Bio 120 chapters 12, 13, 14, and 15
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
1
New cards
Mitosis
a type of cell division that results in two daughter cells having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus
2
New cards
What are the two types of nuclear division?
Meiosis and mitosis
3
New cards
What is cytokinesis?
The cytoplasmic division of a cell at the end of mitosis or meiosis; brings about the separation into two daughter cells
4
New cards
Why do cells divide?
Reproduction
Growth and development
Repair/replace other cells
Growth and development
Repair/replace other cells
5
New cards
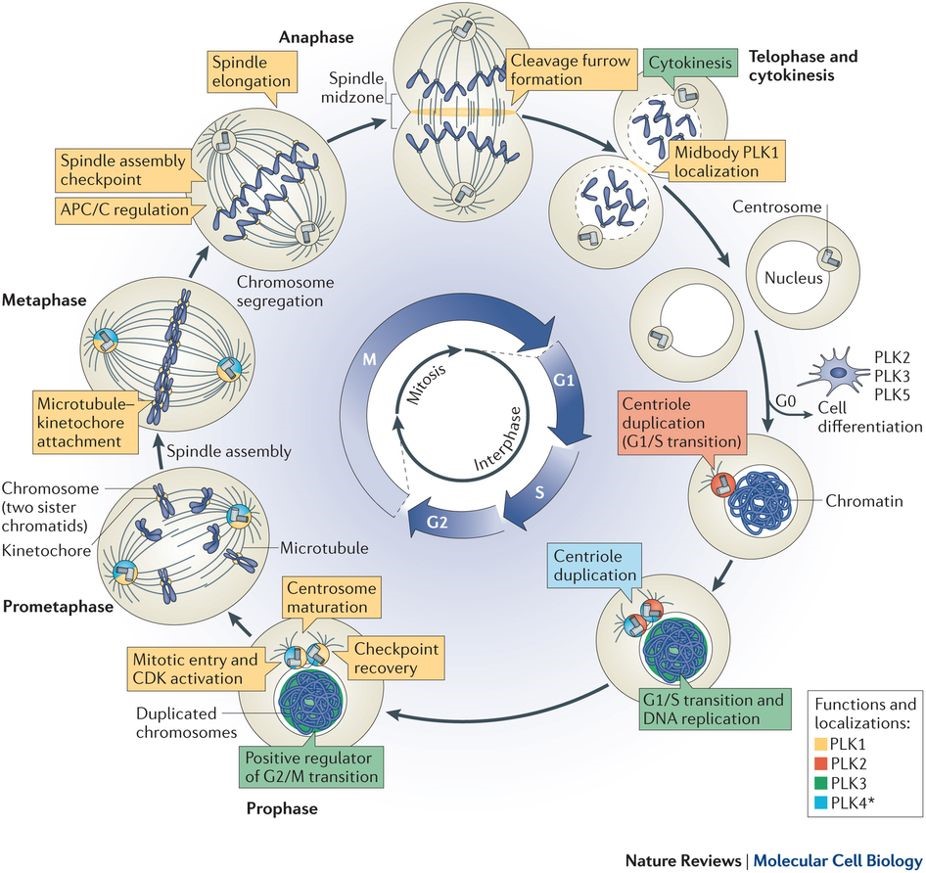
What are the important features of interphase in eukaryotic cells?
Cell acquires nutrients, creates and uses proteins and other molecules, and starts the process of cell division by replicating the DNA. Interphase is divided into three distinct stages, Gap 1, Synthesis, and Gap 2
6
New cards
Be able to draw out the cell cycle; draw out a cell in interphase and explain what’s happening in interphase.
7
New cards
What are the results of mitosis?
