Cell culture
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
cell culture
The maintenance or growth of dispersed cells in a medium after removal from the body
why culture cells?
- more ethical approach
- in vitro model of cellular interactions
- in vitro model of molecular interactions
- in vitro model of cellular/microbial interactions
- use cells as a source of biological molecules for cell-free studies
examples of in vitro models of cellular interactions
- Toxicity assays
- Screening new agents for therapeutic potential
- Estimation of differential sensitivities or susceptibilities of different cell types (ex. radiation)
- Morphological & ultrastructural studies (ex. e- microscopy)
- Studies of cellular responses to various stimuli
- Studies of intercellular interactions
- Studies of complex tissues, organoids
limitations of in vitro models
! what happens in vitro does not always predict what happens in vivo
- cell culture vs. in vivo is vastly simplified system
in vitro
within a glass, observable within a test tube
in vivo
performed or taking place within a living organism
examples of in vitro models of molecular interactions
Assays of:
- DNA replication, damage, and repair
- regulation of gene expression
- protein synthesis
- enzyme activity
- receptor signaling
examples of in vitro model of cellular/microbial interactions
- Assay of cellular responses to bacterial infection
- Assay of cellular responses to fungal infection
- Assay of cellular responses to viral infection
- Assay of host immune responses to infection
- Propagation of virus
HeLa cells
human epithelial cells of a strain maintained in tissue culture since 1951 and used in research, especially in virology.
- cells taken from Henrietta Lacks
