Microbial Systems L.N1
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Lecture N.1
.
What is the cell?
fundamental building block of life
Critical ways how the cell can be distinguished
Growth and reproduction (self-produce), organized and selective , major elements, self-feeding .
Classification of the cells
Prokaryotes (don't have a nucleus) and Eukaryotes (true nucleus)
What are the viruses?
They aren’t real cells, they depend on a host for replication.
What is a prion?
Totally protein
What can abnormal prions do?
They are infectious and can destroy the brain tissue and It can look like a spongy appearance
All bacteria are microbes but not all microbes are bacteria. True or false?
True
For what is the morphologies cell in prokaryotic cell?
They are helpful to characterize cells, filamentous bacteria are dangerous
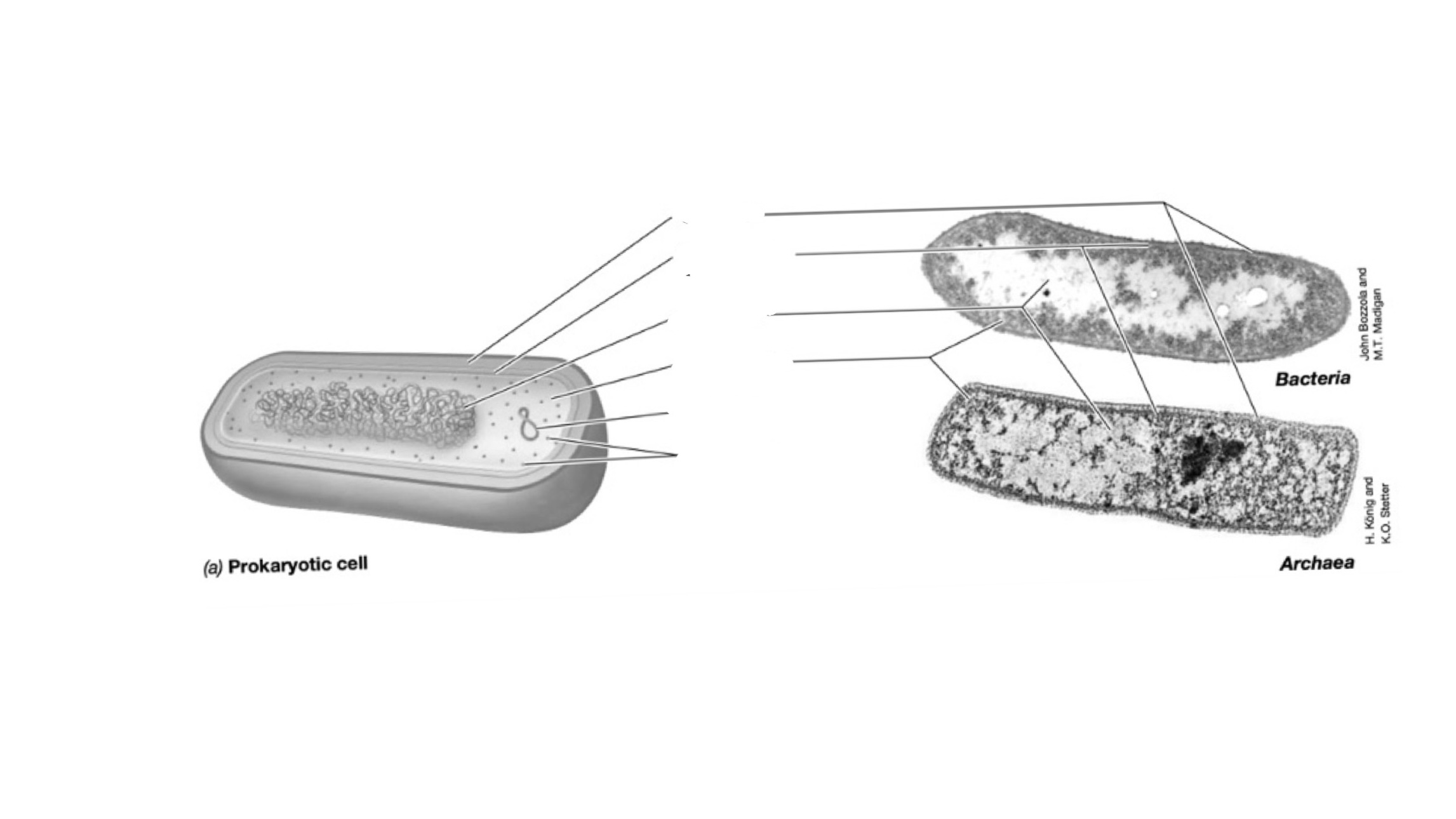
What is the cell structure in BACTERIAL cells?
