BIO120 UOFT TEST 1
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
SNP
Single nucleotide polymorphism
What does SNP let us see?
It lets us see the differences between individuals
Dioecy
The phenomenon of a species having distinct male and female organisms or colonies
What percentage of plants have dioecy?
7%
Bakers law
Long distance dispersal that favours selfing forms because a single individual can start a colony without mates or pollinators
Tangled bank hypothesis
There is an importance in spatial hetergoeneity found in a complex environment in the maintenance of sexual reproduction
Types of natural selection on quantative traits
Stabilizing selection (favours average traits)
Directional selection (favours on extreme)
Disruptive selection (favours both extremes)
Evolution of cyanide resistance
Alleles resisting cyanide are found at low percentage in population
Cyanide presence imposes selection
Resistance spreads
Individuals with resistance have a higher reproductive success
Eventually these genes increase over time
Lenski
Father of experimental evolution
E coli study
20 year experiment where 40, 000 generations were reproduced
Lenski observed how they adapted to only being fed vitamin C at big amounts every other day
They adapted by growing bigger nucleus to be able to break down lots of vitamin C at once and also store it
Gene
The functional unit of inheritance
Located on the chromosomes consisting of DNA
A DNA sequence composed of codons essential for a specific biological function
Princeton scholars
Peter and Rosemary Grant
Galapagos study
Conducted 35 year long study by Peter and Rosemary Grant
Witnessed adaptive radiation in 14 Galapagos finches
Stohastic
Unpredictable or random
Stohastic examples in evolution
Mutation
Recombination
Gene flow
Genetic drift
Genetif drift
Stohastic change in allele frequency due to random variation in fecundity and mortality
Scientific creationsim
Not supported by any empirical observation
It does not infer its principles from observation as does all science
Its assumptions leads to no testable or falsifiable hypotheses
Enzyme electrophoresis
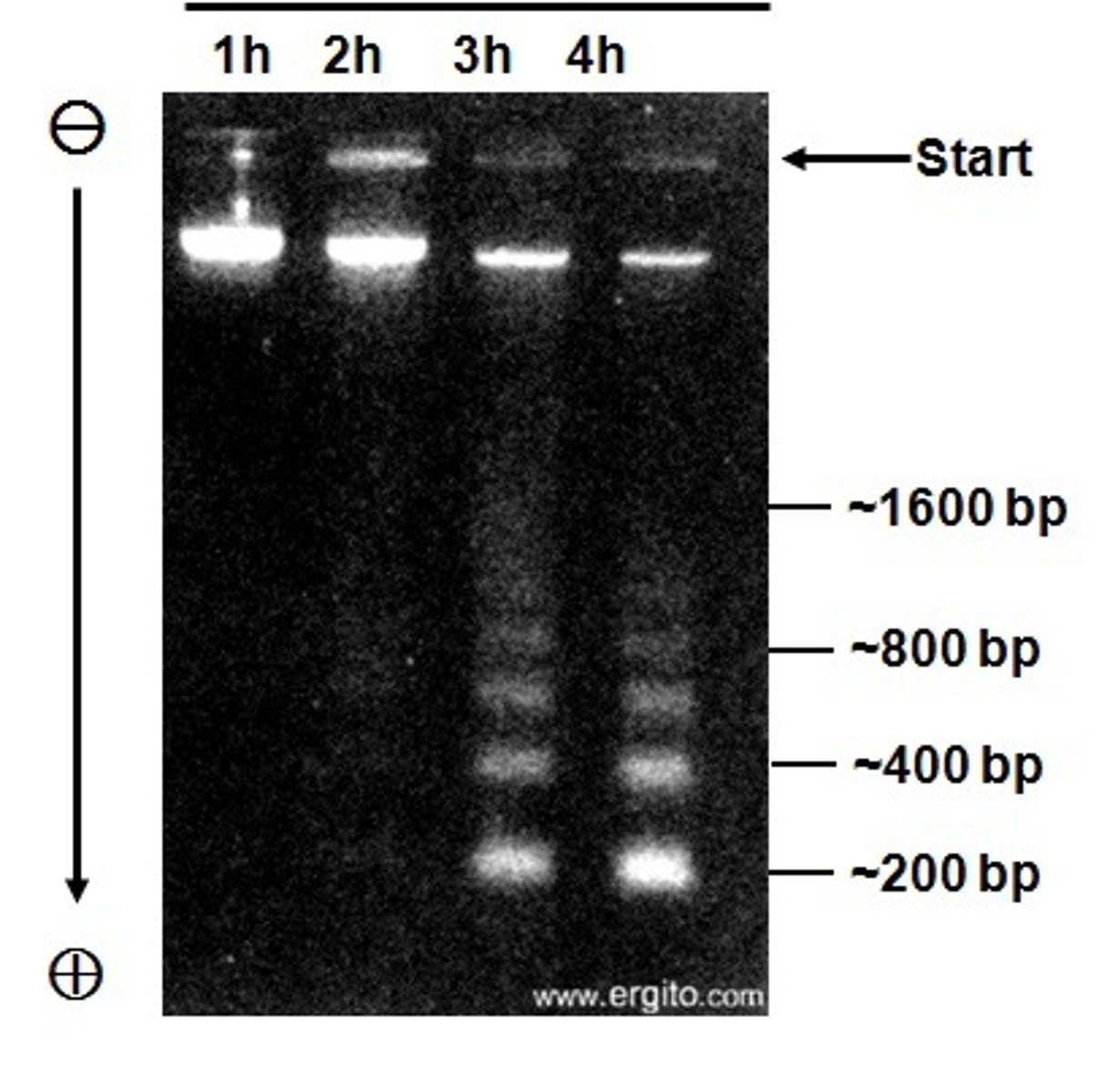
Richard Lewontin
Discovered enzyme electrophoresis
Balance school of population structure belief
There is not a best or ideal genotype; balancing selection favours diversity
Founders of the Balance school of population structure
Ford and Dobzhansky
Inclusions of the balance school
Natural population
Low homozygosity
High polymorphism
Fishers fundamental Theorem of Natural selection
The rate of increase in fitness of a population at anytime is equal to its genetic variance in fitness
Founder of population genetics
Fisher
Classical school of population structure belief
The "wild type" is the best genotype, purifying selection reduces diversity
Inclusions of the classical school of population structure
Lab mutants
