Animal body parts & regions Pre work week 2
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Head
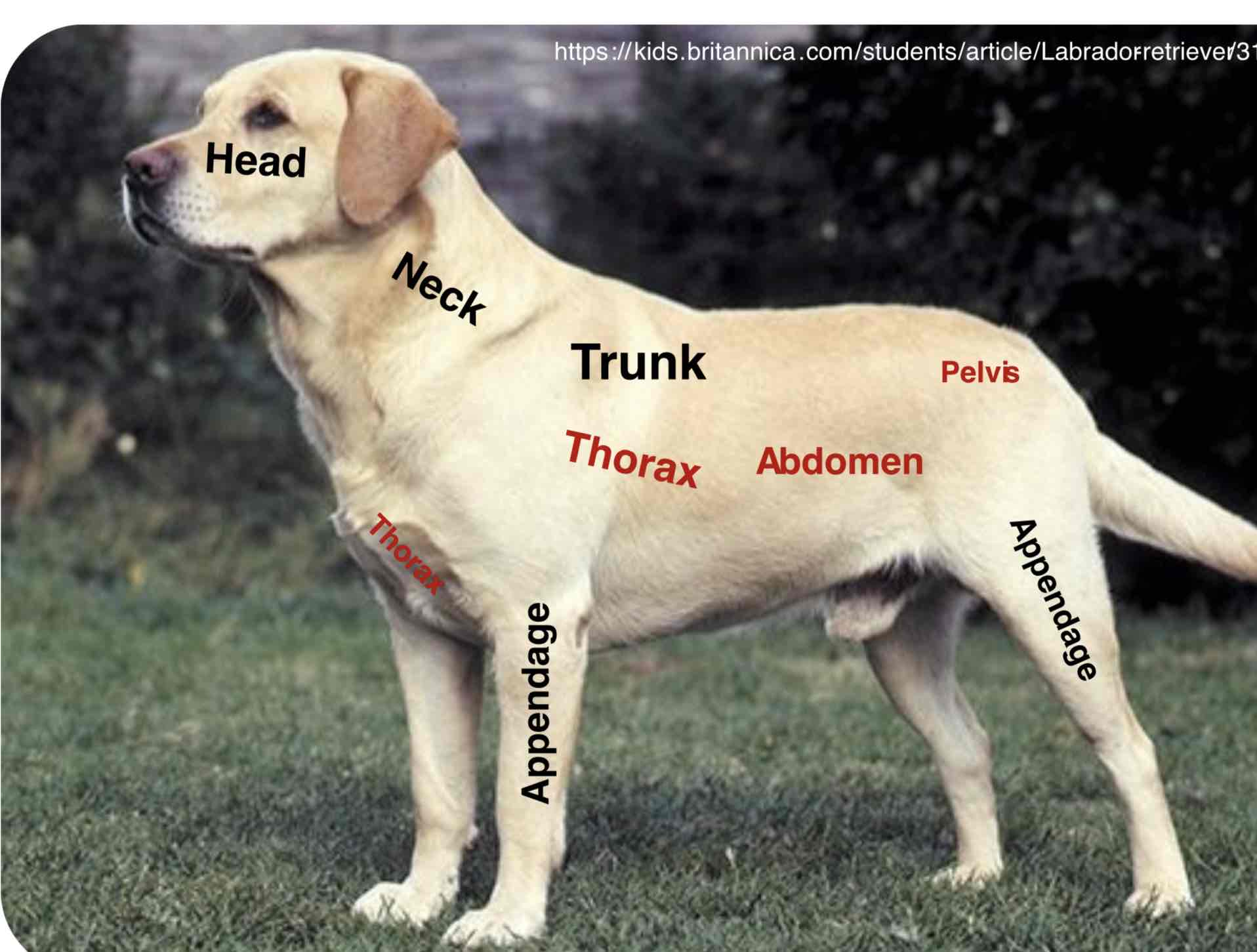
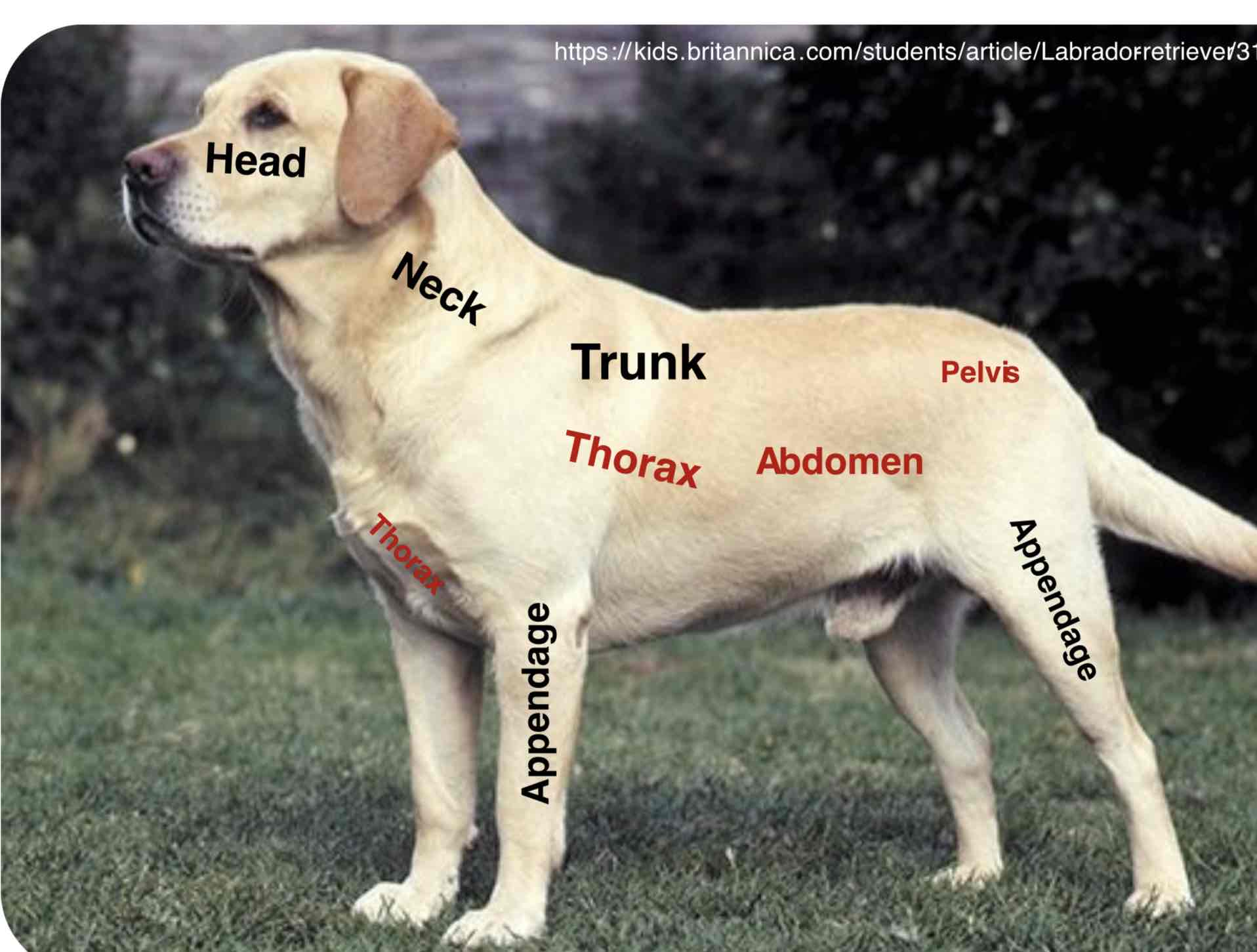
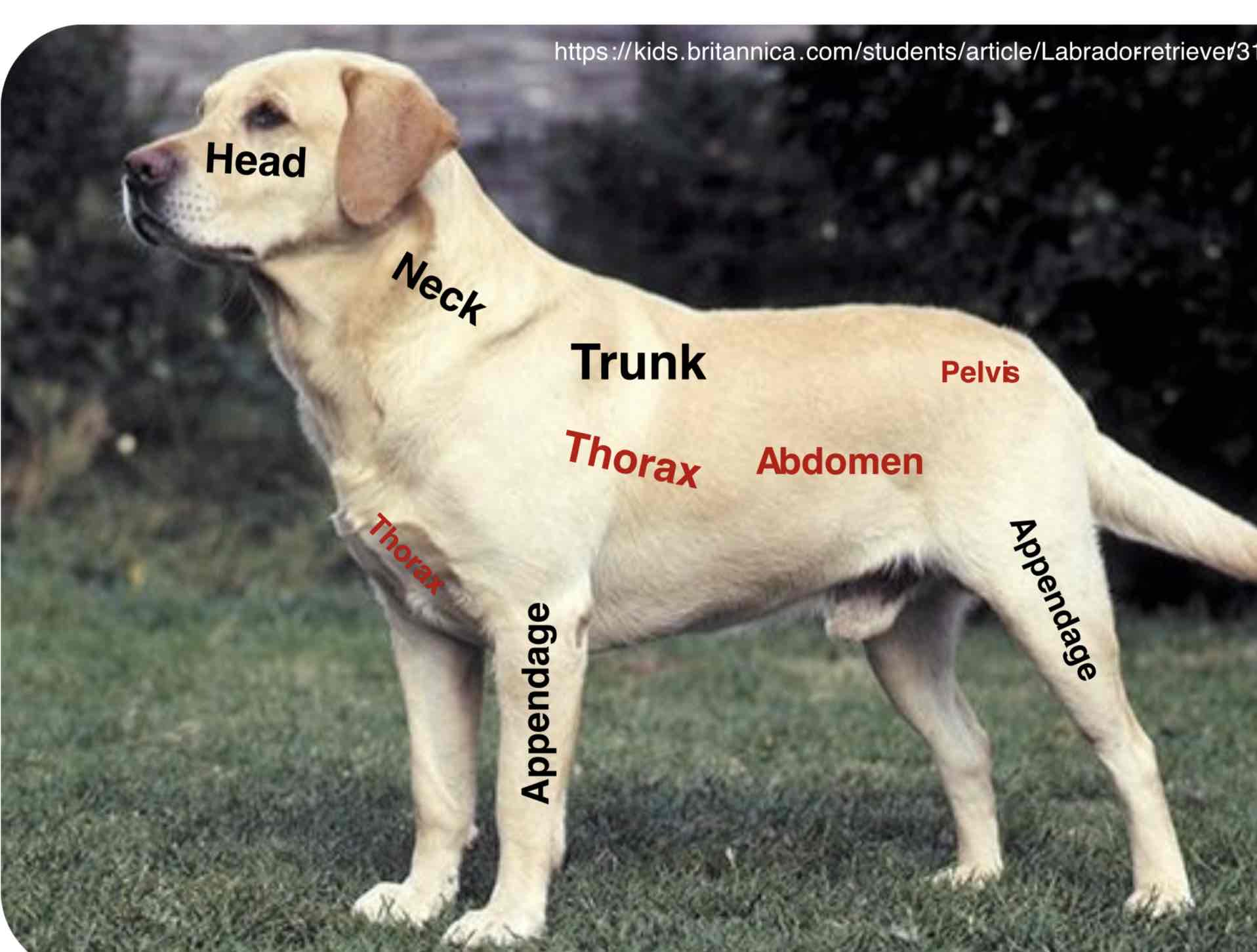
The most forward (Anterior/cranial) Or highest part of a structure or organism. In Vertebrates, It contains the oral and nasal passage, The brain, and the organs of special sense
Neck
The neck is that part of the body connecting the head with the trunk. It contains a trachea, esophagus, blood vessels, spinal cord and cervical vertebrae. The mouse and giraffe have several cervical vertebrae, as most mammals
Trunk
