Science Praxis 5005 (Life Science)
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
Living things
have physical entities and biological processes, such as homeostasis cell division, cellular respiration, and photosynthesis.
What are nonliving things classified as?
inanimate
Cell theory
(biology) the theory that cells form the fundamental structural and functional units of all living organisms
What are the three components that make up cell theory?
1. All living things are composed of cells
2. The cell is the smallest unit of life
3. All cells come from pre-existing cells.
What is the organization of life?
cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus, mitochondria, or any other membrane-bound organelle.
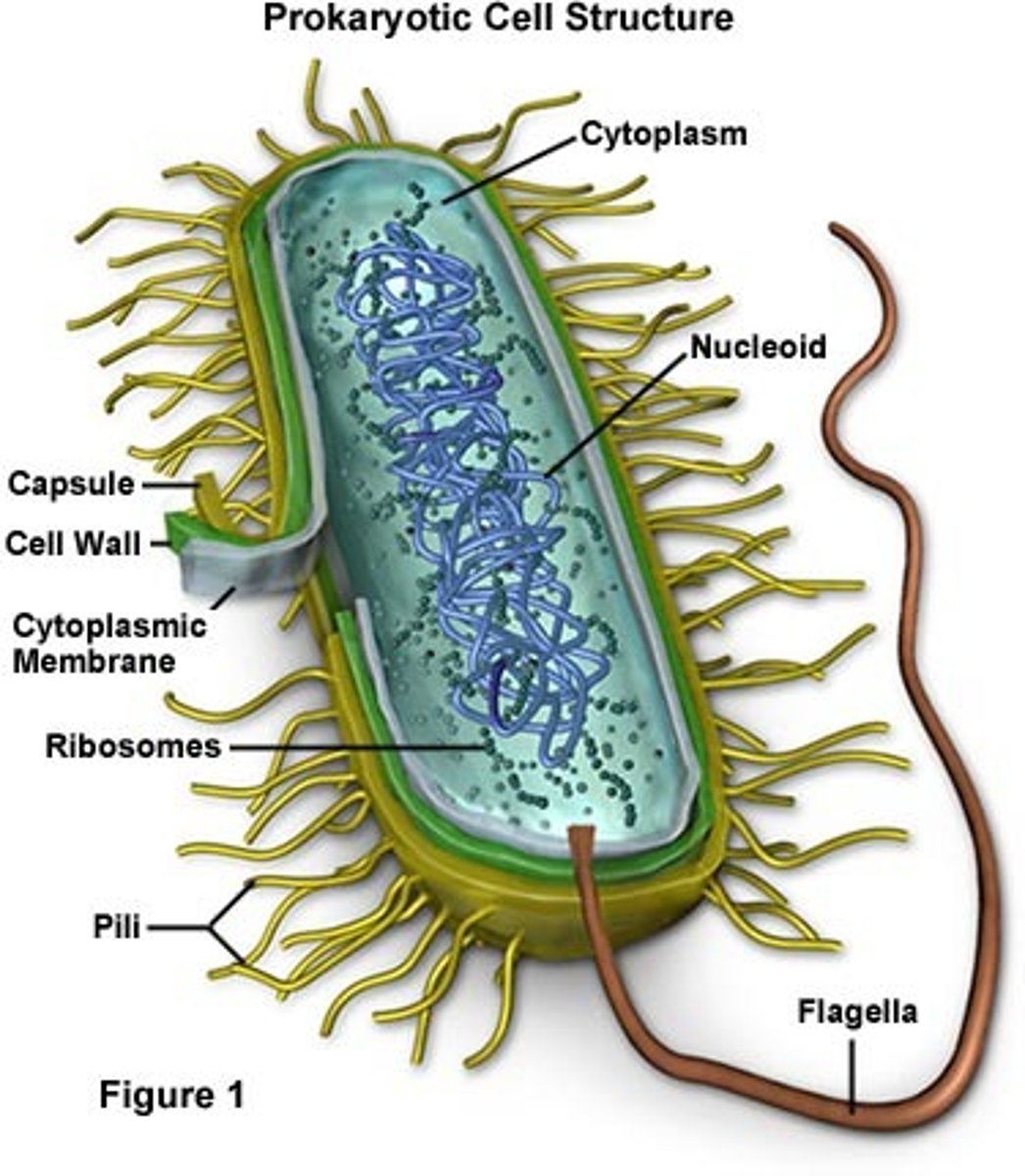
What floats freely throughout the prokaryote cell?
DNA
What are the two domains of prokaryotes?
Bacteria and Archaea
Eukaryote
a multicellular organism that contains a nucleus, mitochondria, and membrane-bound organelles
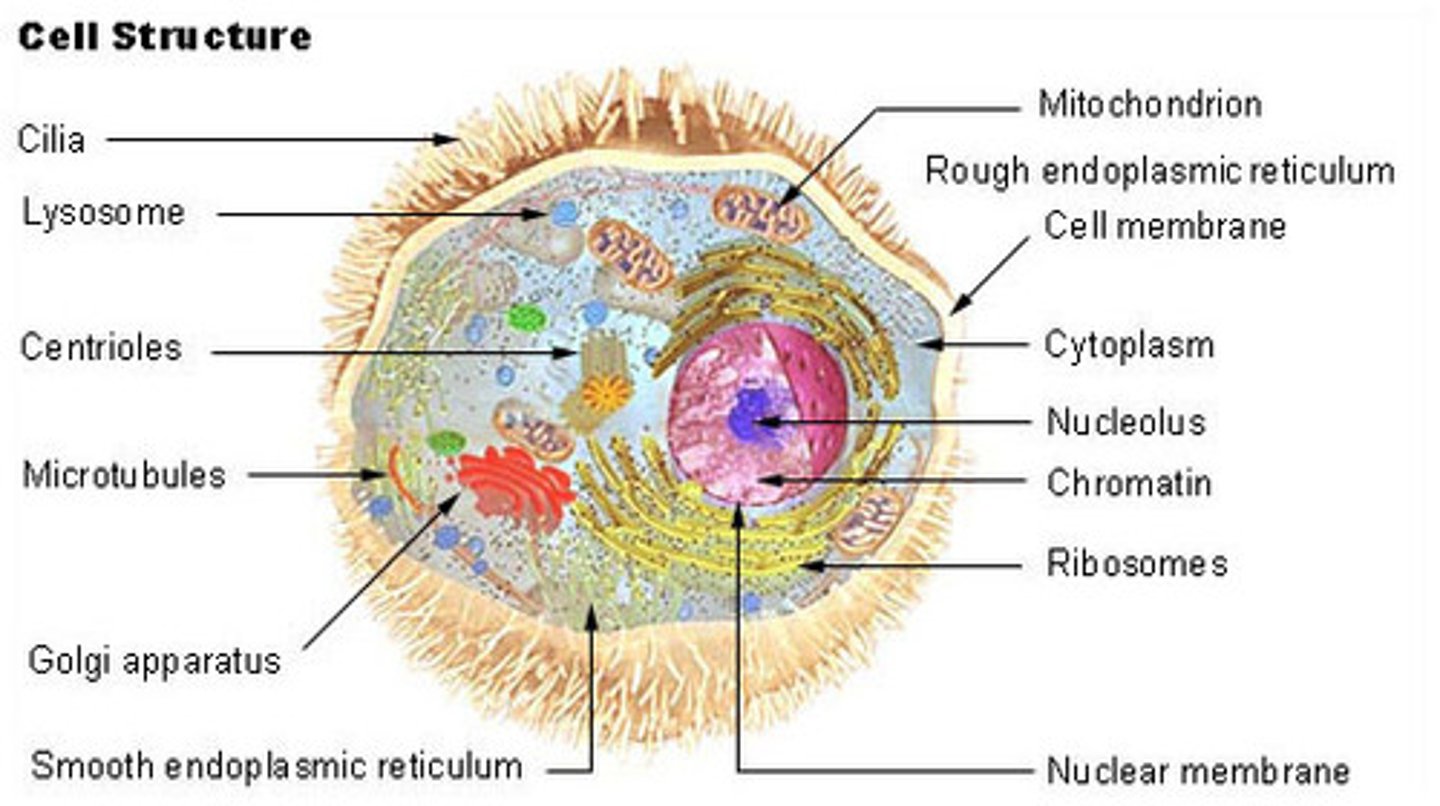
Organelles
the structures within the cell membrane or cell wall
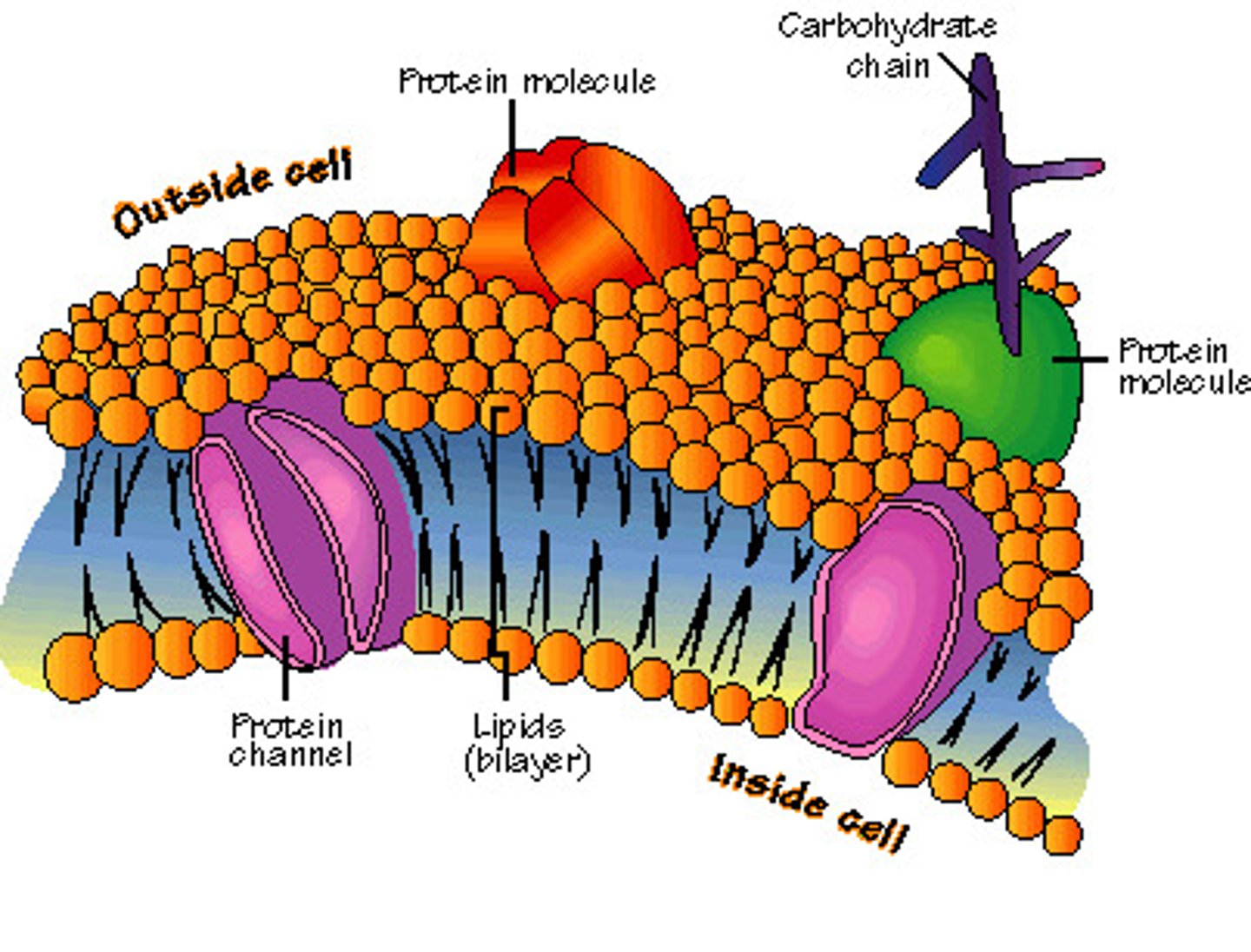
cellular membrane
fluid, the permeable outside covering of the cell. In a plant cell, this is a cell wall and it is rigid.
Nucleus
Command center of the cell. Controls of the rest of the cell.
