NRSE 470: Exam #2
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Endocrine System: Pathophysiology
Glands in the endocrine system store and secrete hormones that regulate homeostasis in the body.
Works on a negative feedback loop
Pituitary Gland
Secretes hormones and influences other endocrine glands
Hormones: ACTH
Cushing’s Disease/Syndrome: Causes and Risk Factors
Causes
Most Common Cause: Overuse of Corticosteroid medications
Pituitary gland tumor
Increase in ACTH
Normal feedback is ineffective
Cushing’s Disease/Syndrome: Risk Factors
Women between the ages of 20 and 40 years are five times more likely than men to develop Cushing’s syndrome.
Adrenocortical carcinoma
Pituitary carcinoma
Glucocorticoid use d/t chronic disorders
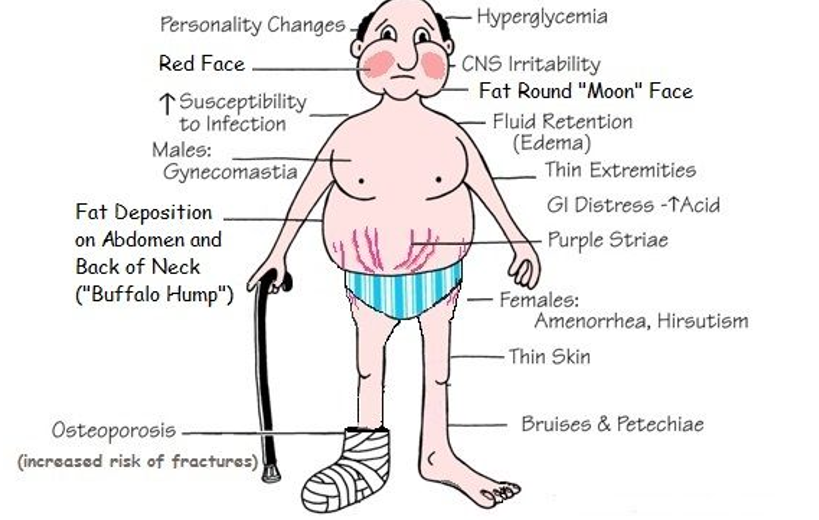
Cushing’s Disease/ Syndrome: Clinical Manifestations
Central Obesity
Buffalo hump
Moon face with red checks
Thin and fragile extremities
Osteoporosis
GI distress / bleed
decrease mucus production in the stomach
Purple Striae
Visual disturbances (if they have pituitary tumor)
Hyponatremic
Excess production of cortisol
This causes them to be hypokalemic, hypocalcemic
Cushing’s Disease/ Syndrome: Labs & Testing
Labs:
2 out of these 3 tests need to come back as positive to receive a diagnosis
Serum cortisol
Urinary cortisol
Low-dose dexamethasone suppression test
Other Labs NOT used to diagnosis
ACTH
K, Ca, Na & Glucose
Cushing’s Disease/ Syndrome: Treatments
Treatments
Depends on the cause
Adrenal
Correction
Pituitary
Surgical removal of the tumor
Corticosteroid medications
Decrease the dose
Cushing’s Disease/ Syndrome:Nursing Role & Complications
Nursing Role
Cardiac function
Decrease risk of injury
Risk for infection
Hand hygiene
Avoid large crowds
Promotion of Skin integrity
Paper tape
Improving body image & coping
Dietitian to help with
hypokalemic, hypocalcemia, hypernatremia
Foods high in potassium, calcemic and low in sodium, high in protein and vitamin D
Fluid restriction
Cushing’s Disease/ Syndrome: Complications
Adrenal crisis / Addisonian Crisis
Ulceration
Decrease production of protective mucus in the lining of the stomach due to increased cortisol
Bone fractures
Immunosuppression
Addison’s Disease: Cause and Risk Factors
Adrenal insufficiency
Dysfunction of the hypothalamus- pituitary gland- adrenal gland feedback
Insufficient production of steroids by the adrenal gland
Risk Factors
Primary
TB
Adrenalectomy
Metastatic cancers
Radiation therapy of the abdomen
Idiopathic autoimmune dysfunction
Secondary
Steroid withdrawal
Pituitary neoplasm
High dose radiation of pituitary gland or entire brain
Addison’s Disease: Acute (Addisonian Crisis)
Causes
Sepsis
Trauma
Stress
Adrenal hemorrhage
Steroid withdrawal
Addison’s Disease: Clinical Manifestations
Weight loss
Craving for salt
Hyperpigmentation of the skin & mucous membranes (increase in levels of ACTH)
Weakens & fatigue
Nausea & vomiting & anorexia
Abdominal pain
Constipation or diarrhea
Sever hypotension (acute)
Hypovolemia
Electrolyte imbalance
Hyponatremia
Hyperkalemia
Hypoglycemia
Hypercalcemia
Addisonian Crisis
Life threatening complication
Clinical Manifestations
Hypotension
Cyanosis
Fever
Nausea & Vomiting
Signs of shock develops
Goal
Prevention of circulatory shock
Addison Disease: Labs & Testing
Labs
Serum cortisol
Plasma ACTH stimulation test
Electrolytes
Testing
ECG
Addison Disease: Treatments
Avoiding circulatory shock !
