Shoulder Girdle
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Acromial end
Side of clavicle that articulates with the acromion
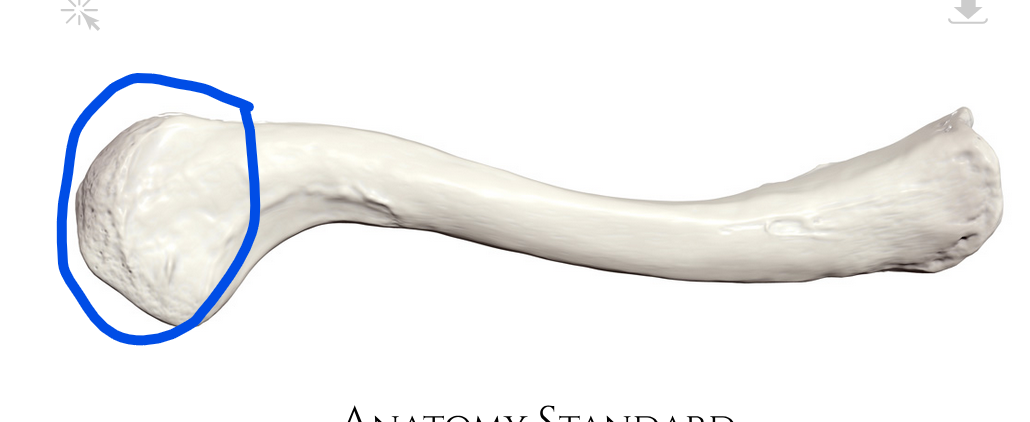
Sternal end
Side of clavicle that articulates with the sternum
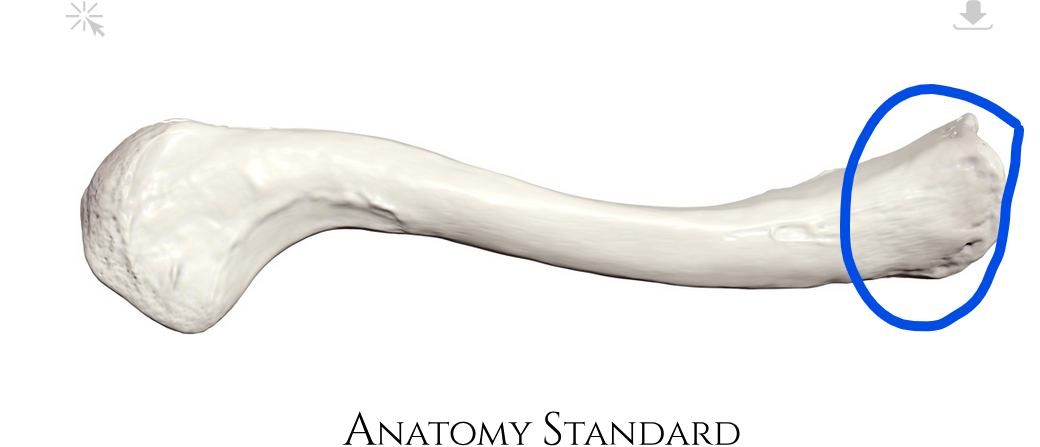
Rugosity for trapezius muscle
Where trapezius muscle connects
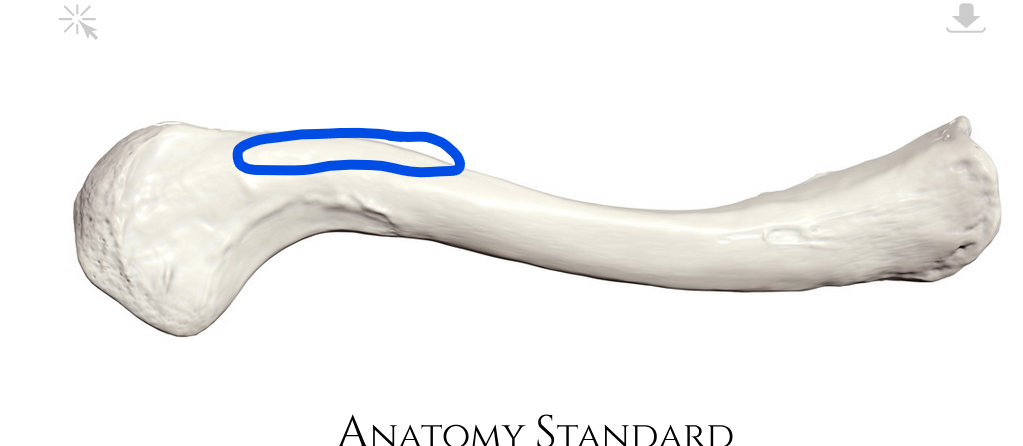
Rugosity for deltoid muscle
Where deltoid muscle connects
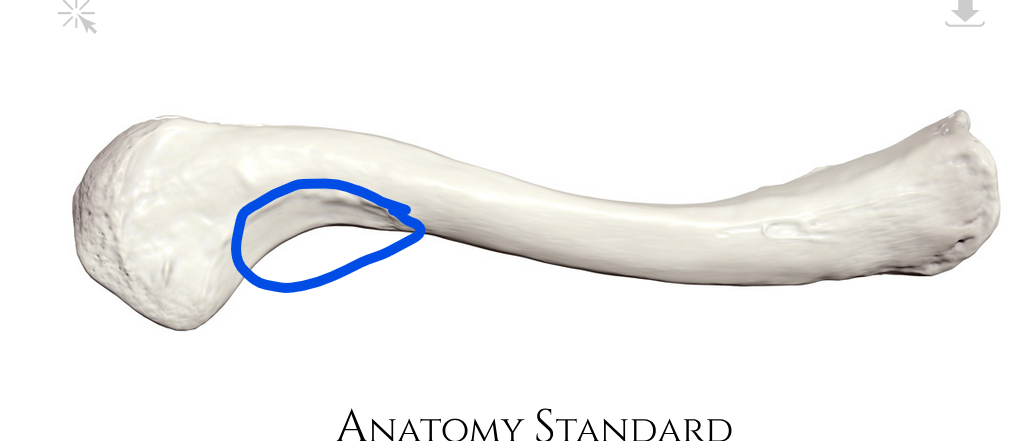
Rugosity for pectoralis major muscle
Where the pectoralis major muscle connects
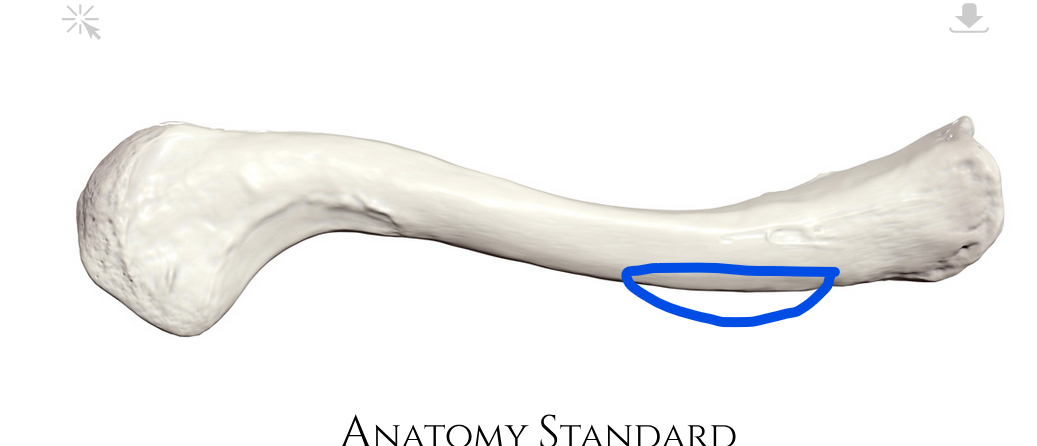
Articular facet for first costal cartilage
Where the first rib contacts the clavicle
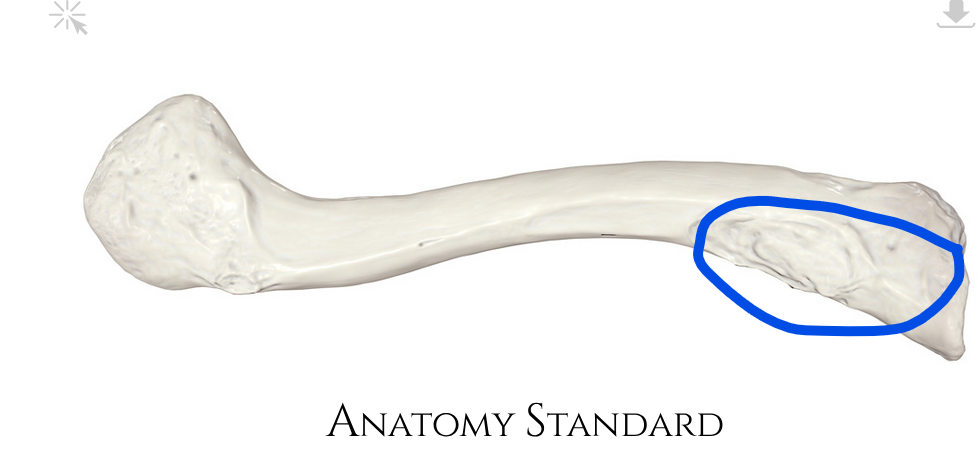
Conoid tubercle
Where the clavicle contacts the coracoid process on the scapula
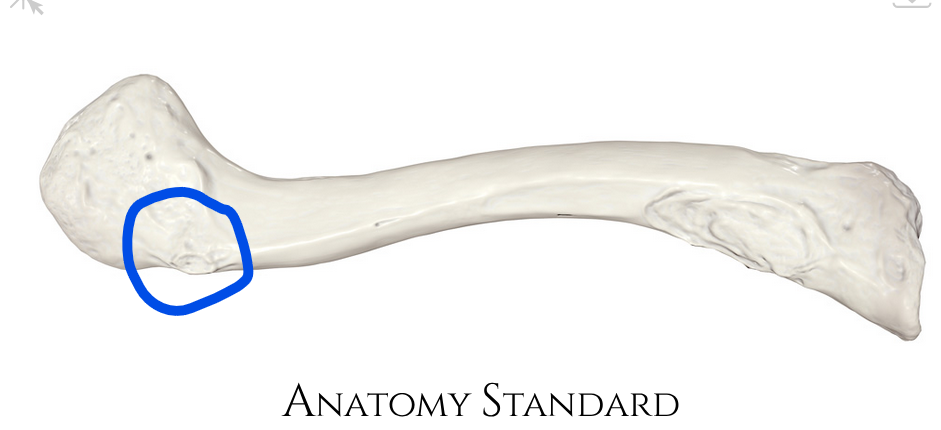
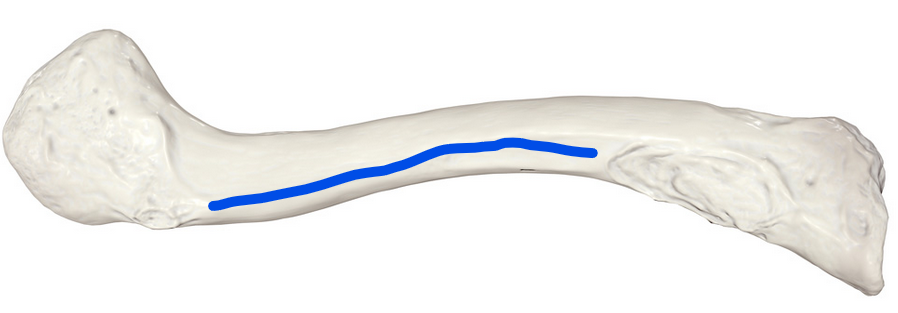
Subclavian sulcus
Groove for the subclavian vein and artery
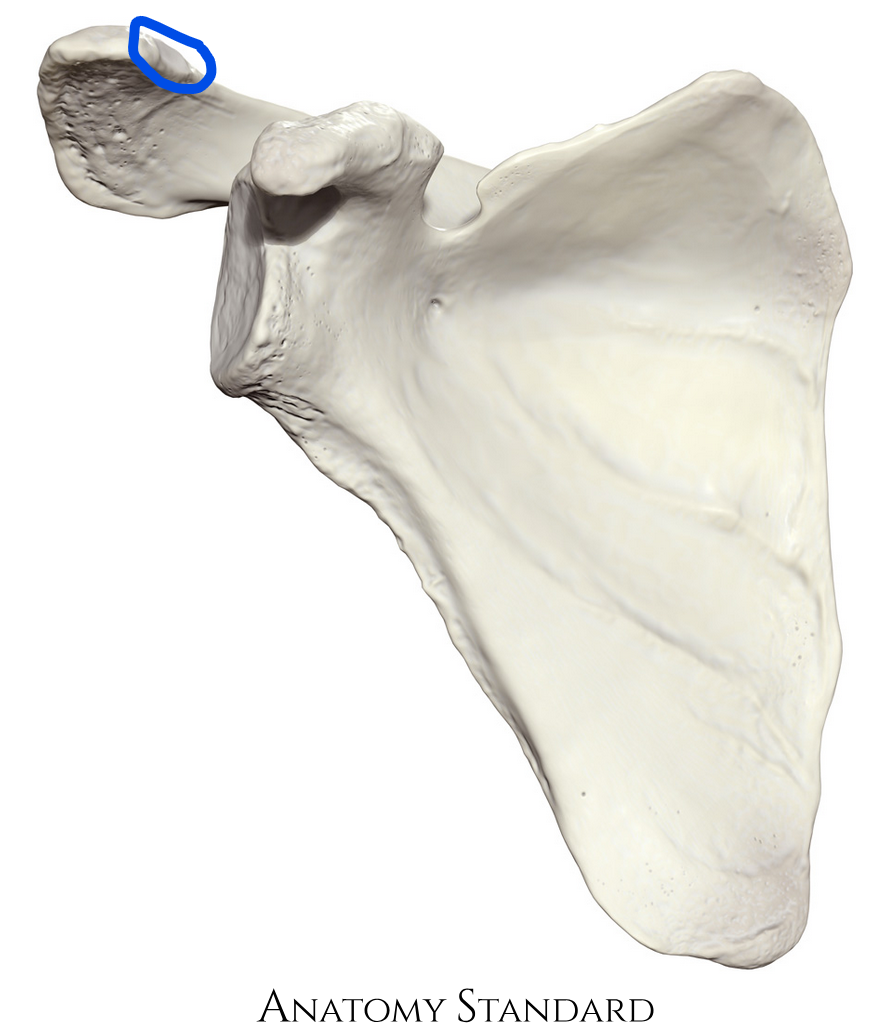
Clavicular facet
Where the clavicle contacts the acromion process
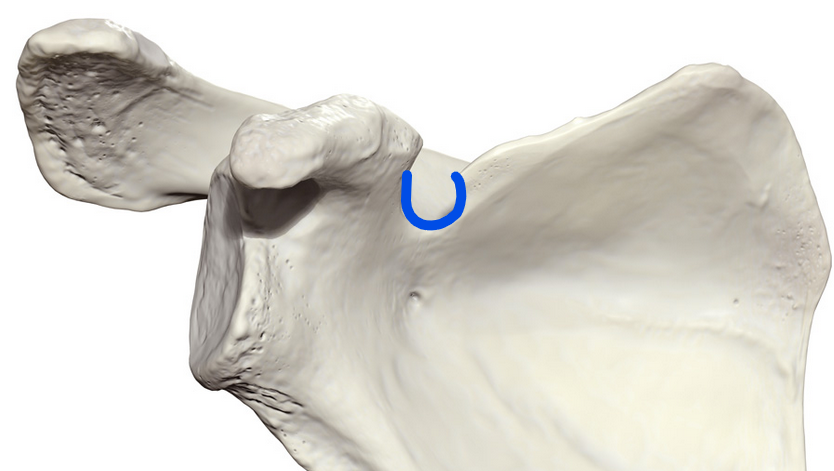
Scapular notch
Groove located on the superior border of the scapula that allows the suprascapular nerve to pass through
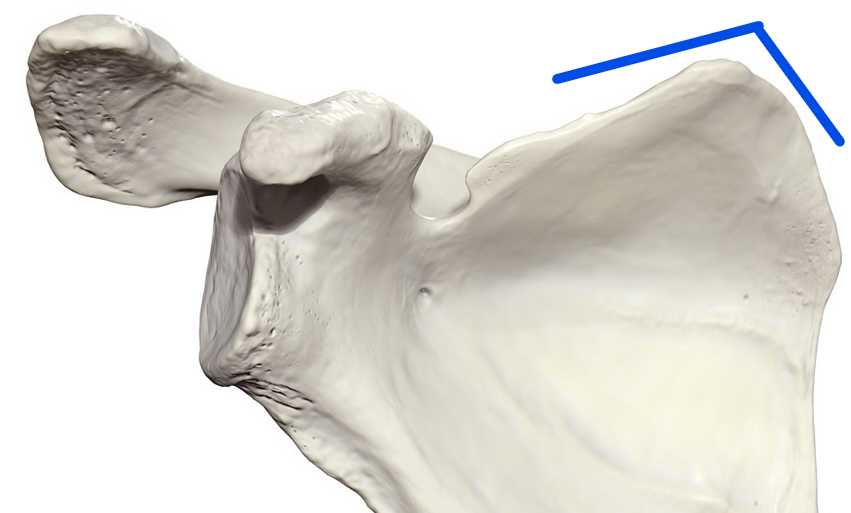
Superior angle