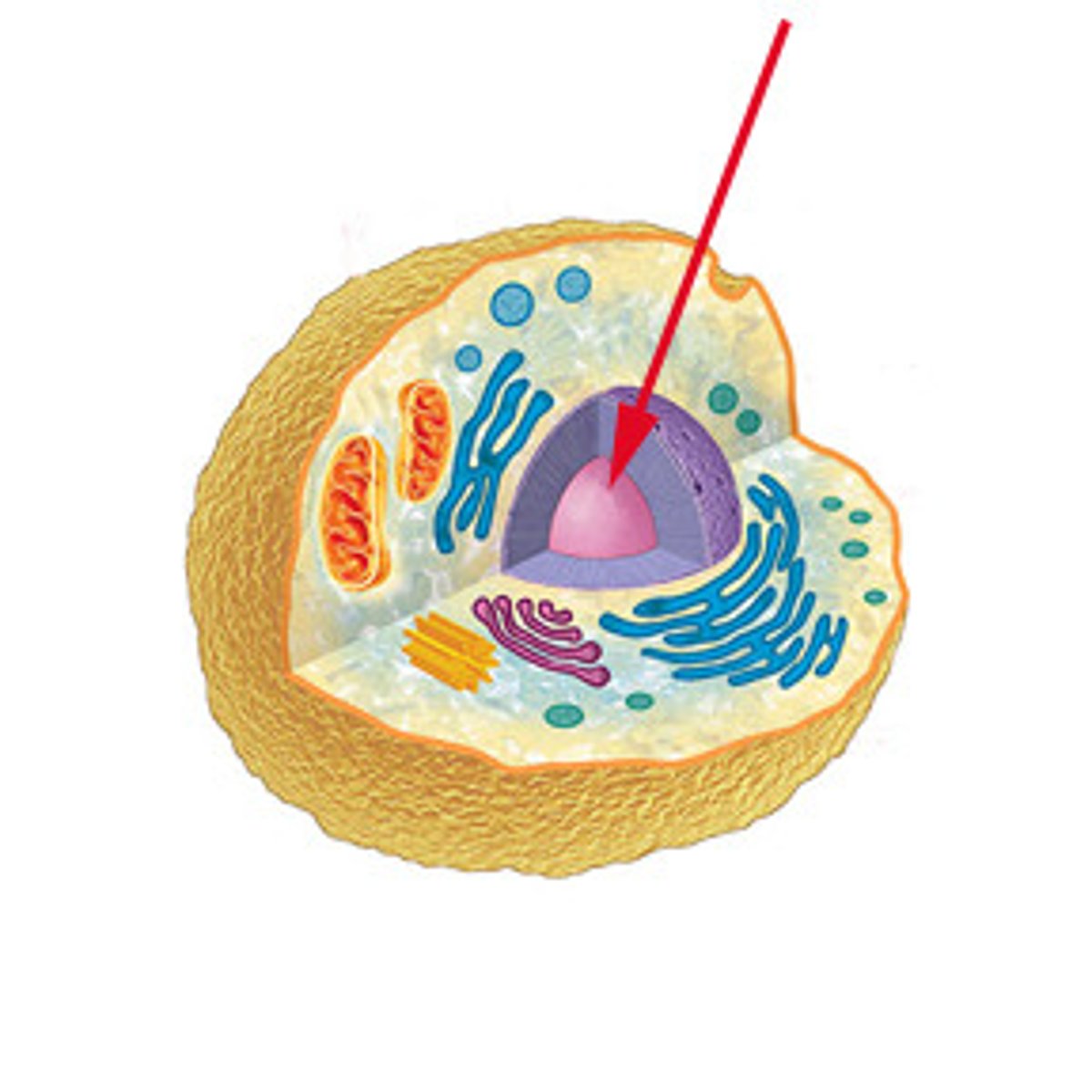
Where does DNA live in eukaryotic cells?
the nucleus
Mitochondria
Powerhouse (energy source) of the cell
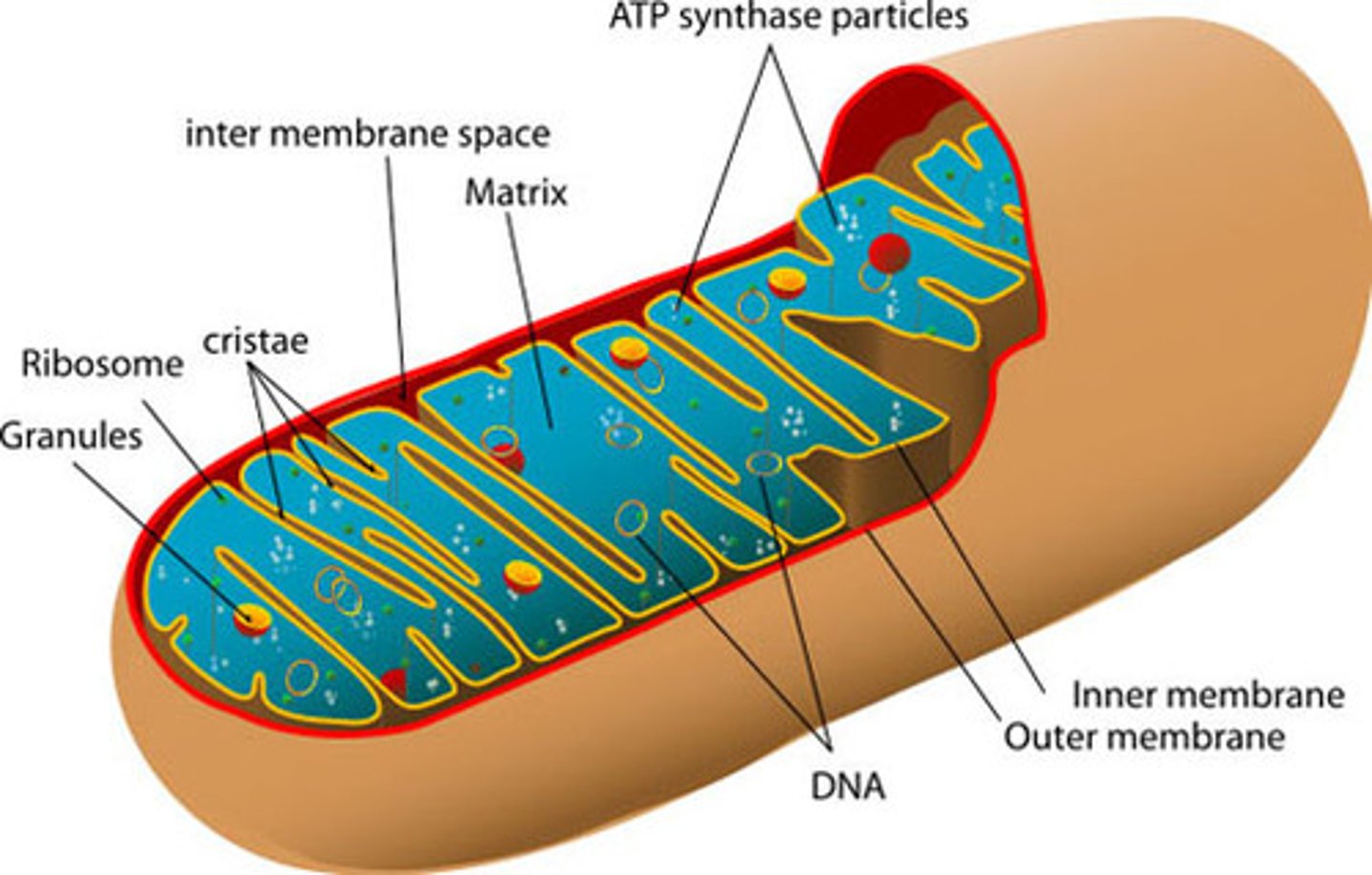
Cytoplasm
Water-like substance in the cell
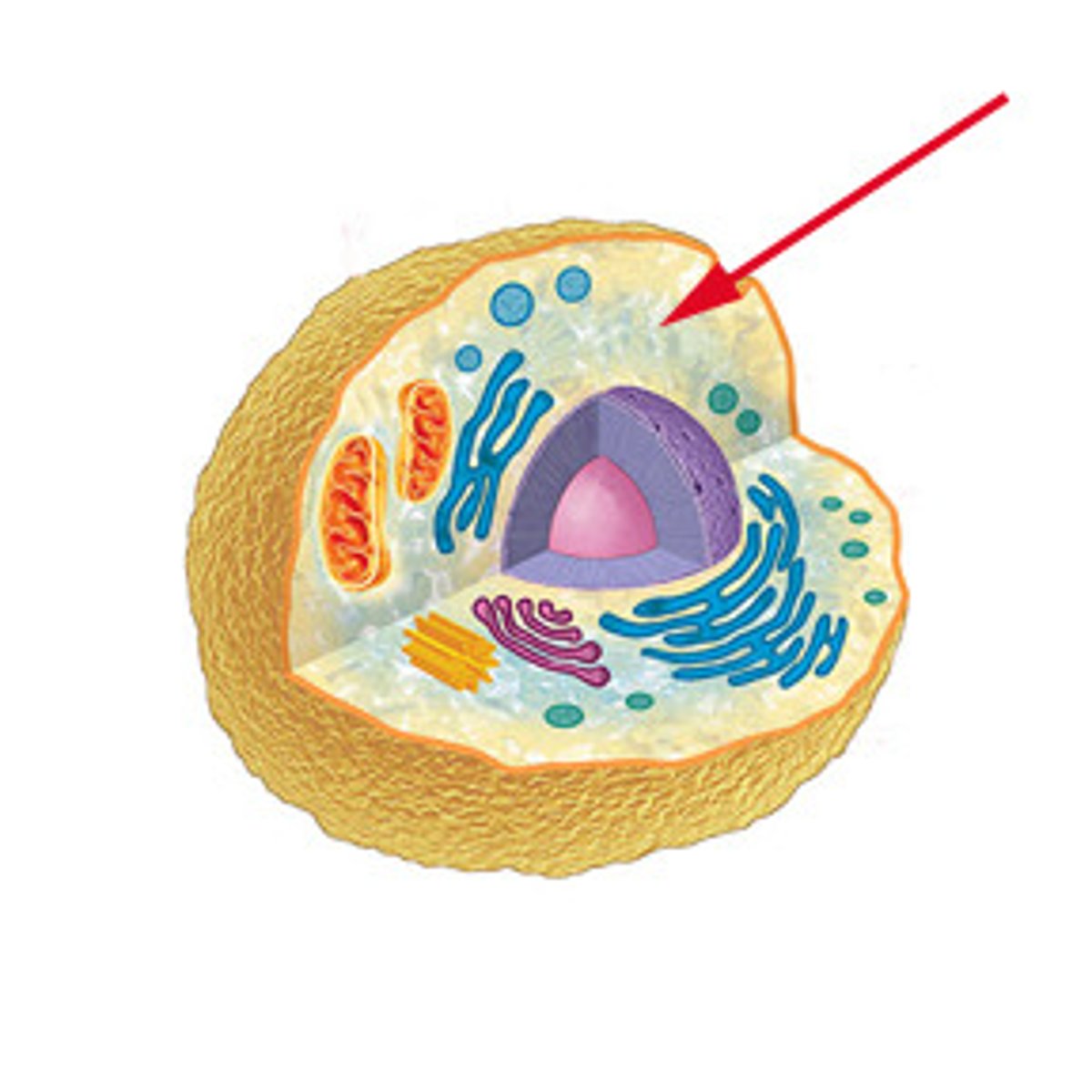
What are Bacteria and Viruses?
prokaryotic cells and can only be seen under a microscope.
Bacteria
usually harmless
Virus
Causes diseases
What are animal and plant cells?
Eukaryotic
Animal Cell
does not have a cell wall or chloroplast and a small vacuole.
Plasma membrane
Cellular respiration
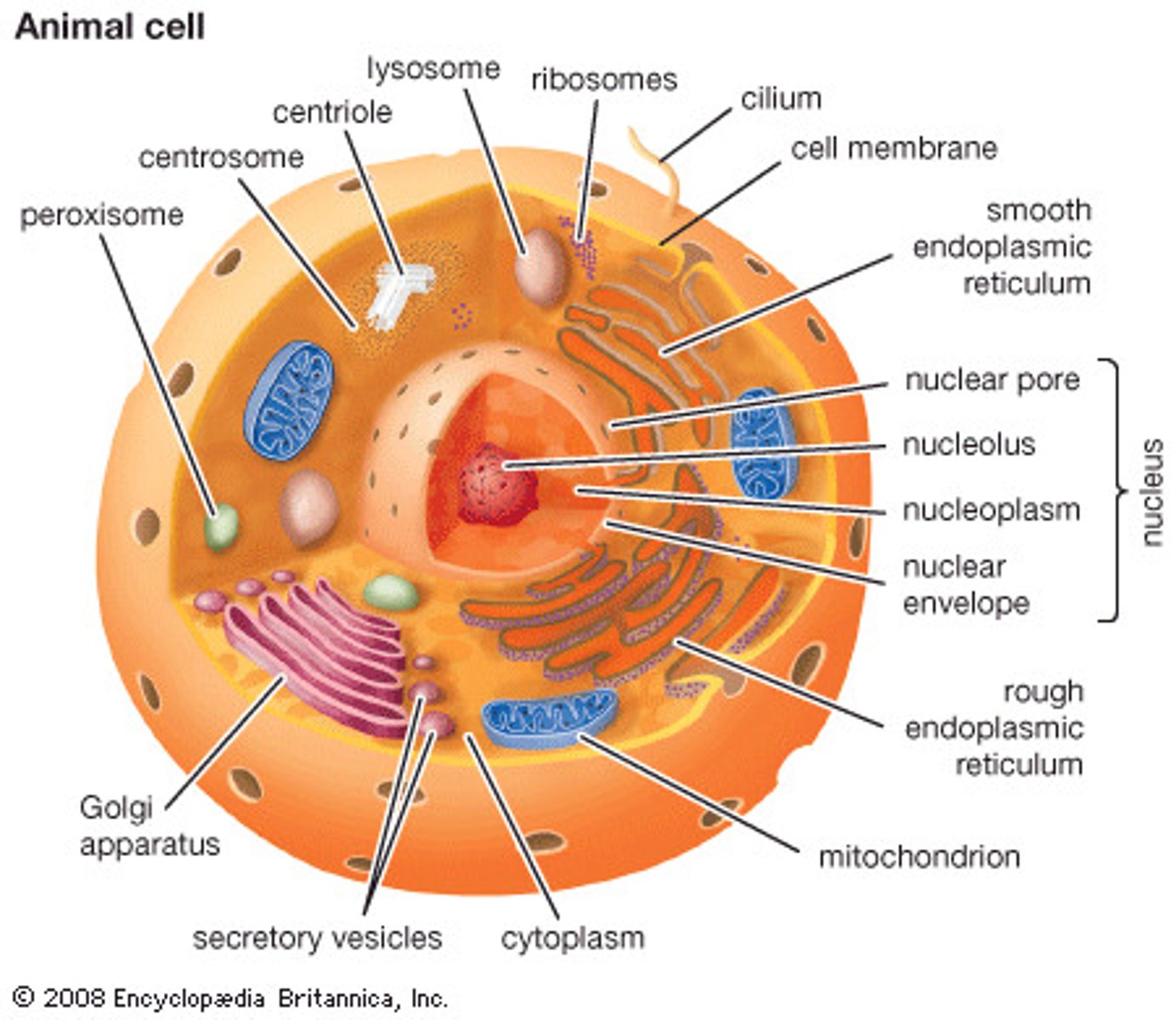
Plant Cell
contains a cell wall, chloroplast, and large vacuole
Photosynthesis

symbiotic relationship
close interaction between species in which one species lives in or on the other
cellular respiration
Animal Cells go through this