pasteurization
A process of heating food to a temperature that is high enough to kill most harmful bacteria without changing the taste of the food.
- developped by Lois Pasteur
Germ theory of disease
idea that infectious diseases are caused by microorganisms
1952 Gey discovery
establishment of a continuous cell line from human cervical carcinoma (HeLa)
cell culture incubator
used for Internal environmental control
- water jacket - temperature stability
- temperature (adjustable)
- atmosphere (CO2, N2, O2, air)
- humidity
- 37 ºC (for most mammalian cells)
horizontal laminar flow hood
- airflow keeps airborne microorganisms and particulates out of area
-> now BSCs used
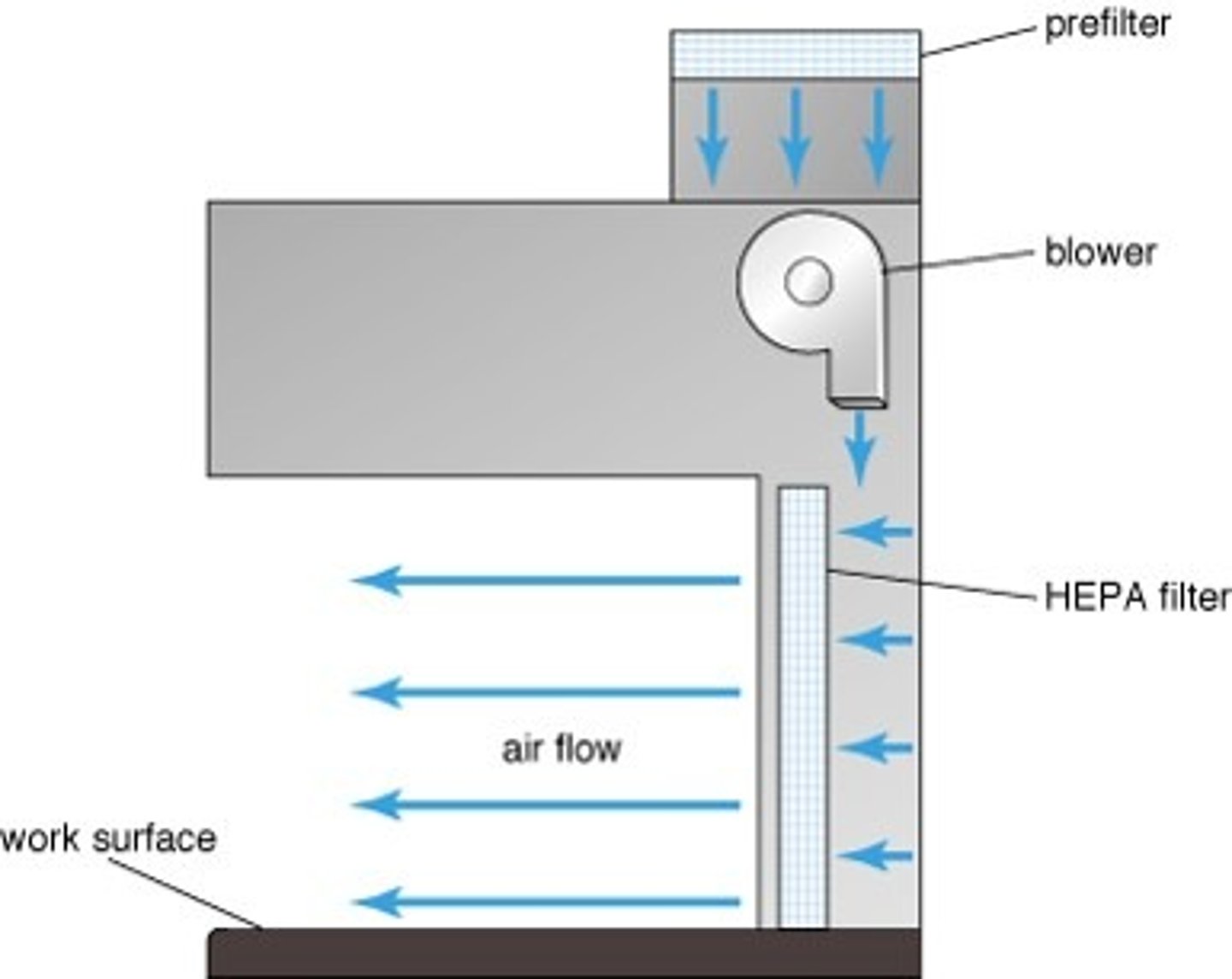
BSC II cabinet
- airflow keeps airborne microorganism and particulates out of work area
AND
- prevents their escape from the work area
- offers greater operator protection
- partial containment
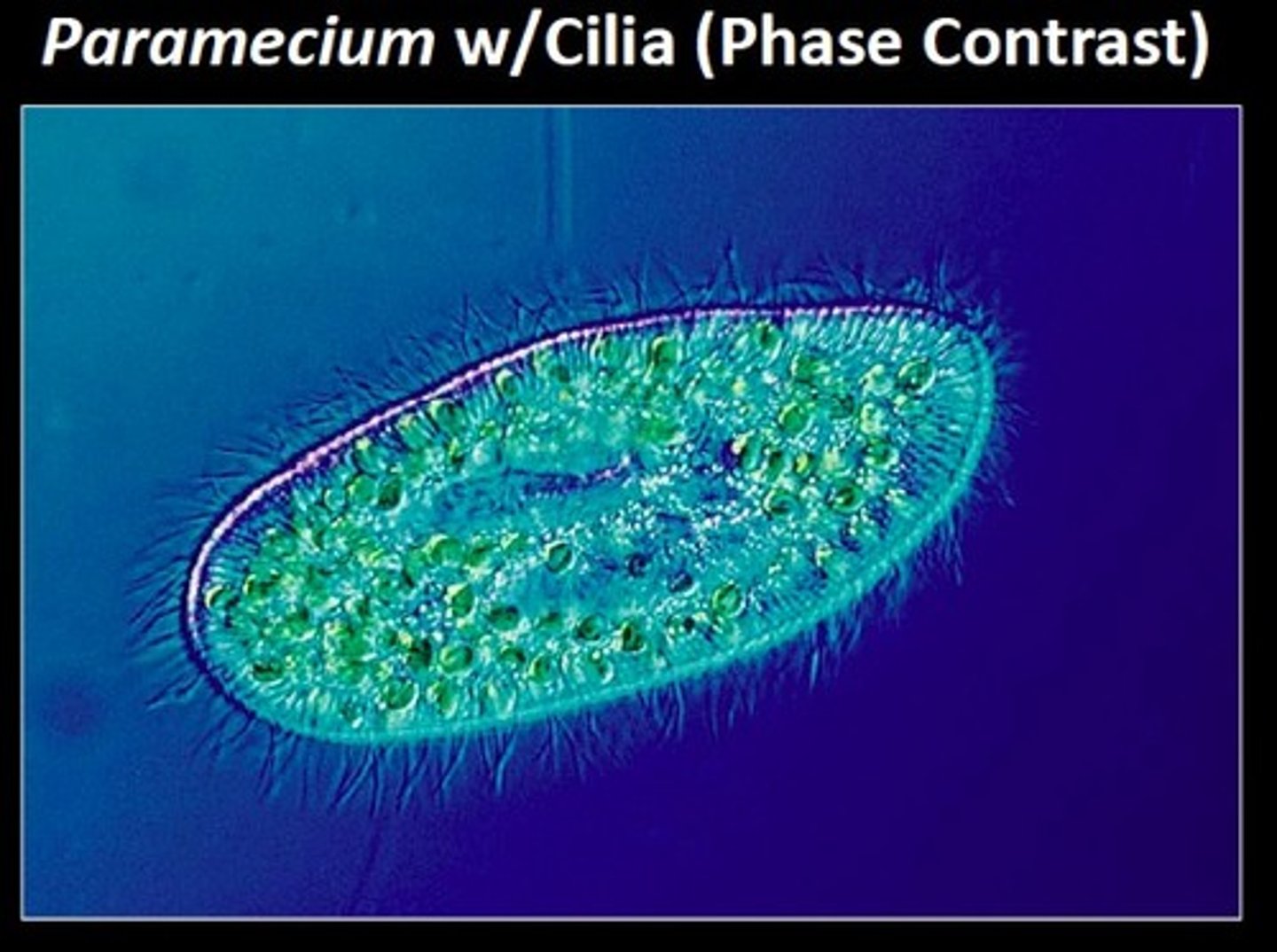
phase contrast microscope
light microscope that enhances contrast; useful in examining living, unstained cells
"inverted" - light source above, lens below
centrifuge
A machine that separates particles in a liquid by rapidly whirling the liquid around a central axis
what we can control: velocity + radius
- important to balance
standard benchtop centrifuge
up to 3000-4000 x g (up to 8000 RPM)
for: sedimentation of cells
highspeed centrifuge
up to ~30,000 x g (up to 17,000 RPM)
used for: sedimentation of virus
ultracentrifuge
up to 200,000 x g (or higher)
up to 60,000 RPM (or higher)
for: sedimentation of nucleic acids, sedimentation of nanoparticles
microfuge
up to 15,000 x g
for small volumes
refrigerator
4 ºC
for reagent storage
freezers
- 20 ºC or -80 ºC
storage of:
