Amines
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
what is an amine

structure of amine
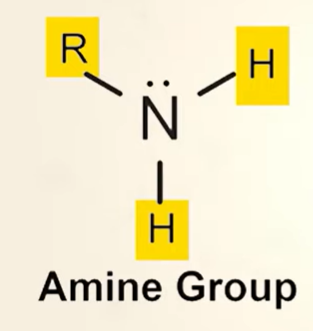
what is a simple amine and mixed amine

Nomenclature of common names of amines

Nomenclature of IUPAC of amines

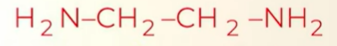
IUPAC name of the structure
ethane-1,2-diamine
note: when more that 1 amine grp is present- you have the e in ethane
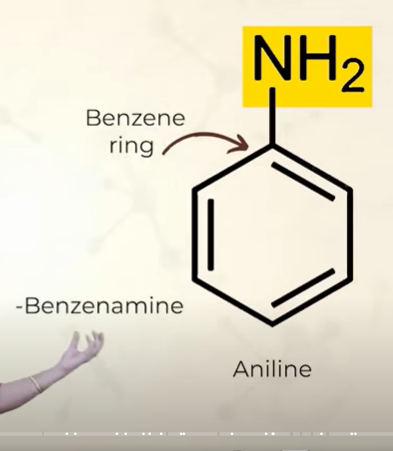
structure of aniline
this is the simplest aryl amine
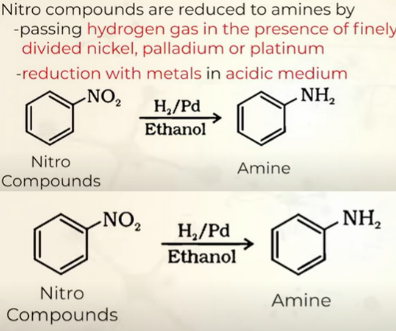
Preparation of amines

prep of amines by reduction of Nitro compounds
2 ways
why is TIN+HCl preferred to make amines?
cus they give a product FeCl2 which hydolyses and gives HCl back again which can again take part in the reaction and supports forward reaction
giving HCl in beginning is sufficient as it gets made over and over again in the reaction
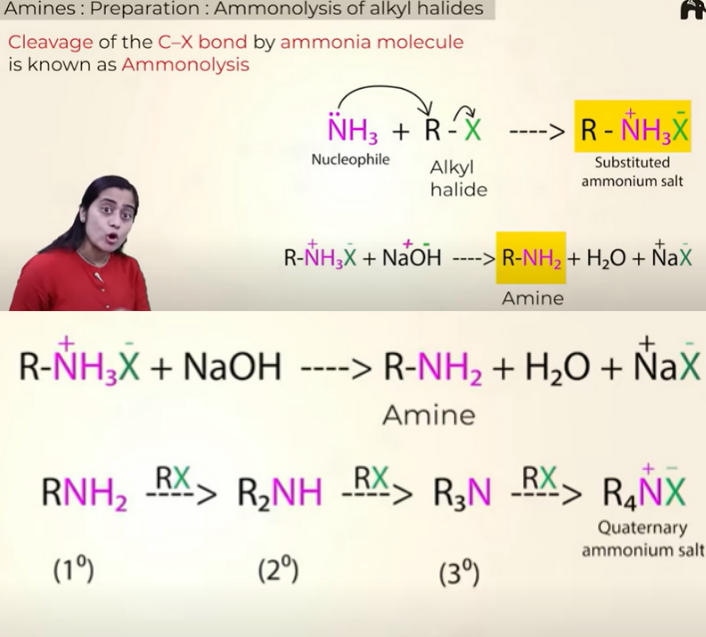
prep of amines by Ammonolysis of alkyl halides
Disadvantage:
you get a mixture of 1o,2o,3o amines
so if you want just primary amine then you can take excess of ammonia
the X in R—X can be chloride, bromide or iodide
their reactivity is as follows:
RI>RBr>RCl
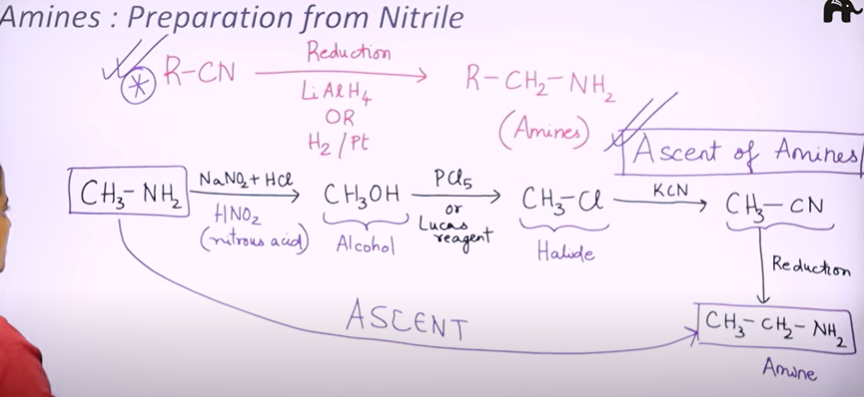
Amines prep from Nitrile(CN) reduction
(Ascent of amines)
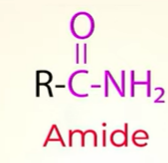
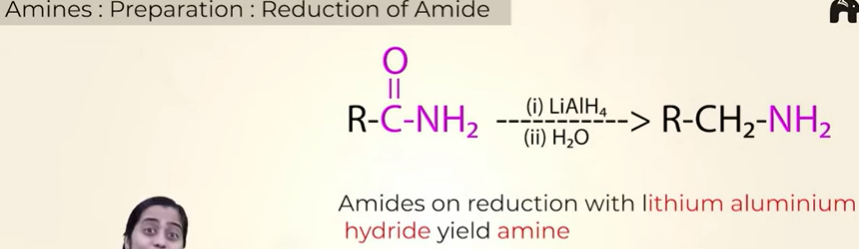
prep of amines from reduction of Amide
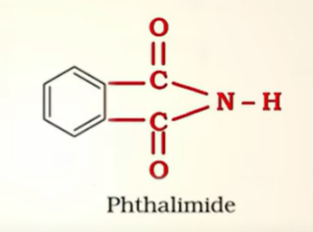
Prep of amines by Gabriel Phthalimide synthesis
note:
only 1o amines can be formed
aryl amines cannot be prepared as the aromatic halide has resonance and partial double bond chr because of which the bond wont break easily
Prep of amines by Hoffmann Bromomide Degradation
the no of C in amine is one less than that it amide
only primary amines can be made