Taking in food in the form of carbohydrates, making energy in the form of ATP, and removing waste.
Photosynthesis
Plant cells make their own food through this process.
Using carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight, and turning them into carbohydrates.
sexual reproduction
involves two parents
Each parent contributes a gamete to the process of reproduction.
Occurs in plant and animal cells
What is a gamete?
sex cell
asexual reproduction
involves one parent
How do prokaryotes reproduce?
asexually through binary fission
While prokaryotes do not go through mitosis...
the cell does split into identical copies
binary fission
when a single parent cell doubles its DNA, then divides into two cells. Occurs in bacteria.
Budding
when a small growth on the surface of parent breaks off to continue growing into adulthood.
Occurs in yeast and some animals.
Fragmentation
when a piece of an organism breaks off, and those pieces develop into a new organism. This happens with starfish.
Parthenogenesis
when an embryo develops from an unfertilized cell.
Occurs in invertebrates as well as some fish, amphibians, and reptiles
Mitosis
a series of steps in creating an identical cell from another cell.
Cell Theory
All cells come from pre-existing cells
Interphase
NOT a part of mitosis
The cell prepares for division. It plumps up and replicates its DNA within its nucleus.
Prophase
The DNA tightly coils into chromosomes to make splitting efficient. The nuclear membrane dissolves. The microtubes or spindle fibers move to opposites sides of the cell.

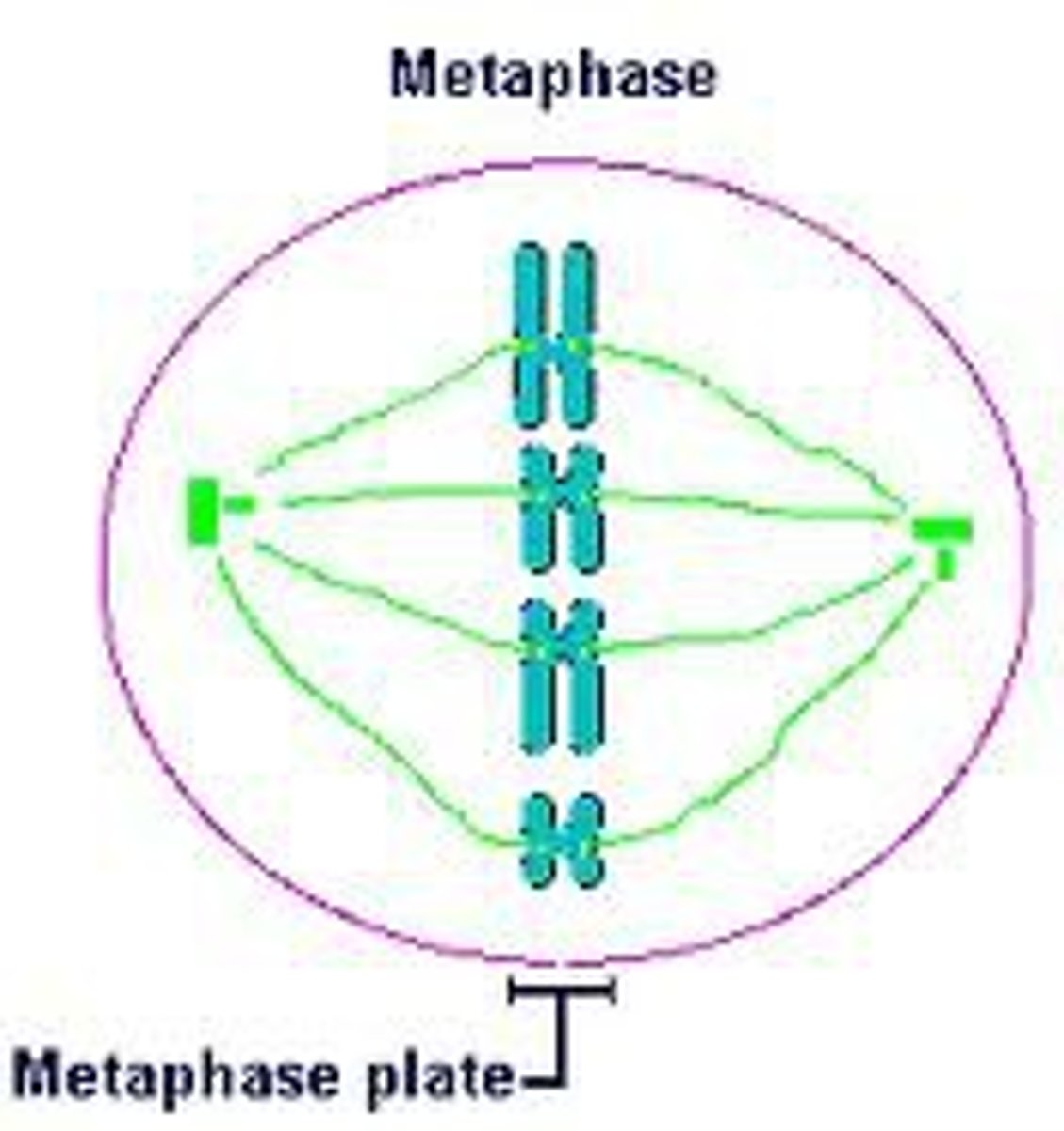
Metaphase
The chromosomes (tightly coiled DNA) move to the middle of the cell. The spindle fibers attach to each chromosome.
