Understanding Chronic Heart Failure: Causes and Treatments
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is Chronic Heart Failure?
Inability for the left ventricle to adequately pump blood.
What percentage of patients with Chronic Heart Failure have normal systolic function but decreased EDV?
½ of patients.
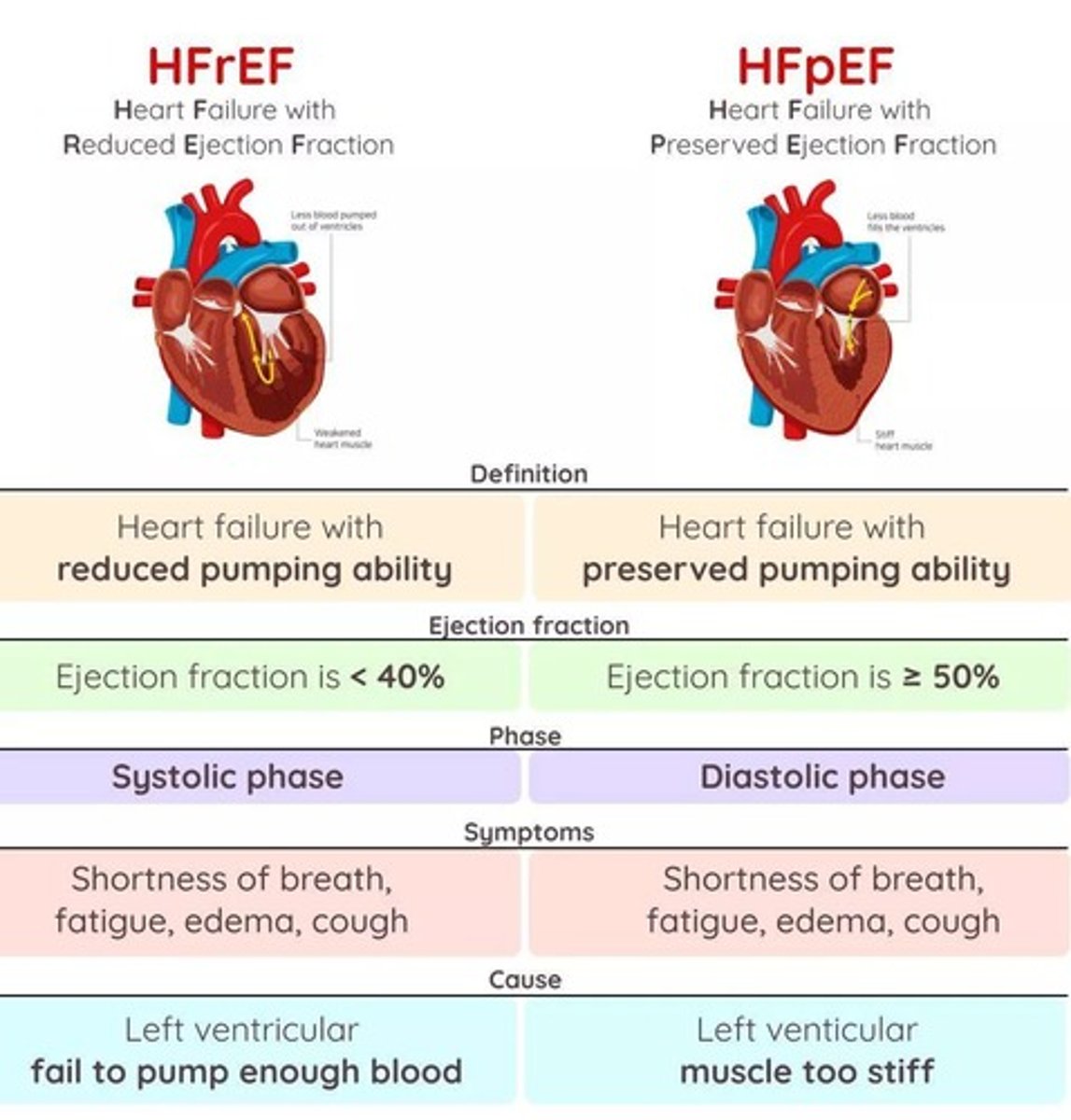
What are the two types of heart failure?
HFrEF (Heart Failure with reduced Ejection Fraction) and HFpEF (Heart Failure with preserved Ejection Fraction).
How many people in the US are affected by Chronic Heart Failure?
6.5 million people.
What is the annual economic burden of Chronic Heart Failure?
~$32 billion dollars.
What is the 5-year mortality rate for patients with Chronic Heart Failure?
~48%.
What are common causes of Heart Failure with reduced Ejection Fraction (HFrEF)?
60% are caused by ischemic heart diseases.
What is a key characteristic of Heart Failure with preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF)?
Generally due to lack of compliance or ability for the left ventricle to relax.
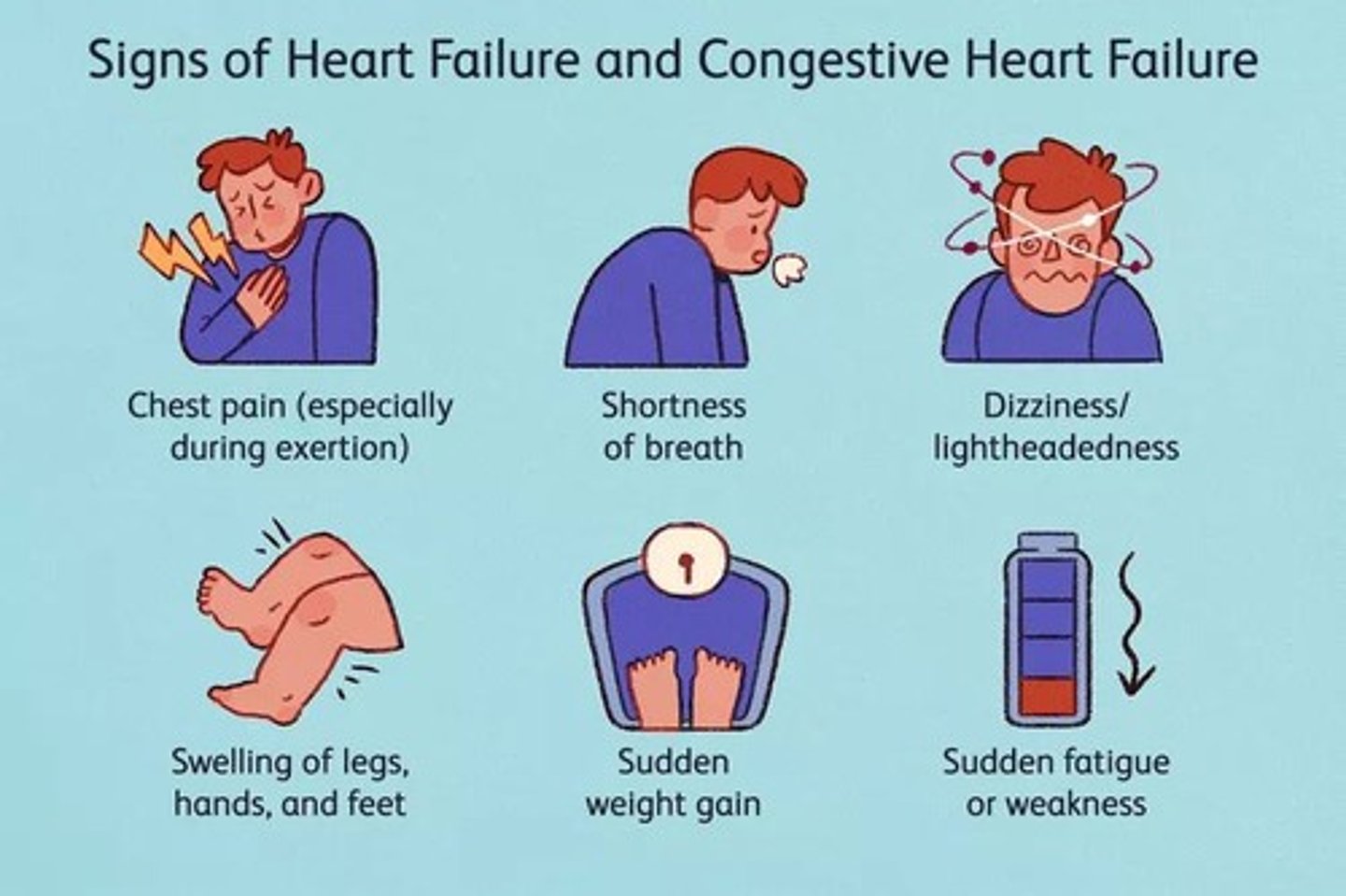
What are some signs and symptoms of Chronic Heart Failure?
