NPTE: RESPIRATORY/ BREATHING
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
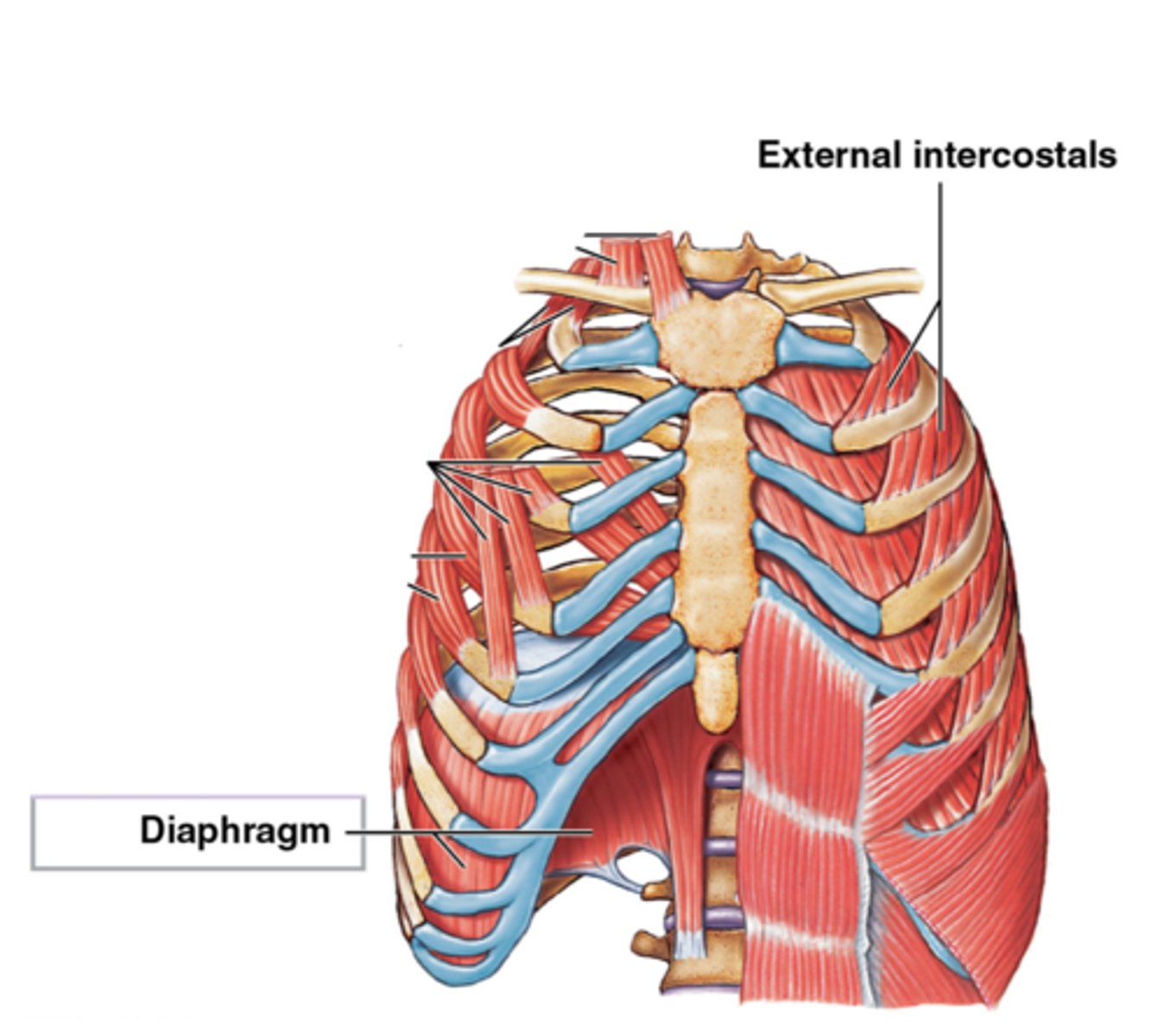
Primary Inspiratory Muscles
DEI
1. diaphragm
2. external intercostals
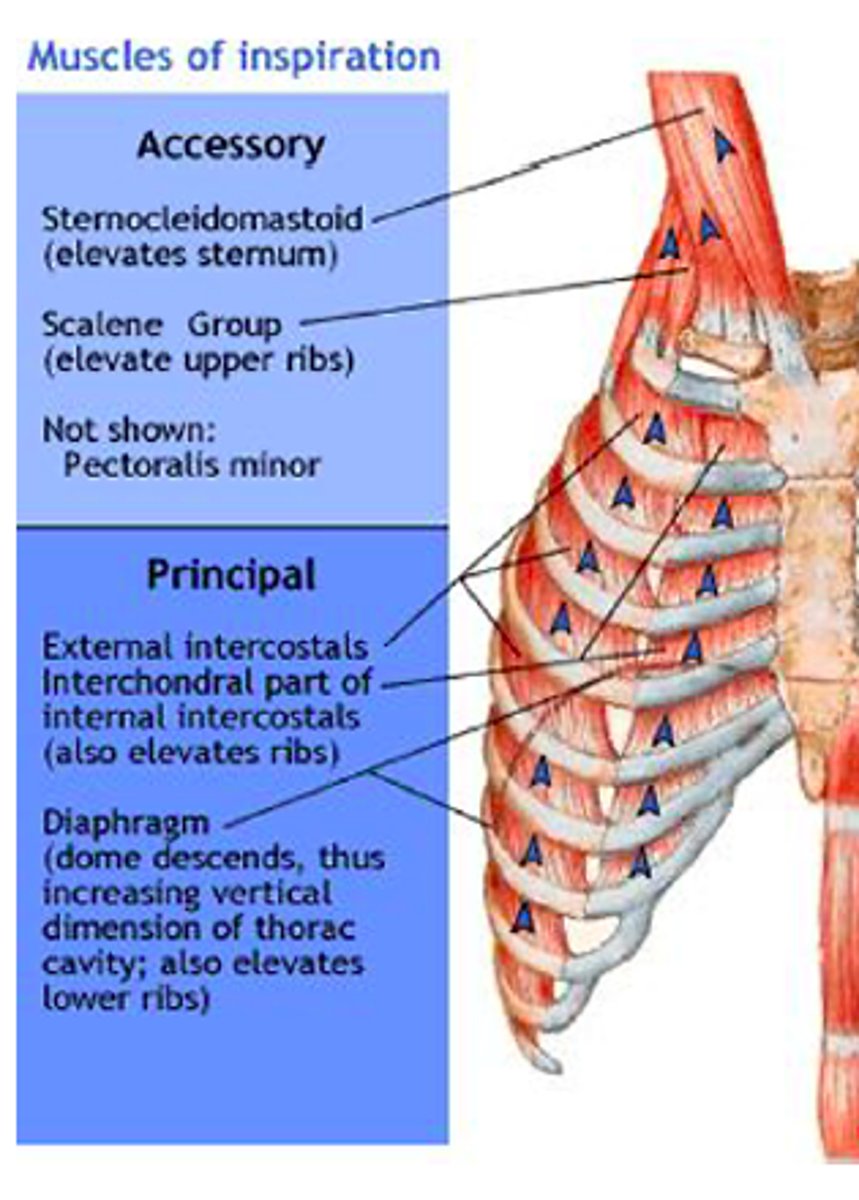
Secondary Inspiratory Muscles
Superficial Neck muscles & chest
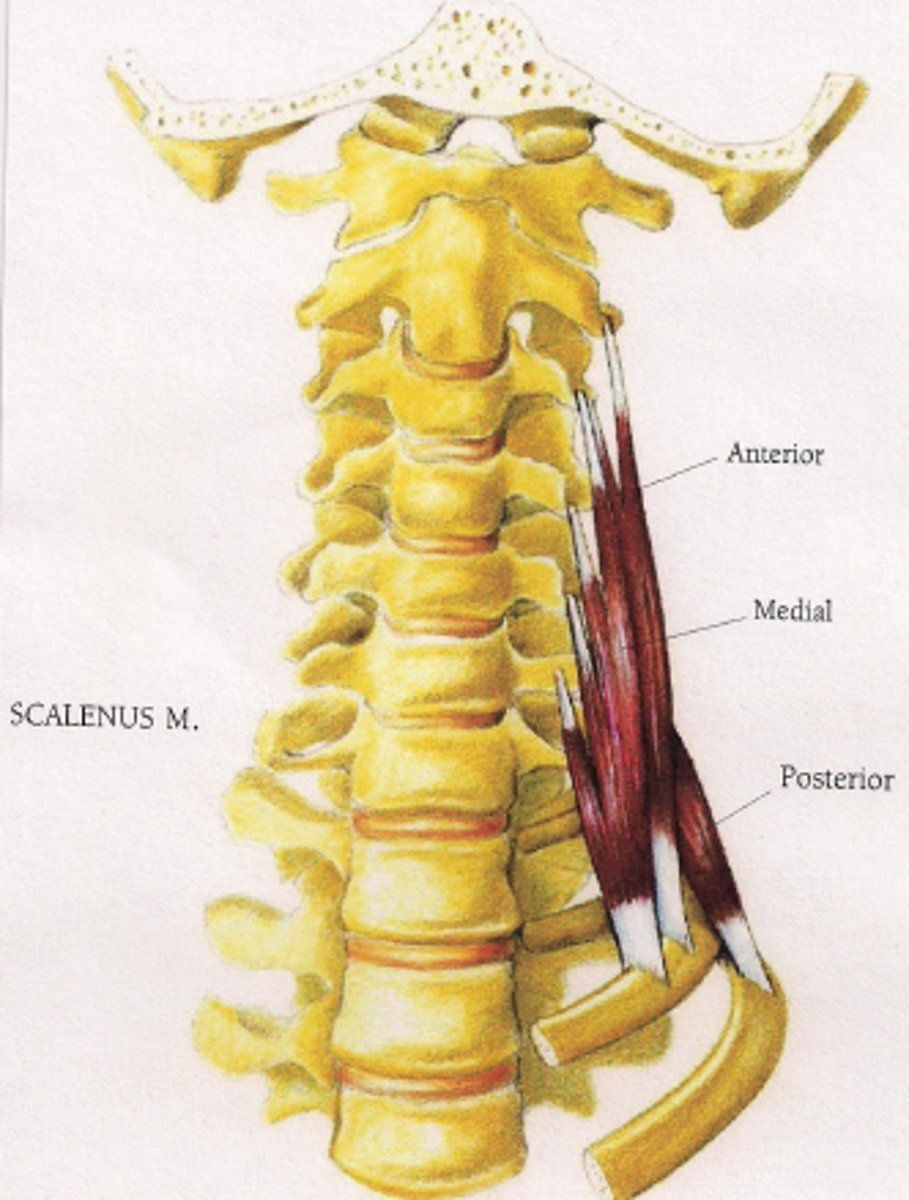
1. scalenes
2. SCM
3. Trapezius
4. Pecs
5. Serratus Anterior & posterior
6. Subclavius
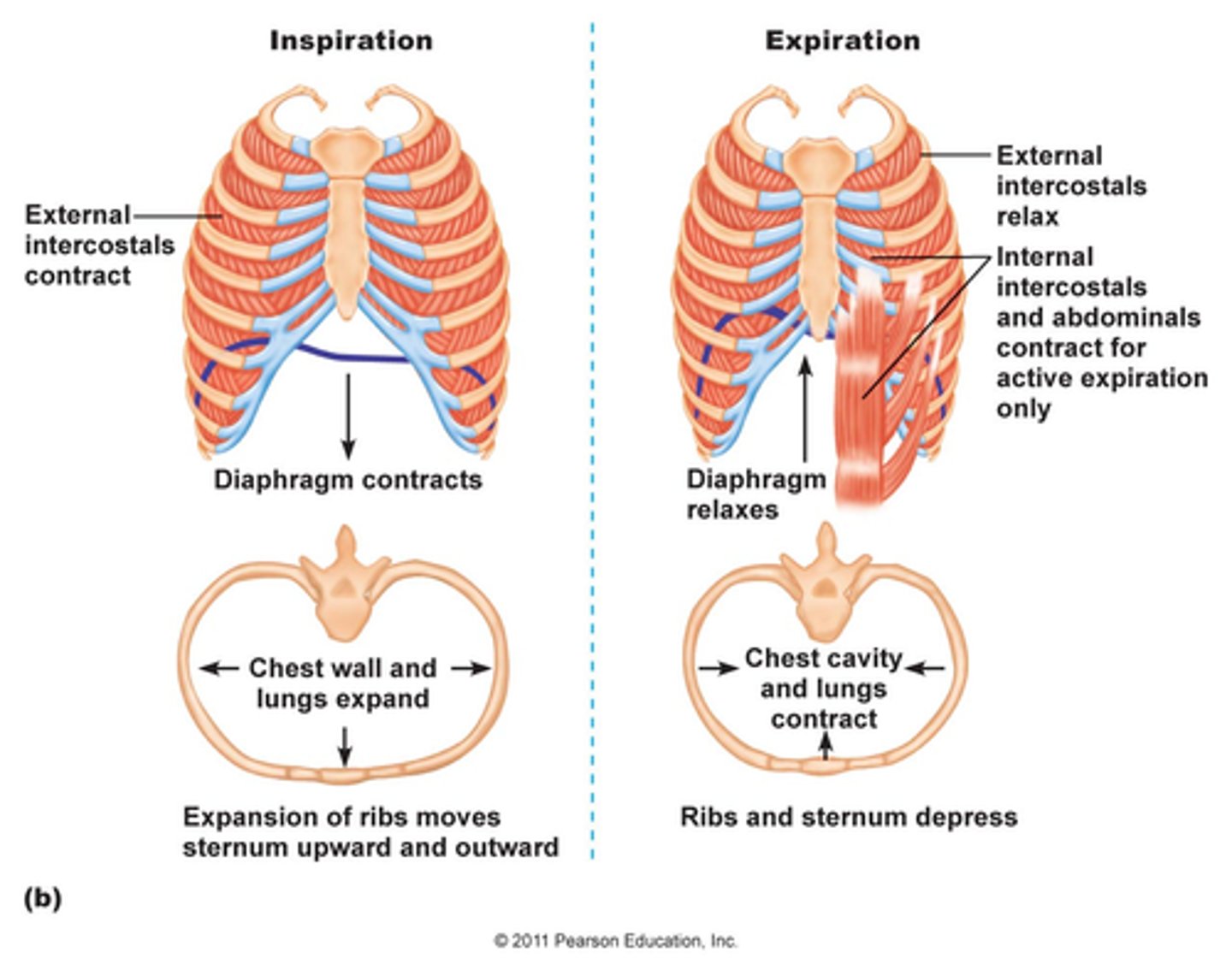
Primary Expiratory Muscles
ABS-II
1. All abdominals
2. Internal intercostals
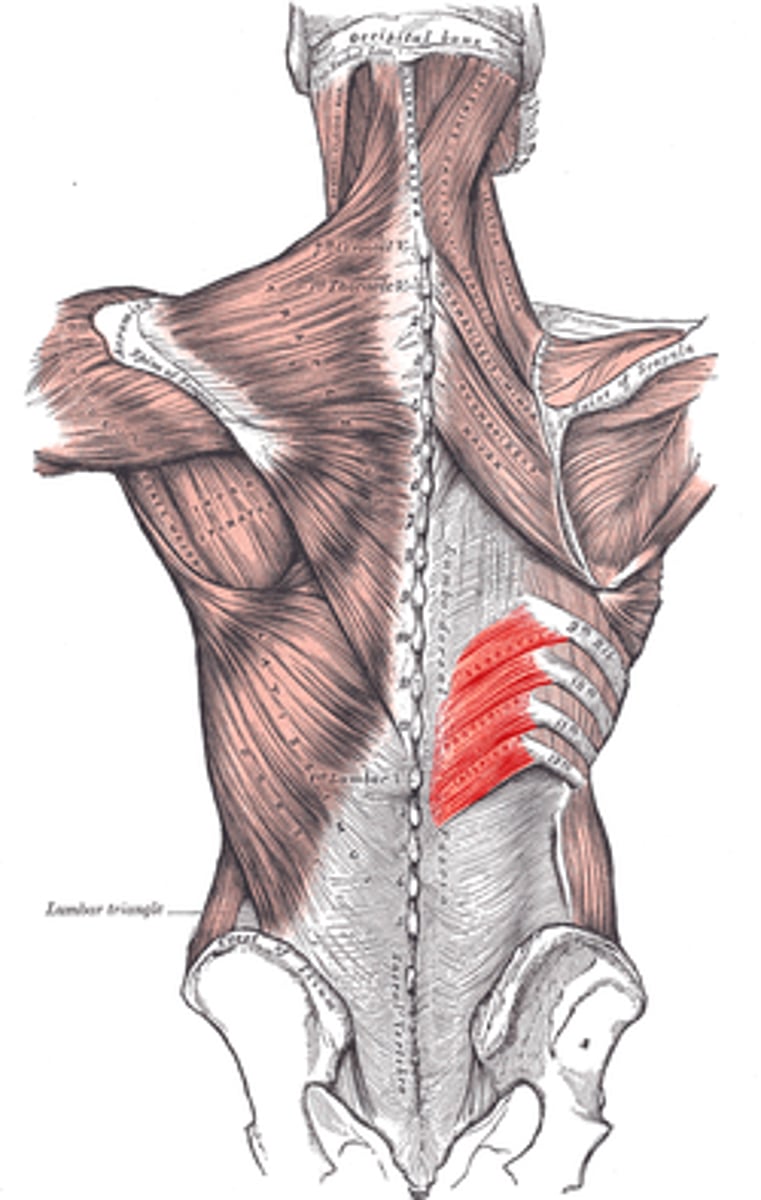
Secondary Expiratory Muscles
LUMBORUM-SPI
1. Serratus posterior inferior
2. Quadratus Lumborum
3. Iliocostalis Lumborum
Anterior Scalene
elevates 1st rib for inspiration
- same side lateral flexion
- OPPOSITE rotation
- B/L cervical flexion
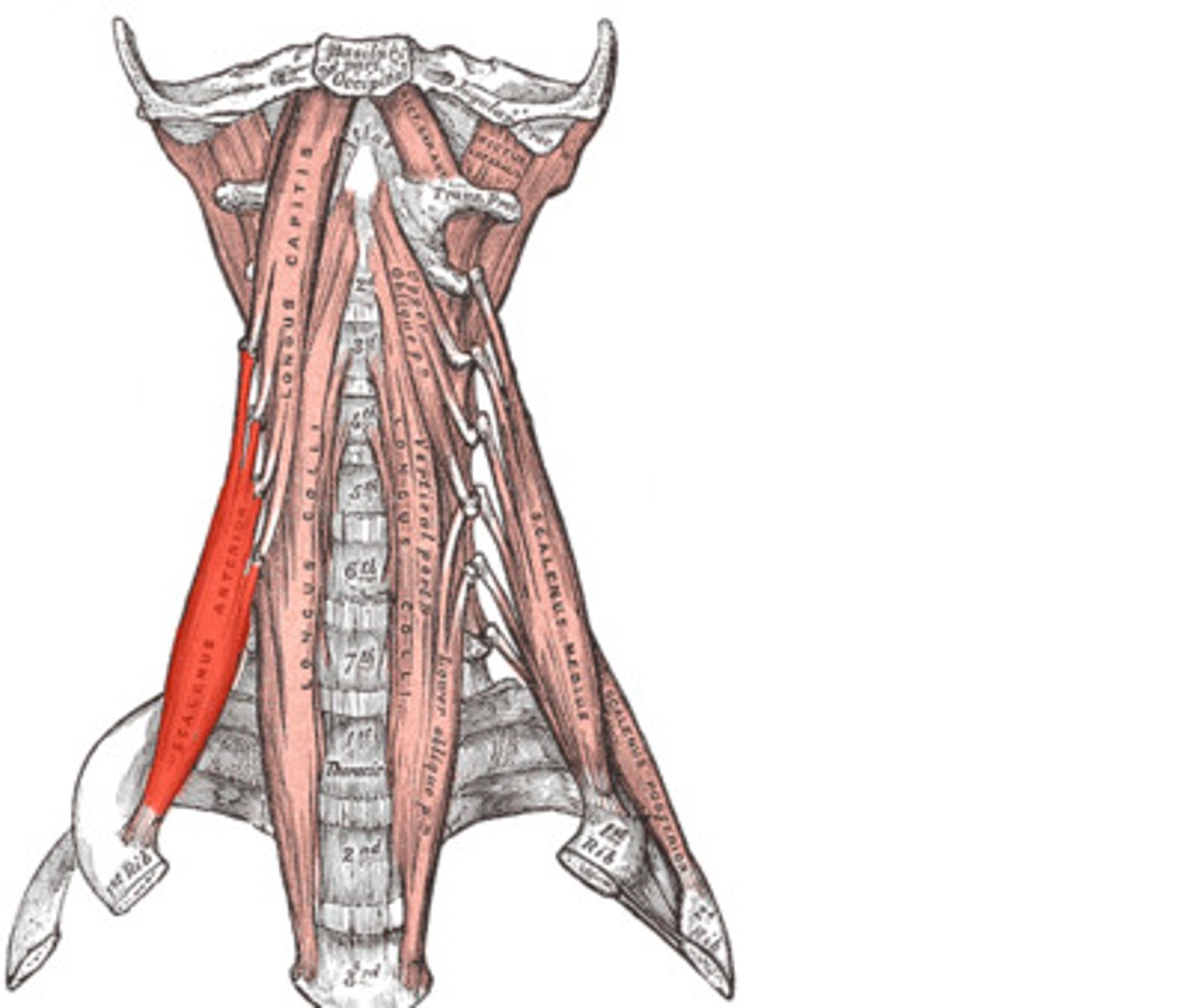
Anterior Scalene (Origin, insertion and innervation)
O: transverse processes C3-C6 (anterior tubercle)
I: 1st rib
X: anterior rami of C4-C6
