Chem 12 - 2.1 Reversibility of Reactions
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
by alternately heating and cooling the NO2 and N2O4 tubes...
we are altering the relative concentrations of NO2 and N2O4
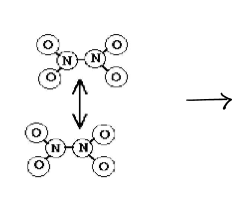
if we were to put some N2O4 in a flask...
the N2O4 molecules would collide with each other and some of them would break apart to form NO2
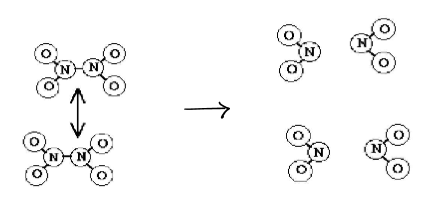
Once the collision of N2O4 to NO2 happens for while…
there is a build up of NO2 molecules in the same flask
once in a while, 2 NO2 molecules will collide with each other and join to forma molecules
reverse reaction!
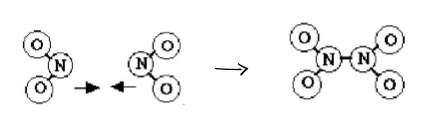
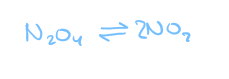
as long as there is N2O4 present…
the forward reaction will keep on happening
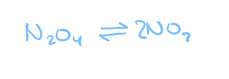
as long as there is NO2 present…
the reverse reaction will keep on happening
At some point in time, a molecule of N2O4 may be breaking up, and at the same time 2 molecules of NO2 might be joining to form another molecule of N2O4, therefore…
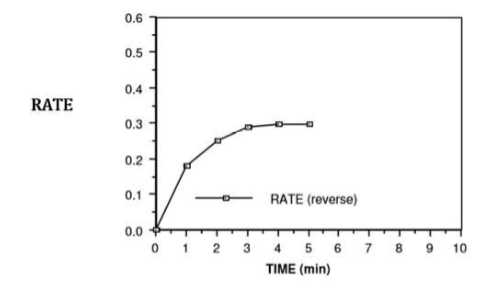
in any reversible reaction, the forward reaction and the reverse reaction are going at the same time
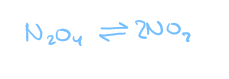
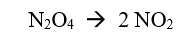
rate of forward reaction
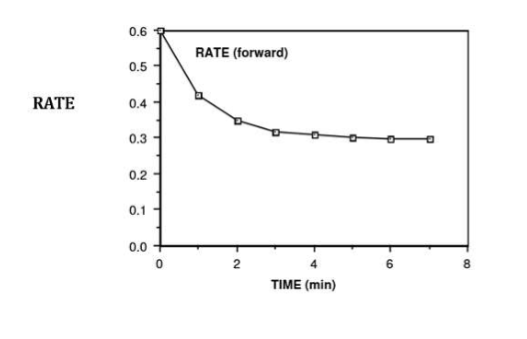
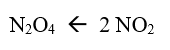
rate of reverse reaction
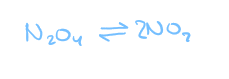
rate of both forward and reverse reaction
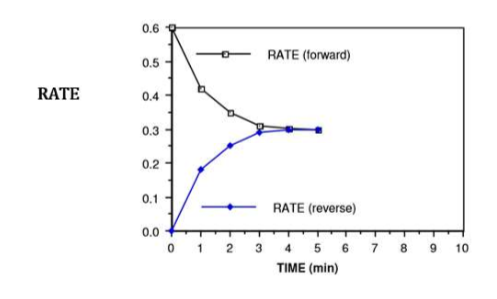
what is happening at t = 4 min
rate of forward reaction = rate of reverse reaction
NO2 is being used up at the same time that it is being formed
because the reverse rate is equal to the forward rate, the N2O4 is being formed at the same rate that it is being used up
therefore, the [NO2] and the [N2O4] is no longer changing
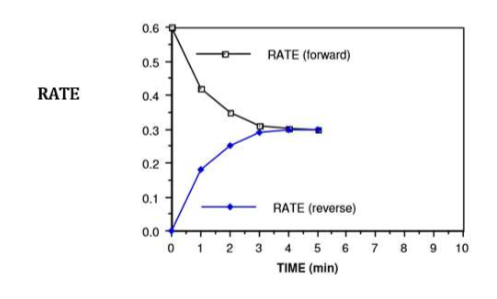
from 4.0 minutes onwards…
the system (container of N2O4 and NO2) is said to be at equilibrium
we have reached a state of dynamic equilibrium
the system for equilibrium must be…
closed
if not closed, other substances might interfere with the reaction or react themselves
changing the temperature can…
alter the rates of the reactions at equilibrium
therefore, for a system to be at equilibrium, the temp must remain constant
the forward and the reverse reaction continue to take place, but…
their rates are equal so there are no changes in concentrations of reactants or products.
the reaction has not stopped
all observable properties are…
constant
(observable properties; concentrations of all reactants and products, total pressure, colour, temp, etc. of the system)
if no changes were made in the conditions and nothing is added or taken away…
a system at equilibrium would remain that way forever, with the forward and reverse reactions continuing to occur, but with no observable changes happening