Structural or functional cardiac abnormalities, elevated natriuretic peptide levels, pulmonary/systemic congestion, fluid retention, exercise intolerance, orthopnea, and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea.
What is the significance of elevated BNP levels in Chronic Heart Failure diagnosis?
Elevated BNP (>100pg/mL) indicates heart failure.
What diagnostic tool is used to assess the left ventricle in Chronic Heart Failure?
Echocardiogram.
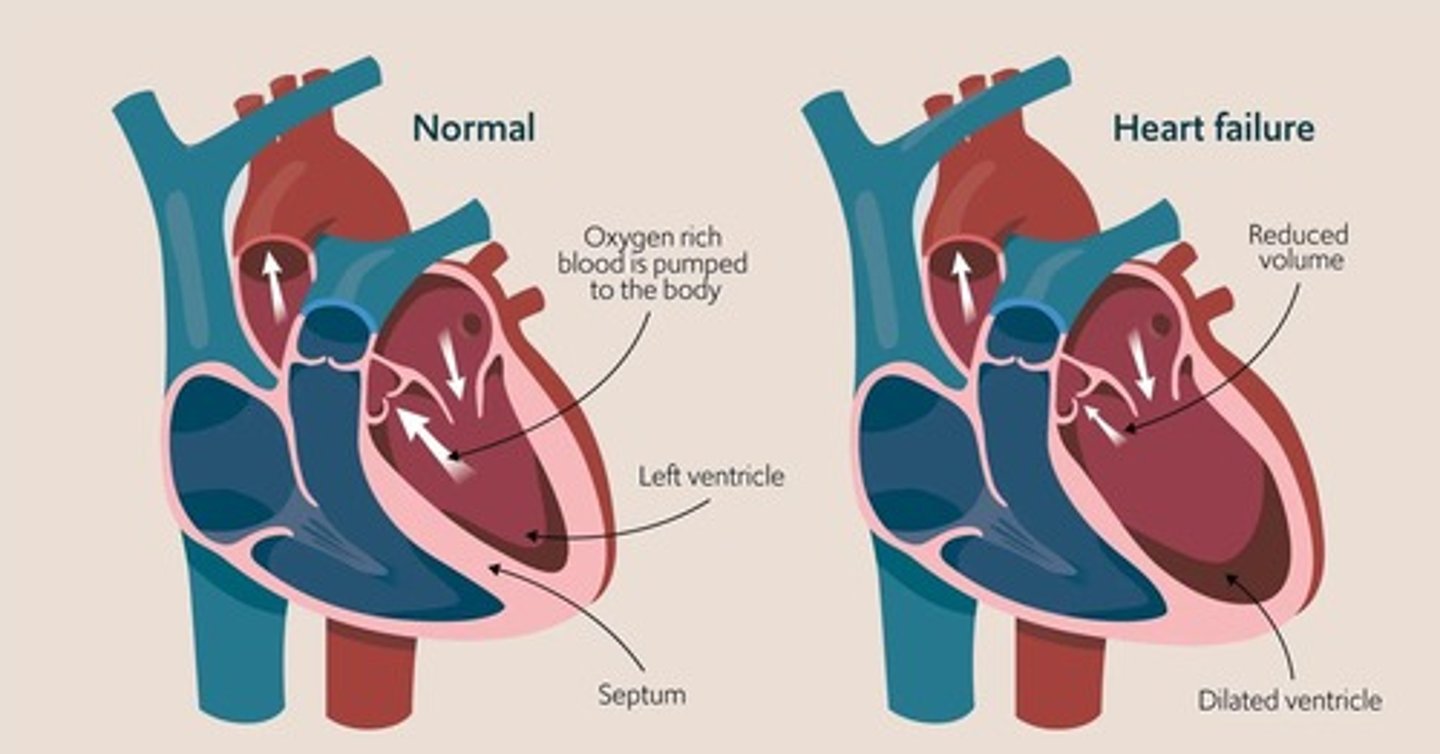
What is the EF% threshold for severely reduced Ejection Fraction?
<45-50%.
What does CPET stand for and how is it used in Chronic Heart Failure?
Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing; it quantifies heart dysfunction and assesses mortality risk.

