Oral Biology 2 Midterm
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
what are the three joint classifications of TMJ?
1. synovial joint
a. boundary lubrication
b. weeping lubrication
2. compound joint
3. ginglymoarthrodial joint
what are the different cavities of the TMJ?
superior and inferior
superior:
location of there articular eminence
inferior:
location of the condyle
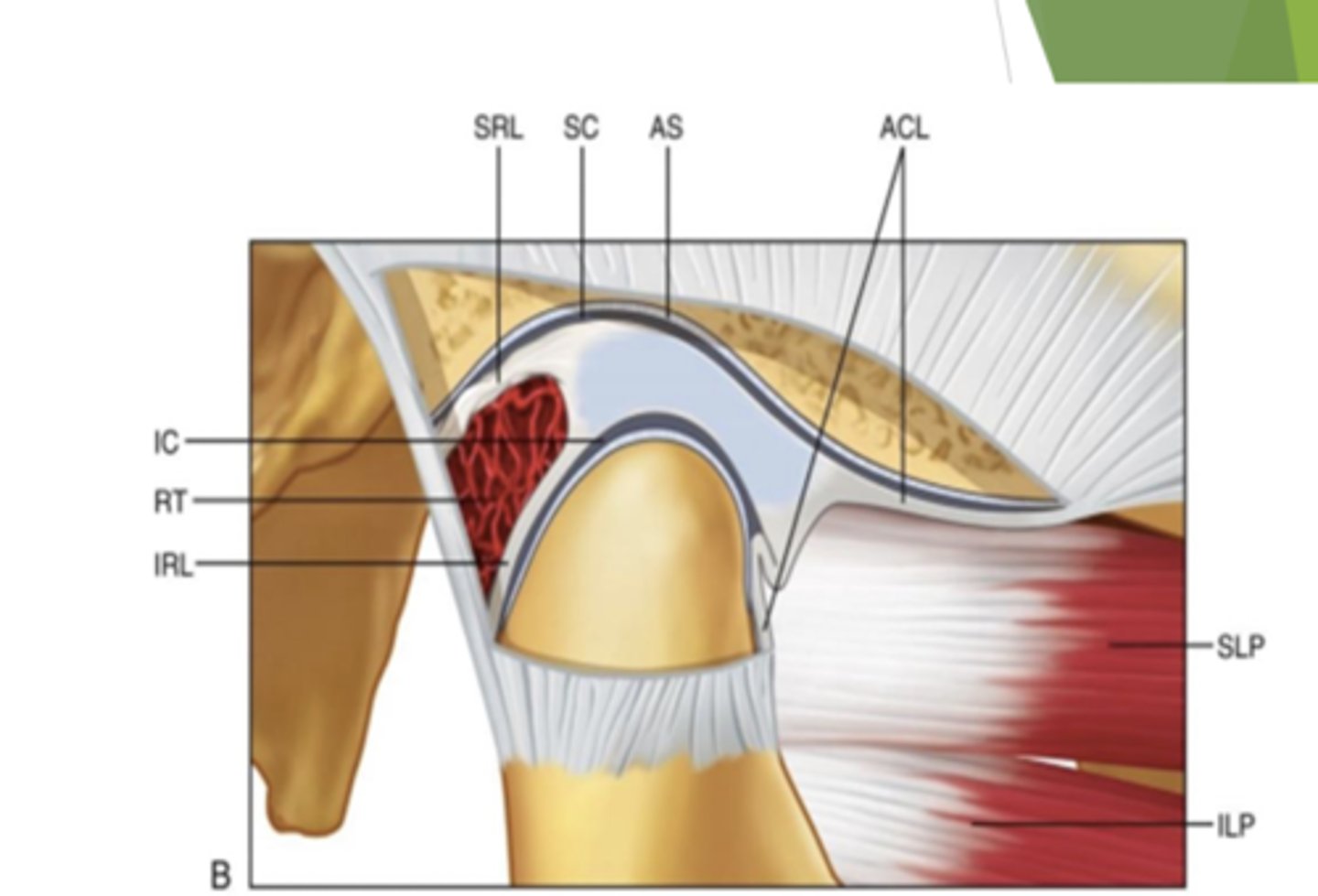
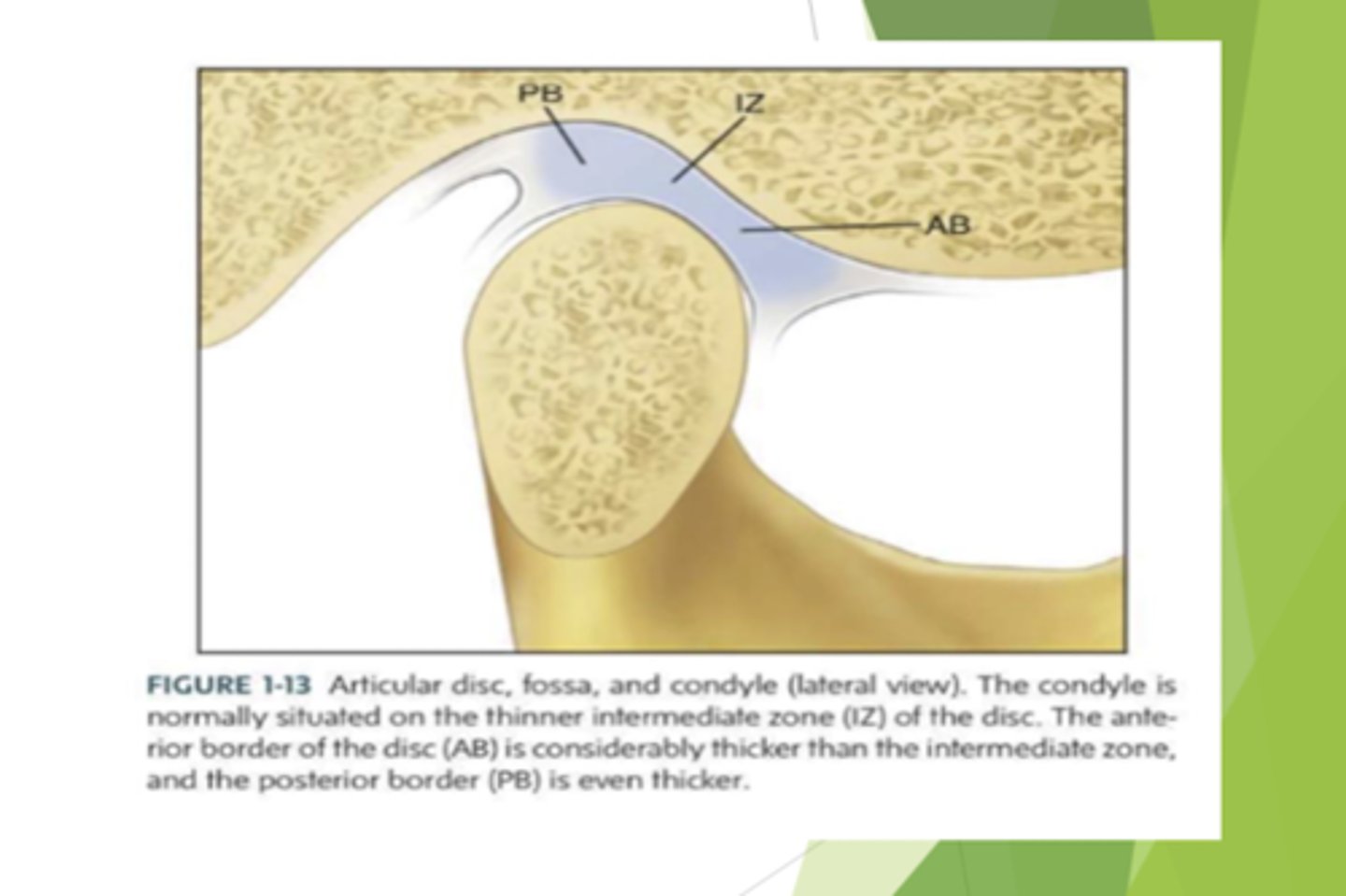
what are the three regions of the disc?
where is the disc located?
posterior border, intermediate zone, and anterior border
the disc is located in the superior cavity
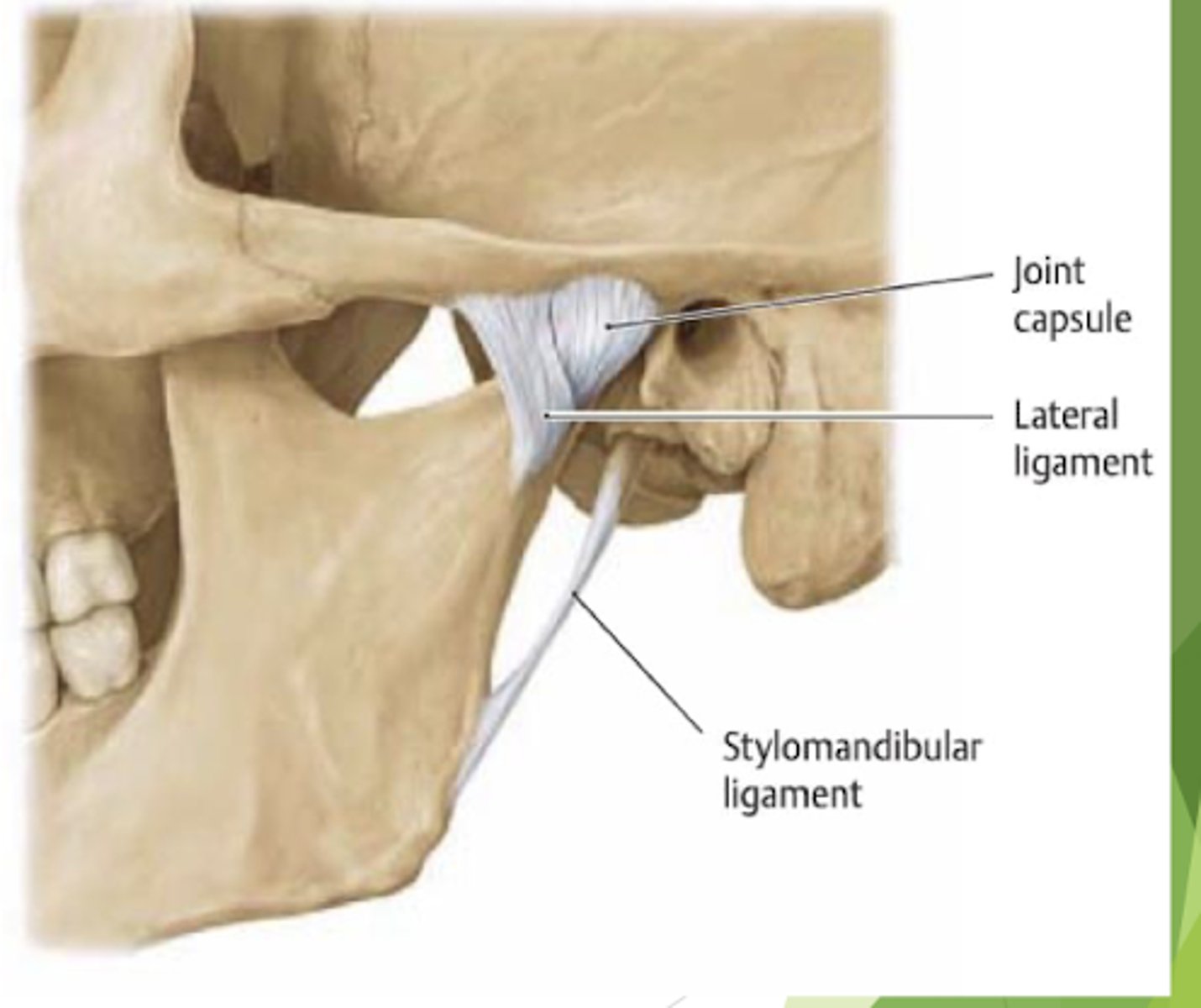
what is being described:
are made up of connective tissue, restrict excessive movement/provide support, and do not stretch past normal length (50mm)
ligaments of the TMJ
what are the functional ligaments of the TMJ?
capsular, collateral, and tempromandibular ligaments
what are the accessory ligaments of the TMJ?
sphenomandibular and stylomandibular
true or false:
the TMJ ligaments have two portions the oblique and outer horizontal
false, the two different portions of the TMJ ligament is the oblique and the inner horizontal
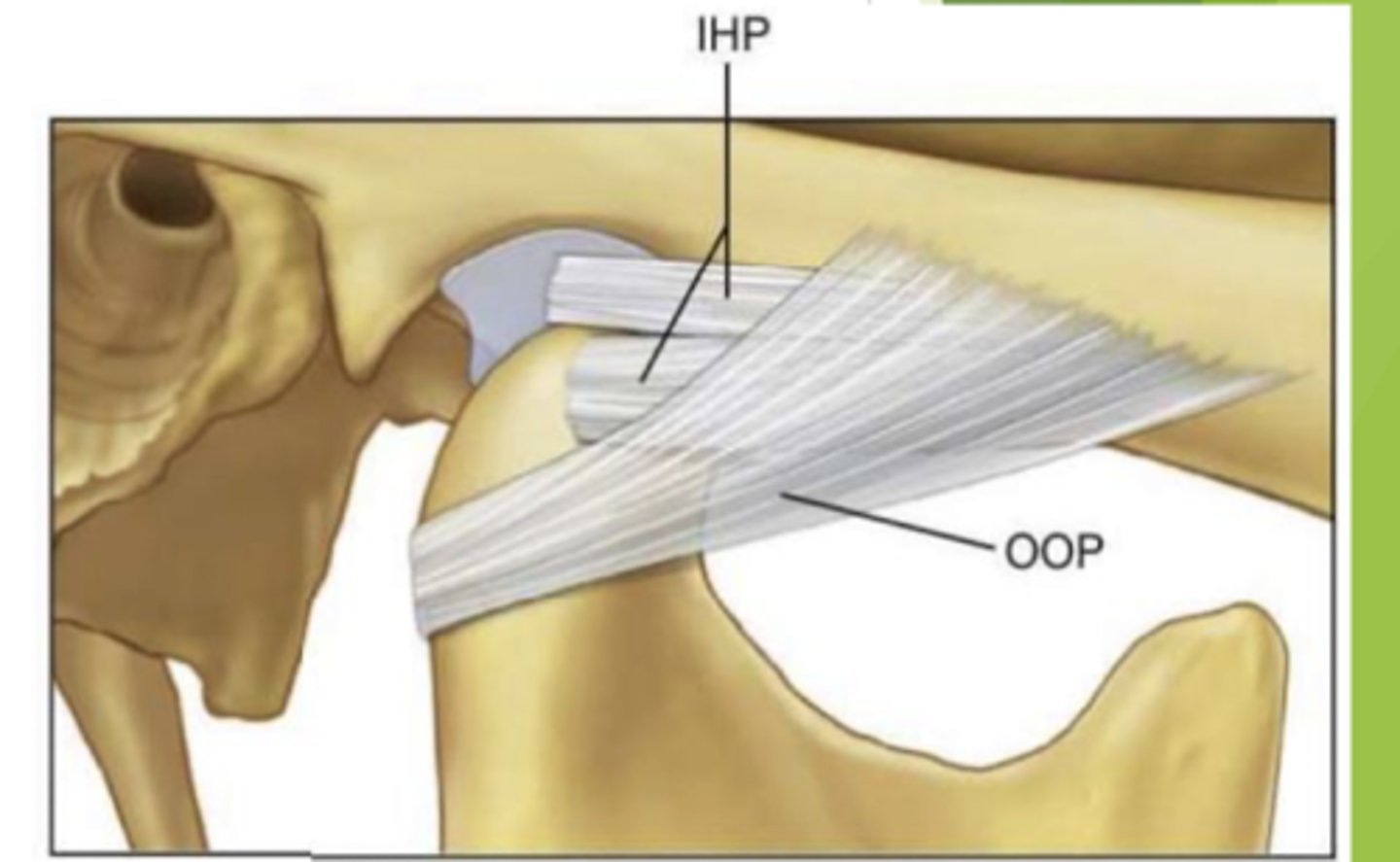
which portion of the TMJ ligament is being described?
limits rotational opening and prevents impingement of neck structures
the oblique portion of the TMJ ligament
what are the functions of the inner horizontal portion of the TMJ ligament?
prevents condyle from moving posteriorly
what are the characteristics of the capsular ligament of the TMJ?
List the functions.