Anaphase
The spindle fibers begin to pull apart the chromosomes, bringing them to opposites sides of the cell for efficient splitting.
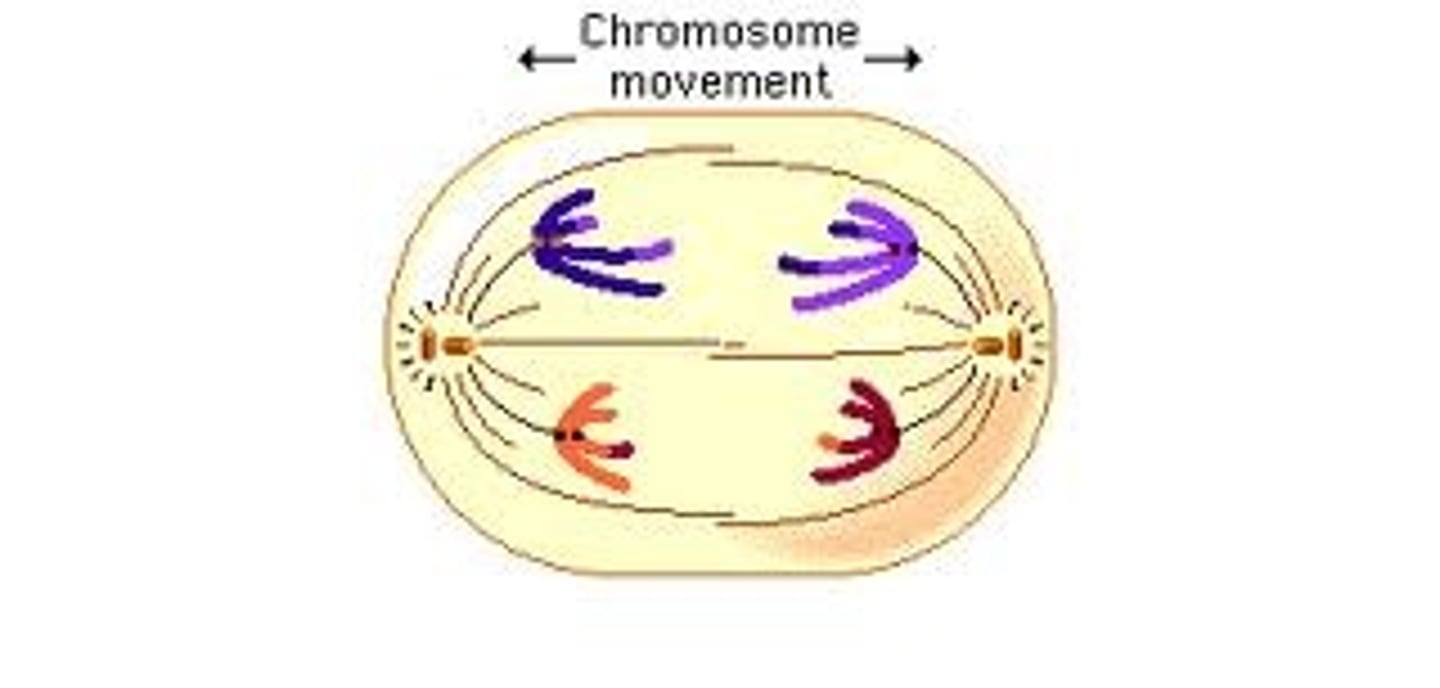
Telophase
With the chromosomes at either side of the cell, the two new cells pinch off, forming two identical sister cells of the original cells.
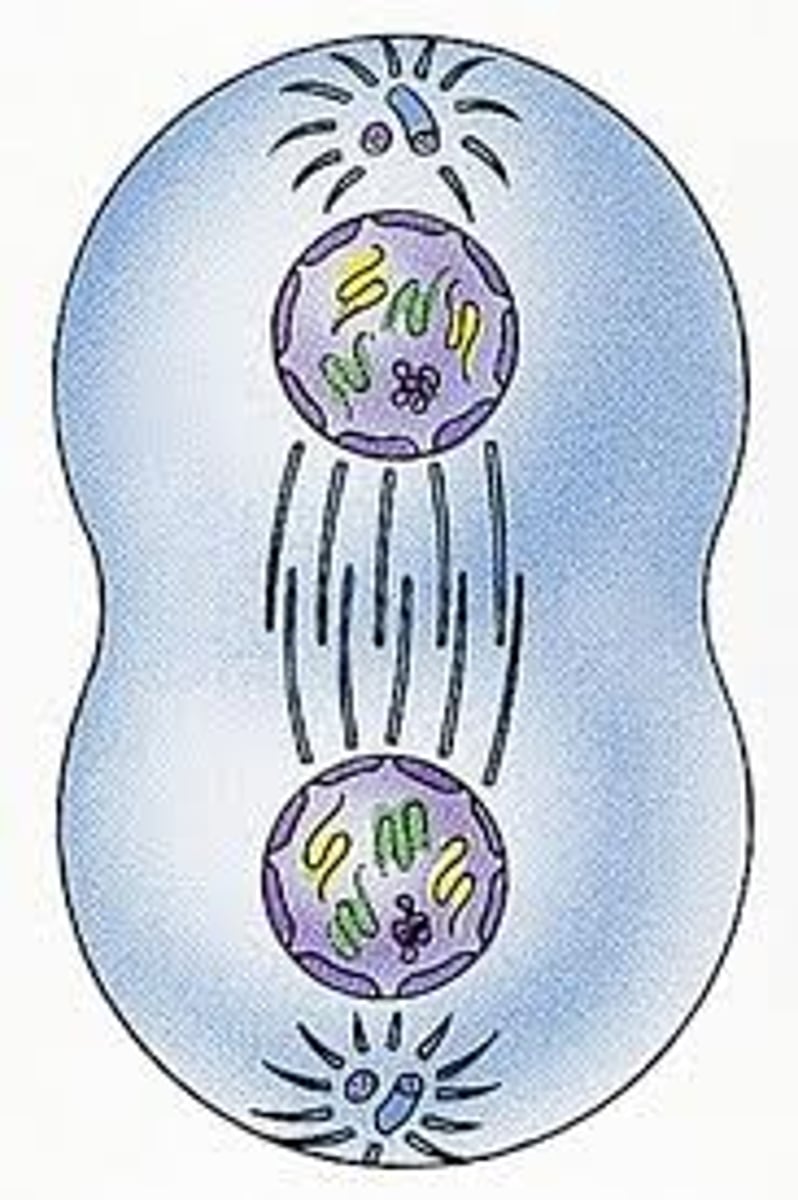
Cytokinesis
when the cell separates into two cells during the final stage of mitosis.