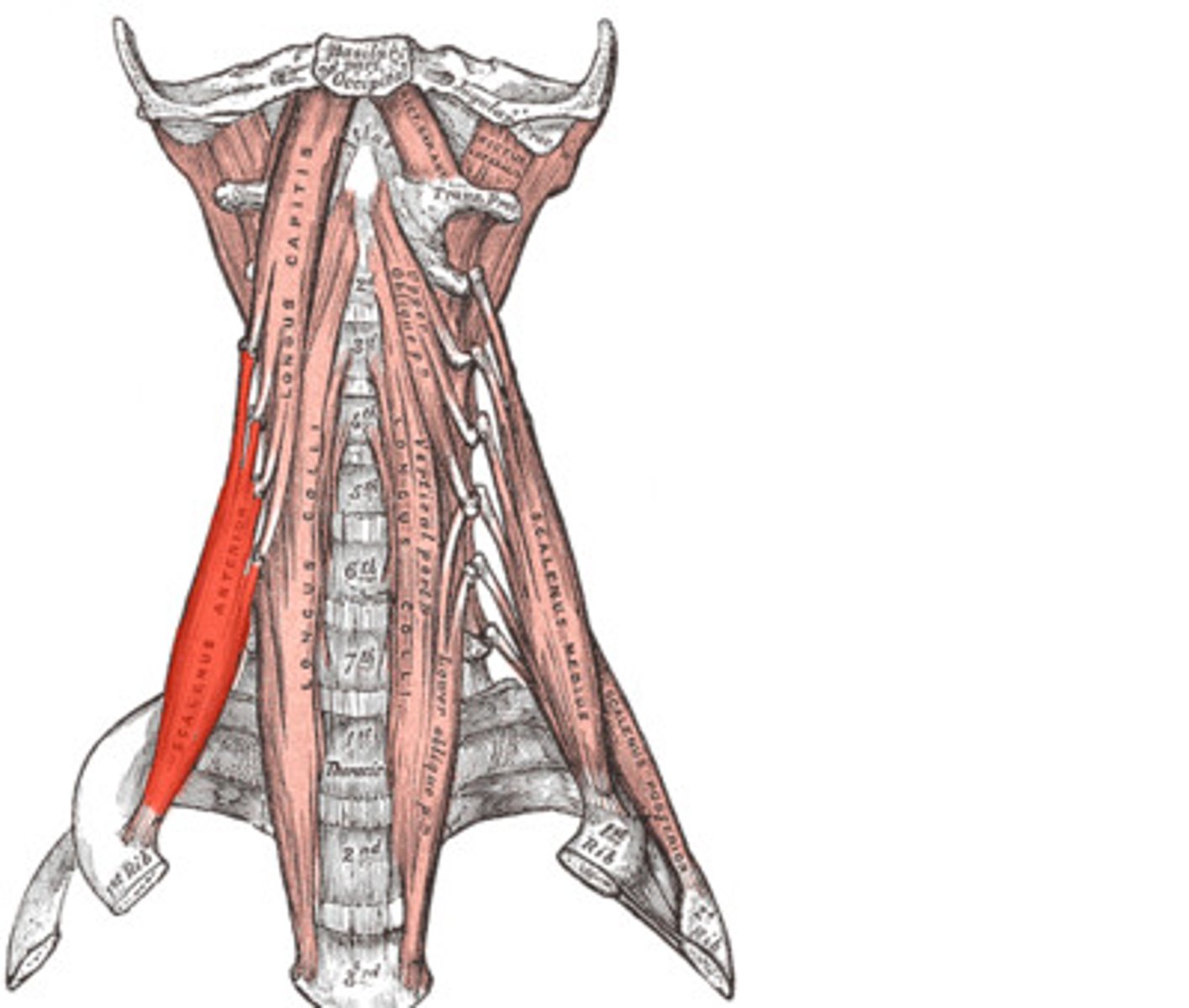
Middle scalene function
elevates rib 1 for inspiration
lateral flexion
middle scalene (origin, insertion, and innervation)
O: transverse processes C3-C7 (posterior tubercles)
I: 1st rib
X: anterior rami of C3-C8
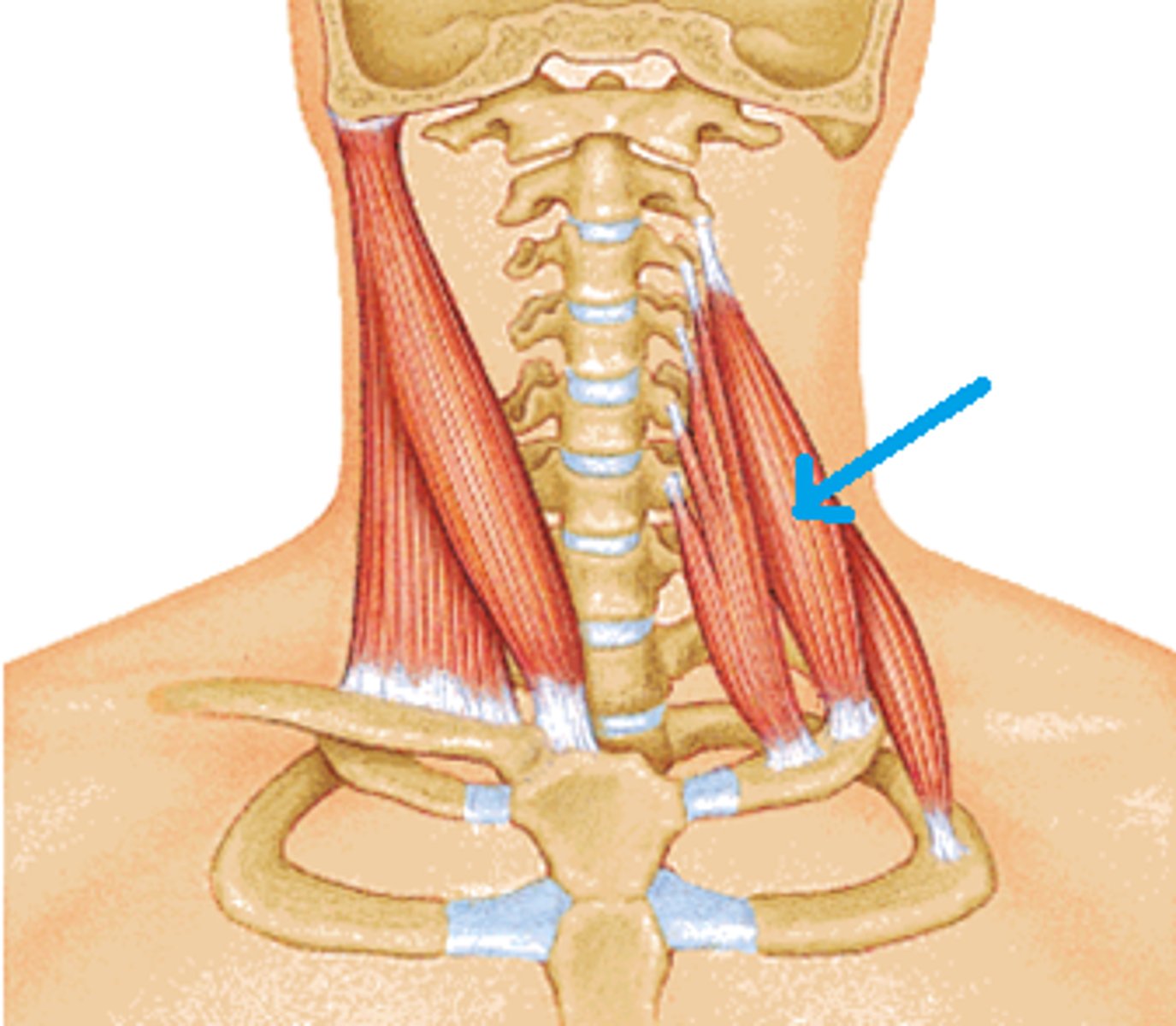
Posterior Scalene Function
Elevates 2nd rib for inspiration
- lateral flexion
Posterior scalene (Origin, Insertion, and Innervation)
O: transverse processes of C4-C7 (posterior tubercles)
I: 2nd Rib
X: anterior rami of C6-C8
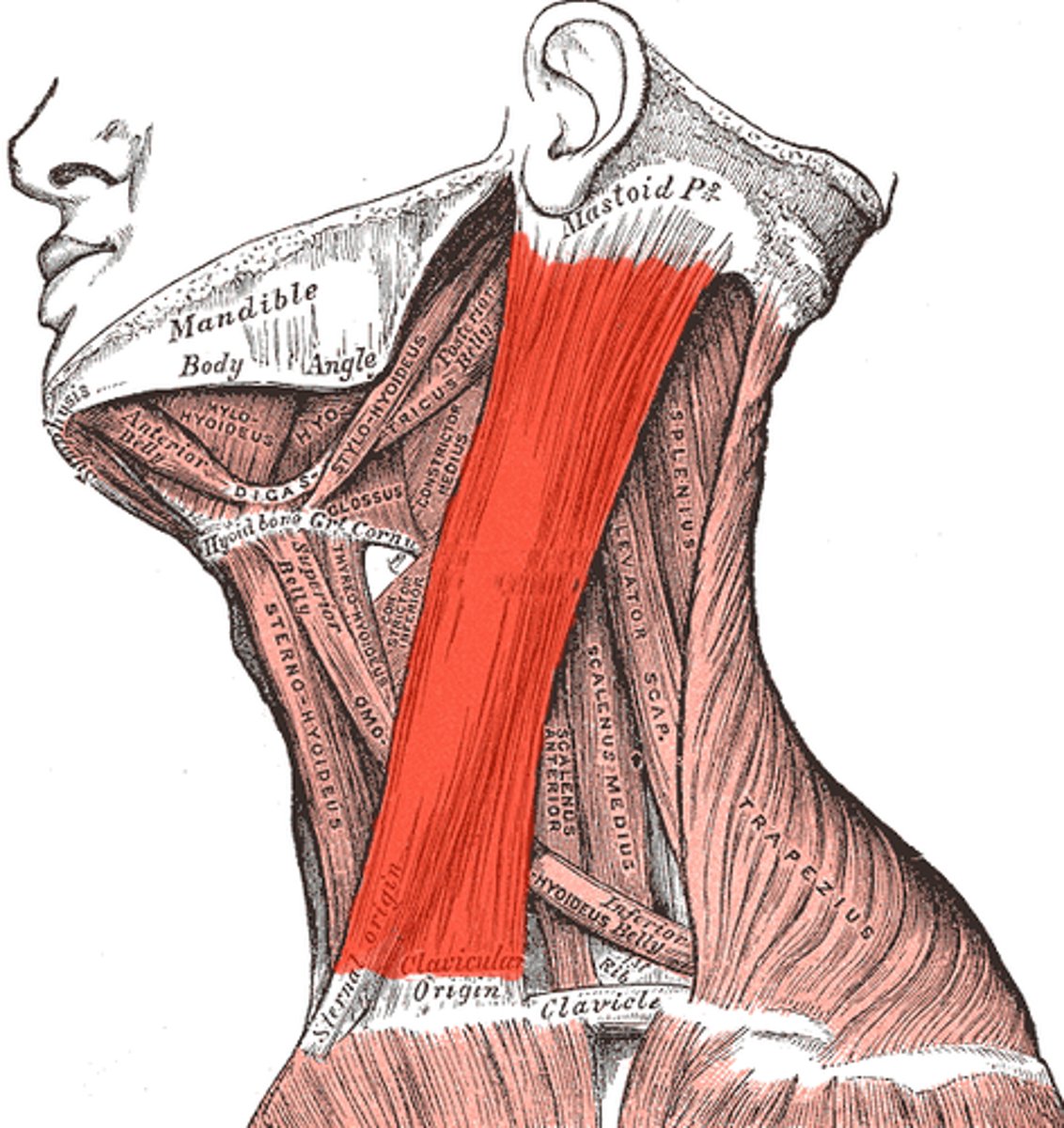
Sternocleidomastoid function
Elevates clavicle & sternum for inspiration
- lateral flexion
- opposite rotation
- B/L cervical flexion
Sternocleidomastoid (origin, insertion, innervation)
O: manubrium (sternum) & medial 1/3 of clavicle
I: temporal bone (mastoid process) & occipital bone (superior nuchal line)
X: Accessory nerve & cervical plexus (C2-C3)
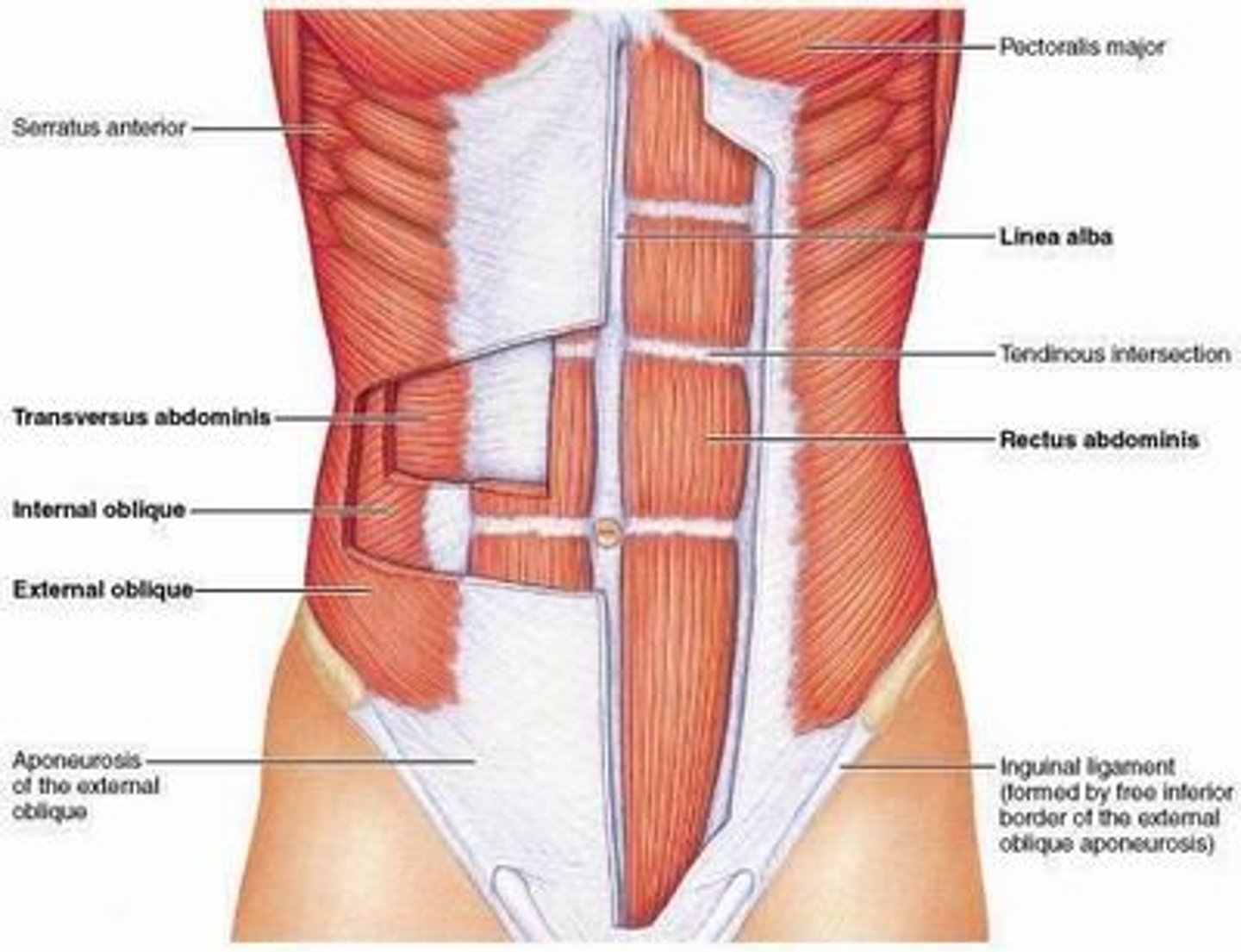
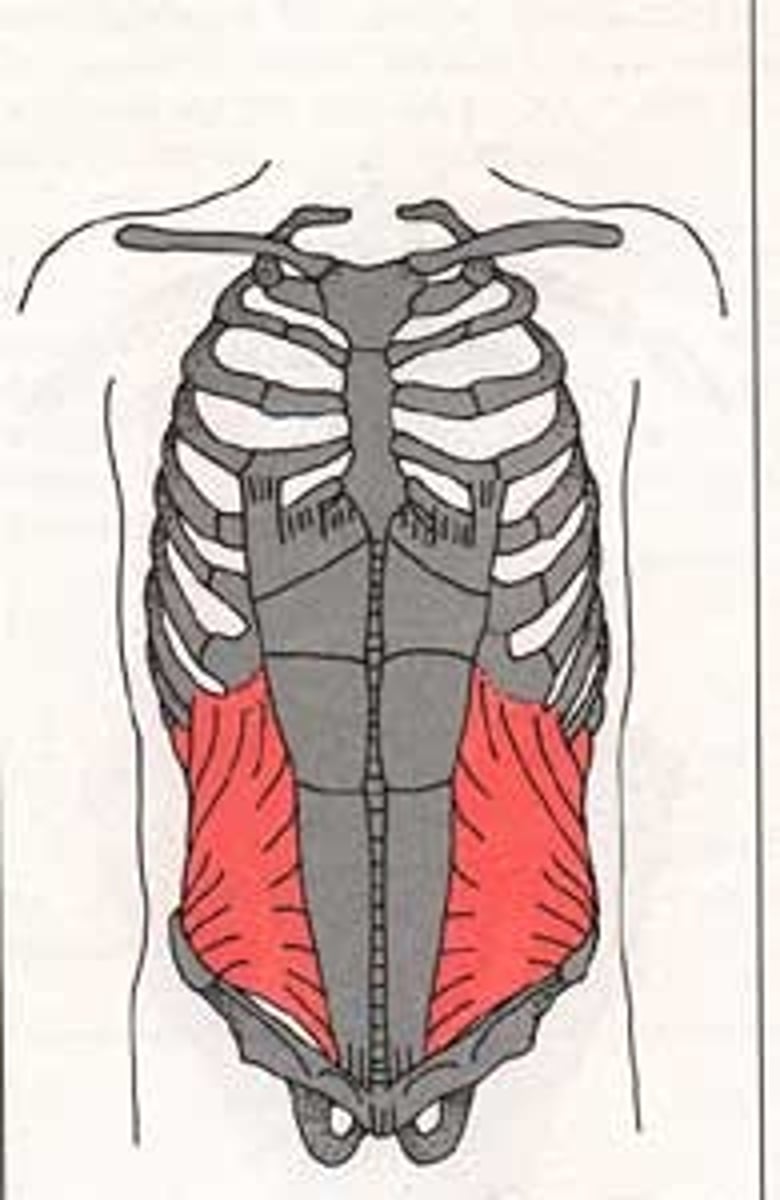
rectus abdominis function
