Roman arts images
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
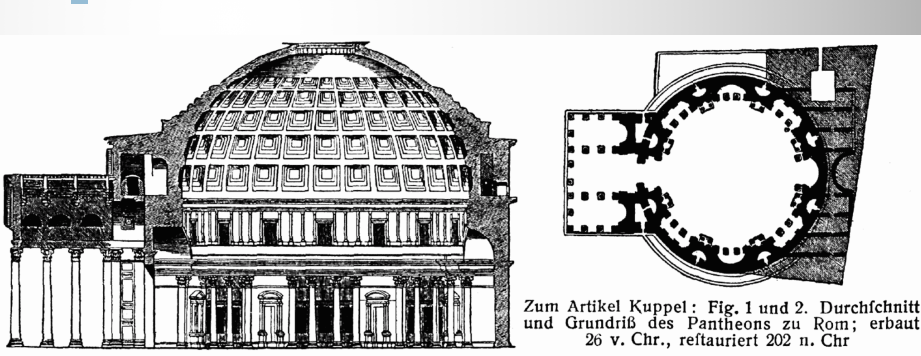
Pantheon
a Roman temple dedicated to all gods, showcasing impressive architecture and a large dome.
3 elements:
Porch
Intermediate block
Rotunda
Inscription: Marcus Agrippa, the son of Lucius, three times consul, built this
Rotunda supported by an excellent concrete drum
Appears to be a solid circular wall, but is structurally far more complex
Eight compound piers that alternate with seven niches and the entrance create a rhythm along the interior
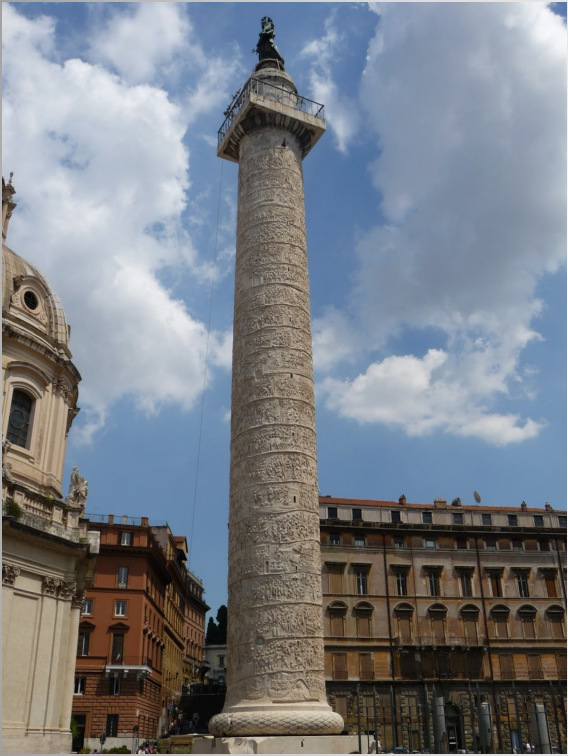

Column of Trajan
Victory column
Serves three purposes
Height records the depth of the excavation needed to create enough level space for building the forum complex
Serves as a triumphal monument for the Dacian campaign
Serves as a tomb for Trajan and Plotina– cremated remains were placed in golden urns in a chamber at the base of the column (not the original intention)
The top originally had a bronze statue of Trajan, replaced with St. Peter
100 Roman feet tall
Decorated with a visual record of Trajan’s Dacian campaigns
23 spiral bands of c. 1 m in height each
2650 human figures, 155 separate scenes narrating key events in the Dacian war
Largest continuous narrative sculpture in Rome
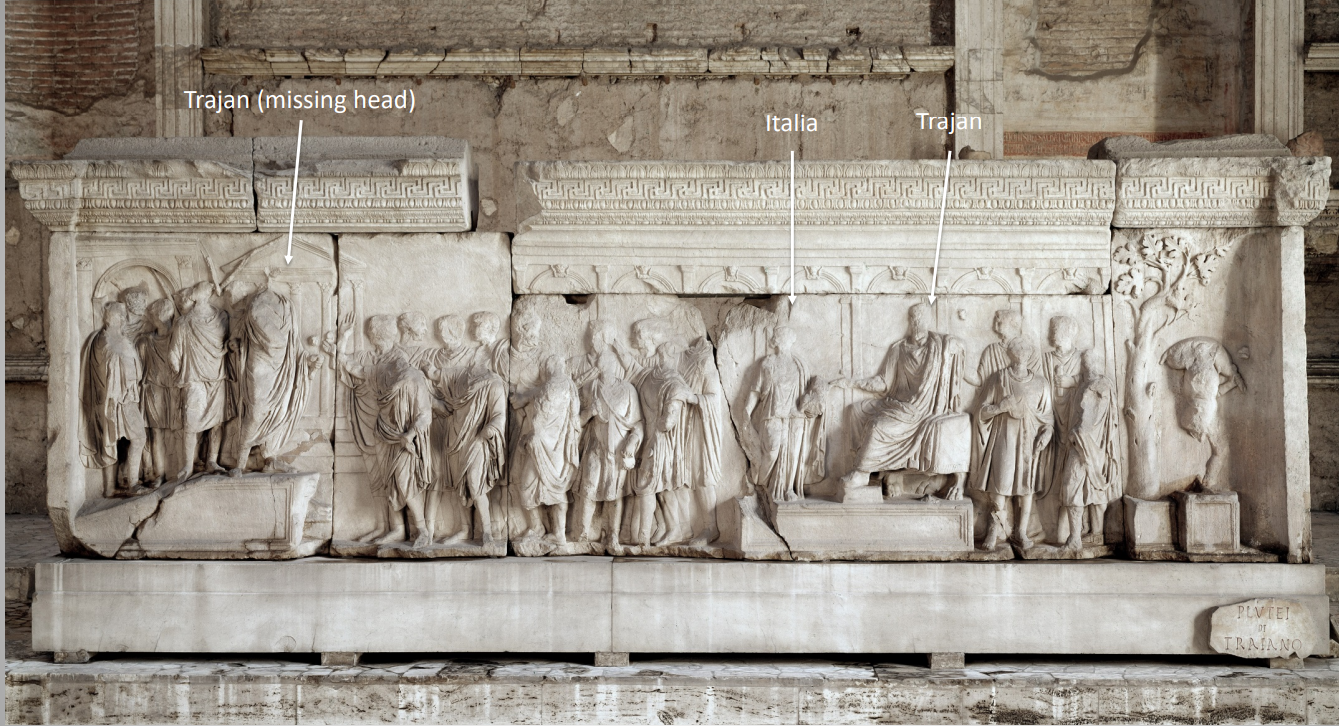

