Amino acids
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Draw the structure of an amino acid, label any groups
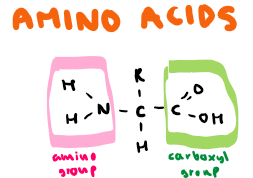
What are properties of an amino acid?
Amphoteric (has both acidic and basic properties)
Chiral (optically active, can rotate plane-polarised light)
What is a zwitterion?
A molecule which has both negative and positive ions.
When do zwitterions of amino acid exist?
Zwitterions only exist at the amino acid's isoelectric point. The isoelectric point is the pH at which the overall charge is 0 (dependent on the R group).
Draw the zwitterion of amino acids?
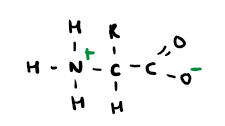
What does an amino acid look like in low pH/pH lower than isoelectric point?
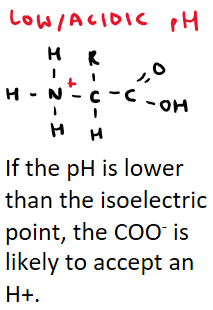
What does an amino acid look like in high pH/pH higher than isoelectric point?
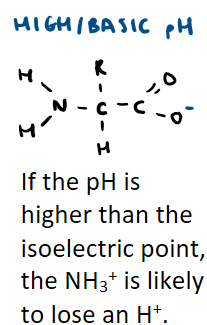
What separating tehnique can you use to separate and identify amino acids?
TLC- Thin Layer Chromatography
Why can TLC be used to separate and identify amino acids?
Amino acids have different solubilities
Describe the steps for TLC of amino acids
Draw a horizontal pencil line on the glass/metal plate (silica or alumina is mounted on it)
Add drops of amino acid mixtures to the line
Place the plate in the solvent (the base line must be above the solvent line)
Leave until the solvent has moved up to near the top of the plate. Remove it from the solvent.
Mark the solvent front and allow it to dry.
Observe the chromatogram to see the position of the amino acids (do this by calculating Rf values)
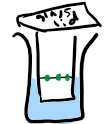
What do you use to visualise amino acids?
Ninhydrin
What does number of spots on your chromatogram tell you?
Number of spots tells you the number of amino acids which make up the mixture
How do you calculate the Rf value?

How can you use the Rf value to identify amino acids?
Once compared against a library of known Rf values, you can identify the amino acid
What are factors that affect the Rf value?
Temperature
Solvent
Make up of the TLC plate
Time spent in stationary and mobile phase
How does time spent in thestationary and mobile phase affect the Rf value?
Different time spent in stationary phase (stuck) and different time spent in mobile phase (travelling), molecules spending more time in mobile phase will travel a longer distance and have a higher Rf value