Business Ethics 1
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
What is Ethics NOT?
based on whether we feel smth is right or wrong
solely related to religion
always abiding by the law 100%
always aligned w/what everyone else does/is socially acceptable
an exact science
Ethics concerns
The moral behavior of individuals based on an established and expressed standard of the group, which is and of itself a collection of individual values
What is business ethics?
Applies a value structure to how businesses should be run
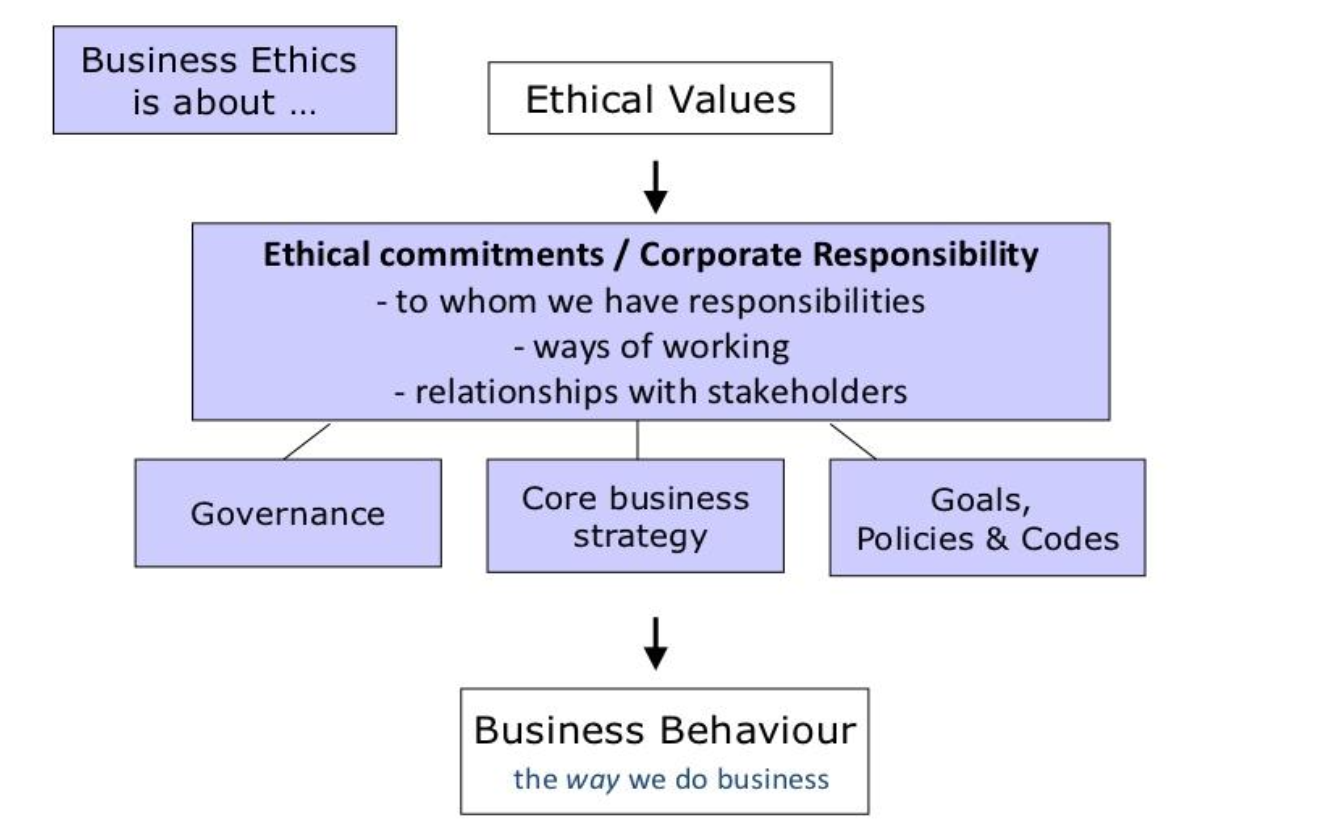
3 Levels of Ethical Decisions
individual
government
organization
Individual Level of Ethical Decisions
employee
manager
entrepreneur
customer
Organization Level of Ethical Decisions
company
corp
start-up
small business
non-profit
Government Level of Ethical Decisions
regulator
incorporator
enforcer
customer
“Pyramid” of Business Ethics
micro
meso
macro
Micro
Groups & individuals
Meso
Institutions and Organizations
working standards/conds
diversity and opportunity
outsourcing
human rights
Macro
Global Issues
Climate change
public health
immigration
etc
5 Theories of Moral/Ethical Reasoning
Universalism
Utilitarianism
Rights-Based
Fairness & Justice
Character & Virtue
Universalism
“do the right thing”
“rule-based morality” - Kant
best moral choices are those that you would want others to make, based on a sense of principle, and respecting others
Utilitarianism
cost/benefit analysis
will this decision create more benefits than harm?
long term effects?
Rights-Based
are human rights at stake?
Are core freedoms/welfare issues being violated?
positive vs negative rights
Positie Rights
education
decent standard of living
security and safety
Negative Rights
life
liberty
personal respect
to be left alone
Positive and Negative Rights according to philosophy
NR restrains other persons or governments by limiting their actions toward/against the right holder. PR provide the right holder with a claim against another person/ state for some good, service, or treatment.
Fairness & Justice
Which option treats people equally or proportionally?
Character & Virtue
Do you live the life you want to live?
how would a virtuous person/org make this decision?
is this a pos or neg precedent?
based on Aristotle
Culture of Integrity
Organizational and External Influences
Business Processes
Individual Ethical Decision Making
Organizational and External Influences
leadership style
compensation structure
incentives
internal/external pressures
= set context for behavior
Business Processes
Strong business process and strict system of controls = discourage unethical behavior
Individual Ethical Decision Making
Ppl make decisions and rationalize behavior according to personal code of ethics
Link between ethics, compliance, and risk
compliance is what keeps many companies in line, as well as risk aversion
Role of Ethics: Proactive vs Reactive
proactive: finding preventative measures so situations can be avoided.
reactive: reacting to something that has already happened
Compliance
objective - external - singular
Compliance really is
a disposition to yield to others
Ethics
Subjective - internal - plural
Ethics really are
A guiding philosophy
Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) Act
Whistleblower Hotline
CEO, CFO certification
Criminal Penalties
Cultural Influences
Family
education
religion
media/entertainment
Organizational Influences
ethical codes
organizational culture
role models
perceived pressure for results
rewards/punishment system
Political/Legal/Econ Influences
Laws
Rules
etc
Individual
Personality
Values
moral principles
history
gender
Ethical behavior is derived from
Cultural/Org/Pol/Legal influences + Role Expectations + Stage of Moral Development > filtered through the Individual
Moderaters for Behavior
Individual Characteristics
Issue Intensity
Structural Variables
Organizational Culture
Determinants of Issue Intensity
greatness of harm
consensus of wrong
probability of harm
immediacy of consequences
proximity to victim(s)
concentration of effect
Questions to ask for ethical decision making
what are the relevant facts?
what are the ethical issues??
who are the primary and secondary stakeholders?
what are the possible alternatives and their ethcis?
what are the practical constraints?
what actions should be taken?
