Chapter 13 - Personality disorders
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Summie
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Personality
A collection of unique traits that influence behaviors, emotions, thoughts and interactions.
Personality traits: traits make our reactions predictable.
Personality is flexible.
Personality disorder
A persistent, rigid pattern of inner experience and outward behavior that repeatedly impairs a person’s sense of self, emotional experiences, goals, capacity for empathy and/or ability for intimacy.
Personality is not flexible.
Personality disorders persist for years.
Personality disorders become recognizable in adolescence, early adulthood (some even childhood).
Comorbidity
People with PD often suffer from another disorder as well.
Classification of PD into 3 clusters by DSM-5
Odd or eccentric PD
paranoid
schizoid
schizotypical
Dramatic PD
antisocial
borderline
histrionic
narcissistic
Anxious PD
avoidant
dependent
obsessive-compulsive
PD in Odd or eccentric PD
Paranoid
Schizoid
Schizotypical
PD in Dramatic PD
Antisocial
Borderline
Histrionic
Narcissistic
PD in Anxious PD
Avoidant
Dependent
Obsessive-compulsive
Difference categorical vs. diemnsional approach
Categorical = PD is either present OR absent
A person suffering from PD does not noticeably suffer from personality traits outside of that disorder.
Dimensional = Disorders are classified based on the severity of traits.
Personality traits range from non-problematic to extremely problematic (PD).
Odd personality disorders
Exhibit odd or eccentric behaviors similar to but less intense than those seen in schizophrenia, such as:
extreme suspicion
social withdrawal
peculiar ways of thinking and perceiving
People rarely seek treatment.
Paranoid personality disorder
Distrust others and are suspicious of their motives.
Avoid close relationships
Confidence in their own ideas is exaggerated

Psychodynamic statement about Paranoid personality disorder
People perceive the environment as hostile due to persistent and unreasonable parental demands or repeated abuse during childhood.
Cognitive-behavioral statement about Paranoid personality disorder
People hold broad maladaptive assumptions, such as “everyone is evil”.
Biological statement about Paranoid personality disorder
Genetic causes.
Effects of Treatment on Paranoid personality disorder
Little effect
People in treatment see patient’s role as inferior and distrust their therapist.
Therapy
Object relations therapist
Cognitive behavioral therapy
Behavioral: therapist helps client to master anxiety-reduction techniques abd to improve their skills at solving interpersonal problems.
Cognitive: therapist guides client to develop more realistic interpretations of other people’s words and actions and to become more aware of other people’s pov
Antipsychotics (help to a limited extent).
Object relations therapists
Emphasize relationships and work on the patient’s deep desire for satisfying relationships.
Cognitive behavioral therapy for Paranoid PD
Behavioral: therapist helps client to master anxiety-reduction techniques abd to improve their skills at solving interpersonal problems.
Cognitive: therapist guides client to develop more realistic interpretations of other people’s words and actions and to become more aware of other people’s pov
Schizoid PD
Exhibit persistent avoidance of social relationships and little expression of emotions.
Prefer to be alone

Psychodynamic statement on Schizoid personality disorder
Patients have unmet need for human contact due to rejecting or abusive parents.
This prevents them from giving or receiving love.
Cognitive-behavioral statement for Schizoid personality disorder
Patients have deficits in thinking.
Their thoughts are vague, empty and meaningless.
They have difficulty understanding their surroundings and recognizing emotions in others
Effects of Treatment for Schizoid PD
Patients remain emotionally distant from the therapist and do not care much about their treatment.
Cognitive behavioral therapy helps patients experience more positive emotions and have more satisfying social interactions.
Group therapy helps if there is a safe environment for social contact.
Medication is of limited help.
Schizotypical personality disorder
Extreme discomfort in close relationships, very strange patterns of thought and perception, and eccentric behaviors.
Patients suffer from ideas of reference and bodily illusions.
Some see themselves as gifted with extrasensory abilities or believe they have magical control over others.
Emotions appear inappropriate, flat or humorless.
Disorder is more severe than paranoid and schizoid PD.
Disorder is linked to schizophrenia and depression.

Ideas of reference
The belief that unrelated events relate specifically to them.
What is Schizotypical PD linked to?
Schizophrenia and depression
Explanation of Schizotypical PD
Correspond to explanations of schizophrenia:
Linked to family conflict and parental psychological disorders.
Deficits in attention and short-term memory, such as problems with backward masking.
Biological:
High activity of dopamine
Enlarged cerebral ventricles
Smaller temporal lobes
Loss of gray matter (genetic basis)
Backward masking
Recognizing visual stimulus immediately after a previous stimulus appeared briefly on a screen and disappeared again.
Biological explanation for Schizotypical PD
High activity dopamine
Enlarged cerebral ventricles
Smaller temporal lobes
Loss of gray matter (genetic basis)
Treatment for Schizotypical PD
Seek to help clients connect with the world and recognize the limits of their thinking and strengths.
Emphasis on increasing positive social contact, alleviating loneliness, reducing overstimulation and helping individuals become more aware of their personal feelings.
Therapy for Schizoid PD
Cognitive behavioral therapy: help evaluate and ignore unusual thought.
Specific behavioral methods (ex. social skills training) help clients fit into society.
Antipsychotics can reduce certain thinking patterns.
Dramatic personality disorders symptoms
So dramatic, emotional or unpredictable that it’s almost impossible for them to have reciprocal and satisfying relationships.
These PD are diagnosed more often than the other types.
Antisocial personality disorder
General pattern of disregard for and violation of other’s rights.
aka. Psychopaths or sociopaths
Criminal behavior is often involved
People often lie, are impulsive, aggressive and reckless and show little respect for others or for rules.
No guilt about the harm they cause and use others for their own gain, without remorse or moral fiber.
Relationships are superficial and unstable
Diagnosis can only be given from age of 18
Who are at greater risk for developing Antisocial PD?
Children with conduct disorder and ADHD.
this disorder is often accompanied by substance abuse
Psychodynamic explanation for Antisocial PD
Lack or parental love in early childhood leads to a lack of basic trust.
These children shut down emotionally and enter into relationships through power and destructiveness.
Cognitive-behavioral explanation for Antisocial PD
Antisocial symptoms are learned through conditioning, especially modeling or imitation.
Patients do not consider the needs of others important
Lack of empathy
Organic explanation for Antisocial PD
Heredity
Specific genes
Lower activity of serotonin
Deficient functioning of brain structures associated with sympathy, jugdement, empathy and adherence to rules
Respond to warnings with low brain and physical arousal, feeling less fear and seeking excitement more quickly
Effectiveness of Treatment for Antisocial PD
Often ineffective, as patients have no conscience, no desire and no respect for therapy.
Often people are forced into therapy.
Treatments that were not helpful: cognitive behavioral therapy and psychotropic medication (ex. antipsychotics).
Borderline personality disorder
Repeated instability in interpersonal relationships, self-image and mood, and by impulsive behavior.
Experience violent and rapidly changing moods, are often angry or irritable, direct their anger sometimes outward sometimes inward to themselves, and feel empty deep inside.

Psychodynamic explanation for BPD
Early lack of parental acceptance leads to loss of self-esteem, increased dependency and inability to cope with separation.
Multiple parental substitutes, divorce, death or trauma such as physical or sexual abuse in patient’s childhood are often involved.
Biological explanation for BPD
Heredity
Specific genes
Lower serotonin activity in the brain
Abnormal activity in certain brain structures (poor communication between brain structures)
Sociocultural explanation for BPD
Cultures that change rapidly create identity problems, a sense of emptiness, high (abandonment) anxiety.
Biosocial explanation for BPD
Combination of internal forces (e.g. difficulty identifying and controlling one’s emotions, social skill deficits, abnormal neurotransmitter activity) and external forces (e.g. an environment in which a child’s emotions are punished, ignored, trivialized or disregarded).
Developmental psychopathology on BPD
People who experience trauma and disrupted attachment with their parents in early childhood develop a disorganized attachment style.
Patients have an inability to mentalize.
Disorganized attachment style
A highly disrupted ability to form healthy relationships in adulthood.
Mentalizing
Capacity to understand one’s own and others’ mental states.
Therapy options for BPD
Traditional psychoanalytic therapy
Often unsuccesful as BPD perceive therapists’ detached approach as rejection and have difficulty accepting interpretations.
Relational psychoanalytic therapy
Focuses on the relationship between patient and therapist → Works better.
Dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT)
Comprehensive treatment approach that includes individual therapy and group sessions.
Teaching social and other skills, using homework assignemnts, and modeling by therapists and rewards for good behavior.
This therapy can be supplemented by taking psychotropic medications.
Relational psychoanalytic therapy
Focuses on relationship between patient and therapist (for BPD, this works well).
Dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT)
Comprehensive treatment approach that includes individual therapy and group sessions.
Teaching social and other skills, using homework assignemnts, and modeling by therapists and rewards for good behavior.
This therapy can be supplemented by taking psychotropic medications.
For BPD.
Histrionic personality disorder
A pattern of excessive emotionally and attention-seeking behavior.
Seek attention through suicide attempts or exaggerating illness.
Equally common in men and women.

Psychodynamic explanation on Histrionic PD
People with this disorder had cold and controlling parents, which made them feel unloved and afraid of being abandoned.
This caused them to behave dramatically to make others protect them.
Cognitive-behavioral explanation on Histrionic PD
Patients are focused on themselves and their own emotions.
They have the assumption that they cannot take care of themselves, so they constantly need others to fulfill their needs.
Sociocultural (multicultural) explanation on Histrionic PD
The disorder is produced in part by cultural norms and expectations, such as encouragement of dramatic behavior in women.
Treatment effects on Histrionic PD
Patients seek help more quickly than those with other PD.
Working with Histronic PD can be difficult because of their demands, tantrums, seductive behavior.
How can treatment help Histrionic PD
Treatment mainly focusesd on helping them recognize their over-reliance, find inner satisfaction and become more independent.
Can be done with cognitive behavioral therapy, group therapy or psychodynamic therapy
Narcissistic personality disorder
Characterized by broad pattern of feelings of grandeur, need for admiration and lack of empathy.
75% are male.

Psychodynamic explanation on Narcissistic PD + Theory
The disorder arises from cold, dismissive parents, with the person defending himself from feelings of rejection, dissatisfaction and unworthiness by seeing himself as perfect and constantly seeking admiration.
Object relations theorists: Grandiose self-image helps convince patients that they are self-sufficient and do not need warm relationships.
Cognitive-behavioral explanation on Narcissistic PD
People are treated too positively, giving children a superior and grandiose attitude.
Children acquire a superior and grandiose attitude when their “admiring or doting parents” teach them to “overvalue their self-worth”, repeatedly rewarding them for minor accomplishments or for no accomplisment at all.
Sociocultural explanation on Narcissistic PD
Family values and social ideas in societies, such as self-expression, individualism and competitiveness, encourage narcissism.
Effectiveness of Treatment on Narcissistic PD
Narcissistic PD is difficult to treat because clients often do not acknowledge their weaknesses and try to manipulate their tehrapists.
Psychodynamic therapists on Narcissistic PD
Try to help clients acknowledge their insecurities.
Not very succesful.
Cognitive behavioral therapists on Narcissitic PD
Teach them to better understand criticism and develop empathy.
Not very succesful.
Anxious personality disorders
Exhibit anxious and fearful behavior.
Symptoms are similar to those of anxiety and mood disorders, but no direct link has been found between them.
Treatments for these disorders are more helpful than for other PDs.
Avoidant personality disorder
Persistent discomfort and inhibition in social situations, overwhelming feelings of inadequacy, and extreme sensitivity to negative evaluation.
Avoid social interactions for fear of rejection and criticism.
They feel inferior, are timid, and have difficulty forming intimate relationships, despite their desire for connection.

