AP 2.7 - CNS
1/300
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
301 Terms
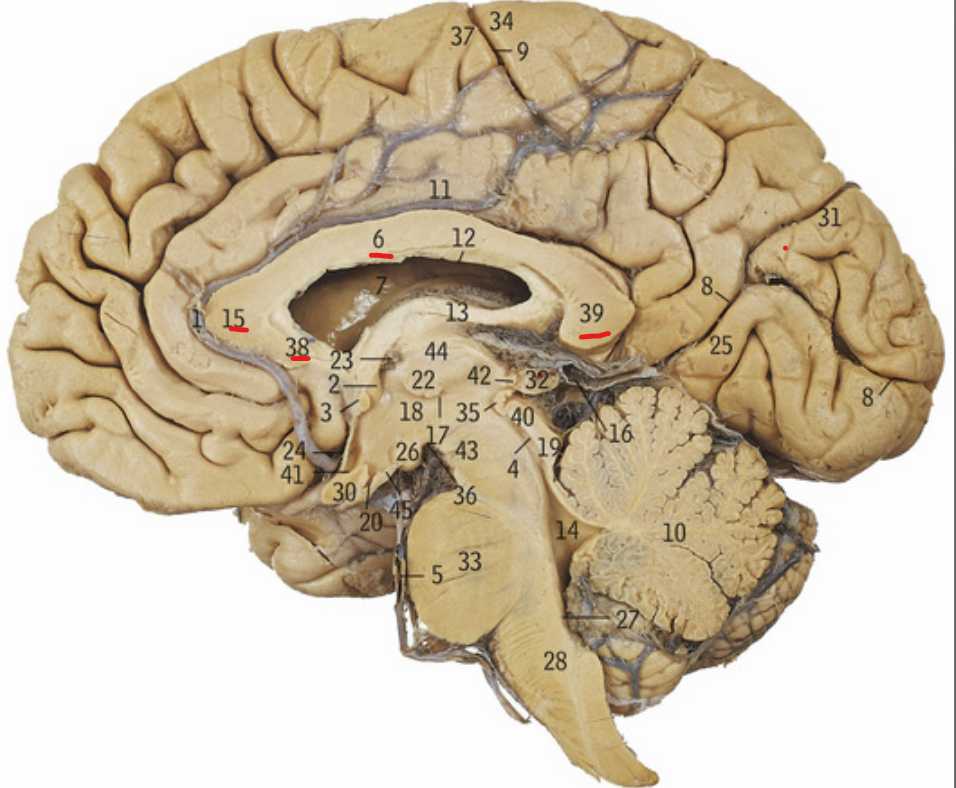
6+15+38+39
Corpus callosum
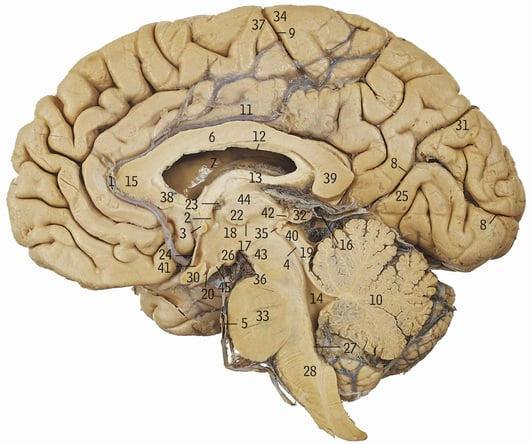
13
Fornix
What does the corpus callosum allow communication between
Cerebral hemispheres
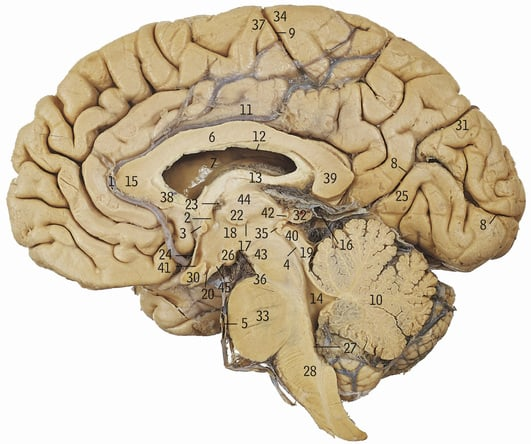
10
Cerebellum
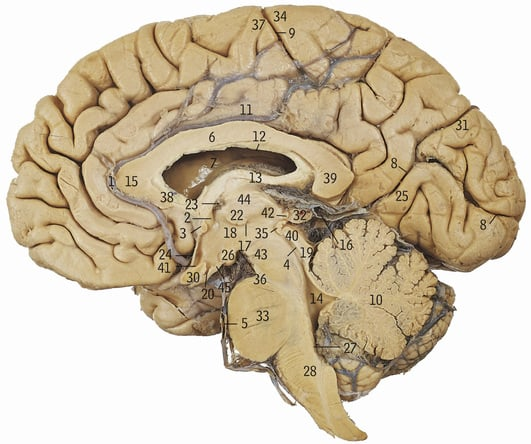
33+28+4+19+40+43
Brainstem
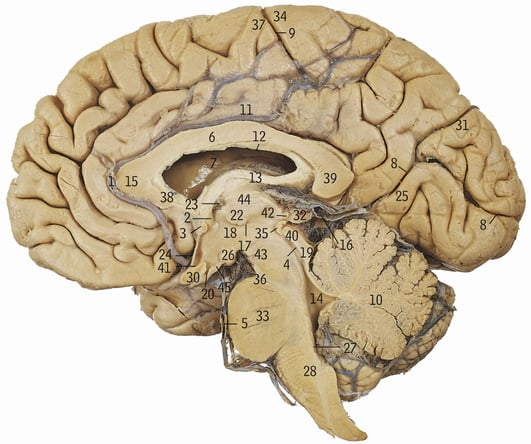
44
Thalamus
33
Pons
28
Medulla oblongata
18
Hypothalamus
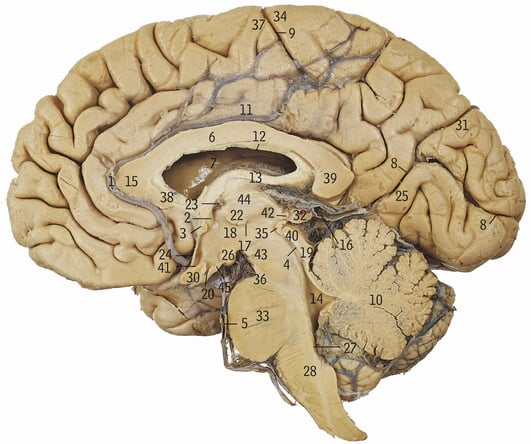
18+44
Diencephalon
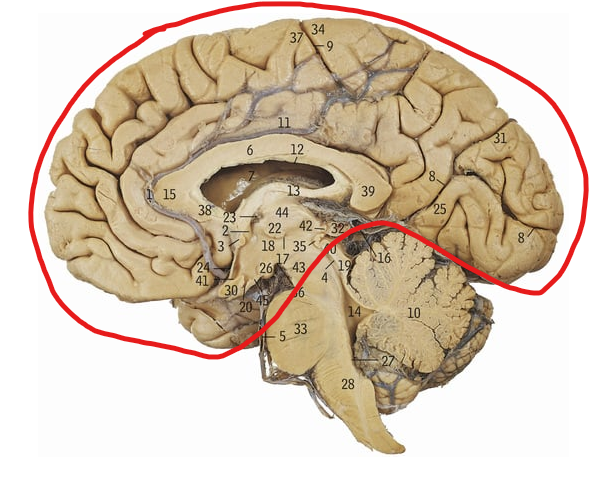
What does the circled area refer to
Cerebrum
What is the forebrain divided into
Telencephalon and diencephalon
What does the hindbrain consist of
Pons, medulla, cerebellum
What is the outer grey matter of the cerebrum called
Cerebral cortex
What is scattered deep within the core of the cerebrum
Basal ganglia
What is white matter divided into
Comissural fibres
Association fibres
Projection fibres
What do association fibres connect
Structures/regions within the same cerebral hemisphere
What do projection fibres connect
Cerebral cortex to the brain stem and spinal cord
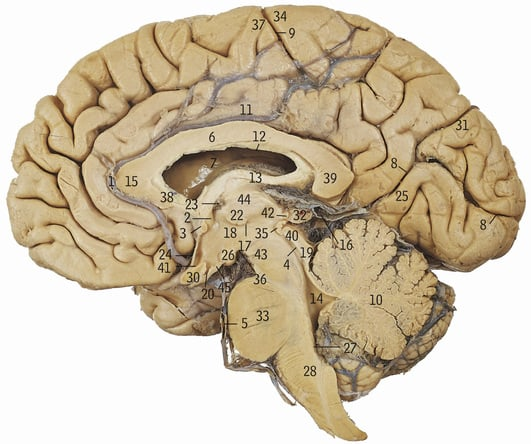
9
Central sulcus
What does the central sulcus mark the boundary between
Frontal and parietal lobes
What does the lateral sulcus mark the boundaries between
The temporal lobe and parietal and frontal lobe
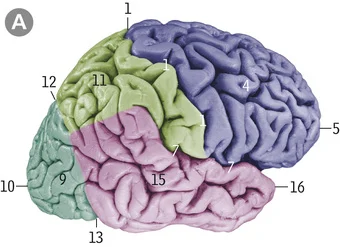
7
Lateral sulcus
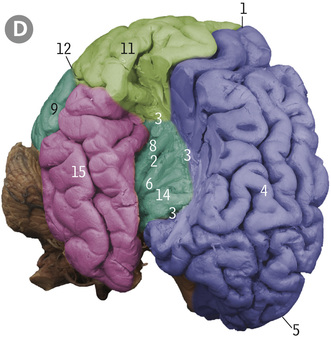
6
Insula
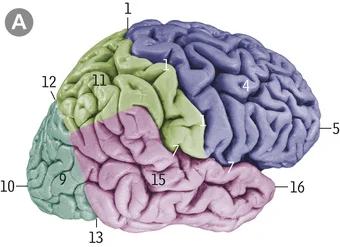
12
Parieto-occipital sulcus
4
Cingulate sulcus
2
Calcarine sulcus
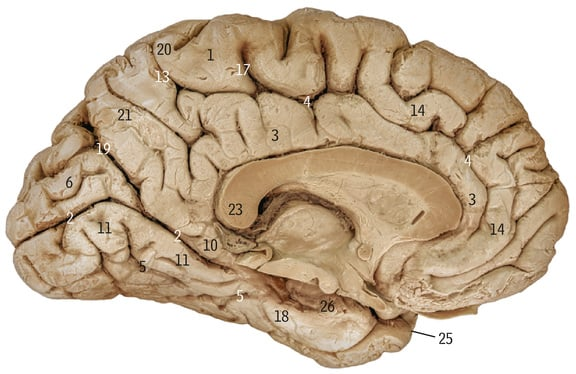
3
Cingulate gyrus
Where is the primary somatosensory cortex located in?
