Genetic Engineering
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
what is the general approach to forward genetics
mutagenise germline of WT organism
self-fertilise or undertake crosses to produce homozygotes for mutation
screen for phenotypic changes of interest
map/sequence to identify impacted gene
use experiments to determine molecular role/interaction of impacted gene
what is transposon mutagenesis
utilizing transposon and restriction enzymes to insert a transposon into germline cells
tagged so you can observe this
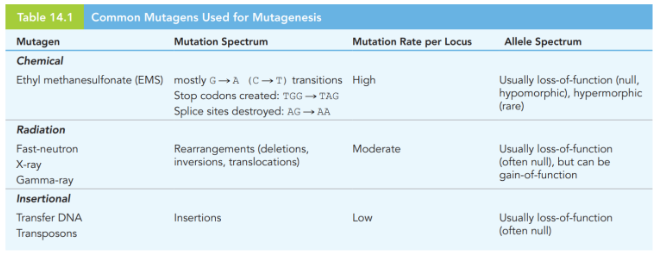
what are major advantages to chemical/X-ray mutagenesis
mutants can be labelled/selected for
inserted gene easily identified
what are some pros/cons to forward genetics
PROS:
genome-wide
unbiased
CONS:
mapping/screening for impacted gene can be difficult
unfocused (you might be interested in particular genes)
what is reverse genetics
starts with a known DNA sequence and manipulates it to understand the gene's function/phenotype
mutant gene to alter function
modify expression
introduce gene to another organism
what needs to be introduced so gene expression/structure can be altered
nucleic acids involved in the system, introduction may be:
transient: exists within/for limited number of generations
permanent: integration with cell’s DNA via recombination
what is the RNAi pathway (summary)
RNAi = gene silencing
Dicer cuts dsRNA
small RNAs load into RISC
guide strand directs RISC to matching mRNA
mRNA is cut or blocked
protein not made.
how can the RNAi pathway be used for gene knockdown
we insert the dsRNA that participates in the pathway
transient: dsRNA introduced to cells/organism
permanently: dsRNA ‘gene’ introduced as transgene
what are some pros/cons for RNAi knockdown
PROS:
provides control via administration
can target all genes in genome
works in many eukaryotes
variable knockdown efficiency
CONS:
variable knockdown efficiency
off-target effects
not applicable in all eukaryotes
how is homologous recombination used for gene knockouts
homologous recombination can be used to “swap” a functional copy of the gene out for a “knockout” copy of the gene
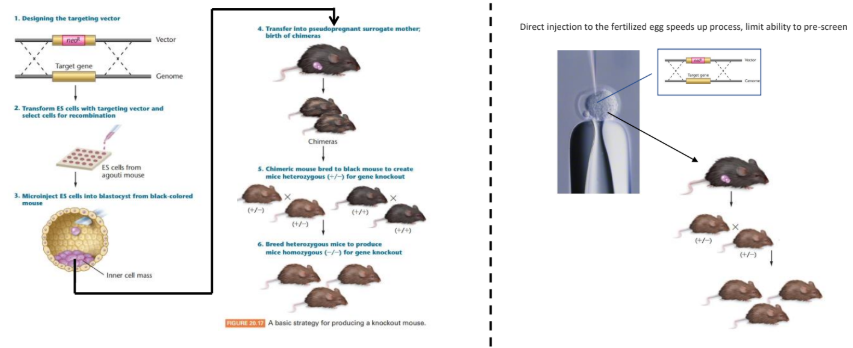
how can positive & negative selection avoid random integration
when homologous recombination occurs, we can have 2 outcomes:
double crossover OR one crossover
since we want a double crossover we can insert a negative marker, this marker will help us find sample that have only undergone one crossover, so they can be removed
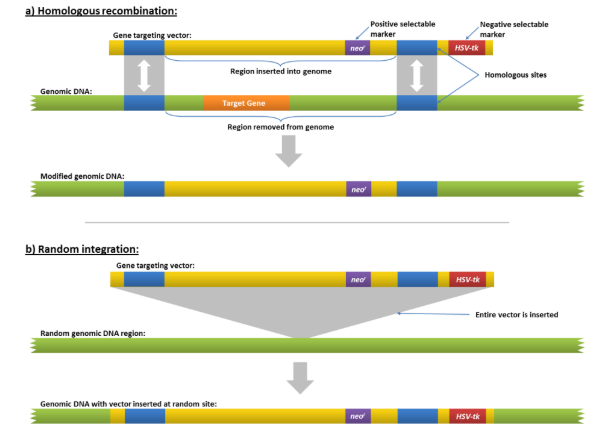
what is a knock-in gene
introduce a novel gene function/expression
entirely new gene
novel component of existing gene
change to a nucleotide
what are some pros & cons of homologous recombination
PROS:
directly target genes
highly efficient
relatively cheap
CONS:
based on occurrence of random events
depends of rate of homologous recombination
off target effects
summarise the process of CRISPR in bacteria
Spacer acquisition: Cas1–Cas2 grab a short DNA “mugshot” (spacer) from an invader and insert it into the CRISPR array.
Expression: The array is transcribed to a long pre-crRNA, then cut into individual crRNAs that each carry one spacer.
Interference: A crRNA loads into a Cas effector (e.g., Cas9 or Cascade). Guided by sequence matching and a nearby PAM, it finds the invader DNA/RNA and cuts it.
what are some pros & cons of CRISPR-Cas9
PROS:
efficiently target any gene
quick & relatively cheap
works in all organisms tested
CONS:
intended alteration may not be achieved
cleavage displays infidelity (off target effects)
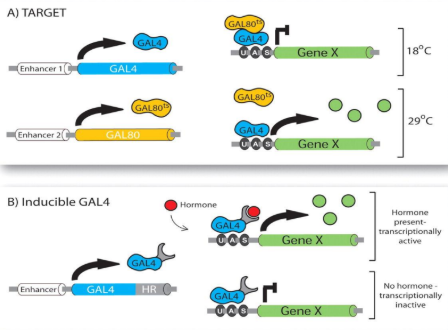
what is the GAL4/UAS system
a system that drives gene expression of a transcript of interest
placing GAL4 expression under a promoter makes this conditional
promoter can be cell/tissue specific
what are some ways that GAL4/UAS system can be controlled
controlled via temperature
controlled via inducer
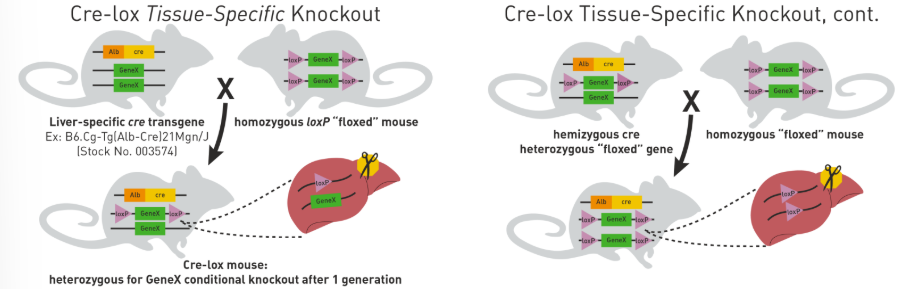
what is the Cre-lox system
a system that conditionally excises genetic material based on the expression of a recombinase
system can be inducible by an agonist