A&P Test 4 Study Guide (Chandler)
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Meninges
three protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
Ventricles of the brain
canals in the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid
lateral, third, fourth
Cerebral aqueduct
connects the third and fourth ventricles
Choroids plexus
forms cerebrospinal fluid
CSF function
nutritive and protective, helps maintain stable ion concentrations in CNS
Spinal cord divisions
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, filum terminale
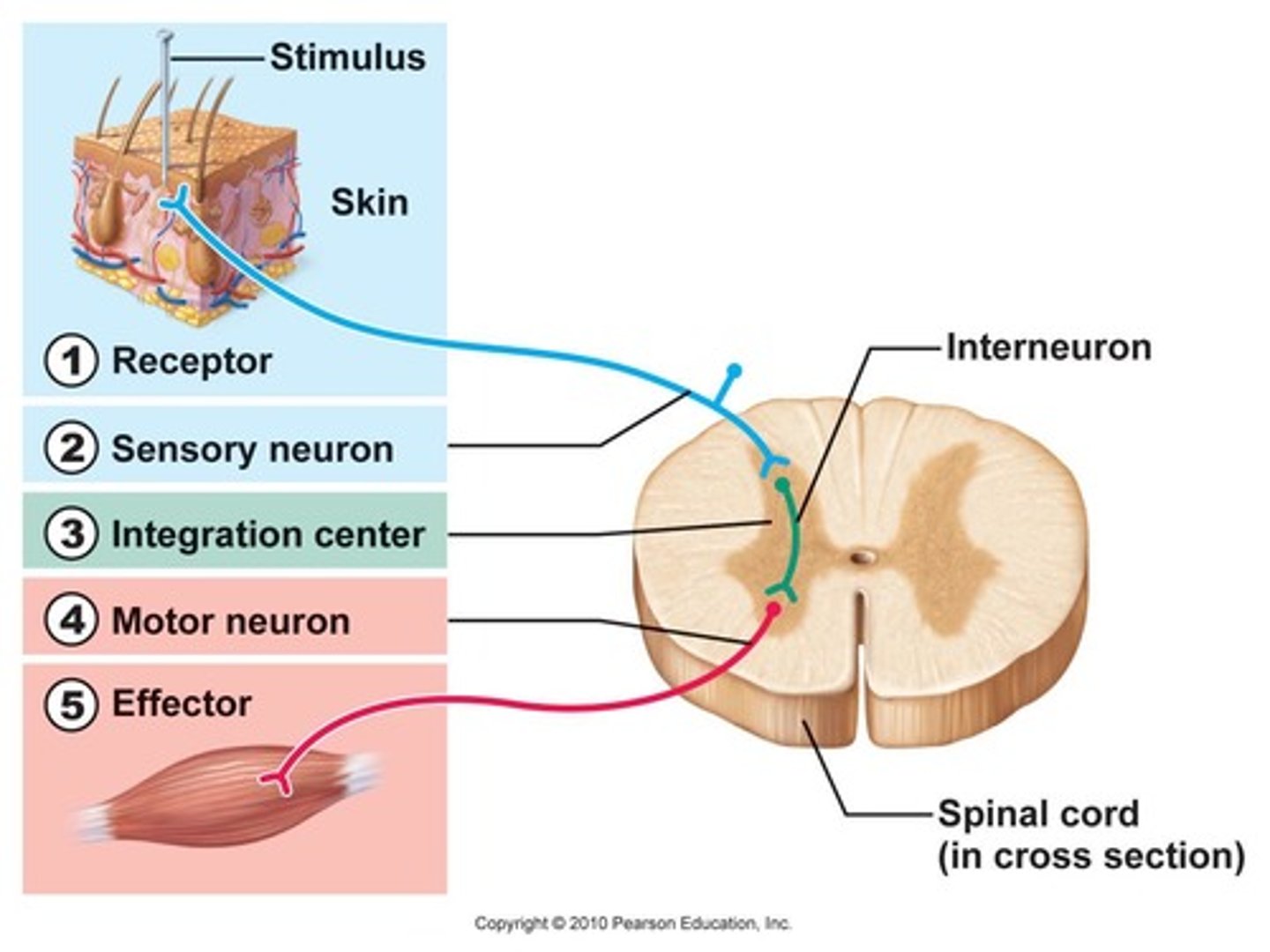
Reflex arcs
automatic, subconscious responses to stimuli within or outside the body
receptor (sensory or afferent neuron) -> central nervous system (motor or efferent neuron) -> effector (muscle or gland)