Postcentral gyrus
Where is the primary motor cortex located in?
Precentral gyrus
If there is stimulation of the primary motor cortex, which side of the body does it elicit contraction of
Opposite side
Where is the premotor cortex located
Anterior to primary motor cortex
Where is Broca’s area located
Inferior frontal gyrus
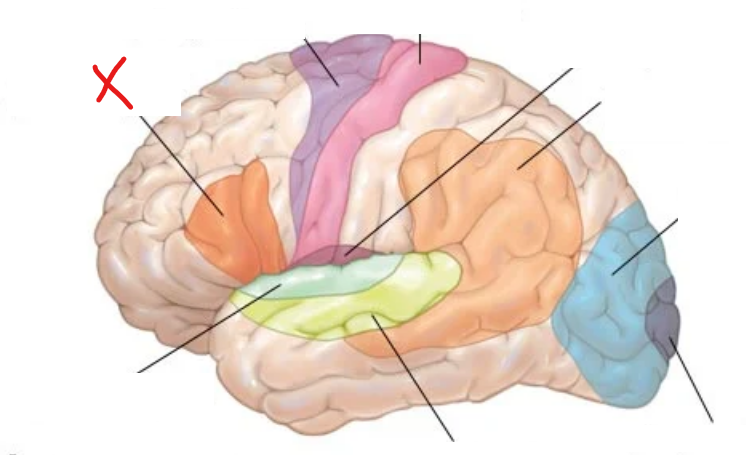
X?
Broca’s area
Where is the primary auditory cortex located
Superior temoporal gyrus
What is the primary auditory cortex responsible for
Conscious percption of sound
What is the name of the area surrounding and immediately posterior to the primary auditory cortex
Auditory association cortex
What is the role of the auditory association cortex
Processes and interprets auditory information
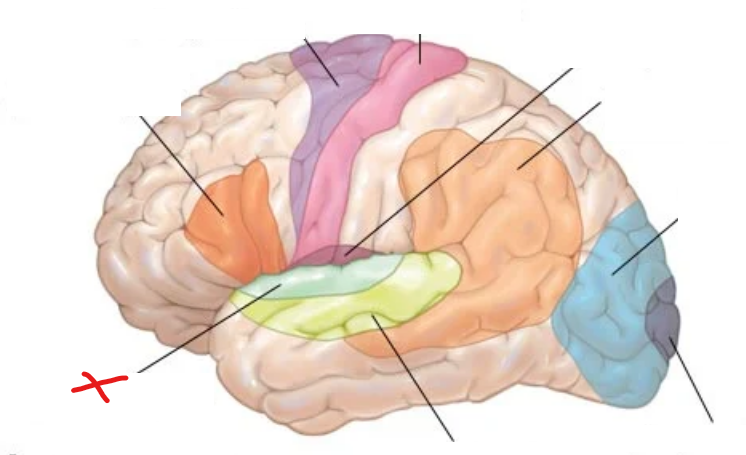
X?
Primary auditory cortex
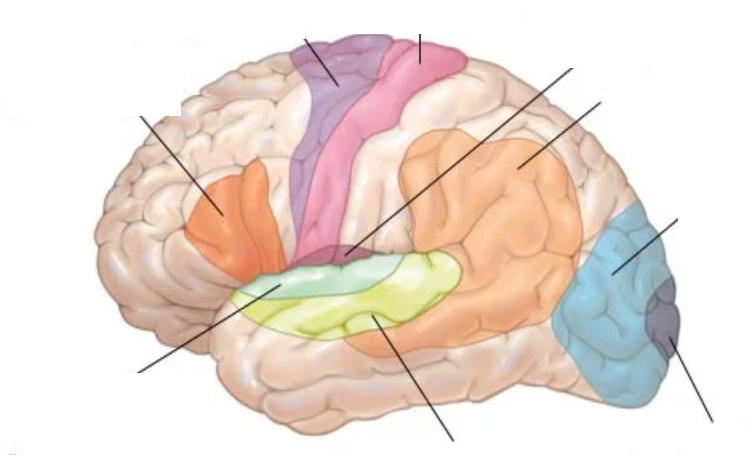
