Study Guide: Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Democritus
First atomic theorist.
Atomos
Means 'uncuttable'.
Billiard Ball or Pool Ball Model
John Dalton's model of the atom.
Dalton's belief
All matter is made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms.
Plum Pudding or Blueberry Muffin Model
JJ Thomson's model of the atom.
Electron
Discovered by JJ Thomson.
Thomson's model description
Negative electrons are embedded in a sphere of positively charged particles.
The Cloud Model
Ernest Rutherford's model of the atom.
Proton and Nucleus
Discovered by Ernest Rutherford.
Rutherford's theory
Atoms are mostly empty space with a small dense positively charged nucleus.
Neutron
Discovered by James Chadwick.
Bohr's expansion
Electrons travel in orbits or shells.
Electron Cloud Model
Current model of the atom with a nucleus surrounded by randomly appearing/disappearing electrons.
Element
A substance that consists of only one kind of atom.
Atom
Smallest particle that an element may be divided into and still be the same substance.
Charge and location of the proton
Positive (+) in the nucleus.
Charge and location of the electron
Negative (-) in shells around nucleus/electron cloud.
Charge and location of the neutron
Neutral (0) in the nucleus.
Atomic Number
Number that tells you the number of protons in each box on the periodic table.
Atomic Mass
Number that tells you the number of protons and neutrons in each box on the periodic table.
Calculating number of neutrons
Atomic mass - Atomic number = number of neutrons.
Horizontal rows on the periodic table
Called periods.
Groups
The vertical columns on the periodic table.
Number of energy levels/shells
What the horizontal rows tell you about the elements in that row.
Number of valence electrons (e-)
What the vertical columns tell you about the elements in that column.
Valence electrons
Number of electrons in the outer shell (determine chemical properties).
Isotope
An atom which has more or less neutrons than it should.
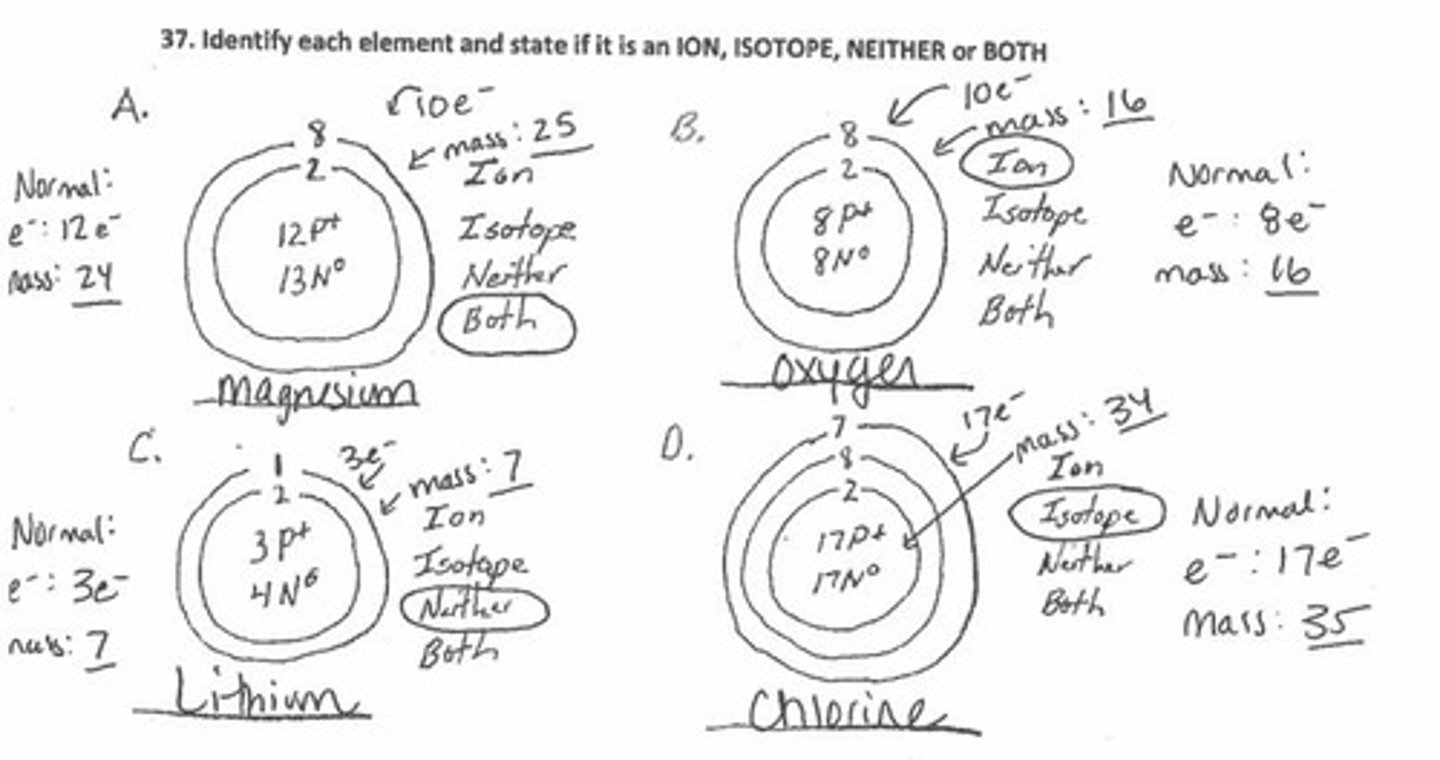
Ion
An atom which has more or less electrons than it should.