Frontal lobe function
involved in motor function: problem solving, memory, judgment, impulse control
Parietal lobe function
somatic sensory processing
Temporal lobe function
hearing and smell
Occipital lobe function
visual processing
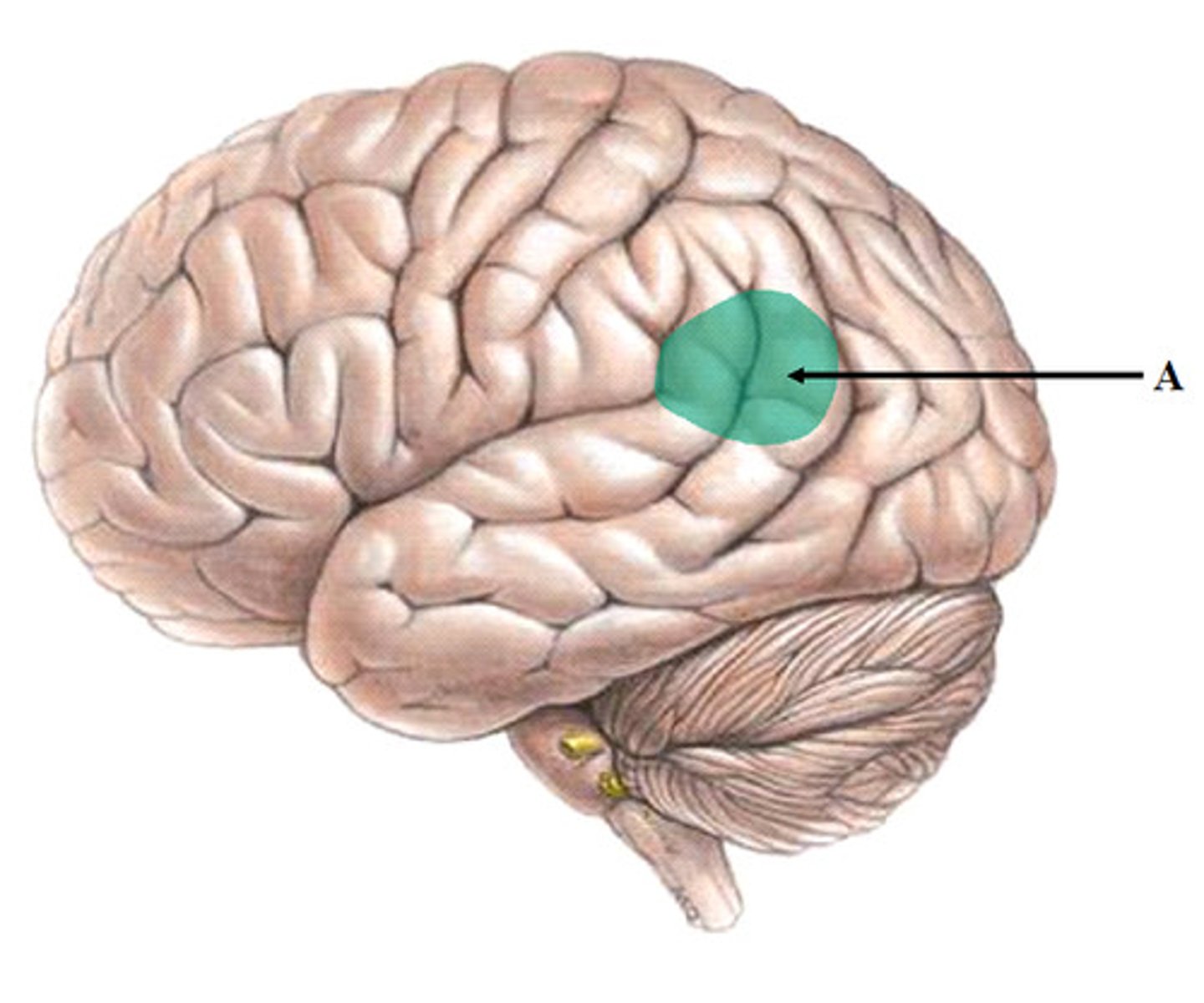
Insula lobe function
memory, taste, and integration of the activities of the other cerebral lobes
Cerebrum function
higher order functions: thinking, personality, sensations, movements, memory
Sulci
grooves
Gryri
ridges
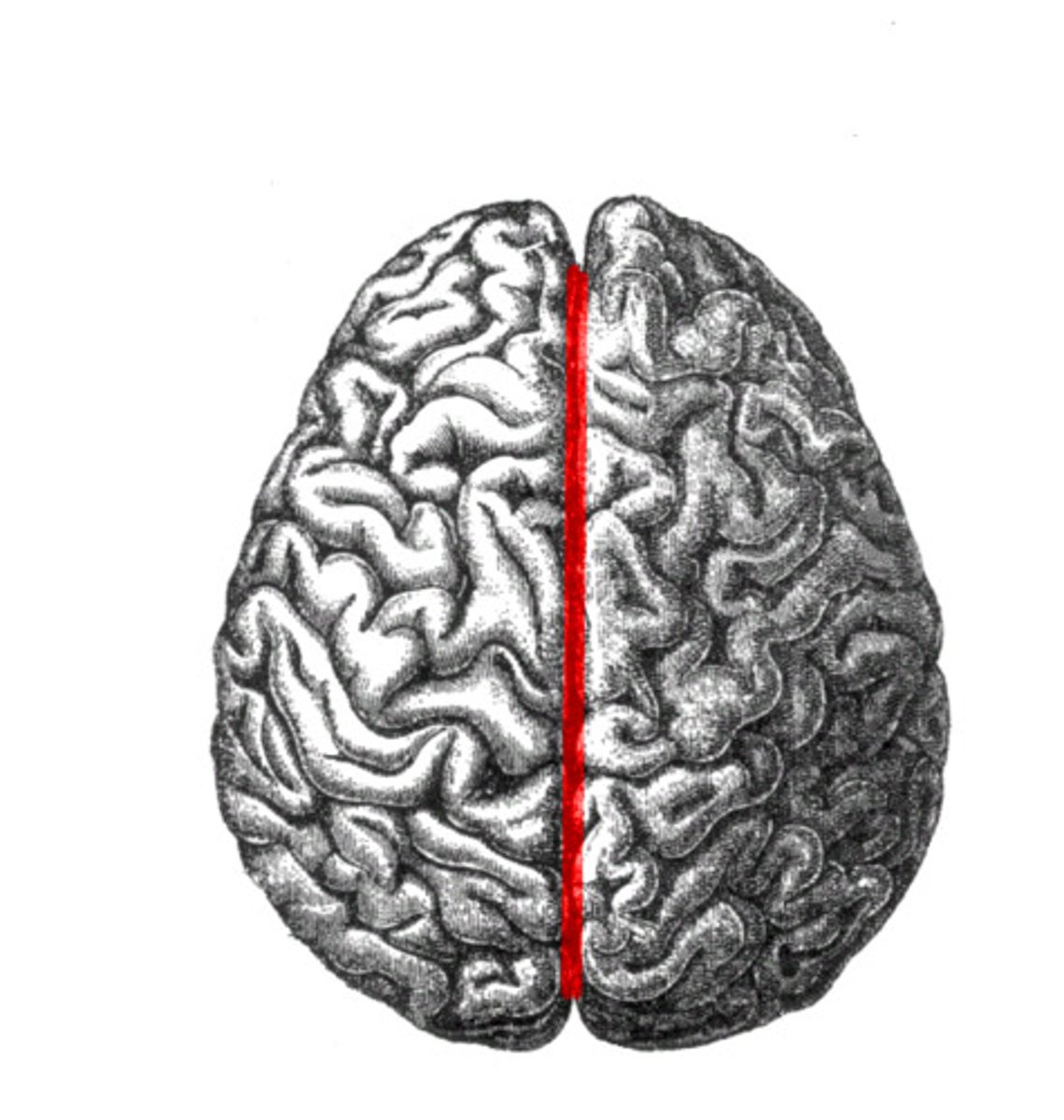
Longitudinal fissure
separates cerebral hemispheres
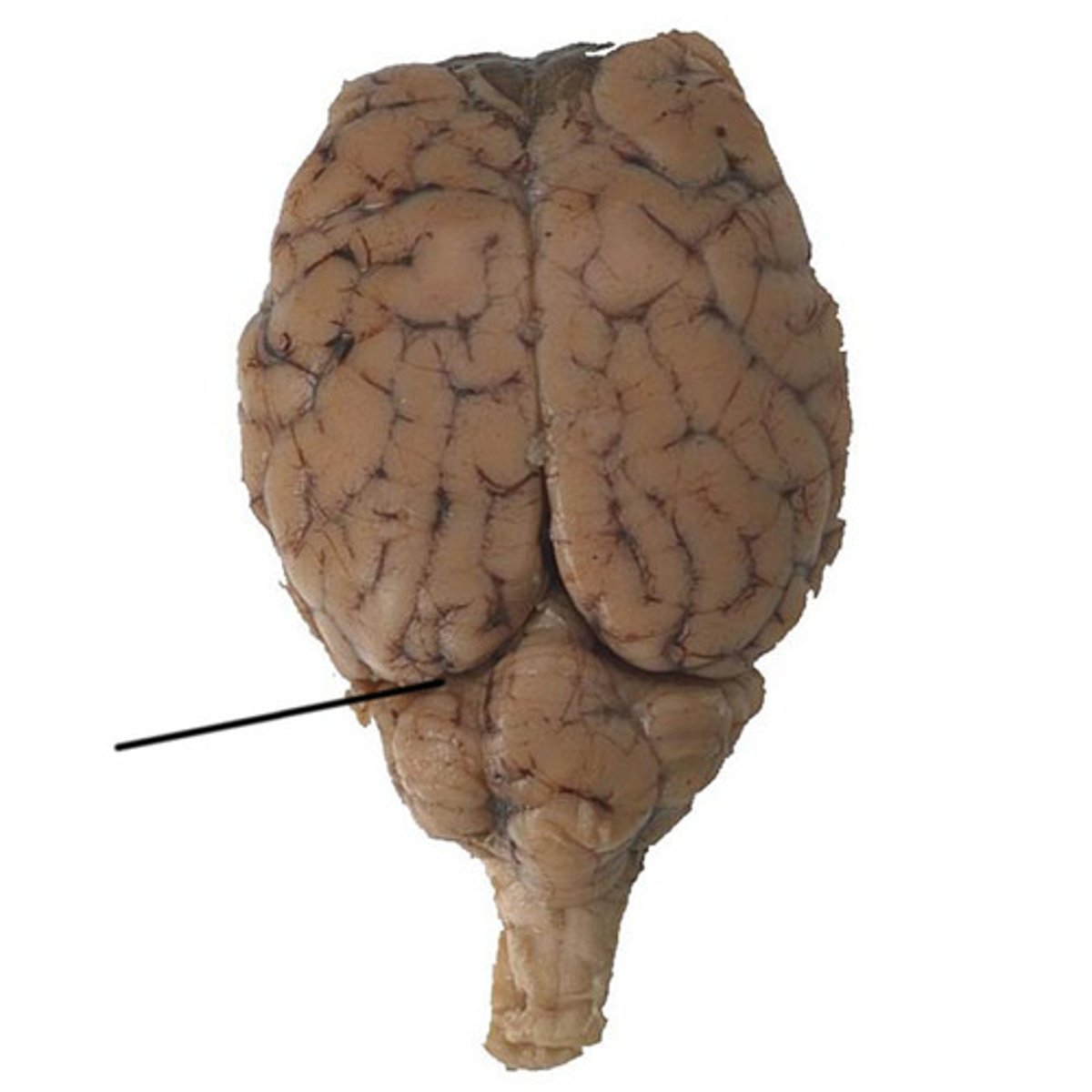
Transverse fissure
separates cerebrum from cerebellum