Anaglypha Traiani
“Sculptural Reliefs of Trajan”
Marble reliefs carved on both sides (unusual)
Each has a suovetaurilia on the reverse and a different historical relief on the front
Both are set in the Forum Romanum
Classicizing Roman historical relief with figures conforming to Classical proportions

Relief of Antinous
a sculptural representation commemorating the youth and beauty of Antinous, often associated with Hadrian.
Met Hadrian at some point in the 120s.
By 128, he was Hadrian’s favourite
Probably only 16/17 years old at the time; Hadrian was 52
Antinous travelled with Hadrian wherever he went
Italy, Greece, North Africa, Asia Minor, Syria, Egypt, Libya
Hadrian saw him as intelligent, they shared a love of hunting, etc.
Deified by Hadrian after his death
Over 100 statues of Antinous were found all over the Empire
made out of marble
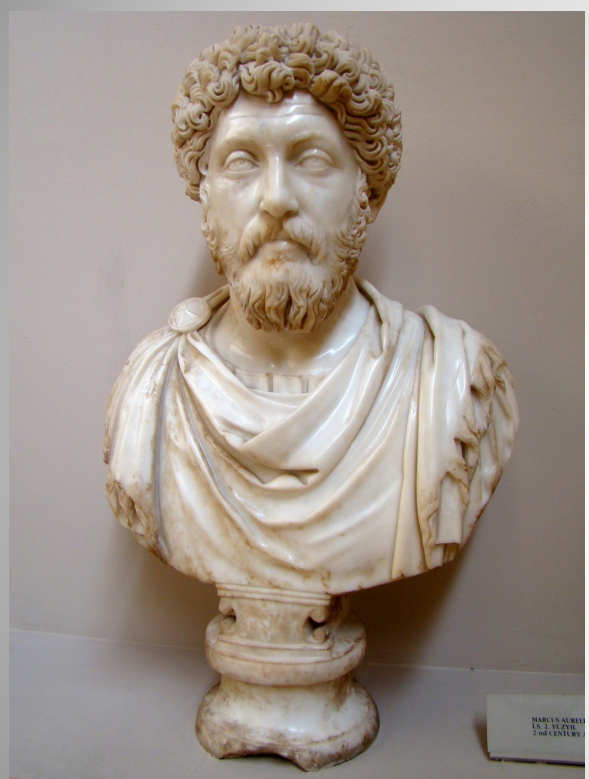

Bust of Marcus Aurelius
Key characteristics:
Long face
Hooded eyes and bags under his eyes
Wrinkled forehead
Distant gaze
Note the individually carved locks of hair, with hollow cores made by a drill
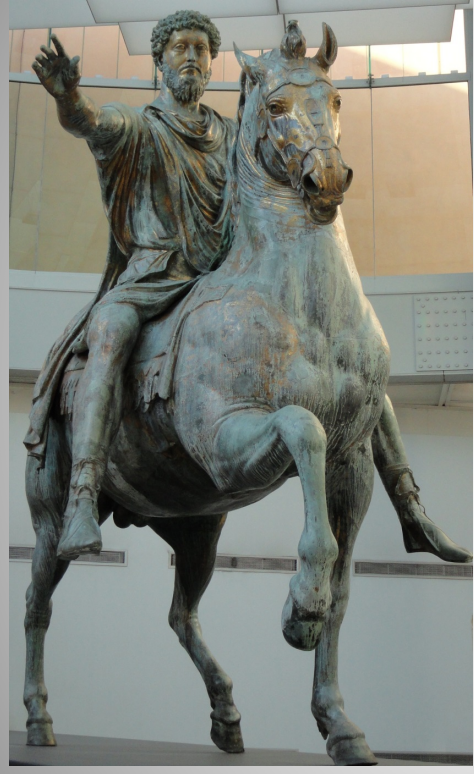

Equestrian statue of Marcus Aurelius
Best-preserved example of a bronze equestrian statue
Survives because in the Middle Ages, it was thought to be Constantine
Wearing civilian dress
His right hand is outstretched as a gesture of clemency
Probably part of a group with a fallen or kneeling German warrior or commander in front of the horse
Or, perhaps, representing his achievements and personal attributes more generally
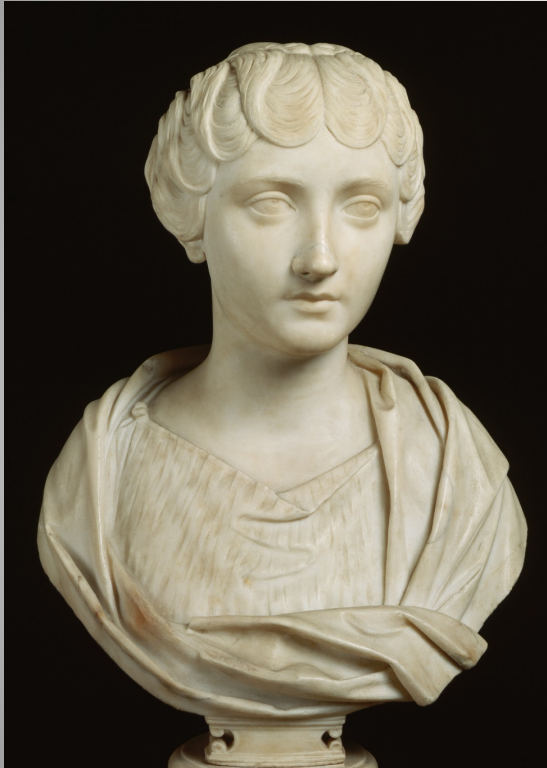

Bust of Faustina the Younger
Wife of Marcus Aurelius
Daughter of Antoninus Pius
Portraits age as she does
This portrait from the earliest period, at age 17
Named Augusta after she gave birth to the first child (of 13)
Hairstyle similar to Hardian’s wife’s
Reflective of a Greek goddess
made out of marble
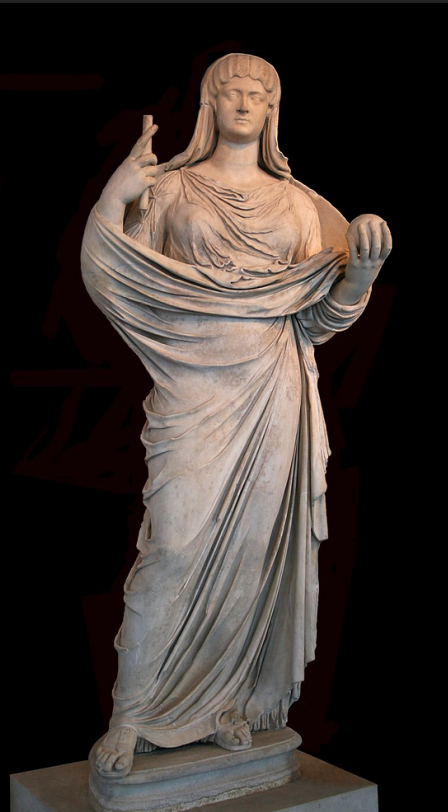