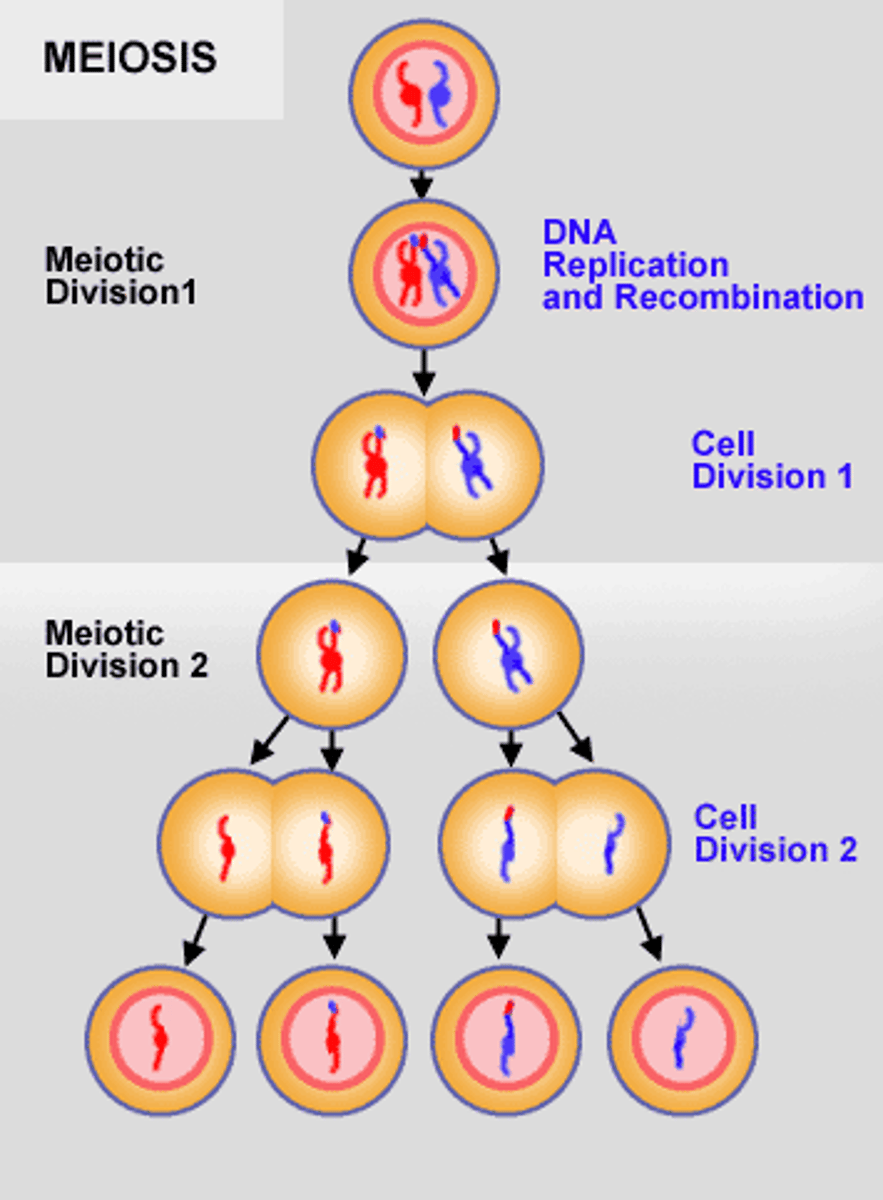
Meiosis
Ensures that humans have the same number of chromosomes in each generation. Two-step process that reduces the chromosome number by half-from 46 to 23 to form sperm and egg cells.
Trisomy
extra chromosome (down syndrome)
DNA
the hereditary material in living organisms
Where is DNA located in eukaryotes?
nucleus and mitochondria
What does DNA contain?
a code using four nitrogen bases
What are the nitrogen bases
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
What are the pairs of nitrogen bases?
Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T)
Guanine (G) pairs with Cytosine (C)
As pair with Ts
Cs pair with Gs
Amino Acids
organic compounds that from proteins.
How many different amino acids are there?
20
chains of amino acids make...
proteins
DNA Replication
the process of making a copy of DNA
What is necessary for the survival of an organism?
DNA replication
What is the process of DNA replication?
1. The DNA unzips
2. Free-flowing nucleotides (As, Ts, Gs, and Cs) bind to the unzipped portion of the DNA
3. Two identical DNA strands are the result
Gene
the basic physical and functional unit of heredity
What are genes made up of?
DNA
How many copies of each gene do you have?
2 copies
one inherited from each parent
Alleles
forms of the same gene with slight differences in their sequence of DNA bases.
Dominance
when the effect of one phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele.
the first allele is... and the second allele is...
dominant, recessive
Example of dominant and recessive
Brown eye color is dominant over blue eye color (recessive)
For a person to have blue eyes...
they must have both recessive alleles
Gregor Mendel
The father of genetics - Experimented with pea plants
What did Gregor Mendel show?
when a true-breeding yellow pea (YY) and a true-breeding green pea (yy) were crossbreed, their offspring always produced yellow seeds.

Metamorphosis
the process of transformation from an immature form to an adult form in two or more distinct stages. There are two types
Complete metamorphosis
the insect goes through four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and imago
What is an example of complete metamorphosis?
a caterpillar changes completely into something else: a butterfly
Incomplete metamorphosis
the insect hatches from an egg and then goes through several nymphal stages
What is an example of incomplete metamorphosis?
grasshoppers gradually get bigger, but they do not change into something else. Each stage of growth looks like a bigger version of the original stage
Evolution
a type of change that happens over thousands of years
What do organisms not do?
evolve
Adaptation
the distribution of traits in the population that is matched to and can change with environmental conditions.
