ch10 - thermochemistry
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Law of Conservation of Mass
mass cannot be created nor destroyed
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy (ex: heat) is conserved; it can change form but cannot be created or destroyed.
Energy
The capacity to do work.
Radiant Energy
Energy from the sun; Earth’s primary energy source.
Kinetic Energy
Energy of motion; KE = 1/2 mv².
Thermal Energy
Energy associated with the random motion of atoms and molecules.
Chemical Energy
Energy stored in the bonds of chemical substances.
Nuclear Energy
Energy stored within the protons and neutrons of an atom.
Gravitational Energy
stored potential energy due to height of object
Heat
Transfer of thermal energy between bodies at different temperatures.
Temperature
Measure of a substance’s thermal energy.
what is the difference between heat and temperature?
Heat refers to the transfer of thermal energy between bodies, while temperature is a measure of a substance’s thermal energy.
Thermochemistry
Study of heat changes in chemical reactions focusing on initial and final states (intermediate steps don’t matter).
System
Specific part of the universe under study.
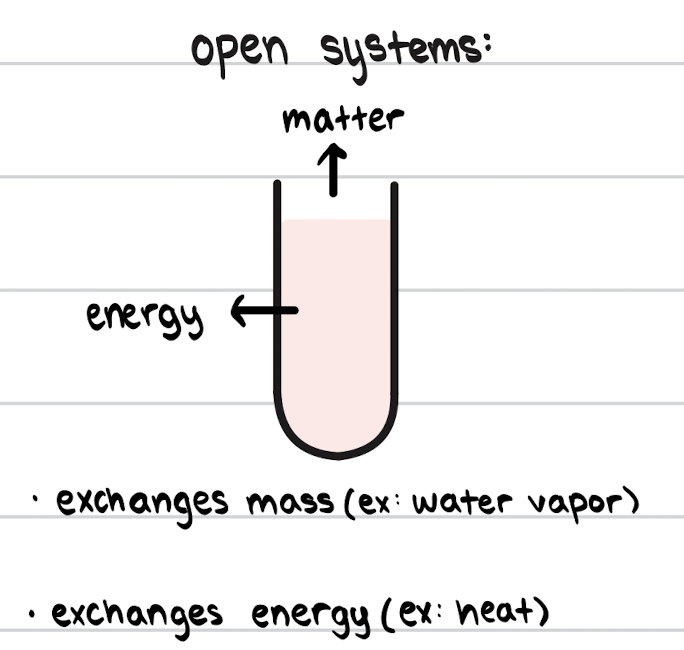
Open System
Exchanges both mass and energy with surroundings.
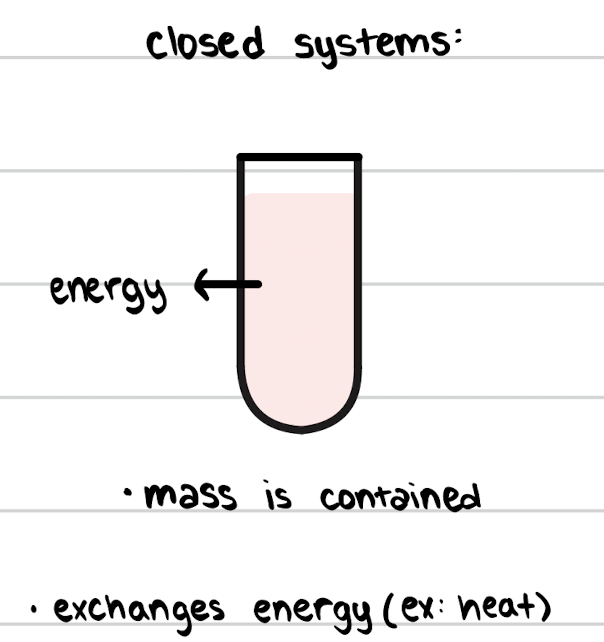
Closed System
mass is contained, but the system exchanges energy with the surroundings.
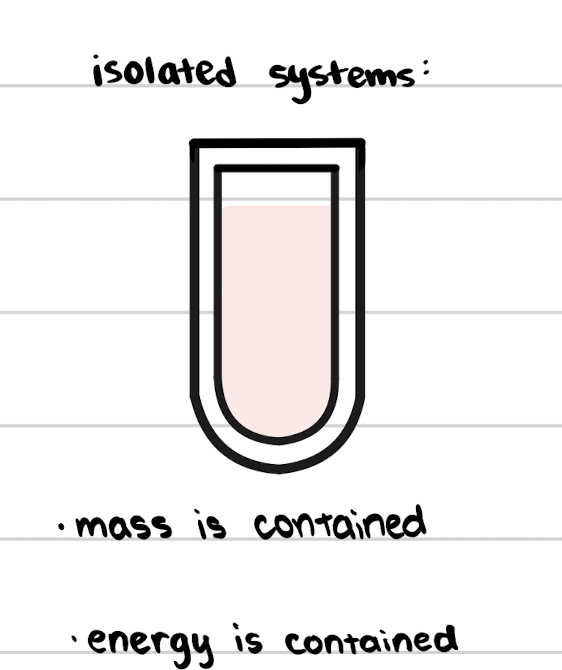
Isolated System
Exchanges neither mass nor energy with surroundings.
Exothermic Process
Releases thermal energy from system to surroundings (ΔH < 0).
In a reaction equation, energy is a product.
Endothermic Process
Absorbs thermal energy from surroundings into system (ΔH > 0).
In a reaction equation, energy is a reactant.
define the First Law of Thermodynamics and its corresponding equations.
Energy can change forms but cannot be created or destroyed; the total energy of an isolated system remains constant.
ΔEsystem + ΔEsurroundings = 0
ΔEsystem = -ΔEsurroundings
ΔE = q + w
w = -PΔV
define the variables in the formula:
ΔE = q + w
ΔE = the change in internal energy
q = heat exchanged between system and surroundings
w = work done on/by the system
w = -PΔV
what does positive work mean? (+w)
work on system by surroundings
what does negative work mean? (-w)
work by system on surroundings
what does positive heat mean? (+h)
endothermic
heat absorbed by system from surroundings
what does negative heat mean? (-h)
exothermic
heat released by system to surroundings
define enthalpy and its corresponding variable and equations.
used to quantify the heat flow into or out of a system at constant pressure
Enthalpy = H
q = ΔH
q = msΔt
ΔE = ΔH - PΔV (same as ΔE = q+w)
ΔH = Hproducts − Hreactants
how do you know if ΔH is endothermic or exothermic?
ΔH = Hproducts − Hreactants
ΔH > 0 = endothermic
ΔH < 0 = exothermic
define the variables in q = msΔt
q = amount of heat absorbed/released
m = mass
s = specific heat
Δt = Tfinal - Tinitial = change in temperature
Bond Dissociation Energy
Energy required to break a specific chemical bond.
Lattice Dissociation Energy
Energy needed to break an ionic solid into its gaseous ions.
Heat of Formation
Heat required to form 1 mole of a compound from its elements in standard states.
compare ΔH and ΔE
ΔH refers to the enthalpy change, or the change in heat flowing in or out of a system at constant pressure.
ΔE represents the change of internal energy in a system.
relationship: ΔE = ΔH - PΔV
Specific Heat (s)
Heat required to raise 1 g of a substance by 1 °C.
Heat Capacity (c)
Heat required to raise the temperature of a given quantity by 1 °C.
Hess’s Law
Total enthalpy change for a reaction is the same regardless of the pathway taken.
only final and initial states of the system are compared, the intermediate states don’t matter (given that the conditions are the same)