The main part of the body to which the head and limbs are attached ( Torso in humans) The trunk contains the viscera (Organs) Of the different body systems. The trunk is mainly divided into the thorax (Thoracic region) The abdomen ( Abdominal region), And the pelvis( Pelvic region)
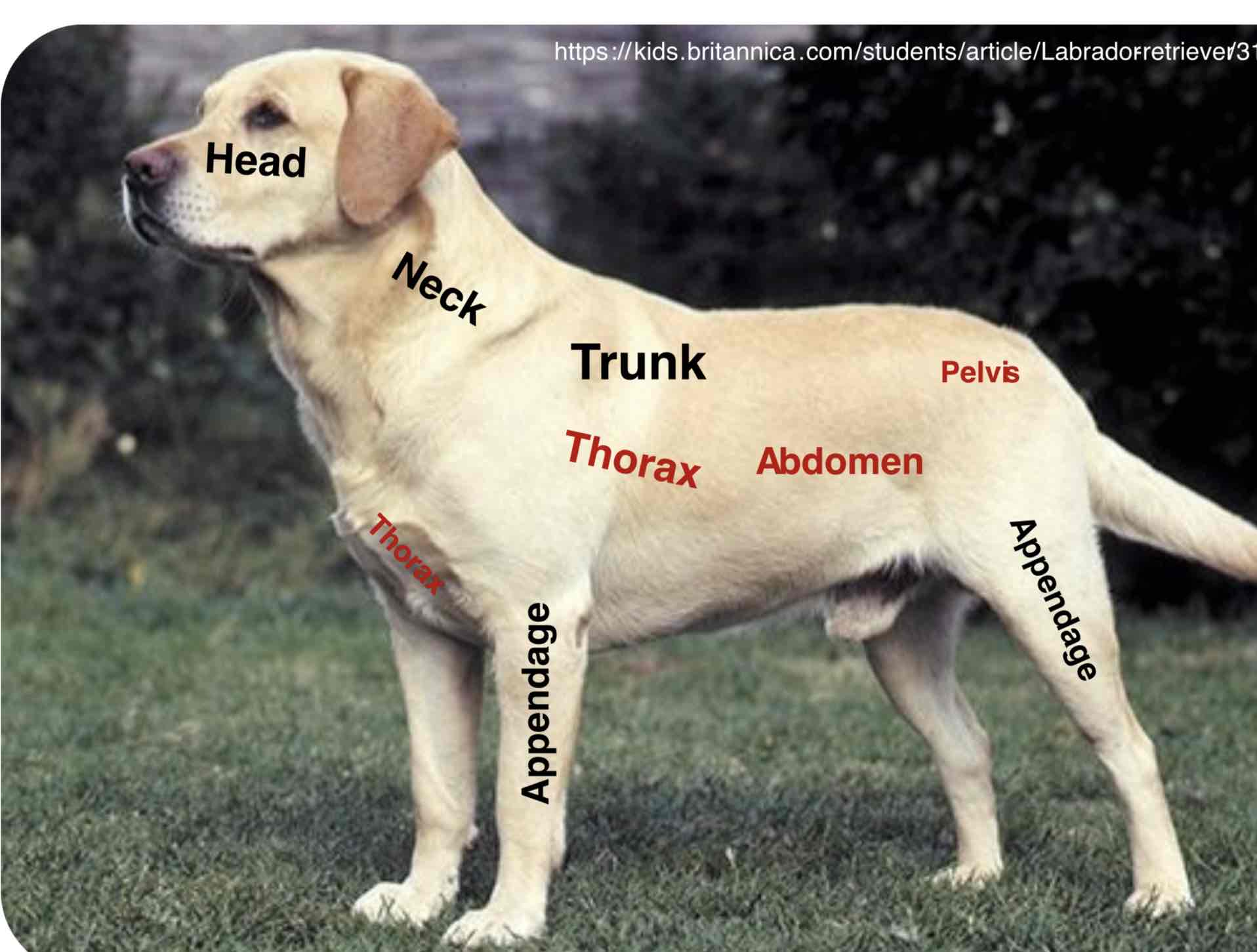
Thorax (Thoracic region)
The part of the body between the neck and abdomen; the chest. Is separated from the abdomen by the diaphragm. The walls of the thorax are formed by pairs of ribs, Attached to the sides of the spine, curving towards the sternum. It contains the thoracic cavity and organs of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems
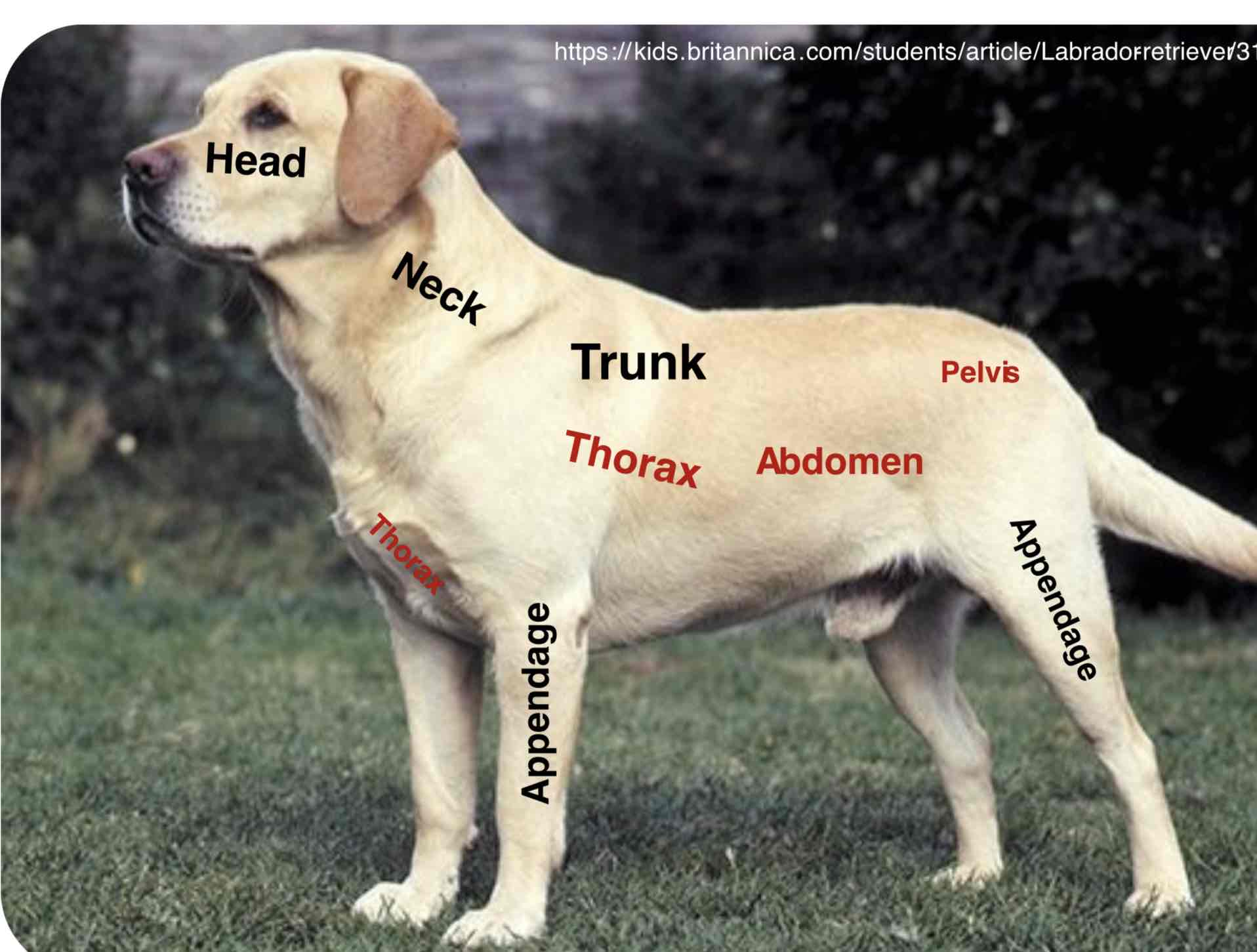
Abdomen (abdominal region)
The portion of the body between the thorax and the pelvis contain the abdominal cavity and organs of the digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems. The wall of the abdomen is mainly formed by muscles.
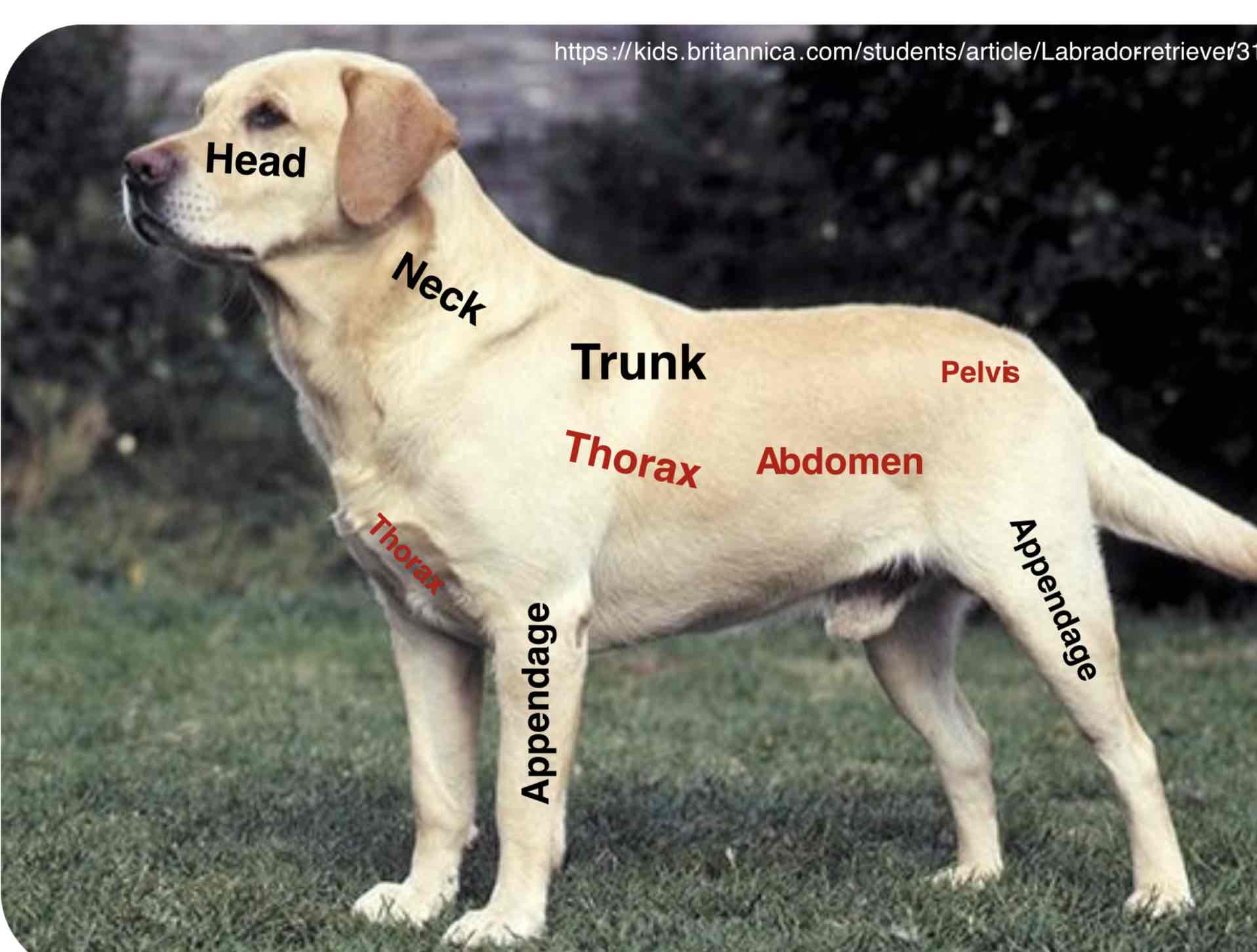
Pelvis (pelvic region)
The caudal portion of the trunk of the body forming a basin. It mainly contains the pelvic cavity and organs of the digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems.
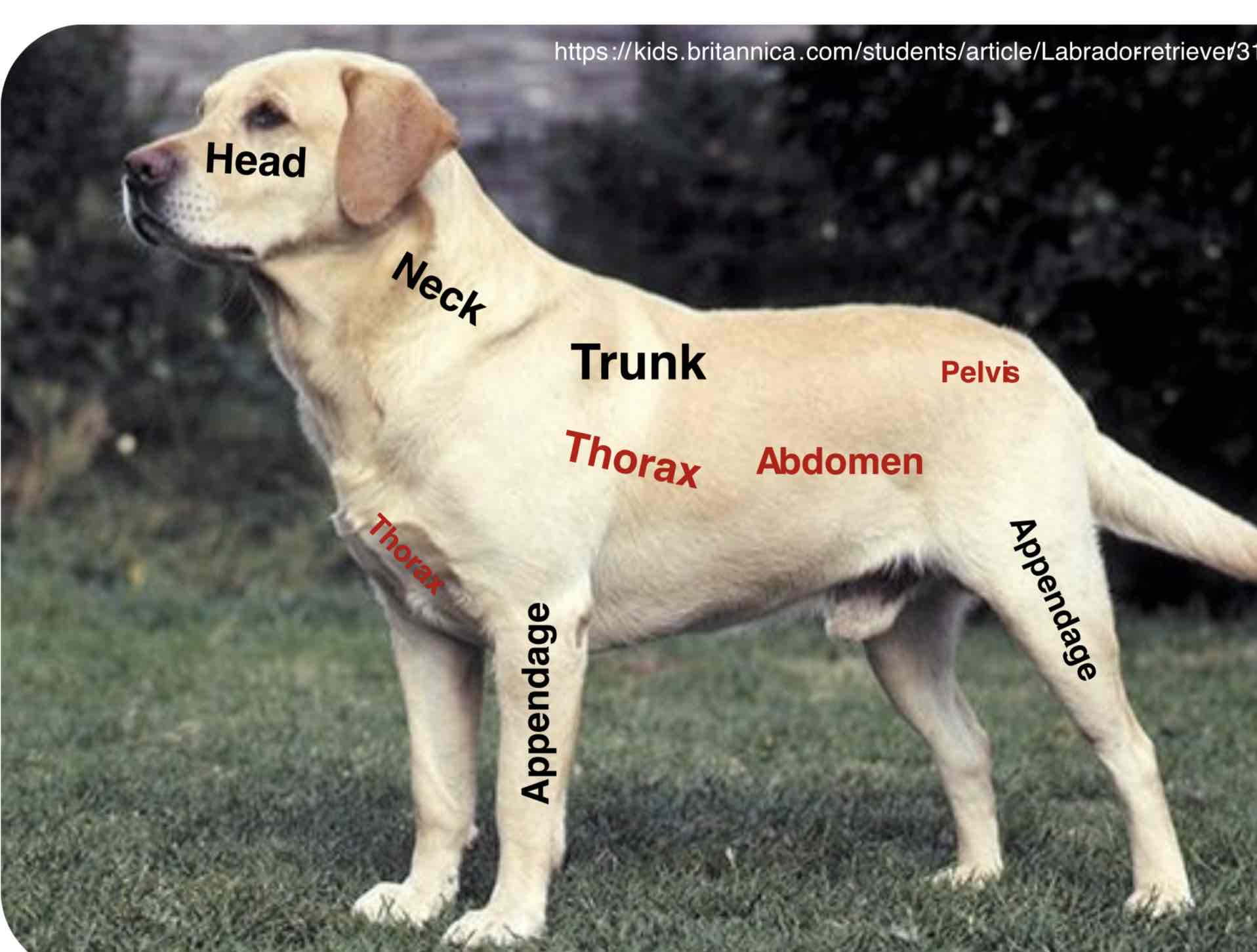
Appendages
Usually a projecting part of an animal body that is typically smaller and of less functional importance in the main part to which it is attached. The limbs (fore and hind) Are examples of the