Statue of Faustina the Younger
Last year of her life
Notice her fuller face
Her eyes were more heavily lidded, with bigger bags under her eyes
Pupils more deeply drilled
Body and pose similar to that used of imperial women since the type of Augustus
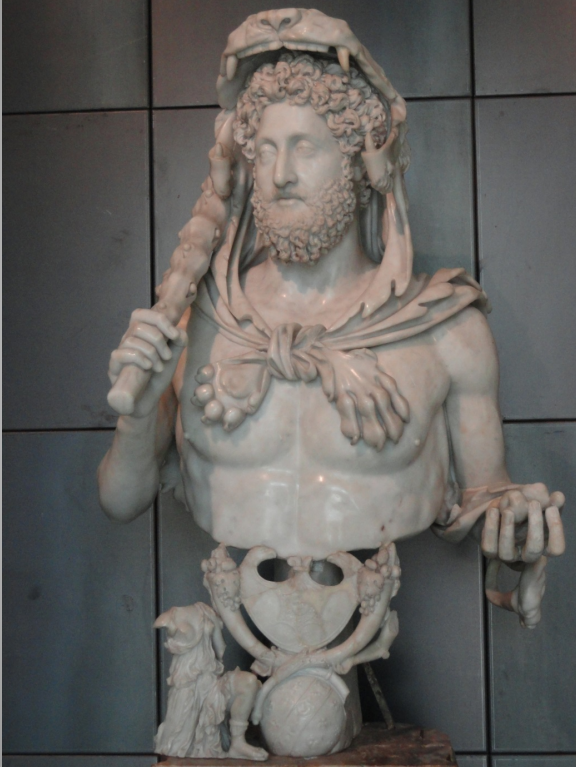

Bust of Commodus
Wears the lion skin and carries the club of Hercules, holding the Golden Apples of the Hesperides
Representing the Labour of Hercules that brought the promise of eternal life for all who believe in him as a saviour figure
Support features the globe, cornucopia, and a kneeling Amazonian figure
Commodus reinforced his position as the son of a god (like Hercules) by dressing as Hercules in staged animal hunts
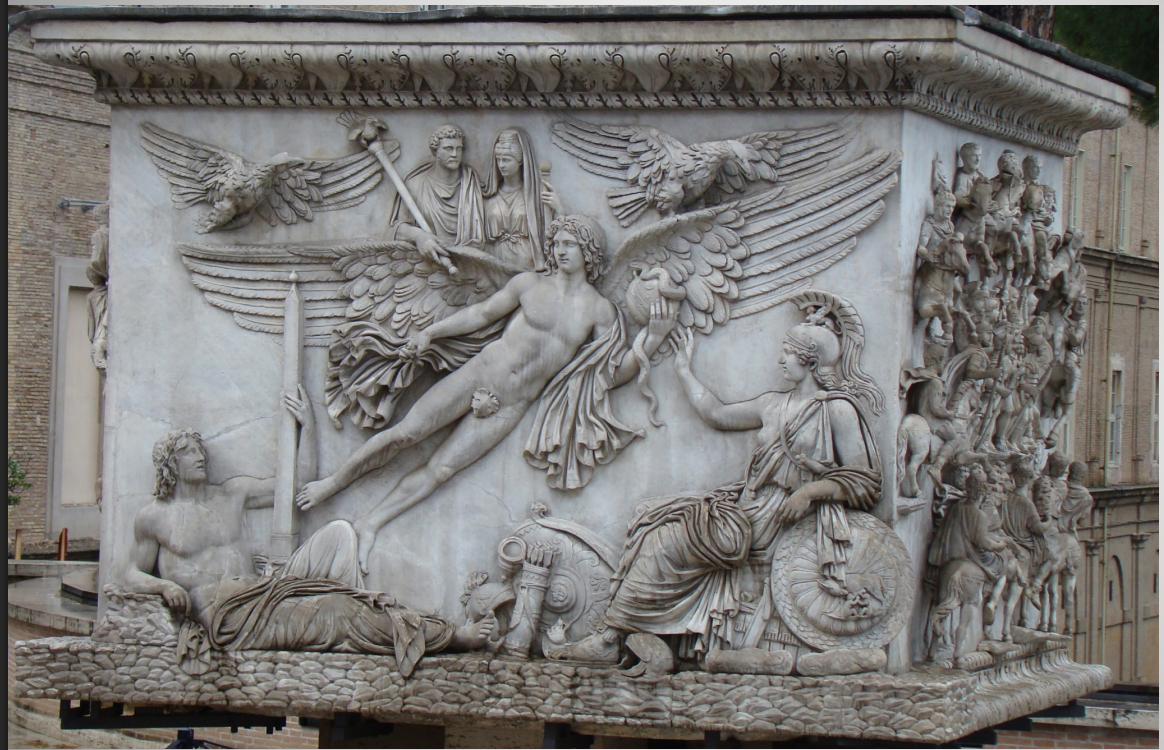

Column of Antoninus Pius
Erected by Marcus Aurelius and Lucius Verus
The column itself was not carved, but the base was elaborately decorated with three reliefs and a dedicatory panel
Celebrating the deification of Antoninus Pius
Military units riding in a spectacle known as a decursio
May be part of the funerary ceremonies
Cavalry encircles a group of 10 soldiers
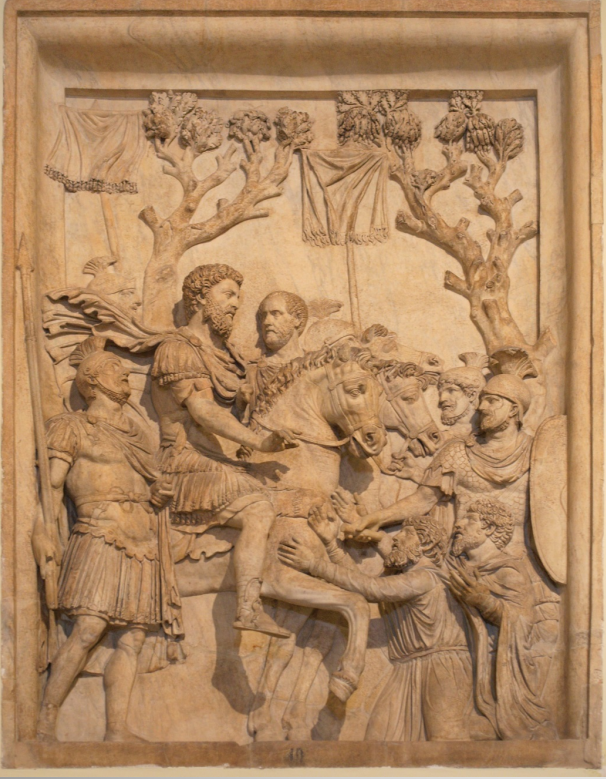

Clemency and Triumph panels, Arch of Marcus Aurelius
Perhaps comes from an arch (or two)
Show the achievements and personal qualities of Marcus Aurelius in traditional ways
Justice, clemency, martial prowess, piety
The clemency panel has a similar style to Trajan’s Column
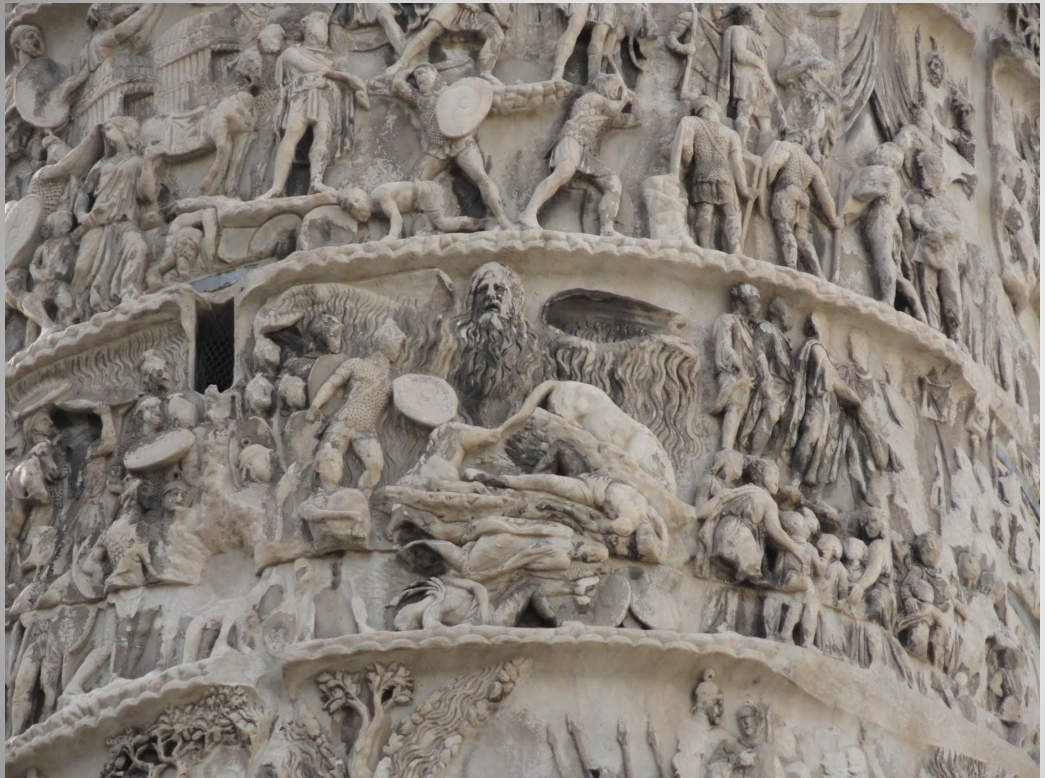

Storm god scene, Column of Marcus Aurelius
Reliance on spiritual intervention to help them win
Compare this with the way Roman soldiers are depicted subduing the Danube on Trajan’s Column
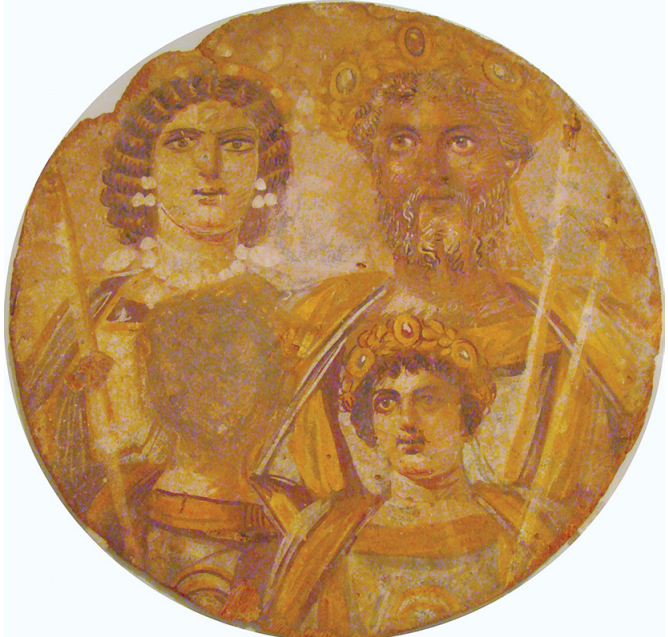

Portrait of Septimius Severus, his wife, Julia Domna, and sons
Combination of Egyptian, Greek, and Roman traditions
Two types of paint, wax-based encaustic and egg-based tempera
Encaustic makes more realistic portraits because it is translucent and takes longer to dry
Greek Classical artistic styles
Red, white, black, and yellow are used in various combinations
Naturalistic portraiture, single light source, asymmetrical compositions (one side turned slightly)
Frontal figures, oversized eyes gazing into the distance
Distinguished as imperial by their diadems, gold-bordered tunics, cloaks, sceptres, and Julia Domna’s pearl necklace and earrings
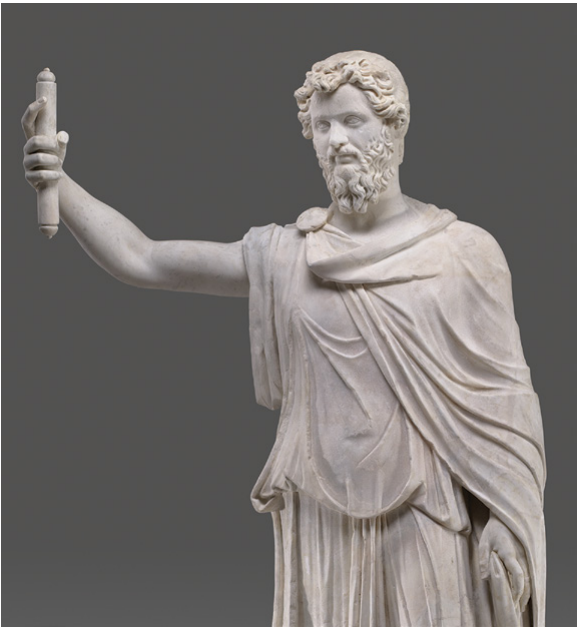