- enzymes, viable bacteria, viruses, long term reagent storage
- do colder if storing for longer
cryobiological storage system
- liquid nitrogen freezer
-196 ºC
- storable of viable eukaryotic cells
sources of tissue
- human biopsy or body fluid
- discarded human tissue
- cadaveric human organ donors
- animal tissues, embryos
preparation of primary culture from solid tissue
- disection
- enzyme digestion → cell culture
- finely chopped → primary explants
- further dissection → "organ" culture
morphology of cell division
- cell drawns in processes
- become round and highly refractile, 'glowing'
- cytokinesis begins
- cytokinesis completes
- cells grow processes
cell proliferation kinetics
- lag phase
- log (exponential) phase
- reach confluence → stationary phase
contact inhibition
a process that stops additional cell growth when cells become crowded
cells that don't divide
ex. macrophage
- terminally differentiated cells
components of typical mammalian cell culture medium
- essential amino acids: body cannot synthesize these
- vitamins: cofactors in biochemical reactions
- salts: maintain proper osmotic pressure, serve as a buffer system for pH changes
- additional components: glucose, whole serum, phenol red, antibiotics, anti-fungals, growth factors, etc.
why is phenol red in medium?
serves as a crude pH indicator
- starts as red, turns orange and yellow as pH drops
passage of adherant cell lines
- aspirate culture medium
- rinse monolayer with buffer
- add trypsin/EDTA to flask
- rap flask on hard surface
- add fresh medum
- transfer to new flask
Trypsin-EDTA
Enzyme used to detach ADHERANT cells from a culture dish
- overexposure can damage cells
propagation of non-adherent cells
- ex. activated lymphocytes, lymphoblastoid lines, etc.