Two identical copies of a cell are formed. Increases the number of cells for growth and development
8
New cards
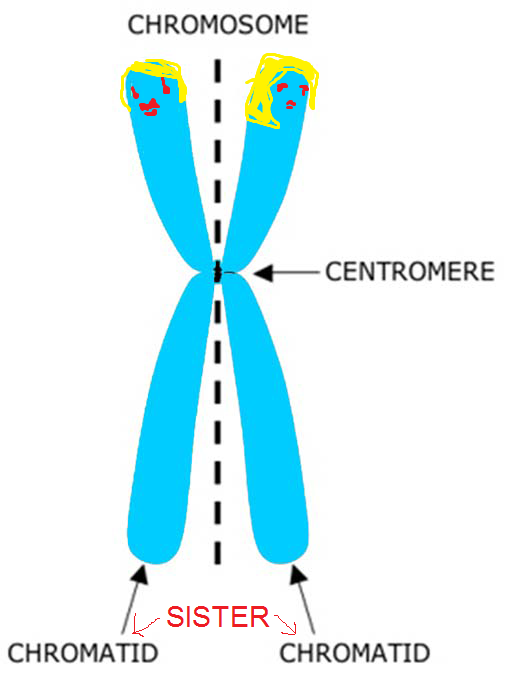
Chromatid
One of two strands of a copied chromosome
9
New cards
sister chromatids
Two chromatids that are joined together at their centromeres
10
New cards
Chromosome
threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found din the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes
11
New cards
Homologous chromosome
same size/shape
12
New cards
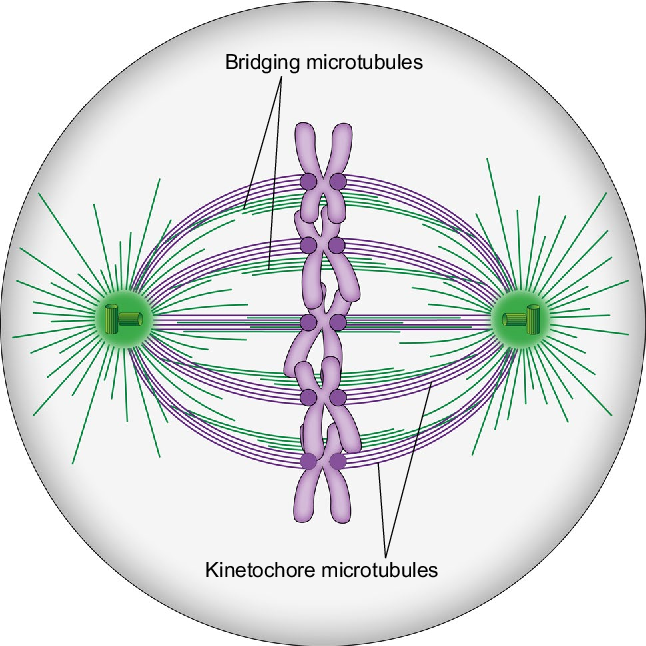
Kinetochore
attach to chromosome and break chromatids
13
New cards
Mitotic spindle
A cell structure consisting of microtubules, which forms during early mitosis and plays a role in cell division
14
New cards
Centrosome
The organizing centers for microtubules involved in separating chromosomes during mitosis
15
New cards
Centromere
The region where the identical DNA molecules are most tightly attached to each other after chromosomes condense
16
New cards
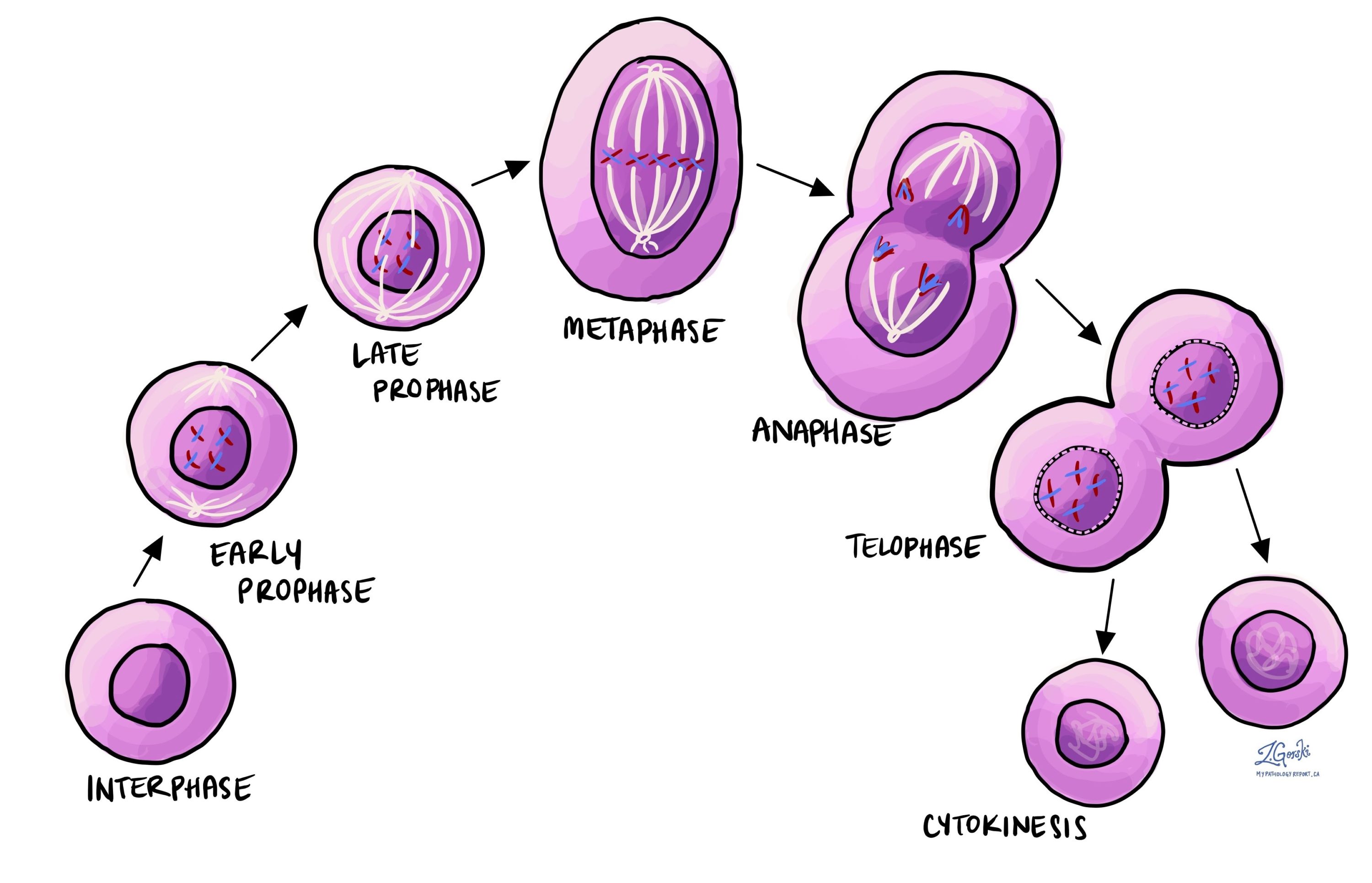
What are the "phases" of mitosis?
Prophase
Prometaphase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase and cytokinesis
Prometaphase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase and cytokinesis
17
New cards
Prophase
