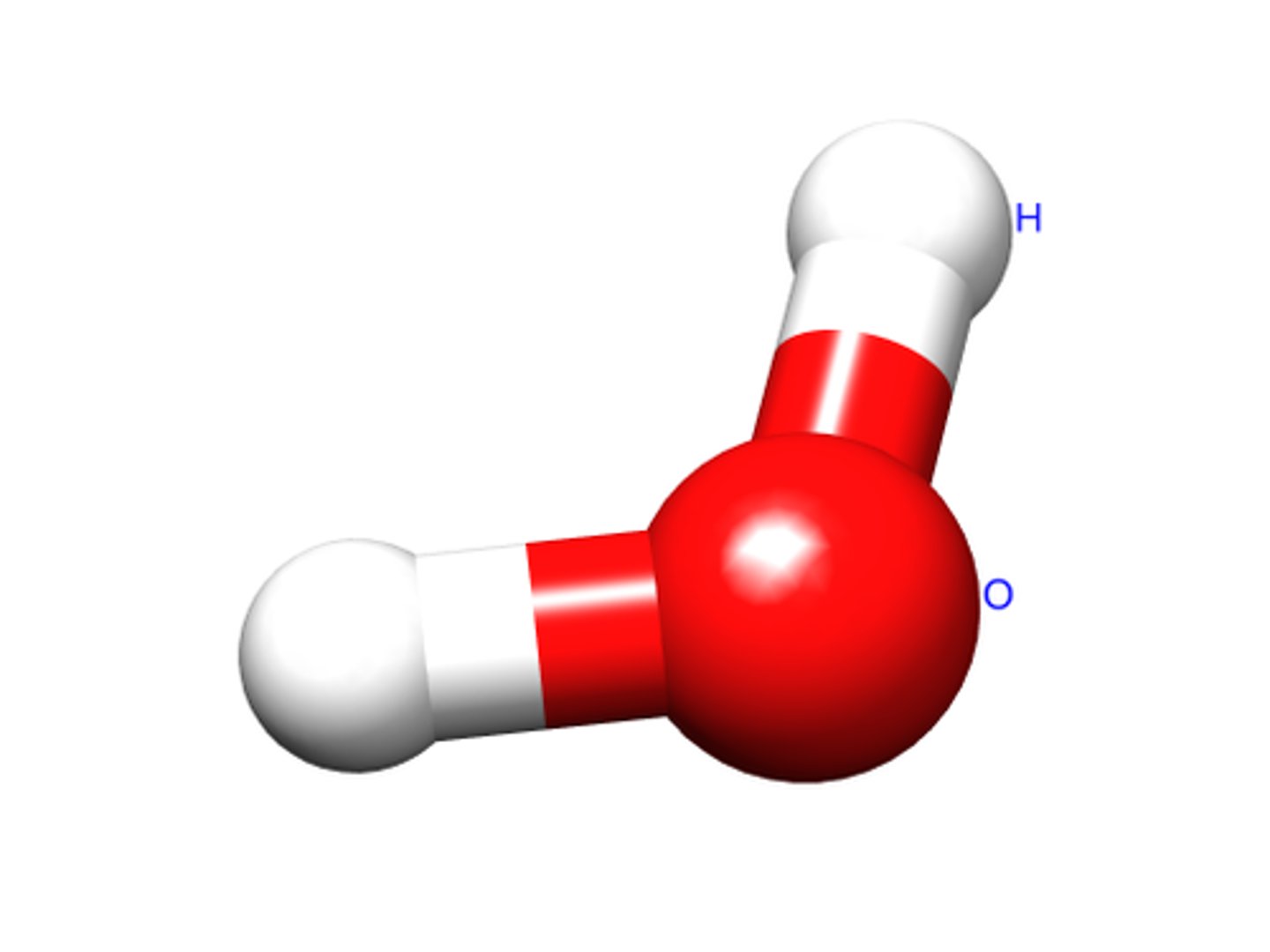
Anaphase
the third phase of mitosis, during which the chromosome pairs separate and move toward opposite poles
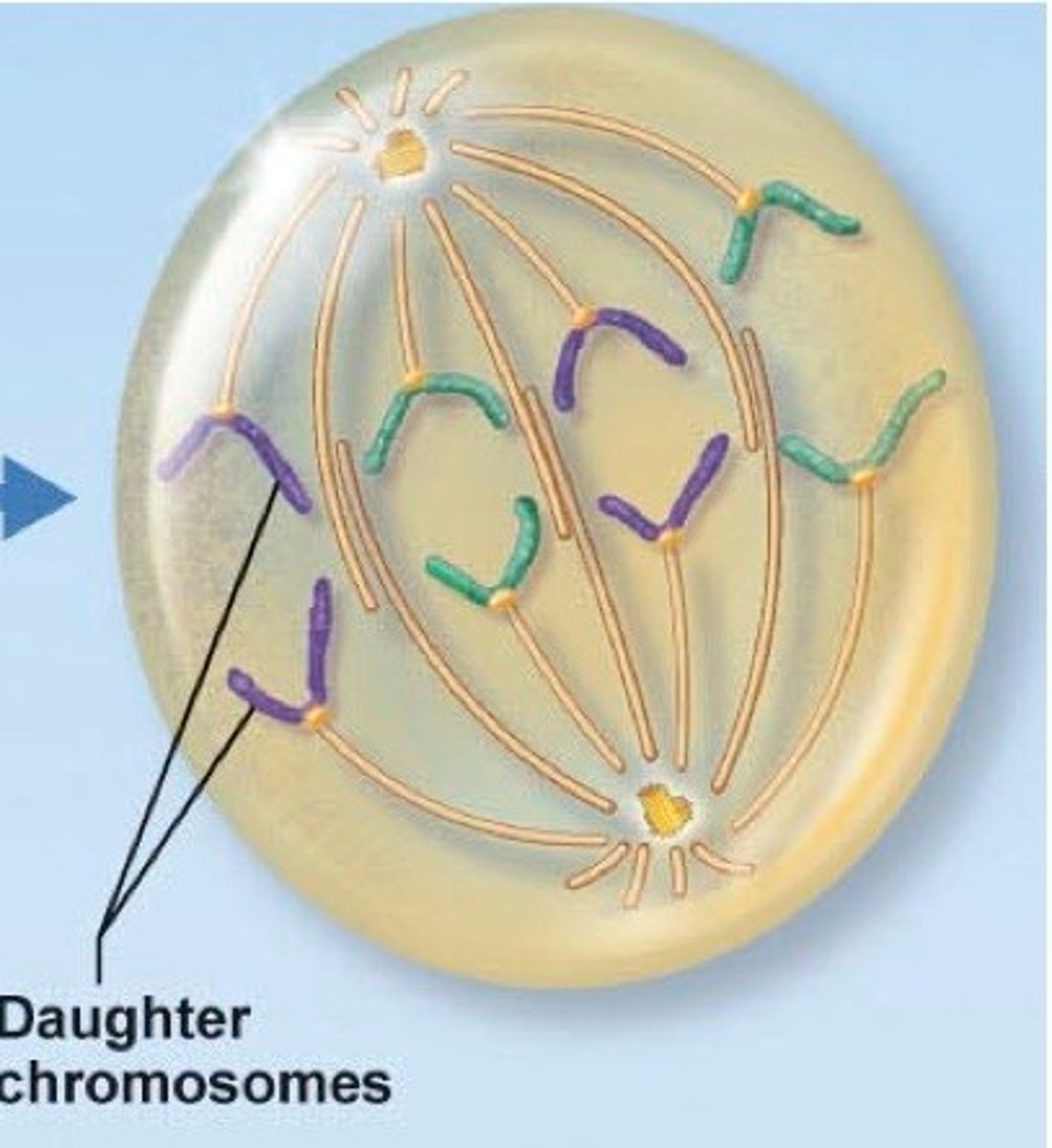
telophase
the final phase of cell division, between anaphase and interphase, in which the chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and two nuclei are formed.