Introduction to Microbiology
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
micro; bios; logus
microbiology is derived from the word ?
Microbiology
Study of very small living organisms
1. Occurrences of microscopic forms of life in disease, immunology, and production of nature vaccines
2. Reproduction & physiology
3. Participation in the processes of nature
4. Harmful & harmless effects in man
5. Significance in science & industry
5 CONCERNS OF MICROBIOLOGY
Microorganisms
Indigenous flora or microbiota
Microorganisms
• Pathogens
• opportunists
1. Bacteriology
2. Phycology
3. Mycology
4. Protozoology
5. Virology
5 SCOPES OF MICROBIOLOGY
General Microbiology
Study of classification of microorganisms how they function
General Microbiology
Encompasses all areas of microbiology
Agricultural Microbiology
Includes the studies of:
- The beneficial and harmful roles of microbes in soil formation & fertility
- In C, N, P & S cycles
- In diseases of plants
- In digestive processes of cows and other ruminants
- In the production of crops and foods
Agricultural Microbiology
• Food micro
• Dairy micro
Biotechnology
• a.k.a. Industrial Microbiology
• Use of microorganisms in industry
Environmental Microbiology & Bioremediation
• a.k.a. Microbial Ecology
• Environment
Environmental Microbiology & Bioremediation
Encompasses the areas of soil, air, water, sewage, food, and dairy microbiology; cycling of elements by microbial, environmental and geochemical processes
Medical & Clinical Microbiology
Study of pathogens, the diseases they cause, and the body’s defenses against them
Medical & Clinical Microbiology
Concerned with epidemiology, transmission of pathogens, dse-prevention measures, aseptic techniques, treatment of infectious disease, immunology, and production of vaccines
Microbial Genetics & Genetic Engineering
Study of microbial DNA, chromosomes, plasmids and genes
Microbial Genetics & Genetic Engineering
Involves the insertion of foreign genes to microorganisms
Microbial Physiology
Contributed to the understanding of the structure & functions of microbial cells
Paleomicrobiology
Involves the study of ancient microbes
Parasitology
Study of parasites
Sanitary Microbiology
Includes processing and disposal of garbage and sewage wastes; purification and processing of water supplies
Veterinary Microbiology
Concern with the spread and control of infectious diseases among animals
Veterinary Microbiology
Major importance:
- Production of food from livestock
- Raising of other agriculturally important animals
- Care of pets
- Transmission of diseases from animals to humans
Girolamo Fracastorius (1546)
Italian physician
Girolamo Fracastorius (1546)
Living germs- agents of communicable diseases
Girolamo Fracastorius (1546)
Transmitted by direct contact with humans & animals & indirectly with objects
Living germs
agents of communicable diseases
Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723)
“Father of Ancient Microbiology”
Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723)
Discovered the microscope
Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723)
- 1st to describe the RBC
- See protozoa
- Classified bacteria into shapes
John Needham
The greatest supporter of spontaneous generation
Francisco Redi (1660)
Demonstrated that animals do not arise spontaneously from dead organic matter
Experiments disproving spontaneous generation

Abbe Spallanzani (1770)
Demonstrated that heated broth, in the absence of air, did not support spontaneous generation
Schroder and von Dusch (1854)
Demonstrated that broth heated in the presence of filtered air did not support spontaneous generation
Rudolf Virchow (1858)
Proposed the theory of biogenesis
John Tyndall (1860)
Demonstrated that open tubes of broth remained free of bacteria if air was free of dust
John Tyndall (1860)
Developed tyndallization to destroy spores
John Tyndall (1860)
Proved that dust carries germs
Louis Pasteur (1822-1895)
“Father of Modern Microbiology”
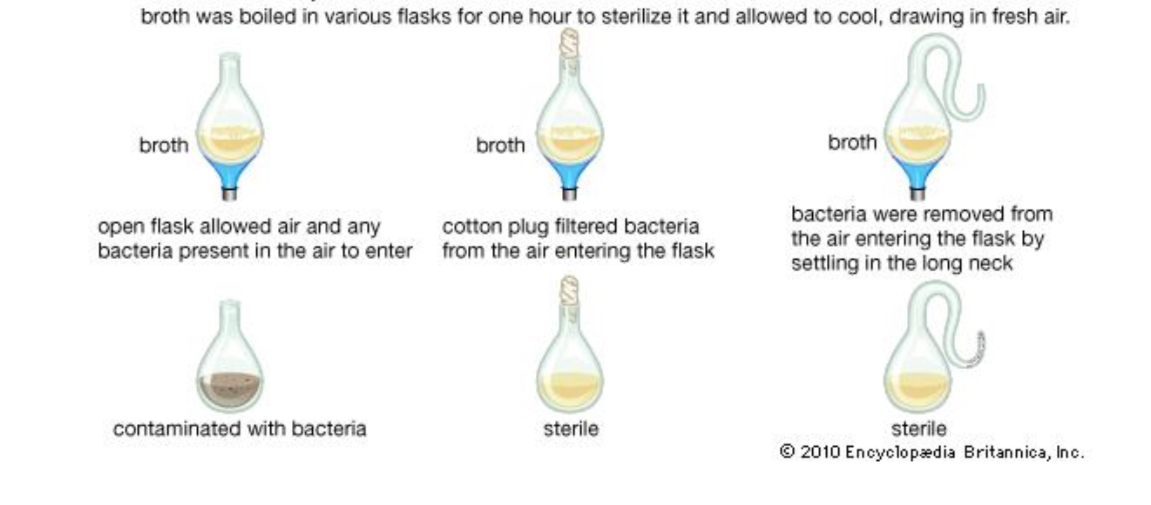
Louis Pasteur (1861)
disproved the theory of spontaneous generation
• Aerobes & anaerobes
Louis Pasteur (1858)
contributed to the understanding of fermentation
Louis Pasteur (1866)
• developed technique for selective destruction of microorganisms
• study of bacterial contamination of wine
Louis Pasteur (1868)
study of diseases of silkworms
—Contribute to Germ theory of disease
—Changes in hospital practices to minimize the spread of disease by pathogens
Louis Pasteur (1881)
attenuated vaccines of anthrax & chicken cholera; swine erysipelas
Louis Pasteur (1885)
immunization against rabies
Louis Pasteur 1859 experiment
Joseph Lister
Concept of aseptic technique
Robert Koch
Developed postulates for proving the cause of infectious diseases; & pure culture concept
Robert Koch (1876)
observed anthrax bacilli
Robert Koch (1882)
• developed solid culture media
• discovered Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Robert Koch
Koch Postulates