Cell wall, cytoplasmatic membrane, nucleoid, cytoplasm, plasmid, ribosomes.
Explain each one
Cell wall: rigidity and protects the membrane (in bacterias they are made of 2 sugars)
Cell membrane: Barriers to influx the nutrient, create a separate environment (Function: transport, support for proteins, outside and inside reactions)
Ribosomes : They are in euk. and prok. , protein synthesizing, prok. only have one free ribosome, 60% rRNA, 40% protein 20nmm in diameter
Nucleoid: Closed circular DNA
Plasmid: Circular, double stranded DNA molecules and replicate independently
What are special membranes in bacterial cells?
Extreme environment, special type of lipid and its called “archaebacteria”
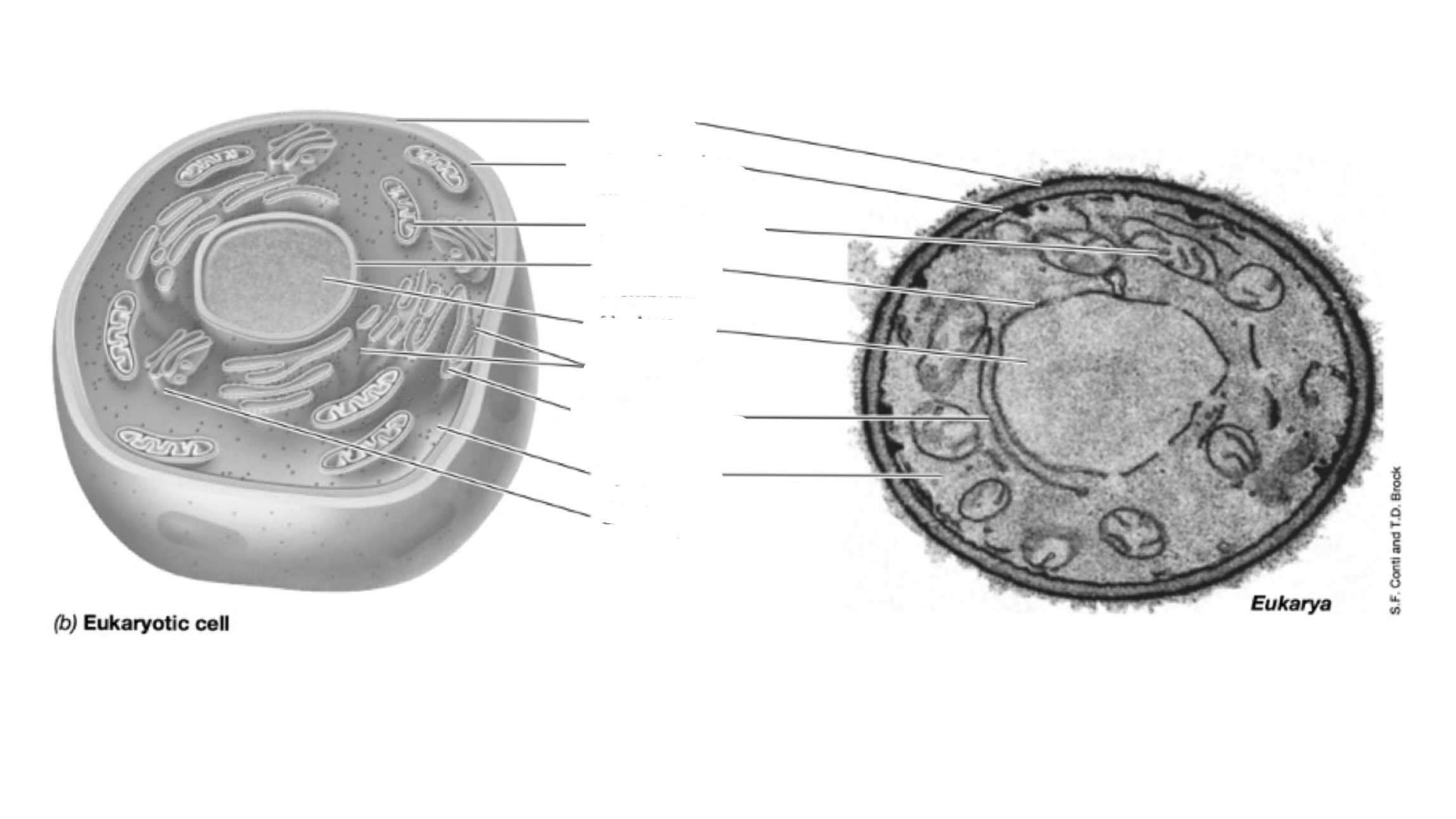
What is the cell structure in EUKARYOTES cells?
Cell wall, cytoplasmatic membrane, mitochondrion, nuclear membrane, nucleus, ribosomes, endoplasmatic reticulum, cytoplasm, Golgi complex
Explain each one
Cell wall: (fungi, plants,animals)
Membrane: basic features (plasma membrane and cytoplasm)