Primary expiration
- flexes trunk & compresses abdominal contents
Rectus abdominis (origin, insertion, innervation)
O: pubic symphysis
I: Xiphoid process
X: intercostal & subcostal nerves (T7-T12)
External oblique function
- primary expiration
- lateral flexion & opposite rotation
- B/L trunk flexion & compresses abdominal contents
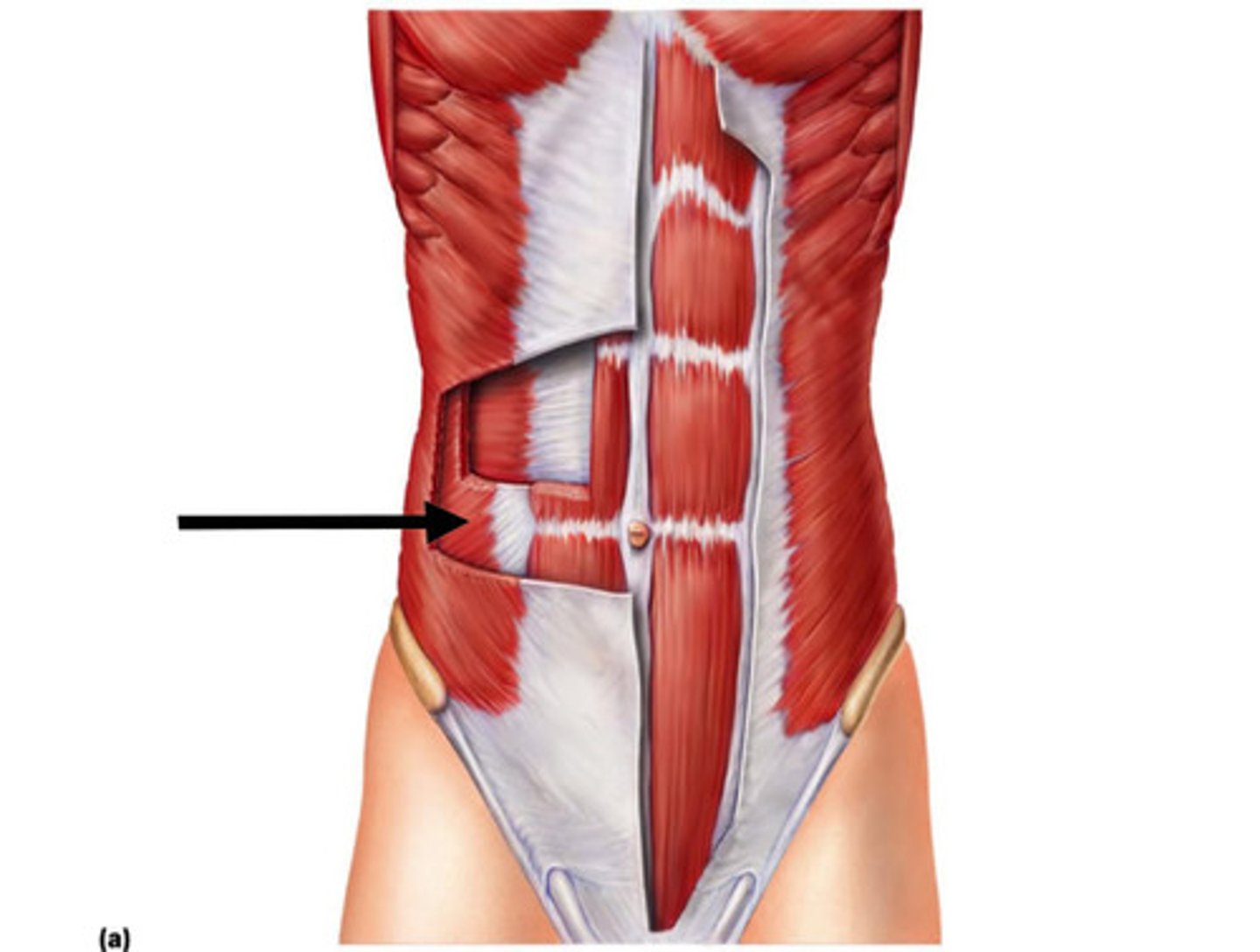
External oblique (origin, insertion, and innervation)
O: External surfaces of ribs 5-12
I: Linea Alba, pubic tubercle, & anterior 1/2 of iliac crest
X: Internal & subcostal nerves (T7-T12) and iliohypogastric nerve (L1)
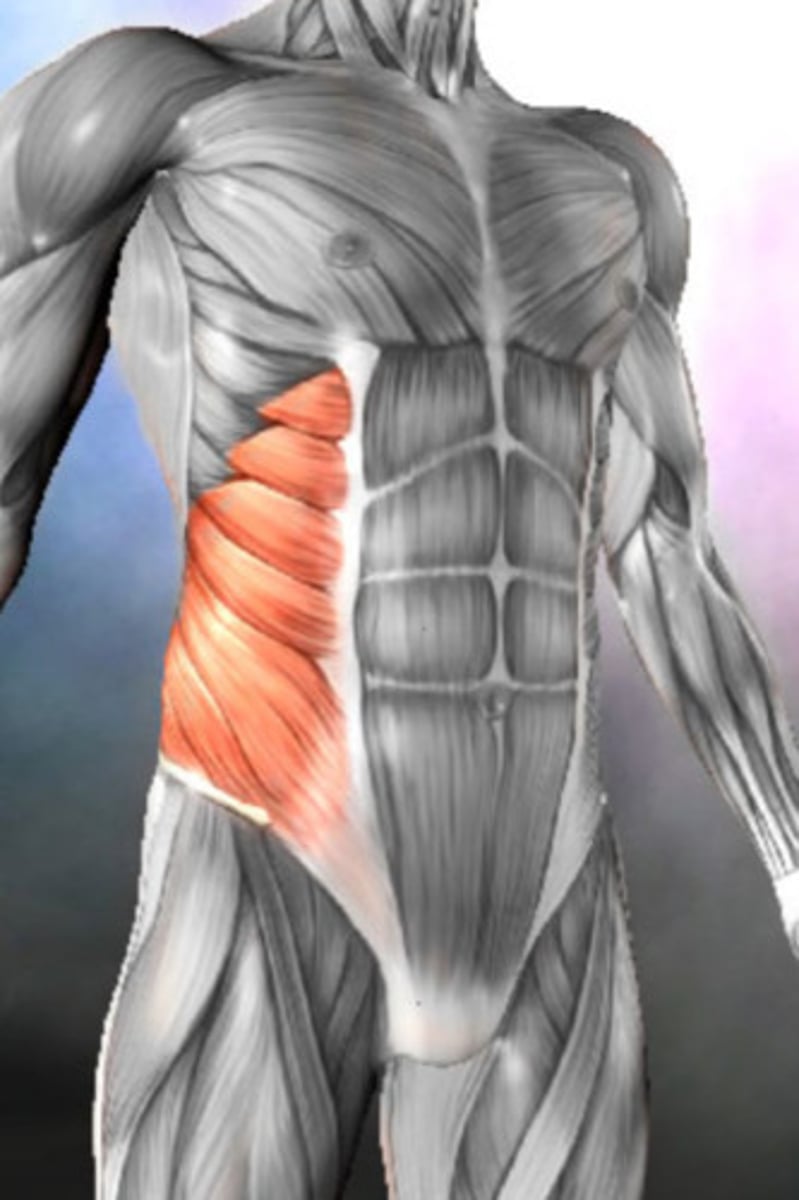
internal oblique function
primary expiration
- lateral flexion & same side rotation
- B/L trunk flexion & compresses abdominal contents
Internal oblique (origin, insertion, and innervation)
O: anterior iliac crest, thoracocolumbnar fascia
I: ribs 10-12, linea alba, pubic crest
X: Internal & subcostal nerves (T7-T12) and iliohypogastric nerve (L1), lilioinguinal nerve (L1)