Physical properties of Amines
1 or 2 carbon amines- gasses
more than 3 - liquids
many more carbons- solid
aromatic amine- are colorless generally but when stored they look colord because of atmospheric oxidation
Sollubility of amines
(alkyl grps are hydrophobic)

BP
Amines form intermolecular hydrogen bonding, therefore boiling point is high
BP of alcohols more than amines
BP directly propotional to molecular mass
Odour of amines
lower aliphatic amines are gasses with fishy odour
higher amines dont have strong odour
character of amines
basic
behave as nucleophiles due to unshared pair of electron
tertiary amine- most basic as it has 3 alky groups(alkyl groups are electron donating shows casic chr) holds true only in gseous state
in acqueous state solvation energy matters (solute and solvent interactions )(solvation energy ensures that the solute in solution is stabilised)
in acqueous amine 2o amine is most basic
in methyl substituted acqueous amine—> most basic 2o,1o,3o
in ethyl substituted acqueous amine—>most basic 2o, 3o,1o
Basic character comparison between alkanamine and ammonia
ammonia< alkanamine
alkanamine has alkyl grp which donates more electron to N
upon adding H+ ammonium ion formed from alkanamine is more stable than ammoniam ion
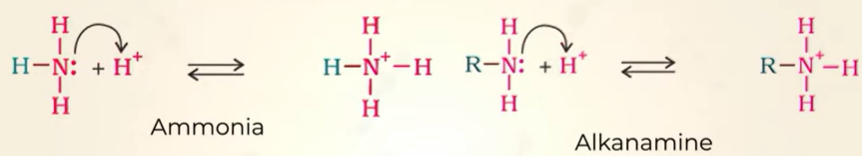
Basic character comparison between arylamine and ammonia
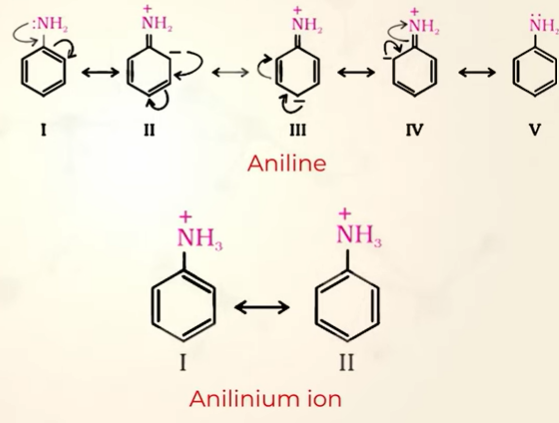
In Ammonia the lone pair is easily available for donation whereas in aniline lone pair of electrons are involved in resonance therefore aryl amines are less basic than Ammonia
aniline less basic than ammonia
aniline when acceps H+ becomes annilinium ion which is less stable than aniline
becuz aniline has more resonance stabilization( has 5 reonating structures, but annillinium has got 2) therefore it would not want to become a less stable structure by gaining H+ (gaining H+ shows basic chr)
but ammonia on the other hand will gain H+ (showing basic chr)
when electron releasing grps are added to aniline - basic chr increases
when electron withdrawing grps are added - become less basic
chemical reactions of amines
Reaction with strong acids
Reaction with aldehyde
Reaction with nitrous acid
Alkylation
Acylation
Oxidation
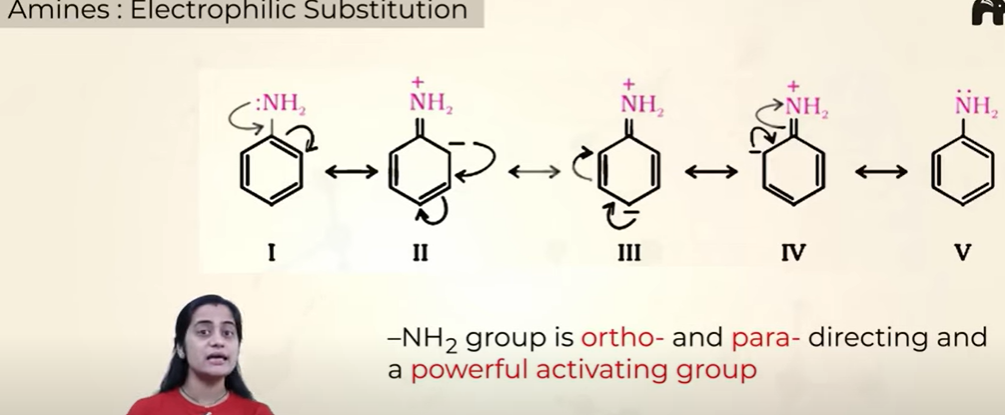
Electrophilic substitution

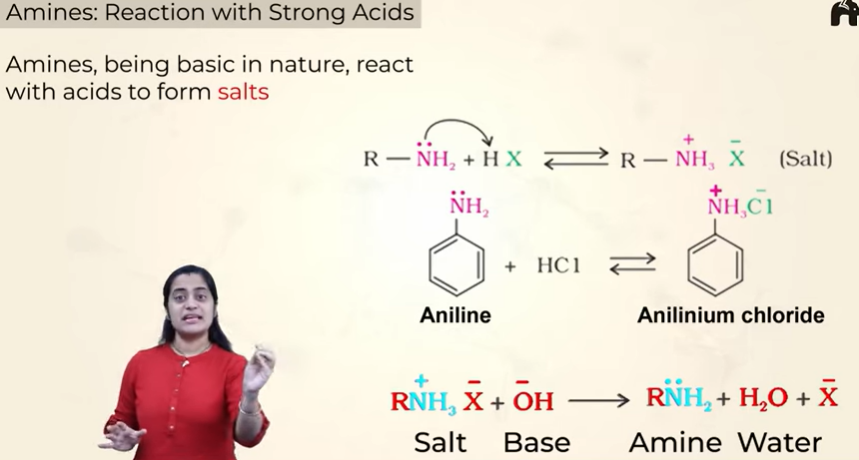
Reaction with strong acids
when reacted with acids they form salts
and when these salts are reacted with a strong base you get the amine back
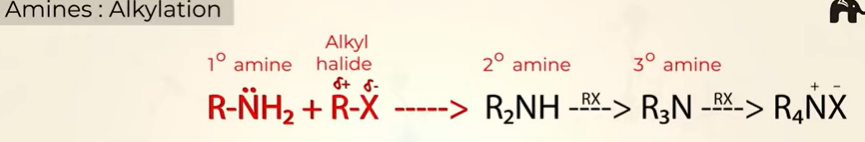
Alkylation
when you keep adding R—X you get primary, sec, tertiary amines followed by a diazonium salt
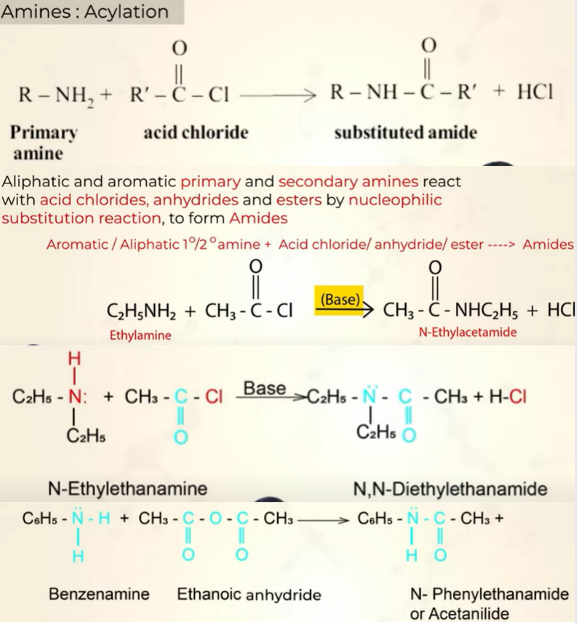
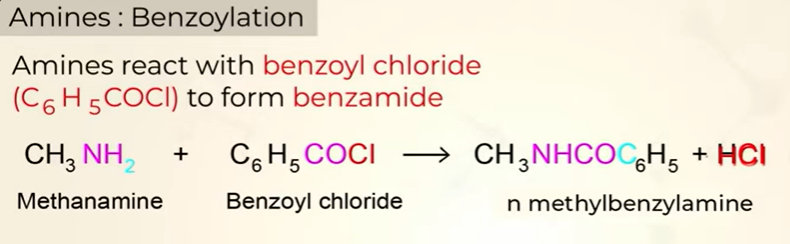
Acylation (RCO)
Compounds with acyl group:
Acid chlorids
Acid anhydricdes
esters