1. retains synovial fluid
2. surround the TMJ
functions:
resist medial, lateral, and inferior forces
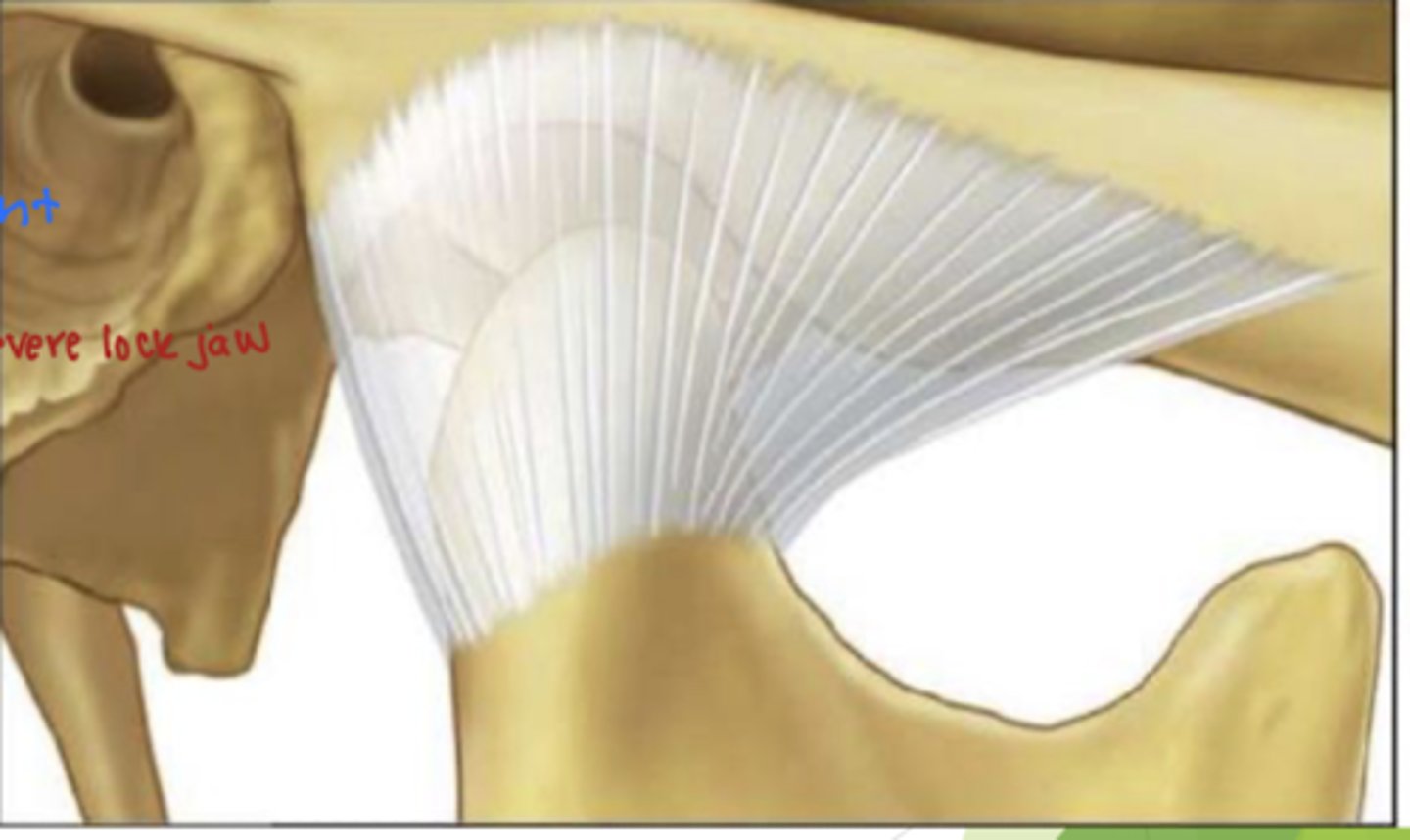
what is a consequence of puncturing the capsular ligament of the TMJ?
why?
puncturing the capsular ligament leads to friction between the condyle and posterior border of the disk
-this can eventually lead to arthritis and lock jaw
the capsular ligament retains synovial fluid
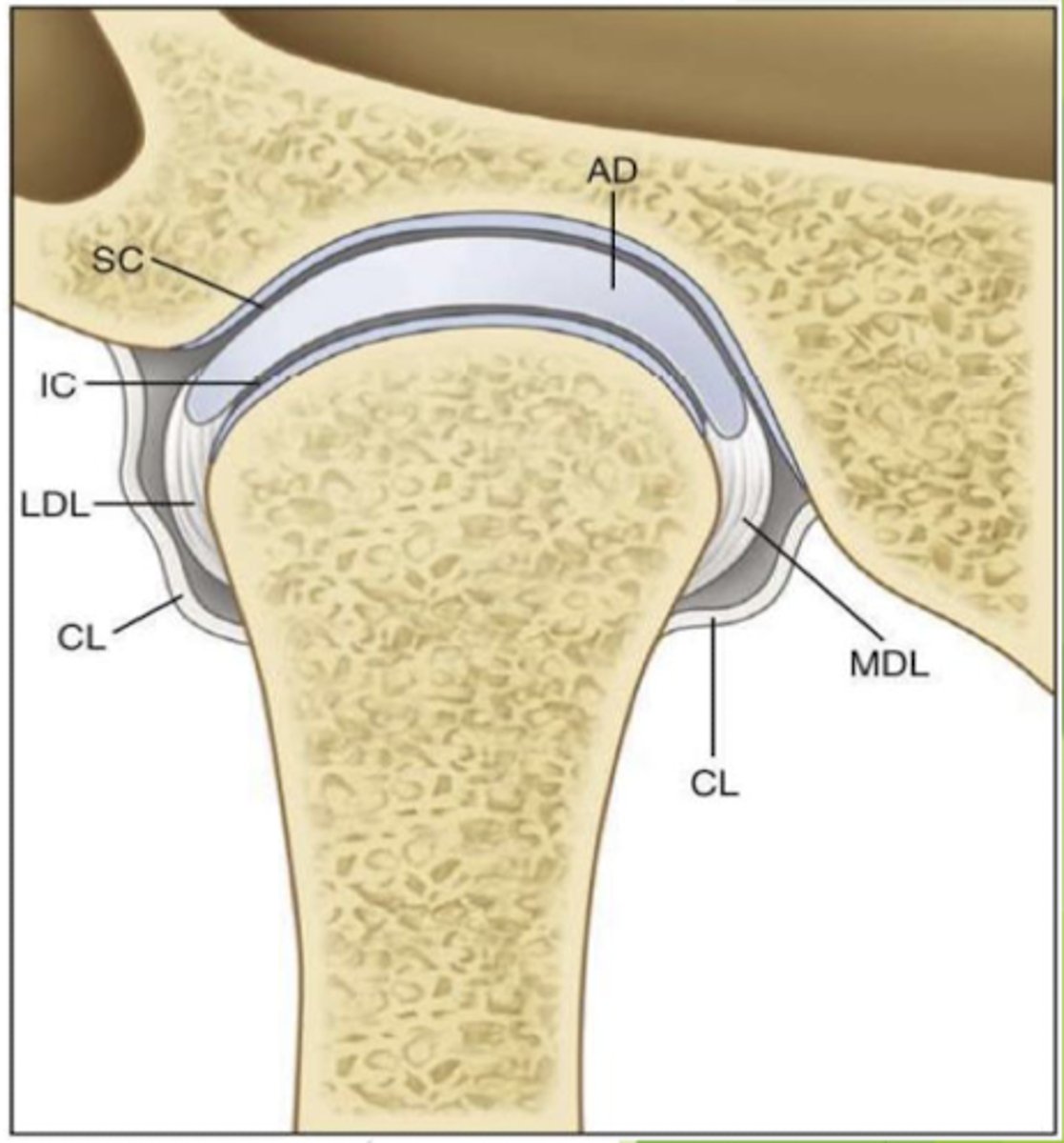
what are the two ligaments that form the collateral ligament?
1. medial collateral ligament
2. lateral collateral ligament
which ligament is being described?
restricts movements that separate the disc from the condyle
collateral ligament
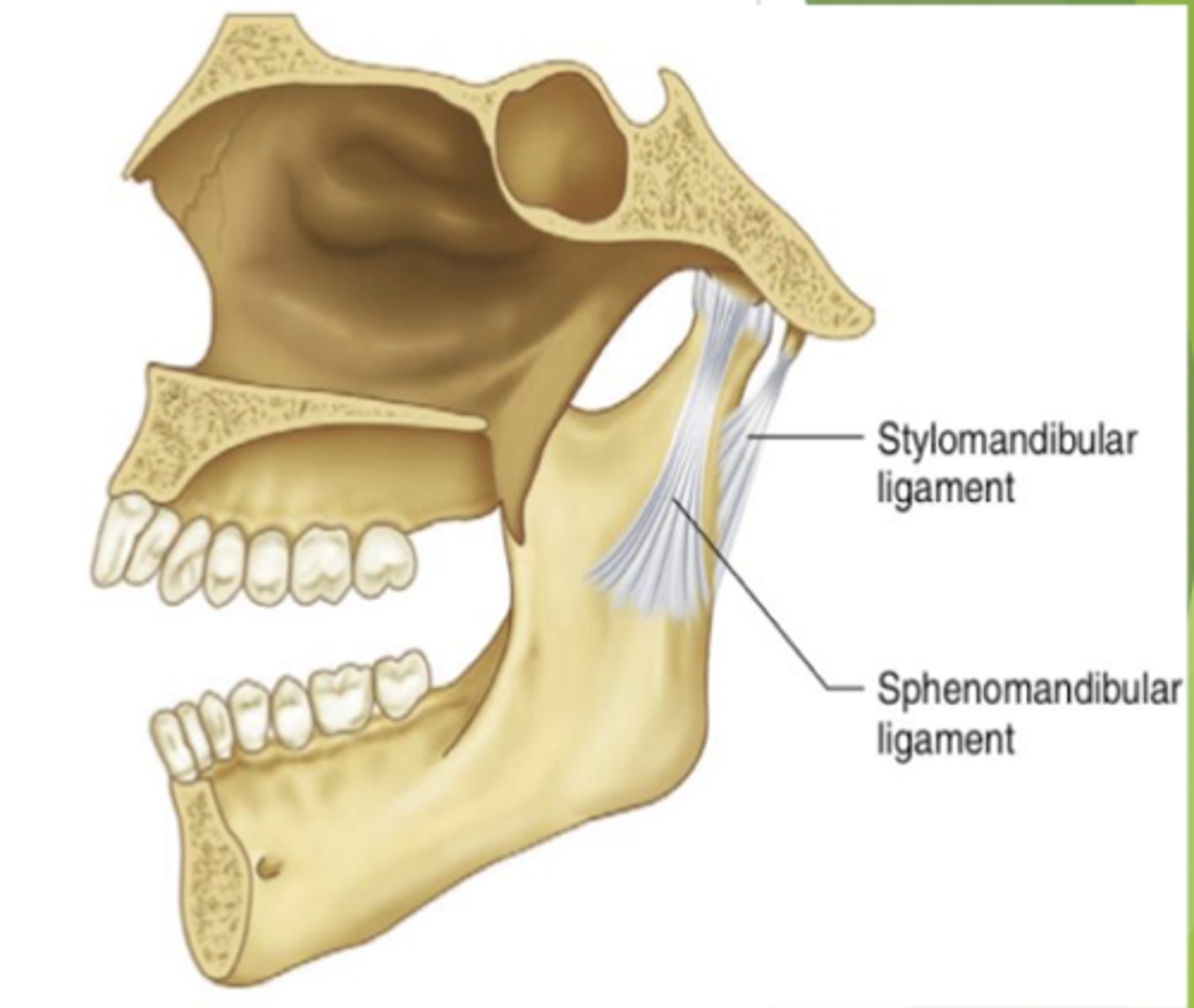
which accessory ligament restrict excessive protrusion?
stylomandibular ligament
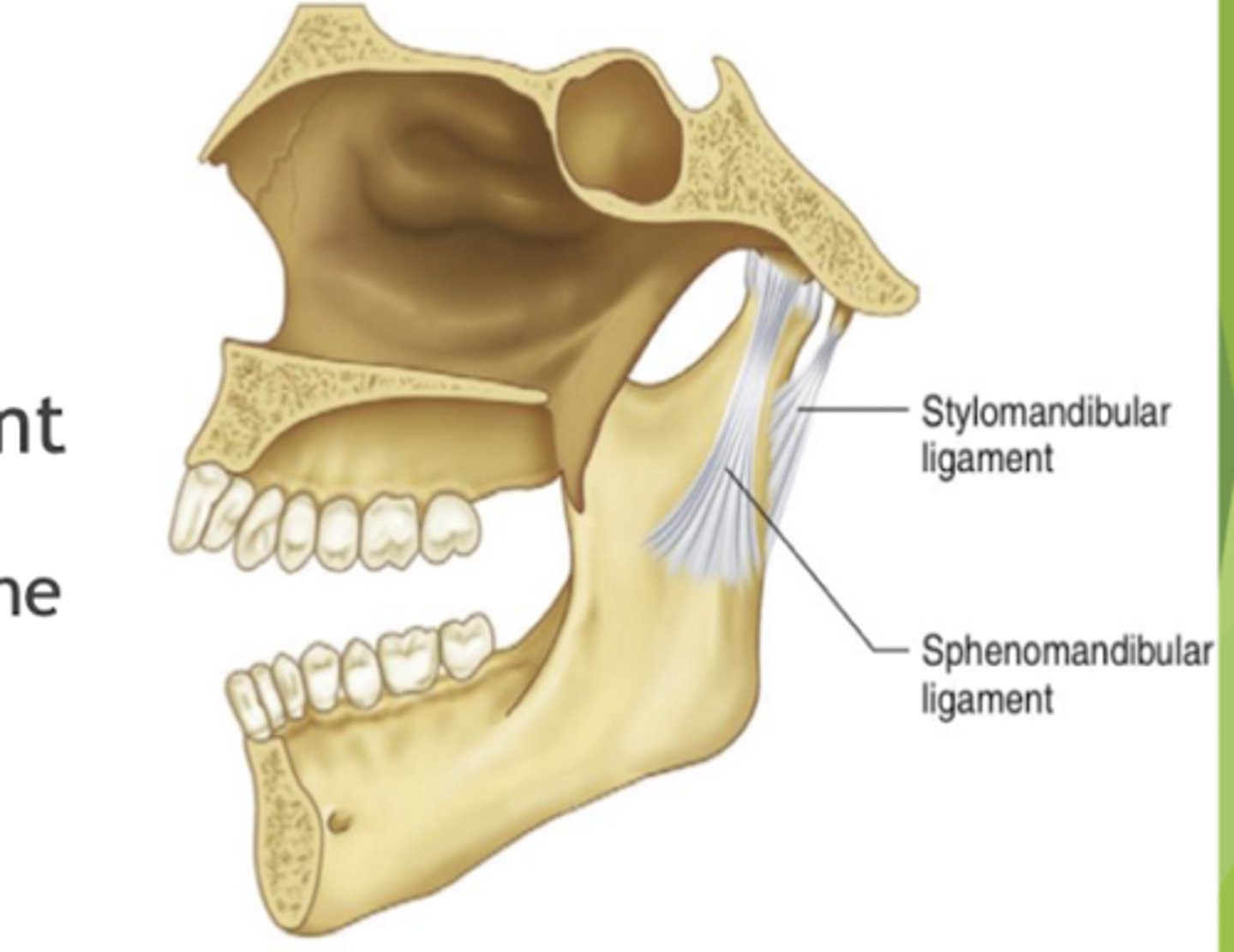
what is the function of the spenomandibular ligament?
limits inferior distention of the mandible
what movement is the condyle making when the mandible initially starts to open?
rotational movement
true or false:
upon further opening of the mouth the condyle continues to rotate
false, upon further opening of the mouth the condyle transitions to a sliding movement
what are the branches of the opthalamic branch(V1) of the trigeminal nerve?
what is the function of V1?
1. nasociliary
2. frontal
3. lacrimal
4. meningeal
carries sensory information from the dura mater to each branch
what are the dental branches of the maxillary branch (V2) of the trigeminal nerve?
what is the function of V2?
1. posterior superior alveolar
2. anterior superior alveolar
3. middle superior alveolar
providing sensory information to the maxillary dentition
what are the dental branches of the mandibular branch (V3) of the trigeminal nerve?
what is the function of V3?
