Chapter 2: condensed and line-bond structures
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
chemical formula
composition of a compound
degree of unsaturation for organic compounds
number of double bonds or rings
dbe
degree of unsaturation
what is the formula for dbe
2(# of C) +2 -(# of H) +(# of N) -(# Hal) / 2
what is the formula for dbe #2
(# of C) +1 - ½ (# of H + # of Hal - # of N)
structural formula
shows connectivity
where can rotation happen?
around single bonds
what is line structure
zigzag format
each end represents a C atom
number of H atoms is understood
line-bond structures and formal charges
we can assume that atoms in a line bond structure have full octets
what do formal charges or lone pairs indicate?
they indicate a modification in the number of bonds compared to “normal”
what is an organic compound?
compound that always has carbon and hydrogen
may contain heteroatoms
what is methane
simplest hydrocarbon
what is methanol
simplest alcohol
what is a functional group
a special group of atoms bonded in a specific way that identifies the class or type of organic compound
what do functional determine
physical behavior like melting point, solubility and chemical reactivity
hydrocarbons
contain only C or H
alkane
c-c single bonds only
alkene
at least one C-C double bond
alkyne
at least one C-C triple bond
aromatic
contains phenyl ring, has double bonds
saturated
maximum number of bonds to other atoms
unsaturated
one or more multiple bonds
alcohol
-OH is attached to a C with only single bonds

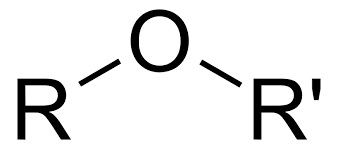
ether
O between 2 carbon groups
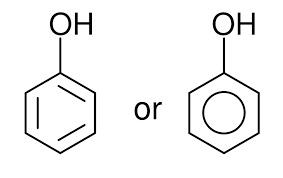
phenol
-OH attached to phenyl ring
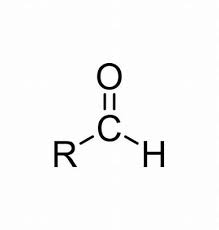
aldehyde
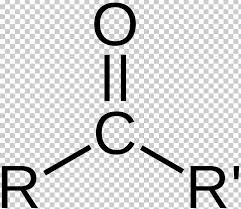
ketone
carboxylic acid
-COOH
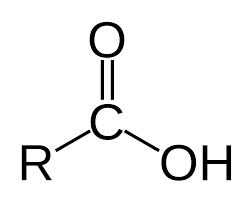
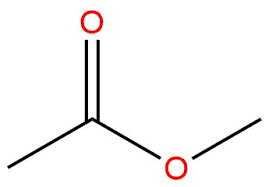
ester
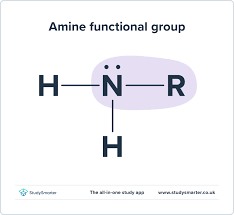
amine
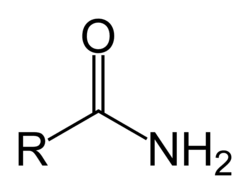
amide
structural isomers
same molecular formula
different structures and different connectivity of atoms