appendages. Further more, The animal body has more specific parts of the head, neck, trunk, and appendages. Remember that the appendages have their parts which may cover the main trunk of the animal body depending upon their attachment into the trunk Example: The shoulders part of the thorax
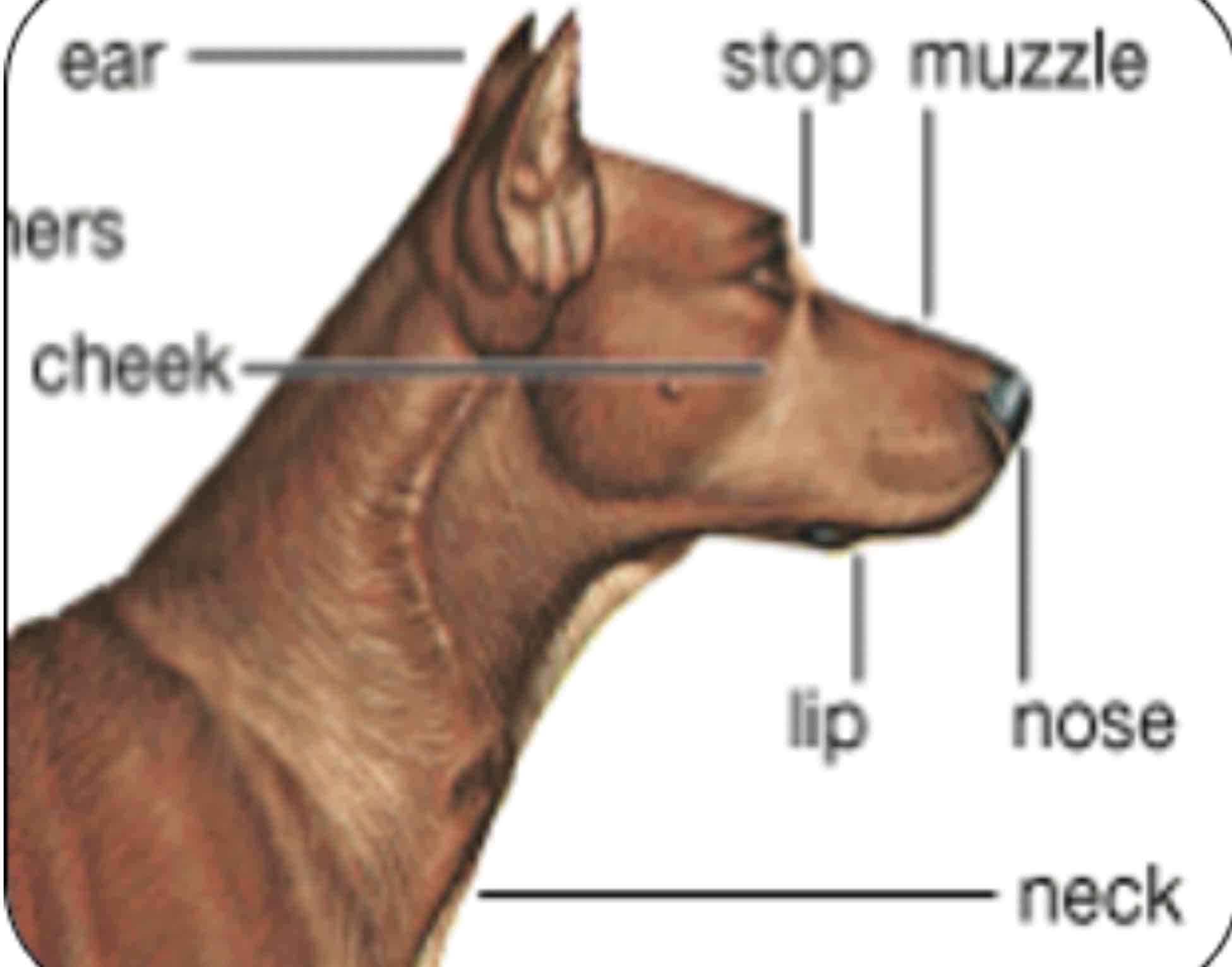
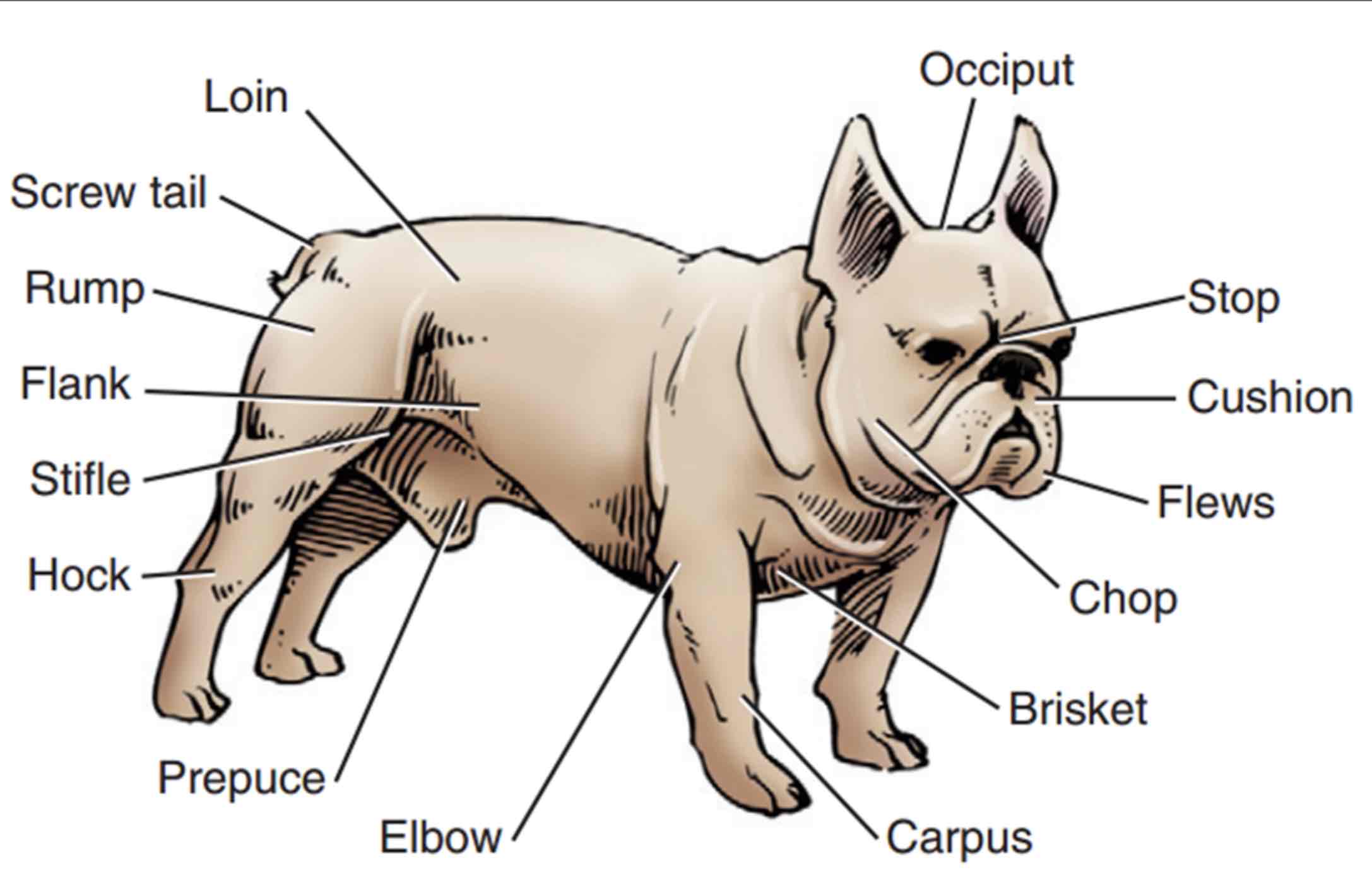
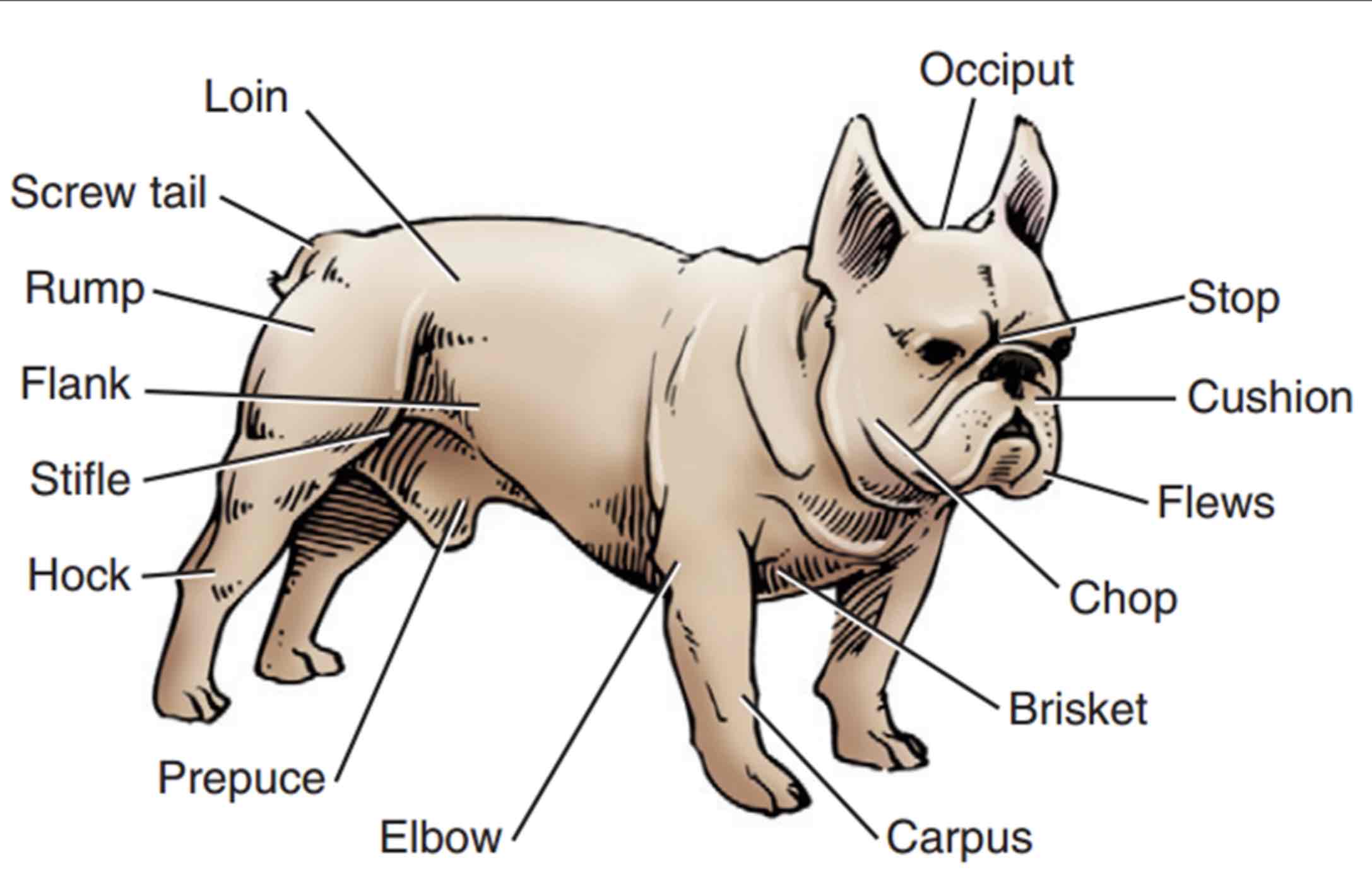
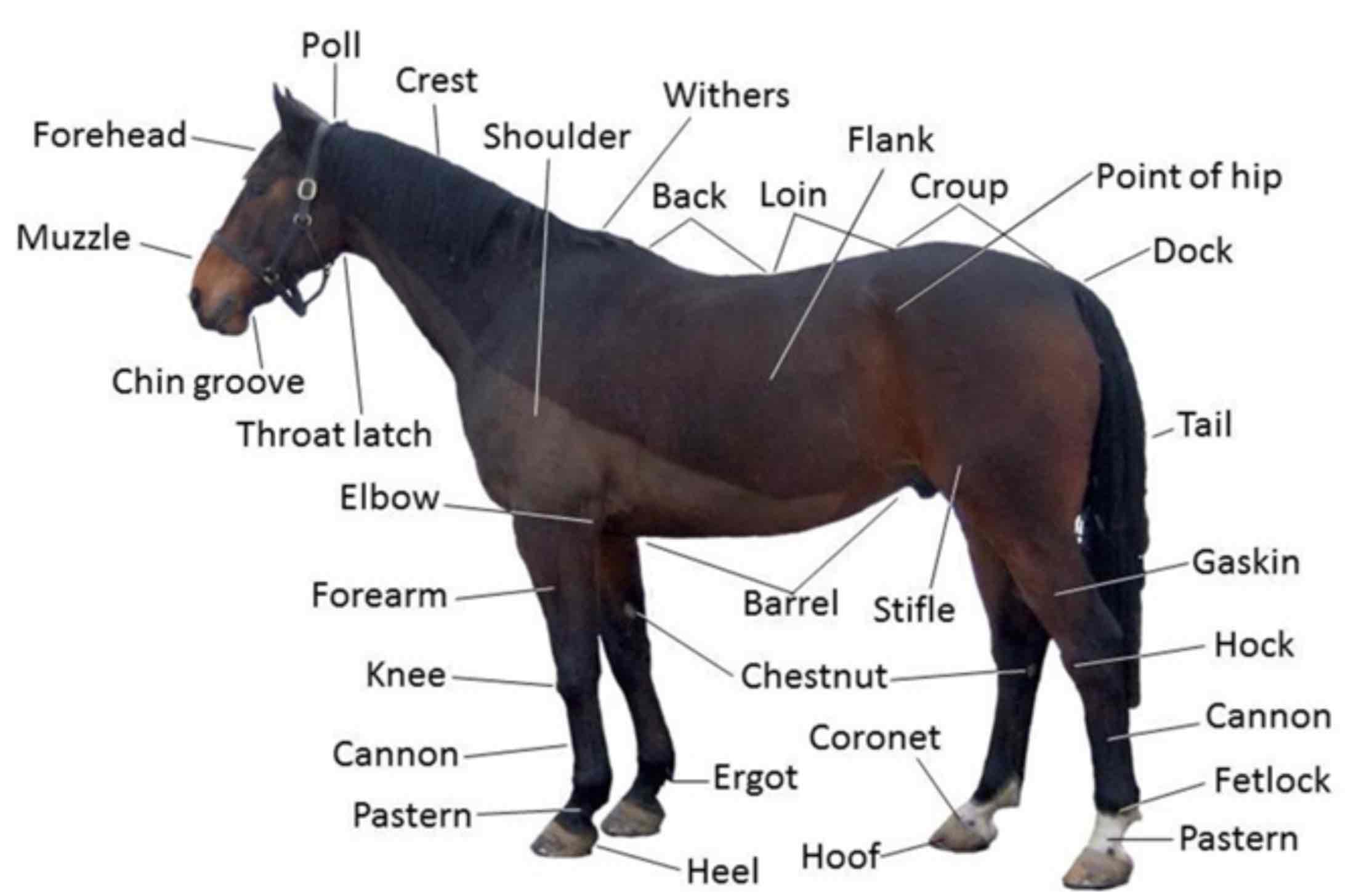
Muzzle
The part of the head in front of the eyes: Nasal bone, nostrils, and jaws. Foreface

Stop
An indention between the eyes where the nasal bones and cranium meat
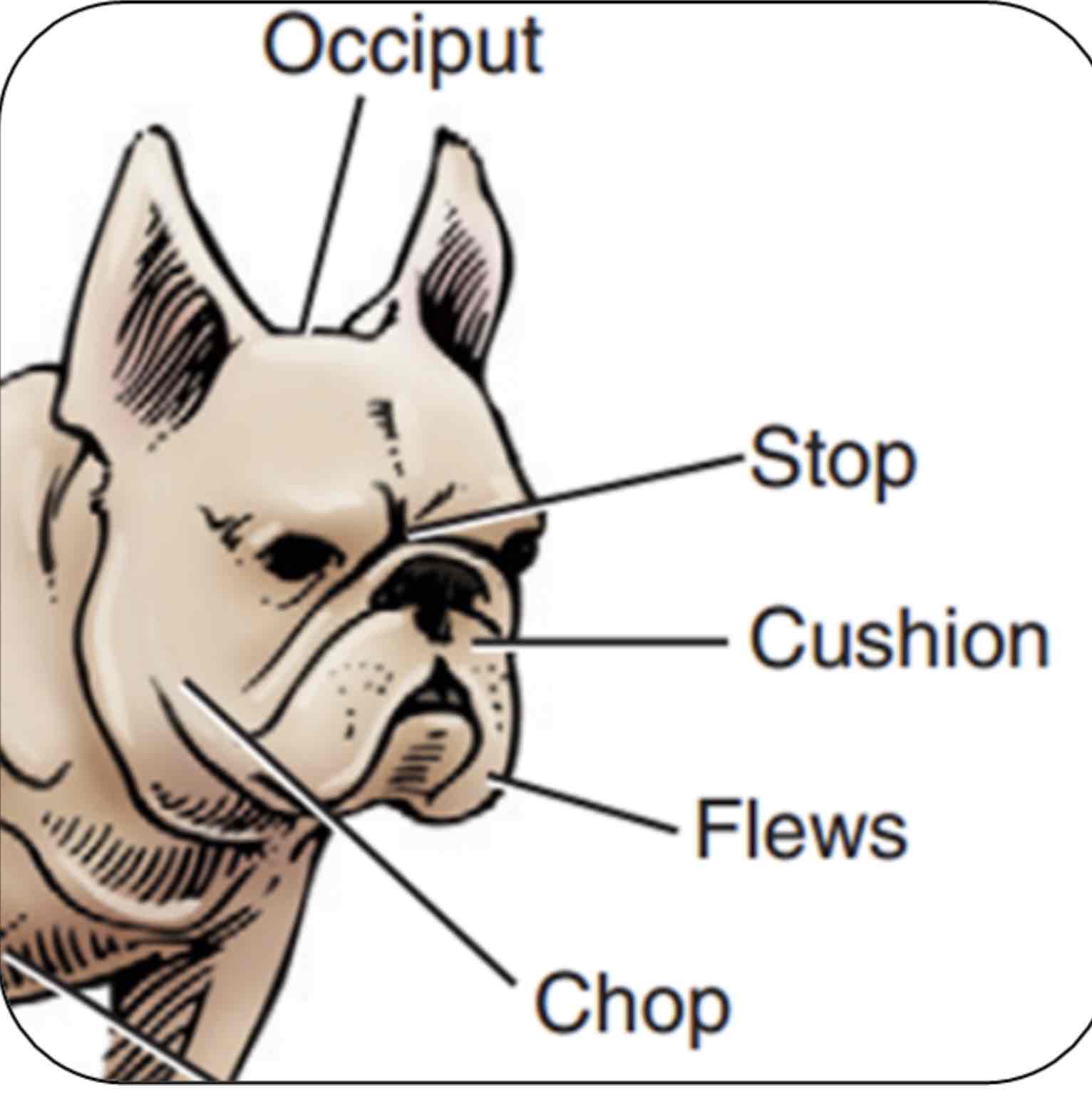
Occiput (poll in large animals)