X?
Auditory association cortex
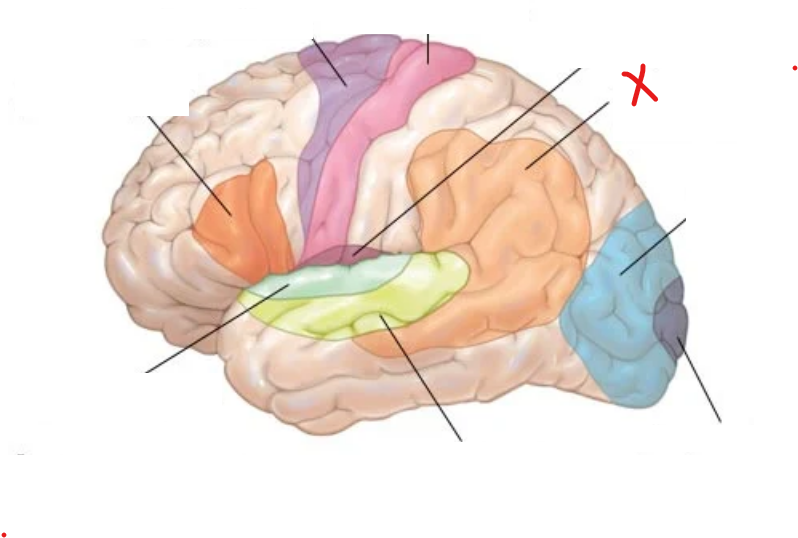
X?
Wernicke’s area
What is Wernicke’s area for
Selecting correct phonemic segment during speech production
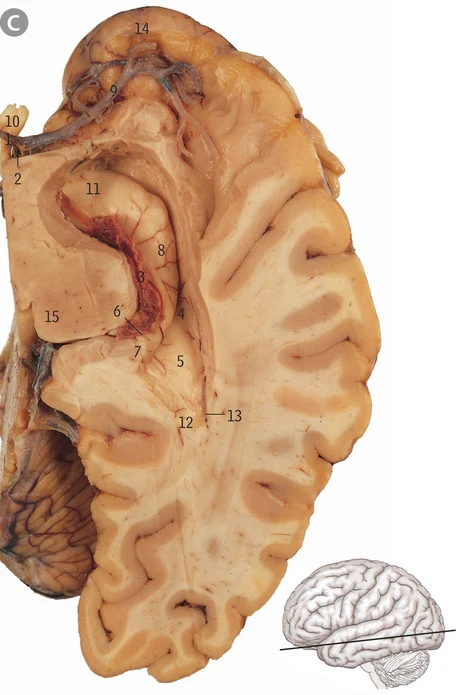
8
Hippocampus
What is the hippocampus’ role
Memory, navigation, emotional aspects of behaviour
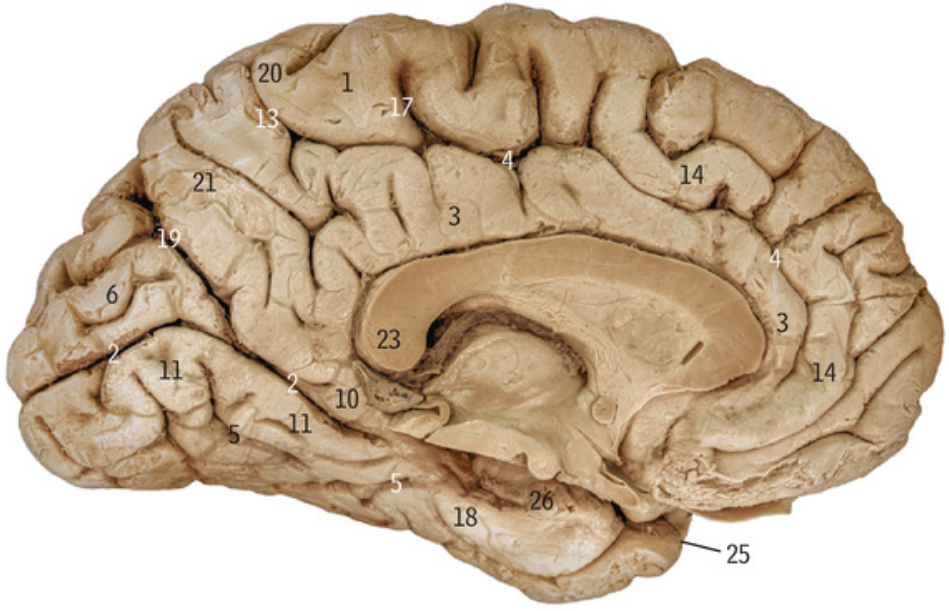
18
Parahippocampal gyrus
Where is the primary visual cortex located
Occipital lobe in calcarine sulcus
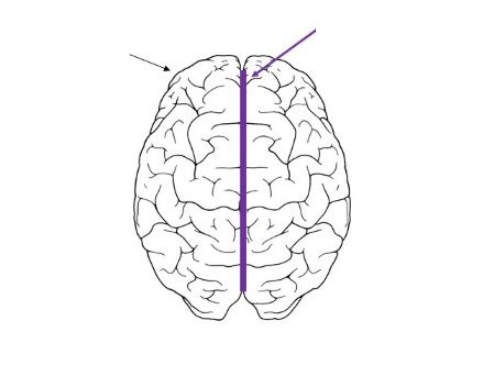
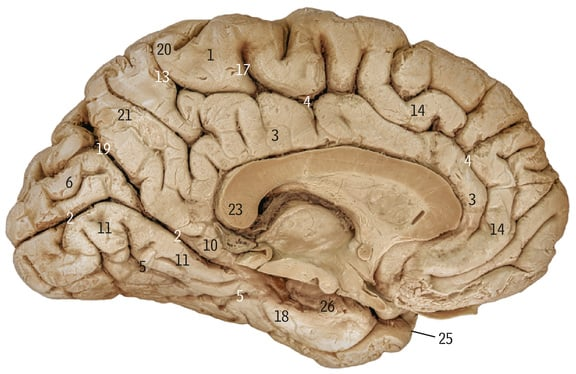
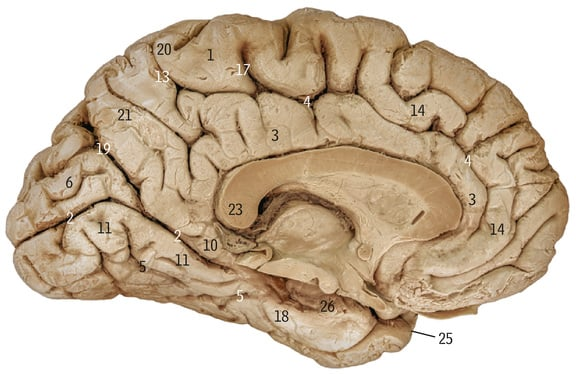
What does the purple line refer to
Greater longitudinal fissure
What artery supplies the area representing the left foot in the primary motor cortex
Right anterior cerebral artery
What artery supplies the area representing the right side of the face in the primary motor cortex