1) Chromatin condenses to form chromosomes: 2 sister chromatids attached with centromere and collusion
2) Nucleoli disappear
3) Mitotic spindle begins to form
2) Nucleoli disappear
3) Mitotic spindle begins to form
18
New cards
Prometaphase
1) Nuclear Envelope ruptures
2) Spindle enters nuclear are:
-Kinetochore fibers: attach to chromosome and break chromatids
-Non-kinetochore fibers
2) Spindle enters nuclear are:
-Kinetochore fibers: attach to chromosome and break chromatids
-Non-kinetochore fibers
19
New cards
Metaphase
Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate
20
New cards
Anaphase
1) Sister chromatids separate
2) Move toward opposite poles:
-Pacman method
-Walking/reeling in method
3) Cell elongates- stretches the cell to make it easier to divide
2) Move toward opposite poles:
-Pacman method
-Walking/reeling in method
3) Cell elongates- stretches the cell to make it easier to divide
21
New cards
Telophase and Cytokinesis
1) Nuclear envelope reforms
2) Nucleoli reappear
3) Chromosomes uncoil (form chromatin)
4) Mitosis spindle disappears
5) Cytokinesis happens
2) Nucleoli reappear
3) Chromosomes uncoil (form chromatin)
4) Mitosis spindle disappears
5) Cytokinesis happens
22
New cards
How does cytokinesis differ in plant and animal cells?
