Citric Acid Cycle Exam/ETC (electron transport chain (oxidative phosphorylation)) #2
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Citric acid cycle
location:
PDH complex?
location: mitochondria
PDH complex
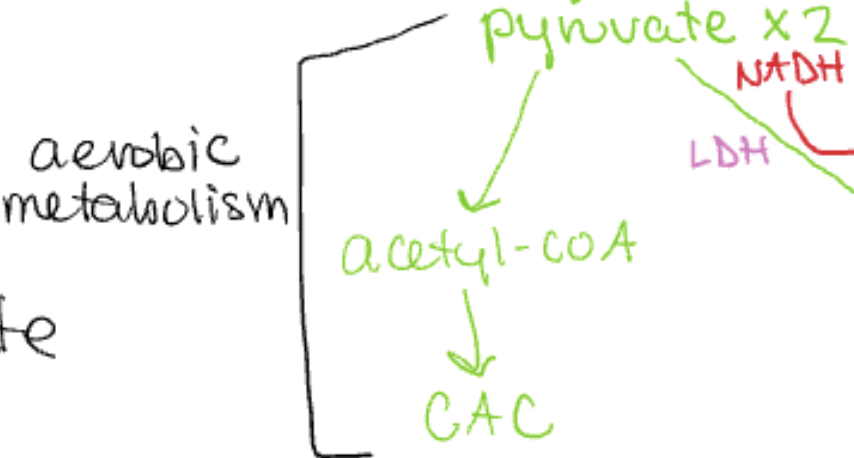
purpose: pyruvate (glycolysis) → Acetyl coA → CAC
aerobic metabolism
E1
coenzyme?
inhibition?
activation?
deficiencies?
coenzyme: TPP → requires thiamine (vit B1)
inhibition: phosphorylation (PDH kinase)
activation: dephosphorylation (PDH phosphotase)
deficincies: 1. congenital lactic acidosis
vit b1 (thiamine) deficiency
E2
coenzyme?
coenzyme: lipoic acid, COA
associated with arsenic poisioning
E3
coenzyme
requires
inhibition
coenzyme: FAD, NAD+
requires riboflamin (vit b2) + niacin (vit b3)
inhibition: acetyl coa/NADH activates PDH kinase
Electron transport chain
location:
purpose:
diagram?
location: inner mitochondria membrane
purpose: increase ATP production
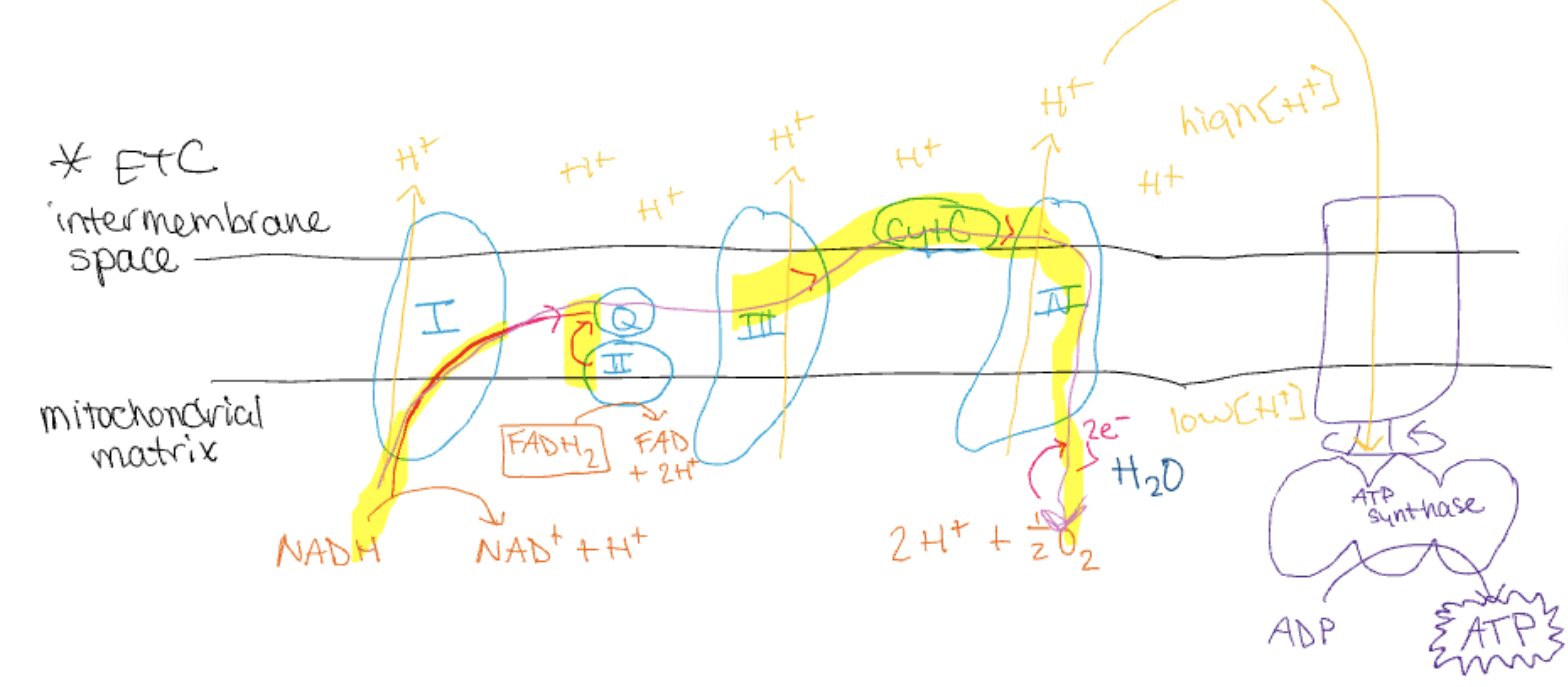
Electron transport chain by steps
Step 1: NADH/FADH2 produced earlier donate electrons (NADH → complex I) (FADH → complex II)
Step 2: Electrons from both complex I and II are transferred to coenzyme Q, then carried to complex III
Step 3: electrons pass through complex III, protons pumped into intermembrane space, contributes to proton gradient
Step 4: Electrons transferred to cytochrome c and carried to complex IV
Step 5: at complex IV, electrons are passed to oxygen, combined with protons to form water
Step 6: Proton gradient generated drives protons back into matrix through ATP synthase (chemiosmosis)
Step 7: Protons move through ATP synthase, rotate enzyme, catalyzes phosphorylation of ADP → ATP