primary and secondary show this reaction. tertiary does not because it does not have any H in N to be substituted
Benzoylation
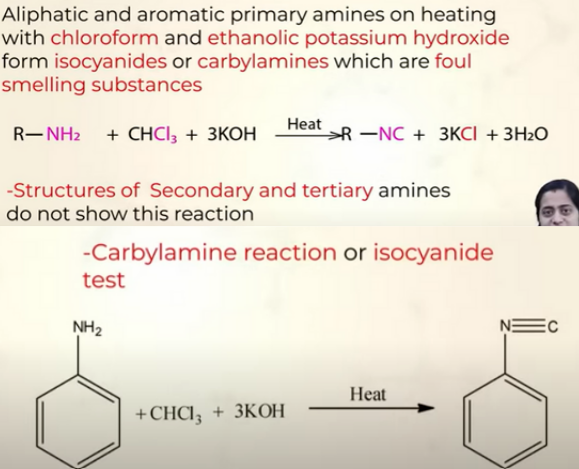
Carbylamine reaction
aka isocyanide test
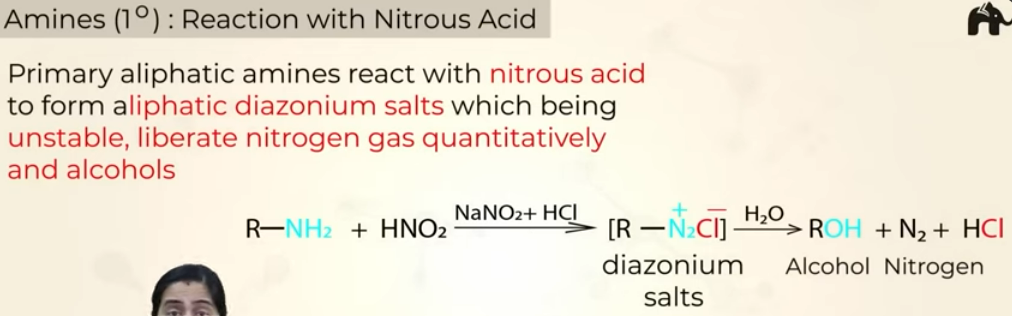
Reaction of 1o amines with Nitrous acid (HNO2)
gives diazonium salt (N2+Cl) —> unstable (but benzenediazonium salts are stable)
HNO2—>NaNO2+ HCl
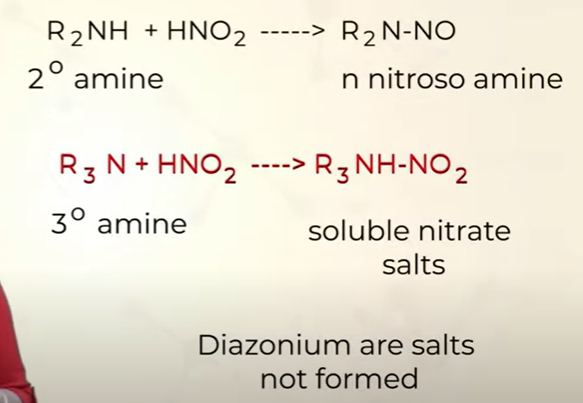
Reaction of 2o , 3o amines with Nitrous acid (HNO2)
Aromatic amines reaction with nitrous acid
they also make diazonium salts (they are stable)