Left middle cerebral artery
What artery supplies the primary visual cortex
Posterior cerebral artery
What artery supplies the primary auditory cortex
Middle cerebral artery
What artery supplies Broca’s area
Middle cerebral artery
What artery supplies Wernicke’s area
Middle cerebral artery
What artery supplies the hippocampus
Posterior cerebral artery
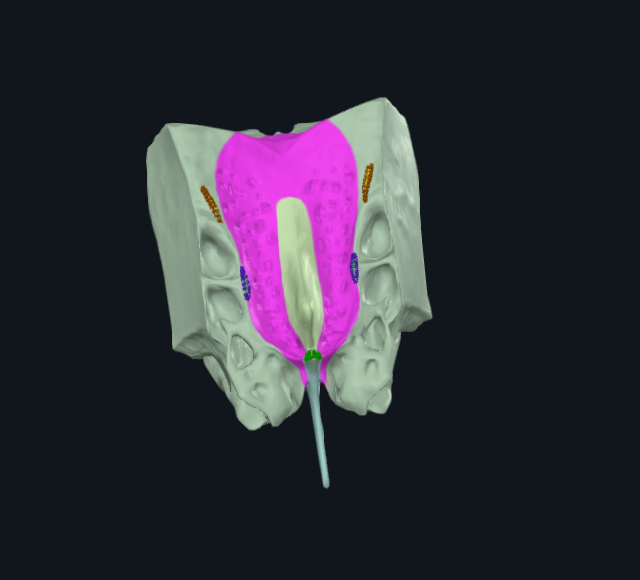
What is highlighted in pink
Cribiform plate
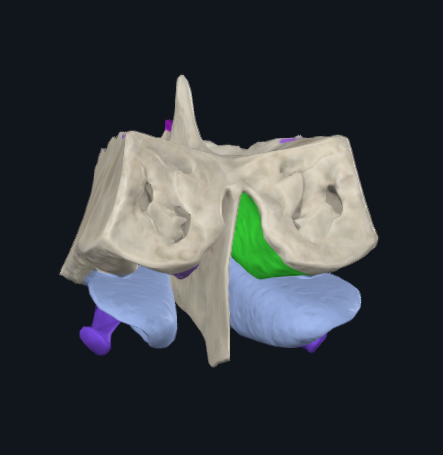
What is highlighted in green
Superior nasal concha
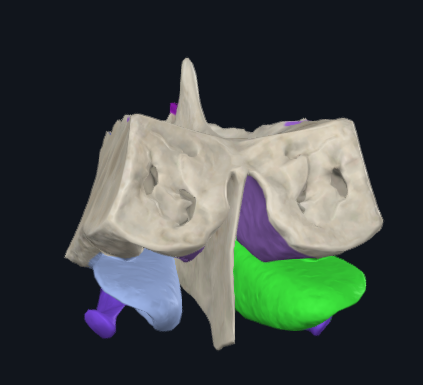
What is highlighted in green
Middle nasal concha
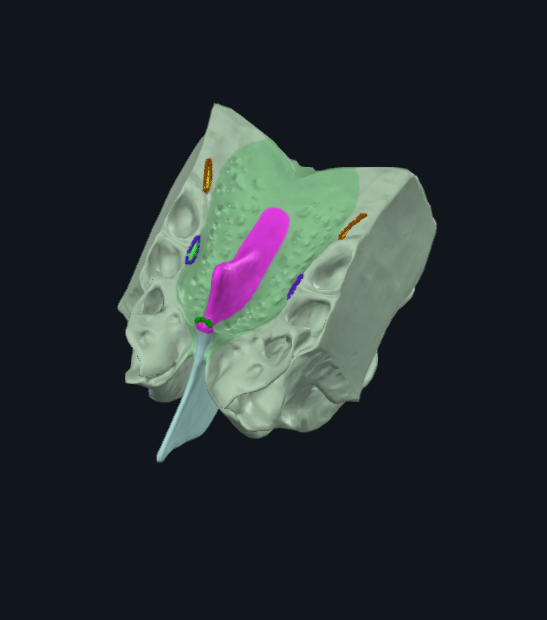
What is highlighted in pink
Crista galli
What attaches to the crista galli
Falx cerebri
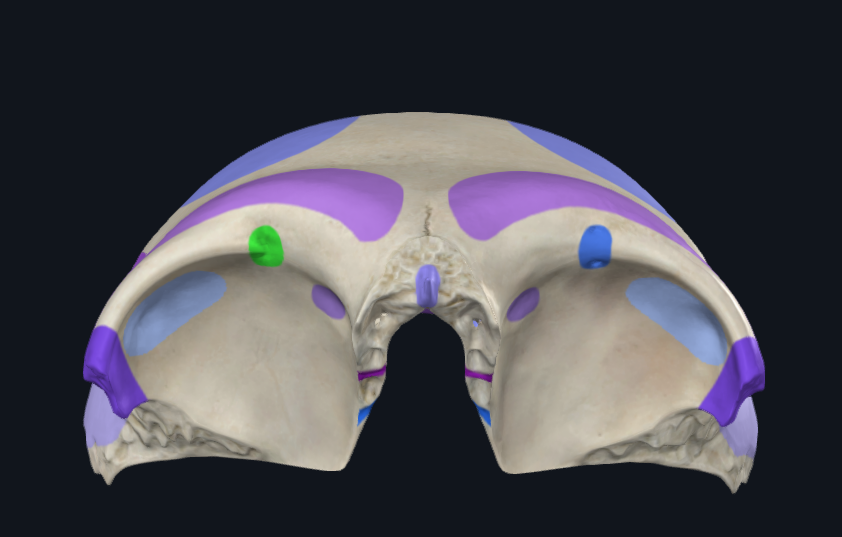
What is highlighted in green
Supra-orbital notch