Upper most medial corner of the scapula
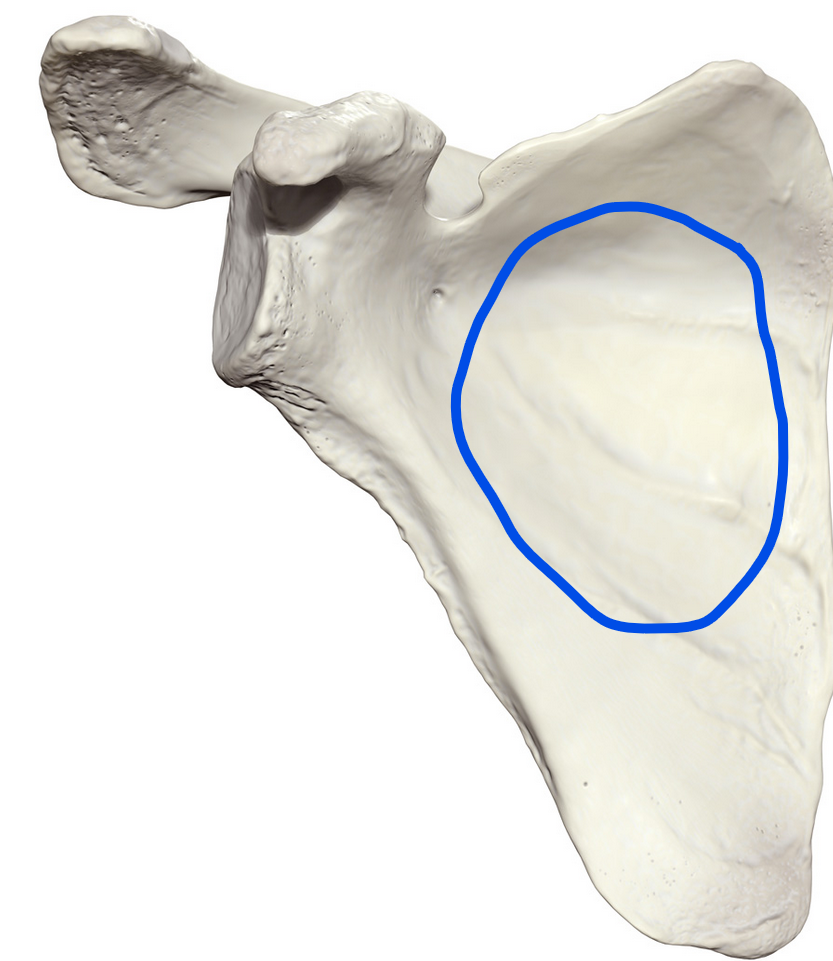
Subscapular fossa
Concave area on the costal surface of the scapula, primarily serving as the origin for the subscapularis muscle
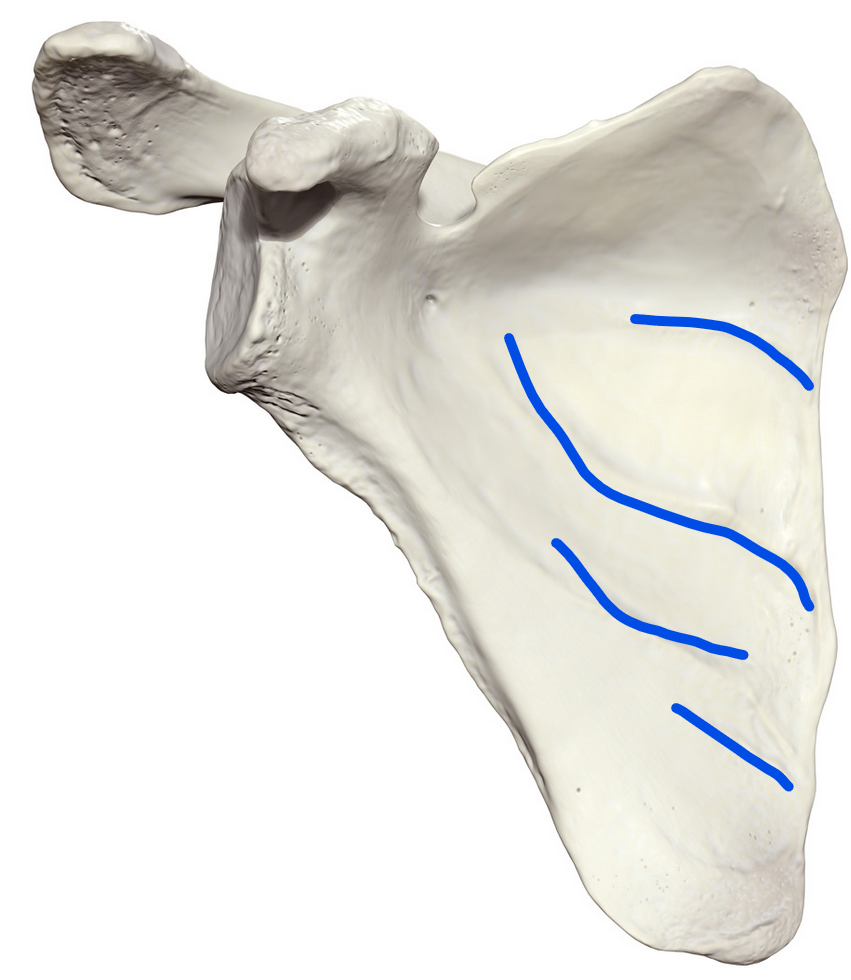
Oblique ridges
Cross the subscapular fossa from superomedial to inferiolateral (parallel to scapular spine); formed by intramuscular tendons of the subscapularis muscle
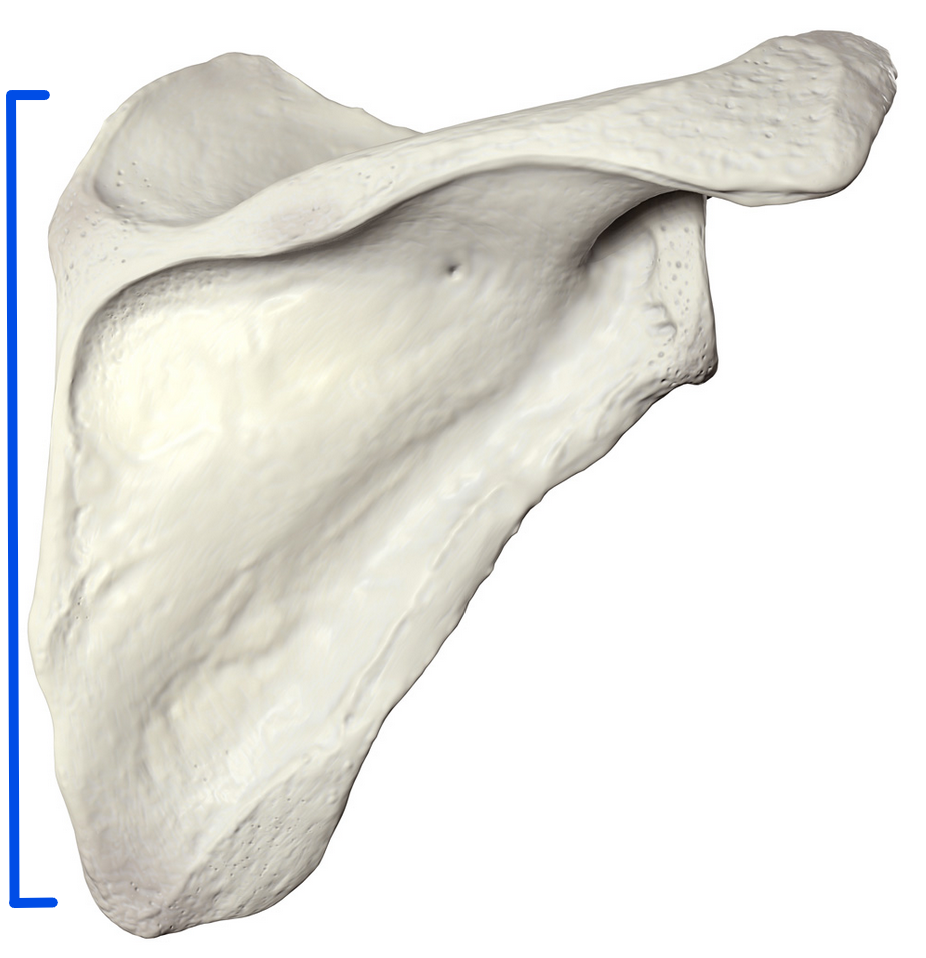
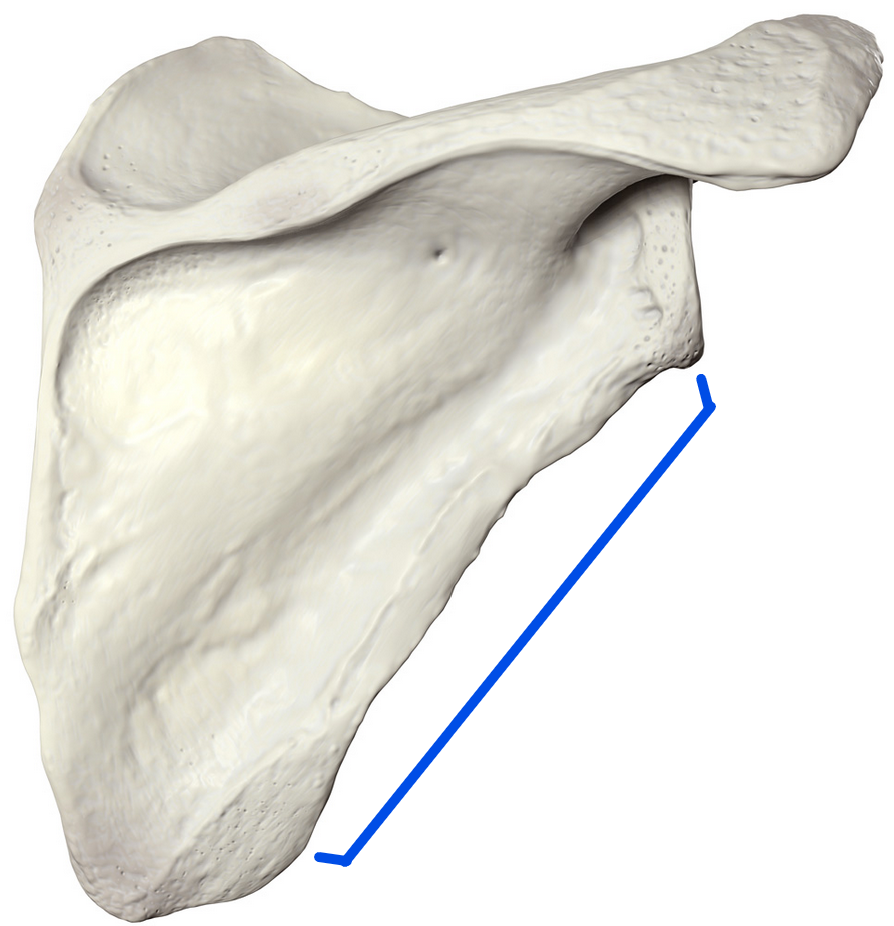
Medial border
Most medial edge of the scapula
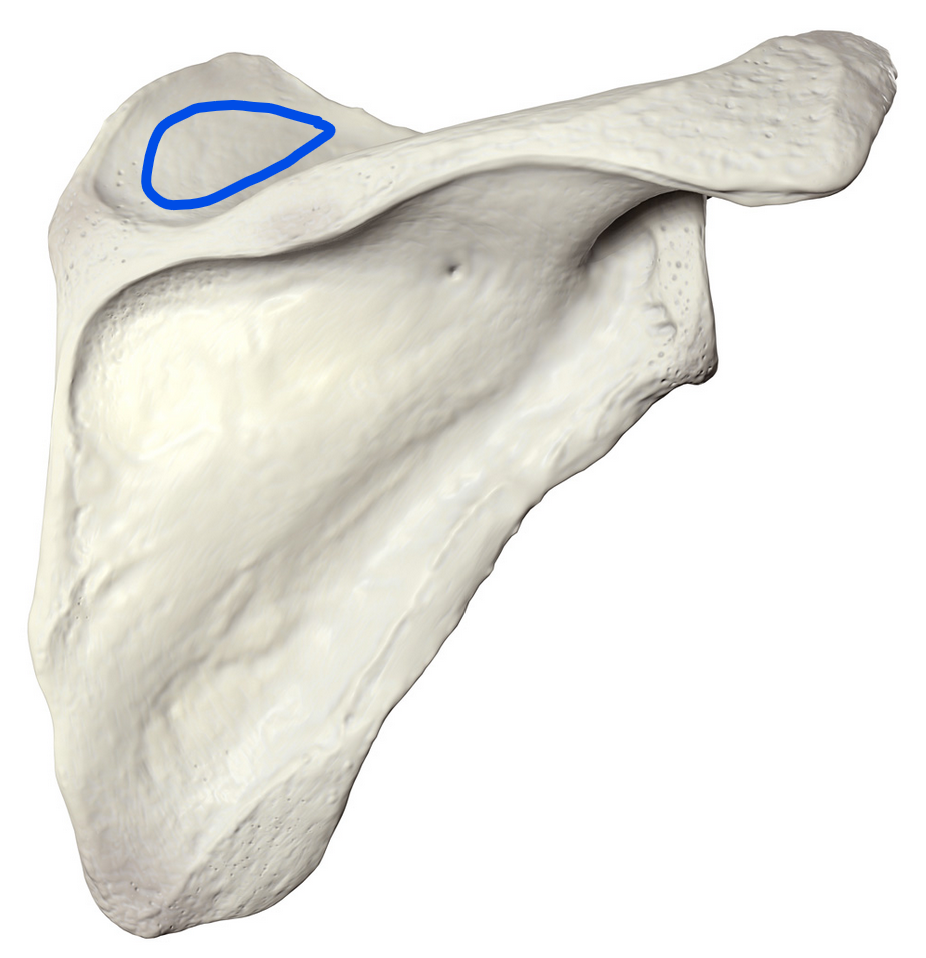
Supraspinous fossa
Concave area located on the dorsal surface of the scapula (shoulder blade), above the spine of the scapula; serves as the origin for the supraspinatus muscle
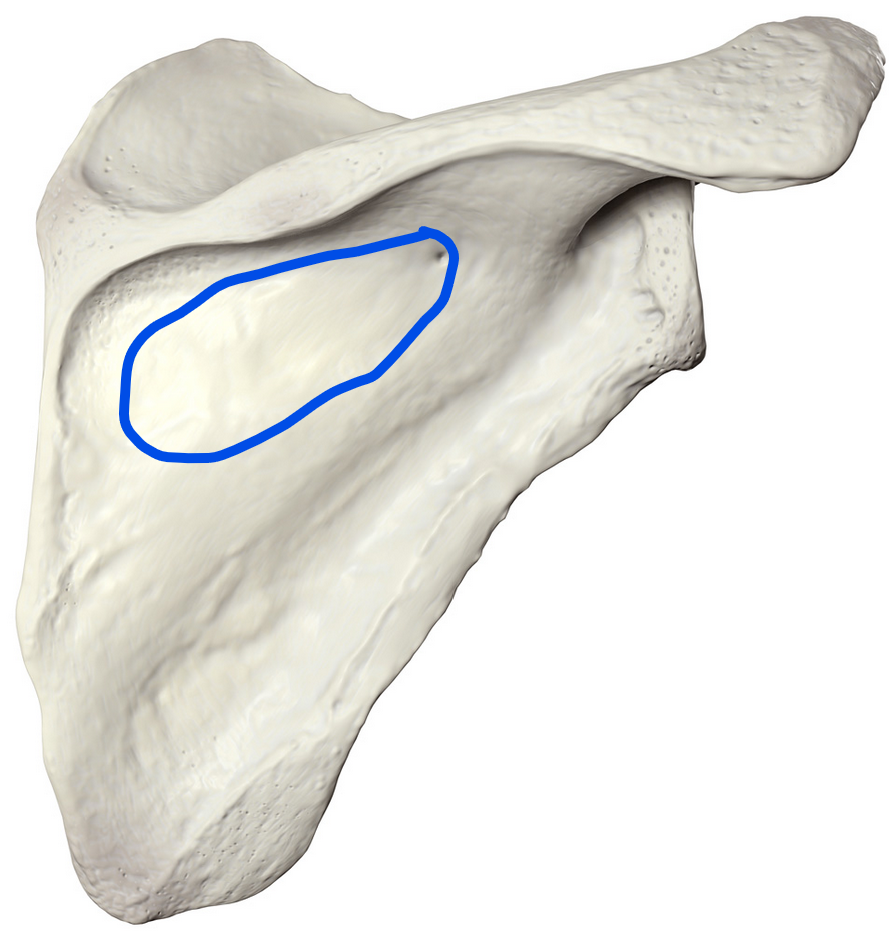
Infraspinous fossa
Large depression located on the posterior side of the scapula, below the spine, and serves as the origin for the infraspinatus muscle
Lateral border
Most lateral edge of the scapula
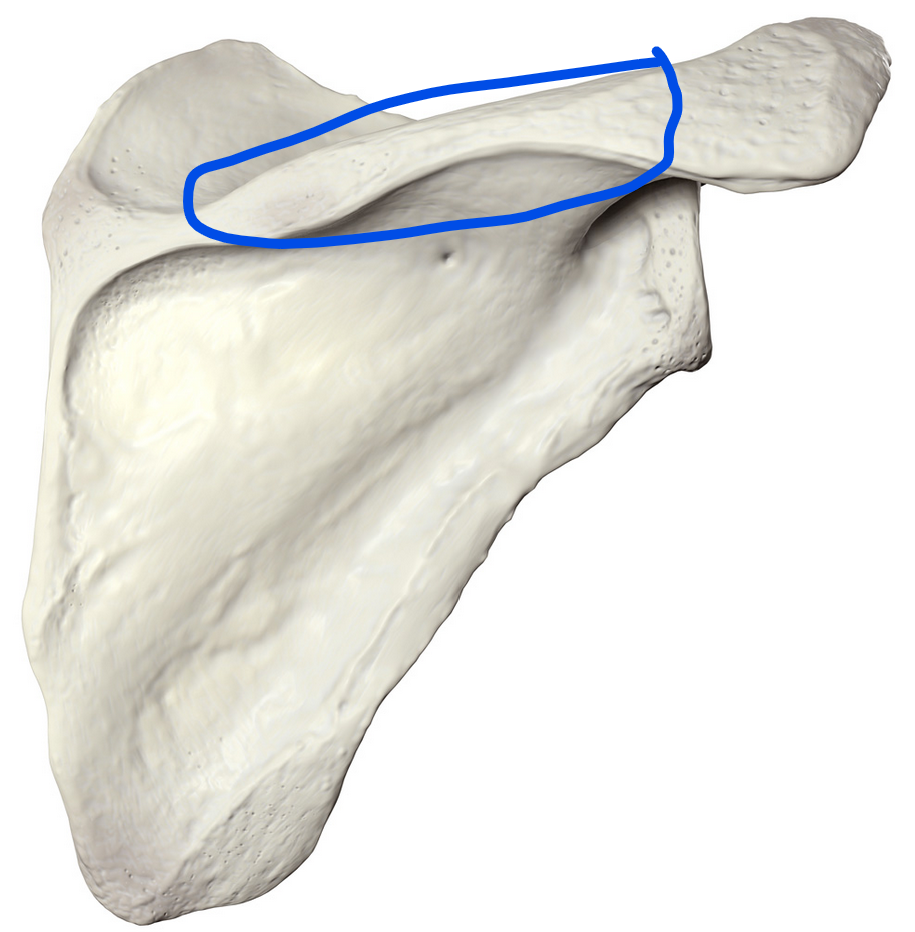
Scapular spine
Prominent bony ridge on the posterior surface of the scapula that separates the supraspinous fossa from the infraspinous fossa
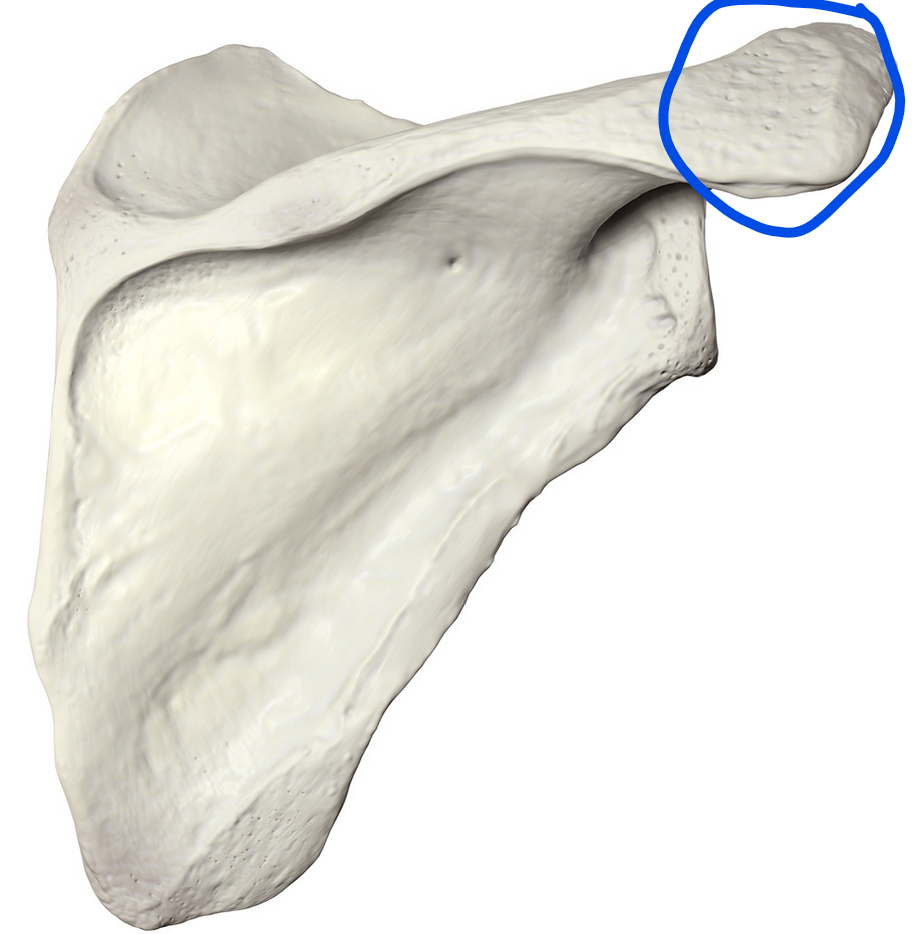
Acromion
Forms the highest point of the shoulder; serves as an attachment site for muscles like the deltoid and trapezius