Natural Selection
Developed by Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace. A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
Mutations
changes in the DNA molecule caused by mistakes during cell division or exposure to environmental factors
What must all organisms be all to do?
grow, reproduce, and maintain stable internal conditions even when the world and environment around them change.
What is the behavior of individual organisms influenced by?
internal cues (hunger and internal temperature) and external cues (changes in the environment)
Homeostasis
The tendency to maintain a stable, relatively constant internal environment.
Cold-blooded
Animals that have a body temperature varying with that of the environment
What are some cold-blooded animals?
amphibians, reptiles, fish, and insects
Warm-blooded
Animals that maintain a constant body temperature, regardless of the temperature in the environment.
What are some types of warm-blooded animals?
mammals and birds
Vertebrates
animals that have a backbone
Invertebrates
Animals without backbones
Open Circulatory System
the blood is pumped into the body cavity and is not enclosed in blood vessel
What types of animals have an open circulatory system?
most invertebrates-insect, crustaceans, most mollusks
Closed Circulatory System
the blood is pumped by the heart and is enclosed in blood vessels
What types of animals have a closed circulatory system?
Most vertebrates-mammals, reptiles, fish, birds
Circulatory and Respiratory System
Responsible for the flow of blood; nutrients, oxygen and other gases, and hormones to and from cells.
What organs are a part of the circulatory and respiratory system?
heart (cardiovascular)
lungs (pulmonary)
arteries, veins, coronary and portal vessels (systemic)
Digestive and Excretory System
responsible taking in food and breaking it up into nutrients the body will use for fuel. It also removes the waste left over after the food is processed for nutrients.
What organs are a part of the digestive and excretory system?
gastrointestinal tract (stomach and intestines)
bladder
colon
kidneys (filter the blood)
Nervous, Endocrine, and Immune System
the master control system
What organs are a part of the nervous, endocrine, and immune system?
brain-hypothalamus, thalamus, and pituitary gland
spinal cord
neurons
hormones
classification system
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
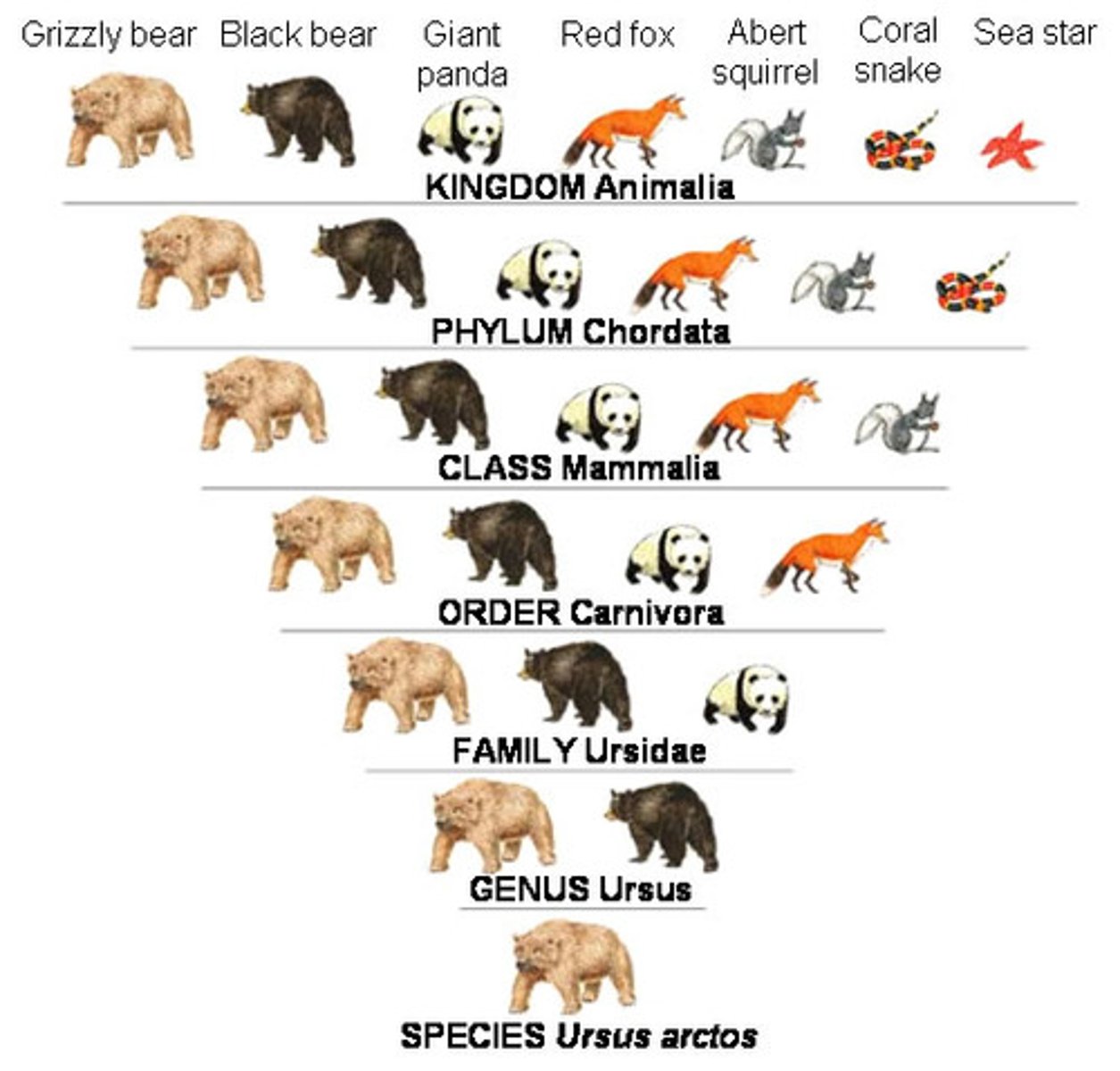
Species
a group of interbreeding organisms that do not ordinarily breed with members of other groups
Ex: Polar Bear
Populations
Comprises all the individuals of a given species in a specific area or region at a certain time. Can evolve over time because of genetic variation.
Ex: Includes all polar bears in the Artic Circle.
Communities
All the populations in a specific area or region at a certain time. There are many interactions among species (food webs)
Ex: polar bears, the penguins, the fish, and the plants make up this...
Ecosystems
The dynamic entities composed of the biological (living) community and the abiotic (nonliving) environment.
Ex: The Artic is made up of the water/ice, the animals, and the atmosphere in that area
Producers (plants)
produce their own food from sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. The bottom of the food web/energy pyramid
Consumers
eat their food, categorized into four categories: