The Escherichia Coli Genome
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture Exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Escherichia Coli (E. Coli)
gram negative bacillus shaped bacterium that is commonly found in the lower intestines of warm-blooded organisms
- 4.64 Mbp
- 4300 genes
how many Mbp is the E. Coli genome? how many genes?
plasmid
small circular double stranded DNA molecules that replicate independently of the host chromosome; provides antibiotic resistance
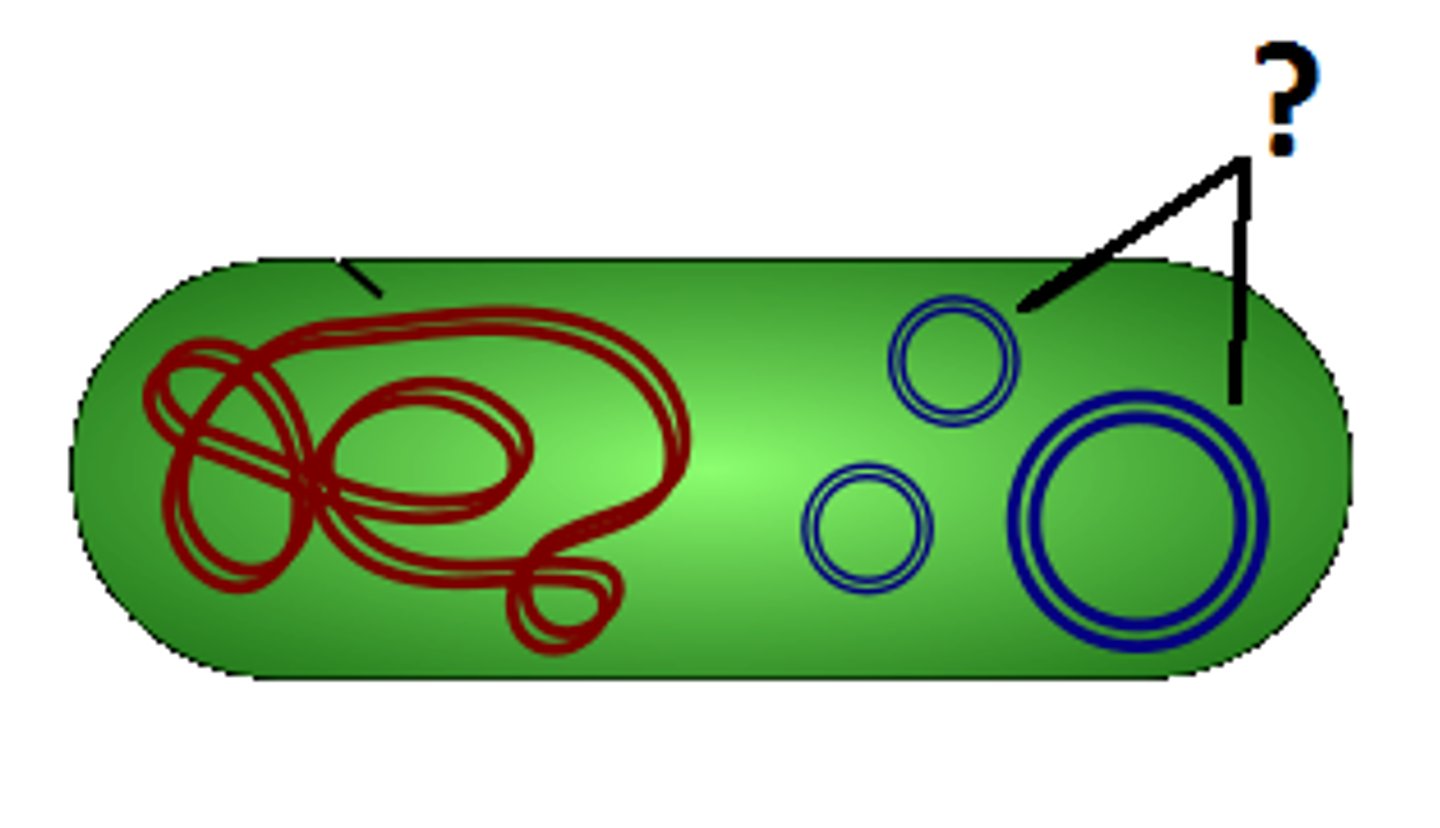
conjugation
how are plasmids often transferred between bacteria?
tra gene - builds the sex pilus (thin protein tube connecting the 2 bacteria) + contains other necessary materials
what gene controls the transfer of plasmids? how?
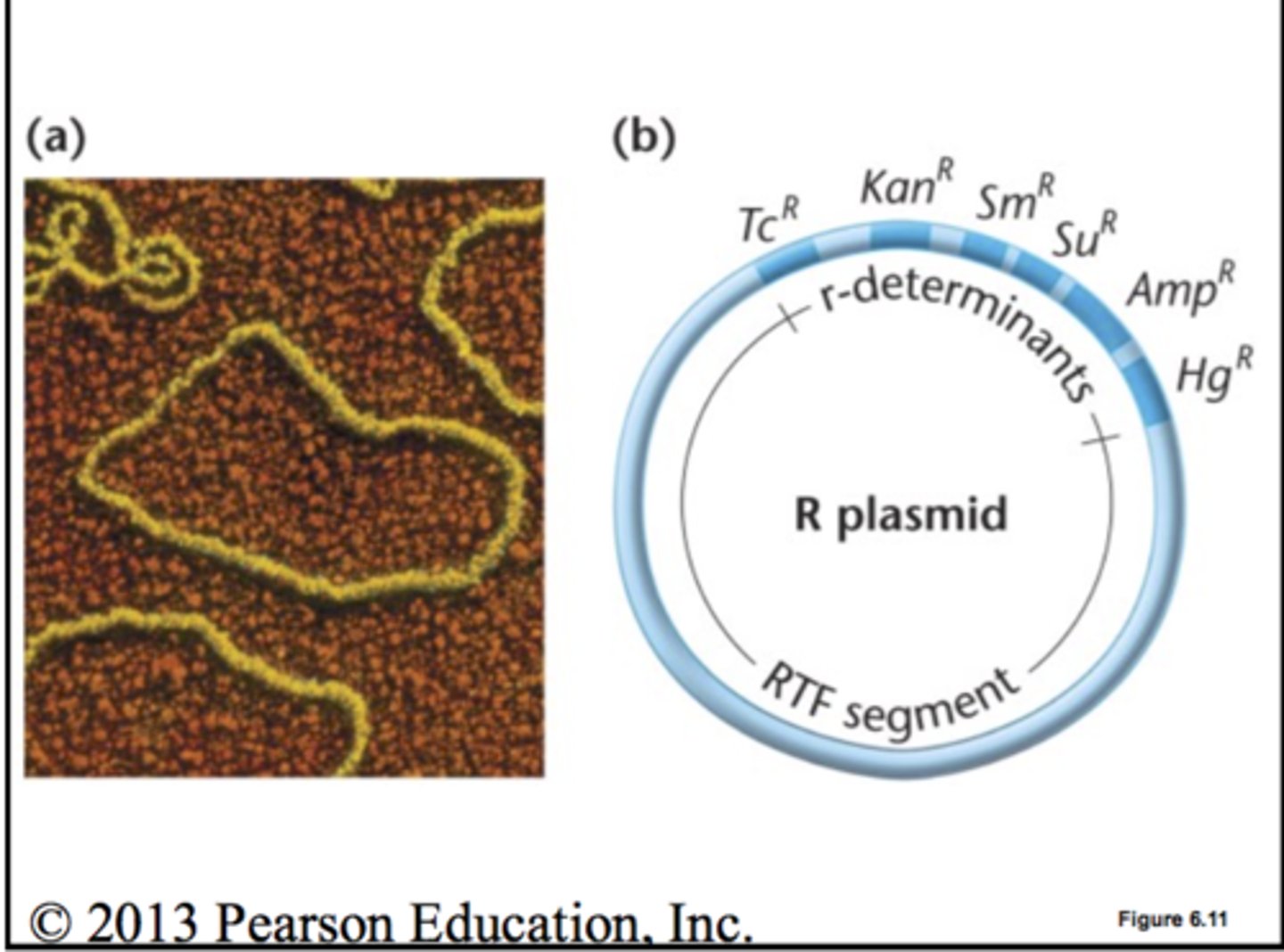
-contains genes that encode resistance to antibiotics
-easily transfer antibiotic resistance to other bacteria
what are 2 characteristics of R-plasmids?
-27F (binds at beginning)
-1492R (binds at the end)
both are used to amplify the 16S gene
what primers are typically used in PCR? why are these primers used?
it is present in all bacteria with regions specific to different bacteria, making the type more identifiable
what is the benefit of amplifying the 16S gene?