Coracoid process
Small, hook-like bony projection on the scapula that helps stabilize the shoulder joint and serves as an attachment point for several muscles and ligaments
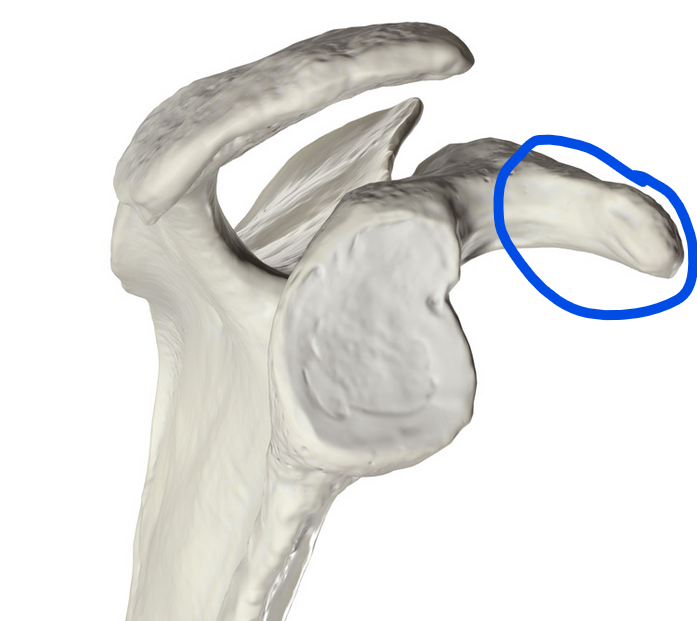
Supraglenoid tubercle
Small, rough projection on the scapula, located above the glenoid cavity, and serves as the origin point for the long head of the biceps brachii muscle
