physics paper 1
1/182
Earn XP
Description and Tags
topics 1-4 : energy, electricity, particle model of matter, atomic structure
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
183 Terms
John Dalton description of atom (3)

(1804)
-solid neutral ball
-atoms of one element are all alike but differ from atoms of other elements
-atoms cannot be subdivided,created or destroyed
JJ Thompson description of atom
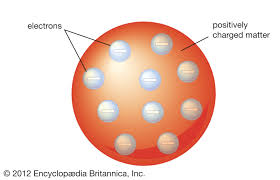
(1904)
-solid neutral ball of positive charge with electrons stuffed in it
-called the plum pudding model
discovered the electron in 1897
Ernest Rutherford description of atom
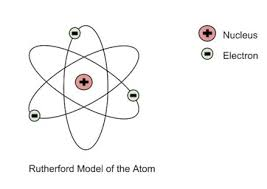
(1911)
mostly empty
nucleus is very small - concentrated positive mass
Ernest Rutherfords Alpha particle experiment
ER tested JJs Plum Pudding model in 1908.
In the experiment Alpha particles were fired at a thin sheet of gold foil.
Some alpha particles went straight through-meaning the atom was mostly empty.
Some of the Alpha particles were deflected- meaning there’s a positive mass in the center of the atom- ER called the nucleus
order of being discovered and who
proton
neutron
electron
electron - jj thompson 1897
proton - Ernest Rutherford 1917
neutron - James Chadwick 1932
similarities of plum pudding model and rutherfords model (2)
-both are neutral
-both have electrons
differences of plum pudding model and rutherfords model
-JJs model is solid whereas Rutherfords is mostly empty
-JJs doesn’t have a nucleus
isotope
an atom with the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons
radioisotope
an isotope that’s unstable and will emit radioactive decay to become stable
alpha decay
what it’s made of,
charge, how big,
mass,
range in air,
stopped by,
how penetrating,
how ionising
made up of two protons and two neutrons- same as helium nucleus
charge= 2+,
relatively large,
mass= 4,
range in air=5cm,
stopped by= paper,
low penetrating,
high ionising
beta decay
what it’s made of,
charge,
how big,
mass, range in air,
stopped by,
how penetrating,
how ionising
made up of an electron
charge=-1,
mass=1/2000,
range in air=1m,
stopped by=mms aluminium,
medium penetrating,
medium ionising
gamma decay
what it’s made of,
charge,
how big,
mass,
range in air,
stopped by,
how penetrating,
how ionising
are electromagnetic waves
charge=0,
mass=0,
range in air= >km,
stopped by=thick lead,
high penetrating,
low ionising
alpha decay question
14/6 C
14/6 C → 10/4 Be + 4/2 alpha particle
beta decay question
14/6 C
14/6 C→ 14/7N+ beta particle (0/-1 e’)
gamma decay question
14/6 C
14/6 C→ 14/6 C +Gamma ray
activity of a source
number of nuclei that decay per second measured in Becquerel (Bq)
count rate of a source
amount of radiation detected per second by a machien called a geiger-mullertube
ion
an atom with either more electrons than protons or the other way round
half life
amount of time it takes for half the radioactive nuclei to decay
contaminated
something that has absorbed radioactive material
irradiated
something that has absorbed some ionising radiation
activity equation
number of decays emitted/time(s)
ionising radiation
radiation that has enough energy to remove electrons from an atom.
background radiation
the radiation that is present all around the environment
fission
when large unstable nuclei will split into 2 smaller stable nuclei
fusion
where two smaller nuclei come together to form one larger nuclei-this releases lots of energy
electric charge
property of materials or particles (just like mass or size)
what is current
-current = amount of coloumbs that pass a point in 1 sec
-metals contain delocalised electrons which move randomly
-when a battery/power source is attached to a metal wire in a complete circuit the delocalised electrons move from neg to pos
-this flow of electrons are the current
-charge is measured in coulombs - 1 Coulomb = 6.24 × 10^8 electrons
charge flow equation=
charge flow (Q)= Current (I) x Time (t)
Q in coulombs (C), I in amps (A), t in secs In equation triangle (Q) at top
series circuit
current?