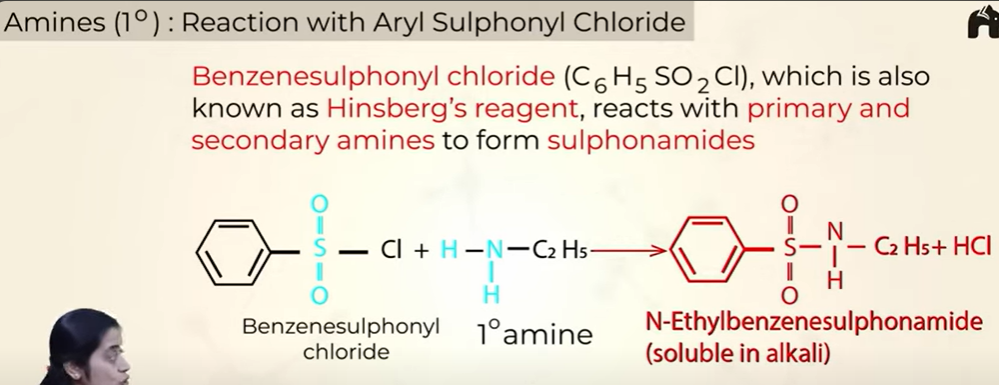
Reaction of 1o amines with Aryl Suphonyl Chloride
soluble in alkali
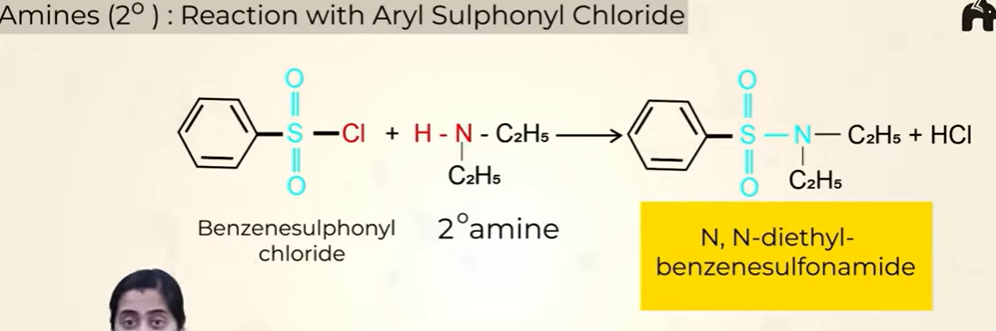
Reaction of 2o amines with Aryl Suphonyl Chloride
insoluble in alkali
Reaction of 3o amines with Aryl Suphonyl Chloride
reaction does not happen
use of Hinsberg reagent

