MLT 1112 Final Exam- Study Guide
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
177 Terms
Diagnosis
Identification of a disease is termed:
Laboratory Assistant
This health care employee primarily processes laboratory specimens for testing, and may or may not perform the venipuncture procedure:
Needed Immediately
The physician placed an order for a stat blood test. This means that the test is:
Accredited
This is when an organization is recognized for being compliant with industry standards:
Autopsy
Determining the cause of death by examining a dead person's body:
Cancer
An uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells:
Certification
This confirms that the requirements for an industry credential were completed:
Nitrile
The most commonly used gloves in the laboratory:
Class C
This class of fire involves electrical wiring:
Class A
This class of fire involves paper:
Class B
A fire involving gasoline is in this class:
Class A
A water fire extinguisher is used for these types of fires:
Rescue anyone in danger
The first action to take when finding a fire:
Quality Assessment
Monitor and evaluate the ongoing and overall quality of the total testing process:
Proficiency Testing
A method to externally evaluate the quality of a laboratory's performance:
Accreditation
A process involving an internal self-study and external peer assessment by which organizations measure their performance against established standards:
HBV
Select the virus that a vaccine has been developed for and encouraged for use by health care professionals:
Waived Complexity Tests
Simple laboratory examinations and procedures that have an insignificant risk of an erroneous result:
Engineering Controls
Controls that isolate or remove the bloodbourne pathogens hazard from the workplace:
Compliance
Following regulations or other mandate is known as:
Diagnosis
Identification of a disease or clinical condition:
CMS
The regulatory agency that regulates all laboratory testing (except research) performed on humans:
FDA
This agency categorizes tests based on method complexity:
High Complexity
This type of testing complexity includes manual methods:
GHS
A common and coherent approach to classifying chemicals and communicating hazard information on labels and safety data sheets:
Type B
The type of immersion oil commonly used in the clinical laboratory:
Resolution
As the numerical aperture increases, the ___________ ability increases:
Anemia
A decrease in hemoglobin and/or erythrocytes is termed:
Erythrocytes
Select the cells that circulate for 120 days:
Erythrocyte Count
Select the test that is always included in a CBC:
Thrombocyte
The major blood component involved in primary hemostasis is the:
Hematocrit Test
This is the packed cell volume of erythrocytes reported as a percentage of total blood volume:
Lymphocytes
Erythrocytes in healthy adults are about the same size as these cells:
Erythrocytes
The RDW detects abnormal variation in the size of:
Leukopenia
A decrease in white blood cells is known as:
Critical Value
A life-threatening clinical laboratory result:
B-Cells
These cells produce antibodies:
Thymus
The T - lymphocyte develops in the:
Monocyte
The largest mature white blood cell in the peripheral blood is the:
Lymphocyte
The smallest white blood cell in the peripheral blood is the:
Fibrinolysis
The breakdown and removal of a fibrin clot is known as:
Anisocytosis
Size variation
Hypoxia
Deprivation of oxygen
Poikilocytosis
Abnormal shapes
Rouleaux
Abnormal formation of cells
PT/INR
This test is used to monitor oral anticoagulation therapy:
Interpupillary Control
This part of the microscope is used to adjust the distance between the oculars:
50x
Select the objective lens that has a total magnification of 500x:
Base
The field diaphragm is located in the ___________ of the microscope:
1000x
The total magnification while using the oil immersion lens is:
Working Distance
The distance between the objective lens and the object being viewed when the object is clearly in focus is known as:
Larger working distance to a smaller working distance
The clinical laboratory student was using the microscope to evaluate a slide when he switched from the 40x objective to the 100x objective to view the cells. Therefore, the student adjusted the microscope from a:
Nosepiece
This part of the microscope is used to secure the objectives:
Aperature Diaphragm Control Lever
This microscope part controls the light being illuminated through the specimen:
Numerical Aperature
This is noted on the objective and indicates the ability of the objective lens to collect light:
Field of View
The total area visible while looking in the microscope is known as:
They bind calcium
When filled with blood, how do these tubes prevent clotting?