Protons
An element is defined by the number of protons it has.
Period
The term that describes the number of 'shells' an atom has.
Group
The term that describes the number of e- on the outer shell of an atom.
Fluorine
Period 2, Group 17.
Calcium
Period 4, Group 2.
Argon
Period 3, Group 18.
Hydrogen
Period 1, Group 1.
Antimony
Period 5, Group 15.
Atom
The largest unit in the list: atom, nucleus, protons, quark.
Nucleus
The second largest unit in the list: atom, nucleus, protons, quark.
Protons
The third largest unit in the list: atom, nucleus, protons, quark.
Quark
The smallest unit in the list: atom, nucleus, protons, quark.
Atomic Number (# of p+)
The number of protons in an atom.
Atomic Symbol
The symbol representing an element.
Name of Element
The name given to a specific element.
Atomic Mass (# of P+ and N0)
The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom.
Increasing atomic number
How the elements are arranged on the periodic table.
Dimitri Mendeleev
The 19th century chemist who created the periodic table.
7
The number of periods on the periodic table.
Energy levels
What the periods on the periodic table tell you about the elements in that row.
Transition Metals
The family of metals that includes Iron (Fe), Cobalt (Co), and Nickel (Ni), which are ferromagnetic.
Alkali metals
The family of metals that is the most reactive and can explode if exposed to water.
Metalloids
Which family has properties of both metals and nonmetals?
Alkali Metals
Which family can explode if exposed to water?
Alkaline Earth Metals
Which two metal families are not found freely in nature?
Noble Gases
Why do noble gases not form compounds readily?
Halogens
Which nonmetal family is as reactive as Alkali Metals?
Halogen
What does the term Halogen mean?
Non-metals
Which family is found in group 1, 14-16, and does not conduct electricity or heat well?
Non-metals
Which family easily forms acids?
Rare Earth Metals
Which family is almost entirely radioactive?
Ion+
What does an atom become when it loses one or more electrons?
Ion-
What does an atom become when it gains one or more electrons?
Isotope
What is an atom that has more or less neutrons than on the periodic table?
Other Metals
Which family when it bonds with other elements creates a light metal or alloy?
Metals vs. Nonmetals
Compare AND Contrast the three differences between metals and nonmetals.
Energy Transmission
Metals: Conductors of heat and electricity. Non-metals: Insulators.
Flexibility
Metals are malleable and ductile, non-metals are brittle.
Luster
Metals have luster (shiny), non-metals are dull.
Fraction/Percentage of Total Elements
Metals 75% (3/4) of periodic table, non-metals 25% (1/4).
Metalloid (Step Line)
What separates metals from nonmetals on the periodic table?
Metalloids
Why are Metalloids called semiconductors? List an example.
Metals
If you were holding the periodic table, where would you look to find the metals?
Nonmetals
Where are all the nonmetals located on the periodic table?
Stable Atom
An atom is stable when its outer shell is full with 2 or 8 electrons.
Noble Gas Family
Why is helium part of the Noble Gas Family?
Ionic Bond
What type of bond forms between a metal and nonmetal?
Covalent Bond
What type of bond forms between two nonmetals?
Polyatomic Bond
What type of bond forms between one metal & at least two different nonmetals?
Ionic Bond Charges
In an ionic bond what are the charges of the metal and nonmetal?