Cleavage groove in animal cells
Cell plate formation in plant cells
Cell plate formation in plant cells
23
New cards
What triggers cell division?
1) Growth/development factors
3) Repair/replace other cells
4) Reproduction
3) Repair/replace other cells
4) Reproduction
24
New cards
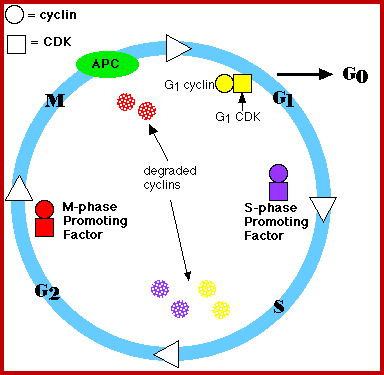
How is mitosis regulated?
1) Checkpoints along the way act like stop signs
2) Really tight regulations that control growth
3) MPF (maturation-promoting factor)
2) Really tight regulations that control growth
3) MPF (maturation-promoting factor)
25
New cards
What happens in meiosis?
-The process of nuclear division in which the number of chromosomes in the nucleus is cut in half, and 4 genetically different nuclei are produced
-Organisms use meiosis when they’re making gametes
-Organisms use meiosis when they’re making gametes
26
New cards
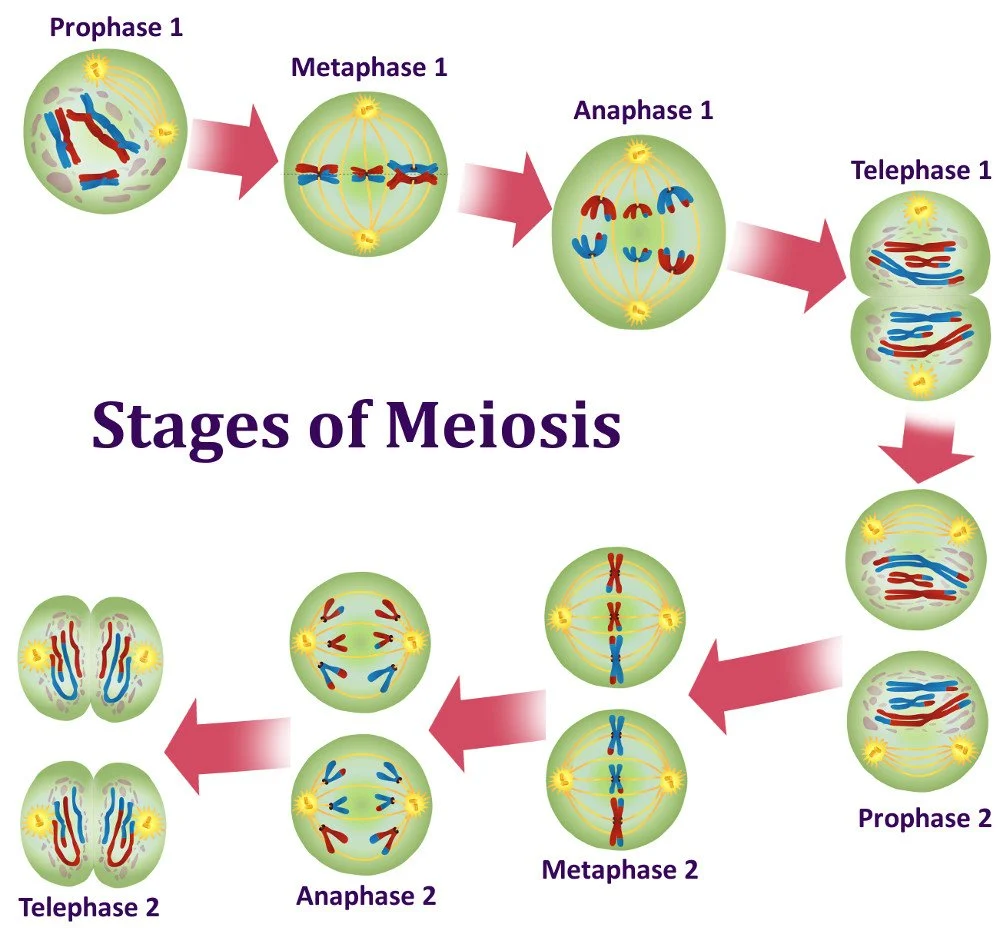
Phases of meiosis/major events
1) Pre-meiotic interphases: cell replicates DNA
2) Meiosis I (reduction division)
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I and Cytokinesis
3) Meiosis II (sister chromatids split)
Prophase II
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Telophase and Cytokinesis
2) Meiosis I (reduction division)
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I and Cytokinesis
3) Meiosis II (sister chromatids split)
Prophase II