Voltage?
where all components are in the same loop
-current is the same everywhere
-voltage shared between the components
parrallel circuit
where components are in seperate loops
-current divided between branches or split
-voltage is shared between the branches
what do electrical circuits transfer
energy between stores
what do electrons (charged particles) carry
energy around a circuit
potential difference
difference in energy between 2 points- measured with voltmeter
1 volt =
1 joule of energy per coulomb of charge
potential difference equation
potential difference (V)= Energy (E)/ Charge(Q)
V measured in volts, E measured in Joules, Q measured in coulombs
in equations triangle E on top
resistance
how difficult its for current to flow through a compound
measured in Ohms
how is resistance caused
delocalised electrons coliding with metal ions
what type of wire has a high resistance
low resistance
long and thin
short and thick
potential difference resistance equation
potential difference (V)=Current(I) X Resistance(R)
V measured in volts, I measured in amps, R measured in Ohms
in equations triangle V on top
ohmic resistor
resistor following ohms law (resistance doesnt change with temp)
so potential difference and current are directionally proportional to each other
what type of gradient has a low/ high resistance
steep gradient- low resistance
shalow gradient-high resistance
power,current and resistance triangle
power on top
power, pot dif and current triangle
power on top
difference between alternating and direct current
(direction electrons move,safer,types of electric)
AC’s electrons move in alternating directions whereas DC’s cureent moves in 1 direction
DC is safer
AC is a type of mains electric
frequency and pot. dif. of mains electric
50Hz (changes direction 50x per second)
230V
why can you get an electric shock if you touch an object that becomes live?
as an electric current passes through you and to the earth and the pot.dif between you,earth and charged object completes the circuit
how does the earth wire prevent you from getting an electric shock
earth wire has low resistance route for the current to reach earth. resistance route is lower than traveling through your body the current passes through the earth wire not you
what does each wire and fuse do in a UK plug
green+ yellow stripes (top)
-is the earth wire
-is a safety feature-stops electric shocks
blue wire (left)
-is the neutral wire
-completes the circuit