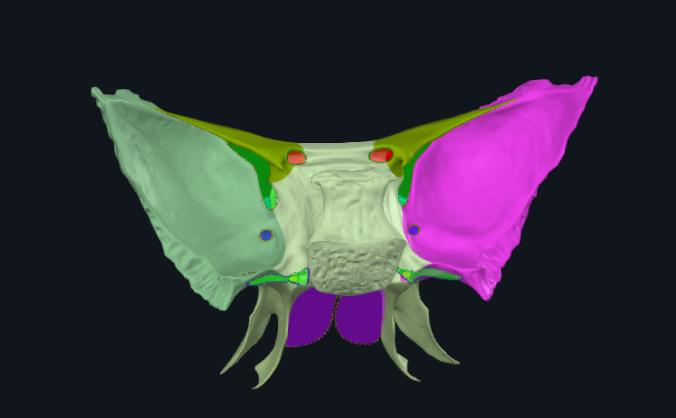
What is highlighted in pink
Greater wing of sphenoid bone
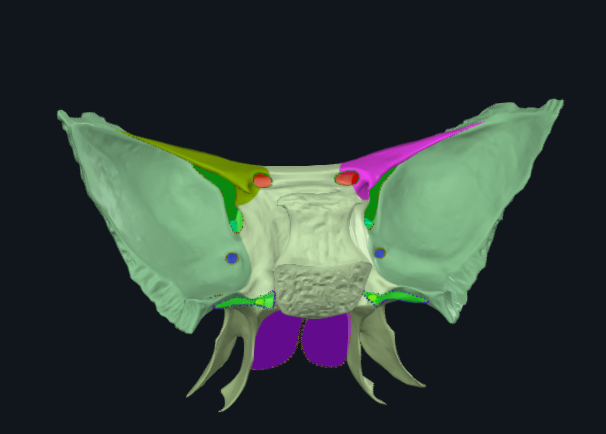
What is highlighted in pink
Lesser wing of sphenoid bone
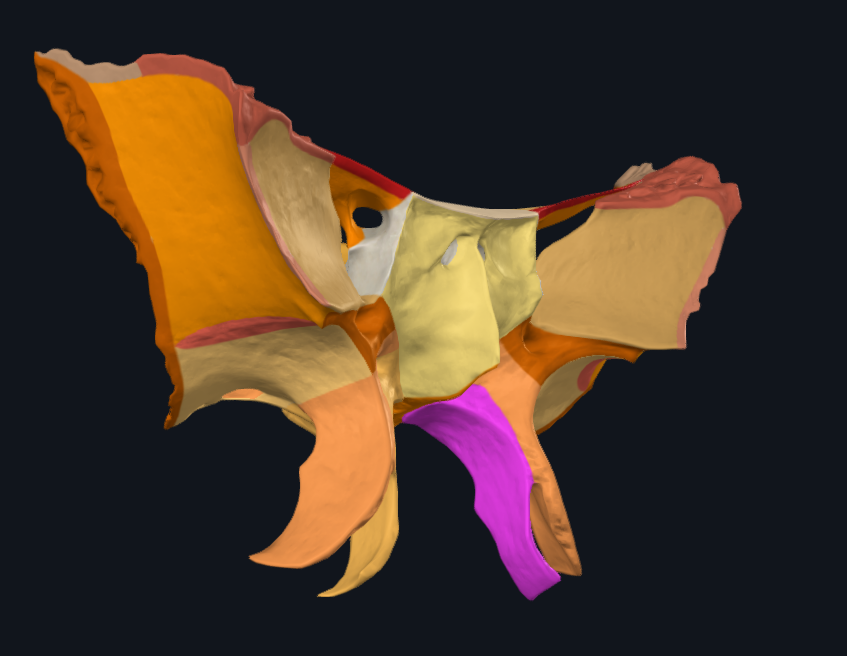

What is highlighted in pink
Medial pterygoid plate
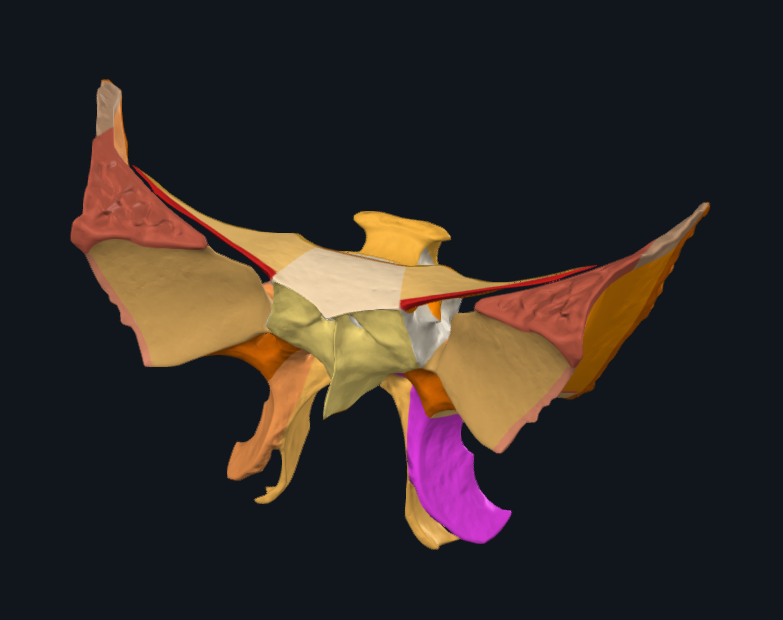

What is highlighted in pink
Lateral pterygoid plate
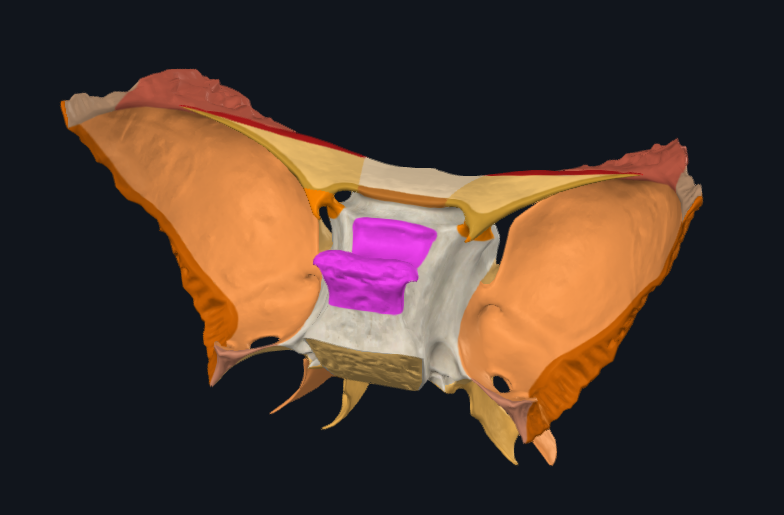
What is highlighted in pink
Sella turcica/pituitary fossa
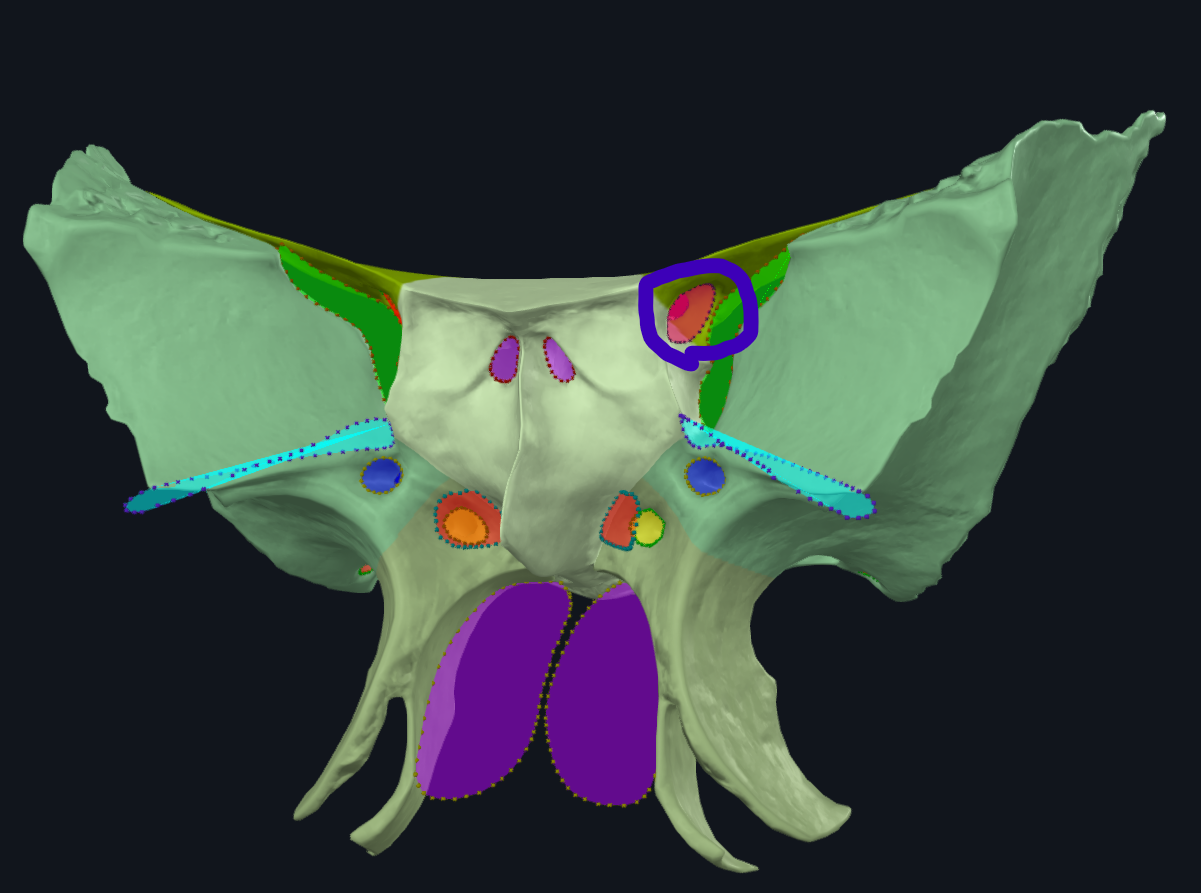
What is circled
Optic canal
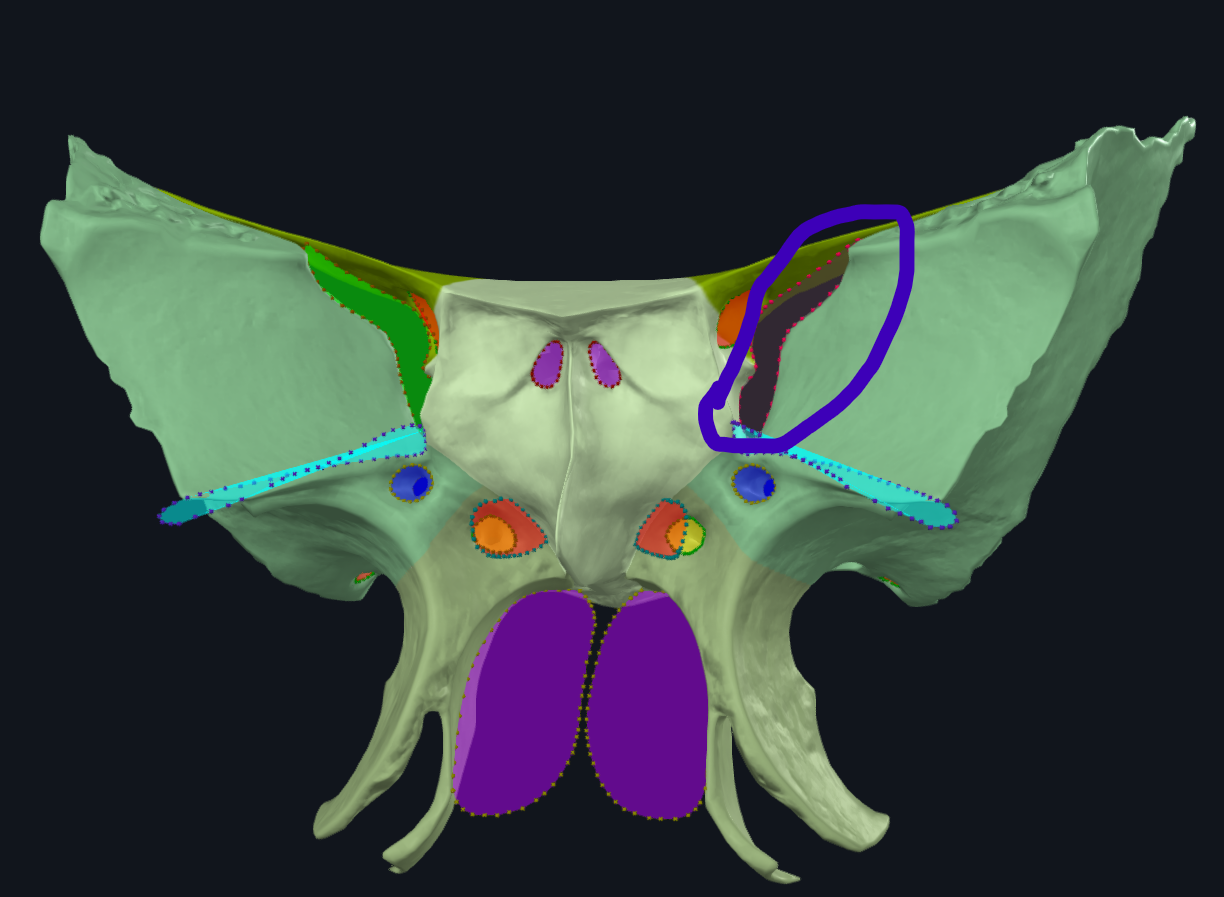
What is circled
Superior orbital fissure
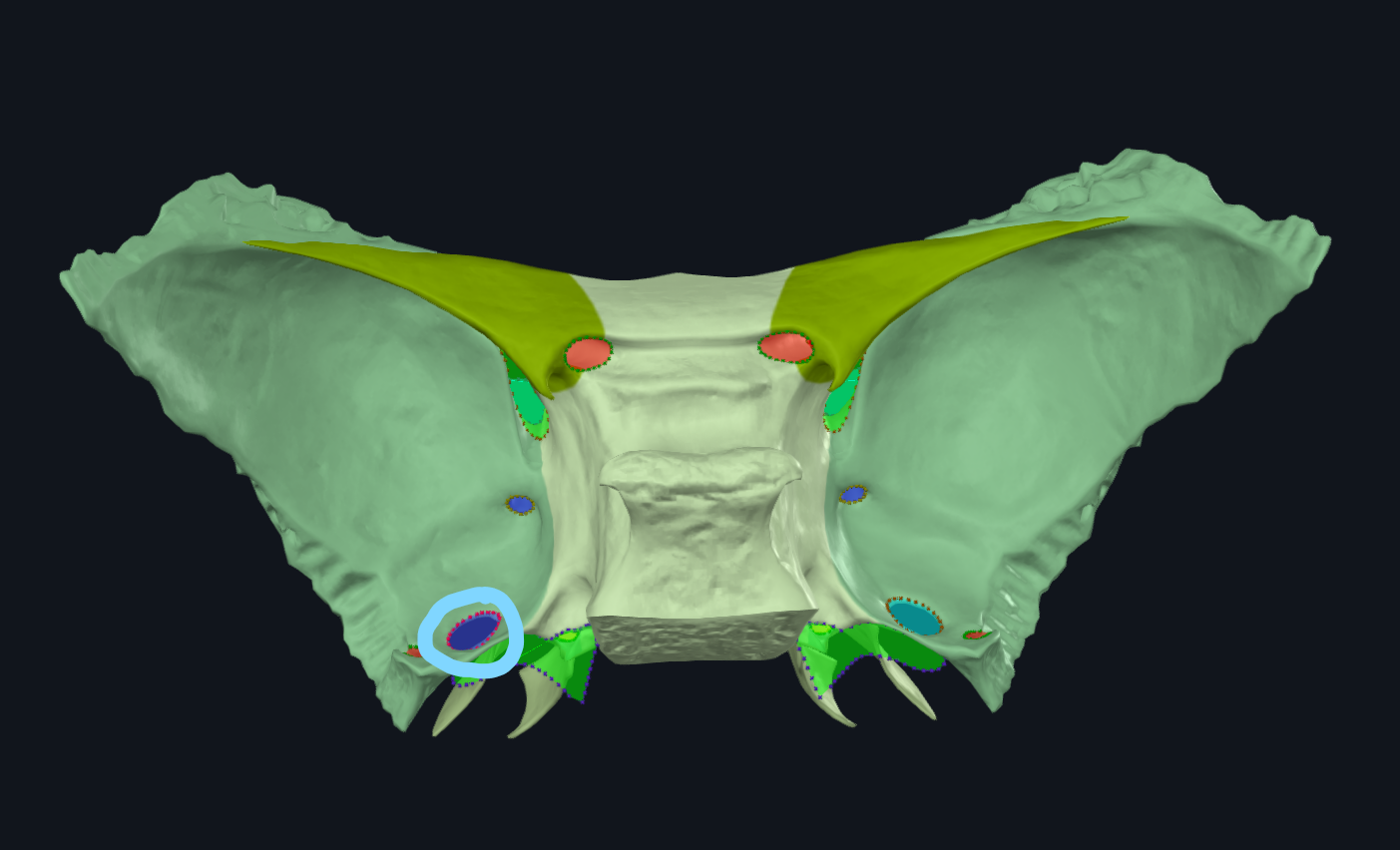
What is circled
Foramen ovale
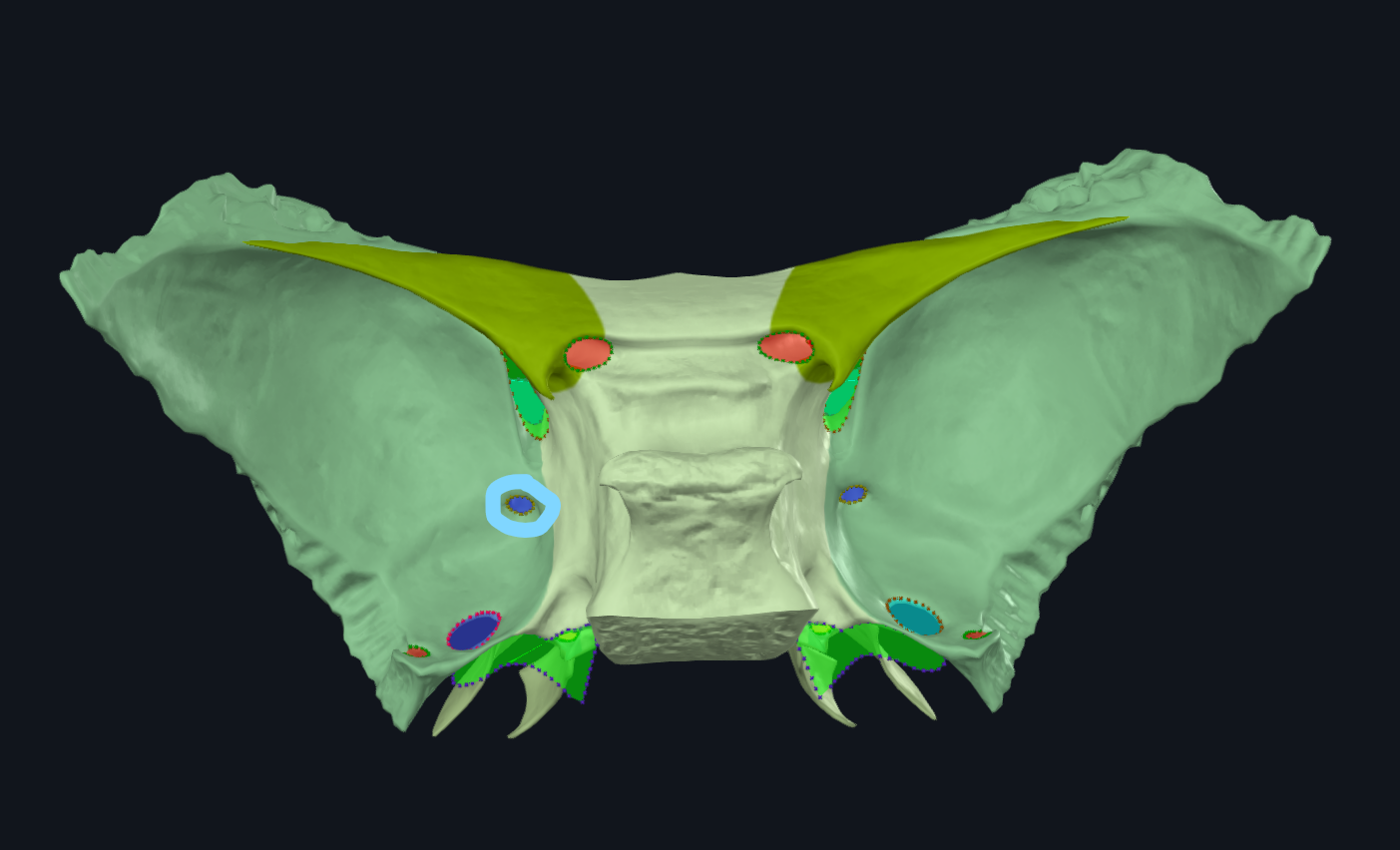
What is circled
Foramen rotundum

What is circled
Foramen spinosum
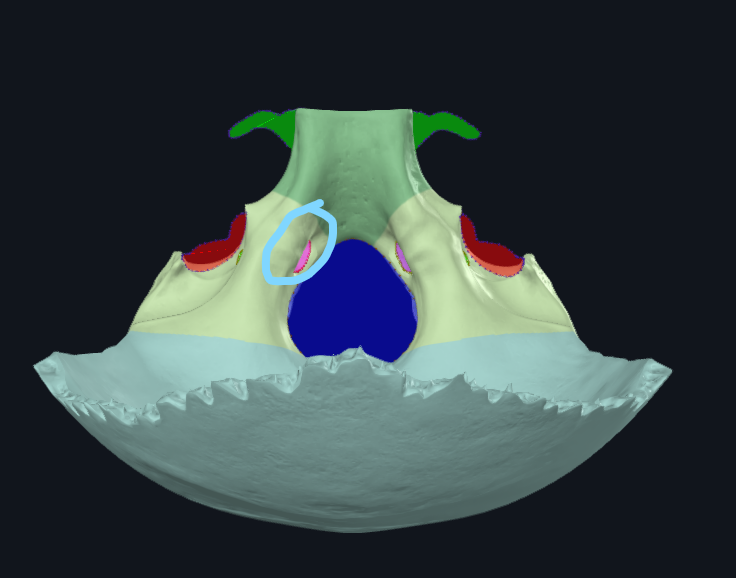
What is circled