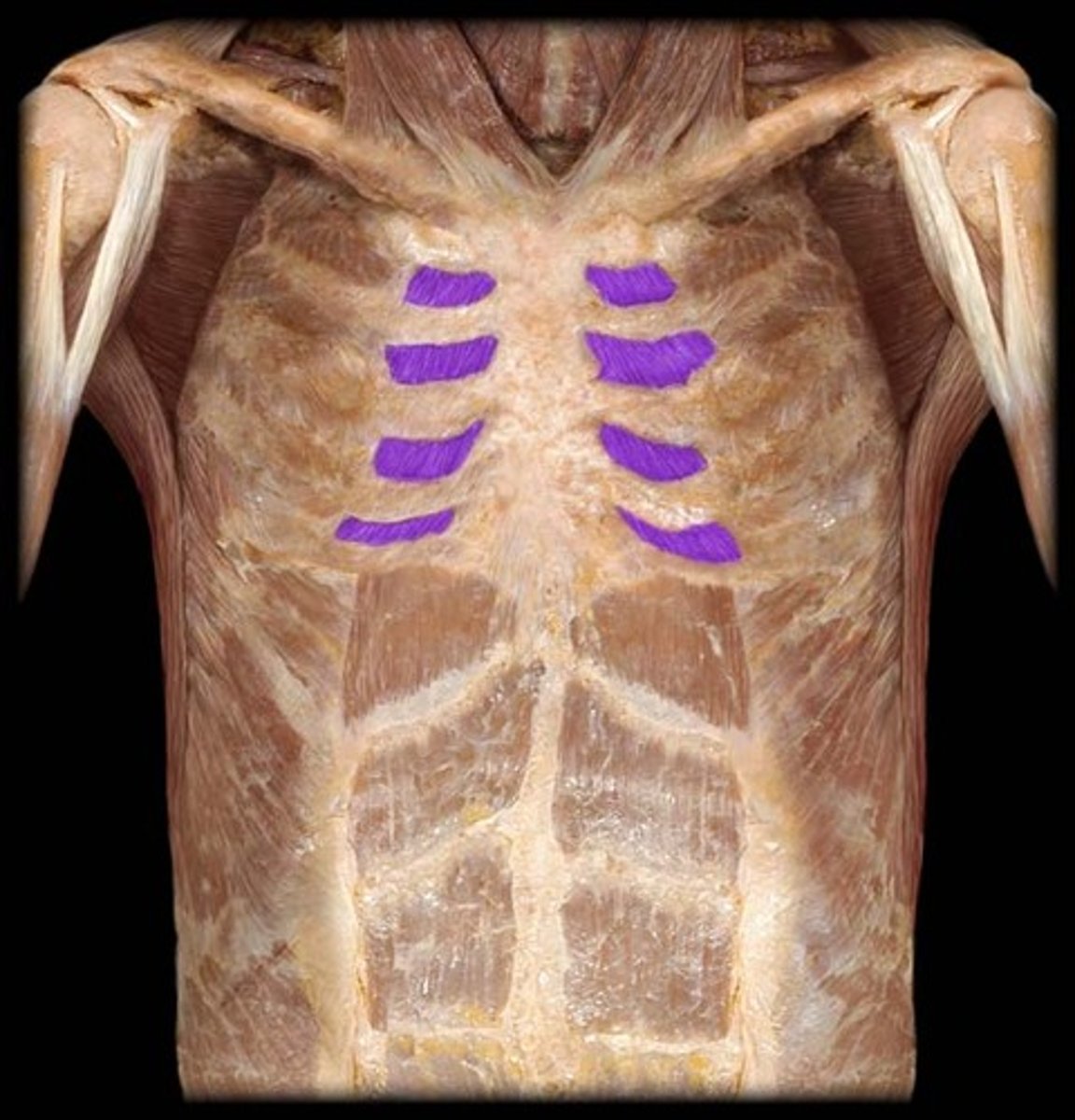
external intercostals function
elevates ribs (inspiration)
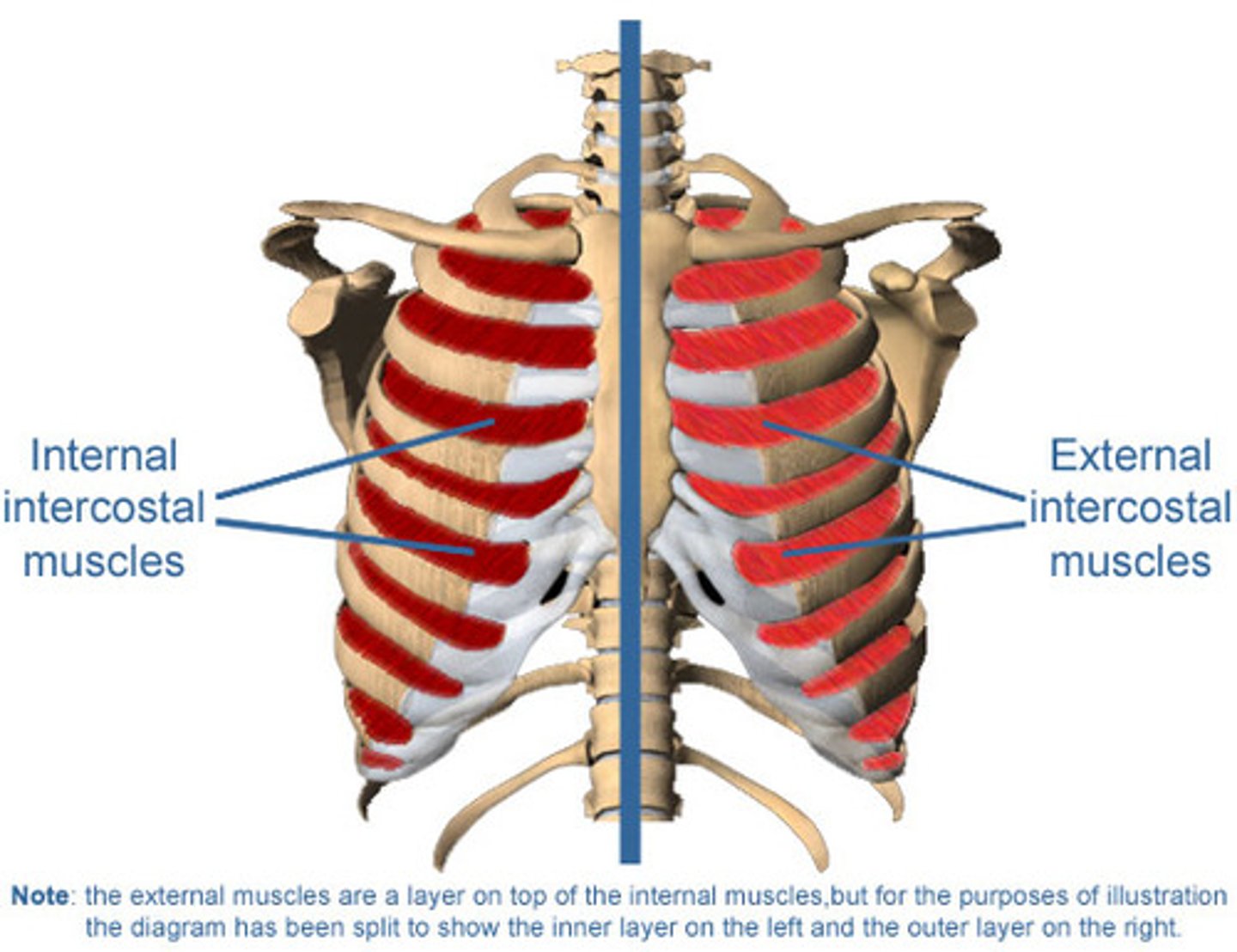
internal intercostals function
depresses ribs (expiration)
What are the uses of Diaphragmatic breathing?
1. increase ventilation & improve gas exchange
2. reduces upper rib cage motion (secondary muscles) during inspiration
3. for obstructive & restrictive pulmonary disease
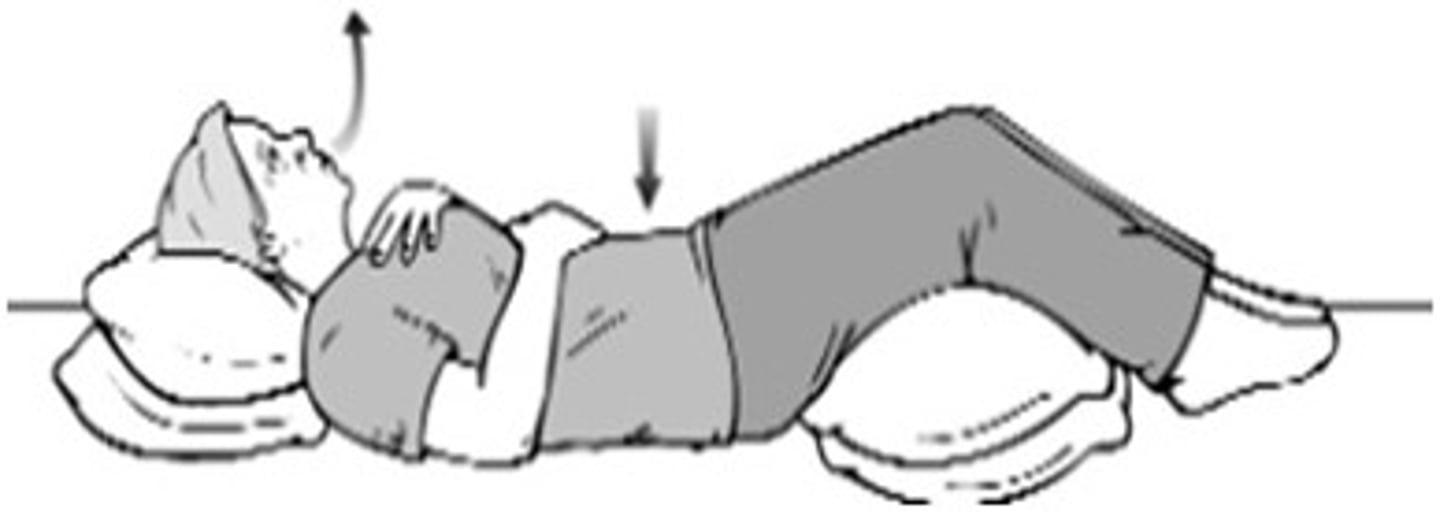
how to perform/ instruction diaphragmatic breathing?
1. maintain PPT
2. apply gentle pressure during exhalation
3. Cue patient to inhale against hand
What are the uses of Lateral costal breathing?
removes lung consolidation/secretions
how to perform/ instruction lateral costal breathing?
1. lay on the uninvolved side (Sidelying)
2. Top arm is abducted above head
3. focus on expanding sides of ribcage laterally
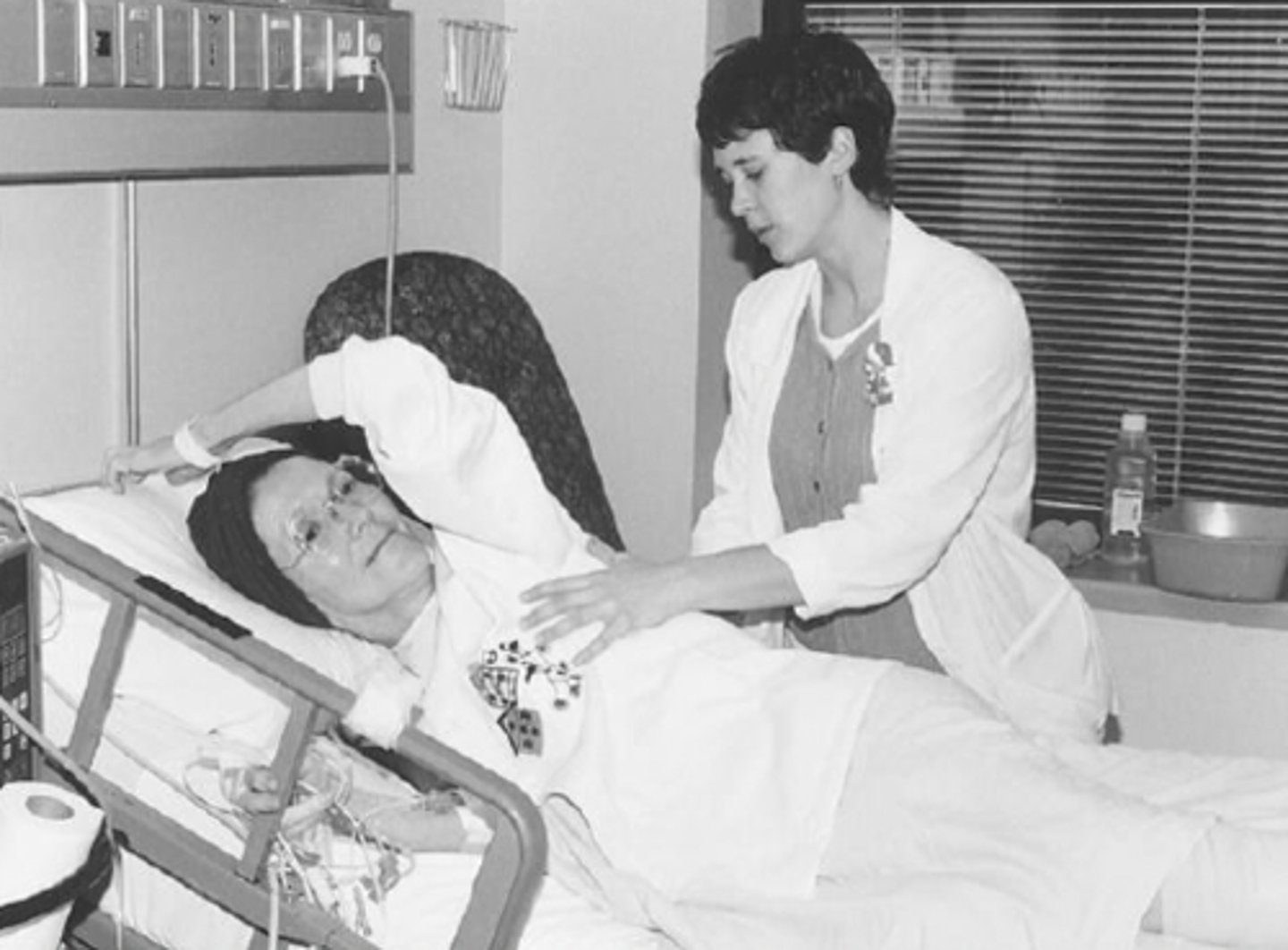
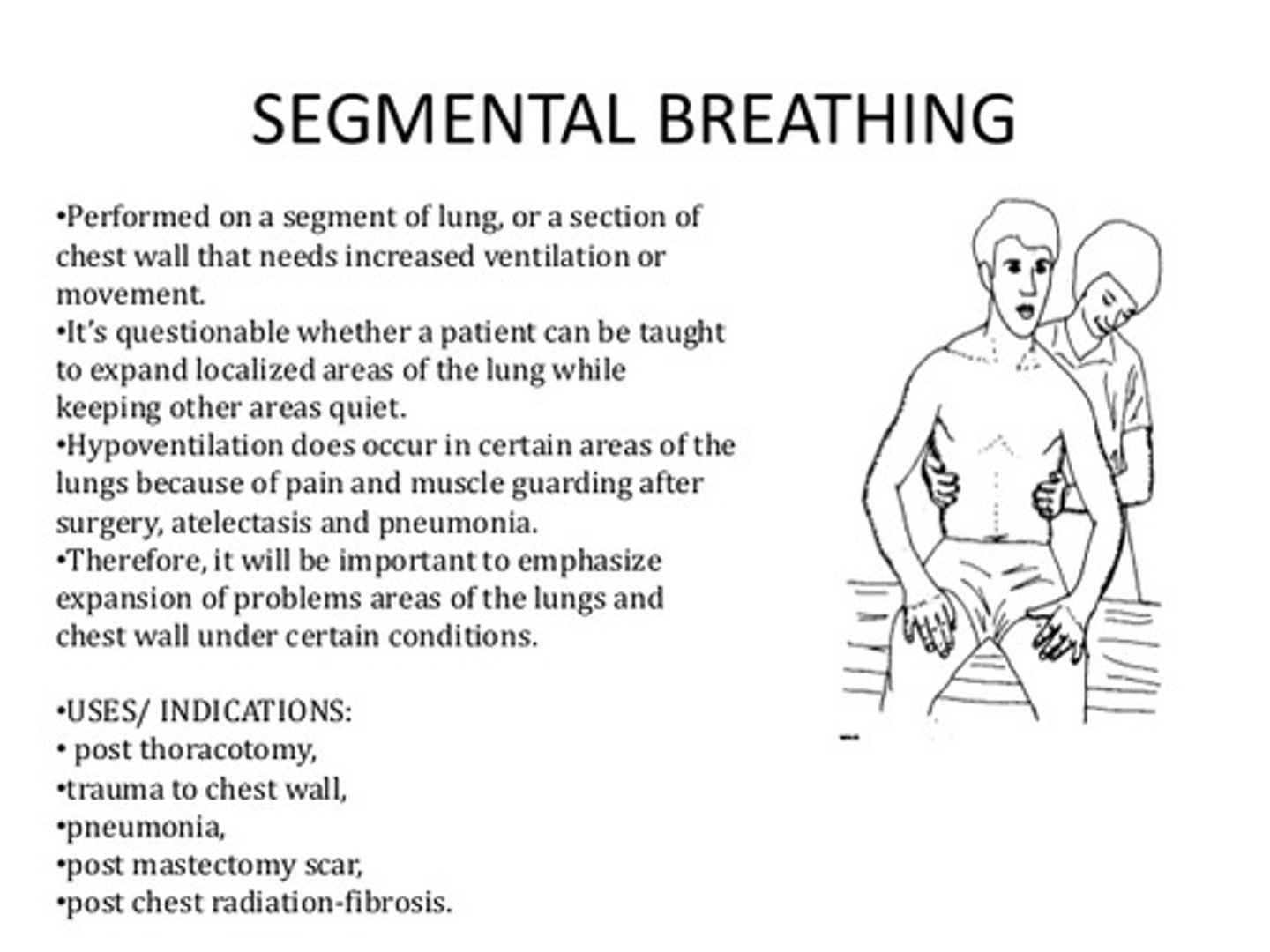
What are the uses of Segmental breathing?