is at 0 V
red wire (right)
-is the live wire
-carries the current to the device
fuse
-connects to red wire
-safety feature-breakes when currents too high
explain each component of the national grid
power station→(electricity leaves)→step-up transformer(pot.dif increases) transmission cables (low current means less energy is lost from heat) →step-down transformer (pot.dif decreased to 230V)→consumer
what would a graph of light intensity against resistance look like
why?
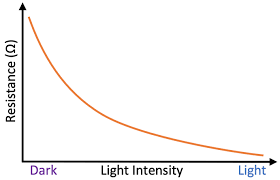
resistance on y axis, light intensity on x axis- line of best fit would be diagnoal left to right with slight drop
as light intensity increases current increases, because there is less resistance
how should you structure a 6 marker when describing an experimant
equiptment
set up
readings
data analysis (only 6 markers)
what is power
when thinking about circuits what is it
whats it measured in
the rate of energy transfer
when thinking about circuits power is the rate of electrical transfer
measured in watts (W)
what does conservation of energy tell us
that energy can never be created or destroyed
whats the potential difference between the neutrala and live wire
230V
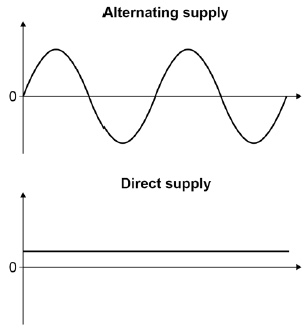
give 2 differences between alternating supply and direct supply
alternating supply doesnt have a consistant voltage
alternating supply changes the direction of its current
resistance
everything that resists or opposes the flow of electrons in a circuit
In 'conventional current', we say that the electrons flow from:
Positive terminal ➔ negative terminal
potential difference
the force driving the flow of electrons around a circuit
current
a measure of the flow of electrons around a circuit
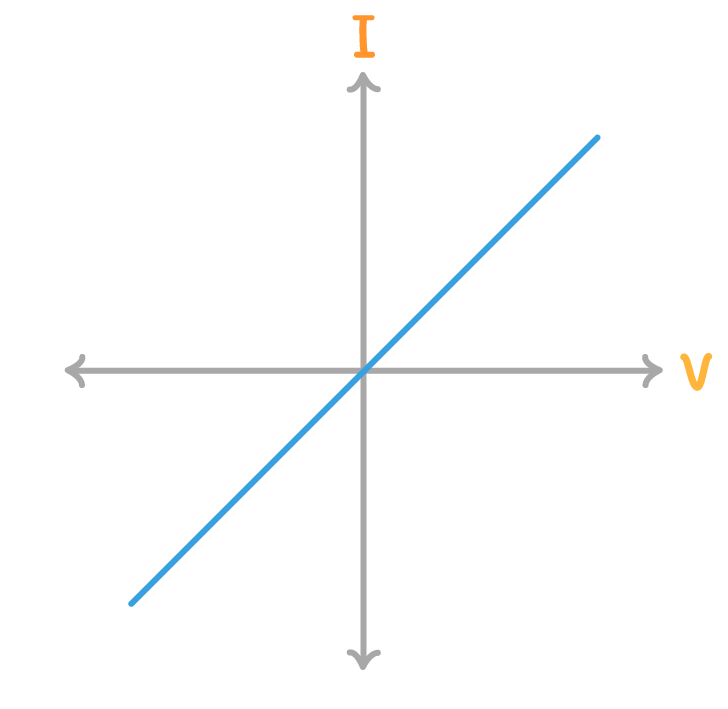
whats this diagram is a current / voltage graph for
fixed resistor
For wires and resistors, increasing the temperature will __________ the resistance.
increase
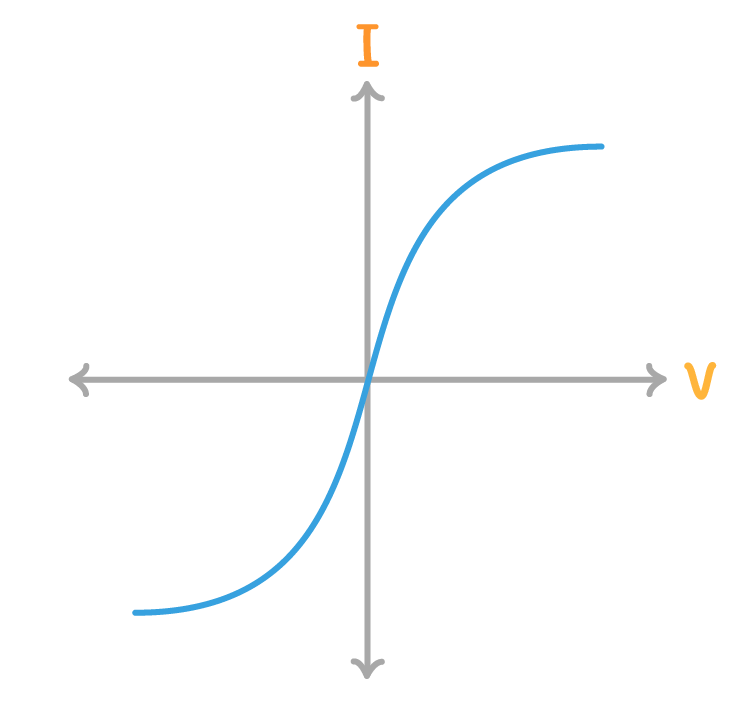
The above diagram is a current / voltage graph for a:
filament lamp
diodes
allow the current to flow in 1 direction
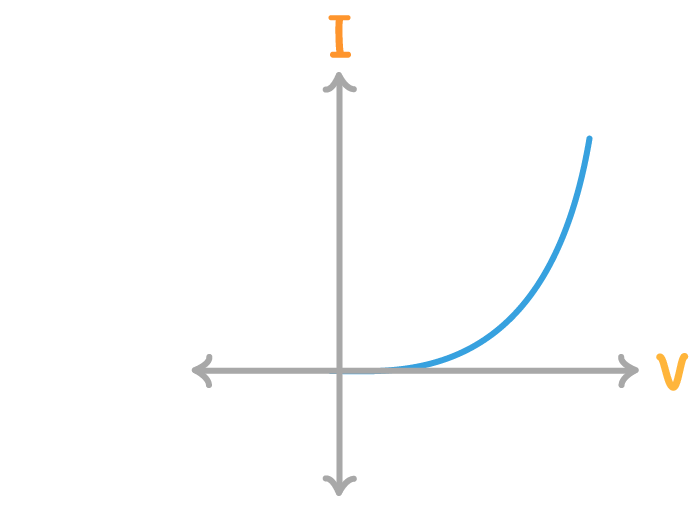
The above diagram is a current / voltage graph for a:
diode
charge
a measure of the total current that flowed within a period of time

diode

fuse
light dependant resistor
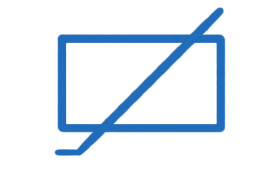
thermistor

variable resistor

fixed resitor
The resistance of a thermistor decreases when the temperature _______.