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Telophase and Cytokinesis
27
New cards
What are the 3 sources of genetic variation in sexually reproducing organisms?
1) Crossing Over
2) Independent assortment of chromosomes
3) Random fertilization of gametes
2) Independent assortment of chromosomes
3) Random fertilization of gametes
28
New cards
Compare mitosis and meiosis
look at image
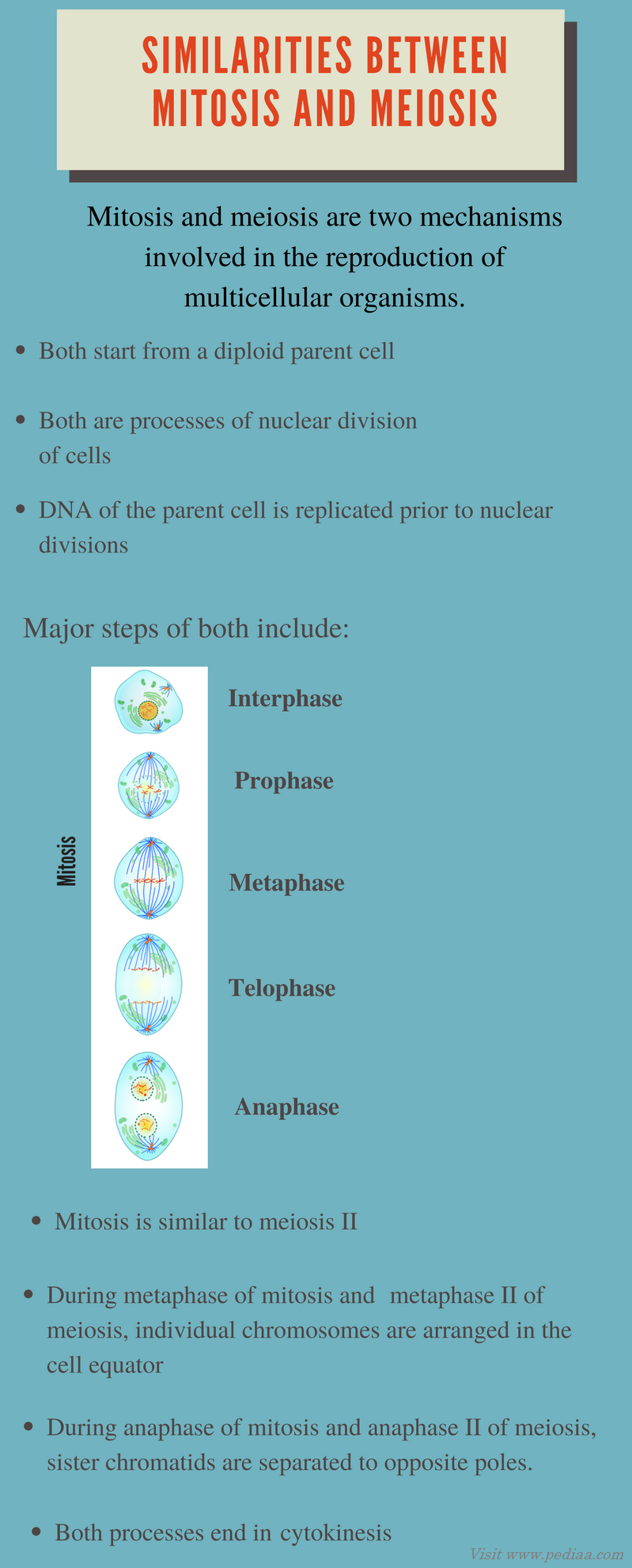
29
New cards
Differences between mitosis and meiosis
look at image
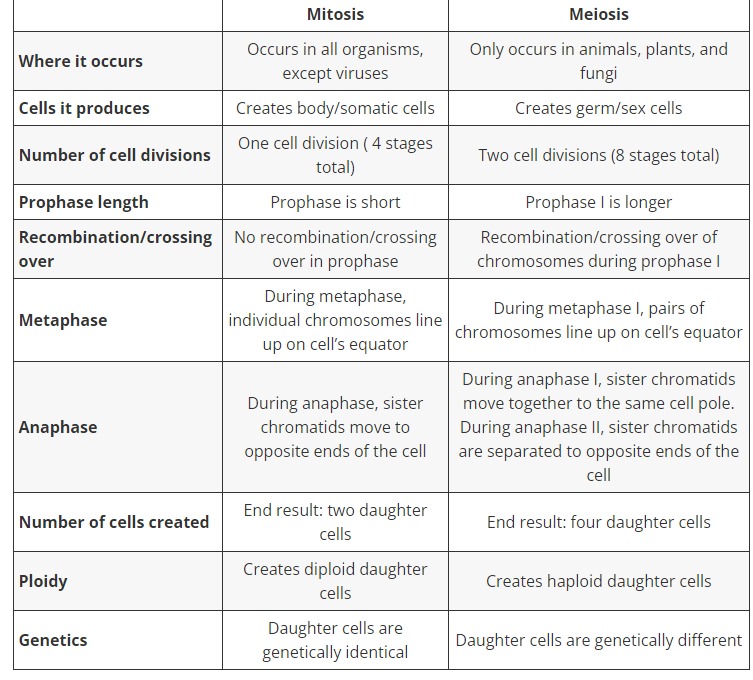
30
New cards
Gametes
An organism's reproductive cells. Also referred to as sex cells
31
New cards
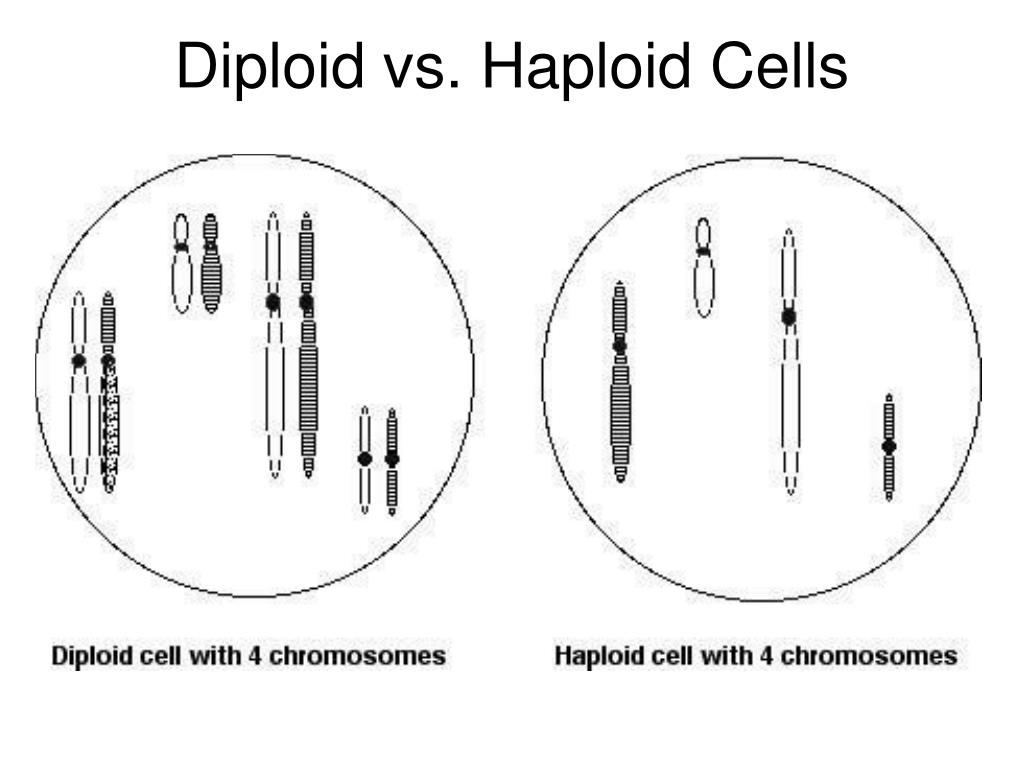
Haploid
Those that have only a single set of chromosomes (n). Haploid cells are formed through meiosis.
32
New cards
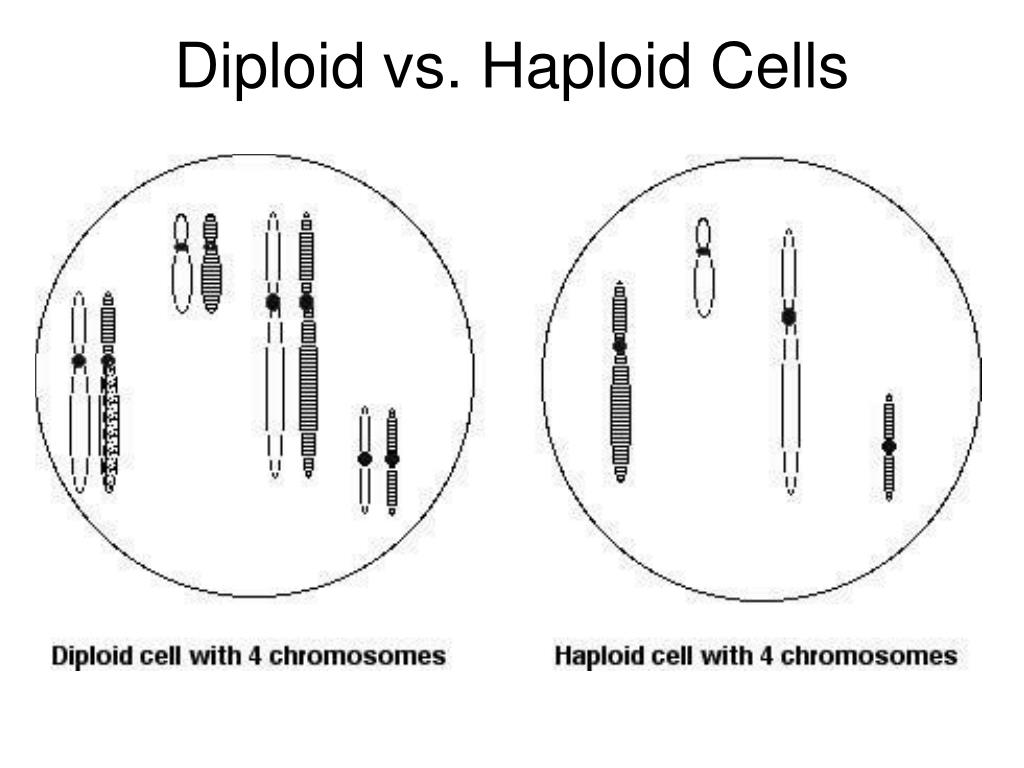
Diploid
Have two sets of chromosomes (2n). Undergo mitosis
33
New cards
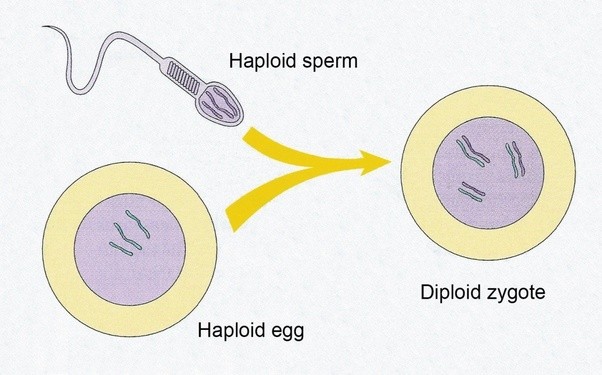
Zygote
a diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes (male and female); a fertilized ovum
34
New cards
What do Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment state? When do these occur? (during meiosis)
Laws of segregation- the 2 alleles for each character segregate (separate) when gametes are made (Meiosis I)
Law of Independent assortment- During the formation of gametes, alleles of 1 gene segregate independently of the allele of a second gene.