improves ventilation to a hypoventilated lung segment
- used post-traumatic pain & incisional pain
- those for at risk for atectasis
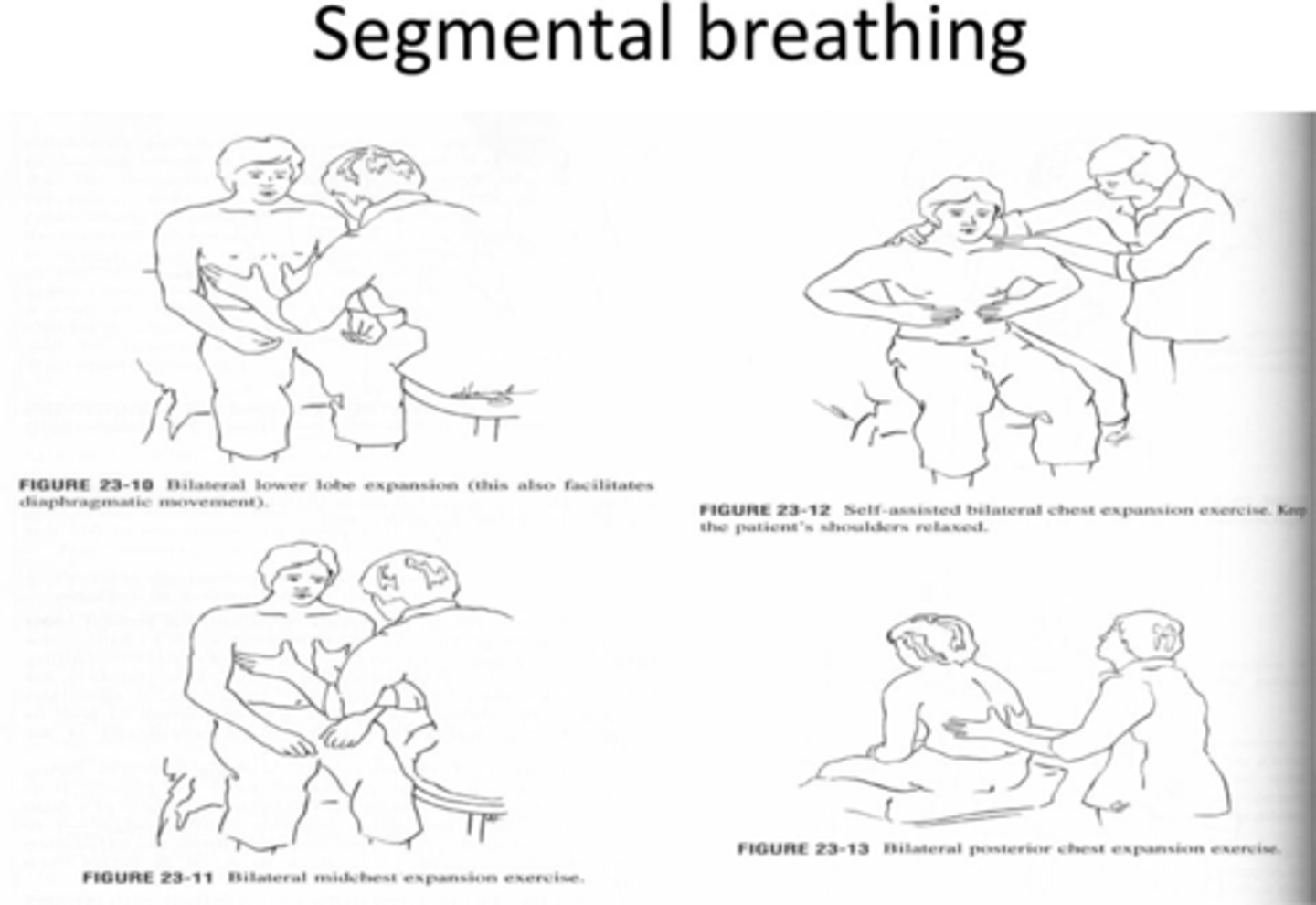
how to perform/ instruction segmental breathing?
1. position patient to target a specific lung segment
2. apply pressure over hypoventilation when patient is exhaling
3. Ask pt to breath against your hand & allow for full inhalation
What are the uses of inspiratory holds?
increase inhaled volume
restore functional residual capacity
- for acute situations (ineffective cough, post-op, lobe collapse)
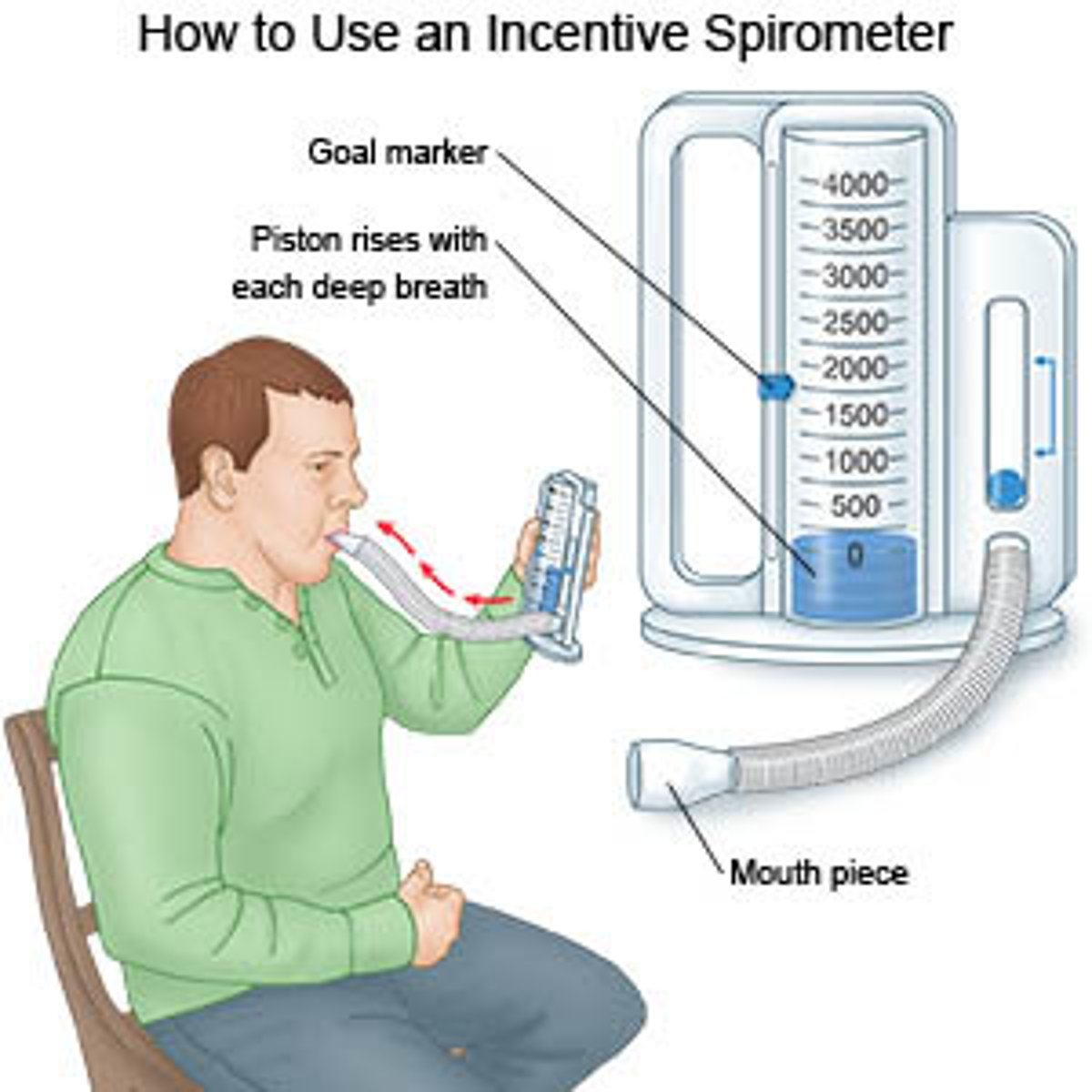
What are the uses of incentive spirometry?
encourages deep inspiration (practices DEEP BREATHS)
helps patients achieve maximal inspiration
- prevents alveolar collapse
- commonly used post-op
what are the uses of pursed lip breathing?
improves gas exchange
- for patients who have dyspnea at rest or minimal activity
- for obstructive disease
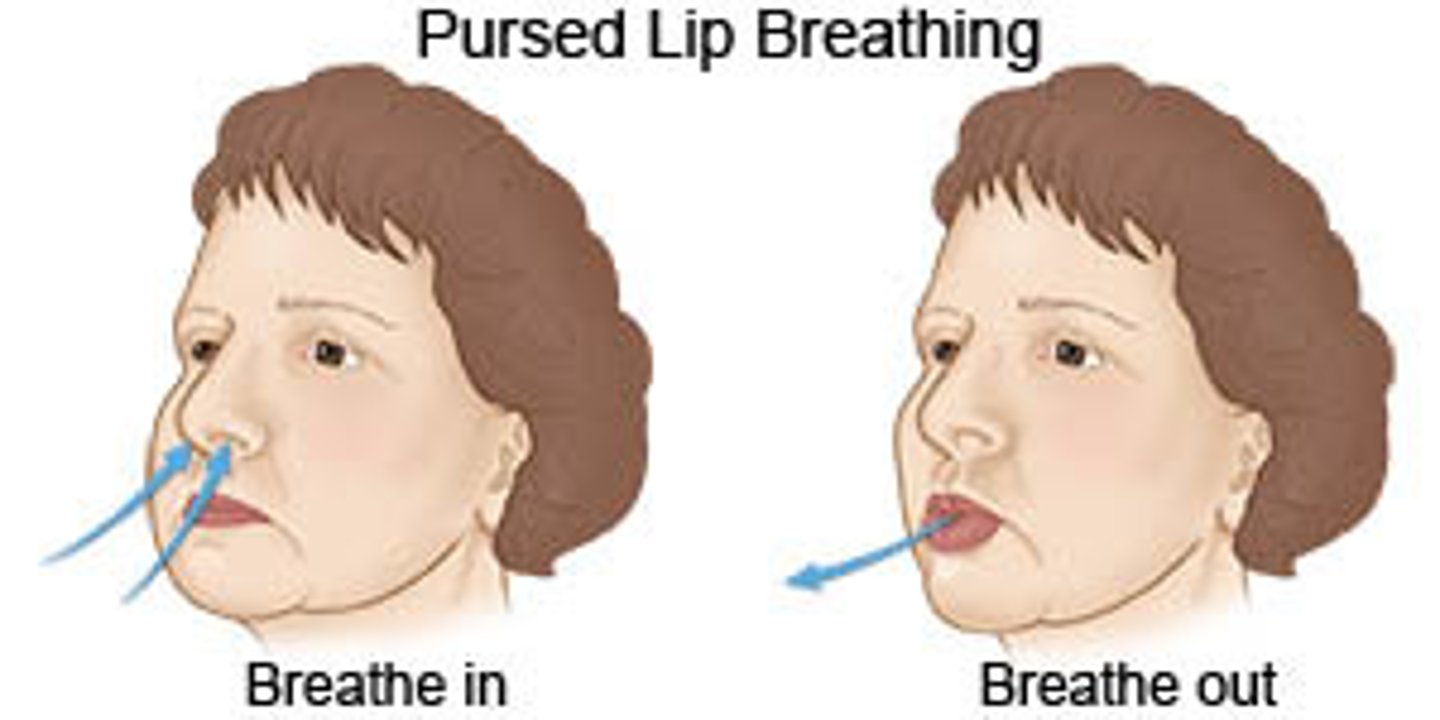
how to perform pursed lip breathing?
1. slowly inhale through nose
2. passively exhale through pursed lips (4-6 secs)
* blow out the candle*
what are the uses of stacked breathing?
used for hypoventilation, atelectasis, & ineffective cough
- also for uncoordinated breathing during ADLs
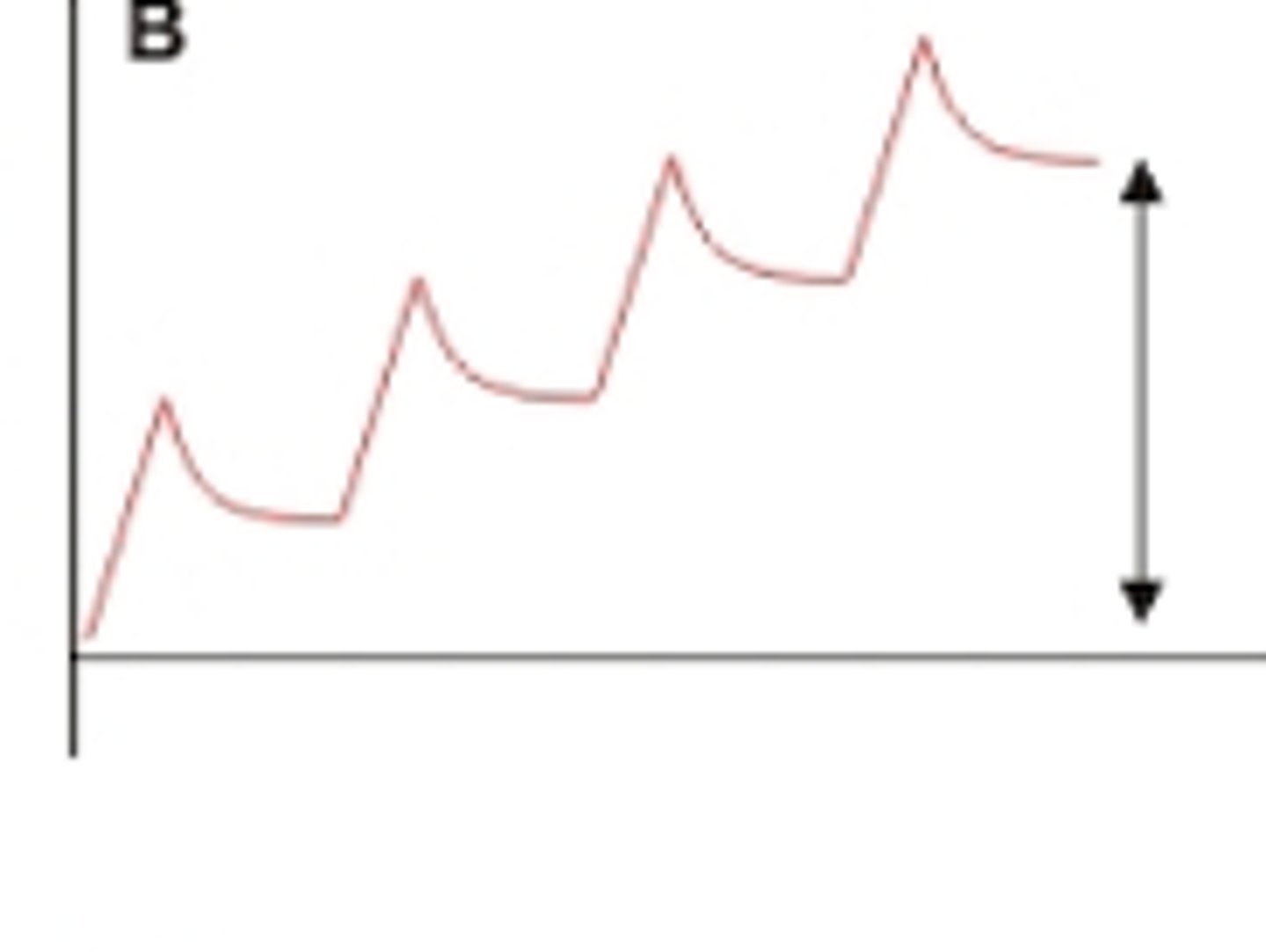
how to perform stacked breathing?
series of deep breaths built on top of previous breaths
each inspiration is held with a minor hold
when should you use upper chest inhibition?
only used after all other techniques have been attempted
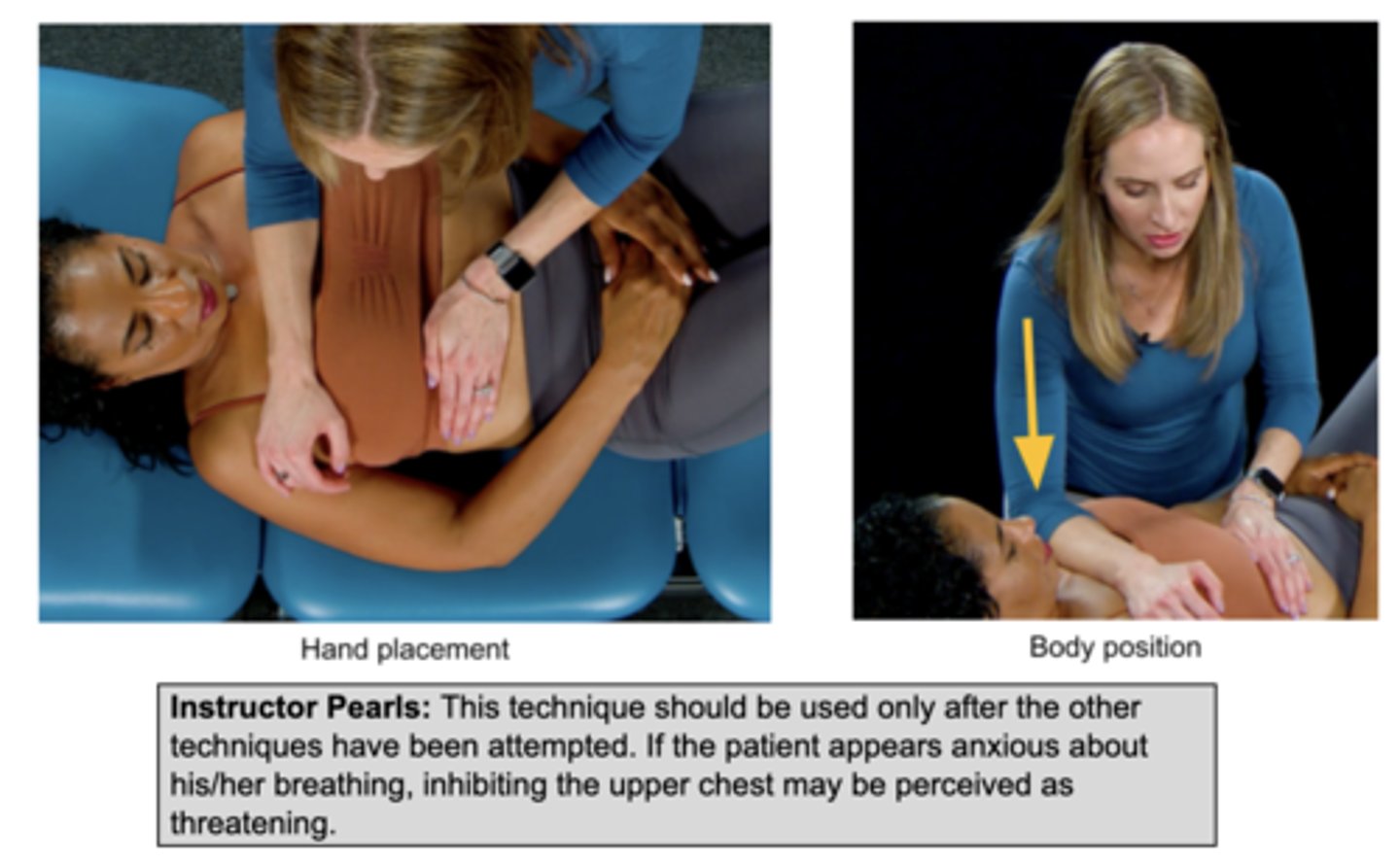
how to perform upper chest inhibition?
apply pressure to upper chest to limit excursion & encourage diaphragmatic breathing
- add more pressure each time
when would you use abdominal strengthening for respiration?
for someone with an ineffective cough
- via abdominal bracing
what can air gulping assist with?
assist with coughing
- for high level cervical spine SCI (i.e. C4 SCI)
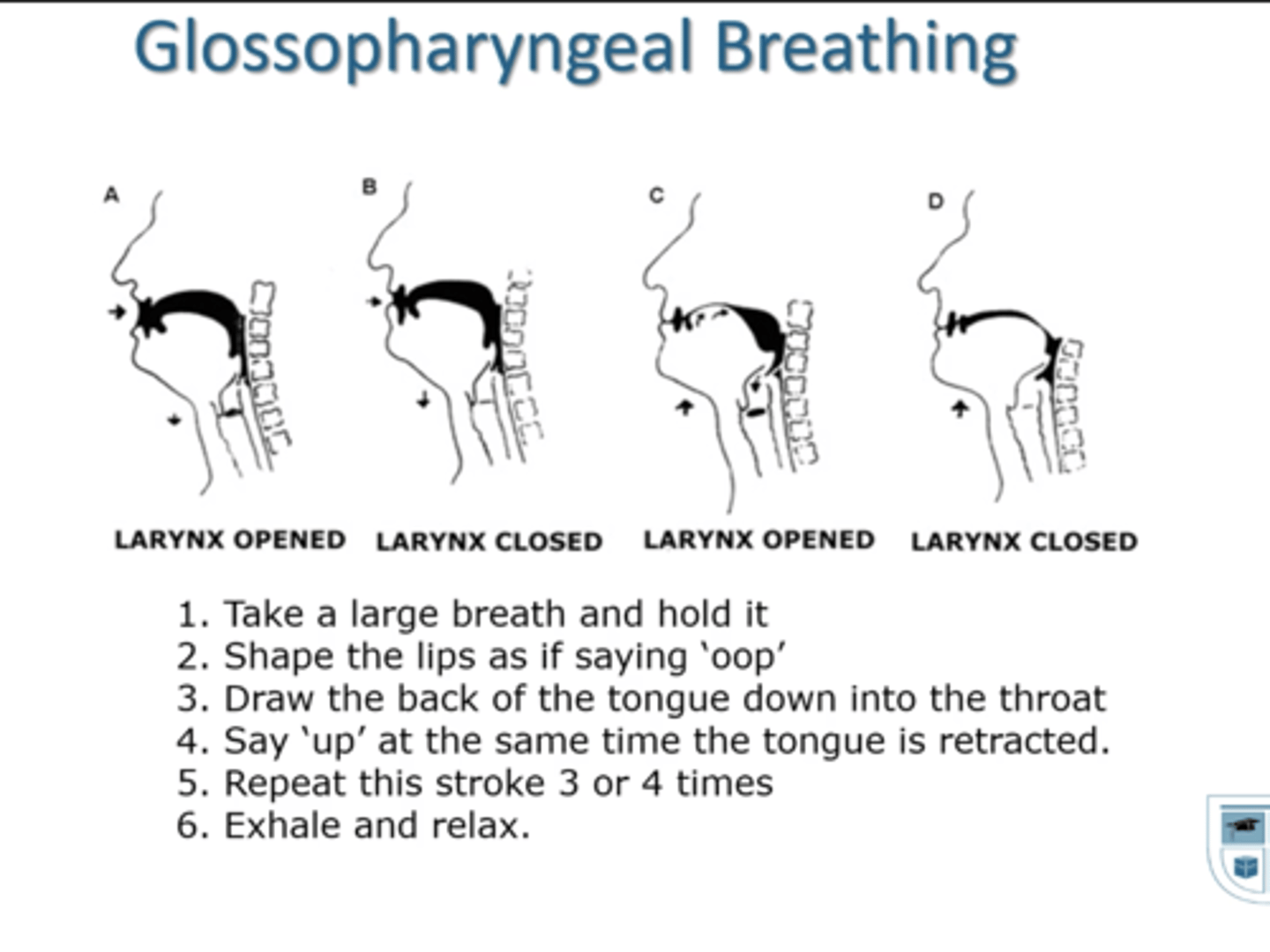
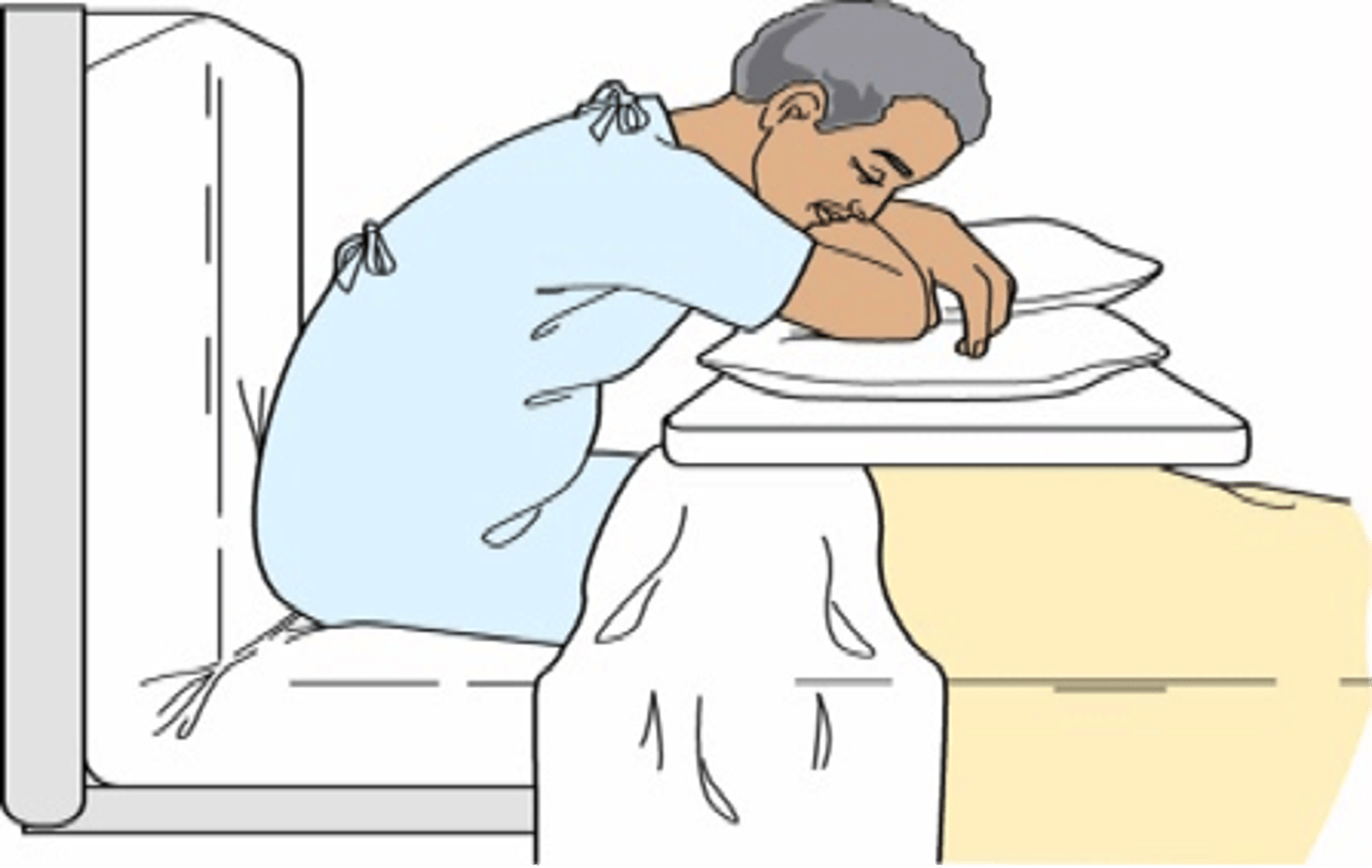
what position can assist with dyspnea relief?
leaning forward with arms supported
- accessory muscles act on the rib cage & thorax = allows for expansion & inspiration
inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
max inspiration
expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
max expiration
vital capacity (VC)
max inhalation + max exhalation
residual volume (RV)
amount of air left in lungs after maximal exhalation (not voluntarily accessed)
tidal volume (TV)
normal inhale and exhale
inspiratory capacity (IC)
the volume of air inhaled after a normal exhale
TV + IRV
functional residual capacity (FRC)
amount of air left after a normal exhale (after tidal volume)
total lung capacity
ALL AIR: vital capacity + residual volume
What does a spirometer measure?
record volumes of air inspired and expired over Time
shows the condition of ventilation/ state of airways
what 3 parameters are specifically measured?
PEFR
FEV1
FEF
FEV1
forced expiratory volume in 1 second
- amount of air forceful exhaled in 1 second
FEF
forced expiratory flow
- between 25 - 75% of exhaled volume
- more specific to smaller airways
what is a normal FEV1 %?
75%
what is a restrictive FEV1 %?
>83%
what is a obstructive FEV1 %?
<70%
< 25%
what is PaO2 and what does it correspond to?
partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood
corresponds to SpO2
what is a normal PaO2?
90-100 mmHg
same as 98-100% SpO2
What is considered an abnormal PaO2? what intervention is recommended?
55 mmHg
same as 88% SpO2
- need supplemental O2
what is hypoxemia?
low level of O2 in arterial BLOOD
- <80 mmHg
What is hypoxia?
low level of O2 in the TISSUE despite adequate perfusion (blood) of the tissue
What 3 parameters make up Arterial blood gases (ABGs)?
pH
PaCO2
HCO3
what are the normal parameters for ABGs?
