PSY3103 week 6 observational learning
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is the behaviour of observational learning?
-the behaviour of a model is witnessed by an observer, and the observer’s behaviour is subsequently altered
-observational learning is often referred to as social learning
What is contagious behaviour?
a more-or-less instinctive or reflexive behaviour triggered by the occurrence of the same behaviour in another individual
What is stimulus enhancement?
the probability of a behaviour is changed because an individual’s attention is drawn to a particular item or location by the behaviour of another individual
What is vicarious emotional conditioning?
is classical conditioning of emotional responses that result from seeing those emotional responses exhibited by others
Is fear in others a US or a CS?
-in fear conditioning, the look of fear in others may function as either a US or a CS
-it is also possible that both processes are involved, and they may even combine to produce a stronger fear reaction
What are the 2 elements of observational learning in operant conditioning?
Two elements: acquisition + performance
-acquisition through observational learning first requires that the observer pay attention to the behaviour of the model
How does observational learning translate into behaviour?
translates into behaviour via the processes of reinforcement and punishment
How do operant consequences modify behaviour?
1. Vicarious reinforcement/punishment
2. Observer’s consequences when performing modelled behaviour
3. History of reinforcement
What is true imitation?
form of observational learning that involves the close duplication of a novel behaviour
Can animals imitate?
-simple stimulus enhancement can result in a duplication of behaviour that looks a lot like imitation
-some researchers believe at least some animals are capable of true imitation
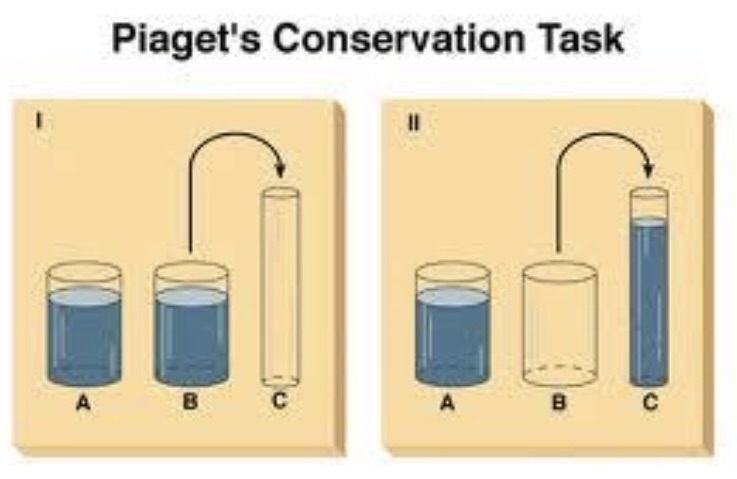
Explain Piaget’s conservation task and cognitive development.
evidence that many cognitive skills can be improved via observational learning
How do drug addictions work with observational learning?
social reinforcement/punishment
What are the 2 main ways parents shape children’s personalities?
1. controlling agents
2. models
What is the connection between children and self-discipline?
-children don’t seem to have strong self-discipline
-children can learn to apply standards of self-discipline via model observation
How does aggression in the home affect children?
-parents who use physical punishment are providing models of aggressive behaviour
• ↑punishment for aggressive behaviour =↑aggression in children
What is a rule?
a verbal description of a contingency
What is an instruction?
how we should respond
Why are rules useful and how does our willingness relate to them?
-rules (or instructions) are extremely useful for rapidly establishing appropriate patterns of behaviour
-ones willingness to follow rules generally may be related to the extent to which they were rewarded in the past for doing so
What are the disadvantages of rule-governed behaviour?
1. rule-governed behaviours are often less efficient than behaviour that has been directly shaped by natural contingencies
2. rule-governed behaviours are sometimes surprisingly insensitive to the actual contingencies of reinforcement
When do say-do correspondences occur?
-occurs when there is a close match between what we say we are going to do and what we actually do at a later time
-parents play a critical role in the development of this correspondence
When are personal rules most effective?
-most effective when they establish very clear boundaries between acceptable and unacceptable behavior
-personal process rules that specify when, where, and how a goal is to be accomplished can significantly affect the probability of accomplishing the goal