Position in which electrophillic substituition takes place
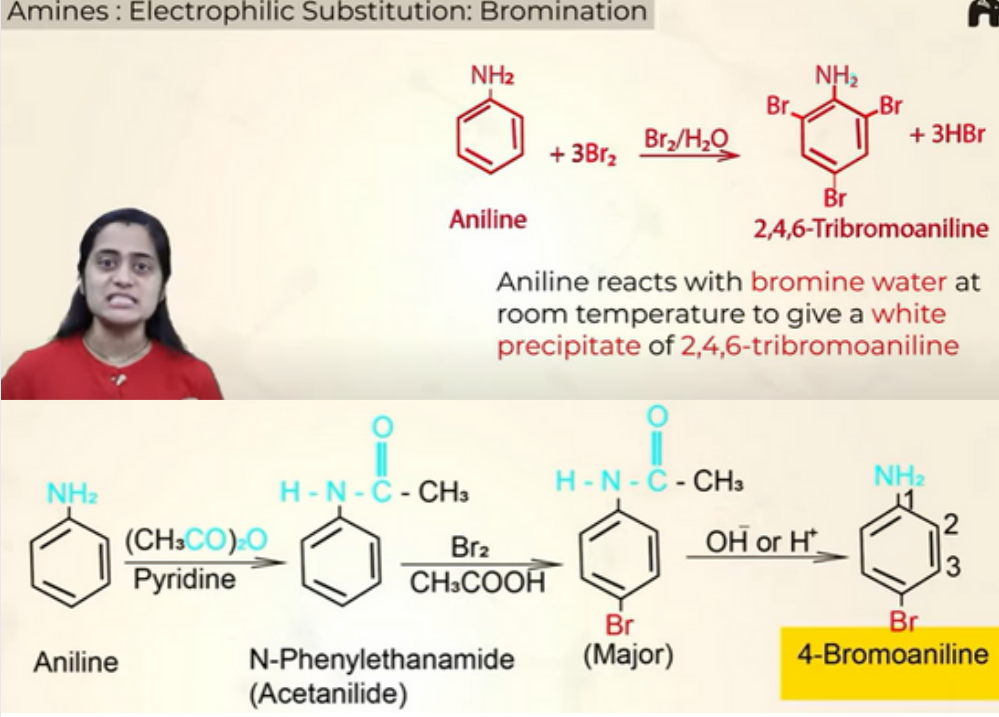
Electrophillic substituition- Bromination
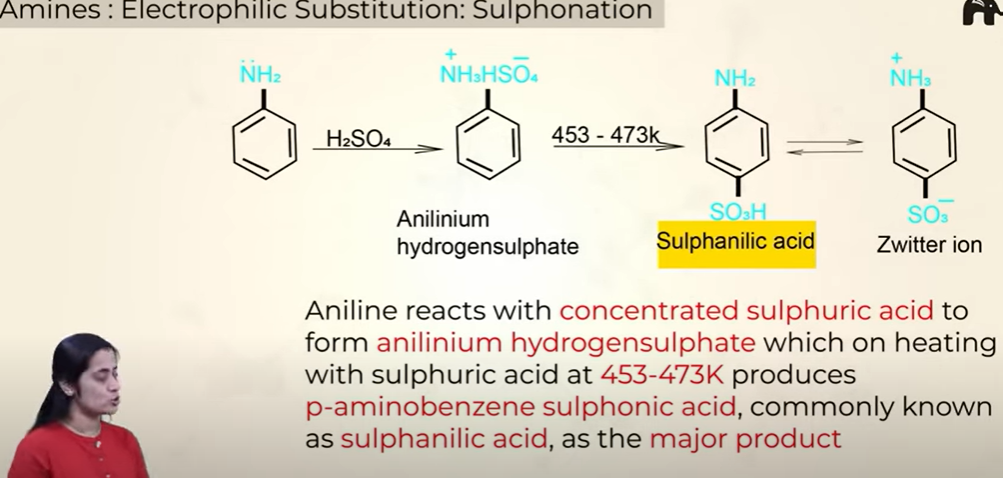
Electrophillic substituition- Suphonation (SO3H)
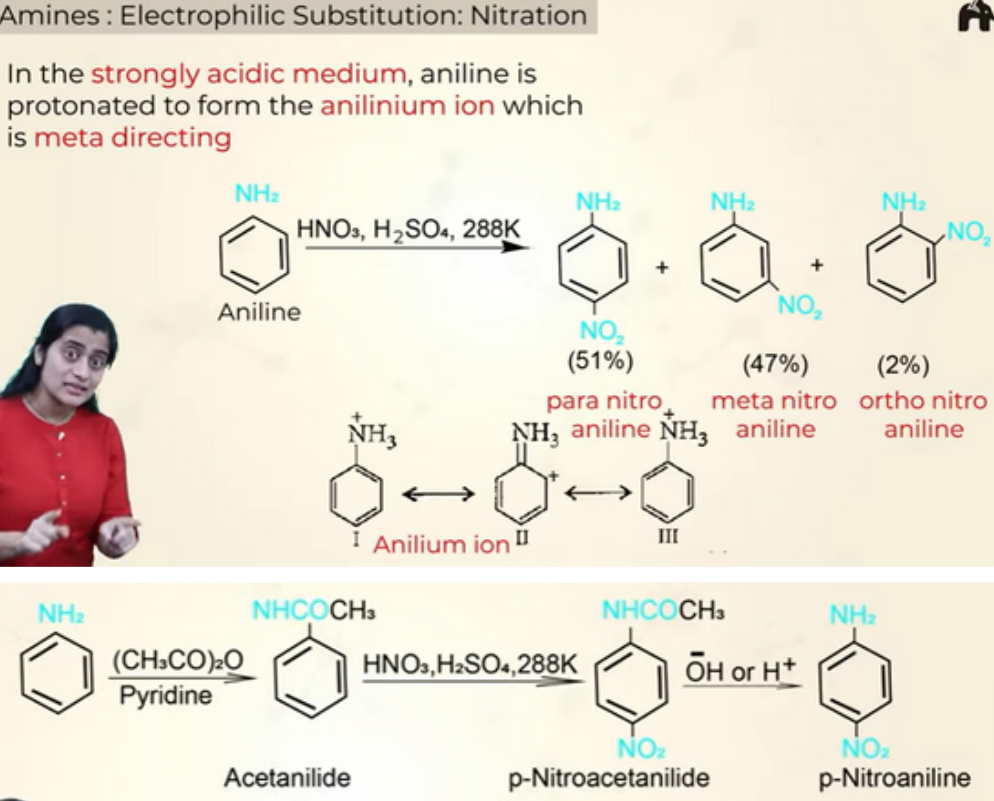
Electrophillic substituition- Nitration (NO2)
Diazonium salts