Ribosomes: Protein synthesizing , rRNA protein radio 1:1 , 25-30 nm in diameter
Endoplasmatic reticulum: only in euk. site of protein synthesis
Mitochondrion: unique strcutres of fungi, plants, animals, ONLY IN EUKARYOTES energy production
Golgi: proteins inside before they are sent, importan in the process of proteins
Nucleus: only in euk., linear DNA with chromosomes
Chloroplasts: organelles made conversion of light to energy
why in the chloroplasts the lost of internal membranes?
because It needs a specific surface area to the activity occurs
What does the mitochondria do?
Produce of chemical energy and is stored in ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
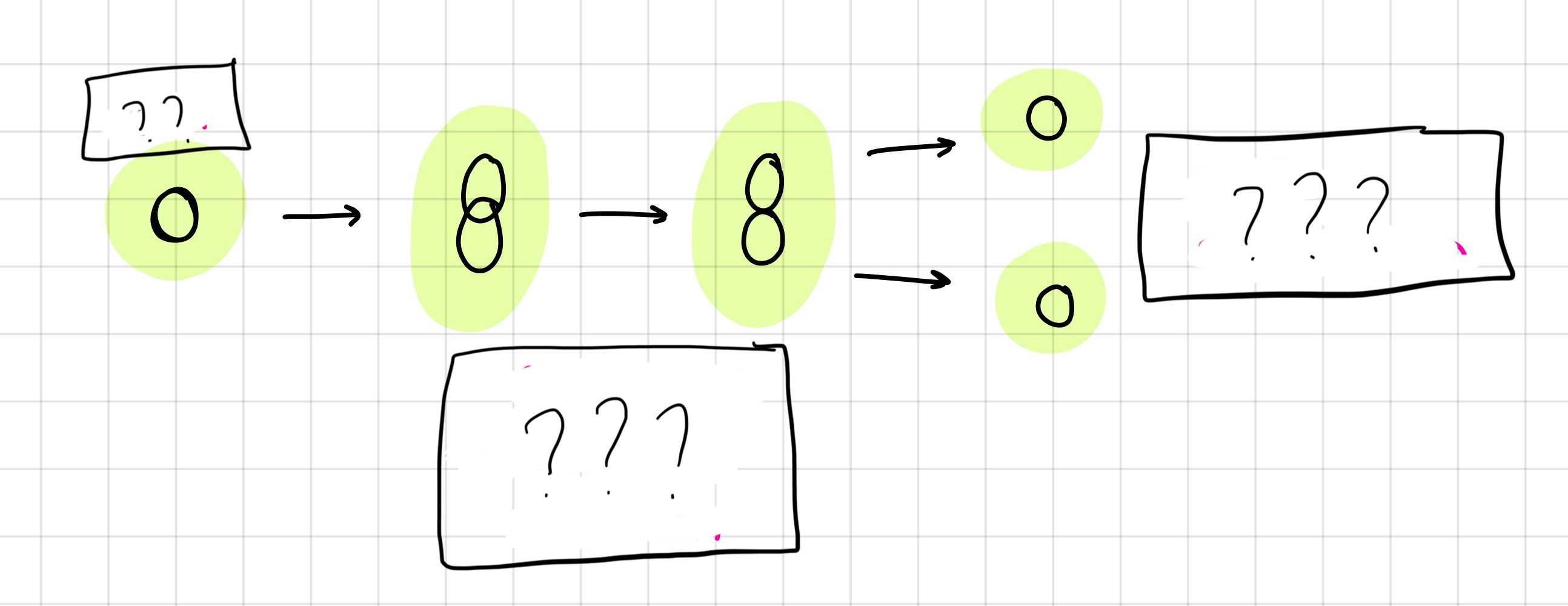
Binary fission of prokaryotes
cell numbers and components double every generation
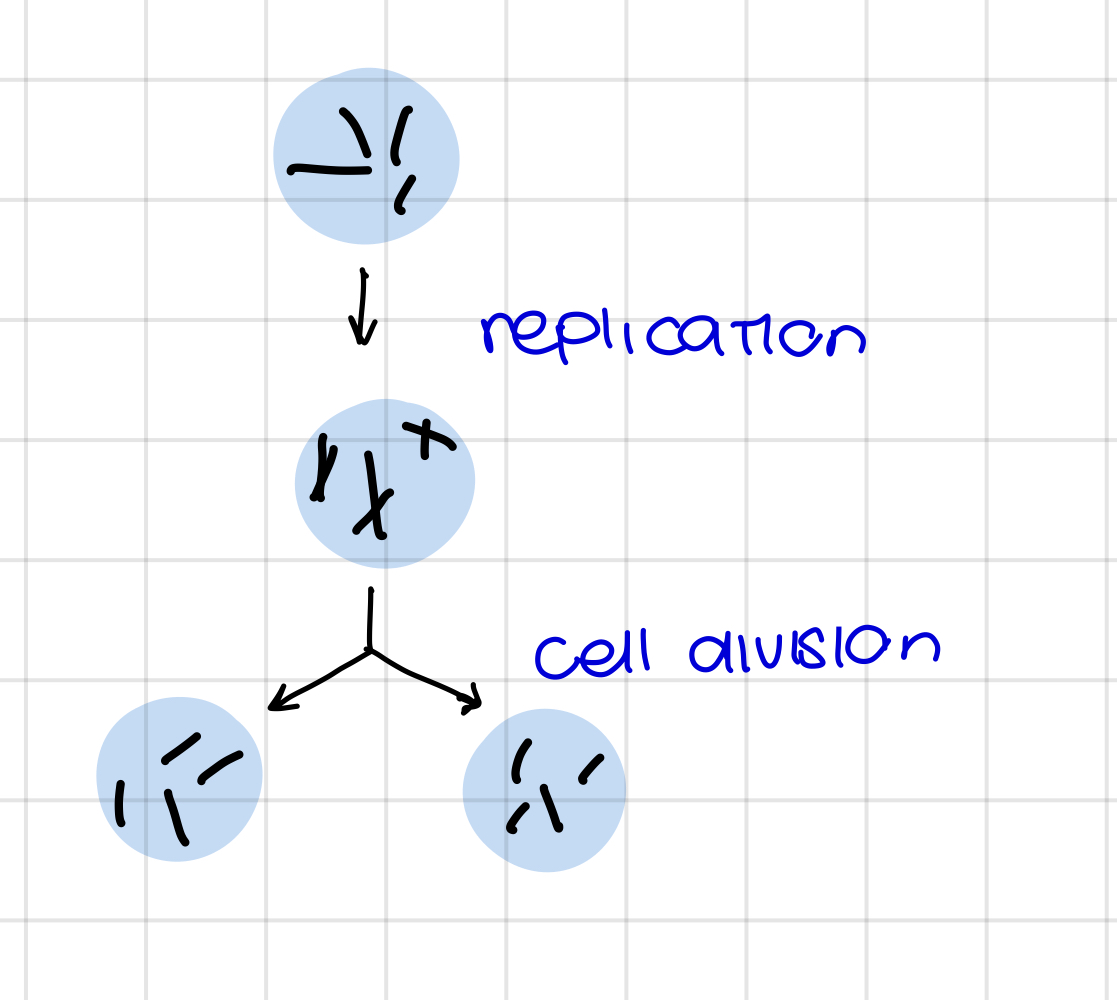
for what is mitosis ?
cell division for growth, cellular reproduction and repair of the body
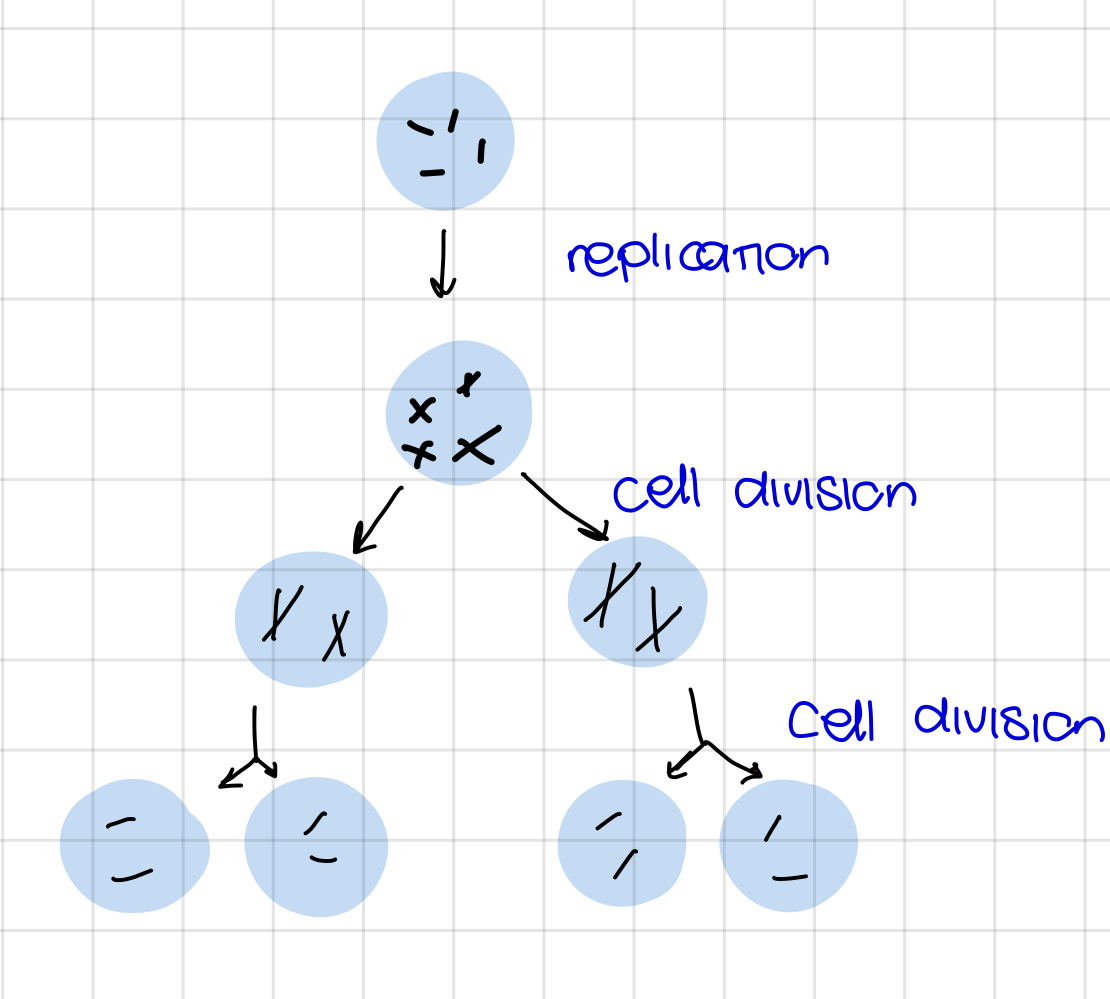
For what is meiosis?