Portrait of Septimius Severus
Portraits initially follow the style of Marcus Aurelius
But, later portraits display features of the Egyptian god, Serapis
Note the parted beard and the four corkscrew locks of hair on his forehead
Antonine-inspired portraiture based on that of Antoninus Pius and, most strongly, Marcus Aurelius.
Classicism
made out of marble
Elements of Aurelius’ portraiture are seen in the curly hair and short, parted beard affected by Septimius
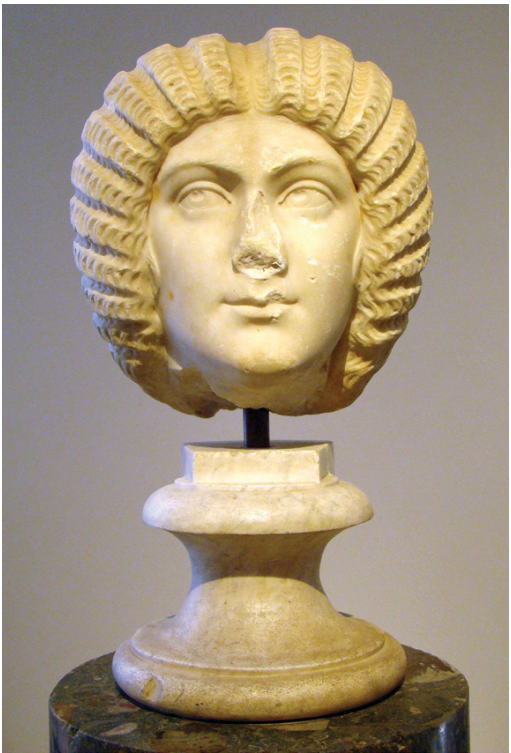

Portrait of Julia Domna
Dating to the beginning of Septimius Severus’s reign
Based on the portraits of Faustina the Younger (wife of Marcus Aurelius)
Widely spaced eyes, long nose, connecting brows, curving mouth with soft folds of skin at the corners
Centre-parted helmet-style hair with a large bun at the base of her neck
She is recognizable from her distinctive facial features, but with major differences in her hairstyle.
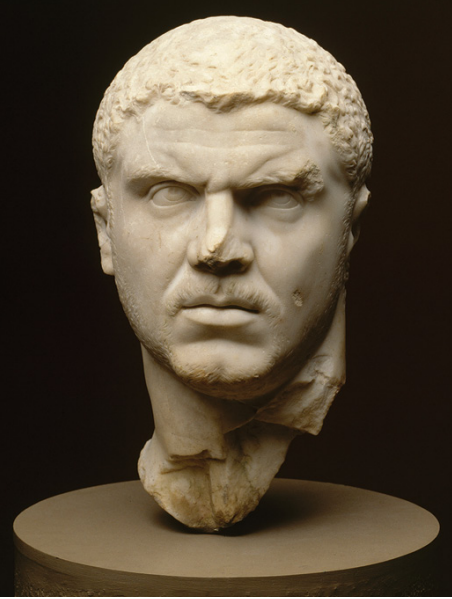

Portrait of Caracalla
Dramatic shift in portrait style
Hair and beards reduced
Focus instead on the elasticity of the skin
Deep lines, chiselled wrinkles, whiskers
Twisted necks, apparent internal conflict, concerned looks
Compared with the distant look of the Antonines
demonstrate a rejection of the Antonine traditions and point the way to the portrait style of the remainder of the third century ce
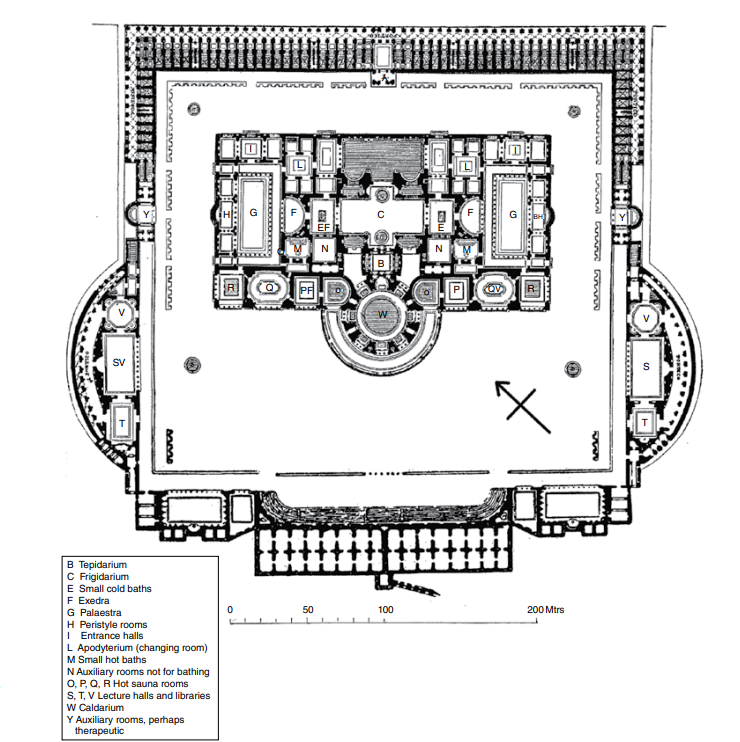
Baths of Caracalla
The bathing block was a spectacular building, huge in scale and lavishly covered with marble floors and wall panels
Brick-faced concrete with complex roofing systems including domes, half domes, cross vaults, barrel vaults

Farnese Hercules
Shows Hercules with the Golden Apples of Hesperides
Similar in scale to the Farnese Bull
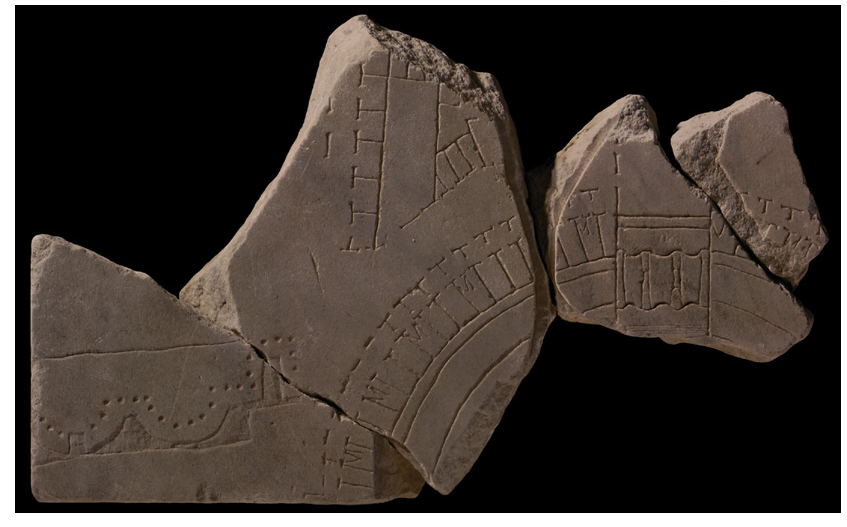