- proliferate in suspension
- estimate cell density by turbidity/cell count
- passage by dilution and transfer
cryopreservation protocol
- culture medium supplemented with 10% dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO)
→ prevents ice crystal formation in cell membranes
- controlled rate freeze
DMSO
→ used when freezing cells to prevent ice crystal formation in cell membranes
major caveat with passing cells
after X passages, are the cells really the same as what you started with?
→use cells at lowest passage for experiments
patterns of proliferation of cells
- normal cells in vitro will reach a point of senescence and death around P14-P20
- transformed cell lines will continue to divide
Properties of transformed cells in culture
- immortal: proliferate indefinitely
- rapid proliferation, high mitotic index
- loss of contact inhibition
- anchorage independent growth → proliferation in soft agar
- ultimate indicator of oncogenic transformation
mitotic index
the ratio between the number of cells in mitosis to the total number of cells.
hemocytometer
Instrument used in counting blood cells
- trypan blue viability assay
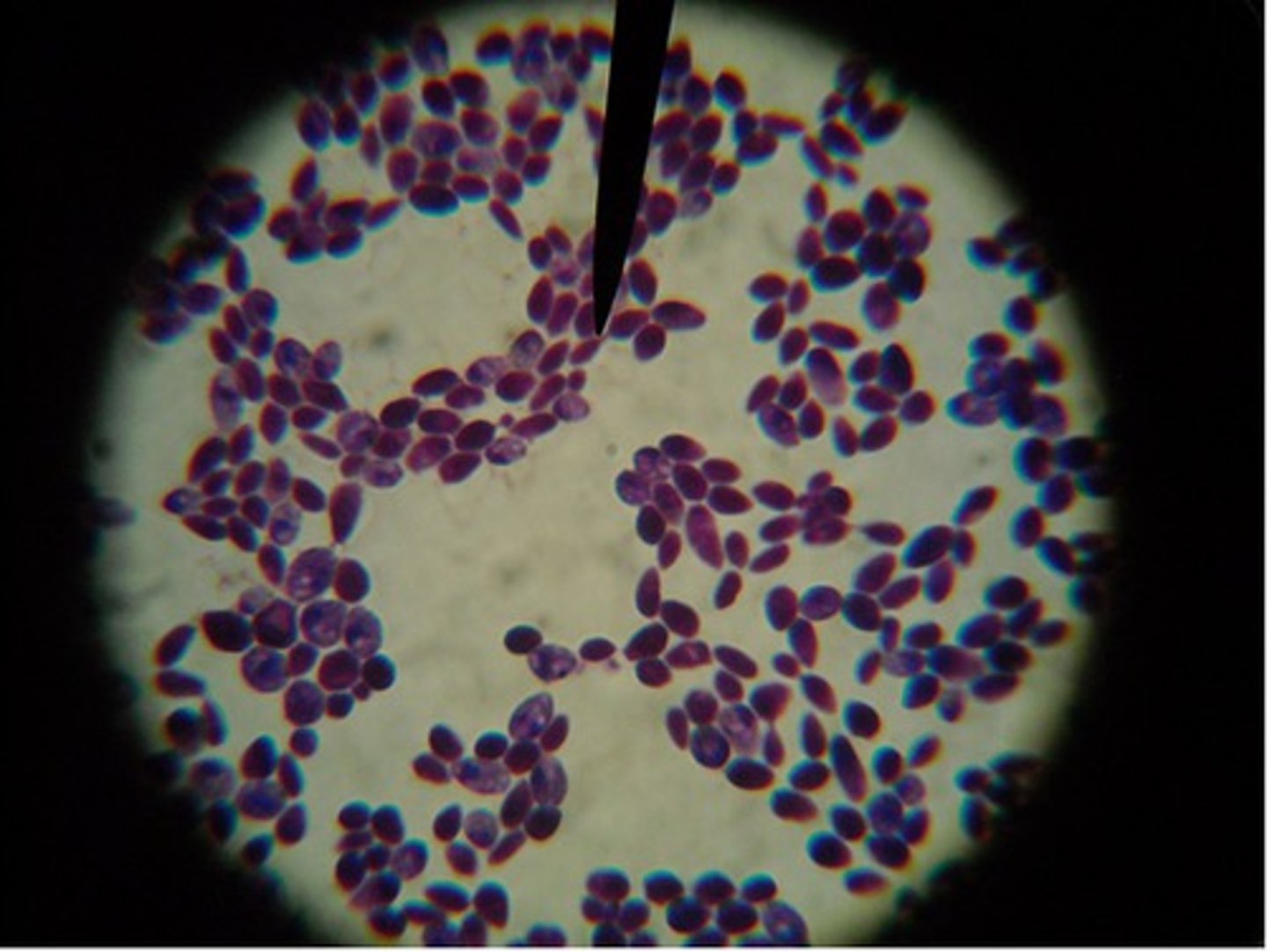
common cell culture contaminants
- fungus: mold, yeast
- bacteria
- Mycoplasma
if bacteria/fungus: media will turn yellow (lower pH) and cloudy
trypan blue
a viability stain used to differentiate dead cells (blue) from living cells (clear)
automated object counter
counts cells
-> makes cell counting very easy, bust it is very costly
yeast contaminated culture
Mold Contamination
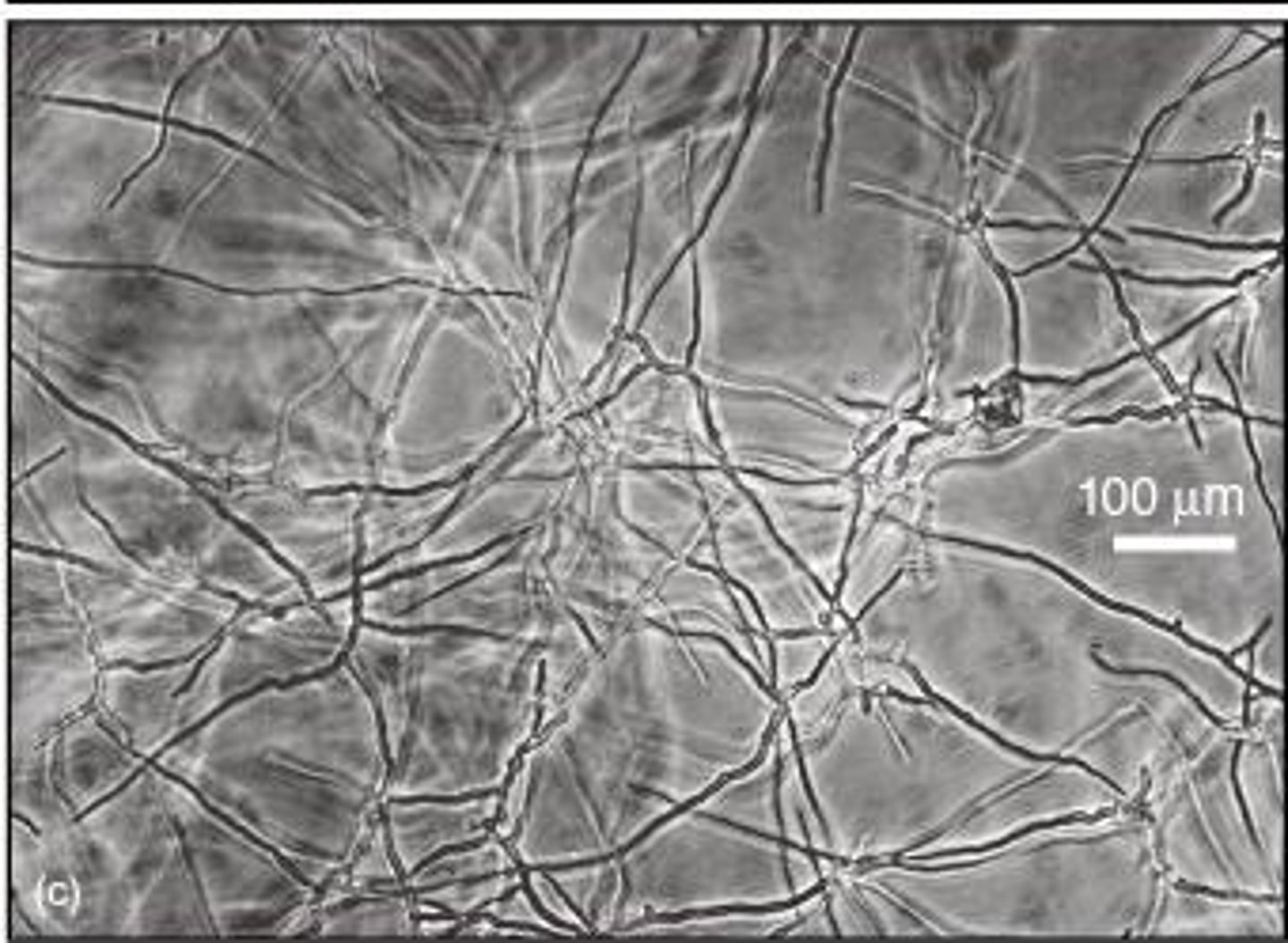
differential interference image
allows you to see bacterial contamination
Mycoplasma
- smallest bacterial genus
- lack a cell wall
- adherent to cell membranes
- do not change media color; difficult to tell if contaminated
how to avoid contamination
- sterilization of all reusable vessels/instruments
- atmosphere control via BSC , incubator
- proper PPE, gloves, lab coat, sleeve protectors
- aseptic technique
gas autoclave
Used to sterilize medical supplies and equipment that cannot be exposed to high heat, pressure and/ or steam; commonly found in specialty practices
uses ethylene oxide: highly toxic
filter sterilization
used to sterilize heat-sensitive liquids
(0.20 micron filters)
aseptic technique
- clean all items with ethanol before placing in hood
- minimize time reagent bottles/culture vessels are open
- clean work surface with ethanol before/after
- decontaminate hood with UV for ~10 min
- seal reagents with parafilm
- frequently inspect incubators/refrigerators
cell markers
technically identifiable characteristic SPECIFIC to a particular cell type of class of cell types
- cell surface or cytoplasmic protein
- particular carbohydrate moiety
- specific enzymatic activity
selection strategies
positive selection: active "capture" of cell type of interest
negative selection: elimination of cells other than those of interest
selection characteristics
- adherence characteristics
- sensitivity to injury (ex. sensitivity to hypotonic disruption)
- cell density (ex. gradient centrifugation to isolate different blood cells)
- rate of proliferation/longevity in culture
- focus formation