Nomenclature of Diazonium salts

Diazonium salts stability
Primary aliphatic amines form highly unstable alkyldiazonium salts
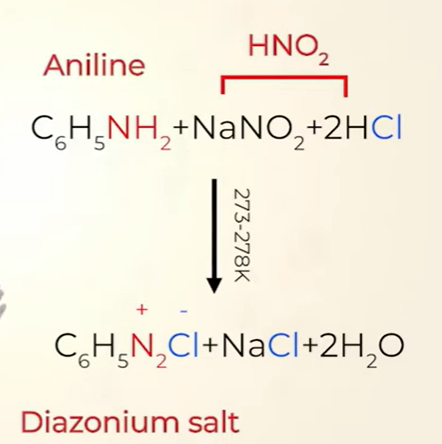
Primary aromatic amines form arenediazonium salts which are stable for a short time in solution at low temperatures (273–278 K) due to resonance
arenediazonium salts made from aromatic amine(aniline )
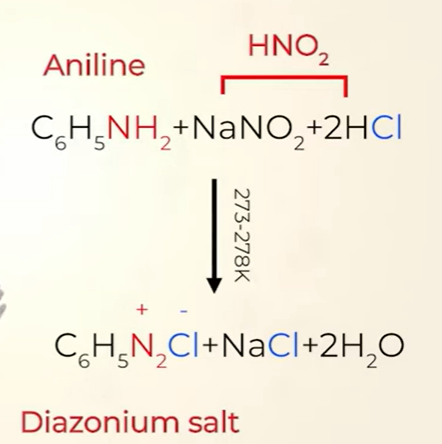
preparation of diazonium salt
The conversion of primary aromatic amines into diazonium salts is known as diazotisation
cannot be stored for long hence used
Physical properties of benzene diazonium salts
exception for solubility in water - Benzenediazonium fluoroborate

Chemical reaction of diazonium salts
mainly:
reactions involving displacement of nitrogen
Reactions involving retention of diazo group coupling reactions
what can N be replaced in chemical reactions of diazonium salts
N2+ is a LEAVING GROUP (leaves in gaseous form)

Diazonium Salts: Replacement by halide or cyanide
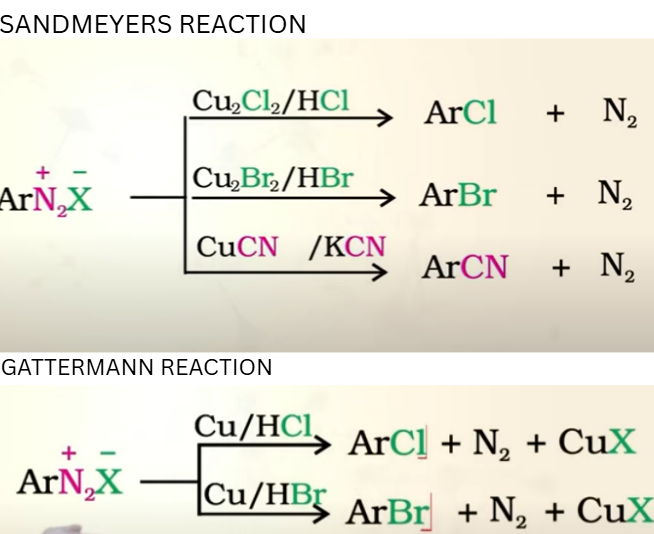
SANDMEYER REACTION (Cl-,Br-, CN-)
Reaction always takes place in presence of Cu ion
GATTERMAN REACTION:
Copper powder and halogen acid
same product in both
SANDMEYERS RXN has better yeild than GATTERMANN
seperate raction for replacemnet with Iodide
Diazonium Salts: Replacement by Iodide