Law of Independent assortment- During the formation of gametes, alleles of 1 gene segregate independently of the allele of a second gene.
35
New cards
Alleles
Different forms of a single gene. Account for variations in characters such as flower color
36
New cards
Genes
A unit of heredity which is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristics of the offspring
-Genes come in pairs. Organisms inherit 2 copies of a gene for the same character
-Genes come in pairs. Organisms inherit 2 copies of a gene for the same character
37
New cards
Dominate
The allele that masks the expression of the other allele
38
New cards
Recessive
The allele that typically isn't expressed
39
New cards
Incomplete dominance
A heterozygous for a character doesn’t show a complete dominance/recessive relationship.
Example: Pink genotype for snapdragons as a result form red and white mixing
Example: Pink genotype for snapdragons as a result form red and white mixing
40
New cards
Co-dominance
An organism is heterozygote for a character and both alleles affect the phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways.
Example: Blood groups. I^a and I^b are both dominant and i is recessive
Example: Blood groups. I^a and I^b are both dominant and i is recessive
41
New cards
Pleiotropy
When a single gene has many phenotypic effects
Example: Sickle cell disease (2 copies of the HbS allele)
Example: Sickle cell disease (2 copies of the HbS allele)
42
New cards
What does the norm of reaction refer to?
Describes the pattern of phenotypic expression of a single genotype across a range of environments
43
New cards
What is X-inactivation?
When an Xist gene on one of the X chromosomes acts to inactivate the X chromosome early in embryonic development
44
New cards
Why are tortoise shell cats almost always females?
In order to be tortoise shelled, the cat's genotype has to be X^oX^b. So, has to have XX, which is unusual in males.
45
New cards
What important contribution to biology did Mary Lyon make?
She discovered the Barr body (x inactivation)
46
New cards
What is a Barr body?
In every female mammal, one of the X chromosomes that's inherited becomes inactivated
47
New cards
How many Barr bodies are found in females with a sex chromosome complement of XX? OR XXX?
XX- one
XXX- two
XXX- two
48
New cards
How do chromosomal nondisjunction and lagging result in abnormal chromosome numbers in cells?
The error in cell division results in a different end number of chromosomes
49
New cards
Nondisjunction
When chromosomes fail to separate properly during cell division (meiosis or mitosis)
50
New cards
Lagging
Delayed movement of a chromosome during anaphase
51
New cards
Aneuploidy in non-sex and sex chromosomes in humans
Non-sex: Fairly common and not an issue
Sex: Not as common, and can have devastating results
Sex: Not as common, and can have devastating results
52
New cards
Alterations of chromosome structure
Trisomy: Extra chromosomes(s)
Monosomy: Missing a chromosome(s)
Polyploidy: Having a whole extra set of chromosomes (23)
Monosomy: Missing a chromosome(s)
Polyploidy: Having a whole extra set of chromosomes (23)