Forma Urbis Romae
It was a large map of ancient Rome, created in the early third century AD,
that displayed the city's streets, buildings, and layouts in intricate detail,
providing valuable insights into urban planning and architecture during that period.
Also known as the Severan Marble Plan
Birthplace of Septimius Severus
Serves to legitimize his rule
How Romans viewed their city like a map/plan
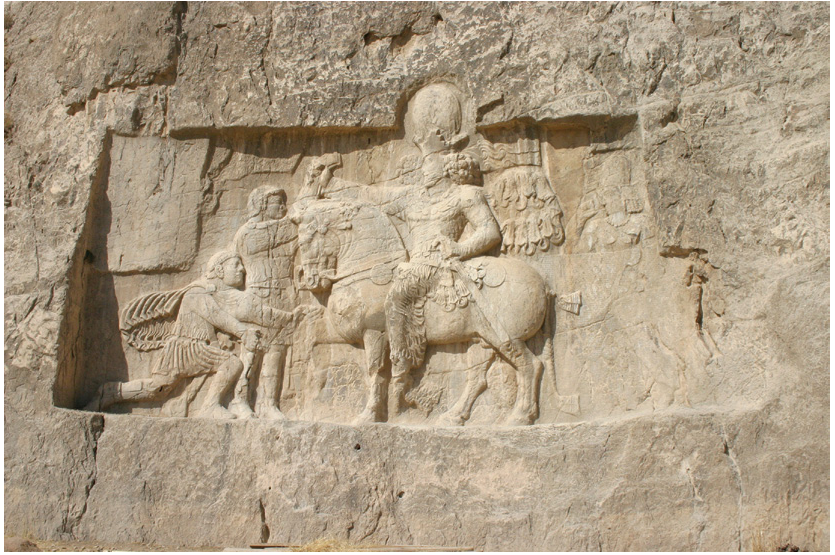

Relief of Emperor Valerian kneeling before Shapur I
253-260
Proclaimed emperor by troops and the Senate
Great upheaval throughout the reign
Invasions by outside groups
Spent most of his time fighting the Persians along the border
Captured by the Persian Emperor Shapur I during a campaign in the east against Persian incursions
First and only emperor to be captured and die in captivity abroad
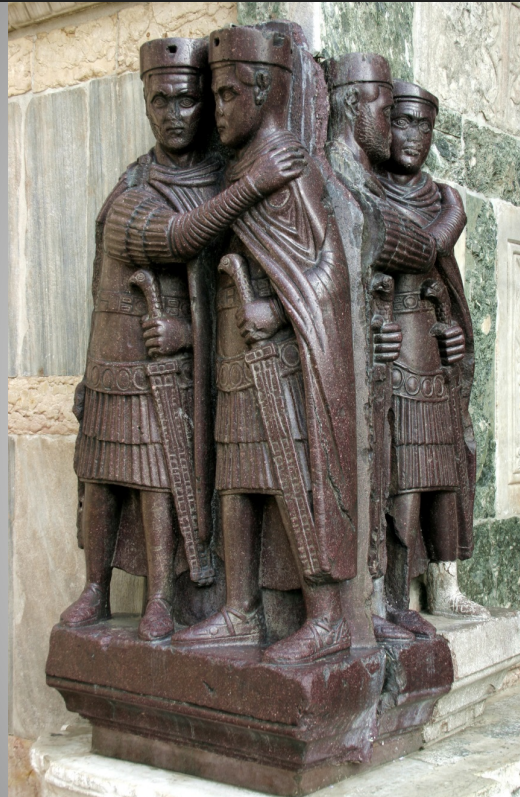

Tetrarchs statue group
Carved in porphyry
Purple is the colour of emperors
Shows the political organization of the tetrarchy
Paired figures in collegial embrace, one Augustus (senior) and one Caesar (junior)
Each senior emperor is bearded while his junior emperor is clean-shaven.
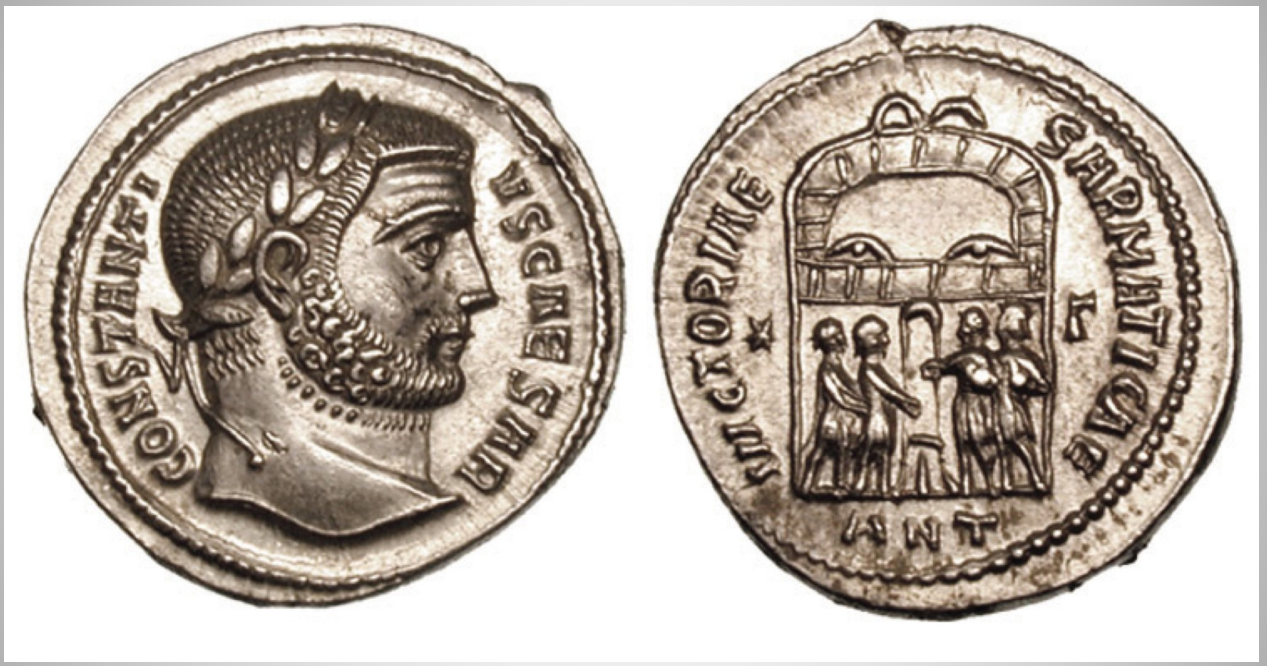

Constantius Caesar, Laureate bust right
creating imagery that celebrated each member of the four in the context of the entire group.
The enclosure has four turrets, symbolizing the Tetrarchs and their military association.
The obverse shows the standard profile portrait of the bearded Caesar or junior emperor, wearing a laurel wreath with his name and title, Constantius Caesar.
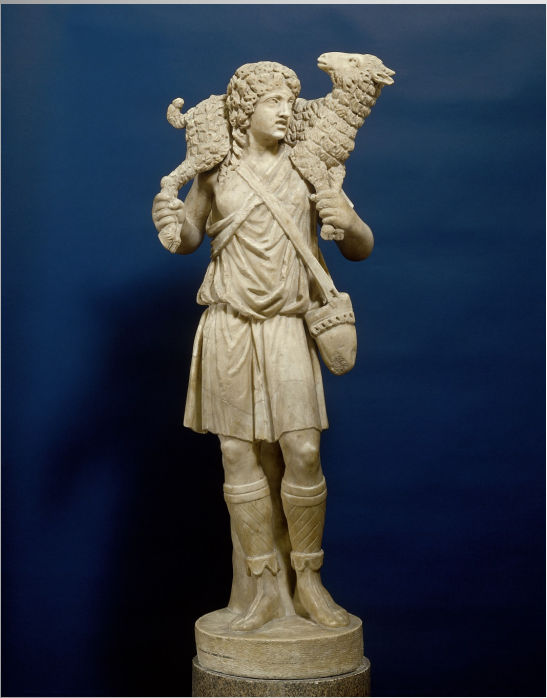

Good Shepherd statue
The pose of the shepherd with a lamb across his shoulders is seen as far back as the Greek Archaic period (6th c. BCE)
Idealized, youthful, clean-shaven
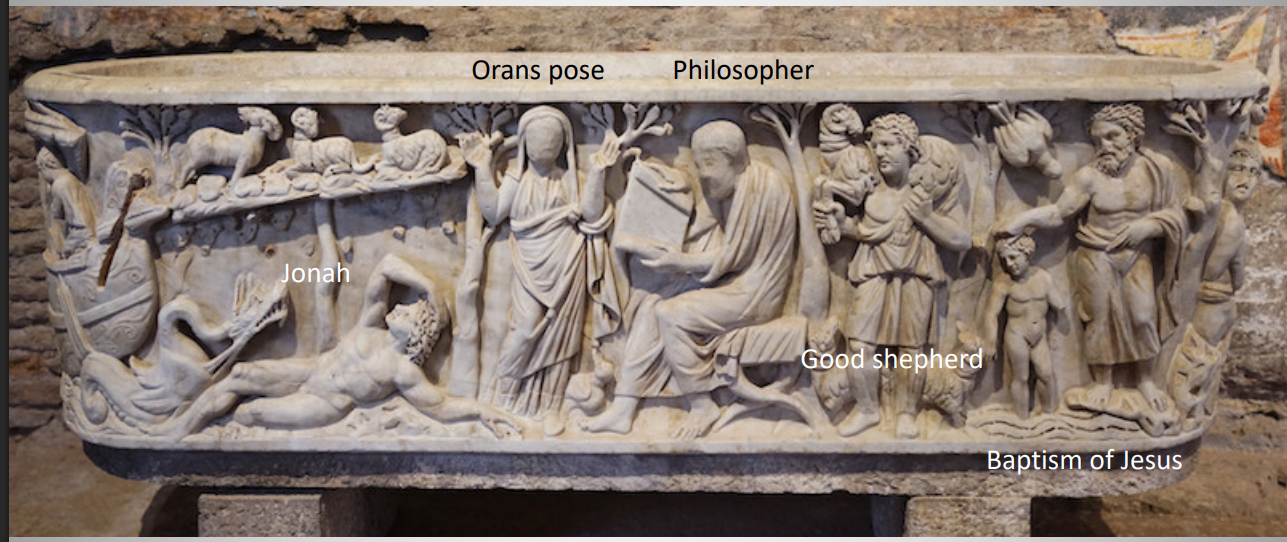

Sarcophagus with the Good Shepherd
depicts scenes from the life of Christ, often including motifs of resurrection and salvation.
made out of marble
The Good Shepherd symbolically represents Jesus Christ as a caretaker and protector of his followers, illustrating themes of faith and guidance.
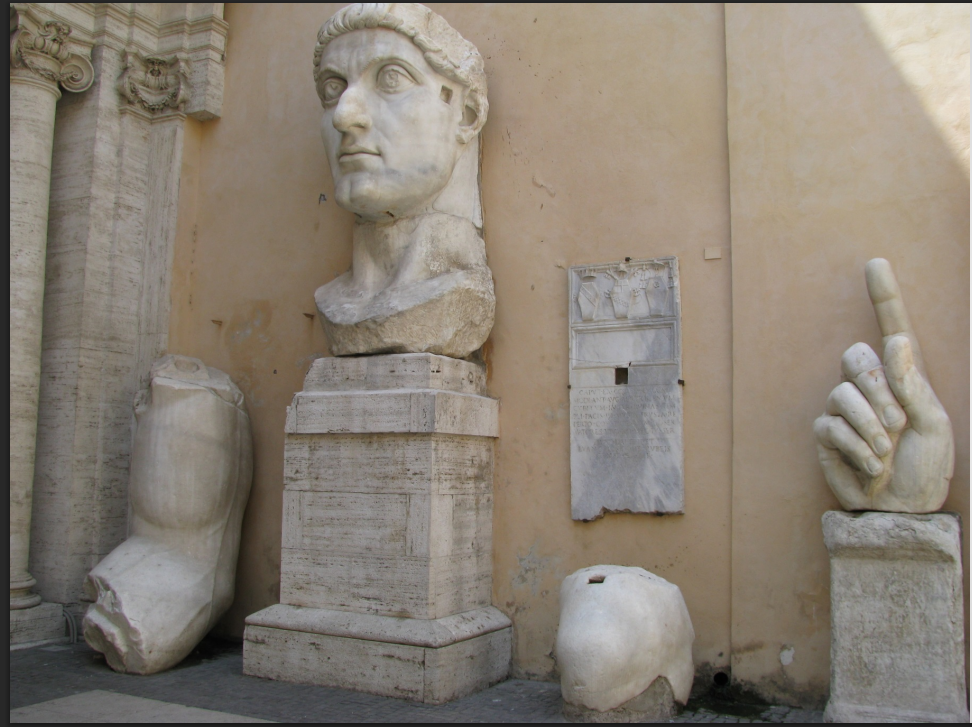

