Module 1 (Cram)
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
A substance used in medicine and veterinary medicine to kill parasites
Parasiticide
A substance used to kill parasitic worms
Anthelmintic
A substance used to kill mites or ticks
Acaricide
A substance used to kill insects
Insecticide
A substance used to kill protozoans
Antiprotozoal
An organism that lives a significant period of its life inside or on another organism, from which it obtains nourishment and shelter and to which it may cause harm
Parasite
Parasite that lives inside a host
Endoparasite
Parasite that lives outside a host
Ectoparasite
Close association of two dissimilar organisms
Symbiosis
Each of the organisms in a symbiotic relationship
Symbiont
Type of symbiosis that is beneficial to both animals
Mutualism
Example of mutualism
Honeybee and flower

Type of symbiosis that is beneficial to one animal without effecting the other
Commensalism
Example of commensalism
Barnacle and whale

Type of symbiosis that is beneficial to one and detrimental to the other
Parasitism
Example of parasitism
Hookworms and dogs
Type of symbiosis that is detrimental to both animals
Synnecrosis
Example of synnecrosis
Heavy ascarid (worm) load killing both parasite and host

Type of life cycle in which the parasite can complete its entire life cycle on one host
Direct life cycle
True or false: A parasite with a direct lifestyle doesn't leave its host for any period of time
False. The parasite may leave the host for a period but does not require another species to complete life cycle
Example of a parasite with a direct life cycle
Bots

Type of life cycle in which the parasite requires one or more intermediate hosts in order to reach infective stage for original host
Indirect life cycle
Example of a parasite with an indirect life cycle
Tapeworms
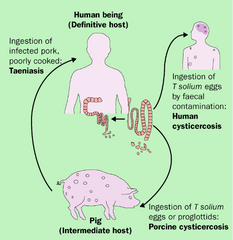
Type of host that harbors adult, sexual, or mature form of parasite
Definitive host
Type of host that harbors larval, juvenile, or immature form of parasite
Intermediate host
Type of host that harbors larval form of parasite encapsulated in tissues, the parasite doesn't undergo any further development in this host
Paratenic host
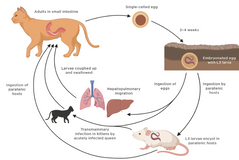
Type of host that is not capable of transmitting the parasite to other animals
Incidental host (or dead end host)
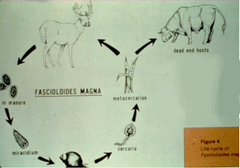
Type of host that refers to wild animals transmitting parasites to domestic animals
Reservoir host

Time that elapses between entry of infective stage of parasite into definitive host and the demonstration of presence of parasite within the host
Prepatent period
What are the four routes of infection (ie. ways a parasite can gain entry into a host)?
Oral ingestion
Skin penetration
Via air passages
Prenatal infection
Name five causes of host injury by parasites and an example for each one (there are 11 total)
Blood loss, fleas suck blood from a cat
Toxins, tick paralysis caused by tick neurotoxin
Disease vectors, lyme disease from a tick
Allergic reactions, flea allergy dermatitis
Physical annoyance, warbles annoy cattle
A severe tapeworm infestation competes with a host for available nutrients, what kind of host injury is this?
Nutrient competition
A severe flea infestation causes anemia in a kitten, what kind of host injury is this?
Blood loss
Liver flukes migrate through the liver causing extensive damage to liver cells, what kind of host injury is this?
Tissue damage
Strongyles block blood vessels, what kind of host injury is this?
Mechanical obstruction
Liver fluke damage activates Clostridium spores, what kind of host injury is this?
Opportunity for bacterial invasion
Strongyles causes damage to the aorta and other blood vessels, what kind of host injury is this?
Scar tissue reactions
Ticks release neurotoxins causing tack paralysis, what kind of host injury is this?
Toxins
Ticks carry lyme disease, what kind of host injury is this?
Disease vectors
The larval form of the nodular worm of sheep creates a neoplasia in the intestines, what kind of host injury is this?
Stimulate neoplasia
Flea saliva causes irritation (flea allergic dermatitis), what kind of host injury is this?
Allergic reactions
Warbles cause gadding (running away) in cattle, what kind of host injury is this?
Physical annoyance
What are the four factors affecting the severity of host damage?
Virulence of parasite
Parasite numbers
Health of the host
Age of host
What are the two Kingdoms that have veterinary parasitology significance?
Kingdom Animalia
Kingdom Protista
What are the three parasite Phylums of Kingdom Animalia?
Phylum Arthropoda
Phylum Platyhelminthes
Phylum Nematoda
What are the two Classes of Phylum Arthropoda?
Remember: "Arthro" means joint, "poda" means feet/legs, so Arthropoda means jointed legs. Think of bugs!
Class Insecta
Class Arachnida
What are the three Classes of Phylum Platyhelminthes?
Sub–Class Eucestoda
Sub–Class Cotyloda
Class Trematoda
What is the common name for Phylum Platyhelminthes?
Remember: Platys are flaty!
Flatworms
What is the common name for Sub–Class Eucestoda?
Remember: "Eu" means true, these are the true tapeworms
True tapeworms
What is the common name for Sub–Class Cotyloda?
Remember: Coty is a loda sh*t, cause its "pseudo" meaning fake
Pseudotapeworms
What is the common name for Class Trematoda?
Remember: It's a fluke I survived the tremor
Flukes
What are the five Orders of Phylum Nematoda?
Superfamily Trichuroidea
Order Oxyurida
Order Ascaridida
Order Strongylida
Order Spirurida
What is the common name of Order Ascaridida?
Ascarids
What is the common name for Order Oxyurida
Remember: You're gonna need "oxy"–clean for your undies if you got pinworms
Pinworms
True or false: Children cannot get pinworms from pets
True
What is the common name for Order Strongylida?
Strongyles
What are the two types of Strongyles?
Hookworms
Blood worms
What are the two common names of members of Order Spirurida?
Threadworms
Heartworms
What is the common name of Superfamily Trichuroidea?
Remember: I do tricks with my whip
Whipworms
Which Kingdom of veterinary parasitology significance consists of unicellular organisms?
Example: Giardia. It causes beaver fever in humans
Kingdom Protista