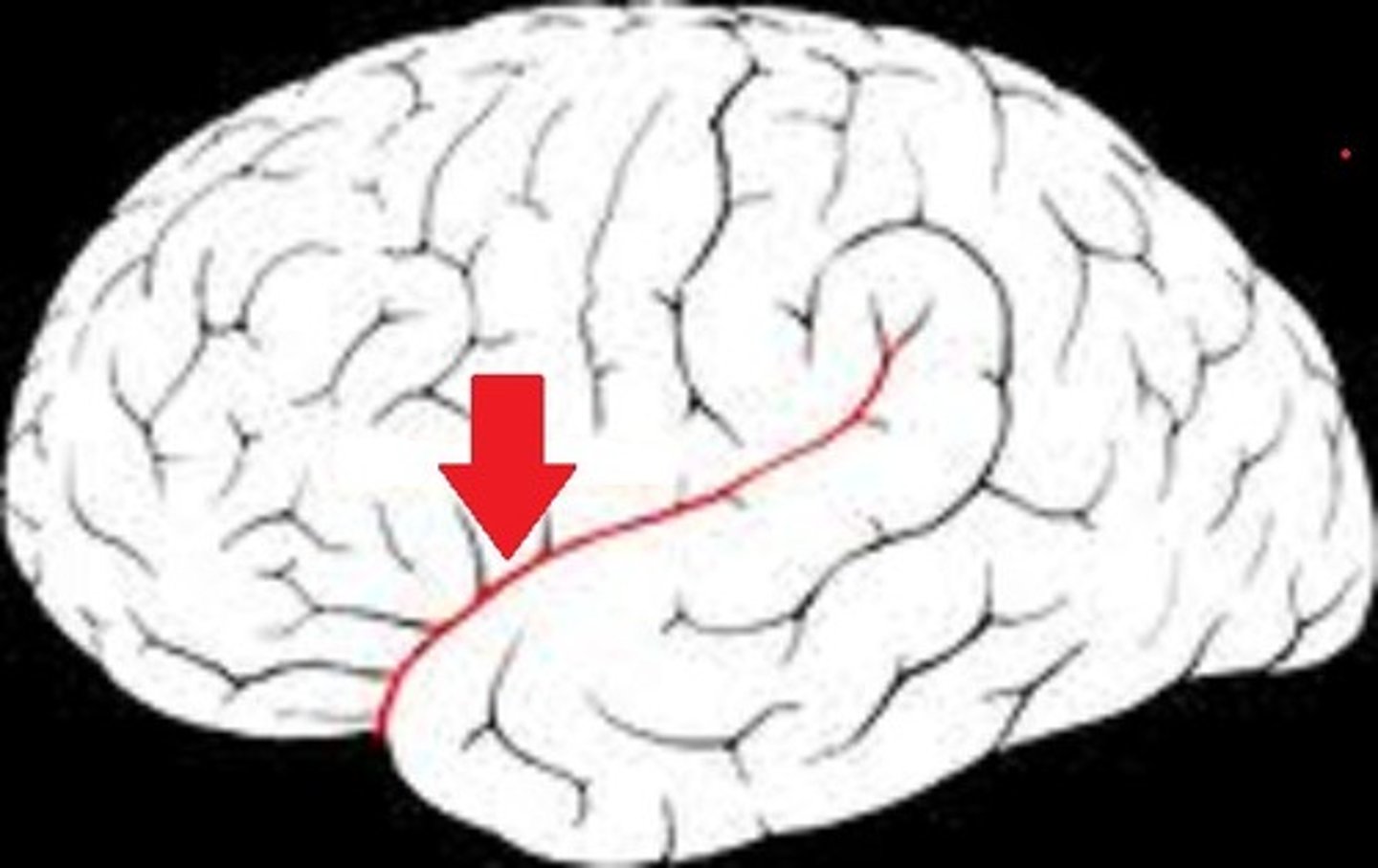
Lateral fissure
separates temporal lobe from frontal and parietal lobes
Cerebral cortex
thin layer of grey matter surrounds outermost portion of the cerebrum
Broca's area
speech production
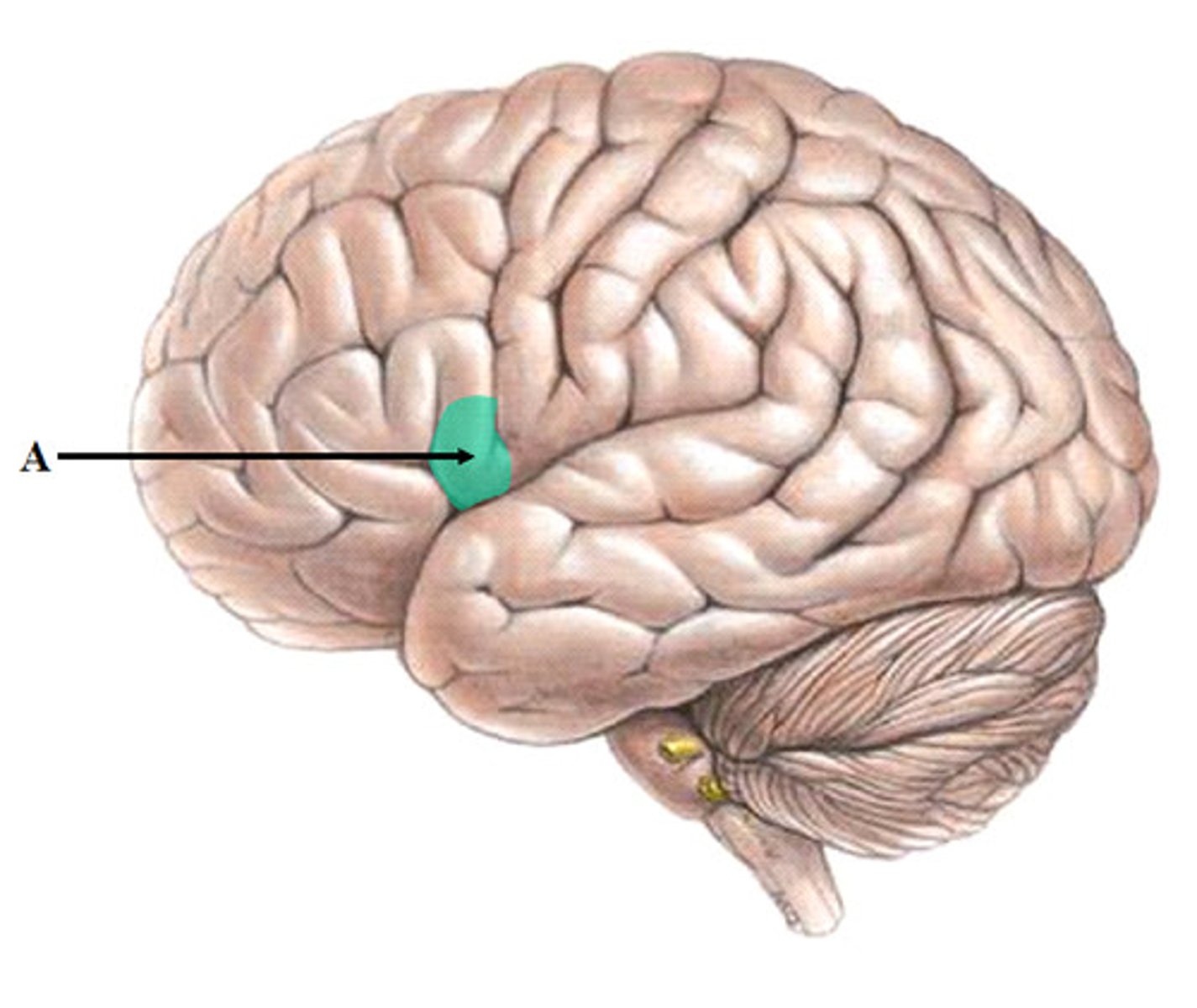
Wernicke's area
language comprehension
Diencephalon
thalamus and hypothalamus
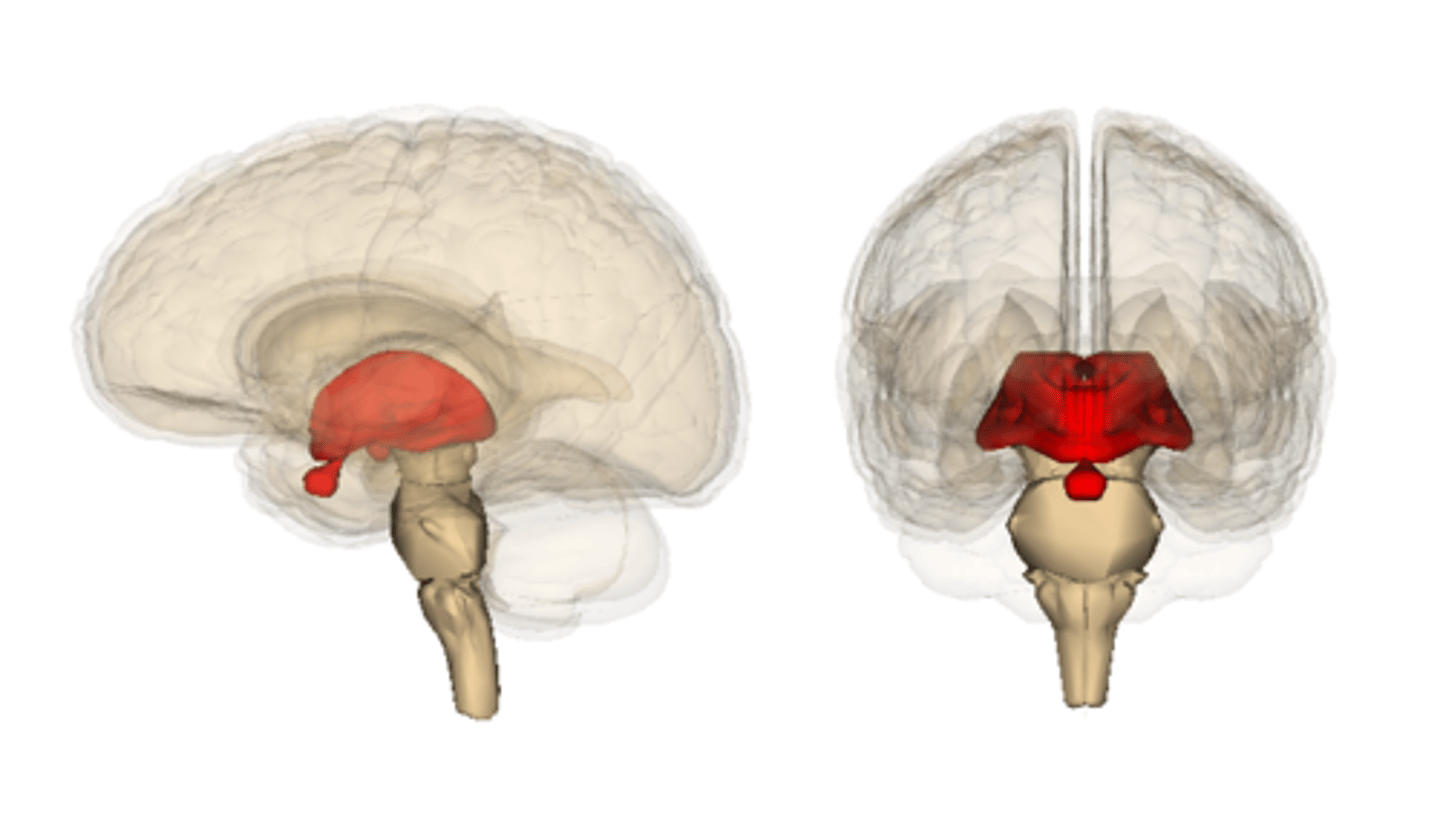
Thalamus
the brain's sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
Hypothalamus
a neural structure lying below the thalamus; directs eating, drinking, body temperature; helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion
Brainstem
responsible for automatic survival functions
Midbrain
A small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward.