High homozygosity
Low polymorphism
Founders of the school of classical population structure
Morgan and Muller
Point mutation
Single base change
Insertion or deletion mutation
Jumping genes
Parthenogensis
Type of asexual reproduction where the off spring develop from unfertilized eggs
Hermaphrodittism
Enabling a form of sexual reproduction in which both partners can act as either female or male
Inbreeding depression
The reduction in fitness of inbred offspring in comparison with outcrossed offspring
Gene flow
The movement of genes from one population to another
Red queen hypothesis
Organisms must constantly evolve, adapt and proliferate not merely to gain reproductive advantage but also to simply survive while pitted against other ever-evolving organisms in an every-changing environment
Selection processes of genetic diversity
Purifying negative selection
Positive selection
Balancing selection
Mutation
A stable change in DNA sequence resulting in a change of genotype
Occurs at a very low but variable rate in all organisms
To be useful must occur in germs cells because somatic mutations are not inherited thus no use to evolution
Artificial selection on quantative traits
Involves controlled breeding and selection for many generations
Selection responses demonstrates that abundant genetic variation exists for polygenic traits
No key info on population genetics because comparative studies are difficult as traits studied are often within a group
Genome
The entire organism's DNA including both genes and non-coding regions
Maintenance of genetic variation/diversity?
Mutation-selection balance
Selection maintaining variation
Characteristics of mutation
It is unstoppable, can't be controlled, it's rate depends on the gene it is mutating and the environment can insult
Theropods
Common ancestor of birds and reptiles
Neil Shubbin
Predicted the right layer of rocks for strata that would show where the transitional spot of fish to reptiles would be
Trees down
An evolutionary expression stating that reptiles had feathers that helped them glide down for food or escaping preadators before actually flying and becoming actual birds
Ground up
An evolutionary expression stating that reptiles had feathers to let them open-arm run and leap to catch prey
Atavisms
throwback genes present but normally turned of
Synonyme for dead genes
Pseudogenes
Recapitulation
A repetition of an evolutionary process from the past in the present during the stages of development/ growth
Barry Hall
Did study on E coli where they were feed lactose. Eventually they developped an enzyme that could break down lactose and digest it
Scott Caroll
Predicted that bugs changing host fruits with different sizes would change their beaker size. Prediction was correct
Arthur Weis
Predicted that flowers that lived in drought environments would eventually adapt to flowering early before the drought season.