sexual reproduction, produces sex cells
Covalent bonds and examples
Macromolecules from small organic molecules (Proteins ←amino acids)
Noncovalent bonds
Determine the shape and stabilize complexes of two or more molecules
Types of non covalent bonds
Hydrogen bonds - complementary DNA
Ionic bondes - ion-protein
Van der waals - protein-protein
Hydrophobic interactions - protein-folding
Which is the most strong chemical bond formed by sharing a pair of electrons?
Covalent bond, one single bond is 80kcal
What is a Hydrogen bonds?
noncovalent bond, interaction of a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom such as oxygen
Hydrogen bonds has solubility decreases sharply with chain length, why? (solubilidad disminuye bruscamente con la longitud de la cadena)
It’s difficult to form organized other arregment, entropy is lower, is more organized and entropy represents caos
Chemical macromolecular characteristics of prokaryotic cells
proteins (50-60%)
carbohydrates (10-15%)
lipids (6-8%)
nucleic acids (DNA - 3% , RNA 15-20%)
Mention the four main families of small organic molecules in cells
Fatty acids → lipids → essential of membranes, energy storage molecules
Sugars → carbohydrates → energy storage and production
Aminoacids → proteins → they’re in everywhere, machines for different process
Nucleotides → Nucleic acids → storing genetic code
Difference between Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic
hydrophilic like water water, hydrophobic water hate oil
Functions of the cytoplasmic membrane
a) permeability barrier: gateway for transport nutrients
b)Protein anchor: Proteins in transport
c)Energy conservation: Generation and dissipation of the proton
what is Transport proteins
accumulate solutes, high selectivity and High specificity
say the types of Carbohydrates
Monosachharides, Disaccharides, Polysaccharides , dehydration reaction
explain monosaccharides
Glucose (blood sugar) , galactose (sugar in milk) , fructose (sugar in honey)
explain dehydration reaction
if We have two molecules, they combine and lose water molecules
explain disaccharides
Structural isomers composed of hexoses.
sucrose (table sugar), lactose (sugar milk), maltose (starch digestion)
explain polysaccharides
polymers of tens to hundreds units
Glycogen (broken back down intro glucose when energy us needed), cellulose (abundant organic molecule in biosphere
What are the proteins?
cell ranges between 40 and 60% of dry weight , functions: transport, enzymes, adhesion motion
Basic structure of an amino acid - protein
Aminoacids determine how is going to be protein, the protein is the transport
molecules containing an amine grupo, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain
Gregor mendel and his peas
1850-mendel performed collect data and uncover the basis principles of genetic
When the chromosomes were discovered?
1800s
Who discovered the structure of DNA
James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953 but its supposed that they steal the idea of Rosalind Franklin
What is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid ) and RNA(ribonucleic acid)
macromolecules composed of monomers called nucleotides
What is a nucleotide base?
They stole tour information to tell your cells how its supposed to work
Mention the Chargarff’s rules
DNA should have a 1:! ratio of pyrimidine and purine bases
The amount of guanine is equal to cytosine and the amount of adenine is equal to thymine