increases
The resistance of a light dependent resistor decreases when the light intensity _______.
increases
In a series circuit, the potential difference of the battery is:
Shared across all of the components
In a series circuit, the total resistance is ________ the sum of the individual resistances of each component.
equal to
In a series circuit, components with a greater resistance will always have a ________ share of the voltage.
greater
what is the current between all paralell loops
shared
The of the current in each loop is equal to the total current.
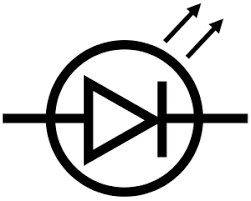
what is it and what does it do
light emitting diode (LED)
emits light when current passes through
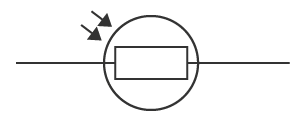
what is thais and what does it do
light dependant resistor (LDR)
detects light levels

what is this and what does it do
fuse
breaks a circuit if theres a fault and too much current to flow- makes it safe
Electric fields can be shown with electric field lines.
Field lines always point from:
pos to neg charge
what is a thermistor
a resistor whos resistance decreases when temperature increases
whats a light dependant resistor (LDR)
a resistor whos resistance decreases when light intensity increases
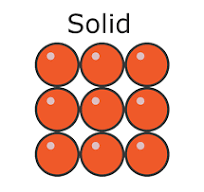
solids
distance between particles
bond between particles
motion of particles
particle diagram
very close
very strong
vivrate
liquids
distance between particles
bond between particles
motion of particles
particke diagram
very close
strong
slide past slowly
gases
distance between particles
bond between particles
motion of particles
particle diagram
far apart
none
very fast, random directions
movement of partciles
what particles have the same and which one js different
simmilar
liquid and gases- can move from place to place
different
soldi- only vibrate
closeness of particles
what particles have the same and which one is diff
simmilar
solids+liquids-as particles are very close
differnet
gasses-particles are very far apart
bonds between particles
what particles have the same and which one is diff
simmilar
solids+liquids-particles are very strong
different
gasses-particles have no bonds holding them together
explain why can gasses be compressed but liquids and solids can’t (5)
-solids liquid particles are close together
-when compressing a solid or a liquid there is no space
-gas particles are far apart
-when compressing a gas there is space to be compressed together
-you cannot compress liquids or solids
explain why gases fill their containers but their liquids and solids cannot have a fixed volume (5)
-a gas bond between particles is none
-so a gas spreads out to fill the container
-a solid or a liquid’s bond between particles is strong
-so when a solid or liquid is in a container the particles stay together
-liquids and solids don’t fill their container/ change their volume
whats a solid turning into a liquid called
whats a liquid turning into a gas called
whats a solid turning into a gas called
melting
boiling
sublimation
whats a gas turning into a liquid called
whats a liquid turning into a solid called
whats a gas turning into a solid called
condensing
freezing
deposition
true or false
temperature describes the average kinetic energy movement of the particles in a substance
True
why will the particles move slower in a cup of tea left on a table in a cold room
particles average temp will decrease
so the average kinetic energy decrease
so the particles move slower
why will the particles vibrate faster in an ice cube left out in the sun on a hot summers day
temp of the ice cube will increase
so the kinetic energy will increase
therefore the particles will move faster
true or false
when bonds between particles are broken the particles loose potential energy
false
bonds between particles are broken the particles potential energy
so
bonds between are made the particles loose potential energy
what state of matter do particles have
thw most potential energy
the least potential energy
gas
solid
does the substance gain or loose potential energy when
a substance melts/boils
a substance freezes/condenses
bonds are broken so substance gains potential energy
bonds are made so the substance looses potential energy