4 Steps of Ethical Decision Making
AWARENESS of an ethical problem
ability to REASON about ethical issues
having the MOTIVATION to act ethically
having the PERSISTANCE to implement ethical action in the face of obstacles
Misc Current Business Ethics Issues
Whistleblowing
Ethical Investment
Lobbying/political donations
Exec Pay
Work/home balance
Sustainability
Conflicts of Interest
Corruption
etc
ShareHolder-Managerial Model
shareholders as most important priority for manager’s decision making
“creating value for shareholders” as a means of dealing with complexity of today
Milton Friedman’s Perspective
Only social responsibility of business is to use its resources and engage in activities designed to increase profits, so long as it engages in open and free competition without deception or fraud
Managerial Model as a
Hierarchical View
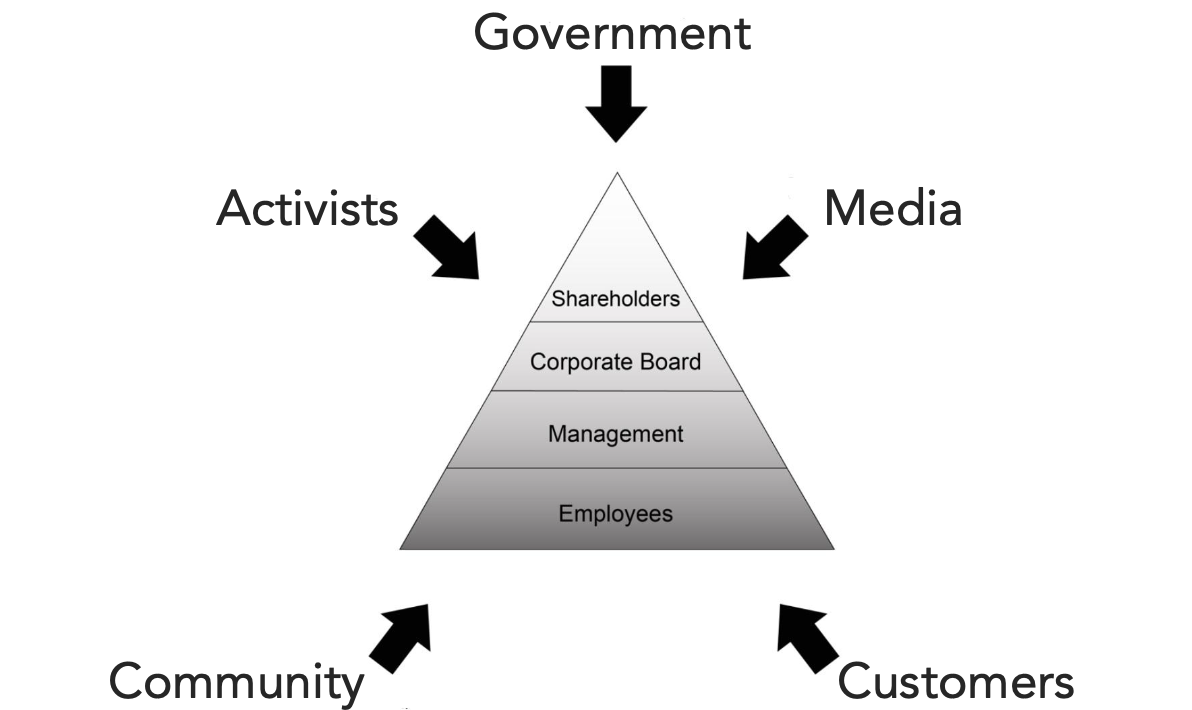
Challenge of Managerial Model
Managers tend to focus internally to firm, are not aware/attentive enough of other interests that could be sources of innovation/growth and are ultimately traded against the interests of shareholders
Managerial Model with an Inward Focus
Separation Fallacy
It is useful to believe that sentences like “x is a business decision” have no ethical content or any implicit ethical point of view.
And, it is useful to believe that sentences like “x is an ethical decision, the best thing to do all things considered” have no content or implicit view about value creation and trade
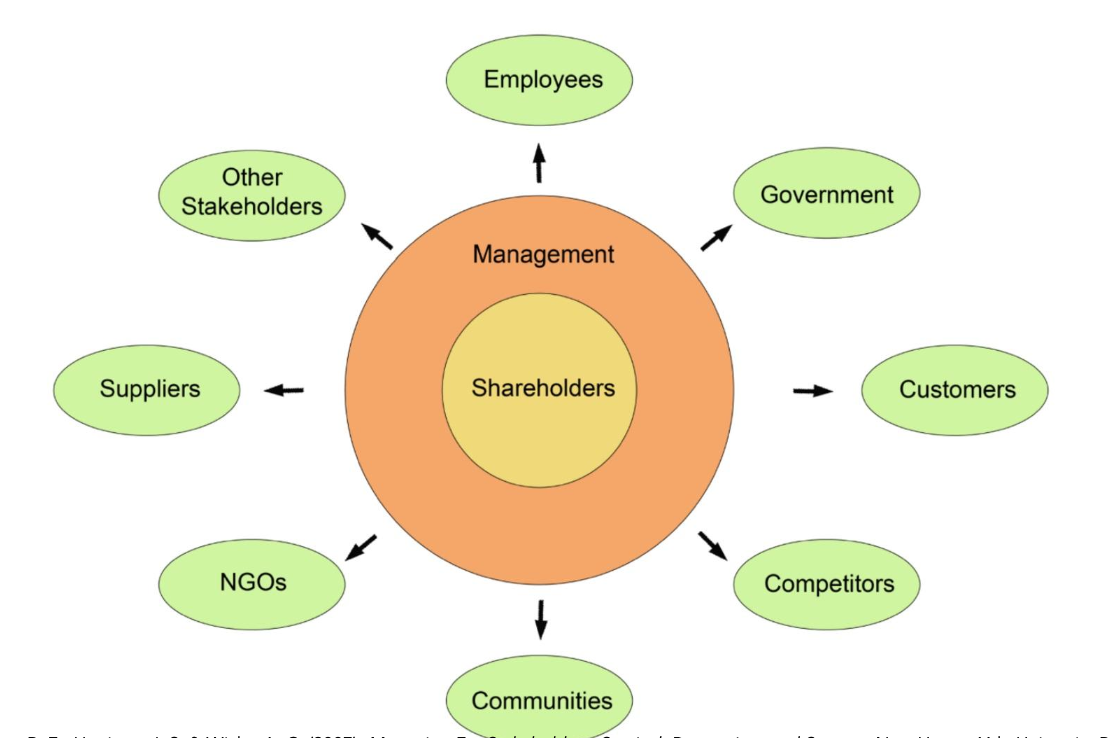
Stakeholder model demonstrates
how business is embedded in a complex set of social and econ networks
in Stakeholder model: Business affects and is affected by
individuals, organizations, and communities
Stakeholder Model says that businesses
have responsibilities to all stakeholders (anyone it affects/is affected by)
Stakeholders and Shareholders as ____ in Stakeholder model
equal
Stakeholder model says that profitability is
just 1 element of more complex econ model that vitally includes ethical decision making
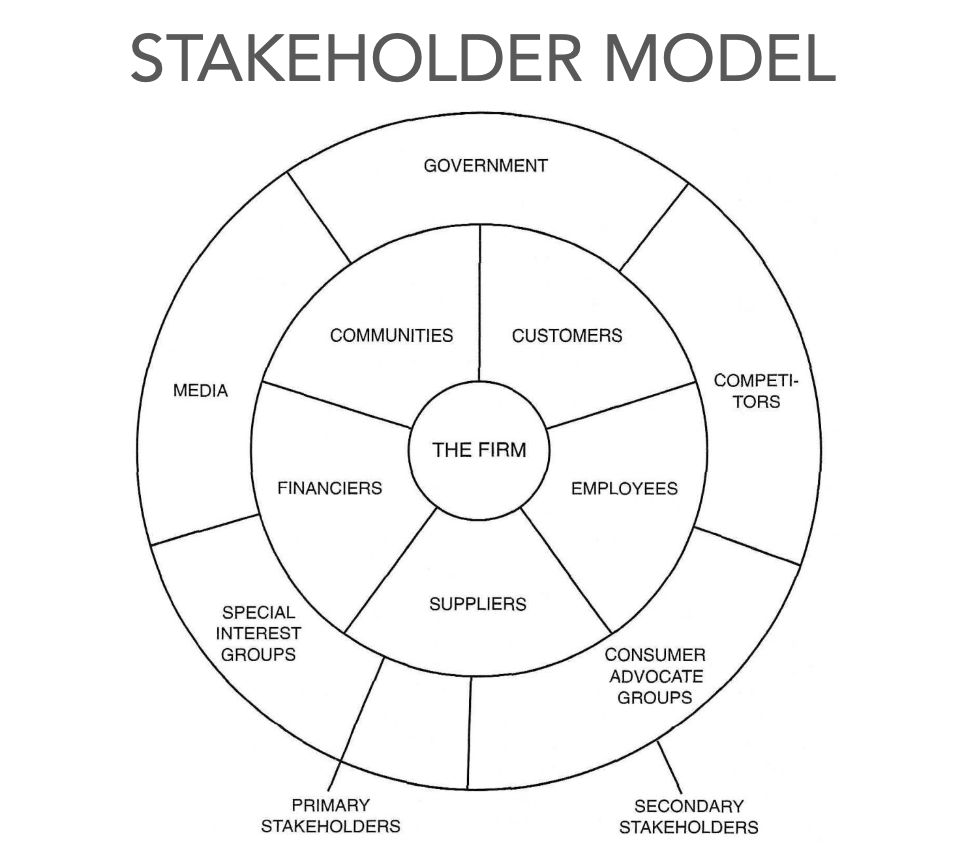
Primary Stakeholders
Suppliers
Financiers
Communities
Customers
Employees
Secondary Stakeholders
Consumer advocate groups
Special Interest Groups
Competitors
Government
5 Barriers to an Ethical Organization
Ill-Conceived Goals
Motivated Blindness
Indirect Blindness
Slippery Slope
Overvaluing Outcomes
Ill-Conceived Goals
We set goals and incentives to promote a desired behavior, but they encourage a neg one
Remedy: Ill-Conceived Goals
brainstorm unintended consequences when making goals/incentives
Motivated Blindness
Overlooking unethical behavior when its in our interest to remain ignorant
Remedy: Motivated Blindness
Root out conflict of interest
Indirect Blindness
Holding others less accountable of unethical behavior if its carried through 3rd parties
Remedy: Indirect Blindness
When outsourcing/handing off work, ask whether the assignment might invite unethical behavior and take ownership of implications