Colossal portrait of Constantine the Great
Originally an acrolithic seated image of the emperor
The body is constructed of a wooden framework covered with drapery
Only the exposed limbs are carved in stone
representing his status and divine authority. It emphasizes the grandeur and power associated with his reign.
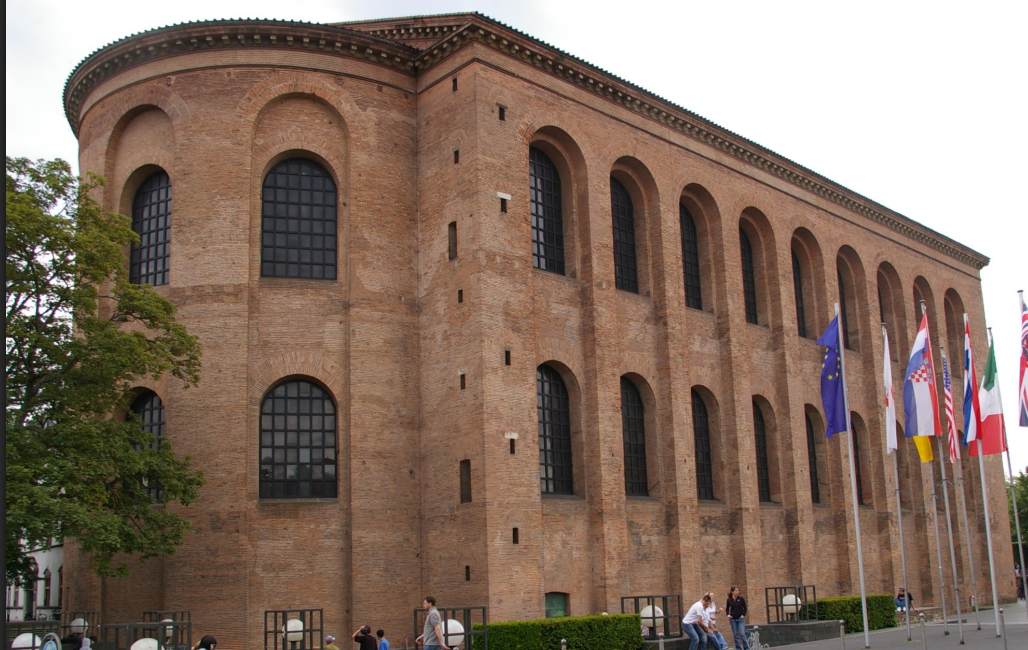

Basilica at Trier
Plain brick with two superimposed stories of windows that terminate in semi-circular tops, giving the appearance of a two-story structure
Recessed windows cause the intervening buttresses to appear to project more than they do
Emphasizes the vertical lines and, therefore, the height of the building
Largest surviving room from the Roman period
The semi-circular apse served to frame the seated emperor as he received his audience
Apse originally covered in mosaics
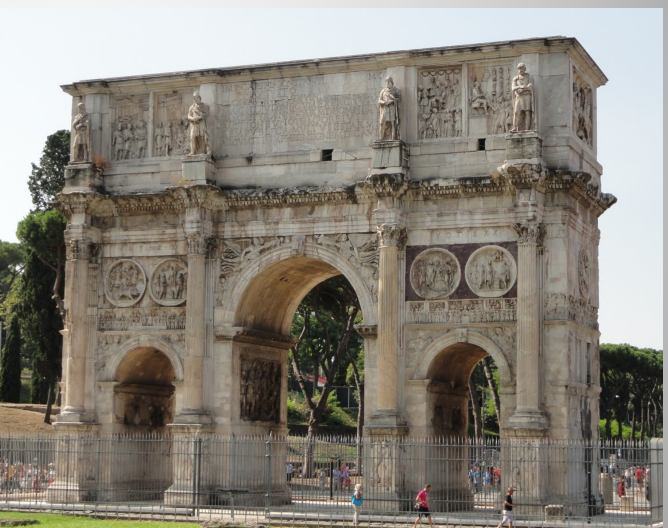

Arch of Constantine
Triple passage arch with tall central passage flanked by two smaller ones
Like the Arch of Septimius Severus
A large amount of sculptural relief decoration is reused material
Spolia
Stock poses for a ruler
Speeches, sacrifice, battles, mercy, hunting.
Facial features recut to look like Constantine
Battle of Milvian Bridge
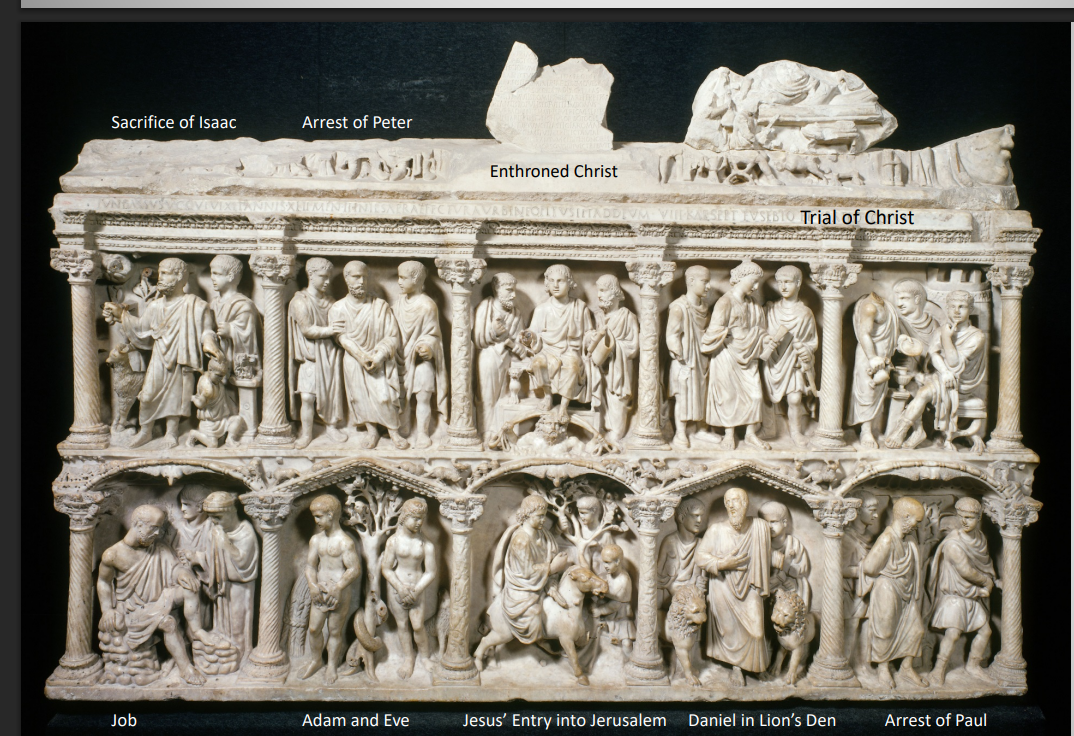

Sarcophagus of Junius Bassus
Not narrative, but thematic
Composition traditionally Roman
The artistic style is very classicizing
Alternating semi-circular and triangular pediments are Asian
Notice that Christ is youthful and unbearded