Diazonium Salts: Replacement by Fluoride

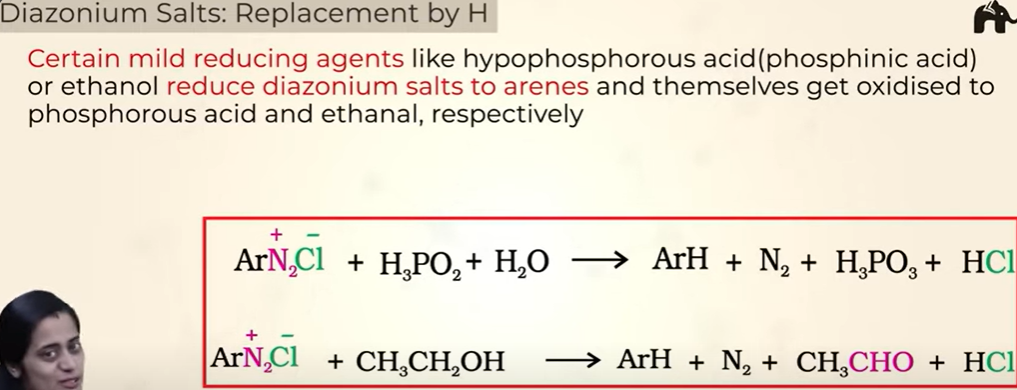
Diazonium Salts: Replacement by H
2 methods:
with alcohol
hypophosphourous acid (phosphinic acid)
Diazonium Salts: Replacement by Hydroxy grp (OH)

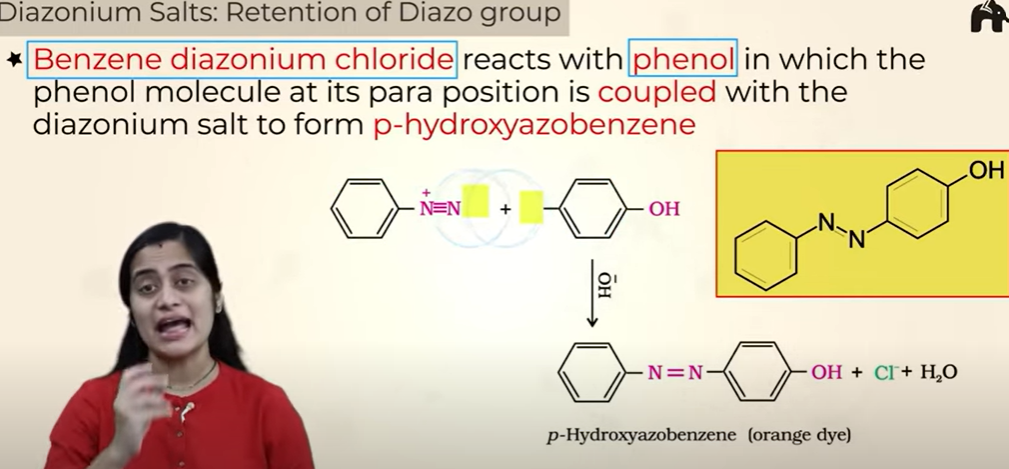
Diazonium Salts: Retention of Diazo group
we get colored products so used as dyes

Retention of Diazo group
orange dye
Retention of Diazo group
yellow dye
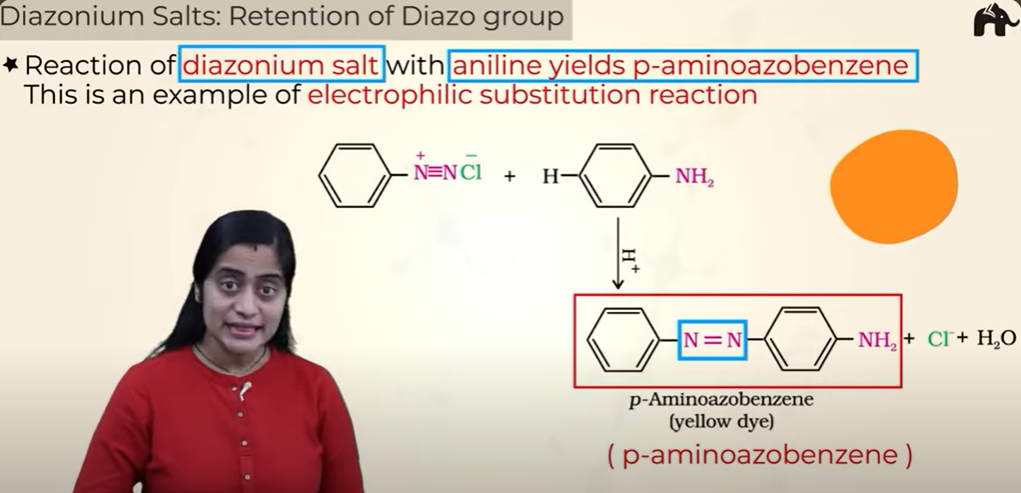
Diazonium saltts importance