Slippery Slope
Less able to see others’ unethical behavior when it develops gradually
Remedy: Slippery Slope
Be alert of even trivial ethical infractions and address them ASAP
Overvaluing Outcomes
We give a pass to unethical behavior when the outcome is good
Remedy: Overvaluing Outcomes
Examine both “good” and “bad” decisions for ethical implications
reward decision processes not just outcomes
Treating Ethics as a Design Problem
“Creating policies that encourage ethical behavior requires an accurate understanding of what drives such behavior.
Myths: Ethics are a property of people
Unethical behavior is largely due to individuals rather than the broader context in which behavior operates
Policy Implication: Ethics are a property of people
Policymakers overestimating stability of ethical behavior and focus on finding/fixing/etc “unethical individuals” overlooking systemic unethical behavior
Myth: Intentions Guide Ethical Action
Good intentions lead to ethical acts, and unethical intentions lead to unethical acts.
Policy Implication: Intentions Guide Ethical Action
Codes of ethics seen as unnecessary for ethical ppl, even if at times good intentions can lead to unethical actions
Myth: Ethical Reasoning Drives Ethical Behavior
Ethical behavior is guided by deliberative reasoning based on ethical principles.
Policy Implication: Ethical Reasoning Drives Ethical Behavior
overestimation of effectiveness of ethics training programs while underestimating imp. of contextual changes for behavior alteration
4 Pillars of Ethical Culture
Explicit Values
Thoughts during judgement
Incentives
Cultural Norms