What is considered chronotropic incompetence in Chronic Heart Failure?
Heart rate much lower than <62% of age-predicted maximum heart rate (APHRM).
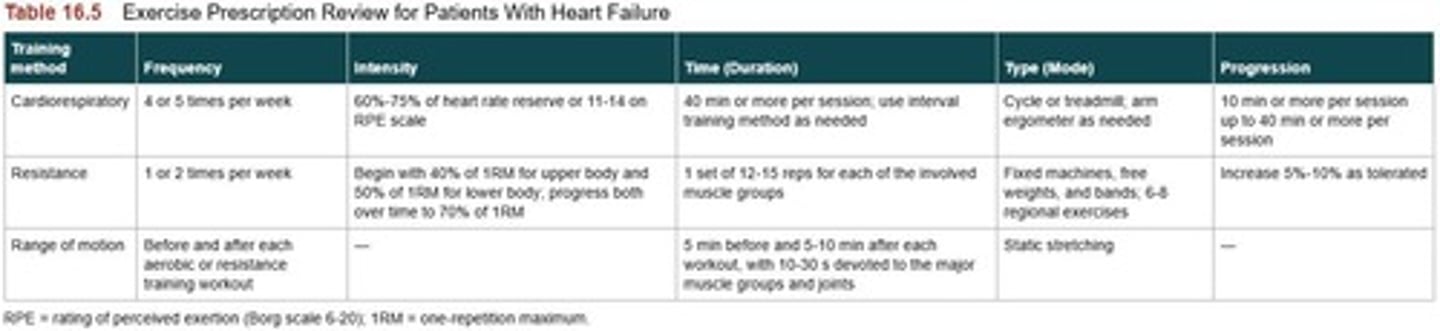
What is a treatment approach for HFpEF?
Regular exercise training can lessen symptoms and improve quality of life.
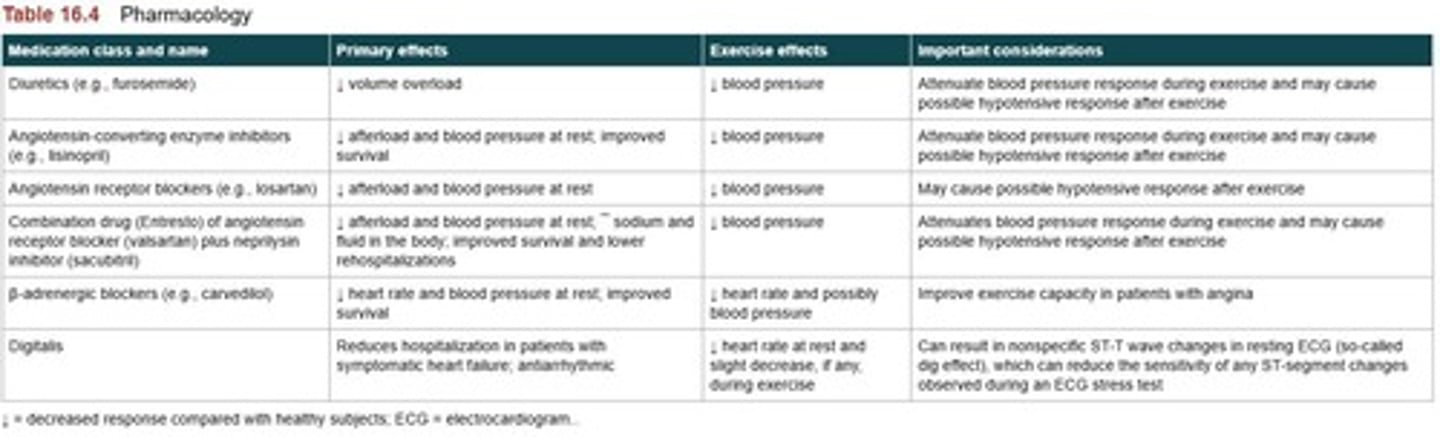
What is the role of medication in treating HFrEF?
Medication is key to help those with HFrEF.
What happens to exercise capacity in patients with Chronic Heart Failure?
Decreased peak power, exercise capacity (30-35%), and cardiac power.
What is the impact of exercise on heart rate and stroke volume in Chronic Heart Failure patients?
Lower stroke volume and heart rate.
What is the significance of peak VO2 in assessing mortality risk?