1. lingual
2. inferior alveolar
3. auriculotemporal
providing sensory nerves to the mandibular dentition
what initiates the condyle to move?
the muscles of mastication
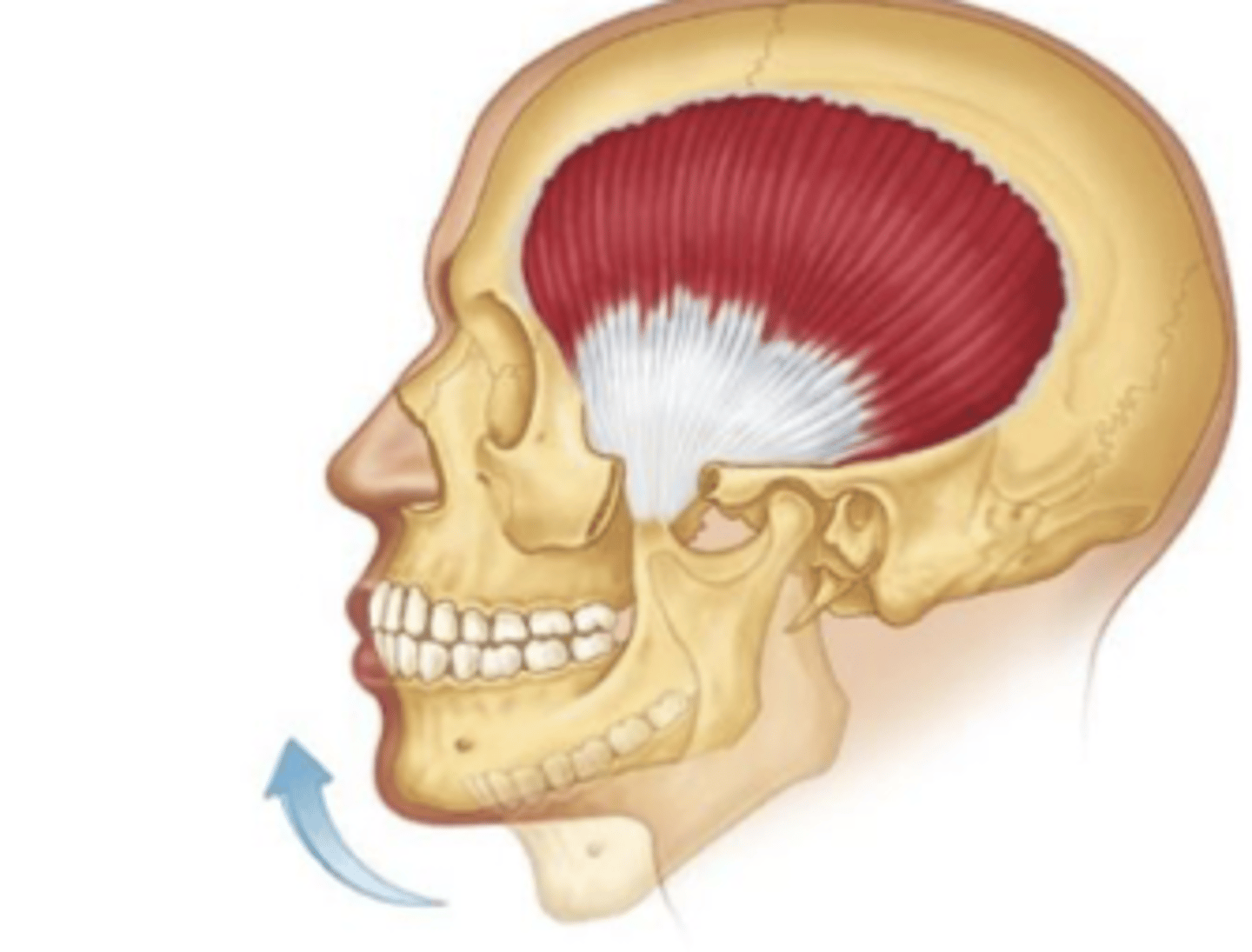
temporalis:
origin?
insertion?
origin: temporal lines
insertion: coronoid process
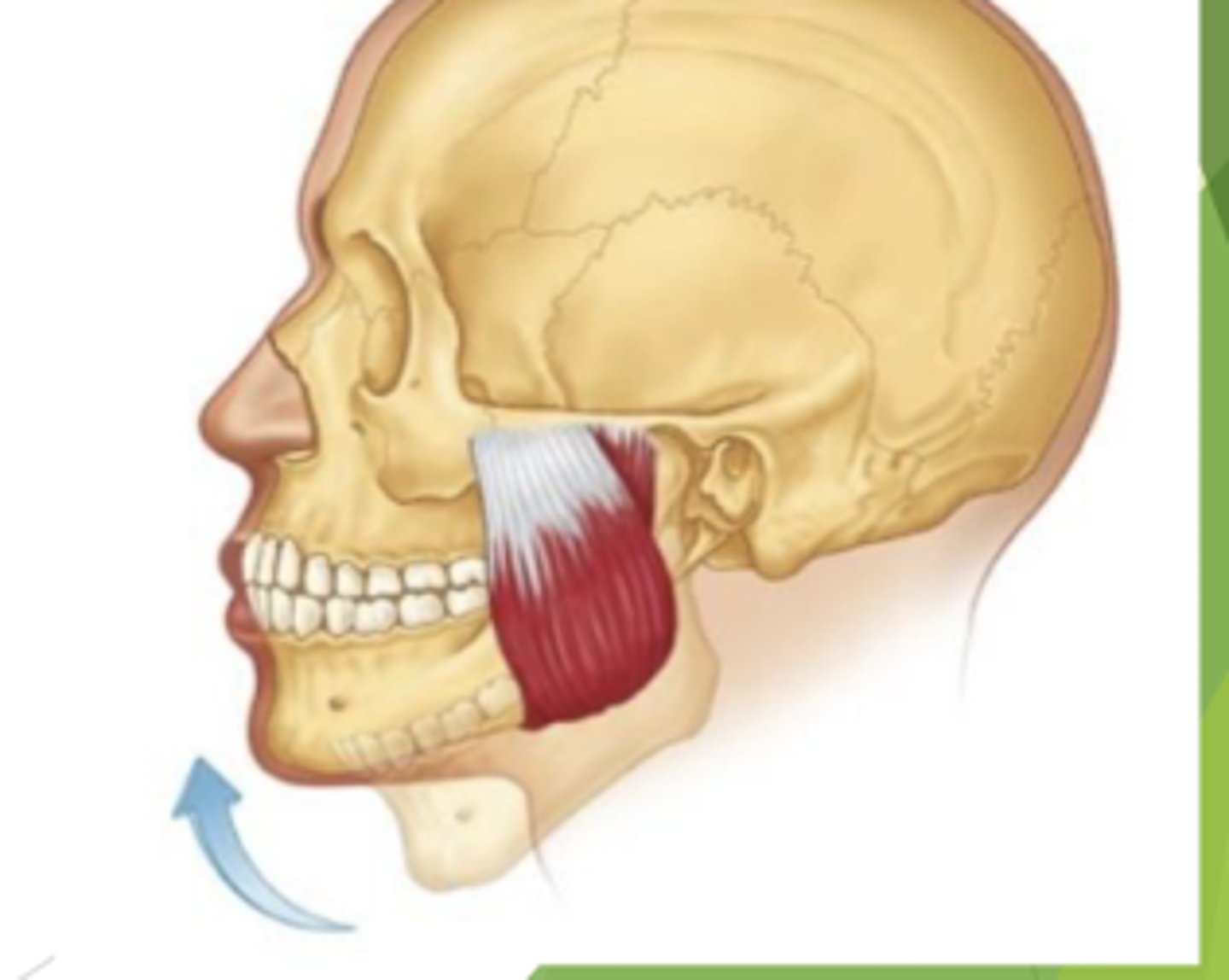
masseter
origin?
insertion?
origin: zygotmatic arch
insertion: gonial angle of the lateral mandible
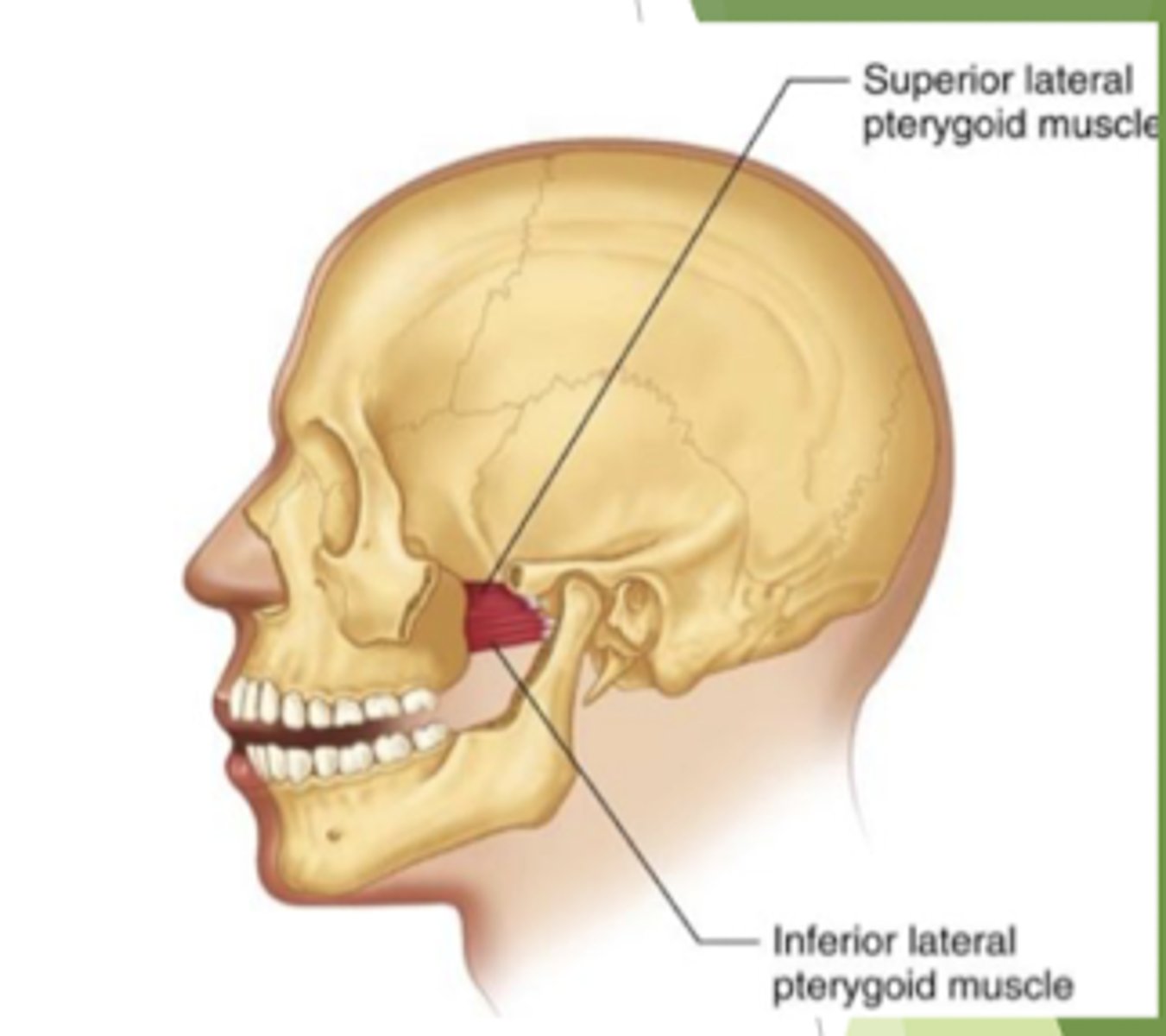
lateral pterygoid
origin?
insertion?
origin: lateral aspect of the lateral pterygoid
insertion: TMJ capsule, disc, and mandibular neck
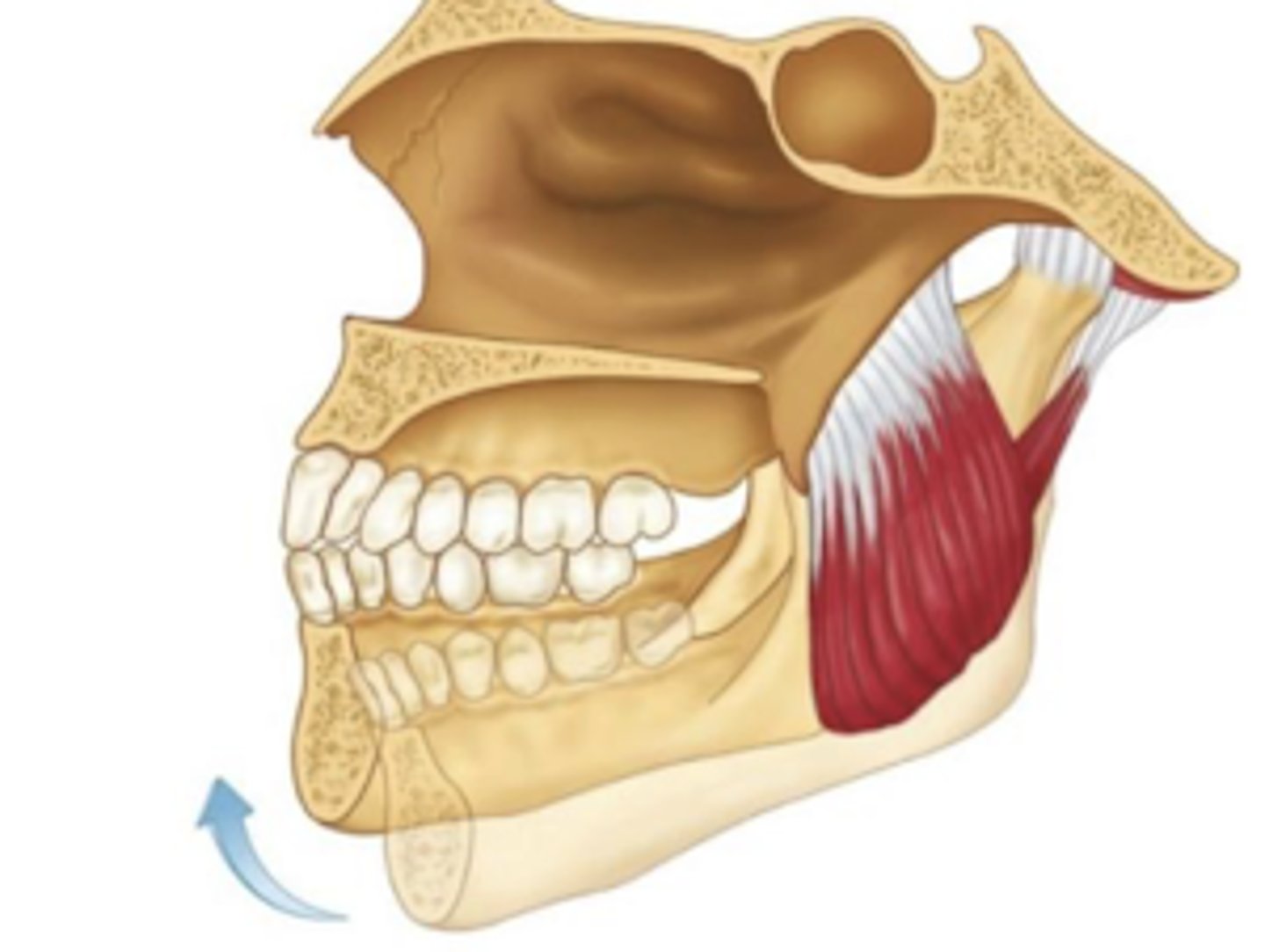
medial pterygoid
origin?
insertion?
origin: medial aspect of the lateral pterygoid plate
insertion: gonial angle of the medial mandible
which muscles of mastication depress the mandible?
lateral pterygoid
which muscles of mastication elevate the mandible?
medial pterygoid, massester, and temporalis
which muscles of mastication protrude the mandible?
1. bilateral contraction of temporalis
2. lateral pterygoid
3. minor contribution from the medial pterygoid
which muscles of mastication retract the mandible?
temporalis
true or false:
medial pterygoid, lateral pterygoid, and masseter all produce bilateral movement
false,
contralateral: medial and lateral pterygoid
ipsilateral: masseter
which openings in the cranium do the trigeminal nerves V2 and V3 traverse through?
V2: ovale
V3: rotundum
what are the functions of the oral mucosa?
1. primordium for developing teeth
2. barrier protection
3. aids in phonation, gustation, secretion, digestion, sensory, and immune
4. thermal regulation (in some animals- not humans)
what are the three different classifications of mucosa?
lining mucosa, masticatory mucosa, and specialized mucosa
which lining classification has non-kertatinizied epithelium?
what are the layers of non-keratinized epitherlium?
lining mucosa
stratum basale, stratum intermedium, and stratum superficiale
true or false:
lining mucosa lines parts of the oral cavity that support chewing activity
false, lining mucosa lines parts of the oral cavity not involved in chewing
-non-keratinized epithelium is not appropriate for abrasive surfaces
which classification of mucosa is located in buccal and labial mucosa, soft palate, ventral tongue, floor of mouth, vestibular sulcus, and alveolar mucosa?
lining mucosa
-each of the listed location were in non-chewing surfaces
do lining mucosa have underlying bone?
no, lining mucosa do not have underlying bone
-connective tissue consists of a superficial lamina propria and a deeper submucosa
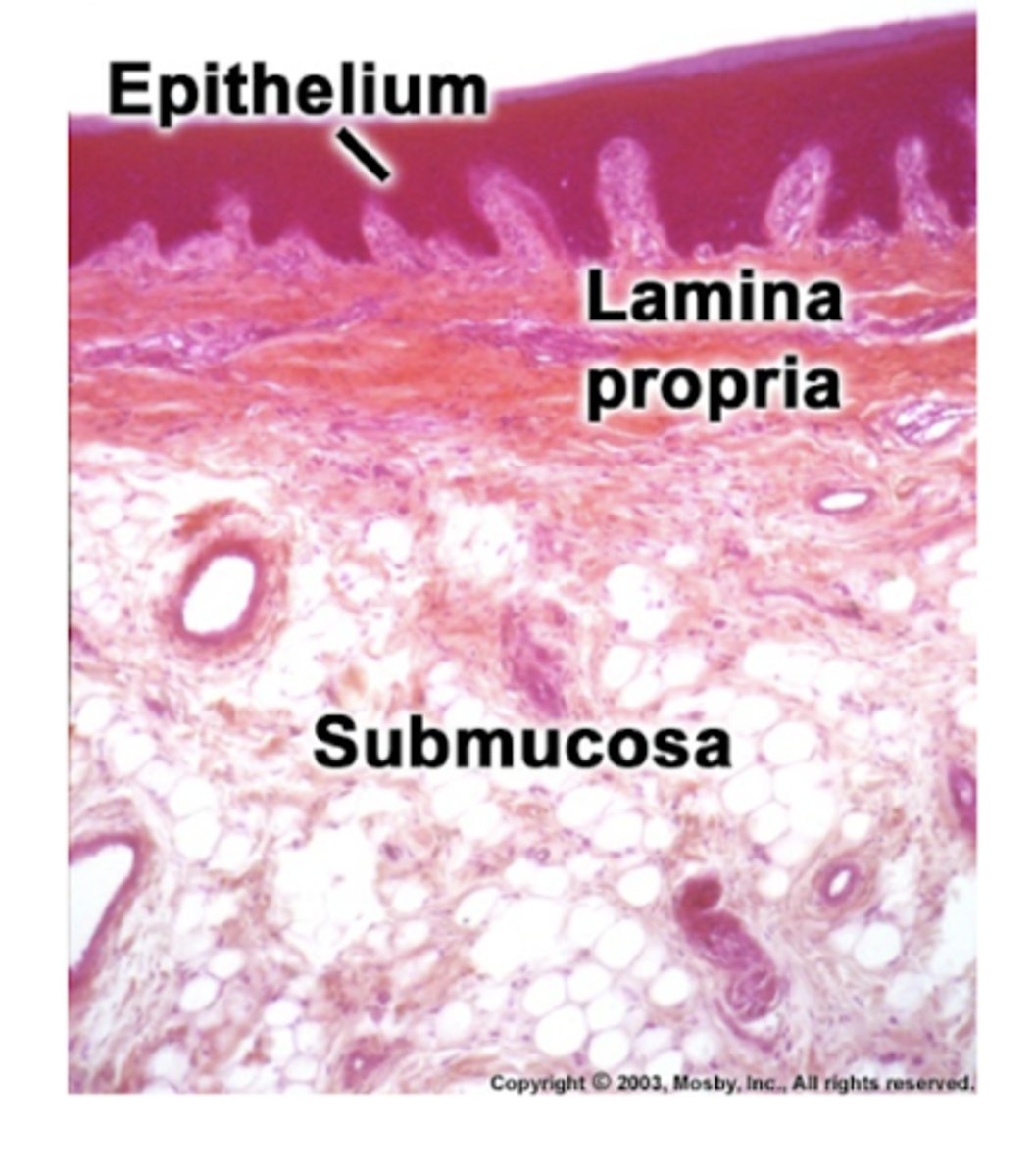
which classification of mucosa assists in chewing?
which type of epithelium does it have?
masticatory mucosa
-bears frictional forces generated during chewing
parakeratinized epithelium
which classification of mucosa is located at the attached gingiva and anterior hard palate?
masticatory mucosa
true or false:
masticatory mucosa has connective tissue that consist of only lamina propria
true,
-lamina propria is attached to periosteum of underlying bone forming a mucoperiosteum
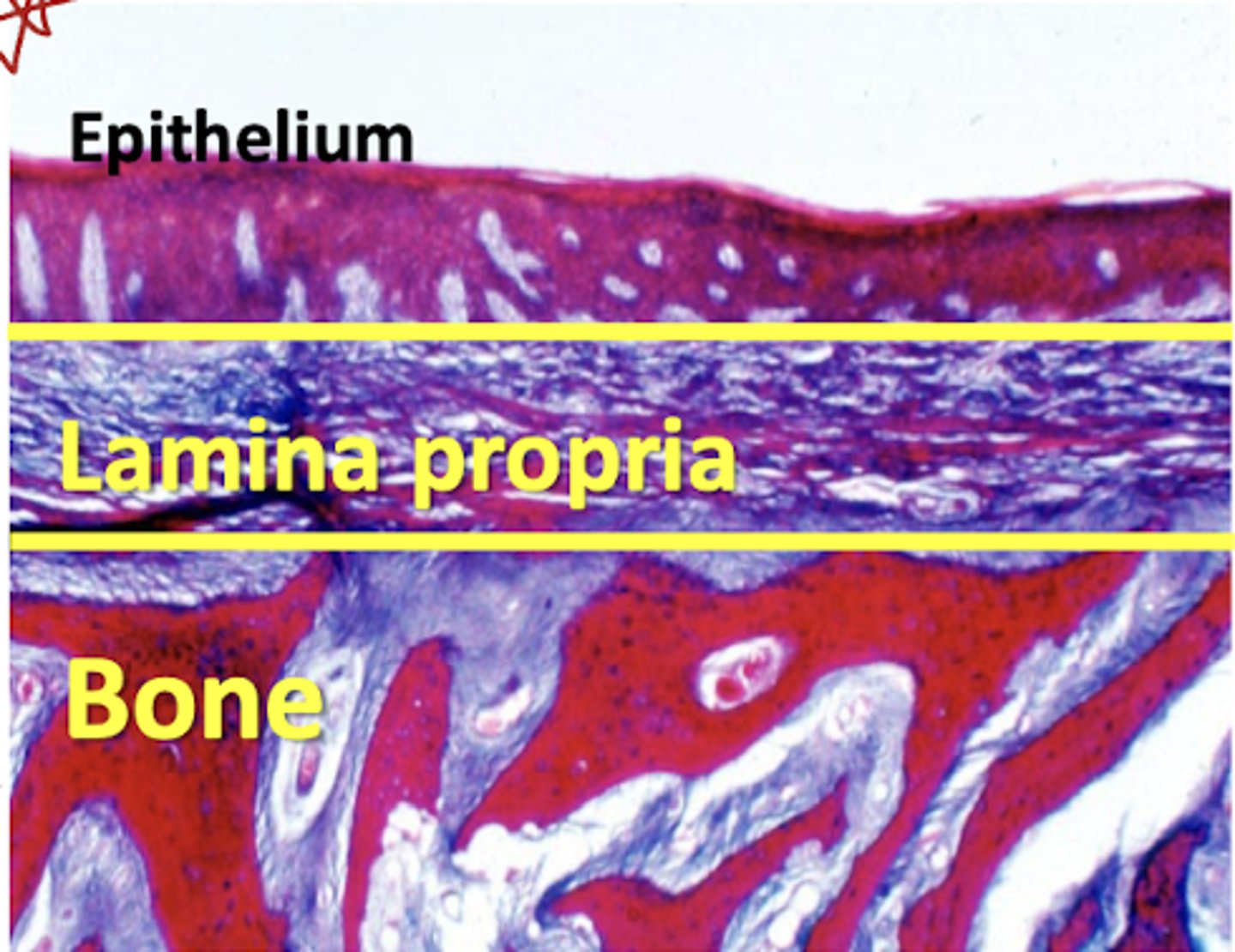
what is the term for lamina propria attached to periosteum underlying bone?
mucoperiosteum
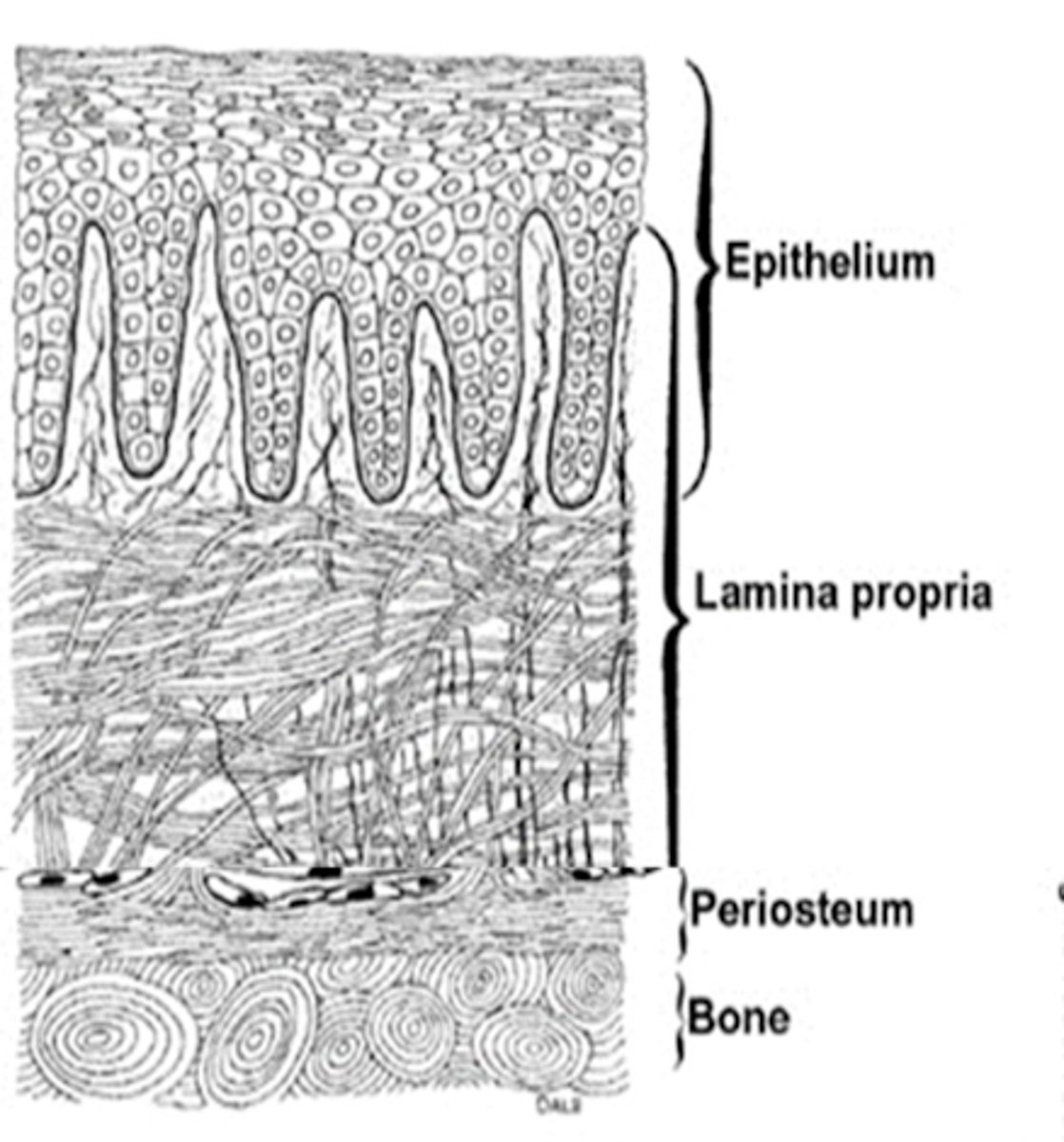
which classification of mucosa do tastebuds and papillae belong in?
specialized mucosa
true or false:
locations of specialized mucosa includes the taste buds and the ventral surface of the tongue
false, specialized mucosa is located in taste buds and the dorsum of the tongue
which classification of mucosa takes part in specialized sensation of taste perception (gustation)
specialized mucosa
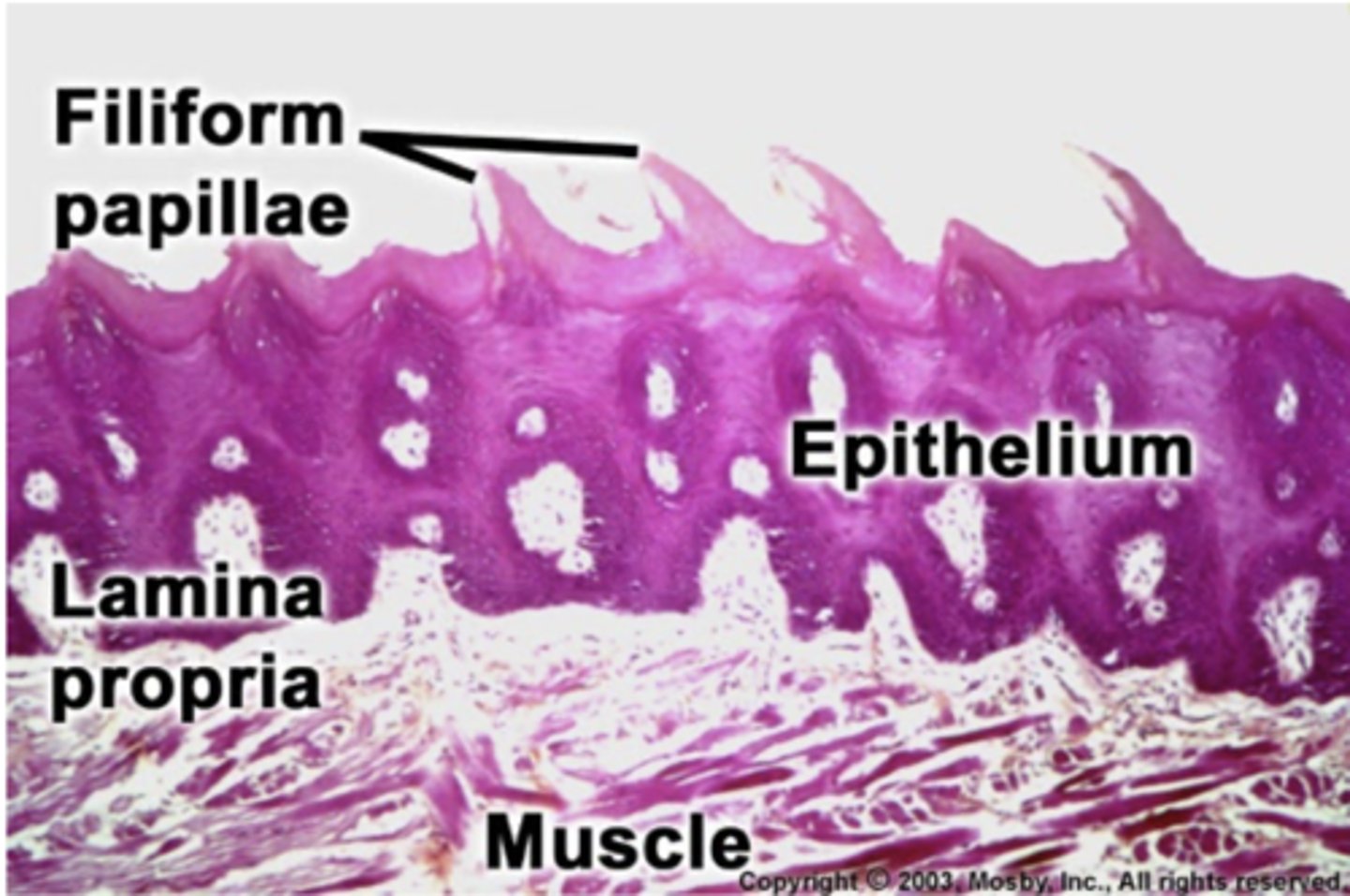
true or false:
only filiform papillae are keratinized
true,
-fungiform, circumvallate, and foliate papillae are not keratinized
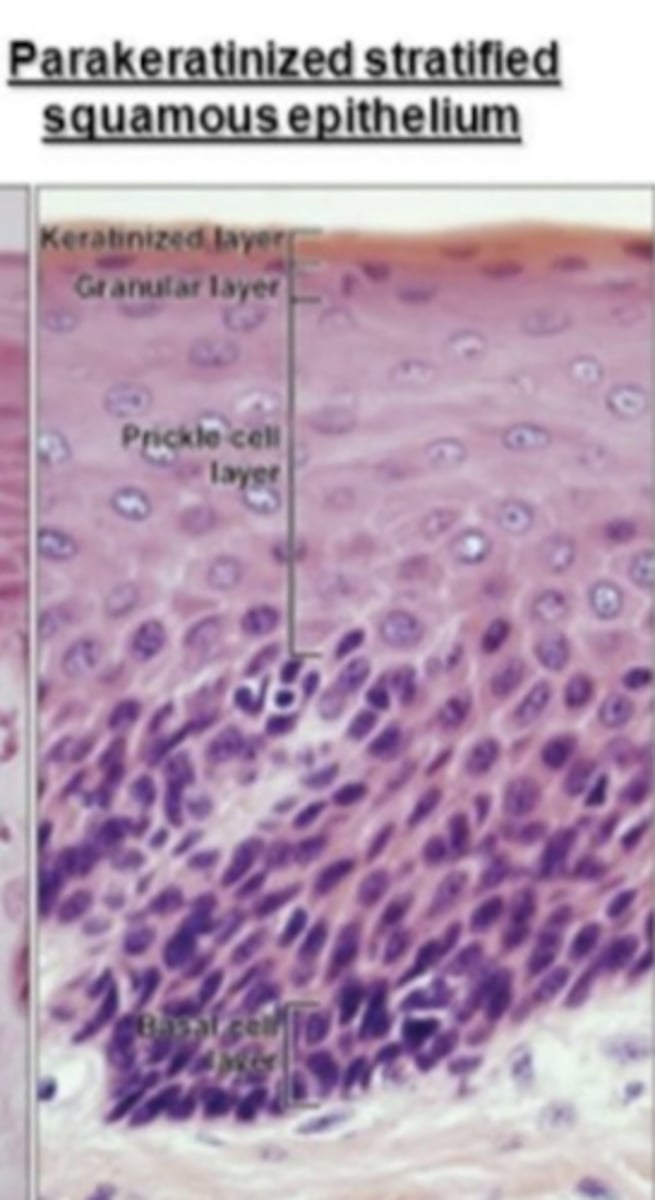
what is the term being described?
shows some keratin formation and retains nuceli
parakeratinized epithelium
-masticatory mucosa
true or false
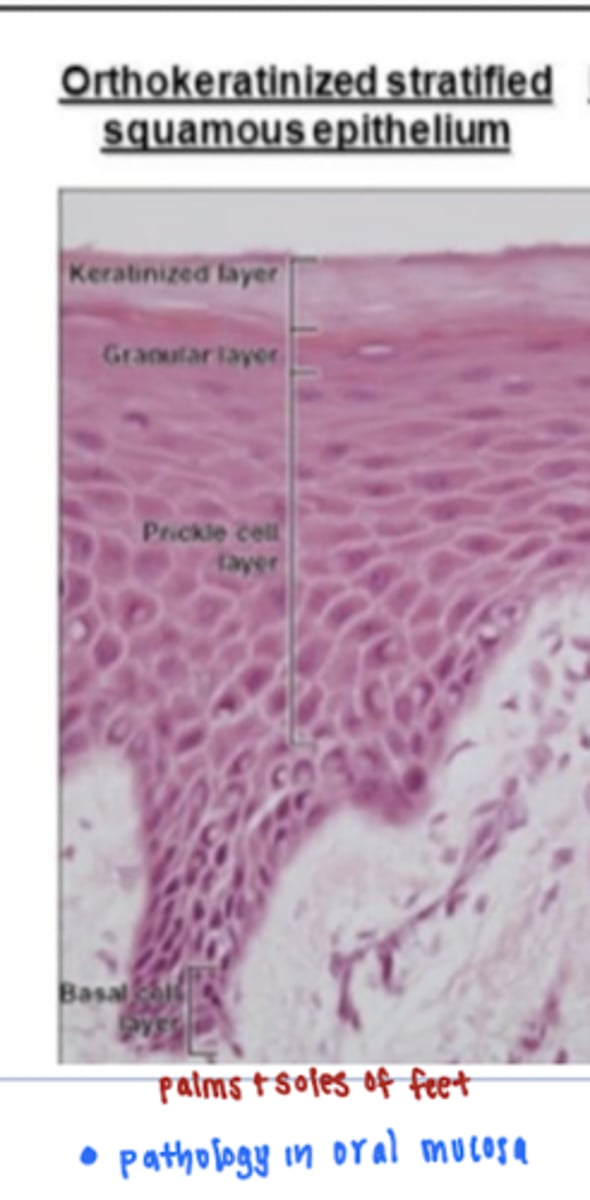
orthokeratinization is common in the oral cavity especially in locations of high impact and force
false, orthokeratinized epithelium is abnormal in the oral cavity
*normally located on soles of palms and feet
-orthokeratinized epithelium is epithelium that shows extensive keratin formation and surface cells are non-nucleated
which nerve innervates the posterior 1/3 of the tongue?