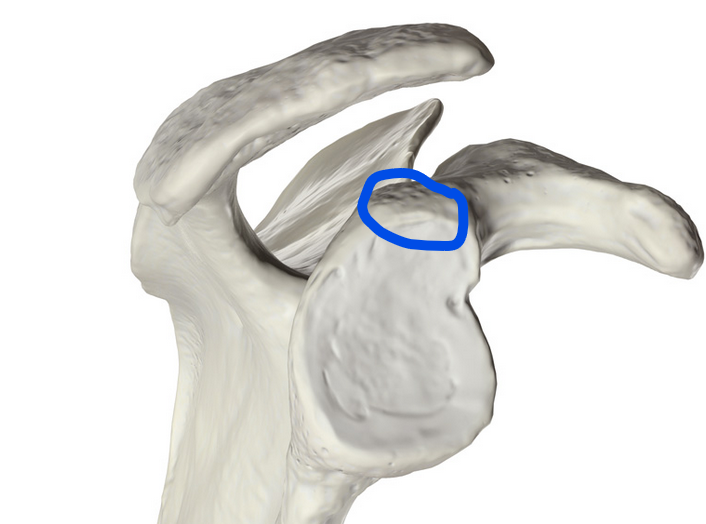
Glenoid fossa
Shallow, pear-shaped surface on the scapula that articulates with the head of the humerus to form the shoulder joint
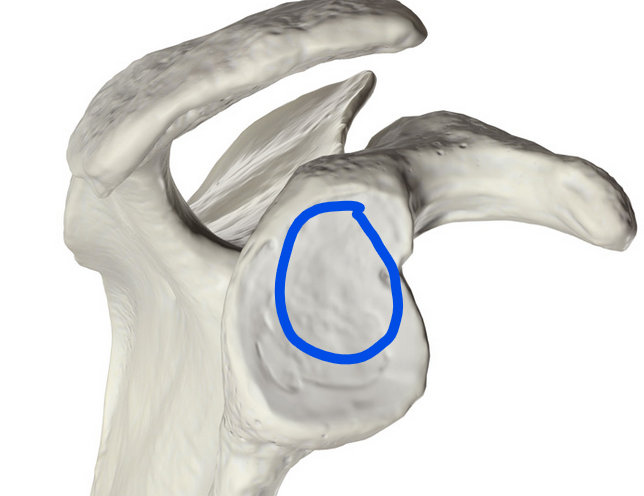
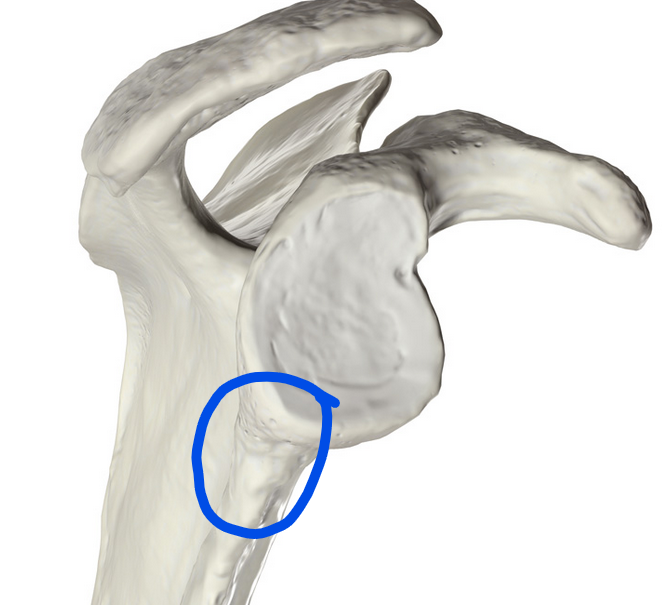
Infraglenoid tubercle
Small bony prominence on the scapula, located below the glenoid cavity; serves as the origin for the long head of the triceps brachii muscle