- selective culture media
- antibody-mediated selection methods (ex. magnetic sorting, fluorescence activated sorting)
- cloning
- antibiotic resistance
selection by cell density
- gradient centrifugation
- ex. isolation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from blood
antibody mediated selection: magnetic
- magnetic labelling of cells
- negative selection: unwanted cells have magnet
- positive: wanted cells have magnet, then are recovered after washing
fluorescence-activated cell sorting
cloning selection strategy
used for the propagation of identical cells from a single cell
antibiotic resistant selection strategy
applies mainly to transfected cells
why use agarose gel when culturing cells?
- to screen for transformed cells
- as a mobility constraint for cells
trans-well coculture inserts
filter membrane inserts of various pore sized; inserted into a culture well
- allows you to culture two different types of cells without having them directly contact each other
ex. use to study the impact of T-cell cytokines upon nearby uninfected endothelial cells
Matrigel
a simulated extracellular matrix
perfusion culture
- the simulation of vascular shear stress
simulates the shear stress felt by vascular cells from rapid blood flow
Organoids
miniaturized and simplified version of an organ produced in vitro in three dimensions that shows realistic micro-anatomy
bioreactor
A vessel or container in which living cells or their products are used to make a product
--> mass production of products of genetically engineered bacteria or eukaryotic cells (ex. hormones, growth factors, etc.)