Medulla oblongata
the continuation of the spinal cord within the skull, forming the lowest part of the brainstem and containing control centers for the heart and lungs (also coughing, sneezing, swallowing, vomiting)
Pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain; sleep and arousal
Limbic system
neural system located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions, drives, and memory
Cerebellum
2 hemispheres connected by vermis; cerebellar peduncles (and midbrain); integrates information about position of body parts, coordinates skeletal muscles, maintains posture
Arbor vitae
white matter of the cerebellum
Cranial Nerve I
Olfactory
sensory, smell
Cranial Nerve II
Optic
sensory, vision
Cranial Nerve III
Oculomotor
motor, raise eyelids, move eyes, focus lens, adjust light enetering, proprioceptors
Cranial Nerve IV
Trochlear
primarily motor, proprioceptors, move eyes
Cranial Nerve V
Trigeminal
both, sensation to the face, chewing
Cranial Nerve VI
Abducens
primarily motor, move eyes, proprioceptors
Cranial Nerve VII
Facial
both, taste receptors, facial expressions, tear glands, salivary glands
Cranial Nerve VIII
Vestibulocochlear
sensory, equilibrium receptors, hearing receptors
Cranial Nerve IX
Glossopharyngeal
both, pharynx, tonsils, tongue, carotid arteries, salivary glands, larynx, esophagus
Cranial Nerve X
Vagus
both, speech, swallowing, viscera of thorax and abdomen, pharynx, larynx, esophagus
Cranial Nerve XI
Accessory
primarily motor, muscles of soft palate, pharynx, larynx, spinal branch to neck and back muscles
Cranial Nerve XII
Hypoglossal
primarily motor, muscles of tongue, some proprioceptors
C1-C8
cervical nerves
T1-T12
thoracic nerves
L1-L5
lumbar nerves
S1-S5
sacral nerves
Dorsal root
sensory (afferent)
come in through dorsal nerves
Dorsal root ganglion
cell bodies of sensory neurons
Ventral root
motor (efferent), go out through ventral
Spinal nerve
union of ventral and dorsal roots
Dermatome
the region of a spinal nerve innervates
Plexuses
network formed by anterior/ventral branches of spinal nerves
C1-C4 cervical
C5-T1 brachial
Intercostal nerves
Somatic nerve fibers
convey information that controls the body's voluntary muscular movements (motor/efferent)
Visceral nerve fibers
innervate blood vessels, glands, and viscera (sensory/afferent)
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart).
sympathetic nervous system
prepares for fight-or-flight (increases rate of respiration, heart rate, adrenaline, vessels in muscles dilate, blood vessels in skin constrict, pupils dilate)
parasympathetic nervous system
prepares for rest-and-digest (slows heart rate, become tired, slower respirations)
Preganglionic fibers
nerve fibers of the autonomic nervous system that connect the CNS to the ganglia
Postganglionic fibers
nerve fibers that present in the autonomic nervous system which connects the ganglion to the effector organ
Cholinergic
parasympathetic
rest-and-digest
Adrenergic
sympathetic
fight-or-flight
(Acetylcholine)
Concussion
Brain is jarred against cranium. Typically characterized by a loss of consciousness, loss of memory, mental cloudiness, or headache
CVA
cerebrovascular accident (stroke)
sudden interruption in blood flow to brain (blockage or rupture)
TIA
transient ischemic attack (mini stroke)
narrowing of blood vessels in the brain, causing a decrease in blood flow and oxygen supply
General senses