Hypoglossal canal
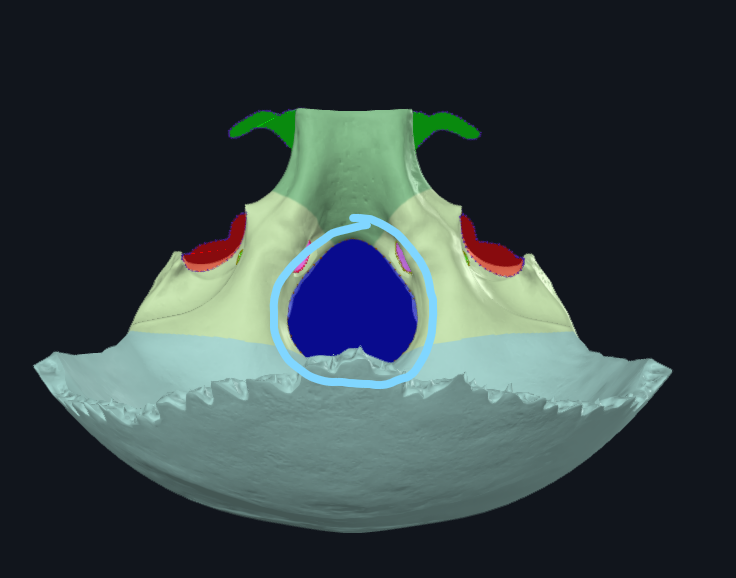
What is circled
Foramen magnum
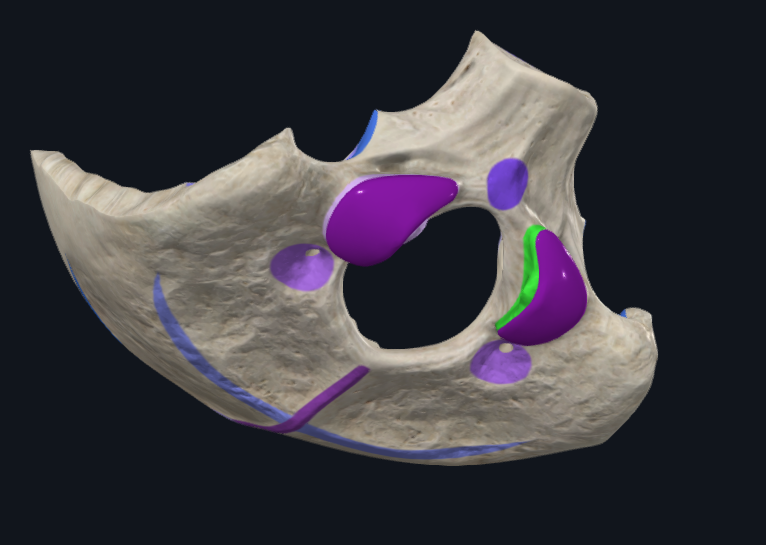
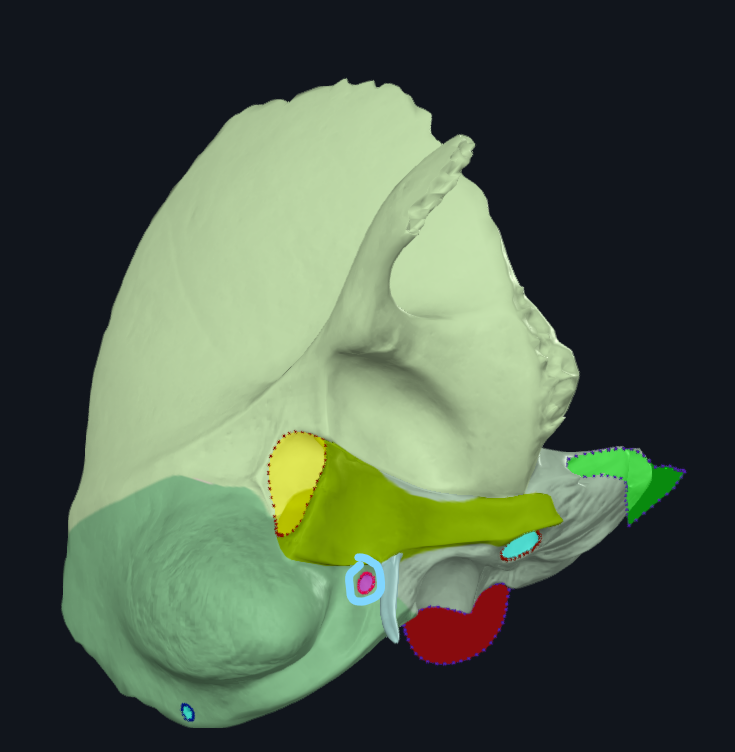
What is highlighted in green
Occipital condyle
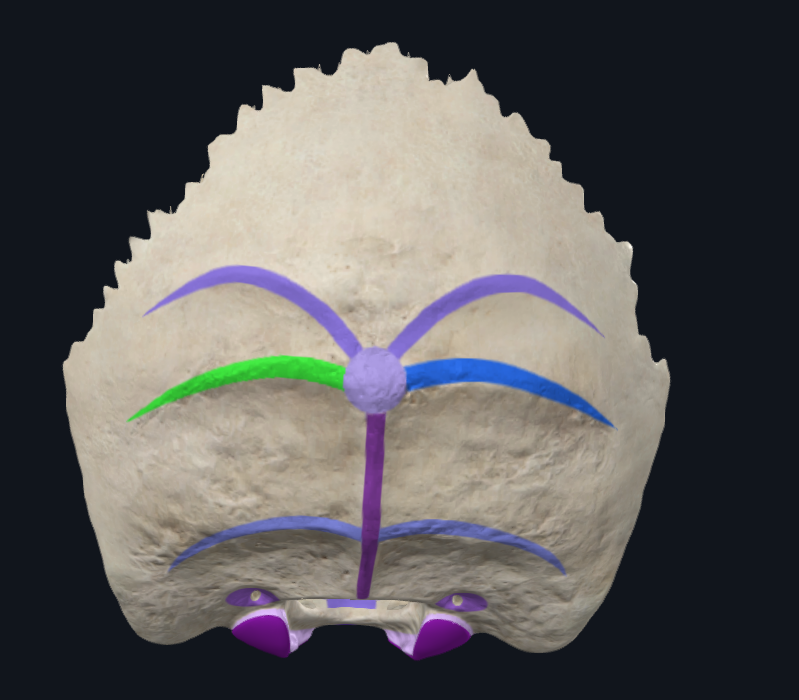
What is highlighted in green
Superior nuchal line
Where do the occipitalis and trapezius attach
Superior nuchal line

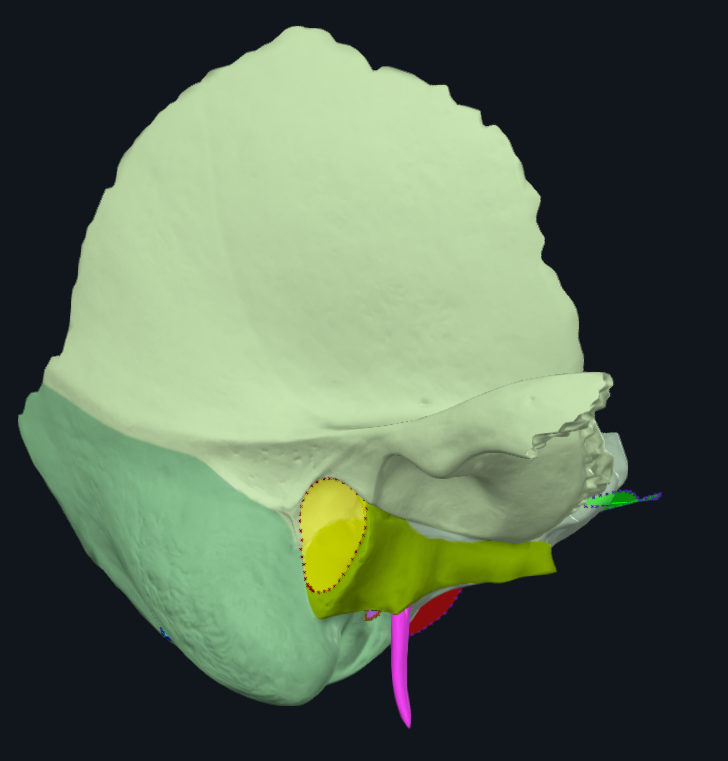
What is highlighted in pink
Zygomatic process of temporal bone
Where does the masseter attach to on the temporal bone
Zygomatic process of temporal bone
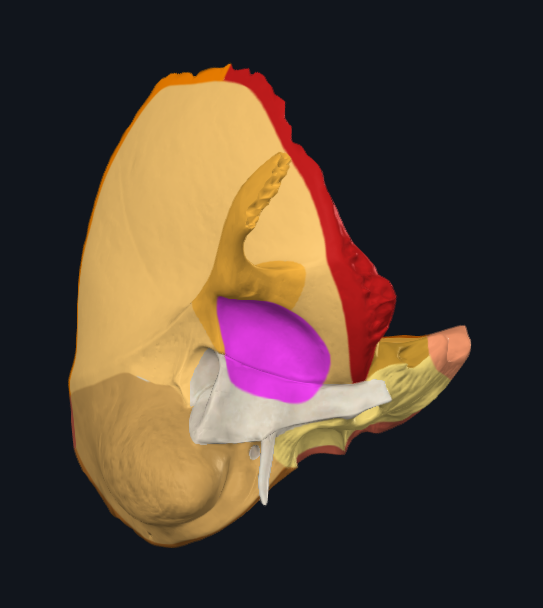
What is highlighted in pink
Mandibular fossa
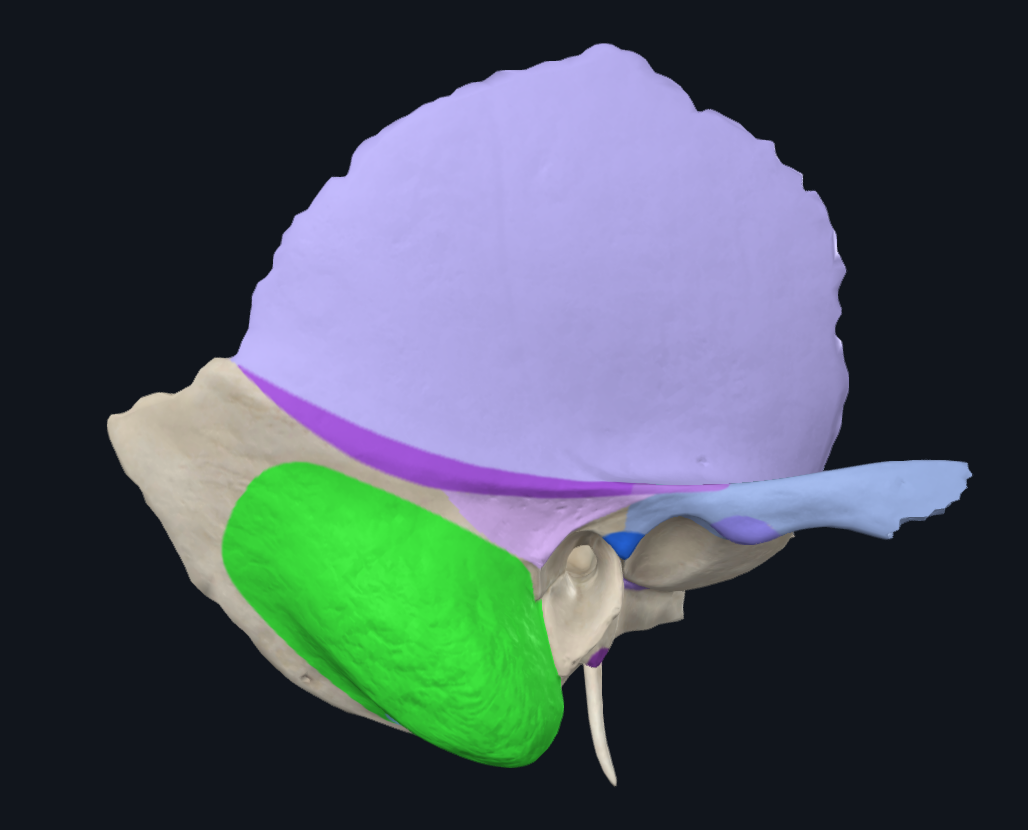
What is highlighted in green
Mastoid process
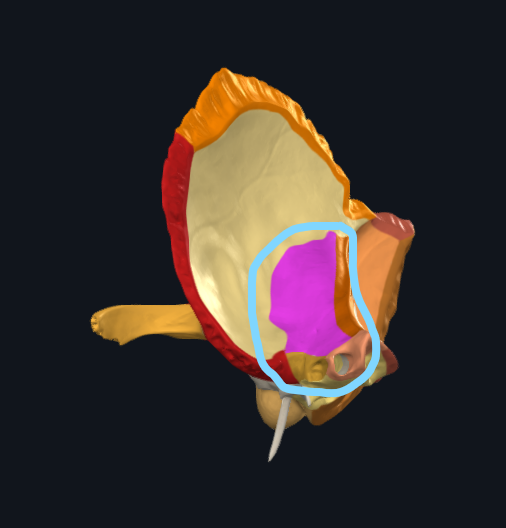
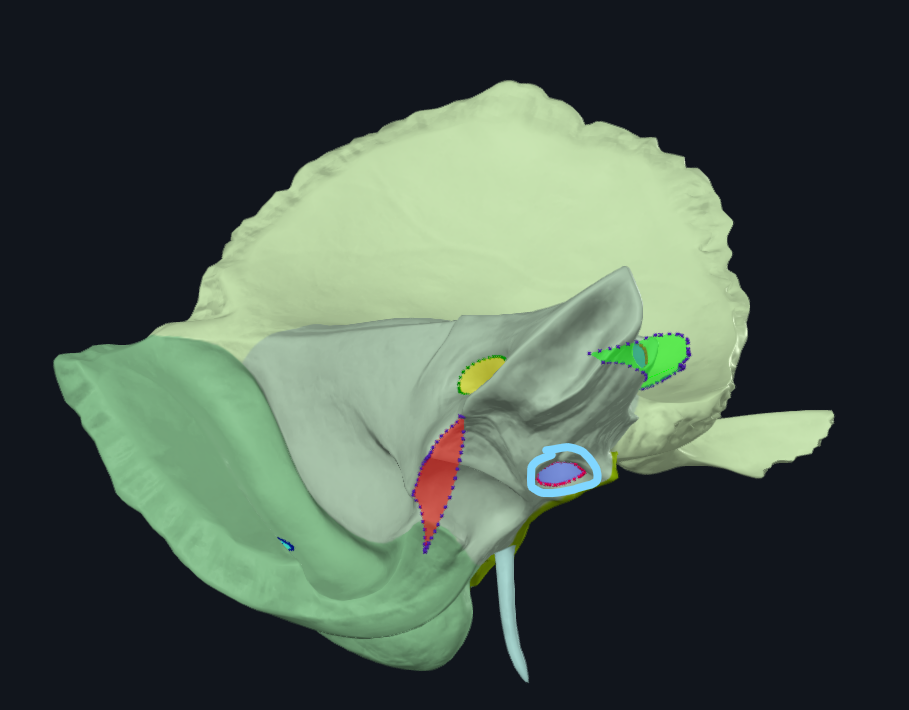
What is the circled area of the temporal bone called