The top point of the skull, Area between the ears/horns
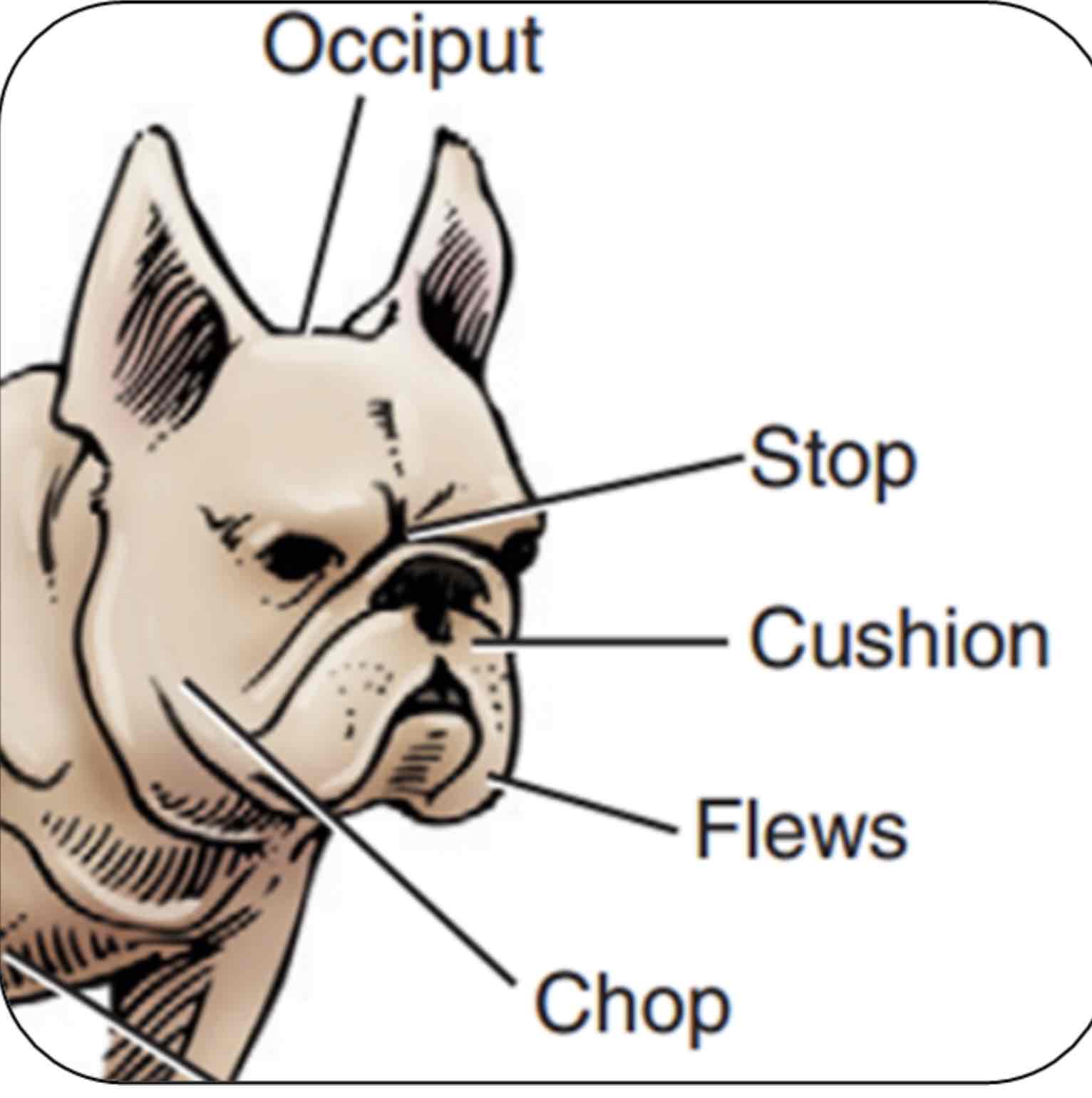
Cushion
Fullness or thickness of the upper lips
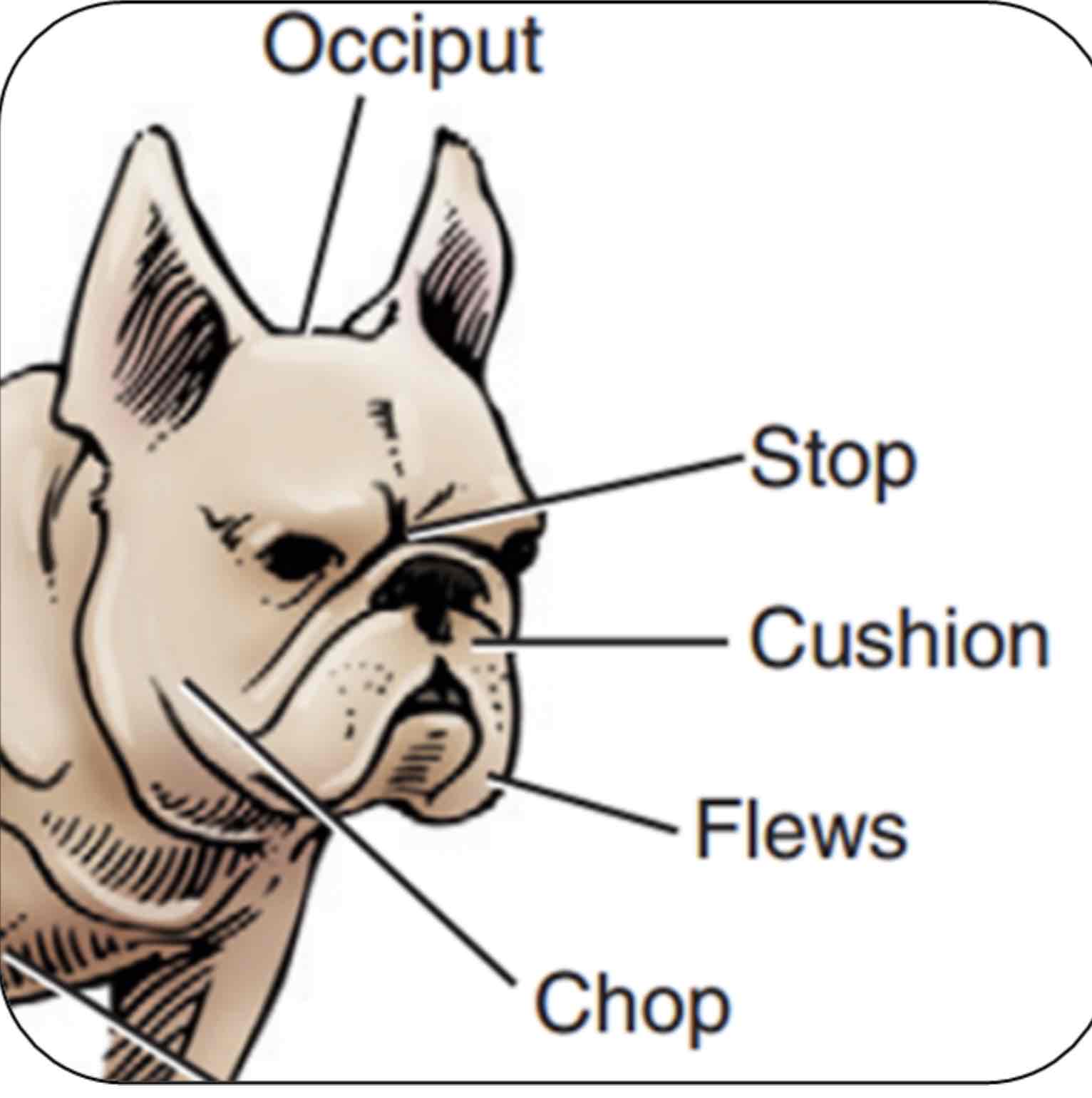
Flews
Upper lip pendulous, Particularly at the inner corners
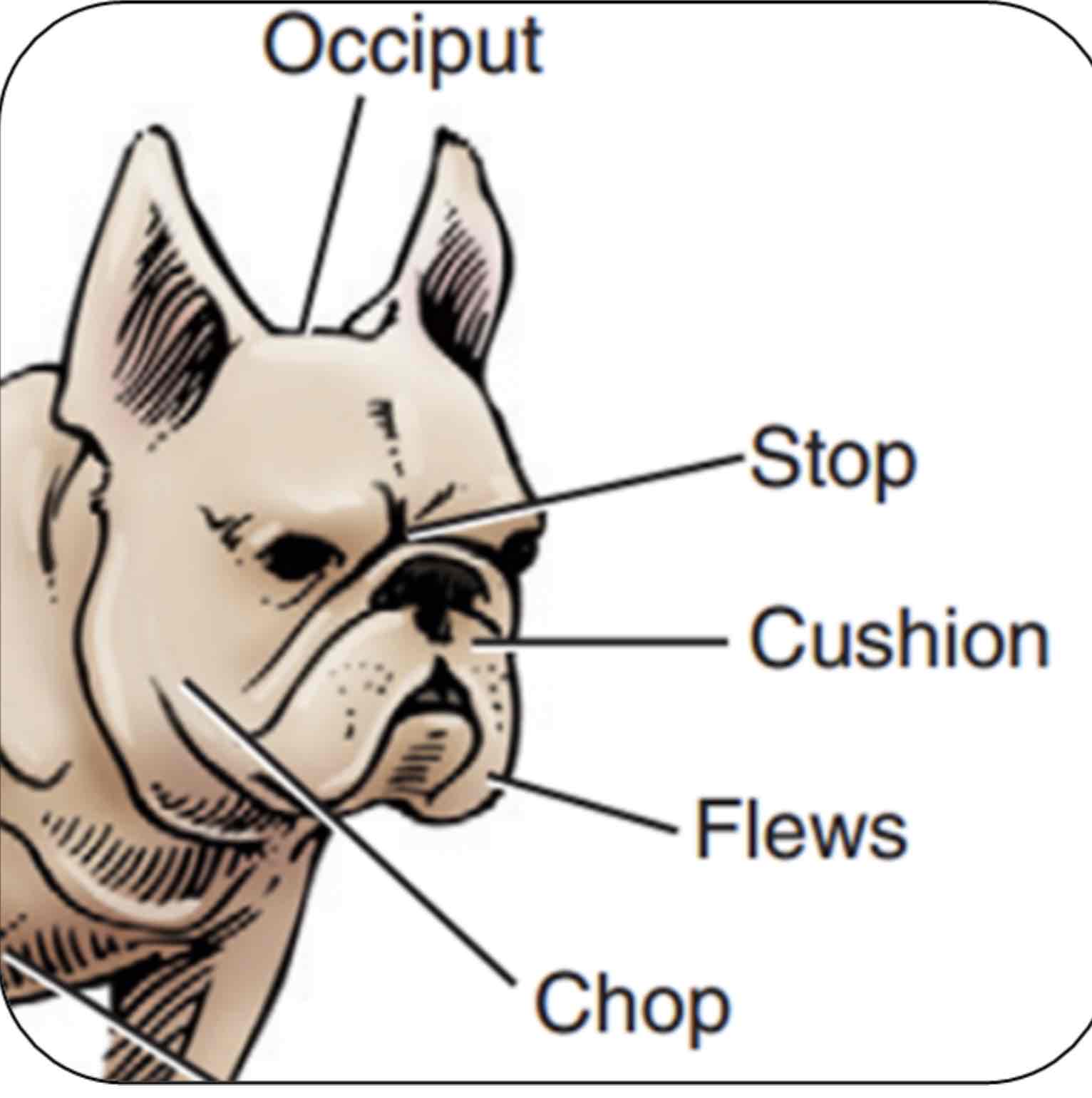
Chop
Jowls or pendulous flesh of the lips and jaws
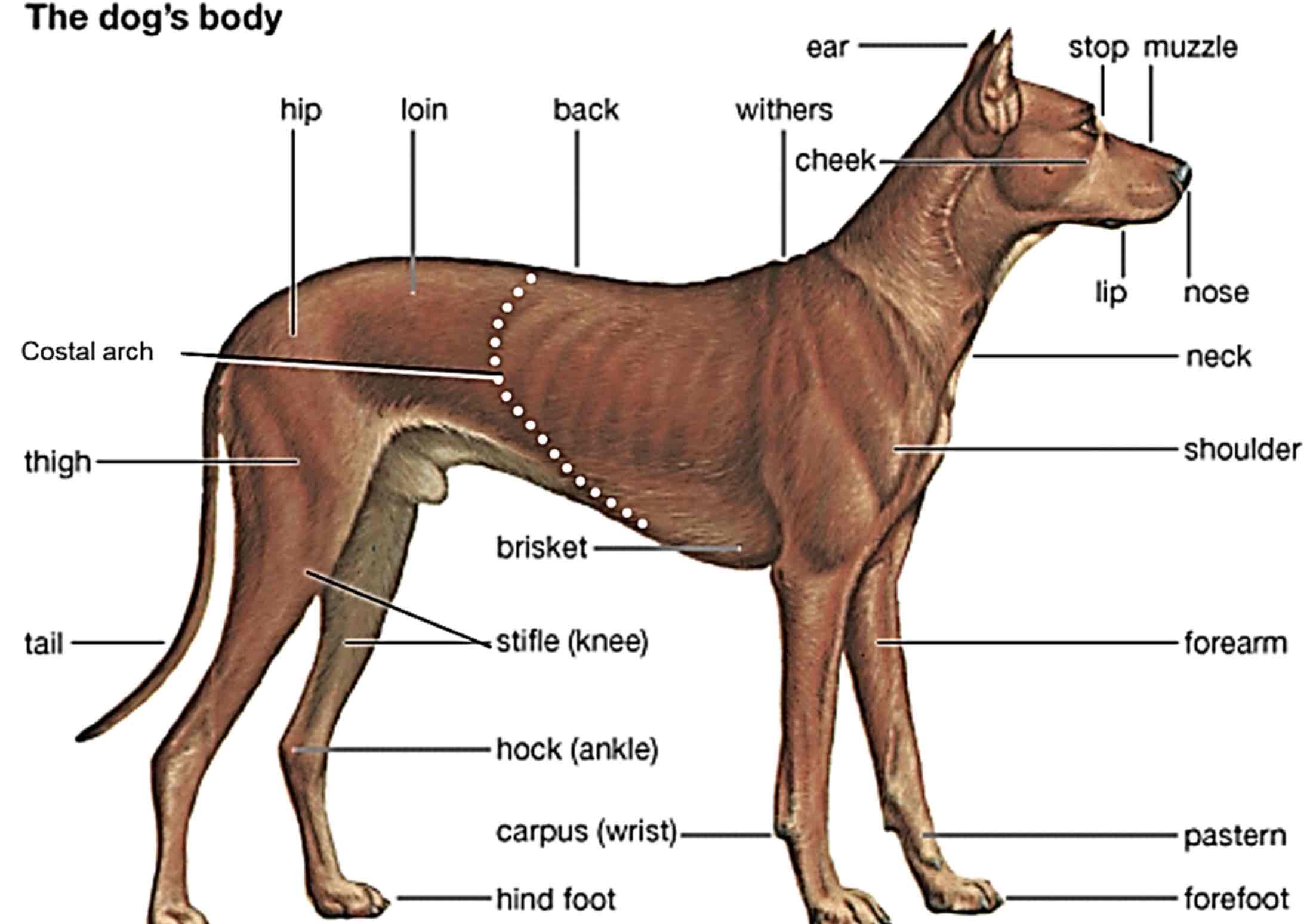
Brisket
Chest, usually refers to the sternum, but in some standards, it refers to the entire thorax
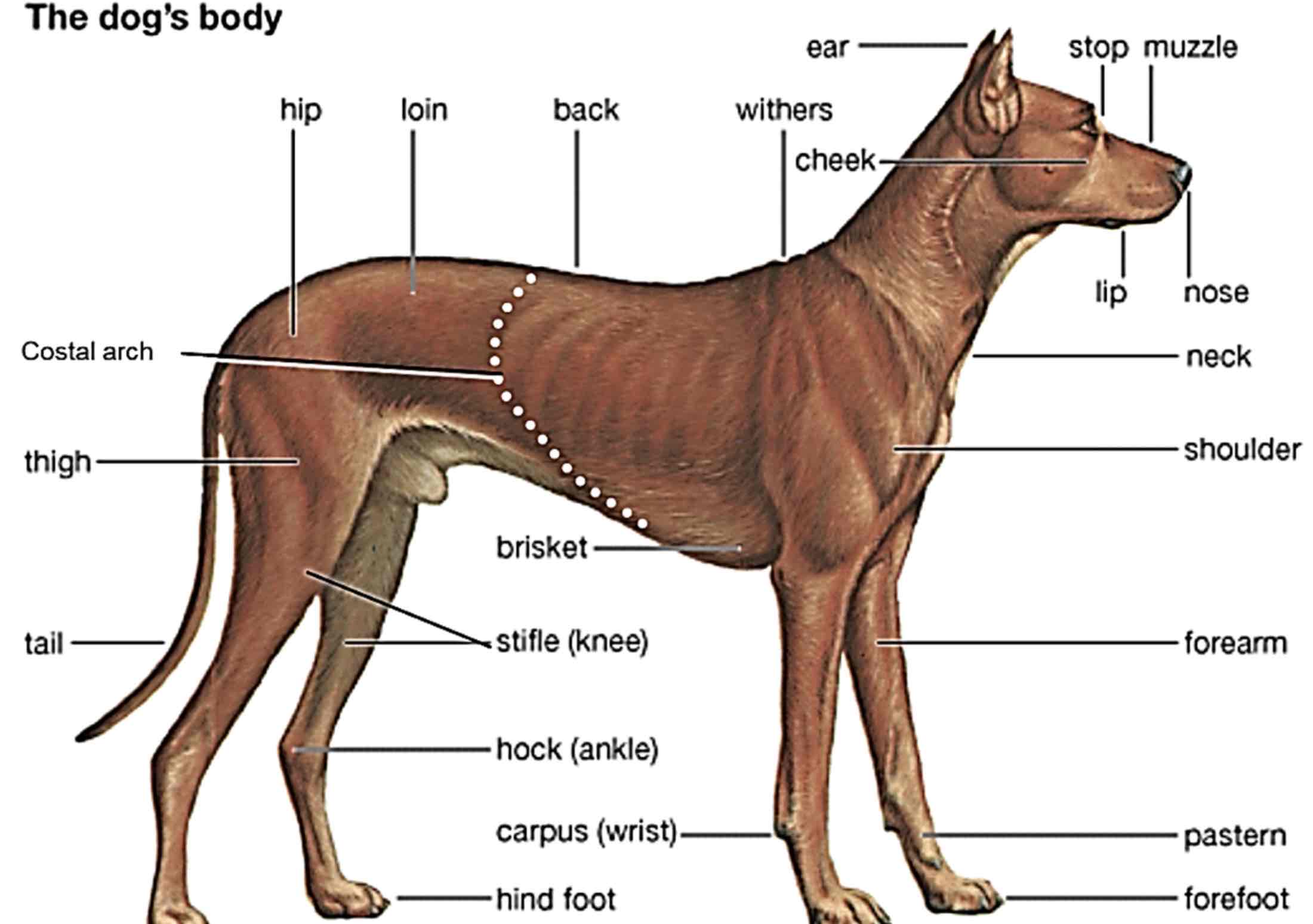
Withers
Highest point of a dogs’s (an animals) Shoulders.
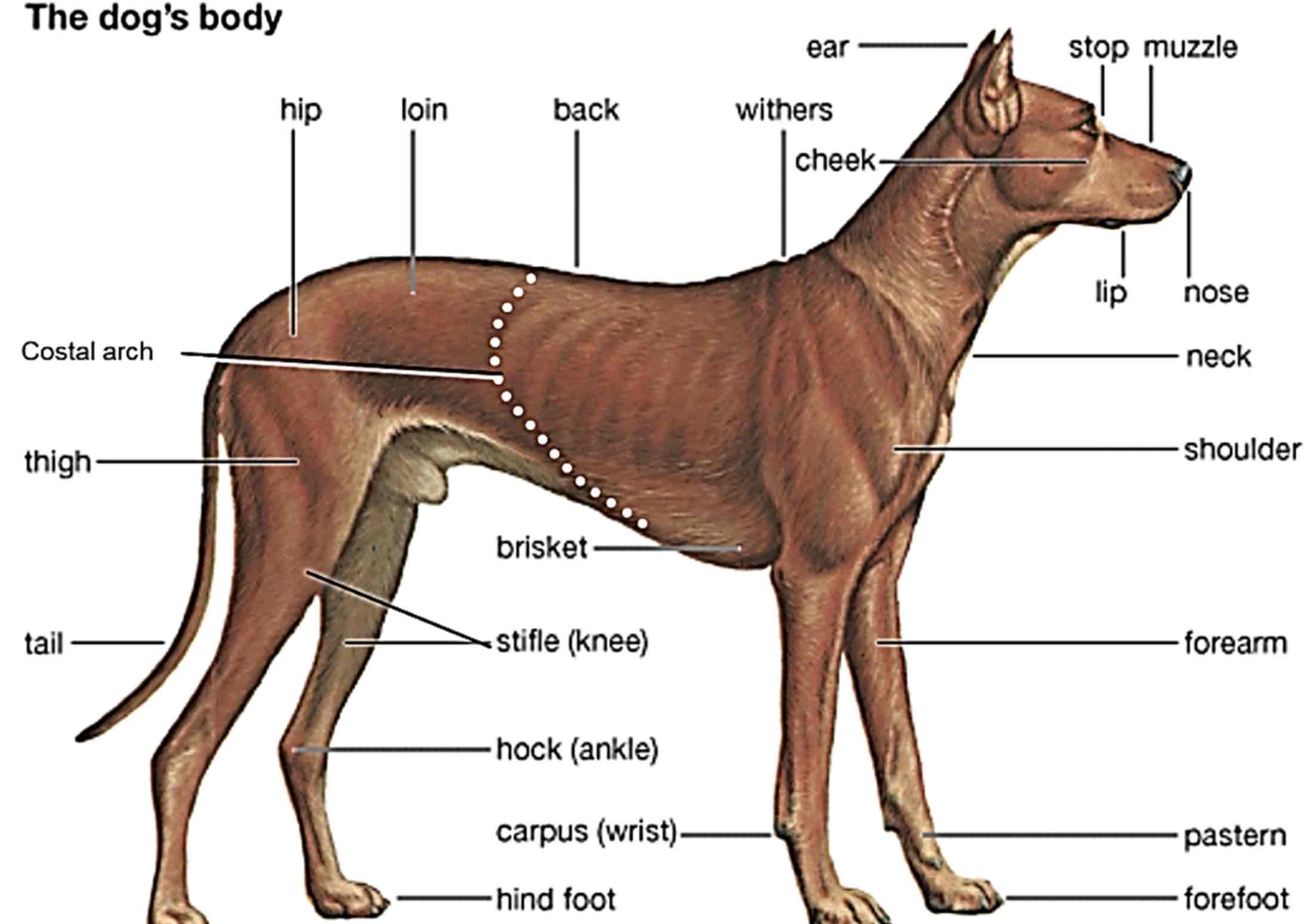
Back
The area of a dogs (Animals) Body extending from the withers to the croup.