Ph = 7.35 - 7.45
PaCO2 = 35 - 45
HCO3 = 22- 26 mmHg
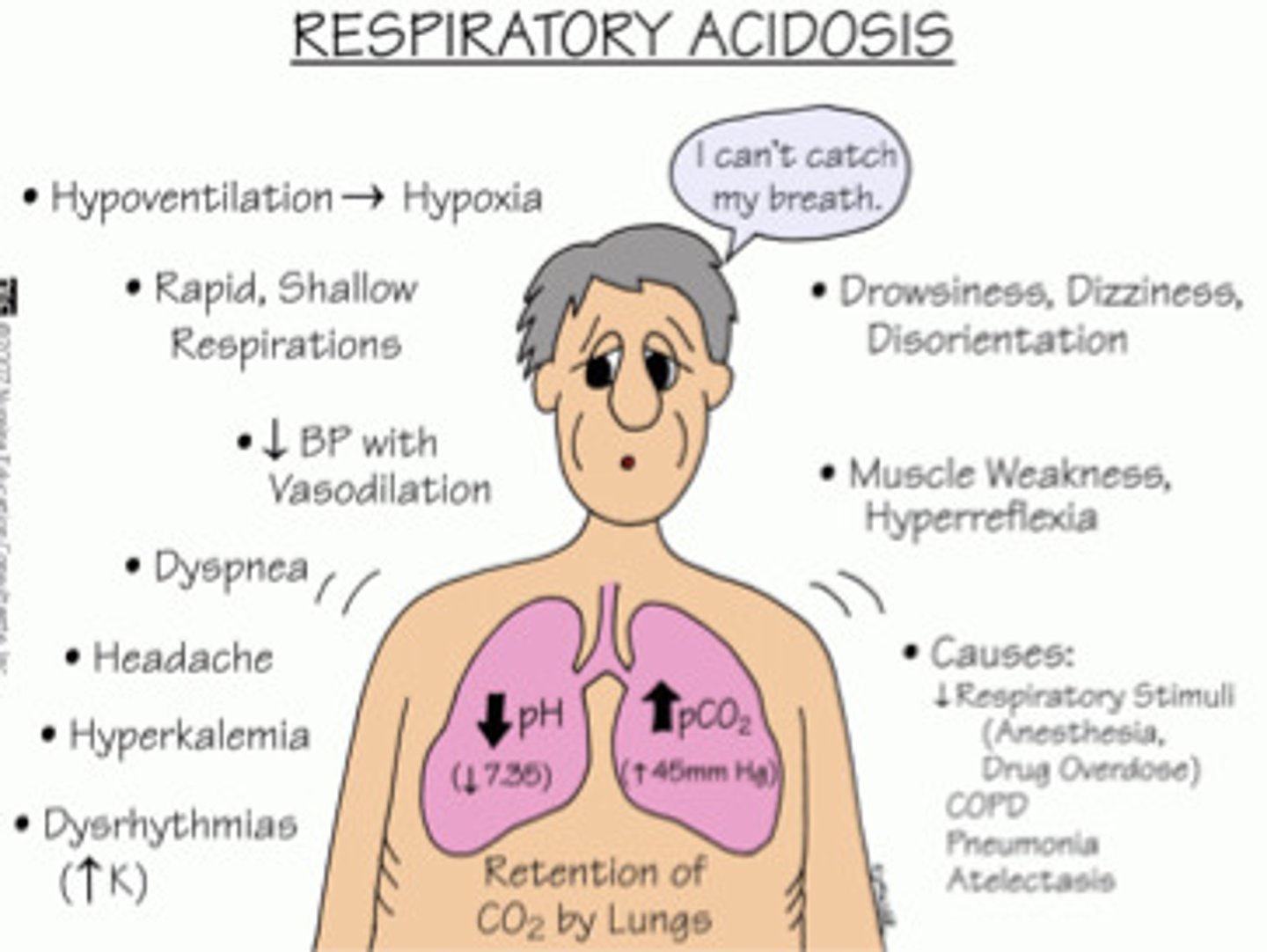
respiratory acidosis symptoms?
low ph & high PaCO2
Causes: COPD & GBS, increased CO2 in lungs
SX: confusion, palpitations, restlessness
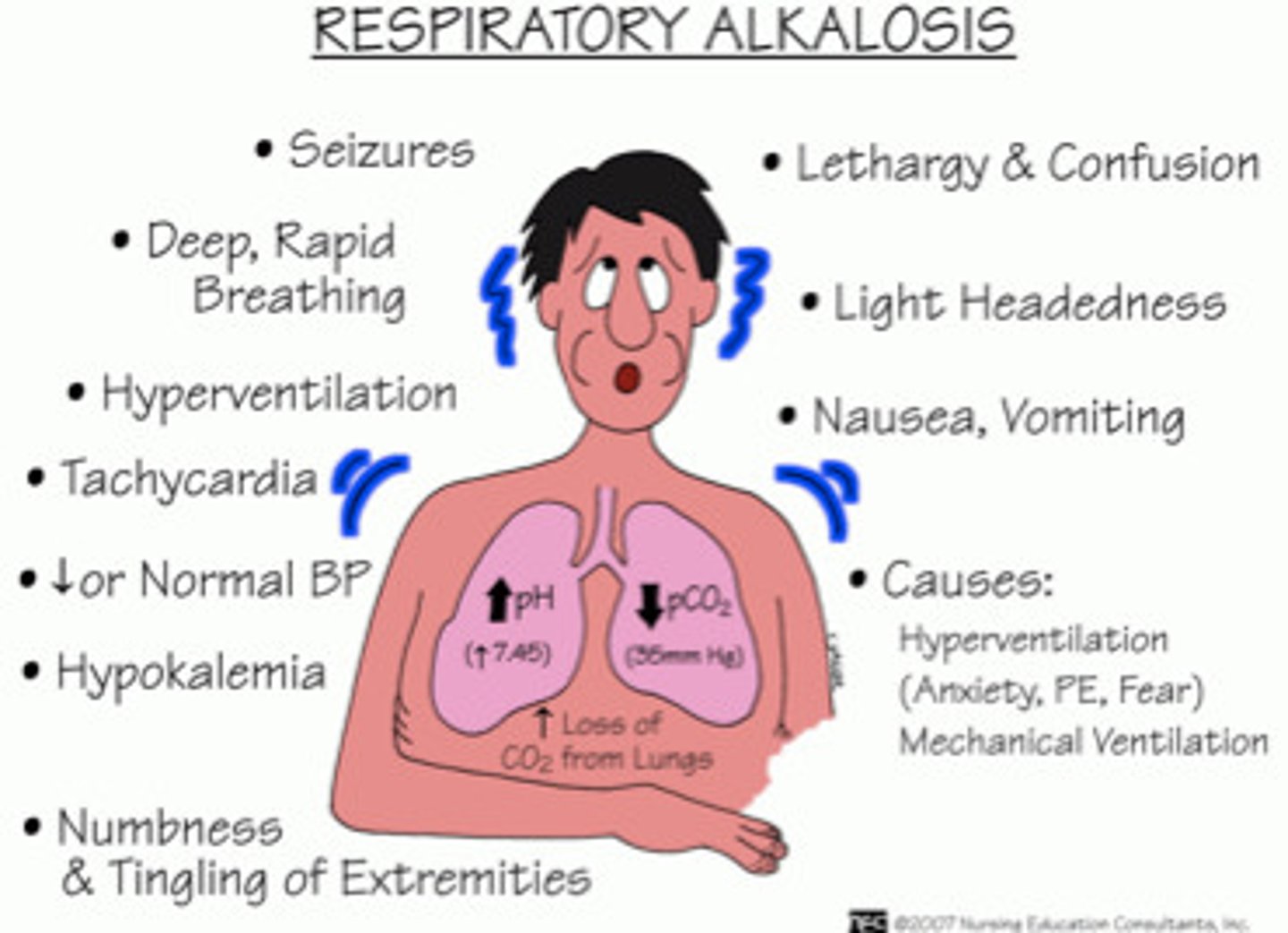
respiratory alkalosis symptoms?
high pH & low PaCO2
cause: hyperventilation, decreased CO2 in lungs
symptoms: tachypnea, dizziness, N&T
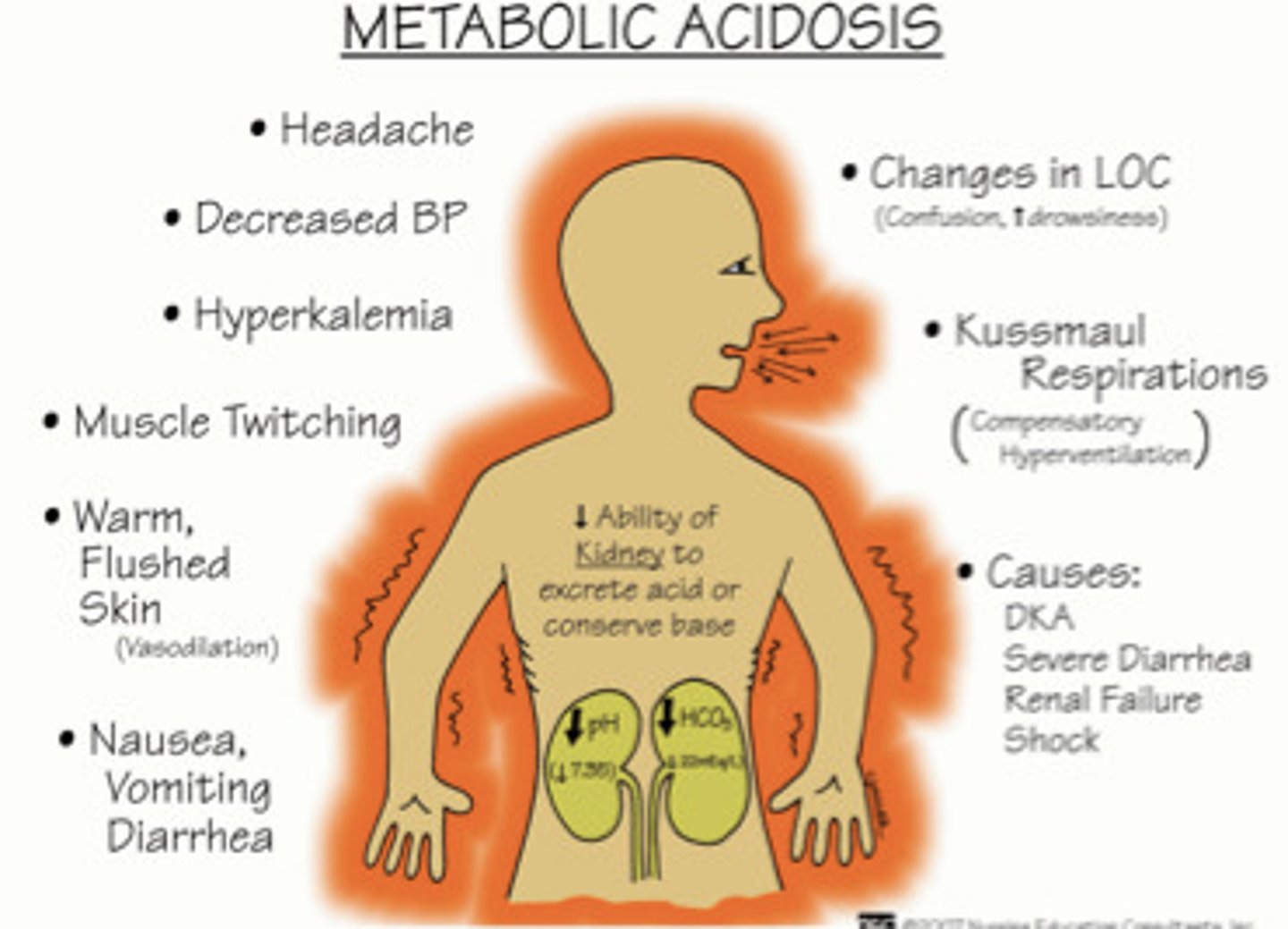
Metabolic acidosis symptoms?
low pH and low HCO3
causes: renal failure, ketoacidosis
Symptoms: muscle twitching, nausea & vomiting
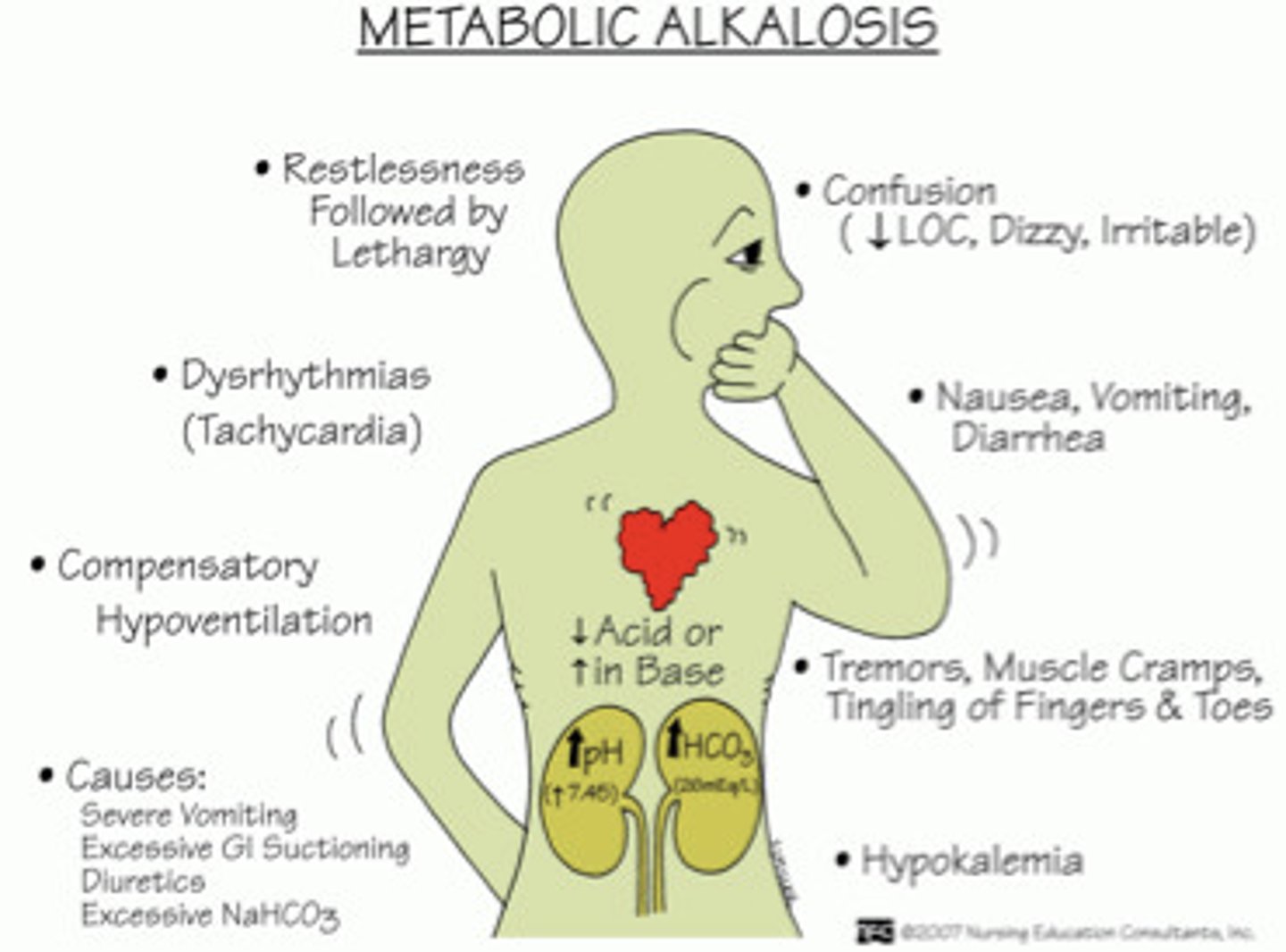
metabolic alkalosis symptoms?