Petrous part
Where is the petrous part of the temporal bone located between
Between the sphenoid and occipital bones
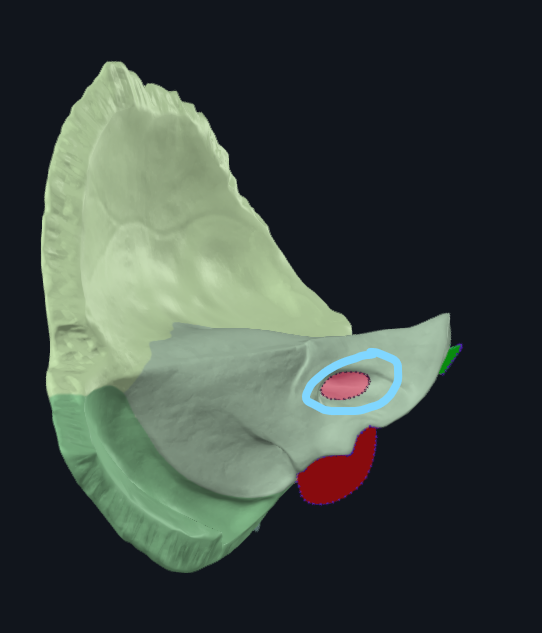
What is circled
Internal auditory meatus
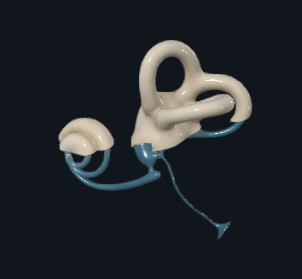
What is this
Inner ear
What is circled
Carotid canal
What is highlighted in pink
Styloid process
What is circled
Stylomastoid foramen
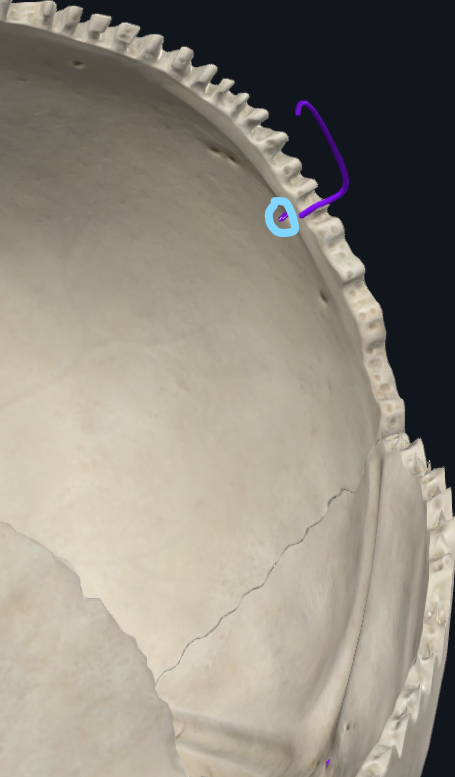
What is the foramen here
Foramen for emissary veins
What is the vertebral artery a branch of
Subclavian artery
What does the vertebral artery travel through
Transverse foramen of C6-C1
What is the internal carotid artery a branch of
Common carotid artery
What is the left common carotid artery a branch of
Arch of the aorta
What is the blood supply to the brain
Internal carotid artery anteriorly, vertebral artery posteriorly