glossopharngeal (CN9)
which nerves innervates the anterior 2/3 of the tongue?
facial (CN7)
which branches of nerve provide:
1. sensory innervation to the tongue
2. taste perception to the tongue
1. lingual branch of V3
2. chorda tympani branch of CN7
which structure has the following feature?
vermilion border, philtrum, and contributing muscle support from the muscles of facial expression
lips
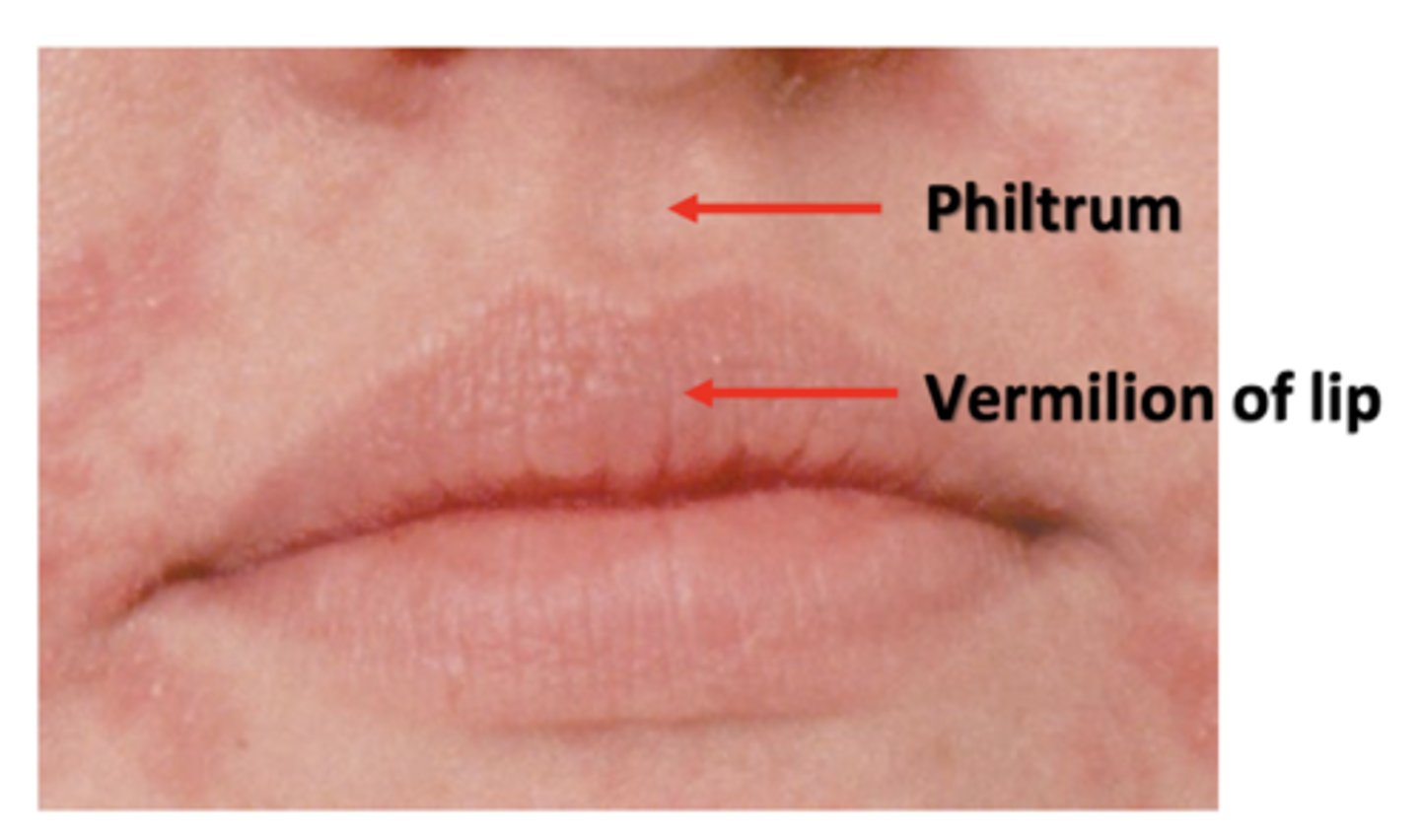
what is being described?
ectopic sebaceous glands found normally in the vermillion border and buccal mucosa
fordyce granules
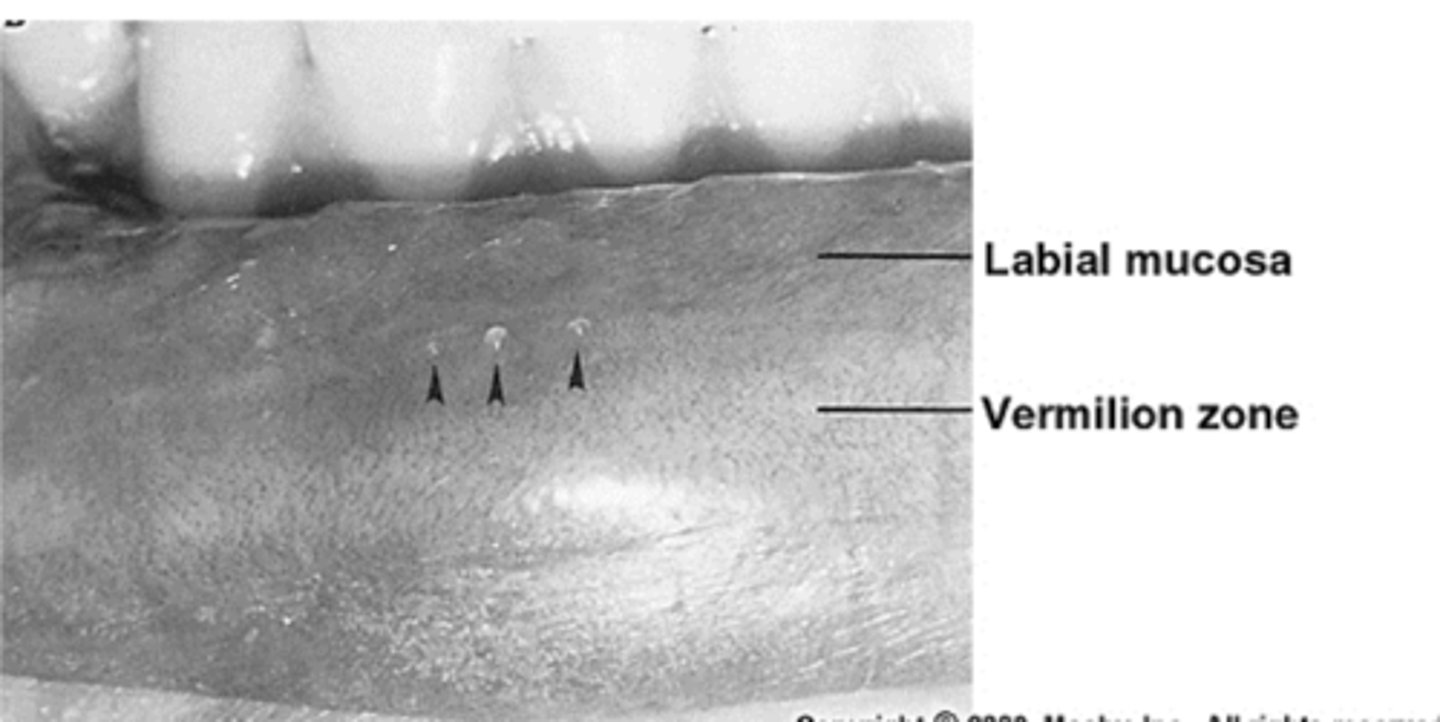
is labial mucosa non-keratinized or parakeratinized?
non-keratinized
-epithelium is overlying lamina propria and abundant submucosa
what does the submucosa of the labial mucosa contain?
minor mucous glands and deep portions contain obicularis oris muscle fibers
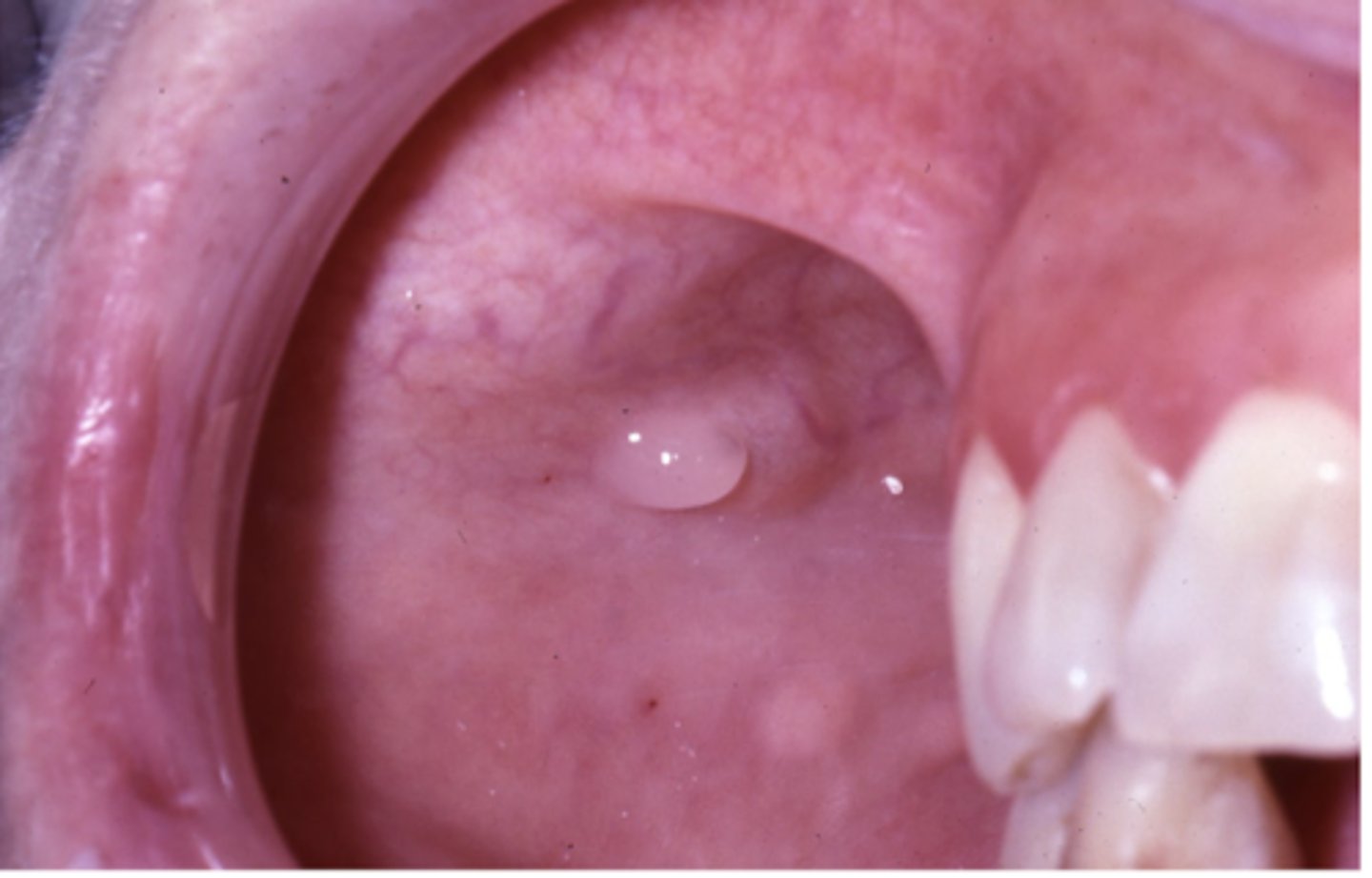
where is stensen's duct located?
the opening of stensen's duct of parotid fland is on the buccal mucosa opposite mesiobuccal cusp of maxillary first permanent molar
which structure contains the prominent mucosal structure called the uvula?
the soft palate
which type of epithelial tissue does the soft palate contain?
non-keratinized epithelium overlies the the loose lamina propria and abundant submucosa
true or false:
lateral portions of the soft palate continue as anterior and posterior walls of the tonsil?
true
which structure is being described?
highly vascularized, non-keratinized epithelium, and anterior midline submucosa contains glands of blandin and nuhn
ventral tongue
*under surface of the tongue
true or false:
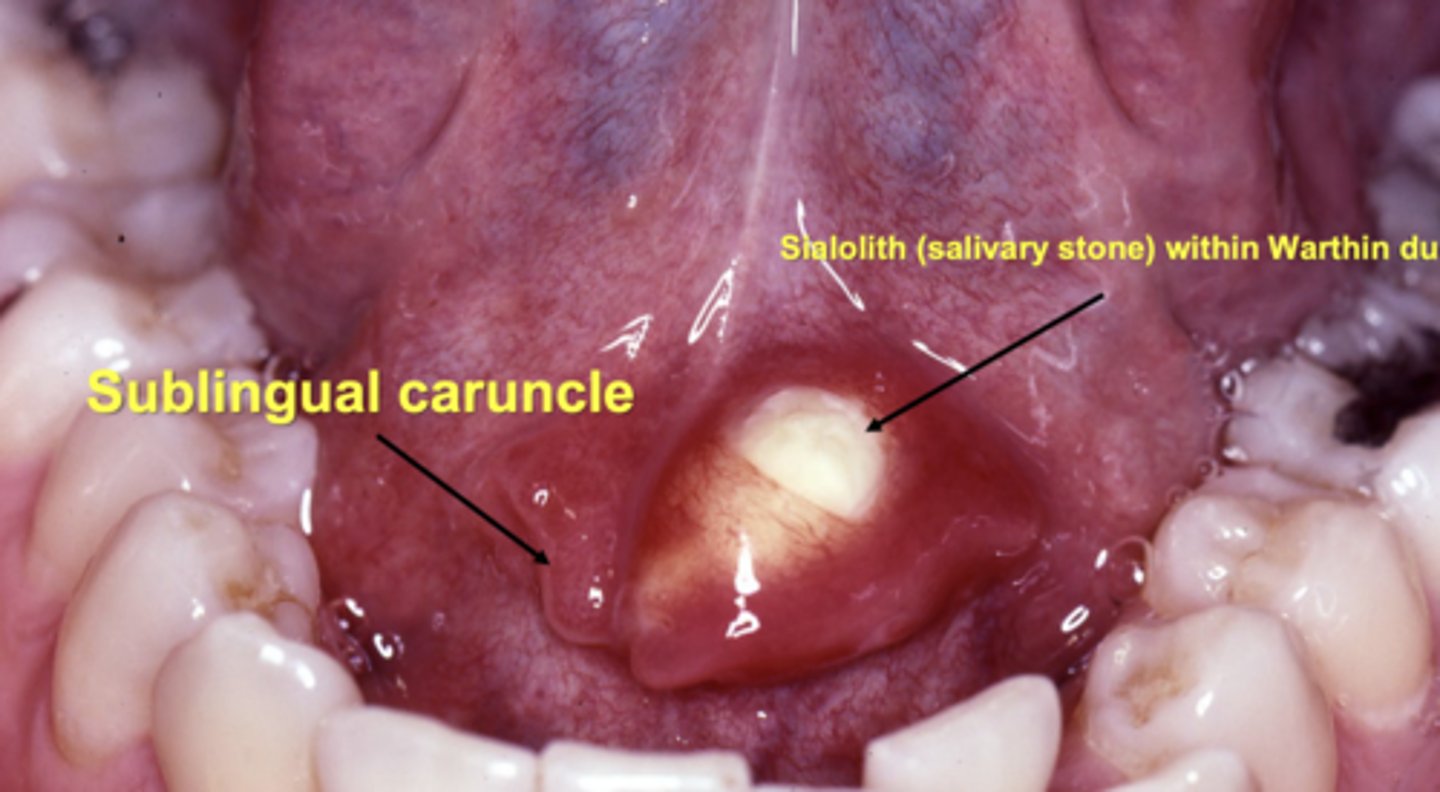
warthin's duct from submandibular and stensen's duct from the parotid gland open on the floor of the mouth
false, warthins duct from submandibular and bartholin's duct from sublingual salivary gland!!
what structure do the warthin's glands and bartholin's duct open on either side of?
sublingual caruncles at the anterior midline on the floor of the mouth
what are the three different portions of the gingiva?
1. marginal gingiva
2. free gingival groove
3. attached gingiva
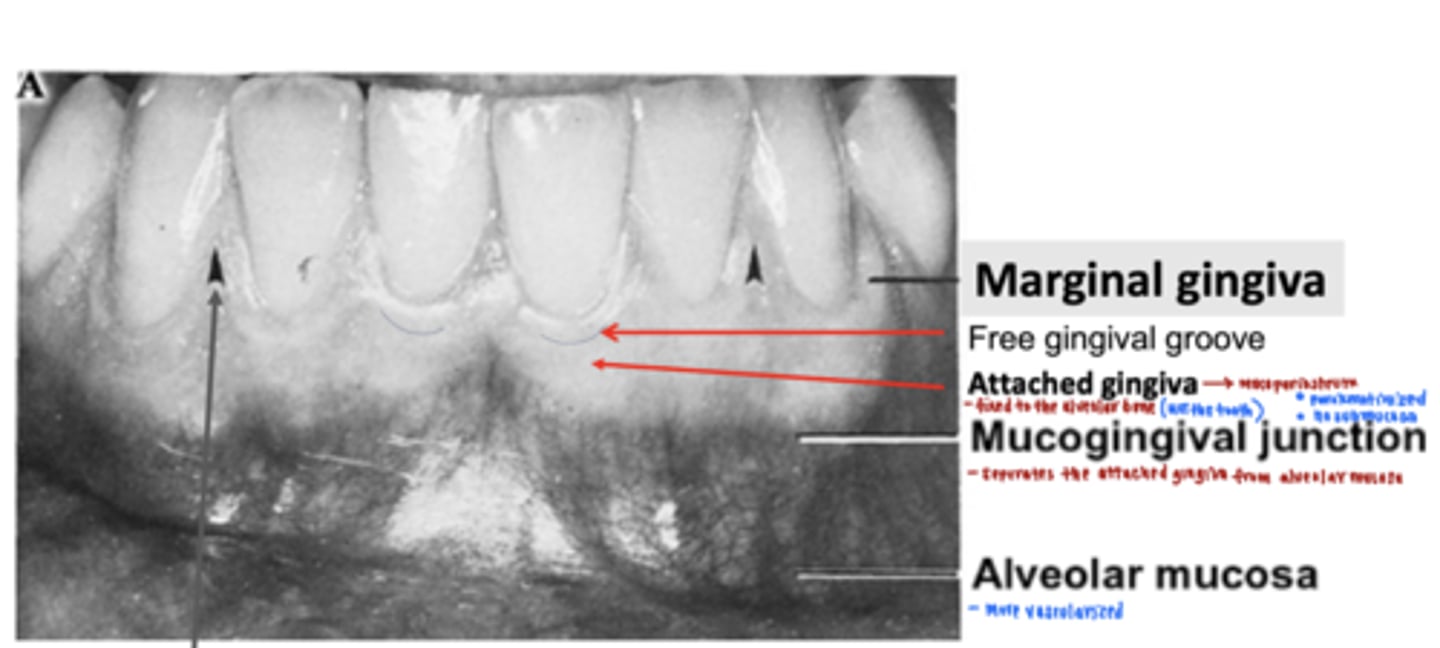
which gingiva is being described?
firmly adherent through its lamina propria to underlying periosteum
attached gingiva
-parakeratinized
what is the free gingival groove?
separates the marginal gingiva from the attached gingiva
which gingiva is being described?
forms the gingival wall of the sulcus, surrounds teeth, 1mm wide
marginal gingiva
what is the mucogingival junction?
junction between the attached gingiva and the alveolar mucosa
**MGJ in perio chart!!!
what is the interdental col?
what is its significance?
a valley-like depression of the gingiva between the facial and lingual interdental papillae
-non-keratinized
integrity important to avoid periodontal disease
what is being described?
junction between the tooth and gingiva
dentogingival junction
true or false:
the DEJ consist of an attachment apparatus
true, the attachment apparatus consist of junctional epithelium and enamel cuticle overlying the enamel
what structures are located on the hard palate?
incisive papilla, rugae, and median raphe
which nerve is carried by the incisive papilla?
nasopalatine vessels and nerve
what type of mucosa is the hard palate?
why?
the anterior hard palate is a mucoperiosteum because lamina propria attached to periosteum
the posterior hard palate is filled with fat and minor mucous glands
what are the two different portions of the tongue?
what landmark separates the two divisions?
1. pharyngeal: posterior 1/3 portion
2. oral: anterior 2/3
the posterior 1/3 and anterior 2/3 are separated by sulcus termanilis
*v-shaped groove
true or false:
fungiform papilla contain the most tastebuds
false, circumvallate papilla contain the most tastebuds
-10-12 in number
-in front of sulcus terminalis
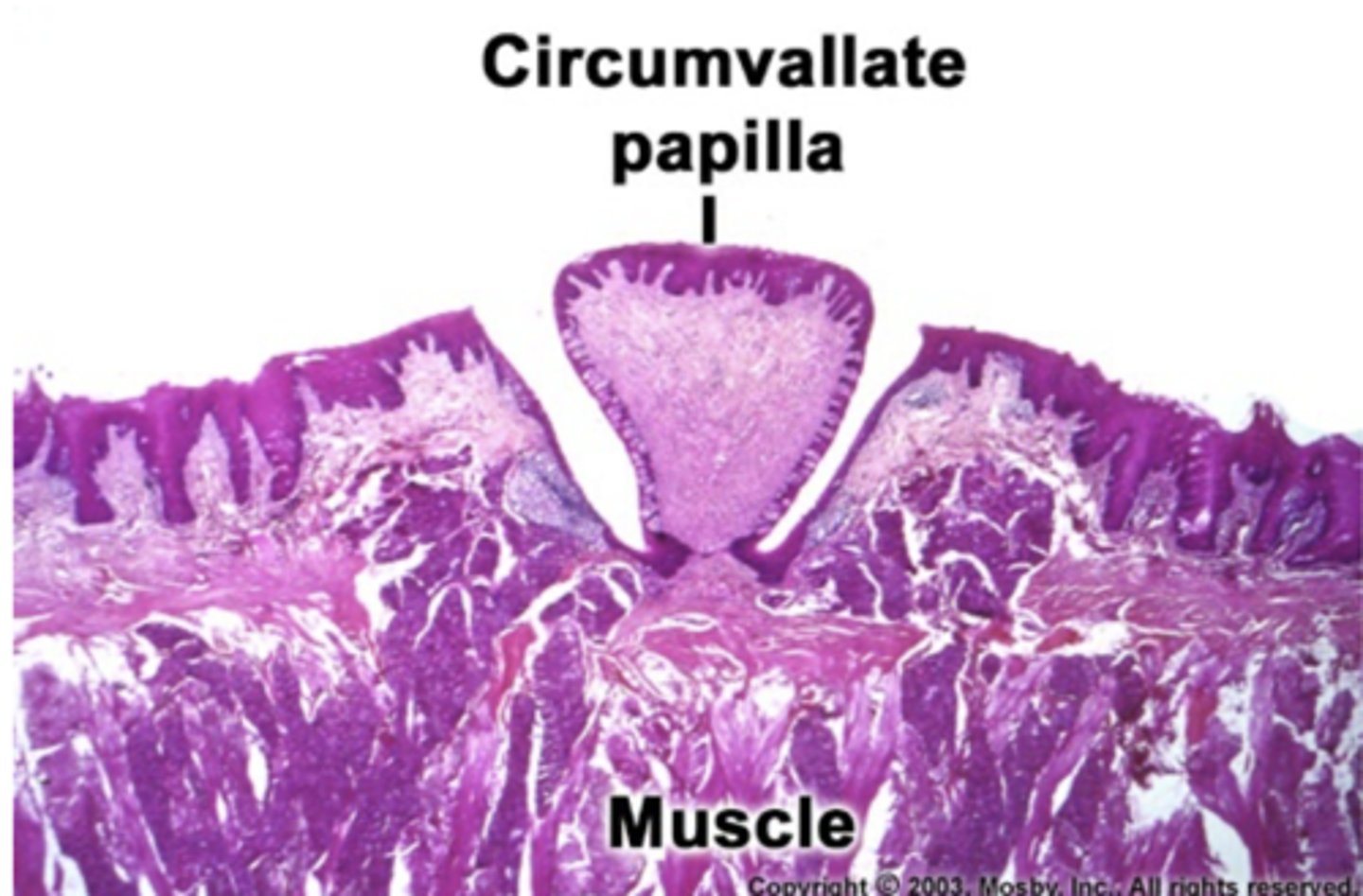
which tastebud is being described?
most numerous, and keratinized
filiform
-located on the anterior 2/3 of the tongue with fungiform
what is the difference between fungiform and filiform papilla? both are located on the anterior 2/3 of the tongue.
fungiform: is non-keratinized and contain a few tastebuds
filiform: is keratinized
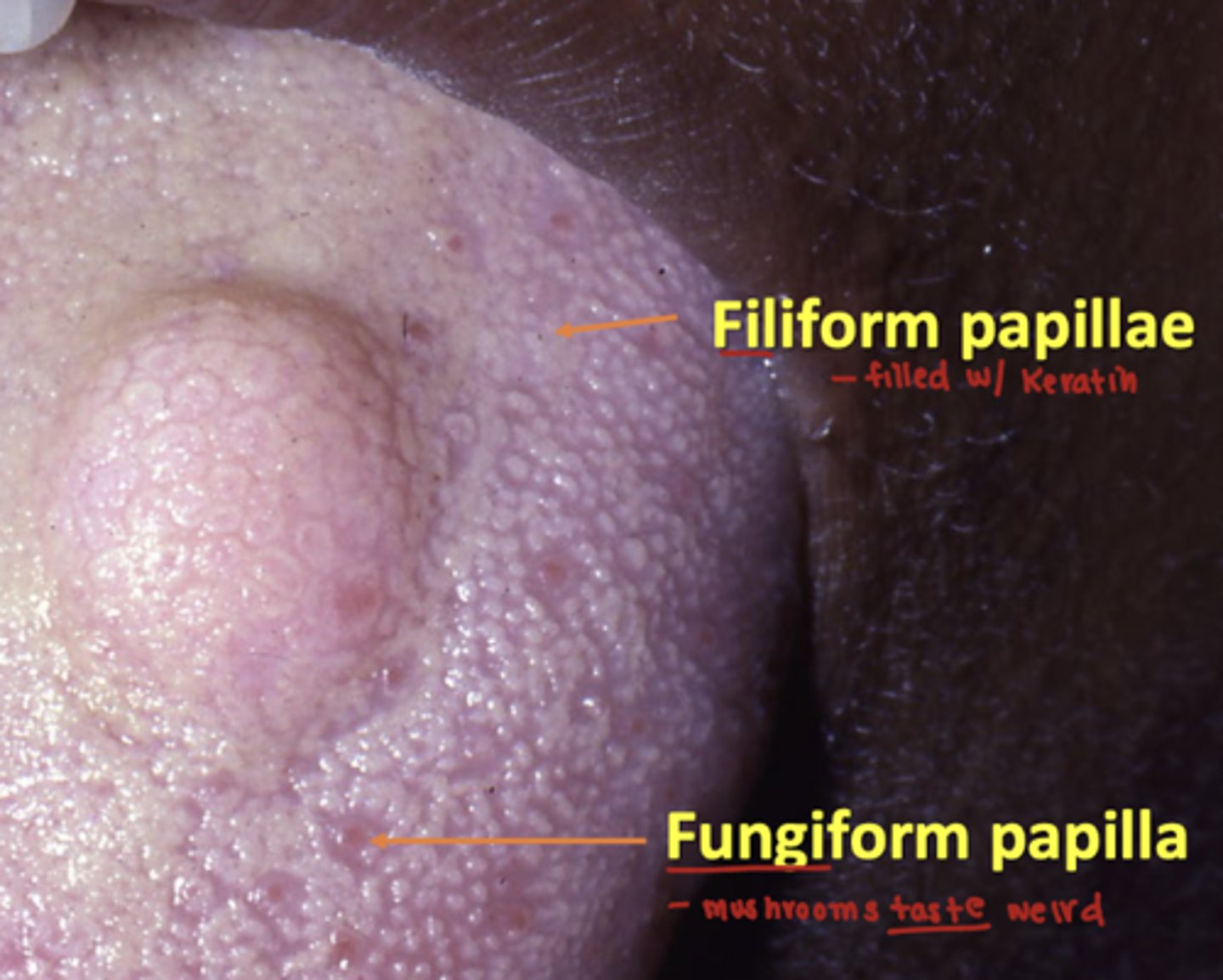
Where are foliate papillae located?
lateral sides of tongue
which papilla contain troughs with von ebners glands?
what type of mucus is produced by von ebner glands?
circumvallate papilla contian von ebers glands
-the secretions flush the troughs debris and help enhance taste
von ebner glands produce serous mucus
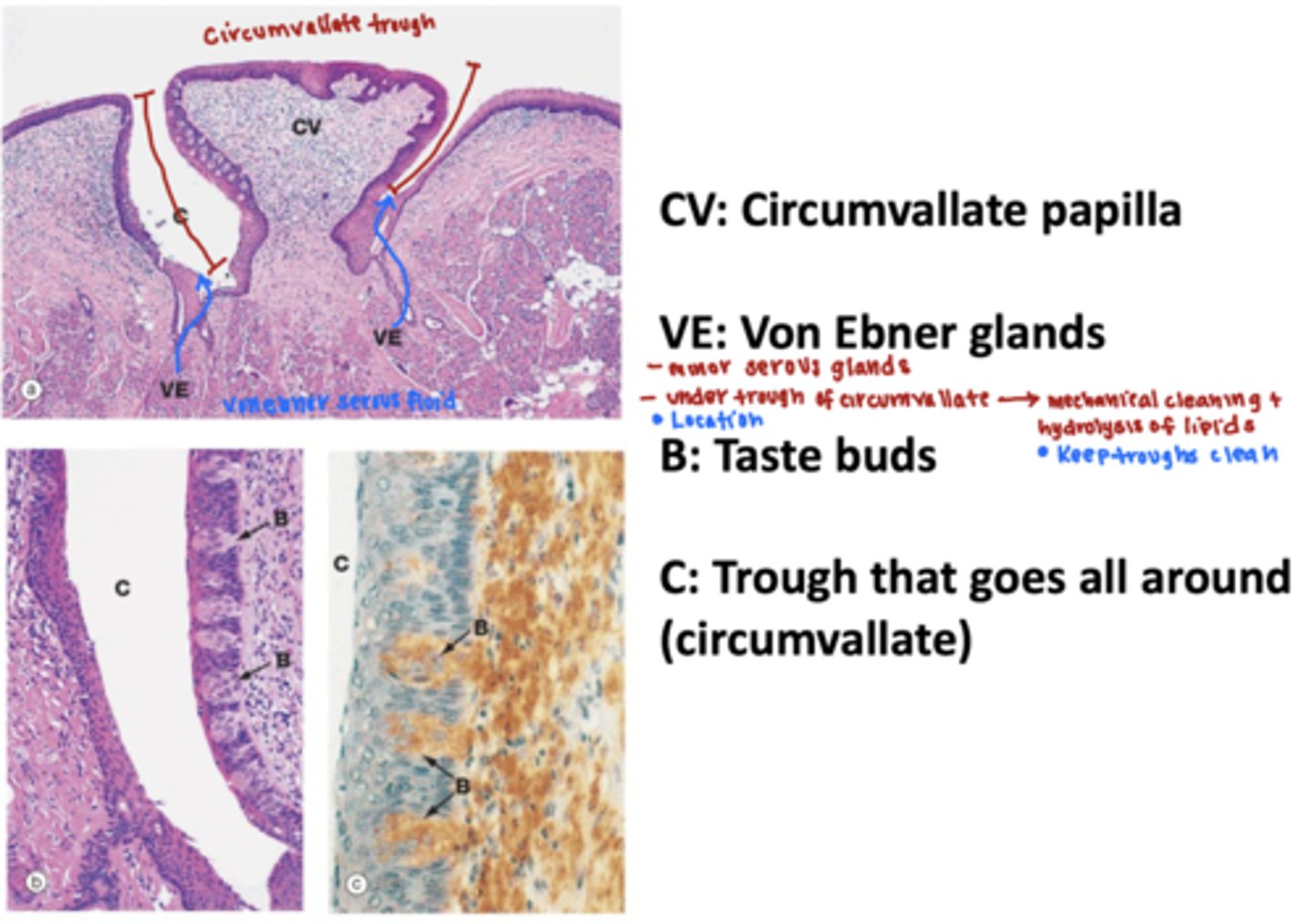
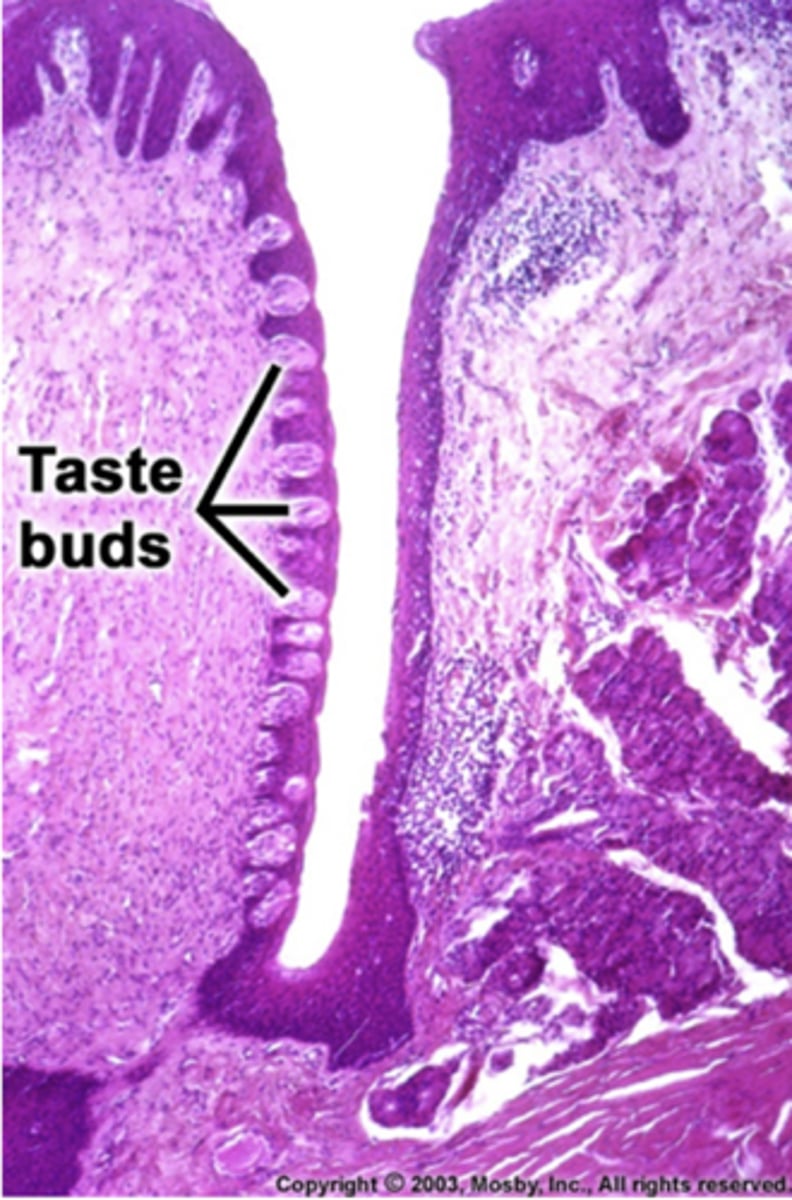
true or false:
the circumvallate papilla have troughs lined with tastebuds
true, the von ebner glands produce a serous mucus that washes debris from the taste receptor to enhance taste.
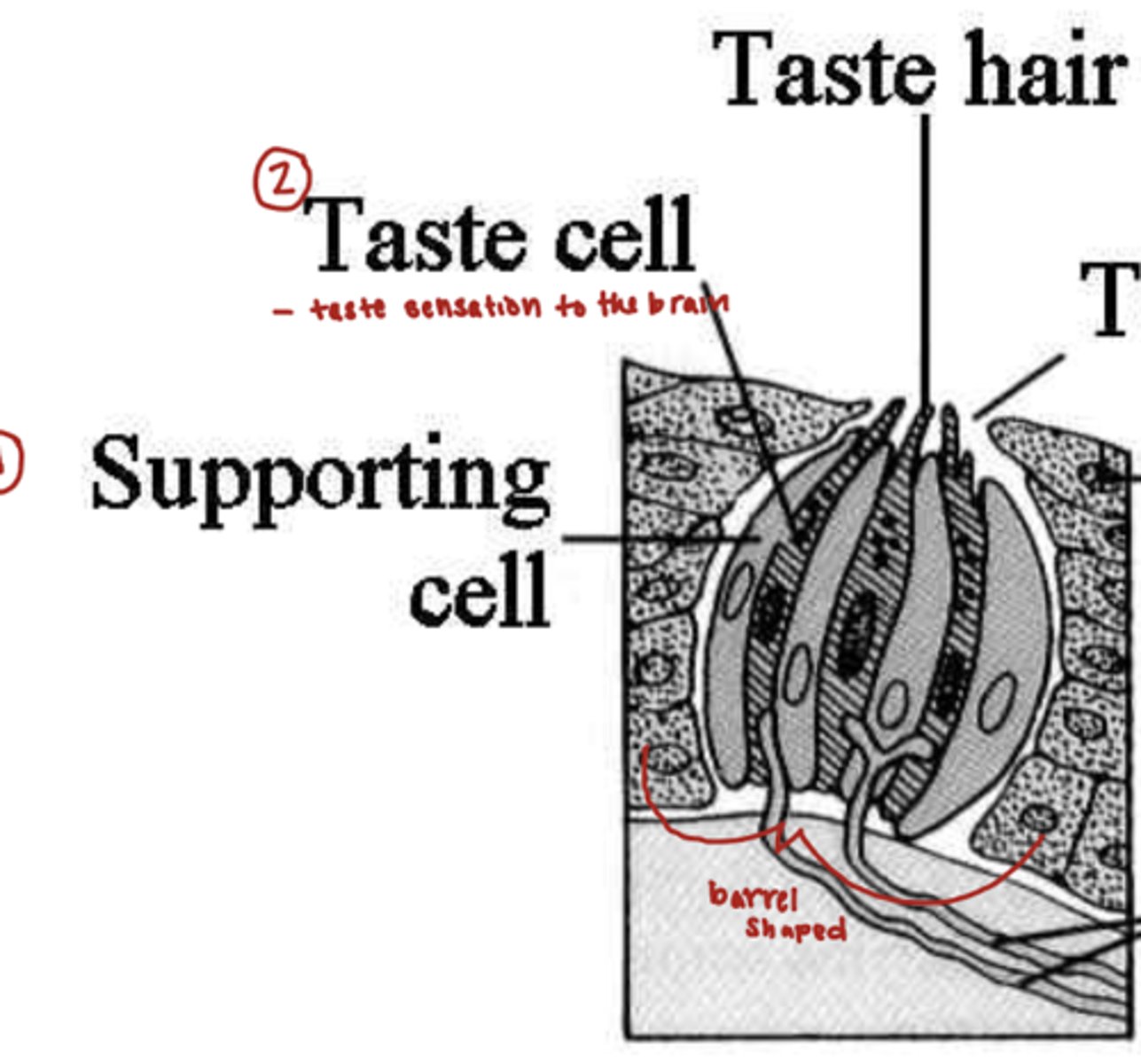
what in the oral cavity is being described?
barrel shaped organ and a lot all over the oral cavity and pharynx
taste buds
what are the two different cells in tastebuds?
taste cell
-transmit taste sensation to the brain
supporting cell
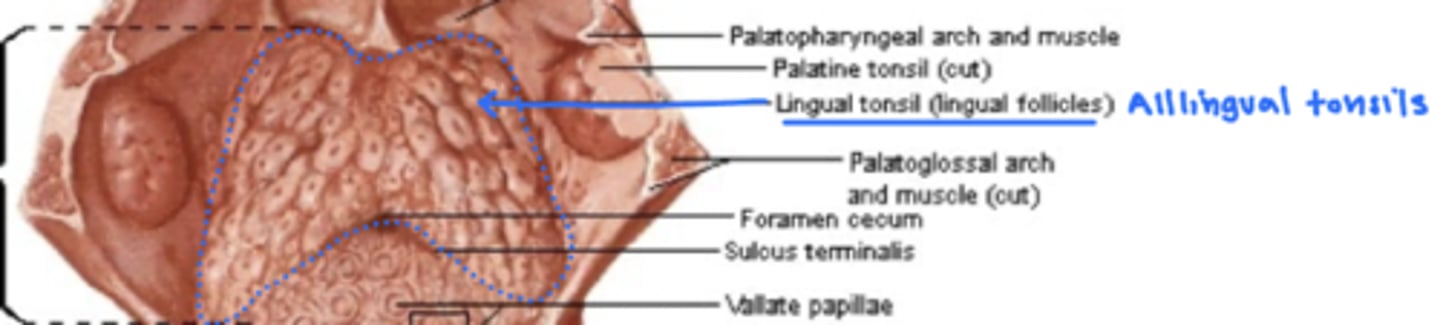
what is foramen cecum?
midline depression just behind the sulcus terminalis from which the thyroid diverticulum descends from the embryon
what is the main function of the dorsum posterior third of the tongue?
explain why.
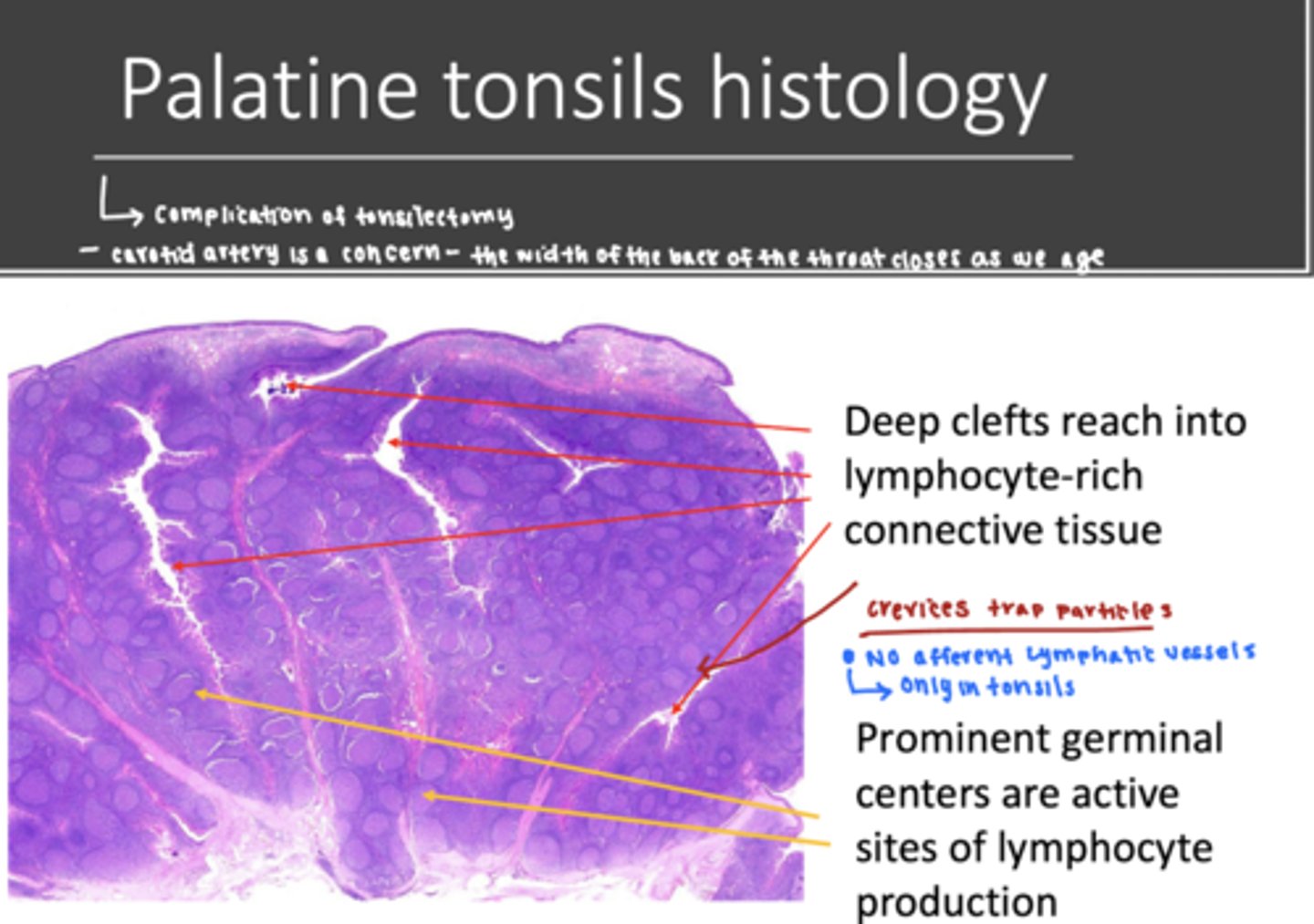
the main function is immune protection.
the posterior 1/3 of the tongue contains a large volume of lingual tonsils
-the crevices of the lingual tonsils trap foreign material
-lymphocytes are constantly surveying the crevices
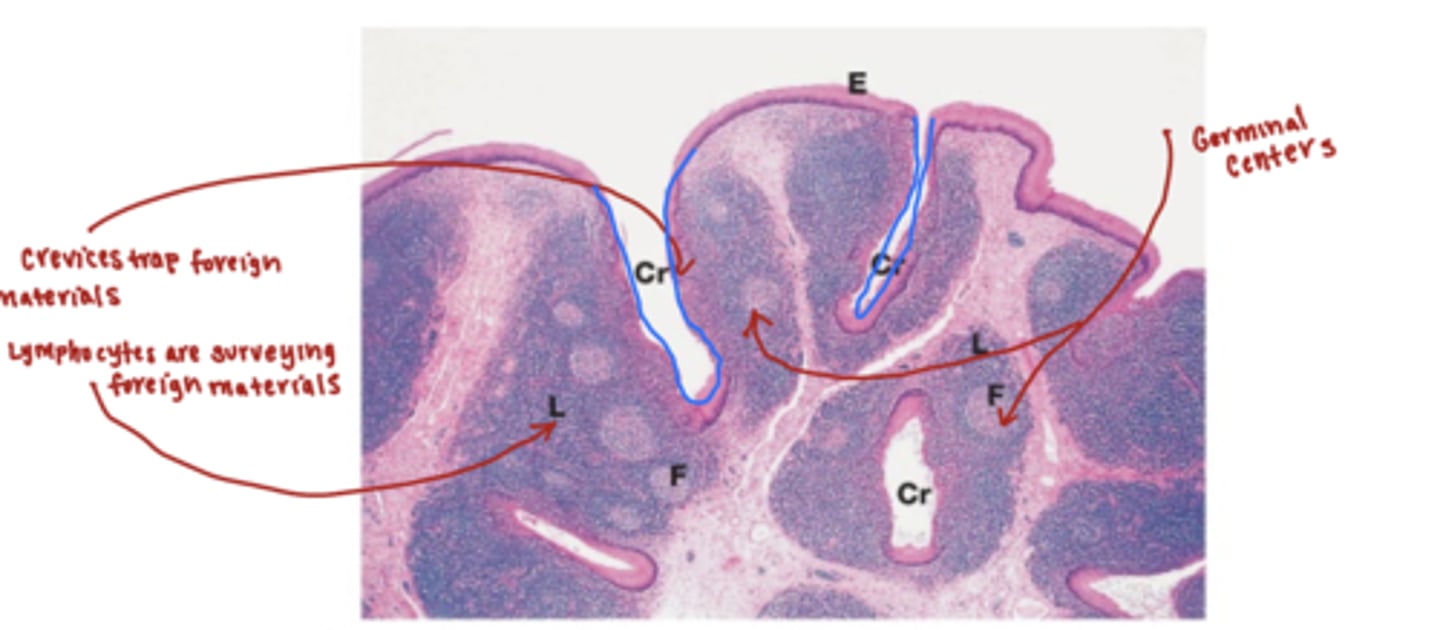
what is the waldeyers ring?
what are the different layers?
An interrupted circle of protective lymphoid tissue in the oral cavity
outer ring: cervical lymph nodes
inner ring: palatine tonsils, lingual tonsils, pharyngeal tonsils, and tubal tonsils
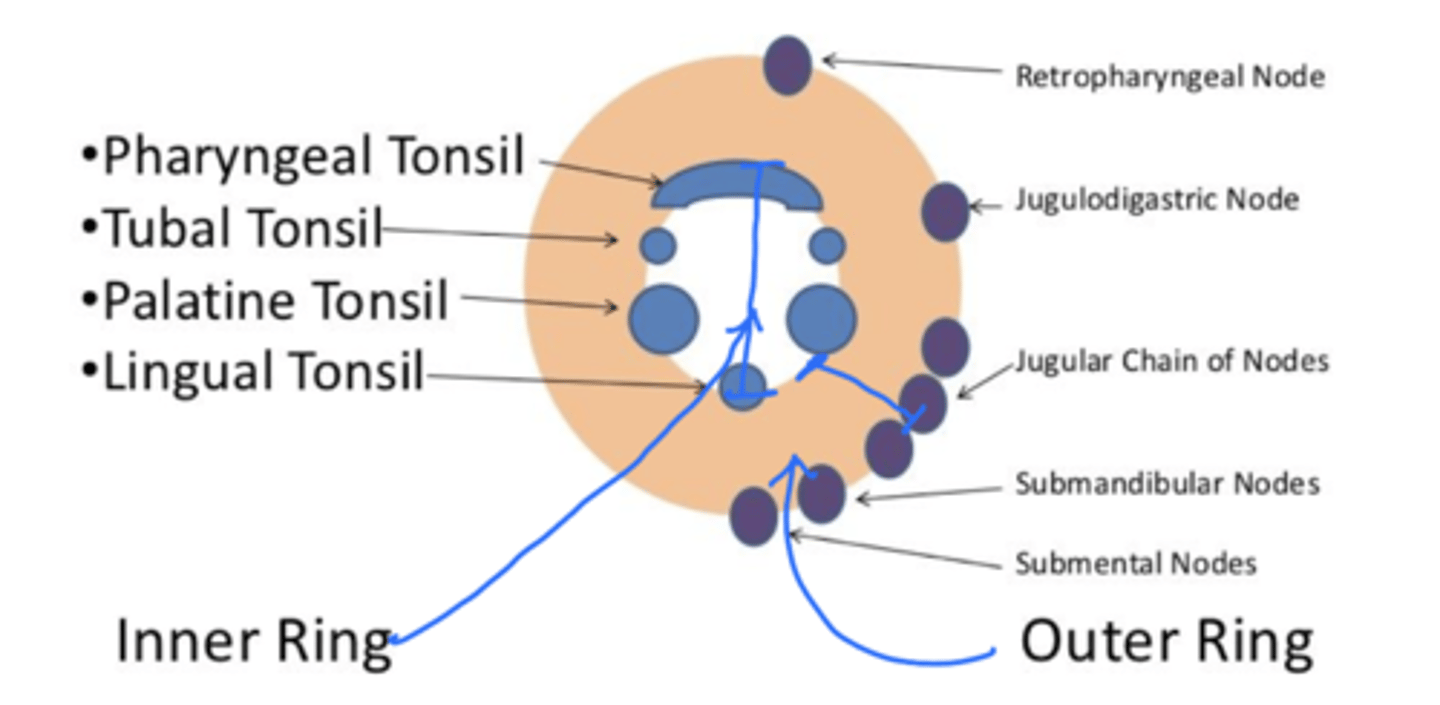
which tonsillar tissue is in the outside ring of the waldeyer's ring?
cervical lymph nodes
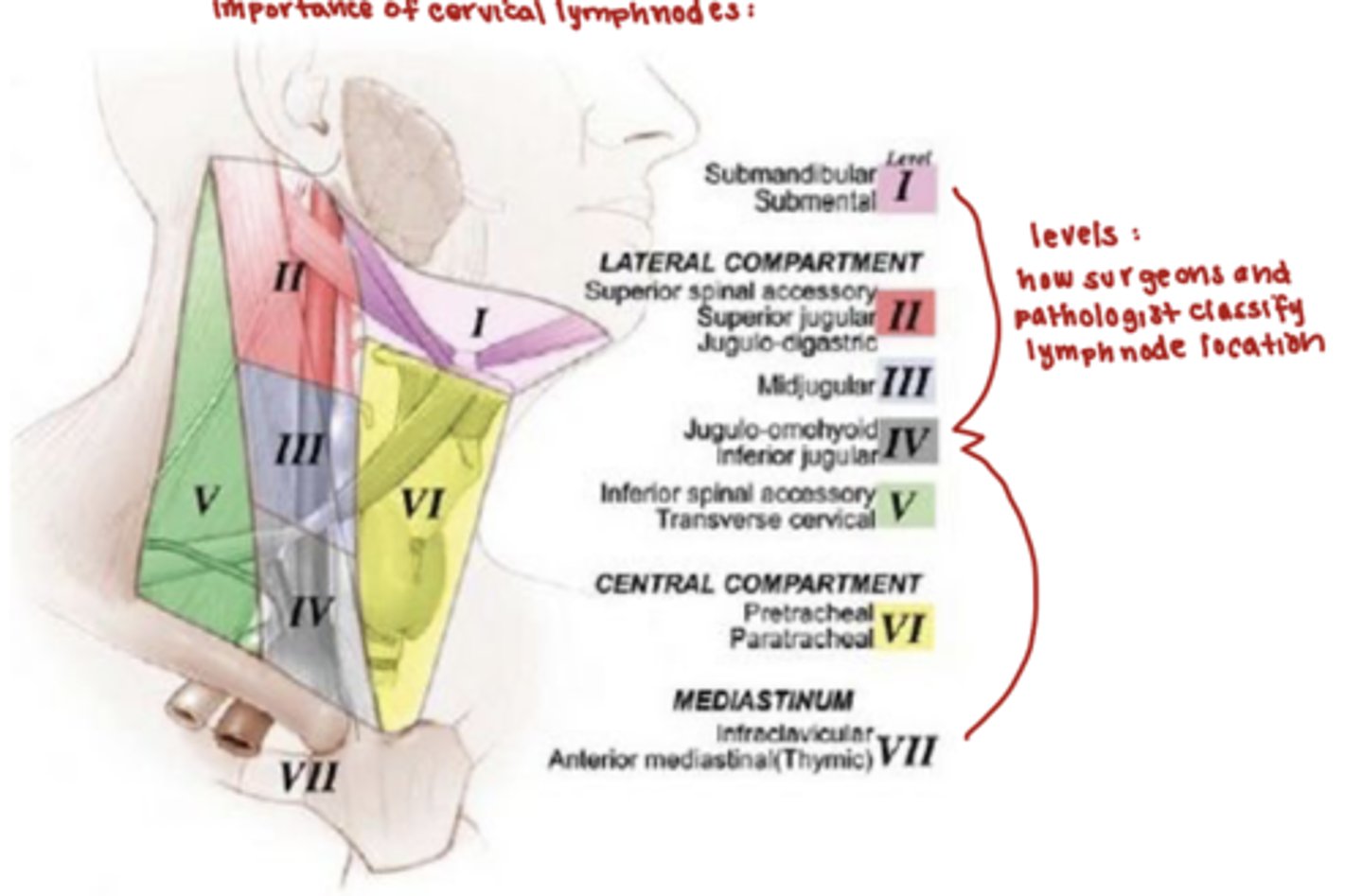
what are the boundaries of the cervical lymph nodes (outside ring)?
the hyoid bone and cricoid cartilage are the boundaries
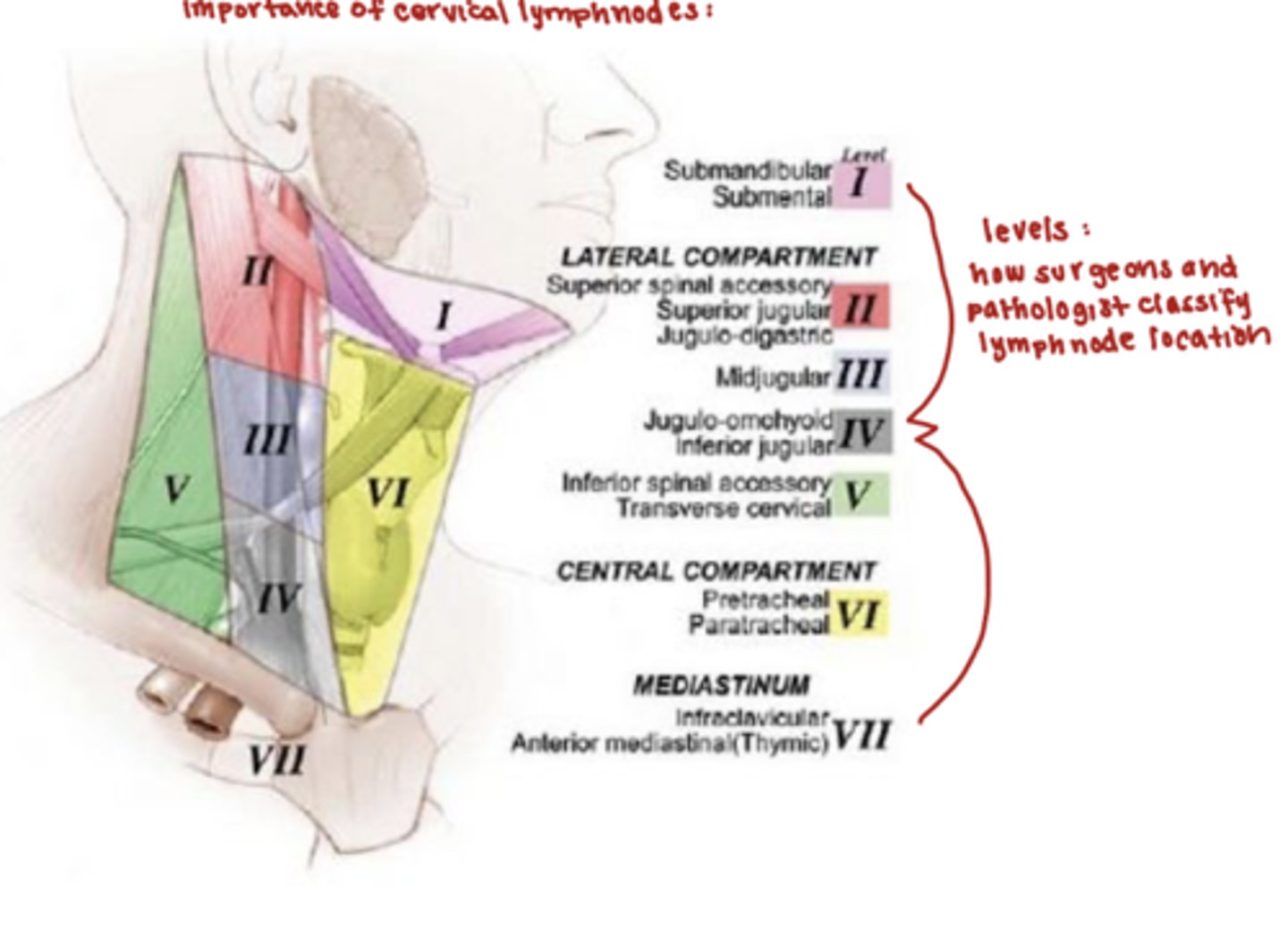
where are lymph nodes located?
throughout the body along the lymphatic channels
what are the function of the lymph nodes?
1. produce cells of the immune system
2. filter and trap microorganisms, foreign materials, and cancer
what is the difference between the paracortex, cortex, and medulla in terms of lymphocytes?
1. paracortex:
-only T cells
2. cortex:
-only B cells
3. medulla
-T cells, B cells, and plasma cells
-immunoglobulin production
true or false:
Lymph nodes and tonsils alike have afferent lymphatic vessel supply
false, unlike lymph nodes tonsils do not have afferent vessel supply
-tonsils do have a efferent lymphatic vessels
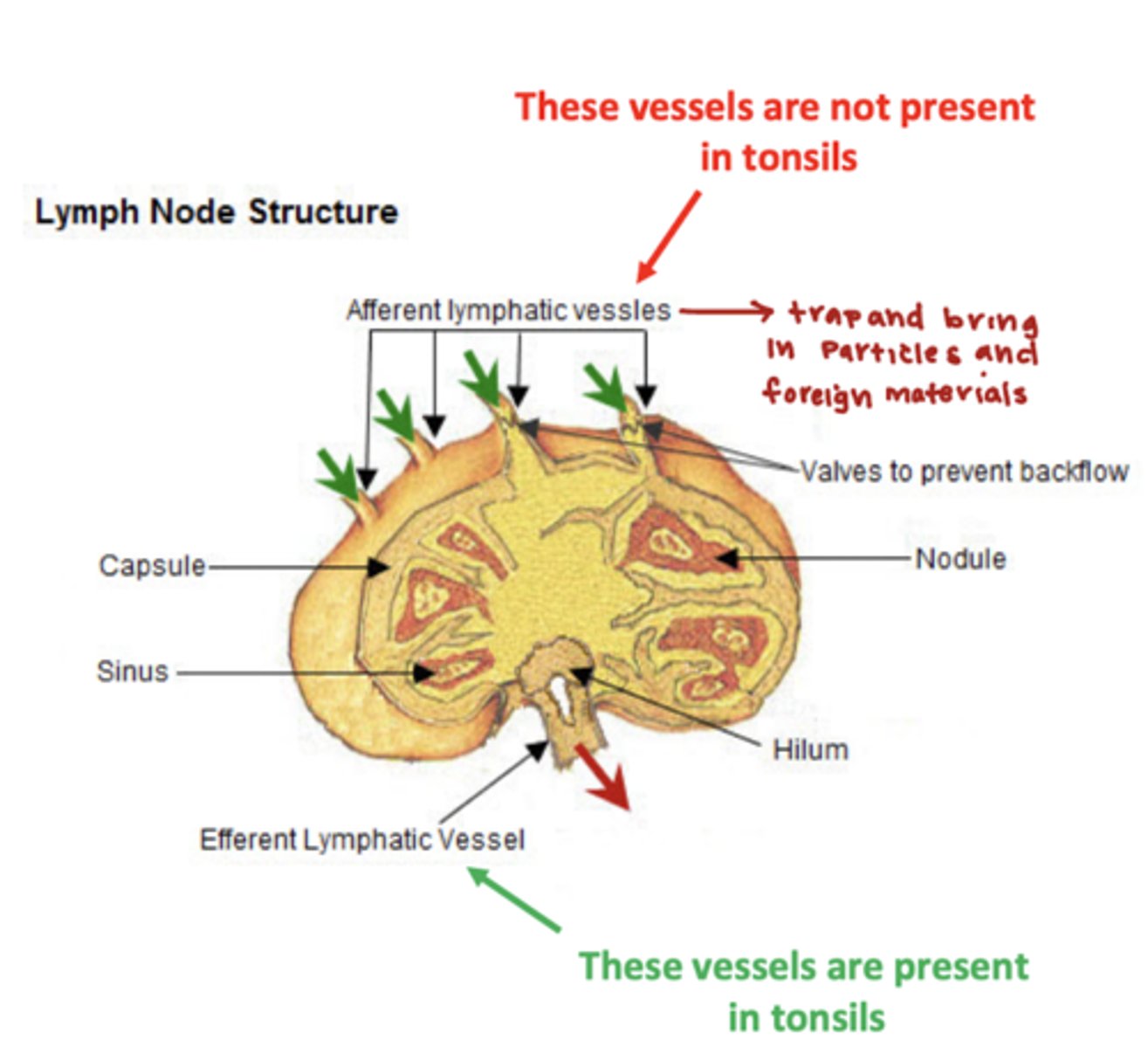
which type of tonsil is being described?
covered by interrupted stratified squamous epithelium
palatine and lingual tonsils
which type of tonsil is being described?
covered by interrupted pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
tubal and pharyngeal tonsils
what is the difference between the major glands and minor glands?
major glands:
1. outside the oral cavity
2. large glands
3. encapsulated
minor glands:
1. small glands within the connective tissue of oral mucous membrane
2. no capsule
which major salivary gland is being described?
1. produces serous secretions
2. stensens duct is its entrance into the oral cavity
3. largest gland, but produces only 25% pf salivary secretions
parotid gland
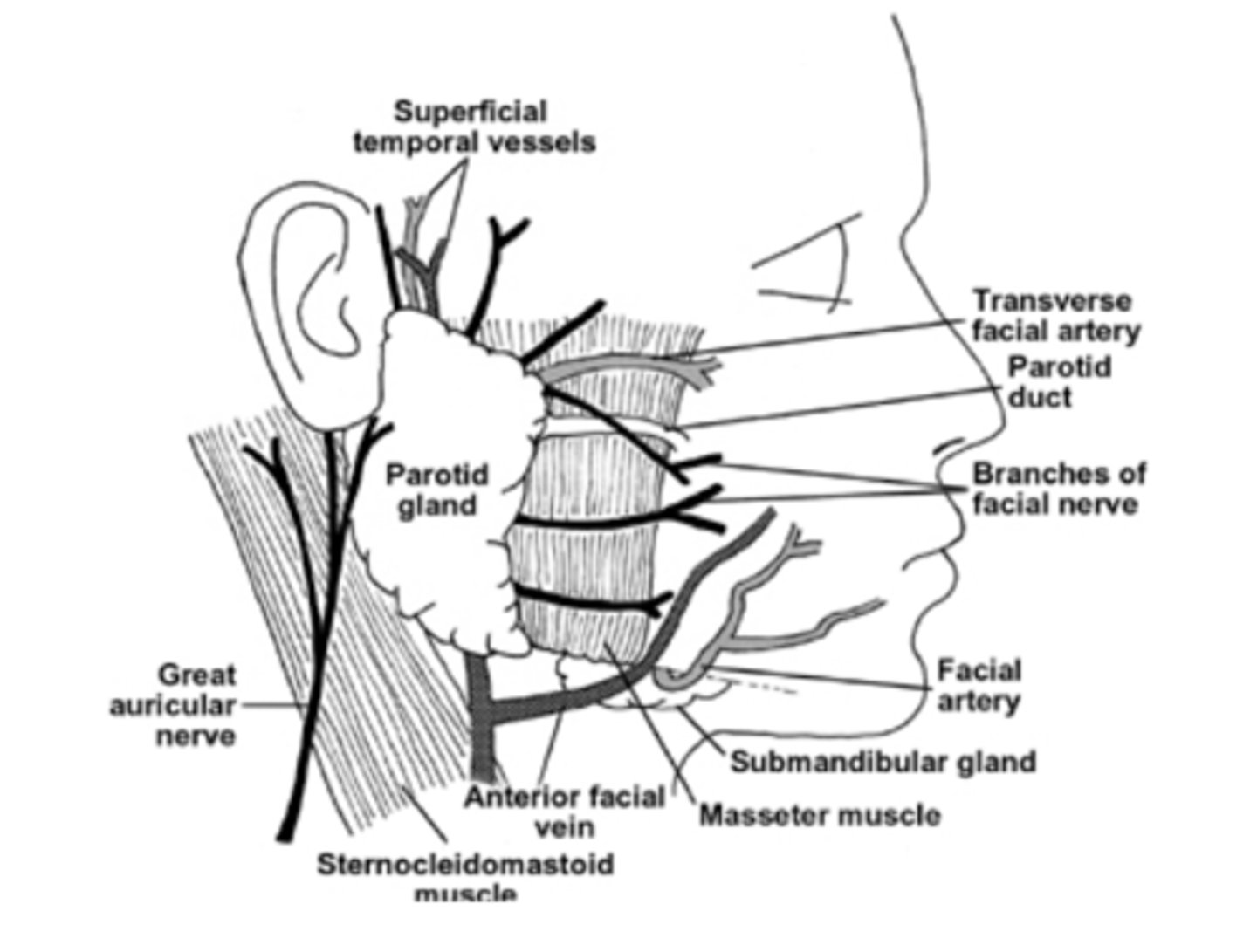
which of the major salivary glands produces a mixed secretion, but is predominantly serous?
how does this gland enter the oral cavity?
the submandibular gland
the submandibular gland enters via the whartons duct at the sublingual caruncle
which major gland produces the most secretions?
the submandibular produces 60% of the secretions in the oral cavity
what are characteristics of the sublingual gland? (secretion type, amount produced, entrance into the oral cavity)
smallest of the 3 major glands
1. mixed secretion, but predominantly mucous
2. 5% produced in saliva
3. enters via duct of bartholin at the sublingual caruncle
which two major glands enter the mouth at the sublingual caruncle?
1. submandibular via whartons duct
2. sublingual via bartholin duct
what is a specific example of a minor salivary gland?
von ebner glands release serous secretions
-only located in the troughs of circumvallate papilla
**all other minor glands produce mucus secretions
where is the maximum distribution of minor salivary glands?
palate