Croup
The region of the pelvic girdle, formed by the sacrum and surrounding tissue. (Rump/buttocks/hips)
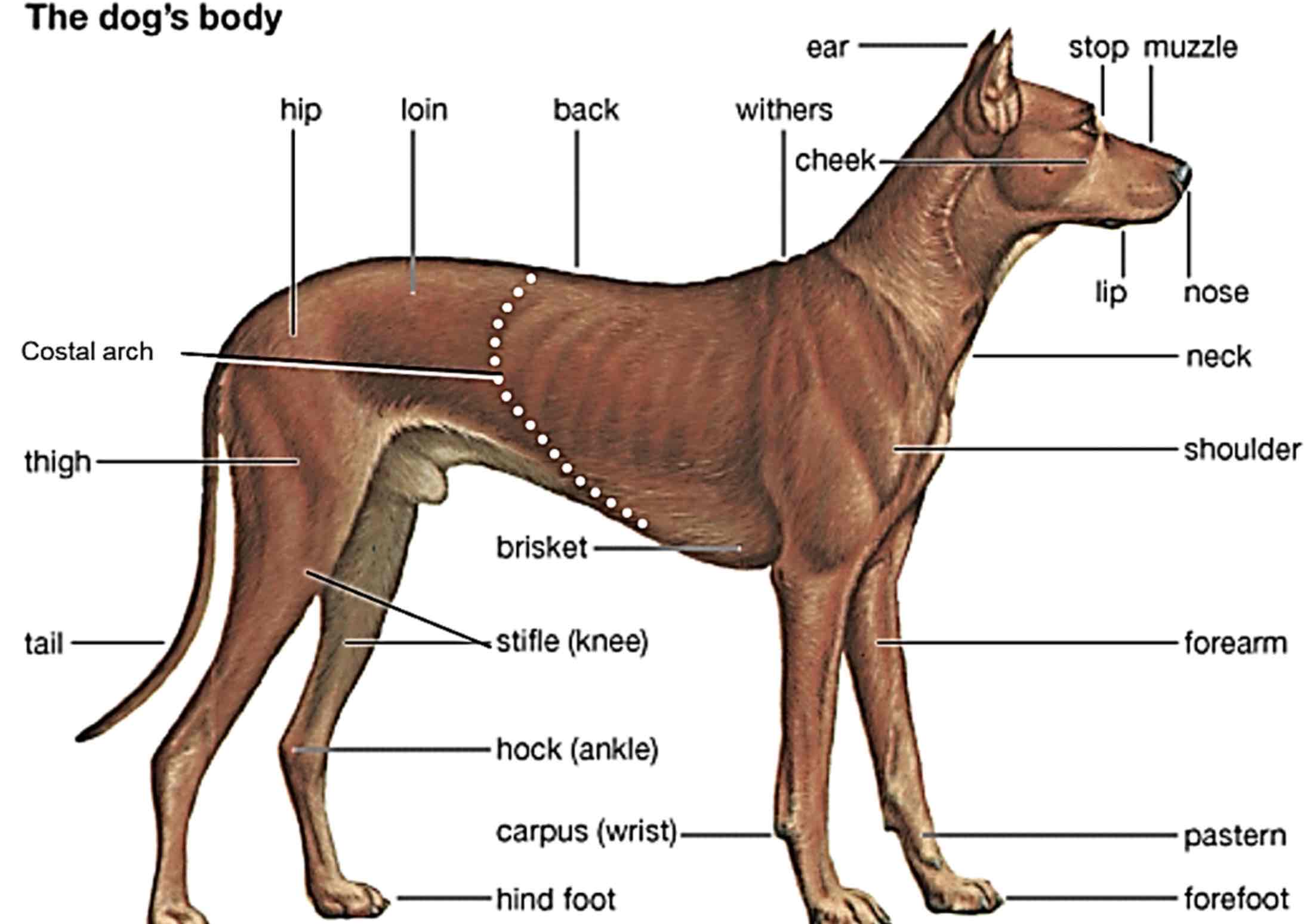
Loin
Area between the last rib and croup, behind the back
Flank
The side of the body between the last rib and the hip
Paralumbar fossa
Area slightly above the flank, both sides of the loin
In the ruminants and horses, the flank and the paralumbar fossa are the common site for taking incisions for abdominal surgeries
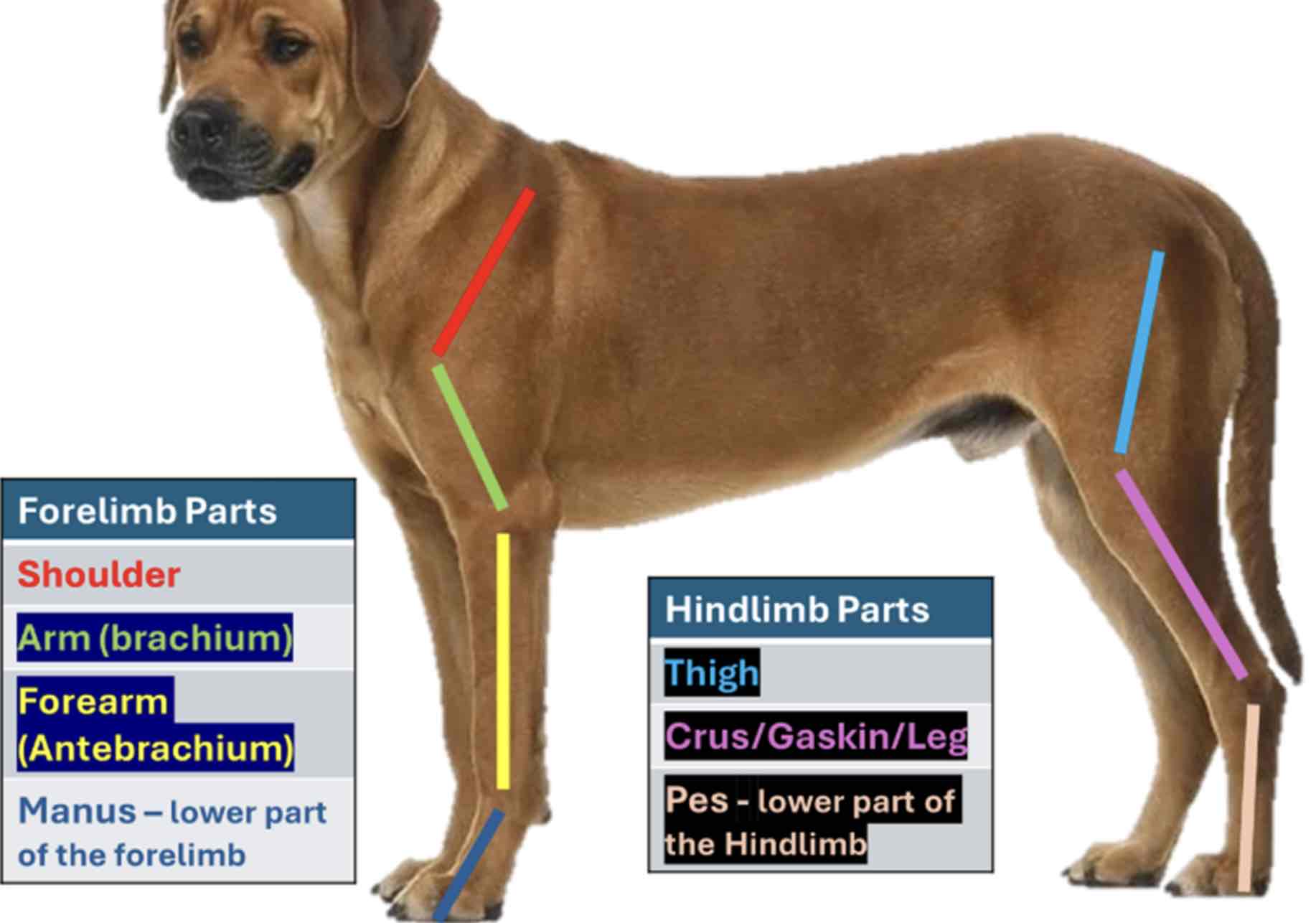
The forelimb Is also called the pectoral limb
From top to bottom (Proximal to distal) The forelimb divided into four regions
Shoulder
Part closely attached to the thorax; It contains scapula
Arm/brachium
The part below the shoulder which contains the bone humerous
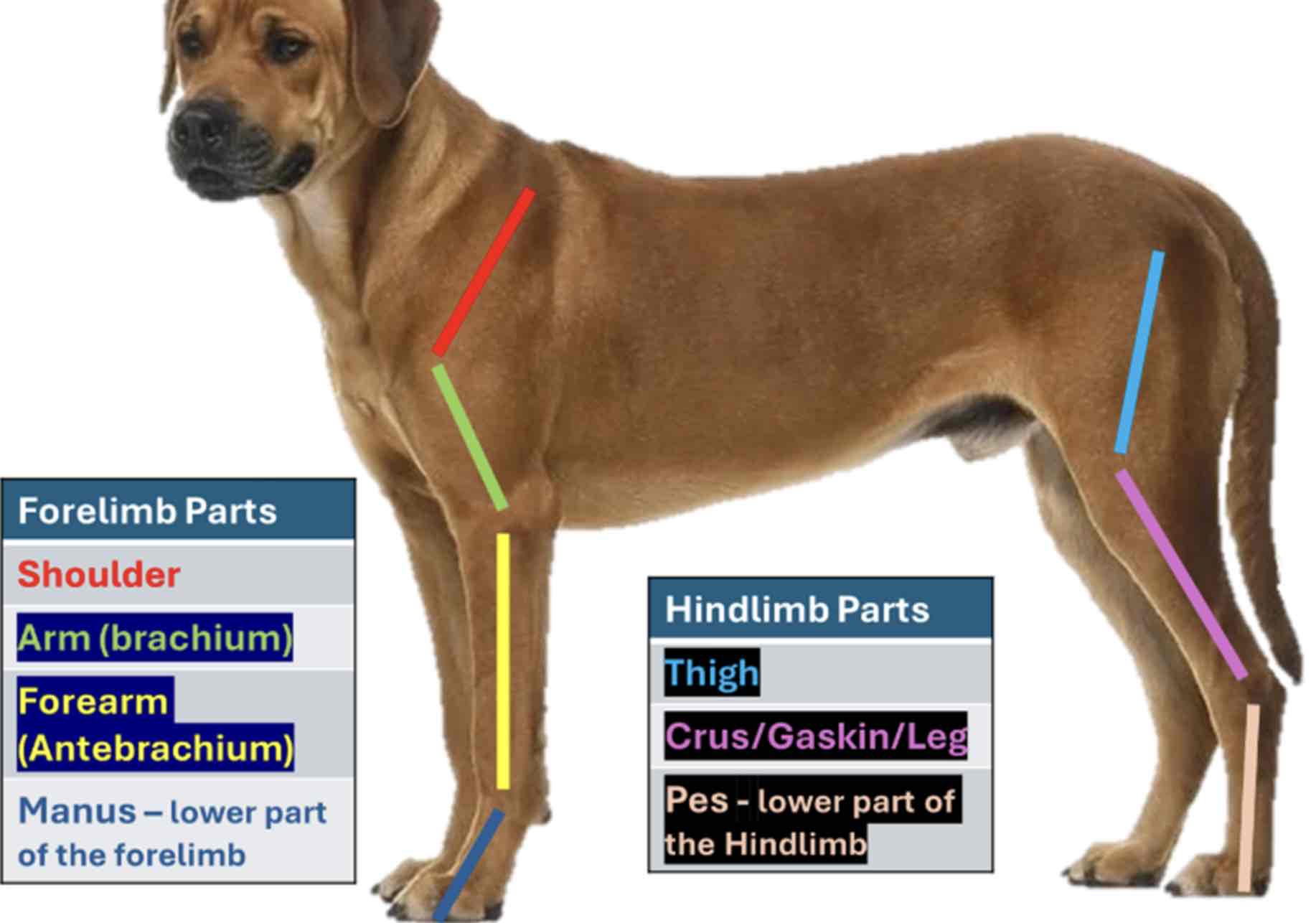
Forearm / antebrachium
The part below the brachium containing the bone radius and ulna
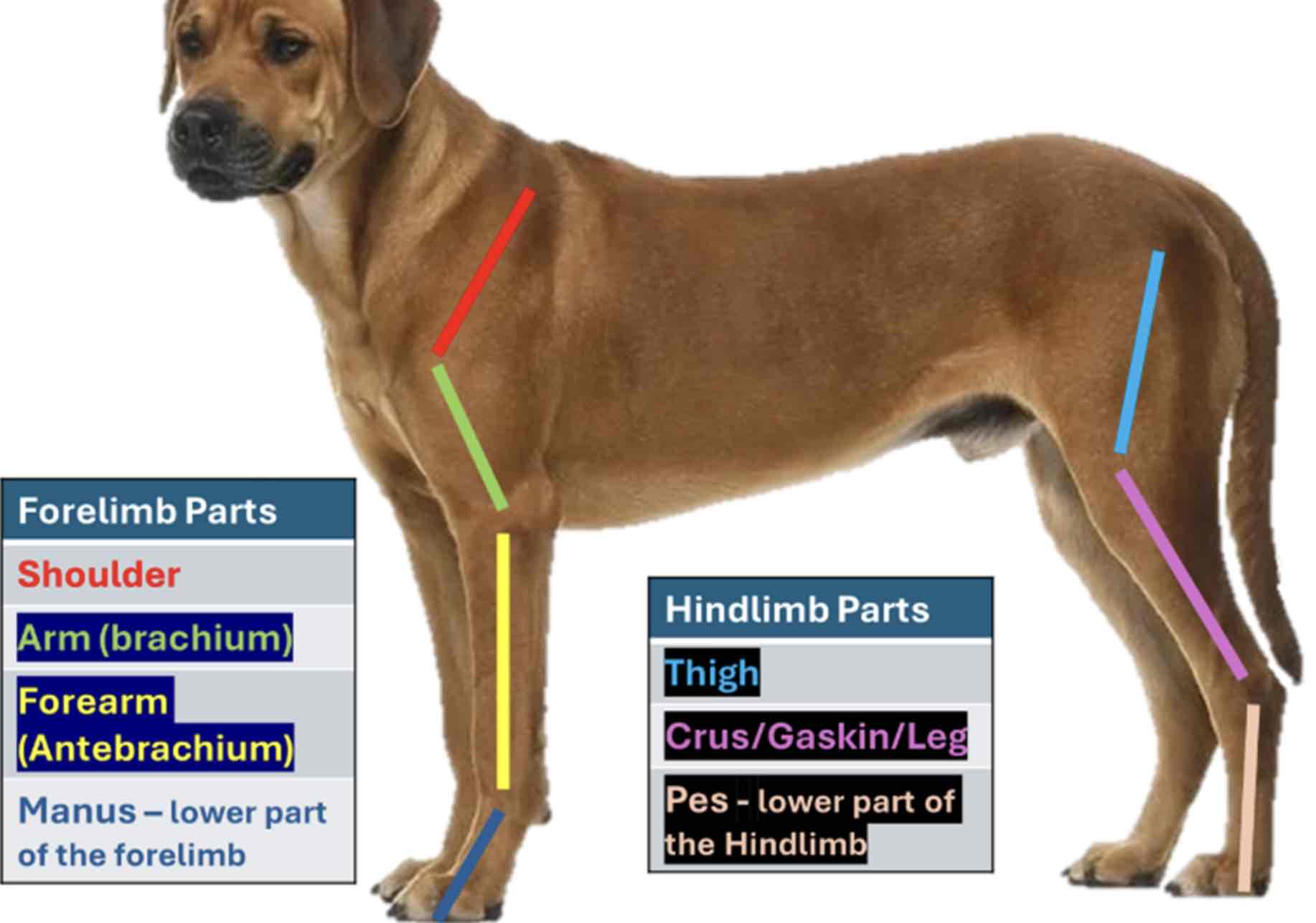
Manus
The forelimb part, including the carpus of the animal. It contains the carpal and metacarpal bones and bones of the digits. The hindlimb is also called the pelvic limb. From top to bottom, hindlimb Is divided into three regions
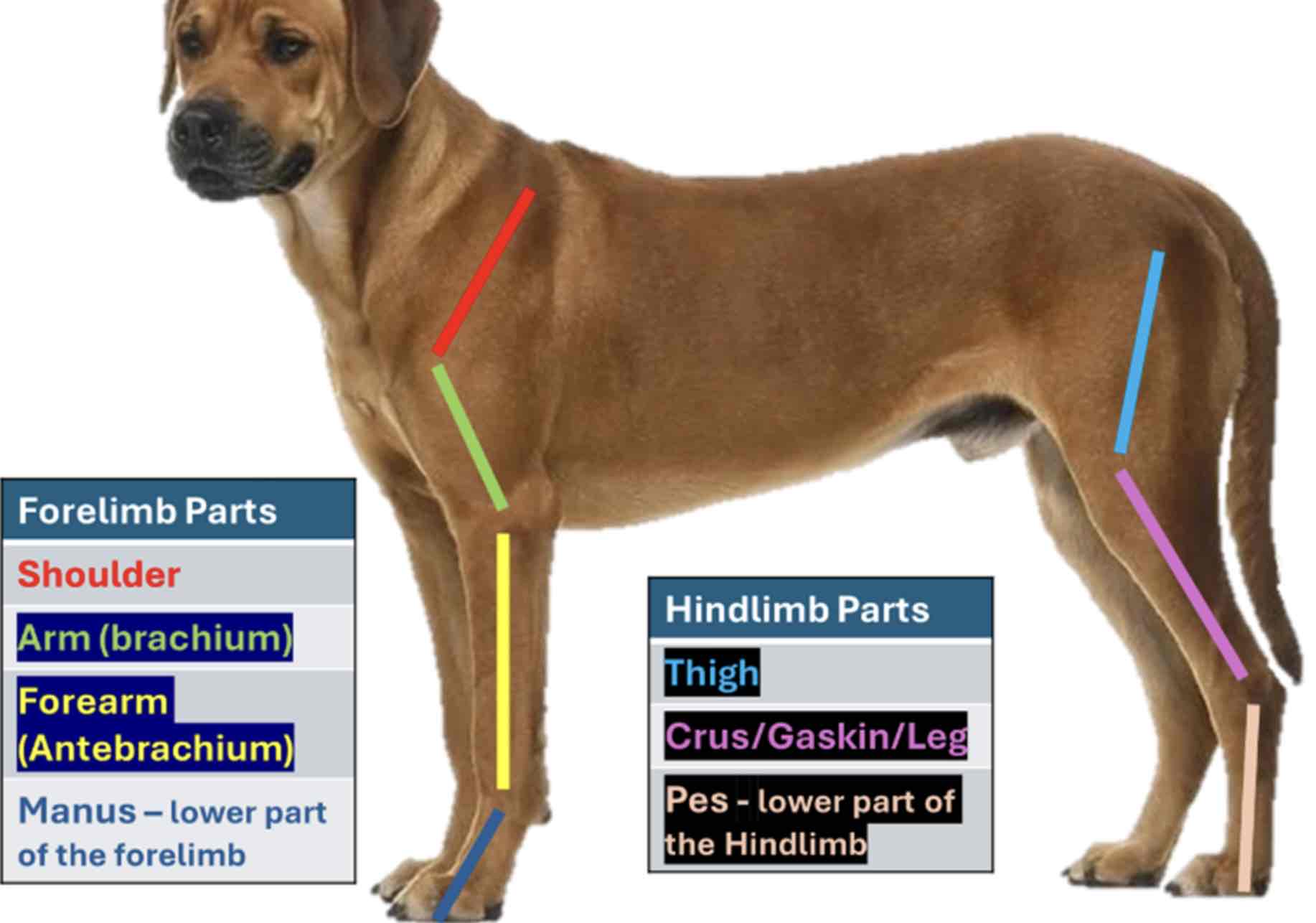
Thigh
The region where the bone femur is located
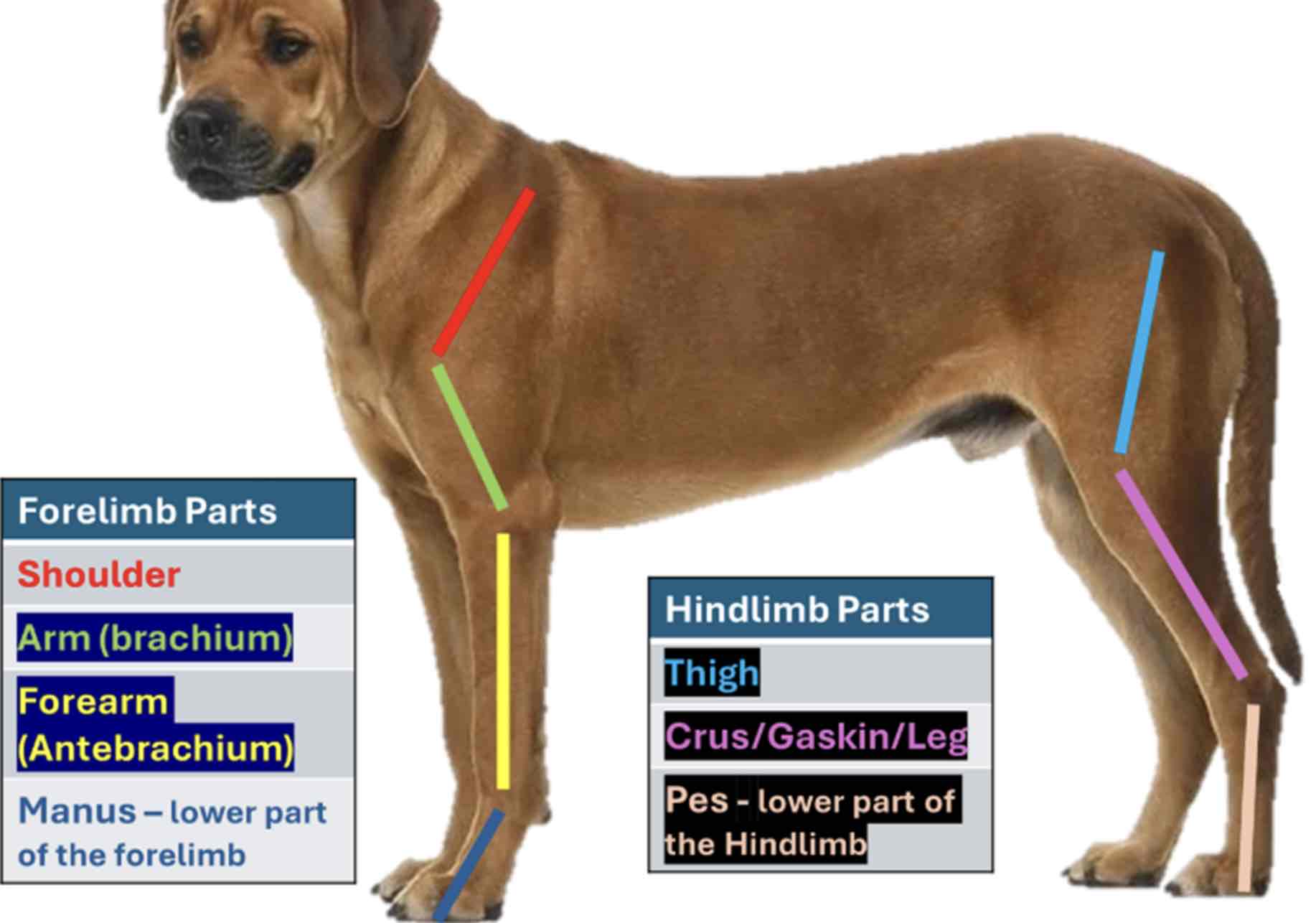
Leg / Crus / gaskin
The part of the hind limb that is below the thigh. It encloses the tibia and fibula
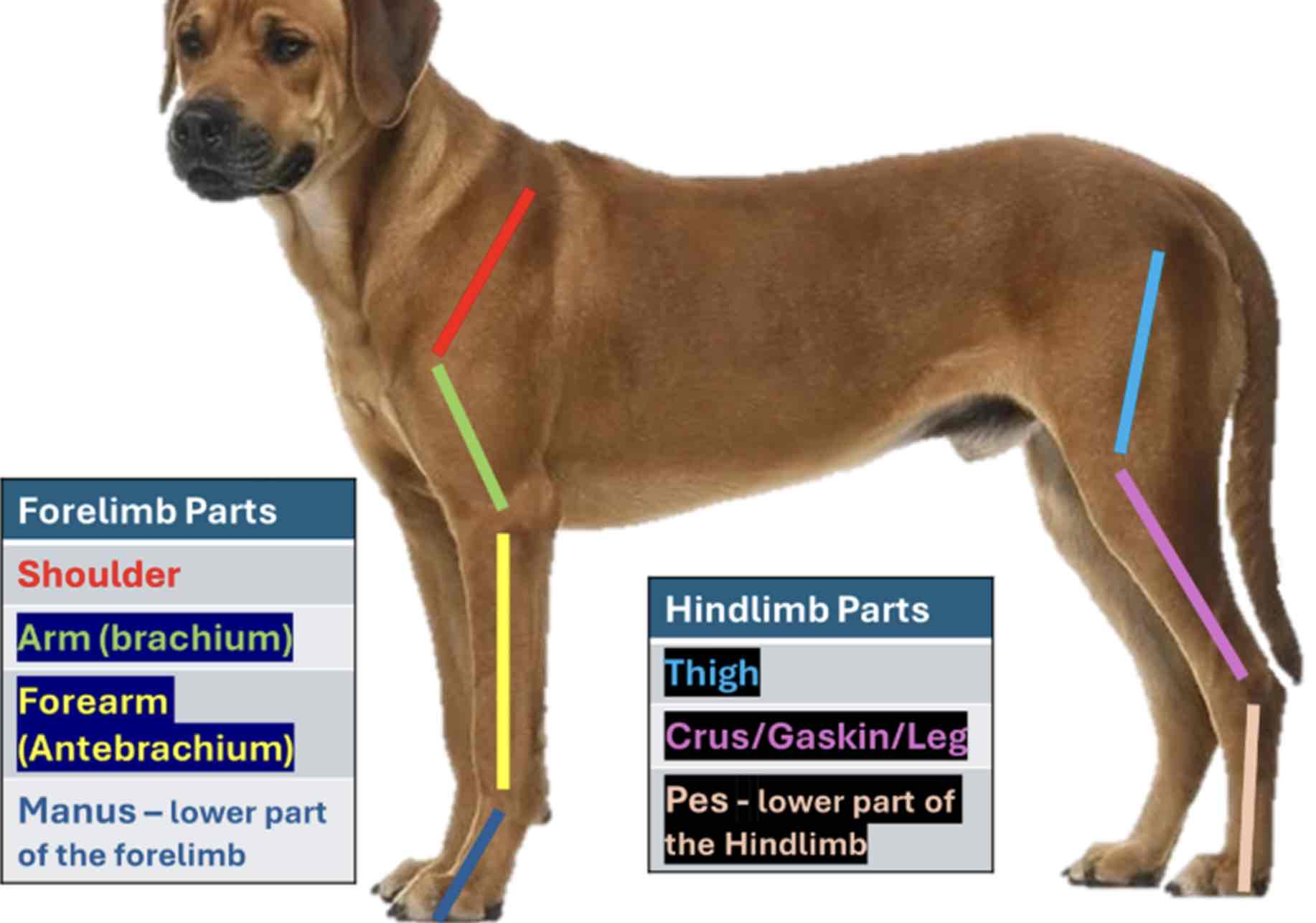
Pes / crus / gaskin
The lowest part of the hindlimb from tarsus, it contains the tarsal and the metatarsal bones and bones of the digits
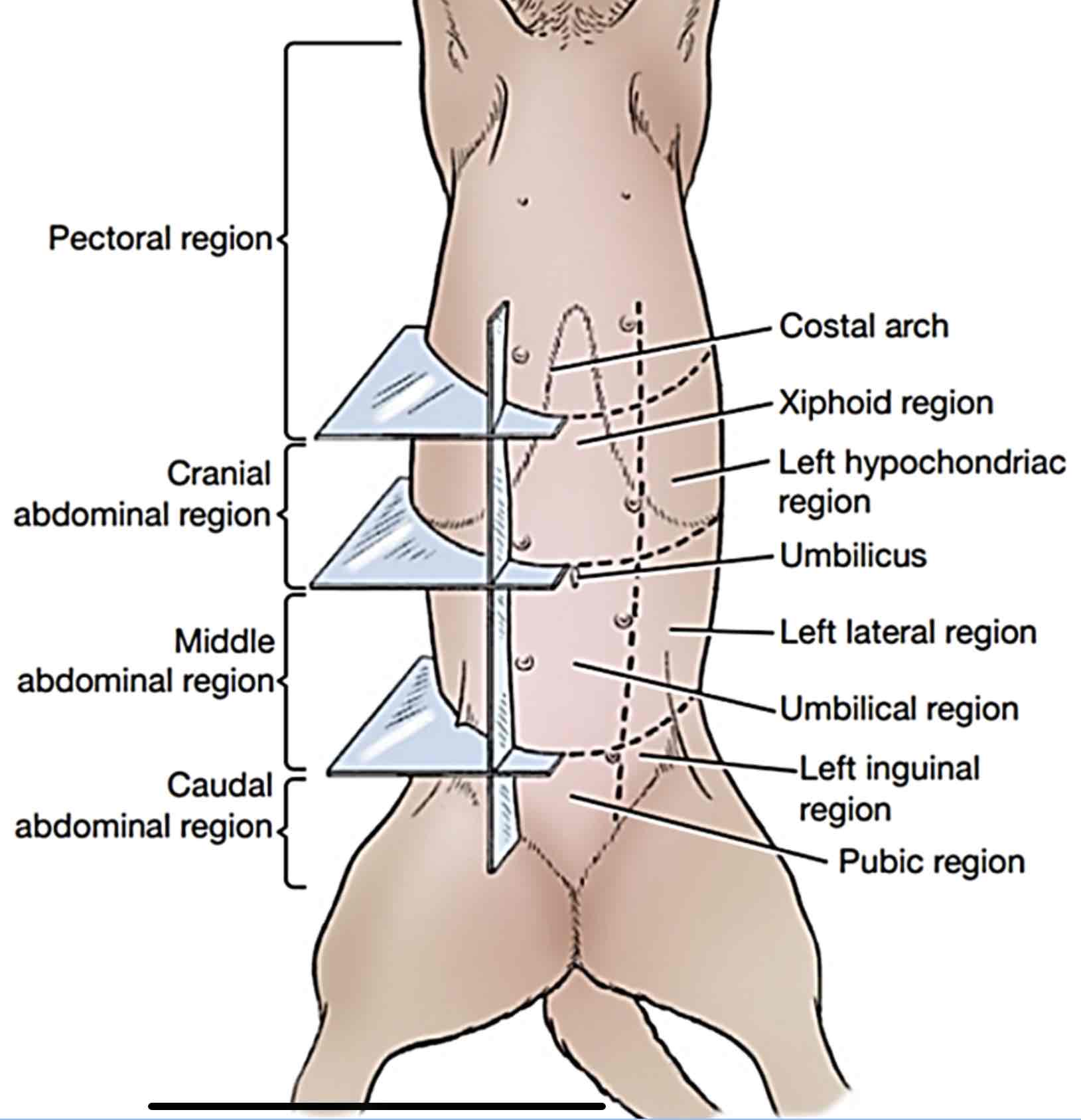
Pectoral region
Includes the girth along the chest of the animal, thoracic walls, and the brisket region
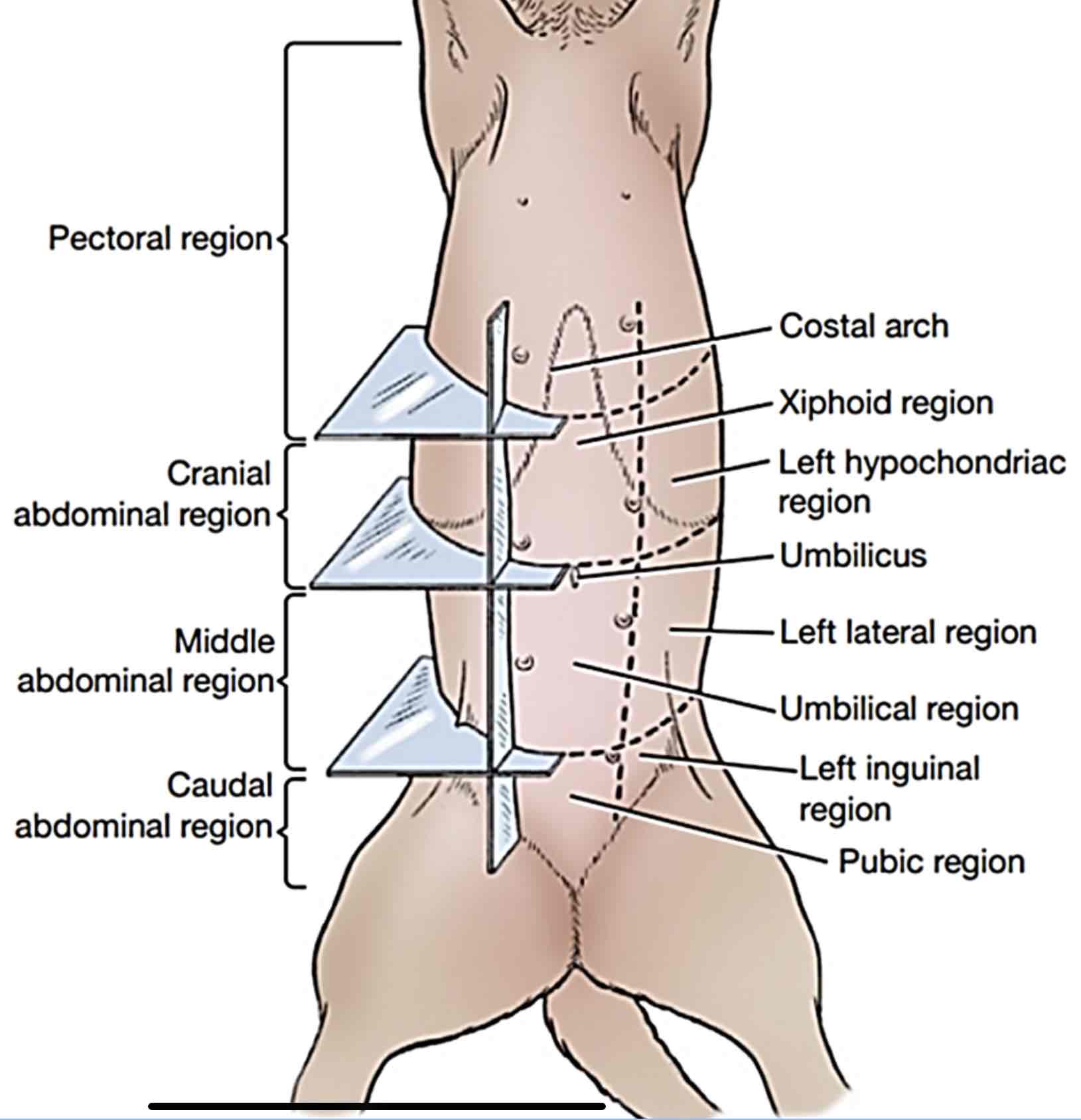
Cranial abdominal region
Includes the backward part of the thoracic wall, the left and right hypochondriac regions; and area of the belly behind the sternum up to the umbilicus, which is called the xiphoid region
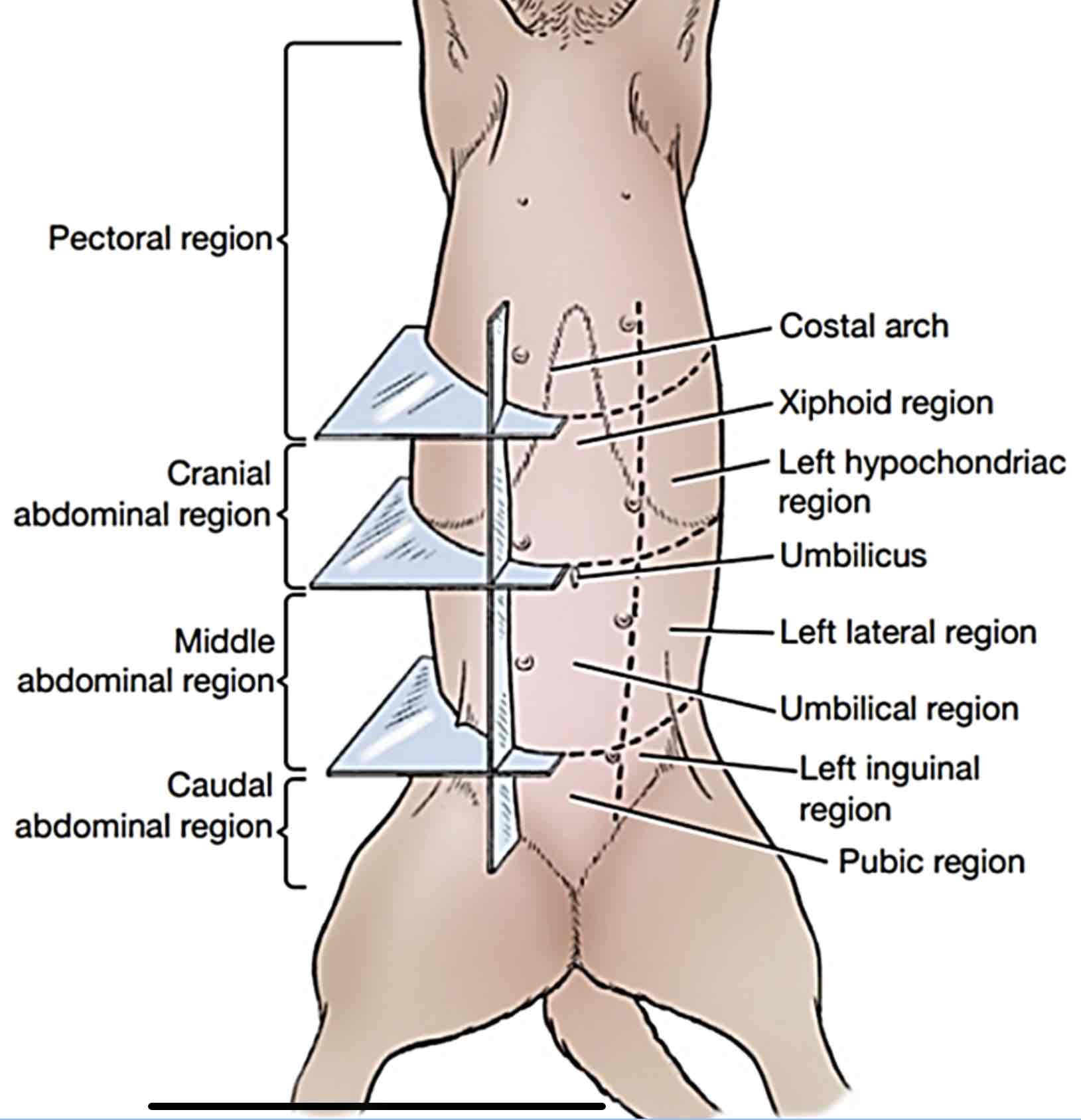
Caudal abdominal region
Includes part of the belly just before the pelvis, the pubic region. The left and right inguinal regions are located on both sides of the pubic region
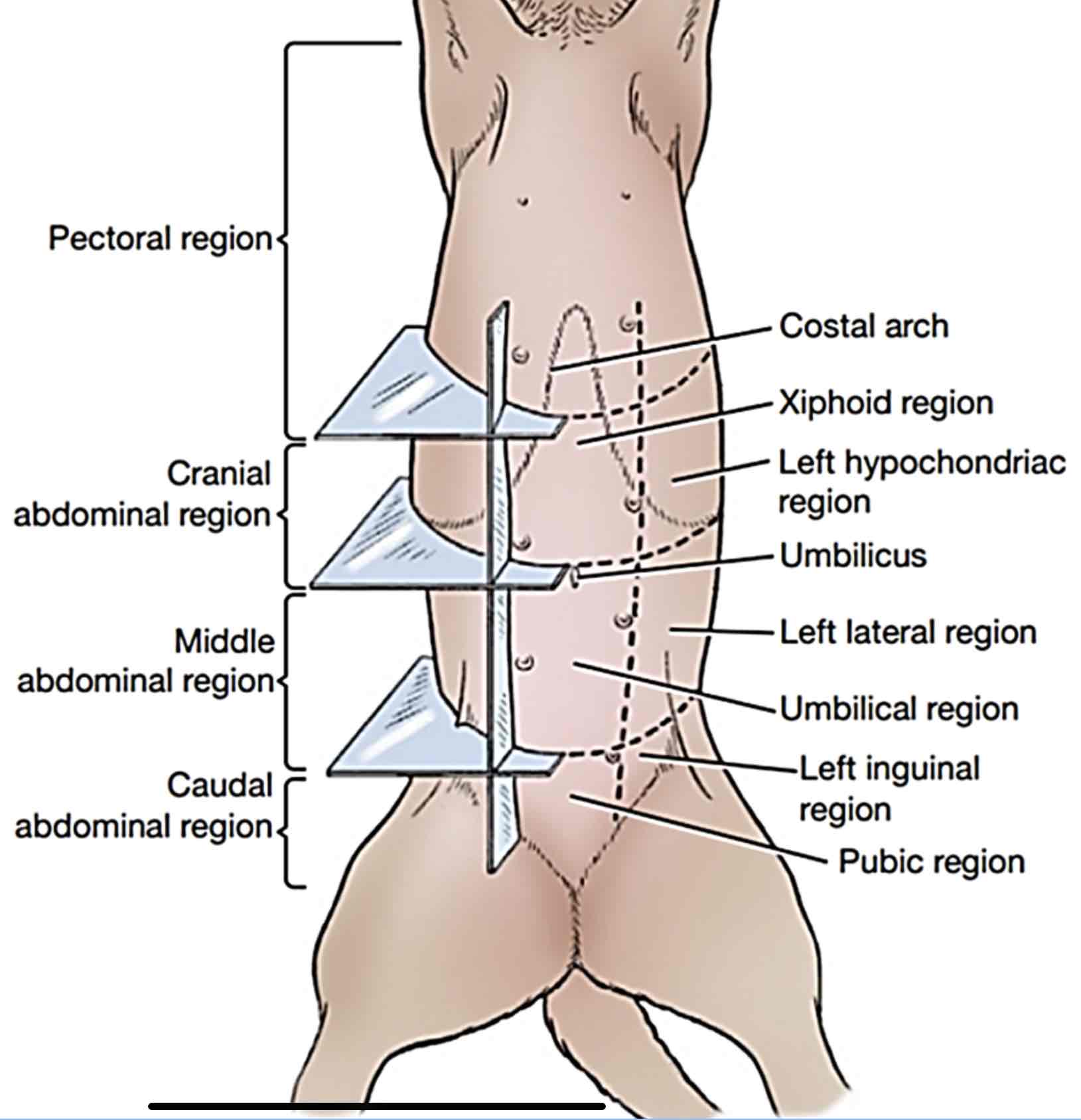
Middle abdominal region
includes part of the belly behind the umbilicus (scar formed after cutting the umbilicus) which is the umbilical region and left and right lateral abdominal regions from belly to the back and loin.