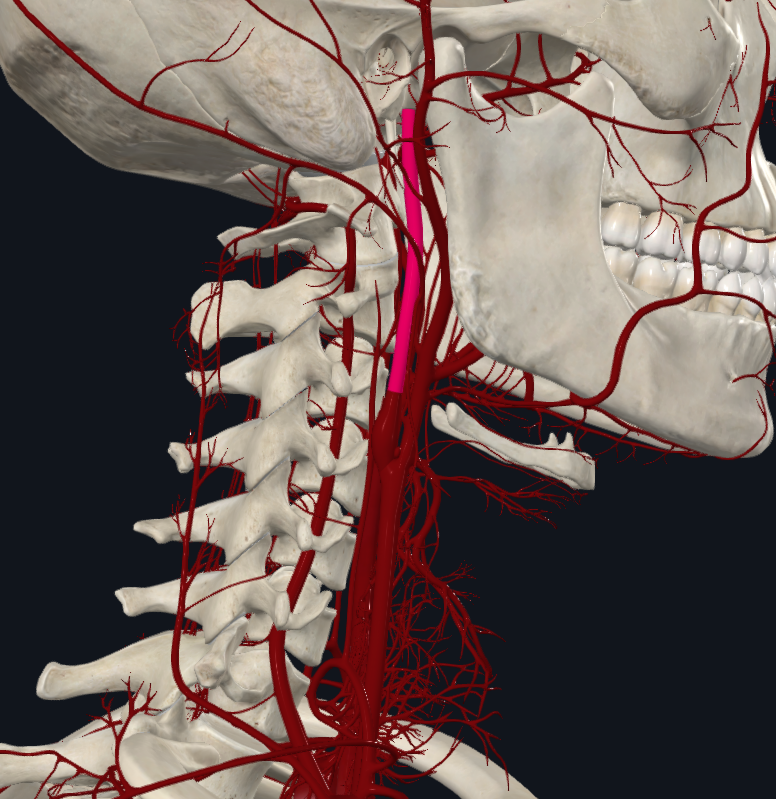
What is highlighted in pink
Internal carotid artery
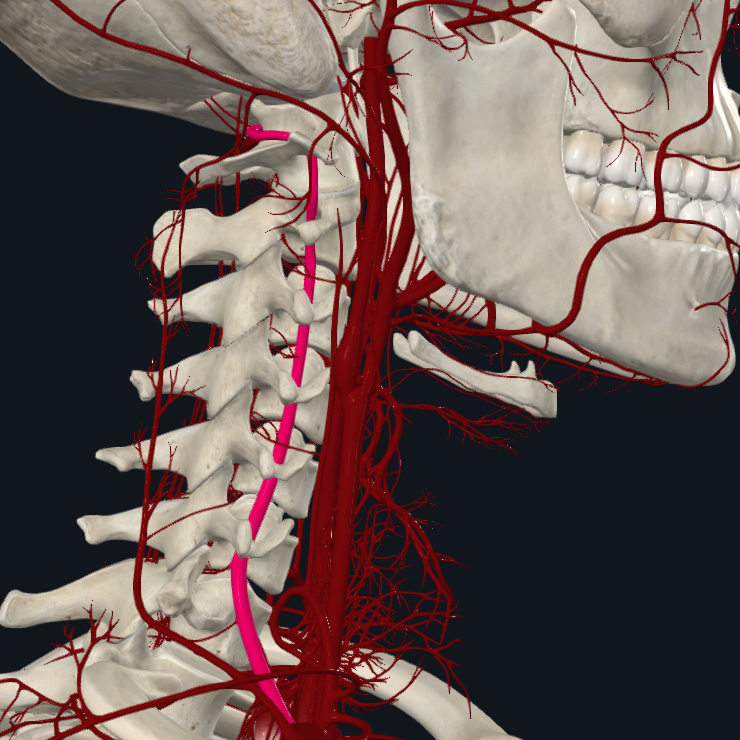
What is highlighted in pink
Vertebral artery
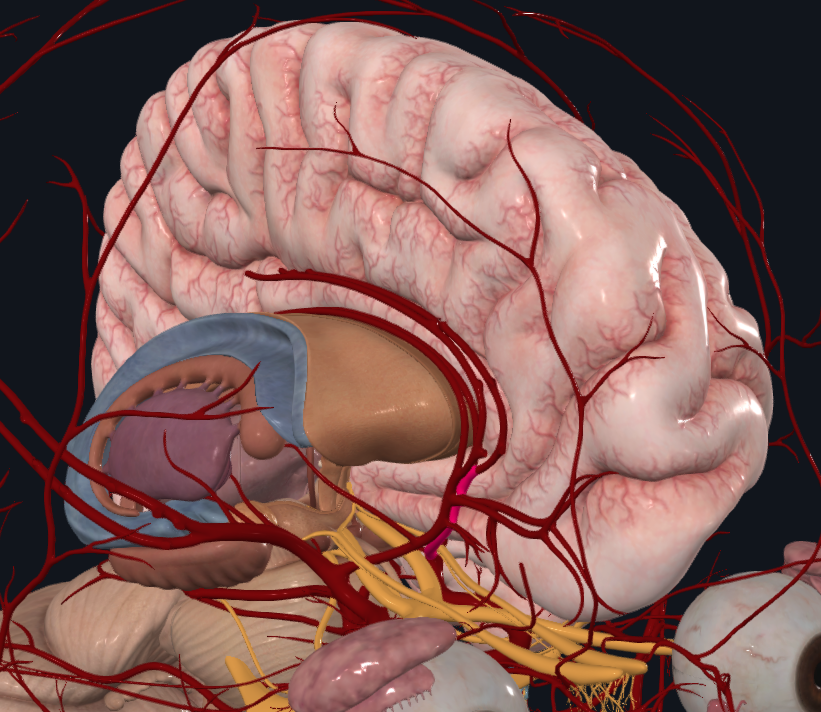
What is highlighted in pink
Anterior cerebral artery
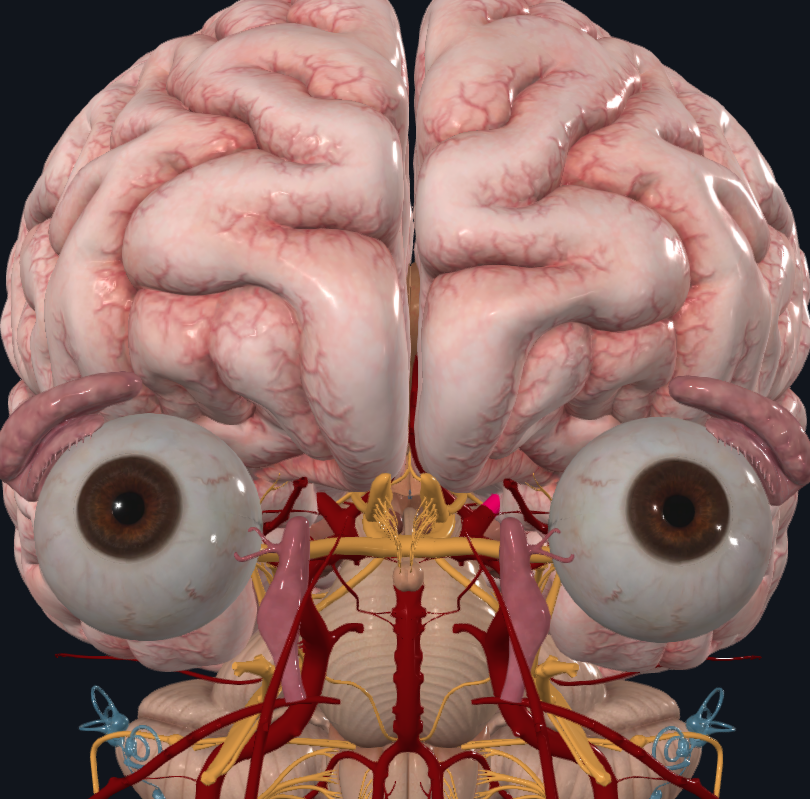
What is highlighted in pink
Middle cerebral artery
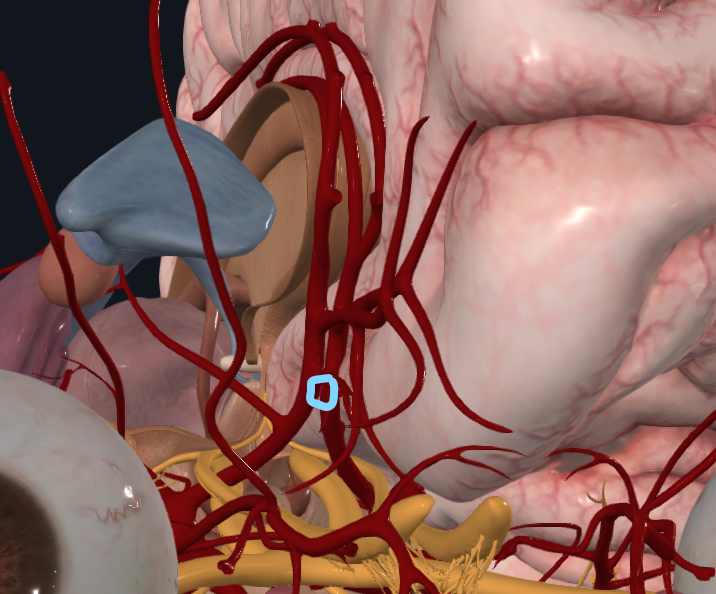
What artery is highlighted (joins the anterior cerebral arteries)
Anterior communicating artery
What do the branches of the middle cerebral artery supply
Lateral surface of frontal, parietal and temporal lobes
What foramen does the vertebral artery enter the cranial cavity through
Foramen magnum
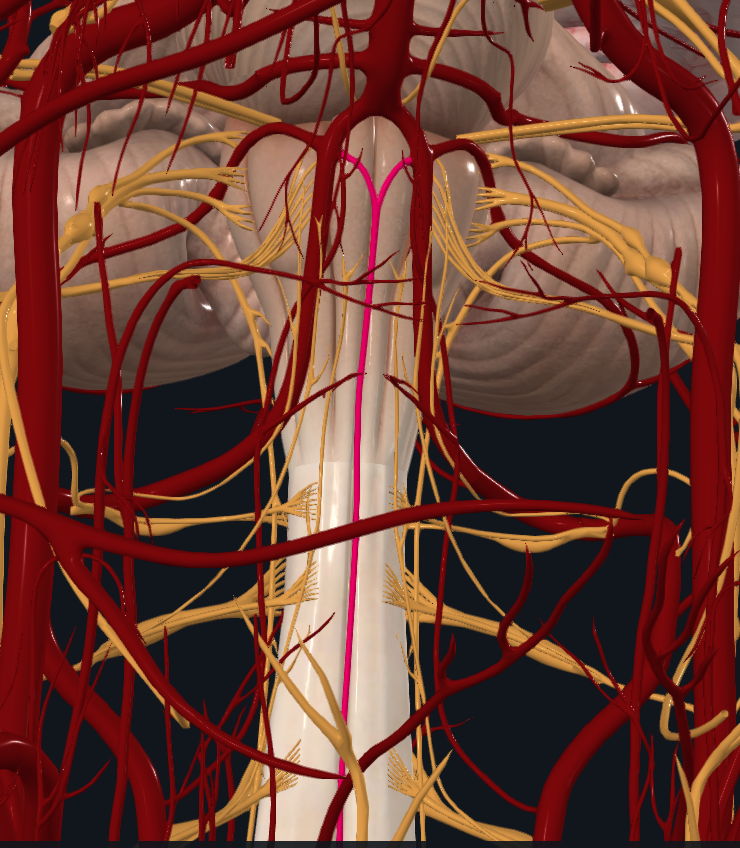
What artery is highlighted
Anterior spinal artery
What does the anterior spinal artery supply
Spinal cord and medulla