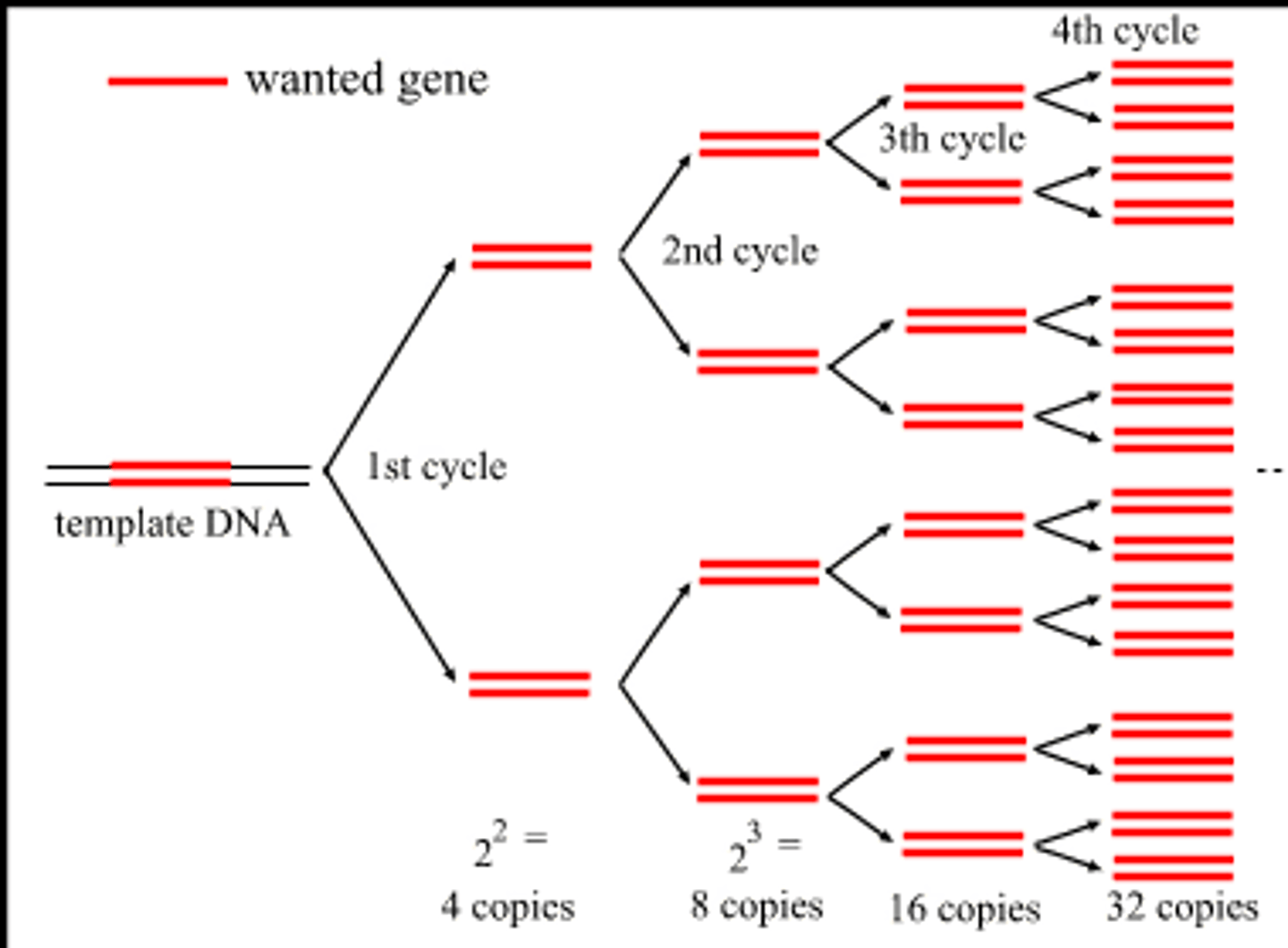
1. denaturation (94-96°C) 2 min
2. annealing (40-70°C) 30 sec
3. elongation (72°C) 1.5 min
repeated 34 times
what are the 3 steps to PCR (+ temp. and time)? how many times is this process repeated?
-DNA template
-dNTP
-polymerase
-buffer
-primers
-water
-Taq polymerase
what is required for PCR? (7)
Kary Mullis
applications:
-phylogenetic studies
-identification of microbes
-forensics
who invented PCR? what are its 3 applications?
agarose gel electrophoresis
technique used to visualize and separate DNA and PCR products
an electric current moves charged DNA molecules through the gel matrix; small m-c move faster (will appear farther down)
how does agarose gel electrophoresis work?
agarose
polysaccharide extracted from seaweed that dissolves in water and forms a gel when cooled