high pH & high HCO3
cause: excessive build up of bicarbonate
symptoms: dysrymthria & hypoventilation
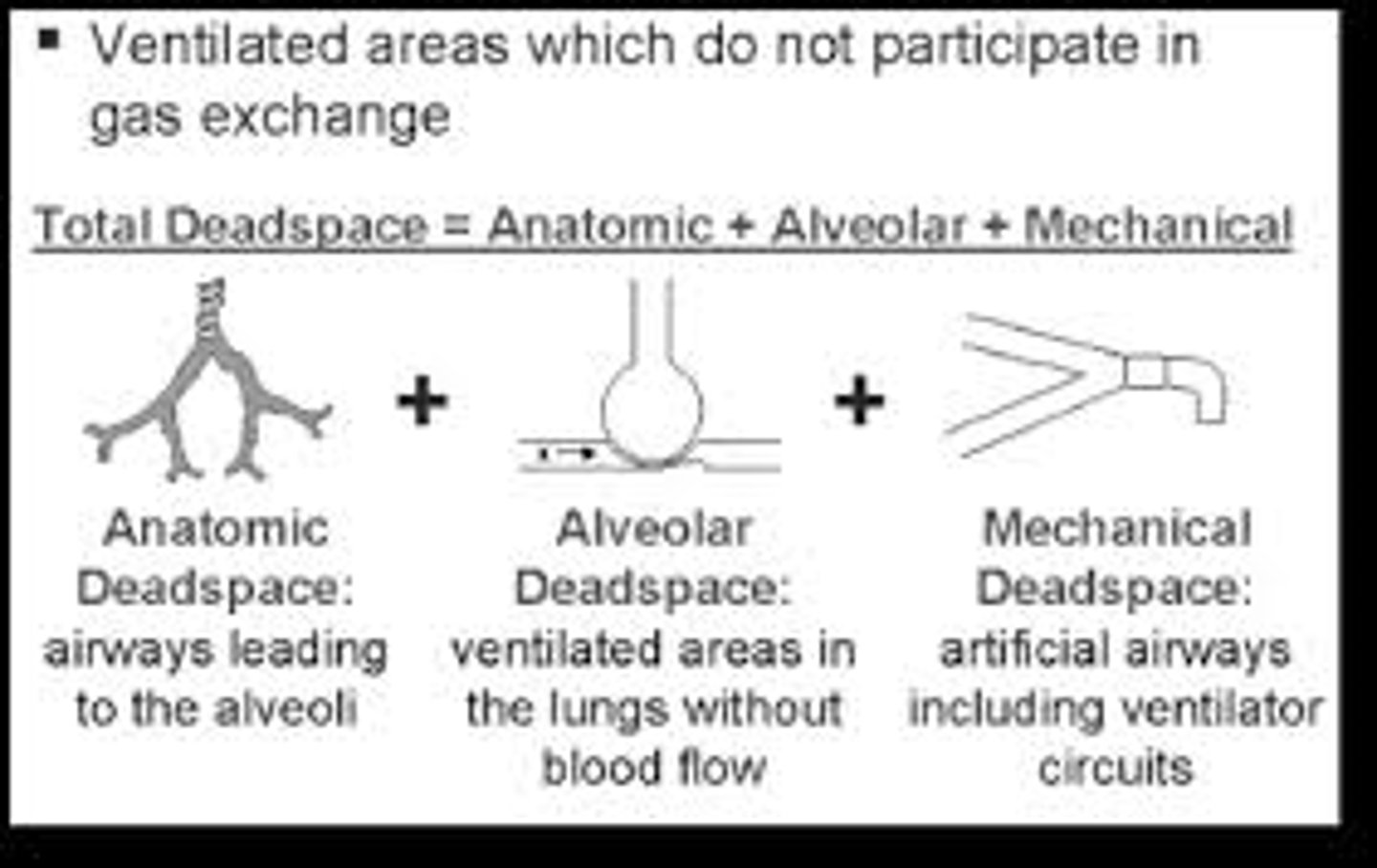
What is dead space?
being well-ventilated but no gas exchange (respiration) occurs
what is anatomical dead space?
blood vessel walls are too thick to allow for gas exchange
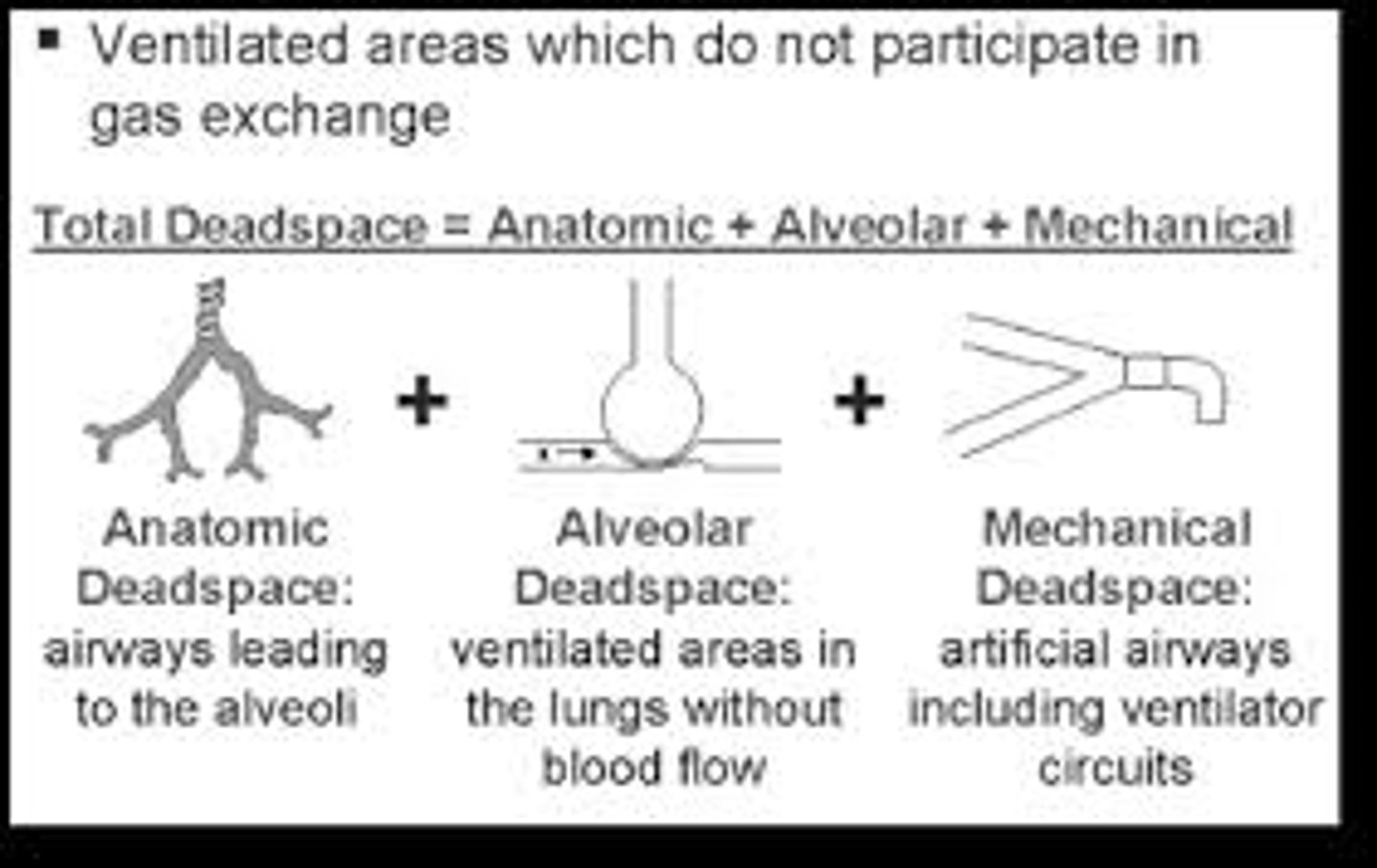
what is Physiological dead space?
not enough perfusion (blood flow) for gas exchange
What is a shunt?
Blood exits the heart without having participated in gas exchange due to atelectasis (alveoli deflate or fill with fluid)
is a tracheal breath sound normal & what does it sound like?
harsh, high pitched sound
normal breath sound
Where are tracheal breath sounds located?
over the trachea
what is the inspiration & expiration ratio for tracheal breath sounds?
I = E
is a Bronchial breath sound normal & what does it sound like?
loud, high pitched sound
normal breath sound
Where are bronchial breath sounds located?
over the manubrium
above the clavicles
what is the inspiration & expiration ratio for bronchial breath sounds?
I < E
- longer expiration
is a bronchovesicular breath sound normal & what does it sound like?
medium loudness
normal breath sound
Where are bronchovesicular breath sounds located?
between scapulae
next to the sternum
what is the inspiration & expiration ratio for bronchovesicular breath sounds?
I = E
is a vesicular breath sound normal & what does it sound like?
soft & low pitched
normal breath sound
Where are vesicular breath sounds located?
remainder of lungs
what is the inspiration & expiration ratio for vesicular breath sounds?
I > E
inspiration is longer
is a wheeze breath sound normal & what does it sound like?
abnormal
continuous high pitched sound exhaling "whistle"
what causes a wheeze sound?
airway obstruction
i.e. asthma, COPD, foreign body
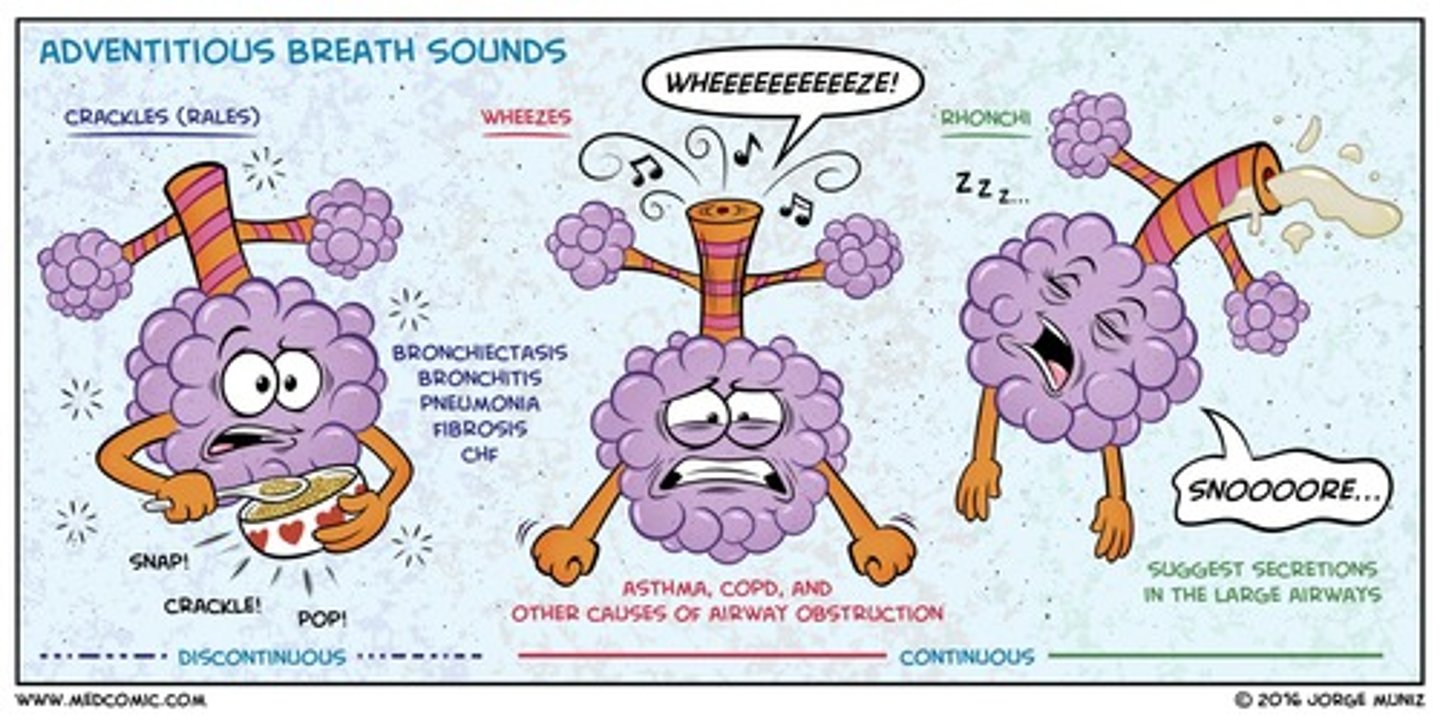
is a crackles (rales) breath sound normal & what does it sound like?
abnormal
high pitched, popping lung sounds "popcorn"
what causes crackles/rales sound?
atelectasis, fibrosis

is a rhonchi breath sound normal & what does it sound like?
abnormal
low pitched rattling sound "snoring"
what causes rhonchi sound?
COPD, pneumonia, bronchitis (secretions trap air)

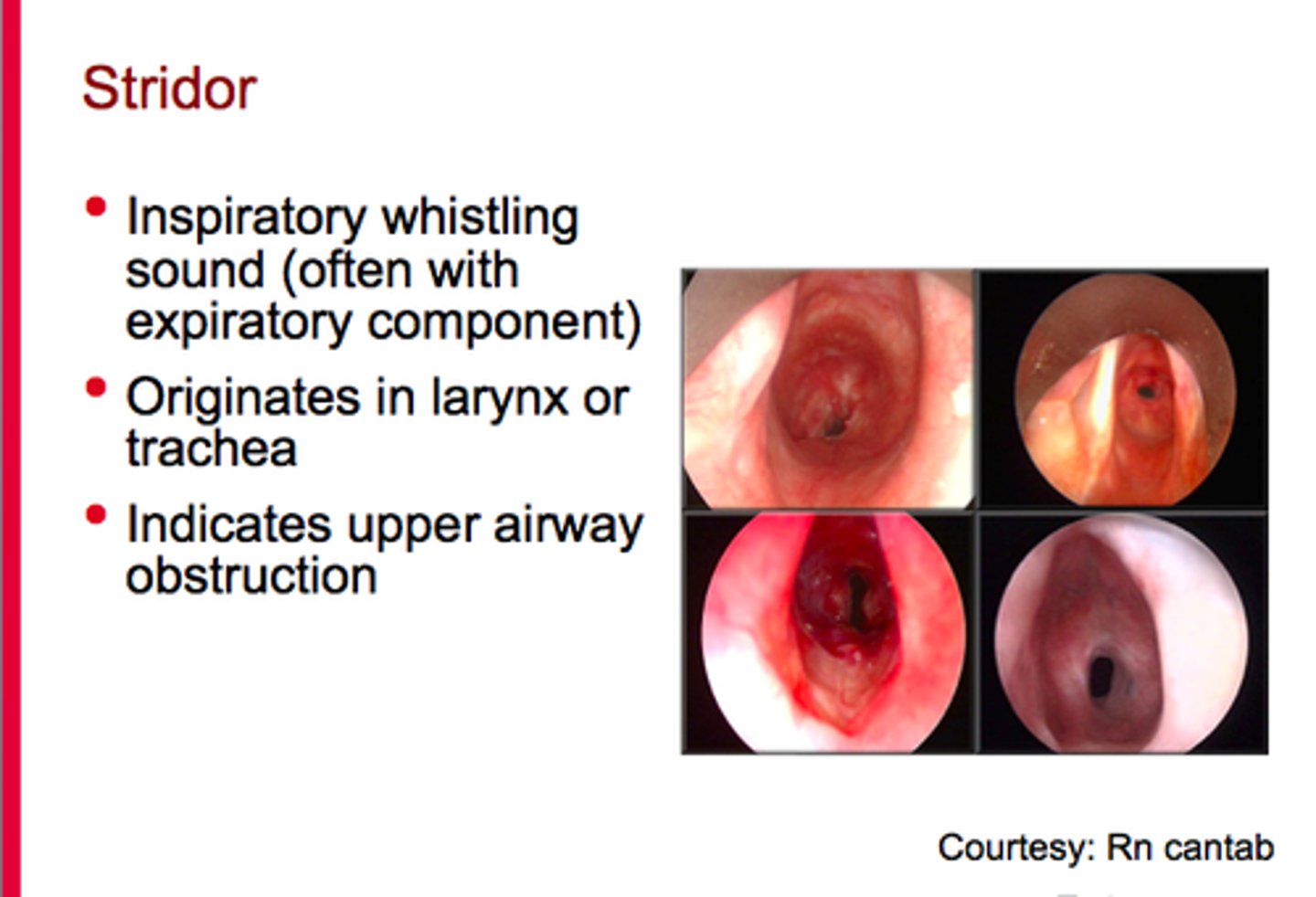
is a stridor breath sound normal & what does it sound like?
abnormal
harsh, high sound sound "crowing"
what causes stridor sound?
upper airway obstruction
- tracheal stenosis/narrowing, foreign object
is a pleural rub breath sound normal & what does it sound like?
abnormal
sounds like 2 pieces of leather or sandpaper rubbing together
what causes pleural rub sound?
pleural inflammation (at lower lateral chest areas)
what does a clear sputum indicate?
normal
what does a yellow sputum indicate?
common cold
what does a green sputum indicate?
bacterial infection
what does a pink frothy sputum indicate?
pulmonary edema, heart failure
what does a red sputum indicate?
blood (new bleeding)
what does a brown sputum indicate?
old blood or dirt
what does a black sputum indicate?
fungal infection, smoking
what does fetid mean?
foul smelling sputum
What does mucoid sputum look like?
thick and Clear, grey/white
What does mucoid sputum indicate?
COPD, asthma, acute viral infections
while performing percussion, you hear a dull thud. what does this indicate?
consolidation, tumor