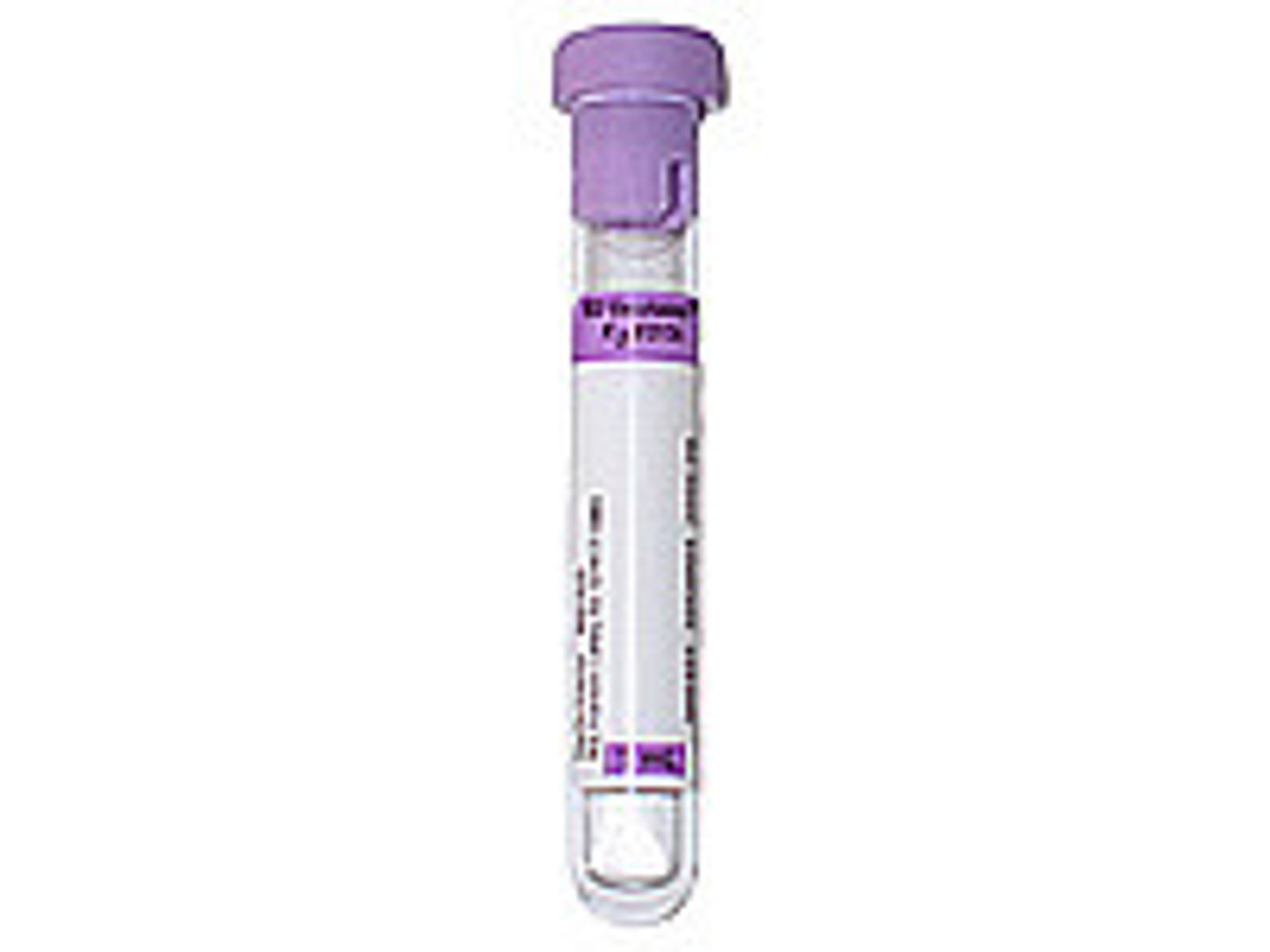
Thrombocytes
These elements of the blood are derived from the megakaryocyte:
Leukocytosis
A white blood cell count of 15.0 x 109/L is known as:
Myeloid Cells
The erythrocytes are derived from:
Capillary
The tiniest blood vessel is known as the:
Peripheral Blood
Blood that circulates throughout the body is known as:
Fibrinogen
A specimen collected in these tubes contains:

Whole Blood
When blood is collecting in EDTA and is not centrifuged, it is considered to be:
Hemoglobin
Select the RBC component needed to carry oxygen:
Nephron
This is known as the functional unit of the kidney:
Uromodulin
The protein produced by the renal tubules:
Urea
This is a by-product formed as a result of the breakdown of protein:
Urochrome
The pigment that gives urine its typical yellow appearance:
On a well-mixed, unspun specimen
The physical and chemical evaluation of urine is performed:
Protein and blood
False negatives for this urine reagent strip test occur with high levels of Vitamin C:
Pyuria
Leukocytes in the urine is known as:
Protein
This urine reagent strip test actually measures albumin:
First morning specimen
Select the preferred urine screening specimen:
Hemoglobin
Bilirubin is formed by the breakdown of:
Anaerobic
Bacteria that grow in the absence of oxygen are called:
Cystitis
Inflammation associated with the bladder is known as:
Urobilin
The pigment that gives feces the characteristic brown color:
Ureter
A muscular tube that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder.
Specific Gravity
This test gives a non-specific measure of the concentrating ability of the kidney:
40x
The microscopic examination of cells in the urine is performed with this microscope objective:
Cystine Crystals
These urinary crystals appear in acid urine. They are colorless with a hexagonal shape. Their presence is always an abnormal finding:
Bilirubin Crystals
These urinary crystals are associated with liver disease:
Polyuria
The patient consistently voids 2600 ml of urine per day. This is known as:
Polydipsia
This is a common symptom of diabetes mellitus:
Oliguria
The patient consistently voids 400 ml of urine per day. This is known as:
Hyposthenuric
The patient's urine specific gravity result read 1.006. Select the term associated with this type of result:
The patient recently had an intravenous pyelogram
The patient urine result for specific gravity read 1.040 by refractometer method. Select the probable explanation:
Reagent Strip pH Test
This urine reagent strip test uses methyl red and bromthymol blue that are sensitive to hydrogen ion concentration. This is the principle for the:
Ketone Test
This urine reagent strip test will yield false positive results if the patient is on levadopa:
Organge
The medication known as Pyridium will cause the urine to exhibit this color:
Ketone Test
Prolonged vomiting and diarrhea may show a positive result on this urine reagent strip test:
Calcium Oxalate Crystal
Select the urinary crystal that may be associated with renal calculi:
Conjugated Bilirubin
This form of bilirubin is water soluble and therefore can be detected in the urine:
Glomerulus
This is also known as the renal corpuscle:
Necrosis
Death of tissue and cells is known as:
Urethra
This is a tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of body:
Squamous Epithelial Cell
These cells indicate vaginal or urethral contamination:
Distal Convoluted Tube
The final concentration of urine occurs here:
Green
Bilirubin in urine that has converted to biliverdin will give urine this color: