Year 10 Biology Revision
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Nucleotide
The basic structural unit of DNA, consisting of a deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate and a nitrogen base.
Gene
The factor that determines an inherited characteristic, located in the chromosomes
A protein code for a feature
Allele
A variation of a gene.
Chromatin
Highly coiled DNA molecule
Protein
An organic compound made of amino acids that controls chemical reactions in the body.
Helicase
Enzyme responsible for separating the two sides of the DNA molecule
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme involved in attaching loose nucleotides to the exposed DNA strand
DNA Ligase
Enzyme involved in reattaching the bonds that hold the nucleotides together to form DNA
Cell Wall
Provides structure, support and protection for the cell
Cell Membrane
Regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell
Chloroplast
Produces energy through photosynthesis and to store food away
Mitochondria
Generates the chemical energy needed to power the cell
Vacuole
To store food waste and water. Sequesters (Cust of)f waste products.
Nucleus
Controls the genetic information and characteristics of an organsim
Cytoplasm
Holds the components and protects them from damage in a cell.
Incomplete Dominance
A form of inheritance in which one allele for a specific trait is not completely dominant over the other allele
Co-Dominance
A form of inheritance in which both alleles for a specific trait present equally in the phenotype
Genotype
The combination of alleles to make up the phenotype. The genes that are present in an individual, usually represented by letters: RR, Rr, rr
Phenotype
The physical appearance of an individual as determined by the genotype
eg) Red hair
Mendelian Inheritance
Natural Selection
The process by which a species becomes better adapted to its environment
Artificial Selection
An evolutionary process in which humans consciously select for/against particular features in an organism
Sexual Selection
The process by which individuals select mates on the basis of heritable traits
Selection Pressure
The pressure exerted by environmental factors in causing the death of organisms with characteristics not suited to the environment.
Eg:
- Predators
- Harsh environment
- Weather
Pressure --> Selection --> Survival advantage --> Reproduce --> Pass on alleles to offspring
Mutation
A new variation, caused by the permanent change in a gene or chromosome
Transmutation
The evolutionary conversion of one species to another
Favourable Trait
Traits that are suited to the environment and favour the reproductive success of an individual
Population
- Has variations
A group of organisms of one species that interbreed and live in the same place at the same time.
Gene Pool
The combination of all the genes (including alleles) present in a reproducing population or species
All available genes and their frequency
Species
A group of organisms that can reproduce with one another and create viable, fertile offspring
Evolution
A process of gradual change that takes place over many different generations
Adaptation
Any change in an organism that improves its chance of survival
Types:
STRUCTURAL
BEHAVIOURAL
PHYSIOLOGICAL
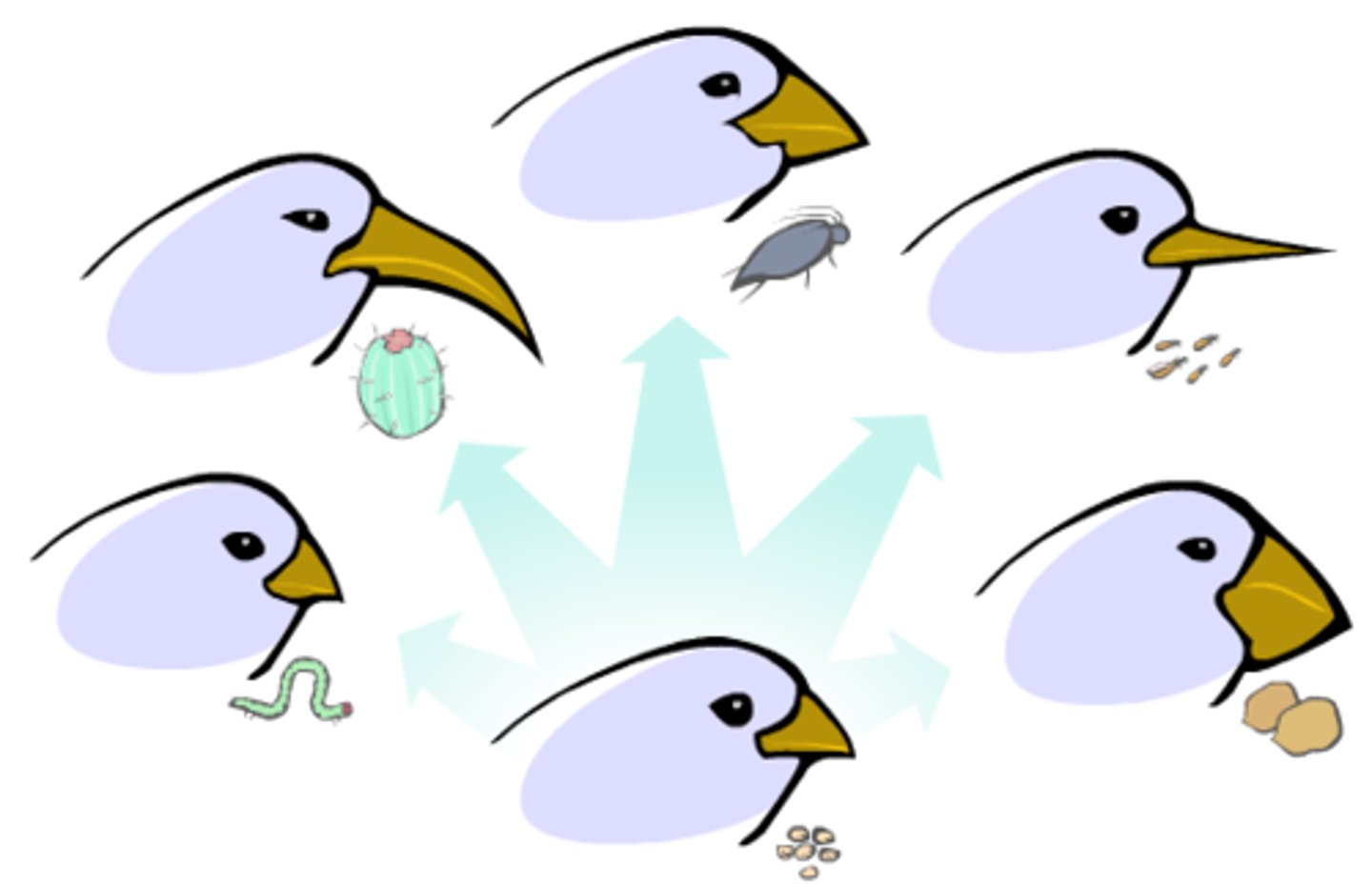
Structural (functional) Adaptation
Adaptations in the design/build of the creature
Eg) Shark teeth backwards and shredding
Behavioural Adaptation
Changes in behaviour that gives a better chance of survival
Eg) Hunting in packs, co-operative hunting
Physiological Adaptation
A chemical body process that improves your chance of survival
Eg) Making spider silk
Extinction
The termination/dying out of a species
Darwin's 4 postulates
- Individuals within a species show variation
- More offspring are produced than survive
- Offspring that do survive have heritable traits (must be able to reproduce and pass on)
- There is a struggle for existence within populations (they grow and change)
Those with desirable variation survive and produce more
EXAMPLE:
Accidental Genetic Drift
Change of allele frequencies due to random changes. One of the five forces that can cause evolutionary change.
- Responsible for random changes in a gene pool
There are two types:
- The founder effect
- The Bottleneck effect
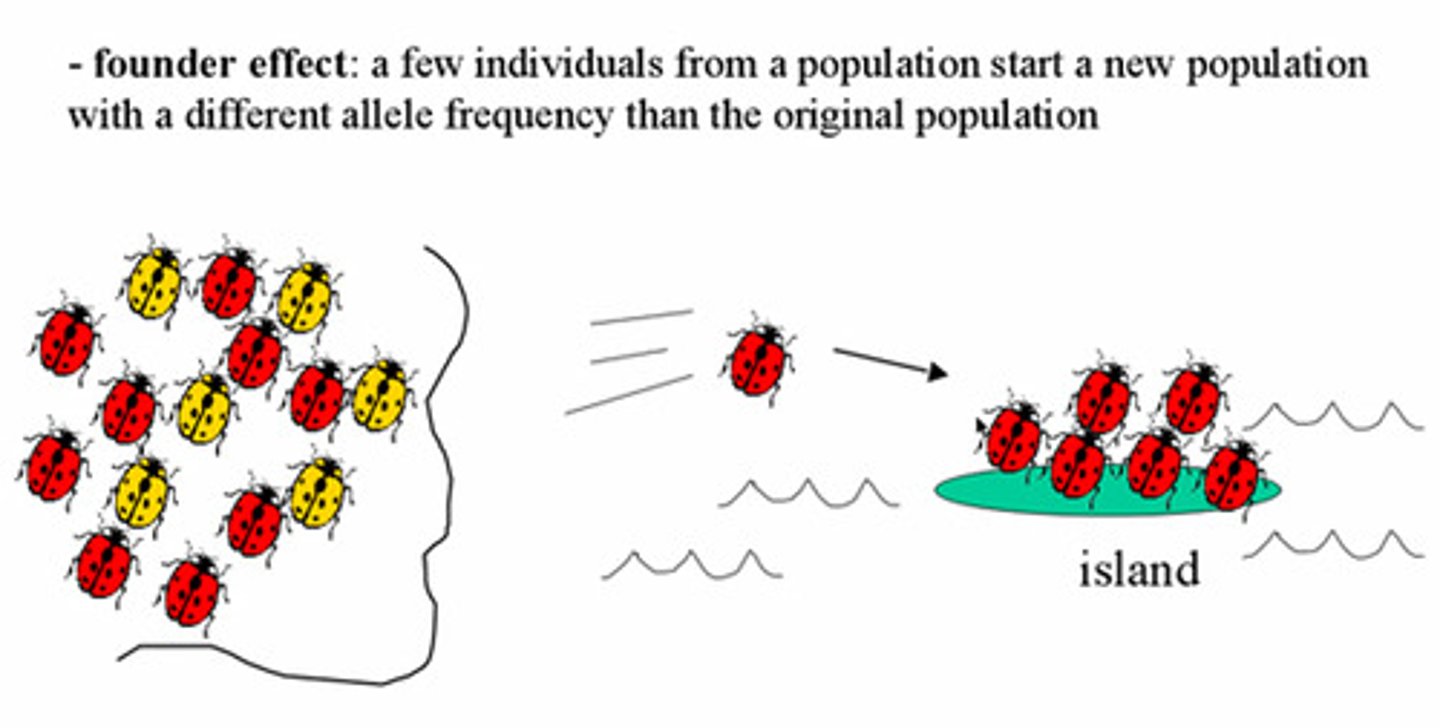
The Founder Effect
One form of genetic drift. It describes the decrease in genetic variability that happens when a small sample of individuals separates from a larger population
RANDOM CHANGE IN ALLELE VARIATION
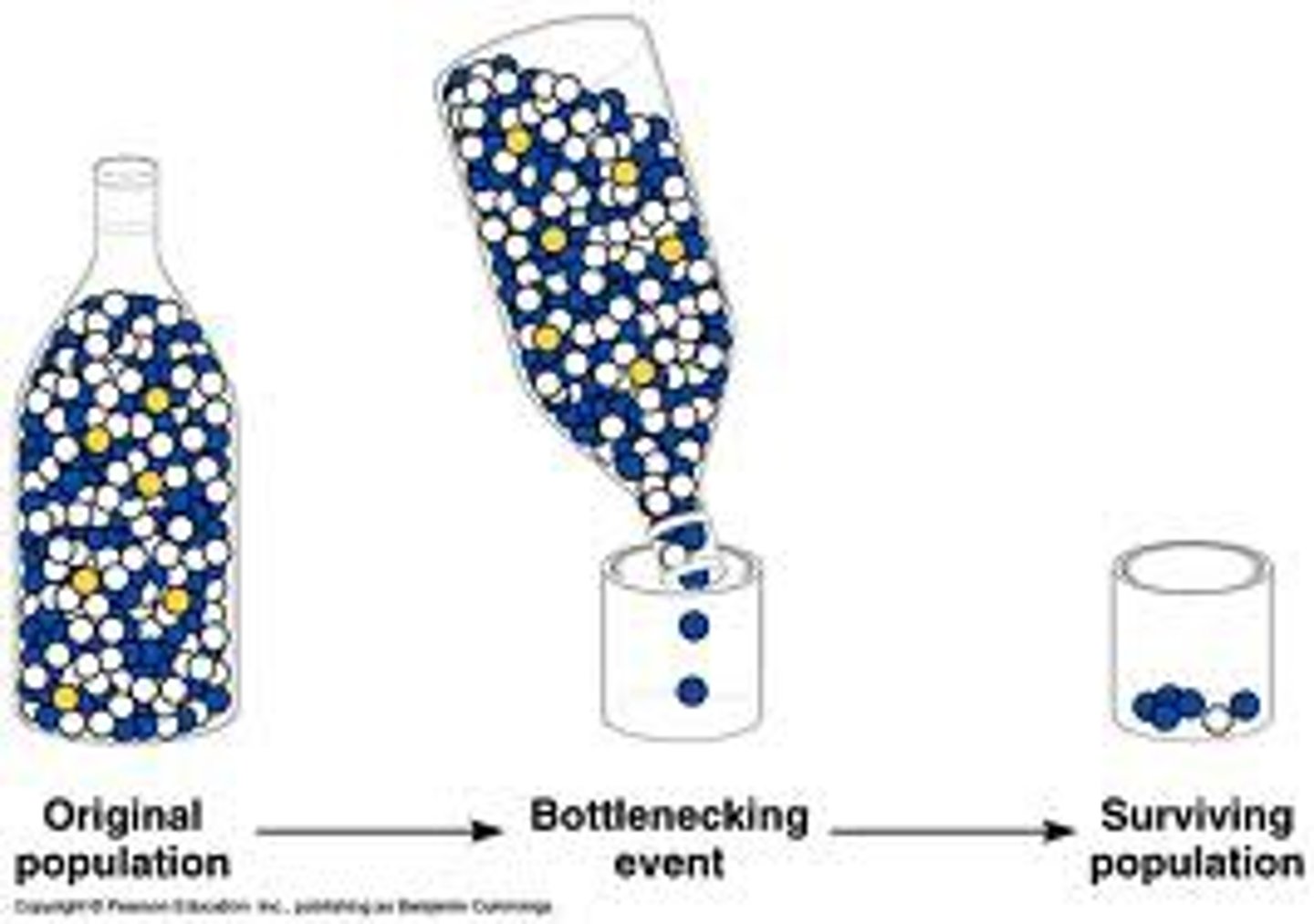
The Bottleneck Effect
Starts with a large population, then through a catastrophic event many individuals are wiped out decreasing the population and genetic variability.
Whatever survives makes a smaller population.
RANDOM CHANGE IN ALLELE VARIATION
Speciation
The formation of a new species due to evolution. They are unable to breed and create fertile offspring with the original population
> Occurs when a group within a species separates from other members and develops its own unique characteristic
Environmental Resistance
> Limits the growth of the population as the population fills up the environment
(Lack of food, change in temp, diseases)
Population size that is limited by Density Independent Factors
- May effect all individuals in a population equally
PHYSICAL FACTORS:
> Rainfall
> Acidity
> Temperature
> Humidity
> Salinity
CATASTROPHIC EVENTS
> Fire > Tsunami
> Flood > Earthquake
> Volcanic eruption > Drought
Population size that is limited by Density Dependent Factors
- Have greater effect when population density is higher
Things that are influenced by the density of the population:
> Food supply
> Disease
> Parasites
> Competition
> Predators
The Class System
Dumb Kings Play Chess On Flimsy Glass Squares
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species.
Human Classes
Domain = Eukaryote
Kingdom = Animals
Phylum = Chordate
Class = Mammal
Order = Primates
Family = Hominidae
Genus = Homo
Species = Sapiens Sapiens
Characteristics of Eucayota
- Multicellular
- Nucleus (DNA)
- Organelles: Cytoplasm, Ribosomes, Peroxisomes, Vacuoles, Mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, Endoplasmic reticulum, Centrosome, etc.
Characteristics of Procaryota
- Unicellular
- No Nucleus (Unorginised DNA)
- No Organelles
The 3 Characteristics of Chordates
1) A Notochord
2) Neural tube
3) Pharyngeal slits/pharyngeal pouches (Gills)
The 7 Characteristics of a Sub Phylum - Vertebrates
1) A bone structure and a backbone -> Vertebra (Spine)
2)A Ventral heart
3) 4 Appendages (arms and legs)
4) Red Blood that circulates through vessels - Hemoglobin and O2
5) An advanced nervous system
6) Bilateral symmetry
7) Tail at some stage (humans have tailbone)
The 2 Characteristics of Mammalia:
1) Have fur or hair covering the body
2) Produces milk/mammary glands
Characteristics of Primates (13 but need to know 6 right now 😃)
1) Large brained
2) Forward facing eyes (2)
3) Colour vision Stereoscopic/Binocular vision
4) Pentadactyl digits (5)
5) Dermal ridge -> Fingerprints
6) Opposability
Classifications for animals: MRS GREN
Movement - Important for organisms to catch food and avoid predators
Respiration - Process of all living things to convert energy that can be used by cells
Sensitivity - How animals respond to their environment e.g. changes
Growth -
Reproduce - Either asexual or sexual.
Excretion
Nutrition
Not studied (53)
You haven't studied these terms yet.