Peak VO2 <10-12ml/kg/min or <50% predicted increases 1-year mortality.
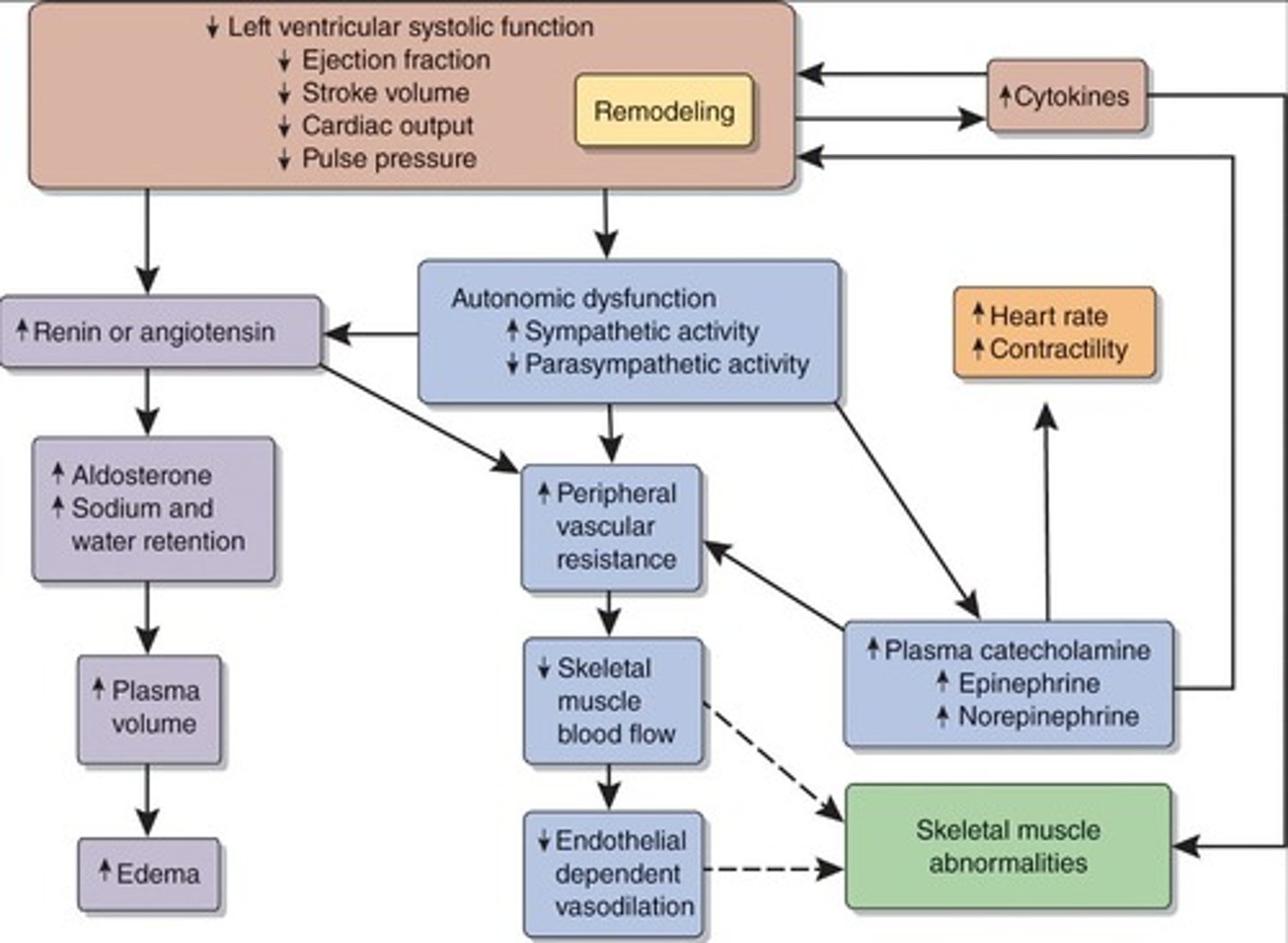
What is the relationship between norepinephrine levels and Chronic Heart Failure?
Higher norepinephrine levels are associated with worse outcomes.
What is a key consideration for exercise prescription in Chronic Heart Failure patients?
Compliance is key and must consider the stage of heart failure or if they've had a transplant.