Treat hypotension
Antibiotics (if infection is cause)
Replacement of corticosteroids & mineralocorticoids
Dietary supplement
Addison Disease: Nursing Role & Complications
Nursing role
Nursing diagnosis- interventions
Education
Addison Disease: Complications
Addisonian crisis
Hypoglycemia
Hyperkalemia/ hyponatremia
Diabetic ketoacidosis AND Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State
Lack of insulin
Usually in patients with Type 1 diabetes
Diabetic ketoacidosis AND Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State: Risk Factors
EMERGENCY
Result of physical stress on the body- examples:
Injury
Illness
Infection
Surgery
Excessive alcohol use
New onset diabetes
Elevated HbgA1C
Illicit drug use
Polypharmacy
Noncompliance with insulin therapy
Diabetic ketoacidosis AND Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State: Medications
Corticosteroids
Antipsychotics
Antidepressants
Diabetic ketoacidosis: Risk Factors
Age 13 to 25
Females
Pervious episodes of Diabetic ketoacidosis
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State: Risk Factors
Age older than 65
African American
Native American
Hispanic
Morbid obesity
Both (DKA& HHS): Causes
Low income, homelessness, and lack of health insurance
Elevated HbA1c
Taking antipsychotic or antidepressant medications
Acute infection or illness
Excessive alcohol consumption
Use of illicit drugs, especially cocaine
Blood glucose levels that are not well managed
Polypharmacy
DKA: Clinical Manifestaions
Metabolic acidosis
Muscle weakness
Dehydration leading to decreased cardiac output
Loss of electrolytes
Cardiac arrhythmias
Kussmaul respirations
Deep, rapid, labored breathing
Decrease perfusion to the kidneys
Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State: Clinical Manifestations
More profound neurological manifestations
Muscle weakness
Profound dehydration
Thromboembolic disease (clot risk)
Decreased perfusion to the kidneys
Acute Kidney Injury
Loss of electrolytes
Cardiac arrhythmias
DKA and HHS: Lab and Diagnostic Studies
Serum blood glucose’
Serum Bicarb: LESS THAN 15
Complete blood count: WBC
Electrolytes
ABGs
Anion gap
Serum osmolality
Urine studies
Ketones present in urine for DKA
Chest X-Ray
ECG
Blood and Urine Cultures
DKA and HHS: Treatments and Therapies
Treatment similar for DKA and HHS
Restore circulatory volume
Treating hyperglycemia
Correcting electrolyte imbalances
Monitor potassium levels
Cannot be replaced too quickly
Potassium is LESS than 3.3 that needs to be treated prior to start an insulin drip
Potassium that 3.3 to 5 can be given along side insulin drip
Potassium reaches 5 replaces stop and just monitor
Treating any underlying causes.
Insulin drip based on patient’s weight
Monitor their Anion gap
DKA and HHS: Role of the Nurse
Education
Insulin
Sick day rules
Community support for insulin
home health to teach how to give insulin
Provide insulin supplies
Teach to check for ketones if glucose greater than 240
Monitor
Vital Signs
Labs
Glucose
Meningitis
Inflammation of meninges/subarachnoid space
Causes
Bacterial (severe, fatal if untreated)
Viral infection
Meningitis: Risk Factors
16 to 23 years old
Group living
Immune compromised
Invasive neurosurgery
HIV
CSF leak
Meningitis: Clinical Manifestations
Fever
Headache
Stiff Neck
Rash
Seizures
Altered level of conciseness
Kernig Sign
Nurse flexes the patient's hip and knee to a 90-degree angle.
Brudzinski Signs
Neck flexion sign: When the examiner passively flexes the patient's neck, the patient involuntarily flexes their hips and knees.
Contralateral leg sign: When the examiner flexes one of the patient's legs, the opposite leg involuntarily flexes.
Meningitis: Diagnostics
Lumbar Puncture
Unless increased Intracranial Pressure
CT scan
Meningitis: Complications
Increased Intracranial Pressure
Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion (SIADH
Septic emboli.
Seizures & Epilepsy: Causes
Structural
Genetic
Infectious
Metabolic
Immune
Unknown
Seizures: Types
Generalized
Focal
Unknown
Stages
Prodromal
Aura
Ictal
Postictal
Seizures & Epilepsy: Triggers
Stress
Fatigue
Flashing lights
Alcohol
Stimulants
Seizures & Epilepsy: Safety
Airway protection
Side-lying
Padded rails
NO objects in mouth
Seizures & Epilepsy: Treatments
Antiseizure meds
Benzodiazepines first-line
Phenytoin
Levetiracetam
Monitor drug levels & interactions
Surgical/implant options
Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Responsive Neurostimulation
Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy
Seizures & Epilepsy: Complications
Status Epilepticus
Sudden Unexpected Death in Epilepsy (SUDEP)
Psychosocial impact.
Seizures & Epilepsy: Patient Education
Seizure Journals
Med Adherence
Lifestyle Modifications.
Parkinson’s Disease: Clinical Manifestations
Progressive loss of dopamine-producing neurons in substantia nigra; Lewy bodies hallmark.
Tremors
Rigidity
Bradykinesia
Postural Instability
Depression
Fatigue
Autonomic Dysfunction.
Spinal Cord
Send sensory stimuli from the body to the brain
Send motor instructions from the brain to the body
Direct reflexes
Spinal Cord Injury: Risk Factors
Motor vehicle
Falls (over 65)
Acts of violence
Sports related
More common in men than females
Spinal Cord Injury: Classification
Classified on where the injury is located
Types
Impact –consistent compression
Impact – intermittent compression
distraction injury
transection and laceration
Spinal Cord Injury: Clinical Manifestations
C1 to C4
Ventilator dependence
C1 to C8
Limited proprioception
T1 to T8
Affects trunk movements
Lack of abdominal control
T9 to T12
Limited abdominal control
L1 to S5
Loss of bowel and bladder functioning
Affects sexual function
Spinal Cord Injury: Testing
CT
MRI
X Ray
Spinal Cord Injury: Complications
DVT
Neurogenic Shock
Medical emergency
within the first 24 hours
Cant regular blood pressure , heart rate, temperature
Inadequate blood flow to vital organs
Autonomic Dysreflexia
Life threatening
Above the T6 level
Caused by a trigger
Can be triggered by different things:
Pain, impaction, a full bladder
Usually happens after the first year of a spinal cord injury
Clinical Manifestations
Severe headache
Facial flushing
Diaphoresis
Spinal Cord Injury: Treatments
Pain control – pharmacology
Physical Therapy, Occupational Therapy, and Speech Therapy.
Trach care
Treatment depends on symptoms
Spinal Cord Injury: Key Take Aways
Realignment and stabilization of the spine with the use of mechanical force or a brace must be done as soon as possible to prevent further damage.
Halo Fixation device
Head Injury: Types
Concussion
Subdural Hematoma
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Head Injury: Risk Factors
Car accidents / Crashes
Falls
Males more than females
Contact sports
Military service
Substance use
Falls
Polypharmacy
Head Injury : Clinical Manifestations
LOC - Difficulty waking
Pupillary dilation
Headache
nausea
Agnosia
Ataxia
Aphasia
Loss of balance , Weakens of limbs
Personality changes, Amnesia
“Halo sign”
Indication of CSF leak
Runny nose, fluid coming out of ear’
Yellow ring our the fluid indicates leak
Symptom management heals on its own
Head Injury: Testing & Imagining
CBC with Diff
Blood Glucose
Electrolytes
Toxicology
Imaging
CT, MRI, X-Ray
ABGs
Head Injury: Complications
Cushing's Triad
Late finding
Hypertension
Low Blood respirations
Bradycardia: Low heart rate
Widening pulse pressure
Frequent neuro checks: Glowscow Coma Scale
Opening eyes: 1-4
Verbal response: 1-5
Motor Response: 1-6
Increased Intracranial Pressure
Brain Herniation
Pulmonary Edema
Head Injury: Treatment/ Therapy/ interventions
Frequent Assessment
Medications
Anti-Seizure meds
Decrease ICP
Barbiturates
Opioids
Craniotomy
Therapeutic hypothermia
gets the brain swelling down
Spinal precautions
Collar / back board / log rolling
Head Injury: Positioning
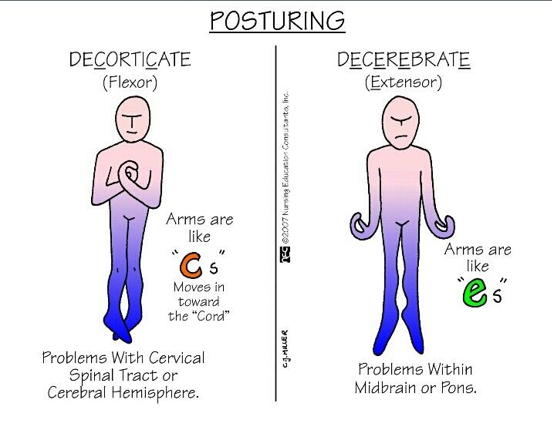
Decorticate (Flexor)
Decerebrate (Extensor)
Decorticate has a better survival rate then Decerebrate
Head Injury Complication: Subdural Hematoma
Older Adults at risk
Can be misdiagnosed as a Stroke
Clinical Manifestations
Persistent headache
Confusion
Neasua and vomiting
Memory loss
SEVERE
Seizures
Patients taking blood thinners, hypoglycemic patients
Small hematoma: Treatment
Rest
Frequent monitoring
no long term complications
Self healing
Large hematoma: Treatment
EMEREGENCY TREATMENT
Surgical intervention to remove the hematoma
Head Injury Complication: Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Causes
Aneurysm rupture
Uncontrolled hypertension
High mortality rate if left untreated
Frequent monitoring
Complete the Glowscow Coma Scale
Monitor for signs of…
Brain Herniation
ICP
Clinical Manifestations
“I have the worst headache of my entire life”
Nausea / Vomiting
(Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion) SIADH
Body makes TOO MUCH Antidiuretic hormone
Causes
Stoke
Head trauma
Brain tumors
Risk Factor
Repetitive damage to the pituitary or hypothallus
C
Urine output decrease
Hyponatremia
Neurological manifestations can occur
Seizure
Cerebral edema
Coma
Treatment
Fluids
3% sodium chloride
Monitoring sodium intake hourly
DO NOT REPLACE SODIUM TOO QUICKLY
Foods high in sodium
Diabetes Insipidus
Body does NOT MAKE enough Antidiuretic hormone
Cause
damage to pituary and hypothalamus gland
High Urine output
Hypernatremia
Complications
Dehydration
Electrolyte imbalance
Medication
Desmopressin
Treatment
Treat the underlying cause
Restore water balance and normalize Antidiuretic hormone
Stroke
Disruption of blood supply
Types
Ischemic
Risk Factor: A-Fib not on anticoagulants
Hemorrhagic
Injury on the right side of the brain, displays on the left side of their body
Injury on the left side of the brain, displays on the right side of the body
Stroke: Clinical Manifestations
Sever headache
Vertigo
Gait impairment
Trouble articulating
Unilateral numbness
Hemiparesis (one-sided muscle weakness)
Expressive & Receptive Aphasia
Loss of depth perception
Vision changes
Agnosia
Inability to recognize familiar people, objects or sounds
Stroke: Risk Factors
Hypertension
Hyperlipidemia
Diabetes
Smoking/ alcohol / substance
Maintain healthy weight/ regular exercise
Stroke: Screening
NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS)
HIGHER than 10 = severe stroke
Glasgow coma scale
Stroke: Testing
CBC
Coagulation Panel
ECG
CT/ MRI
Within 25 minutes of arrival to ED
Angiography
Dysphagia screening
Stroke: Treatment/ Therapy/ Interventions
TPA
give 3 to 4 hours after onset of an ischemic stroke
Breaks down the clot
Restores blood flow
Thrombolytic medication
Anticoagulants
Antiplatelets
Antiepileptics
Antihypertensives
Other medications
Stool softeners, antianxiety
Angioplasty
Thrombectomy
Carotid Endarterectomy
Stroke: Key Take Aways
Patient Education
Modified diet
Thicken liquid
no straw
Pureed diet
FAST
Facial drooping
Arm weakness
Speech
Time
Macular Degeneration: Risk Factors, Comorbidities & Impact on Health
Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration
causes fluid to leak under the macula
causing visual distortion
Dry age-related macular degeneration
Causes the retinal tissue to break down
Risk Factors
Smoking
Hypertension
Comorbidities
Cardiovascular and renal conditions
Impact on overall health
ADLs
Depression
Anxiety
Risk of Falls
Macular Degeneration: Education
Smoking session
Diet
Physical activity, maintain healthy weight
Control chronic conditions
Amsler grid
Vision test used to check for changes in central vision, particularly distortions or blind spots
Macular Degeneration: Treatment / Therapy
Ophthalmological examination
Fluorescein angiography
Uses a fluorescent dye to visualize the blood vessels in the retina
Early detection/ preservation of vision
Medication
Carotenoids lutein
Zeaxanthin
Anti-VEGF injections
Photodynamic Therapy
Cataracts: Risk Factors
Age
Diabetes mellitus
Hypertension
Traumatic eye injury/ surgery
Use of steroids
Previous eye surgery
Family history
Overexposure to sun or ultraviolet (UV) rays
Smoking
Alcohol use disorder
Obesity
Cataracts: Clinical Manifestations
Vision is not clear
Hazy
Pain- free
Cataracts: Patient Education
Smoking cessation
Diet
Leafy green vegetable
protect from sunlight
Fall risk
Visual aids
Magnifier
Large print material
Cataracts: Treatment/ therapy
Nurses will assess for _______ by first assessing visual acuity using a Snellen eye chart.
Cataract extraction surgery
Glaucoma: Risk Factors & Comorbidities
Irreversible loss of vision
Elevated intraocular Pressure
2 types:
Primary Open Angle
Angle Closure
Risk Factors
Age
Black & Hispanic
Eye injury/ trauma
Family history
Chronic health conditions
Comorbidities
High blood pressure
Diabetes
Hyperlipidemia
Glaucoma: Treatments
Tonometry
Measures the pressure inside the eye
Eye drops
Lowering Intraocular Pressure (10 to 21 mm Hg)
Preserving vision
Surgery
Post-op care
Post-Operative Infection
Elevated temperature
Purulent drainage
Vision changes
Intense eye pain
Glaucoma: Patient Education
Lifestyle modifications
Eye Drops
Goal is preserving vision
Frequent monitoring of Intraocular Pressure
Less than 21
Middle & Inner Ear : Risk Factors
Middle ear
Recurrent colds
Enlarged adenoids
Trauma
Changes in air pressure
Inner ear
Chronic- after age 40
No known cause
Autoimmune disorder
Viral infection
Genetic
Middle & Inner Ear: Clinical Manifestations
Vomiting
Nausea
Blurry vision
Cold sweats
Trembling
Hearing loss
Headaches
Imbalance/ dizziness
Congestion in the ear
Ear fullness
Middle & Inner Ear : Treatments
Medications
Diuretics & Corticosteroids
Motion sickness medications
(Meclizine, valium, promethazine, ondansetron)
Determine the cause of hearing deficit
Remove occlusion
Hearing aids
Cochlear implants
For severe hearing loss
Hearing test
Audiometry
Tympanogram
Weber and Rinne test
ENG
Finger rubs or Whispered voices
Middle & Inner Ear : Key Take-Aways
Patient Education
Avoid foods high in sugar
Avoid nicotine, caffeine, and alcohol
Limit sodium (edema)
Meniere’s disease
Causes debilitating vertigo.
Develops from an excessive accumulation of fluid in the inner ear..
Treatment with diuretics and steroids can help alleviate the manifestations.