receptors are widely distributed: skin, various organs, joints
Special senses
specialized receptors confined to structures: vision, hearing, taste, smell
Chemoreceptors
smell and taste
Nociceptors
pain receptors
Thermoreceptors
respond to changes in temperature
Mechanoceptors
sensitive to pressure, touch, vibration, and bending of skin
Photoreceptors
respond to light
Proprioceptors
sense tension (such as in muscles)
Baroreceptors
sense to pressure (such as blood pressure)
Sensory adaptation
a decrease in sensitivity to a constant level of stimulation
Such as not noticing the noise of traffic while in class
Meissner's corpuscles
sensitive touch receptors in the dermis
abundant in hairless portions of skin, lips; fine touch
Pacinian corpuscles
Common in deeper subcutaneous tissues, tendons and ligaments
Detect heavy pressure and vibrations
Free nerve endings
common in epithelial tissues, simplest receptor
respond to pain and temperature, sense itching
Referred pain
pain that is felt in a location other than where the pain originates
caused by nerve crossings; visceral pain
Acute pain
myelinated, sharp pain, well localized
Chronic pain
unmyelinated, dull throbbing, hard to pinpoint
Role of thalamus in pain
allows person to be aware of pain
Role of cerebral cortex in pain
judges intensity, source; emotional and motor responses
Basic ear anatomy
auditory canal, eardrum, ossicles, cochlea, nerves, brain
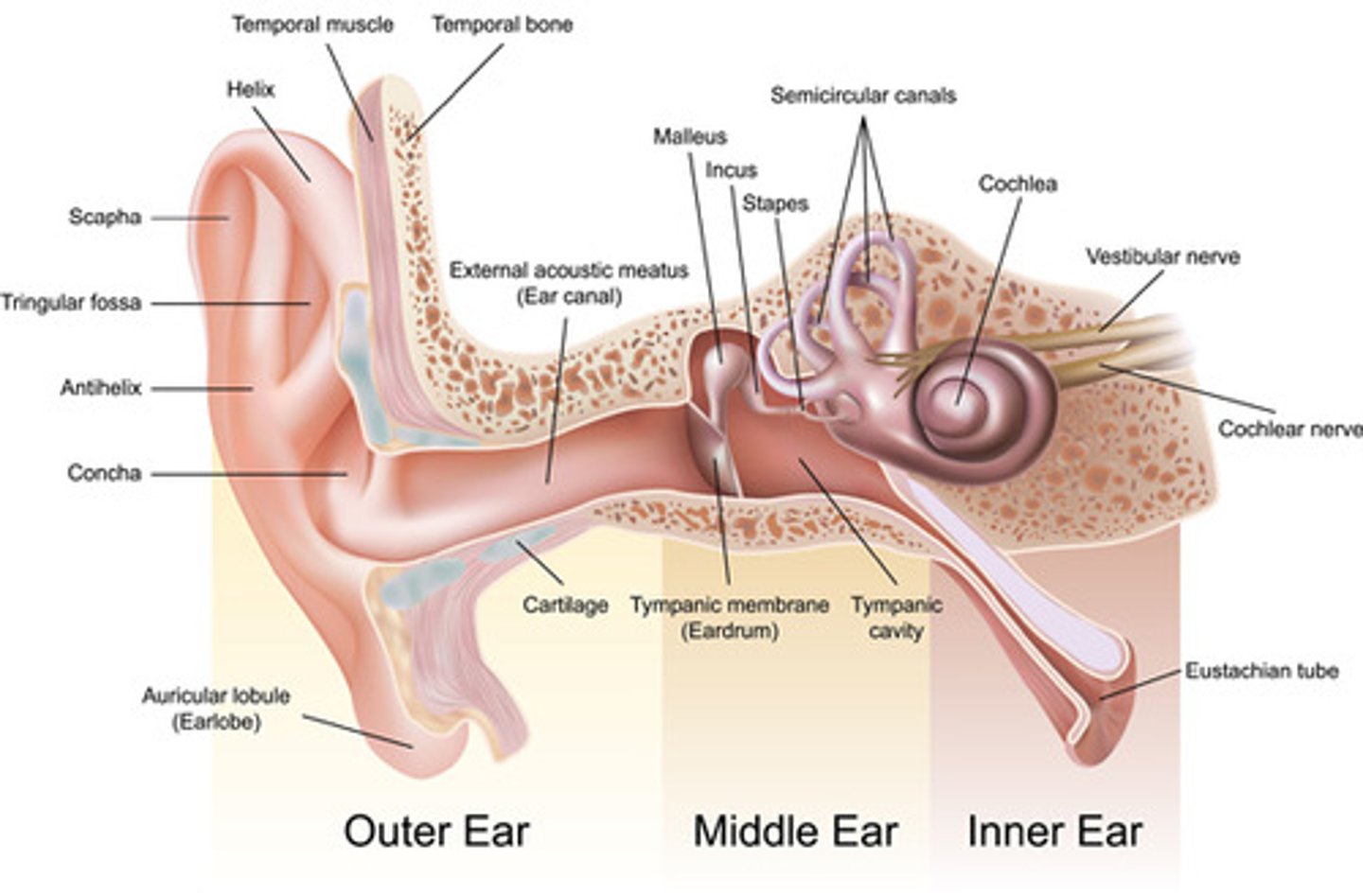
Pathway of hearing
When sound enters the ear, it is funneled into the external acoustic meatus by the outer structure called the auricle. This sound vibrates the tympanic membrane which vibrates the auditory ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes). The last of these moves back and forth in the oval window, and this motion causes a signal to be formed and taken to the brain by the acoustic/cochlear nerve.
Static equilibrium
the perception of the orientation of the head when the body is stationary
Dynamic equilibrium
semicircular canals, sense rotation and movement of head and body. OToliths move and stimulate hair cells (crystal like stones on top of hair cells)
Role of semicircular canals in equilibrium
needed for dynamic equilibrium
Role of macula in equilibrium
needed for static equilibrium
Eyelid function
Moisten, cover, brush debris from eye
Conjunctiva function
Secretes mucus to lubricate the eye (forms seal between the surface of the eye and the eyelid to prevent particles from getting trapped behind the eye)
Lacrimal apparatus function
produces, distributes, and removes tears
accomodation of lens
thickening of the lens to see close objects
Path of light through the eye
The path of light from outside your eye to your retina starts with light going through your cornea, passing through the aqueous humor; through the pupil, who's size is controlled by the iris. The light then passes through the lens and through the vitreous humor, finally hitting the retina, which contains rods and cones which sense light. The first of these light-sensitive structures have a long and thin shape, and are sensitive to low light and black & white images. The second has a short and blunt shape, and is sensitive to color images.
Myopia
nearsightedness; problems with the shape of the cornea or lens
Hyperopia
farsightedness; problems with the shape of the cornea or lens
Presbyopia
loss of elasticity of the lens of the eyes