Difference Social anxiety disorder and Avoidant personality disorder
Social anxiety disorder focuses on fear of social circumstances.
Avoidant PD includes fear of close social relationships.
Psychodynamic explanation for Avoidant PD
Focuses on general feelings of shame and insecurity.
This may arise from childhood experiences, such as parents ridiculing their child after they wet their pants, causing the child to develop a negative self-image.
Cognitive-behavioral explanation on Avoidant PD
Harsh criticism and rejection in childhood lead to the assumption that others around them will always judge them negatively.
In addition, parents fail to develop effective social skills, which perpetuates this disorder.
Focus of treatments and types of therapy on Avoidant PD
Focus on building trust to prevent patients from avoiding sessions or distrusting their therapist. This can be done with:
Psychodynamic therapy: recognizing and resolving unconscious conflicts.
Cognitive behavioral therapy: helping clients to change troubling beliefs and thoughts, deal with painful emotions and improve self-image.
Social skills training and exposure treatments increase social contact.
Group therapy: practicing social interactions.
Medication: anti-anxiety and antidepressant medications to reduce social anxiety.
Dependent personality disorder
Pattern of affection and obedience, strong separation anxiety and a constant need to be cared for.
They have feelings of inadequacy and helplessness.
Many stubbornly cling to relationships with partners who mistreat them physically or psychologically.

What disorders does Dependent PD occur in combination with?
Depression
Anxiety disorders
Eating disorders
Suicidality
Psychodynamic explanation for Dependent PD
Unresolved conflicts during the oral phase in childhood
Early parental loss or rejection leading to separation anxiety (object relations)
Overinvolved and overprotective parents leading to dependency, insecurity and separation anxiety.
Cognitive-behavioral explanations on Dependent PD
Unintentionally rewarding the child for exhibiting affectionate behavior
Punishing independence
Modeling dependent behaviors of parents
Maladaptive beliefs: “I am inadequate and helpless to deal with the world” and “I need to find someoen to protect me so I can cope”.
Dichotomous thinking, such as “If I want to be dependent, I must be completely helpless.
Dichotomous thinking
Black and white thinking
Treatment focus for Dependent PD
Focused on getting clients to see that they can be responsible for themselves.
Can be done with psychodynamic therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, group therapy or antidepressant.
Also family therapy or separate therapy for partner/parent can help.
Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder
Intense focus on orderliness, perfectionism and control that the person loses flexibility, openness and efficiency.
Patients are focused on organization and details that they fail to grasp the purpose of the activity.
As a result, they are often behind on schedule.
They set unrealistic high standards for themselves and others, are never satisfied with their performance and often refuse to seek help or cooperate.
They are afraid of making mistakes and therefore may be reluctant to make decisions.
The disorder is twice as common in men as in women.

Freudian explanation on Obsessive-compulsive disorder
Patients are anal-retentive: due to too strict toilet training during the anal phase, they become filled with anger and remain fixated on this phase.
Psychodynamic explanation on Obsessive-compulsive PD
Early problems with parents over control and independence create anger.
Cognitive-behavioral explanation on Obsessive-compulsive PD.
Illogical thought processes, such as dichotomous thinking, keep the disorder going.
Effectiveness of Treatment on Obsessive-compulsive PD
Treatments are difficult because patients often do not think there is anything wrong with them.
They only seek help when they start suffering from other diseases, such as depression or anxiety disorders.
Treatments that can be used: psychodynamic therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy or SSRIs.
Difference between Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder (OCPD) and Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
There is no consistent link between the two.
People with OCPD are more likely to suffer from major depressive disorder, anxiety disorder, or substance use disorder than OCD.
Big five
The basic structure of personality consists of 5 traits:
Openness to experience
Conscientiousness
Extraversion
Agreeableness
Neuroticism
OCEAN
Personality disorder — Trait specified (PDTS)
People with PD score high, low or somewhere between the Big 5. In the dimensional approach of the DSM-5, people with PDTS have personality traits that severely impair their functioning.
Avoidant PD on the Big 5
High levels of Neuroticism
Medium levels of Agreeableness and Conscientiousness
Very low levels of Extraversion and Openness
Which 5 groups does Personality disorder — Trait specified (PDTS) focus on?
Negative affectivity
Experiencing negative emotions frequently and in an intense way.
This includes emotional lability, anxiety, separation insecurity, persistence, submissiveness, hostility, depression, suspicion, and strong emotional reactions.
Detachment
Tendency to withdraw from others and social interactions.
Limited emotional reactivity, depression, suspicion, withdrawal, anhedonia, avoidance of intimacy.
Antagonism
Behaving in such a way that it puts them at odds with others.
Manipulation, deceit, megalomania, attention seeking, insensitivity, hostility.
Disinhibition
Exhibiting impulsive behavior without thinking about possible future consequences.
Irresponsibility, impulsiveness, distractibility, risk-taking and imperfectionism / disorganization.
Psychoticism
Experiencing things in an unusual, bizarre way and having unusual beliefs.

Score of person with Dependent PD on PDTS

2 Criticism on Dimensional approach to the DSM-5
Too much latitude for diagnosticians, allowing them to diagnose personality disorders for many different personality types.
The requirements of the new system are too cumbersome or complicated.
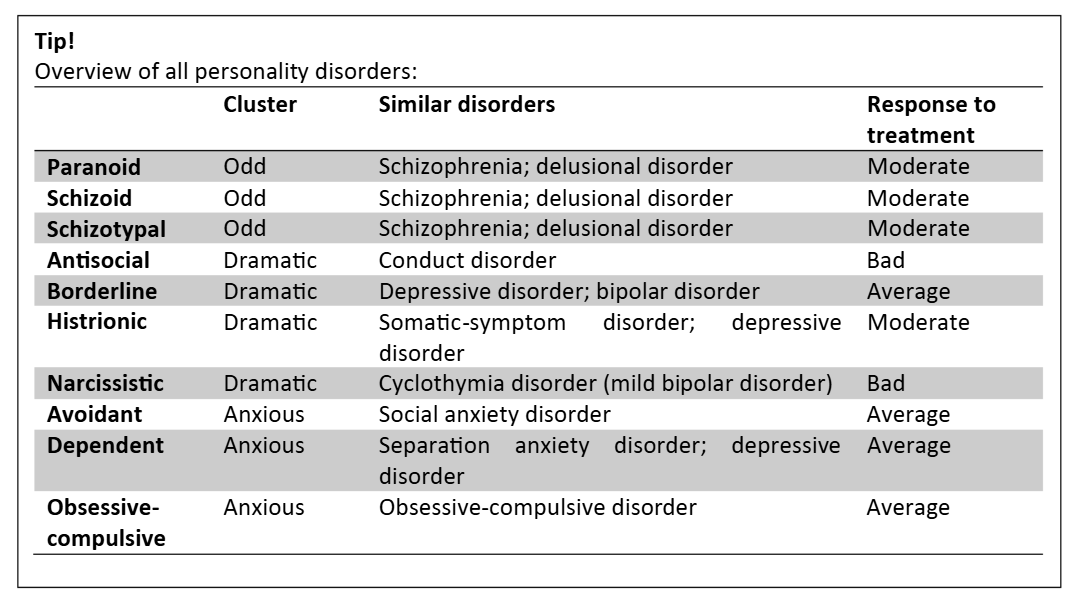
Overview of all personality disorders