Osteoporosis Pre-class
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Recommend appropriate calcium and vitamin D supplementation: How much elemental calcium in calcium carbonate?
40%
Recommend appropriate calcium and vitamin D supplementation: How much elemental calcium in calcium citrate?
21%
Recommend appropriate calcium and vitamin D supplementation: Based on NOF recommendations, how much calcium is recommended for women ≥ 51 years old?
1200 mg/d
Recommend appropriate calcium and vitamin D supplementation: Based on NOF recommendations, how much calcium is recommended for men 50 - 70 years old?
1000 mg/d
Recommend appropriate calcium and vitamin D supplementation: Based on NOF recommendations, how much calcium is recommended for men ≥ 71 years old?
1200 mg/d
Recommend appropriate calcium and vitamin D supplementation: Based on the National Osteoporosis Foundation, how much vitamin D is recommended for adults age ≥ 50 years?
800 - 1000 IU (1000 IU = 25 mcg)
Recommend appropriate calcium and vitamin D supplementation: Based on the American Geriatric Society, what is the minimum vitamin D supplementation (w/ Ca) for adults to reduce the risk of fractures and falls
at least 1,000 IU (w/ Ca)
Recommend appropriate calcium and vitamin D supplementation: Based on the Endocrine Society, what is the amount of vitamin D supplementation for adults ≥ 65 years for the prevention of falls and fractures?
800 IU/d
Recommend appropriate calcium and vitamin D supplementation: What is the goal 25(OH) vitamin D level?
30-50 ng/mL or ≥ 30 ng/mL
Recommend appropriate calcium and vitamin D supplementation: What is the range of 25(OH) vitamin D is treatment indicated?
25(OH)-vitamin D <20 ng/mL
Recommend appropriate calcium and vitamin D supplementation: What is the frequency of administering 50,000 IU vitamin D (D2 or D3) for repletion?
once a week
Recommend appropriate calcium and vitamin D supplementation: What is the maintenance amount of Vitamin D supplementation?
1500-2000 IU daily
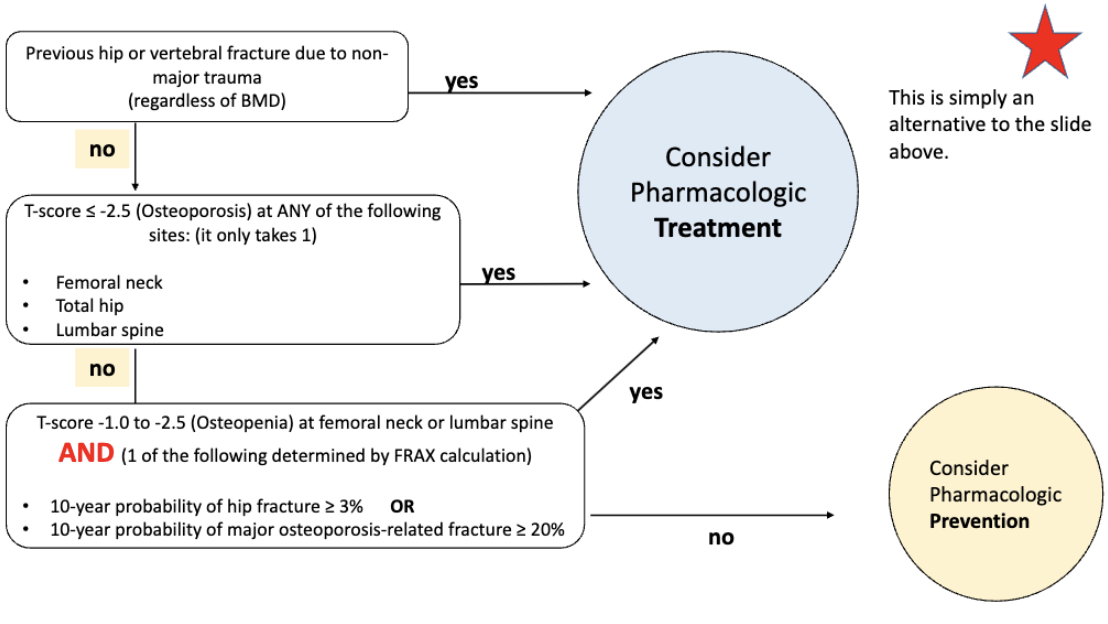
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
Which medications are used for treatment?
bisphosphonates
raloxifene
calcitonin
PTH analog
denosumab
romosozumab
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
Which medications are used for prevention?
bisphosphonates
raloxifene
estrogen
estrogen/bazedoxifene
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
Which medications are used for BOTH treatment prevention?
bisphosphonates
raloxifene
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
Which medications can be used in men?
bisphosphonates
PTH analogs (teriparatide)
denosumab
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
When taking Bisphosphonates, what should be told to the patient (aka when they are about to take the medication)?
Take in the morning, on an empty stomach with 6-8 oz of plain water
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
After a patient has taken their dose of bisphosphonate, the patient should follow what instructions?
No food/beverage for ≥ 30 minutes, Remain sitting/standing for ≥ 30 minutes
Why should patients follow the strict counseling for bisphosphonate?
to improve bioavailability and reduce risk of esophageal ulceration
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
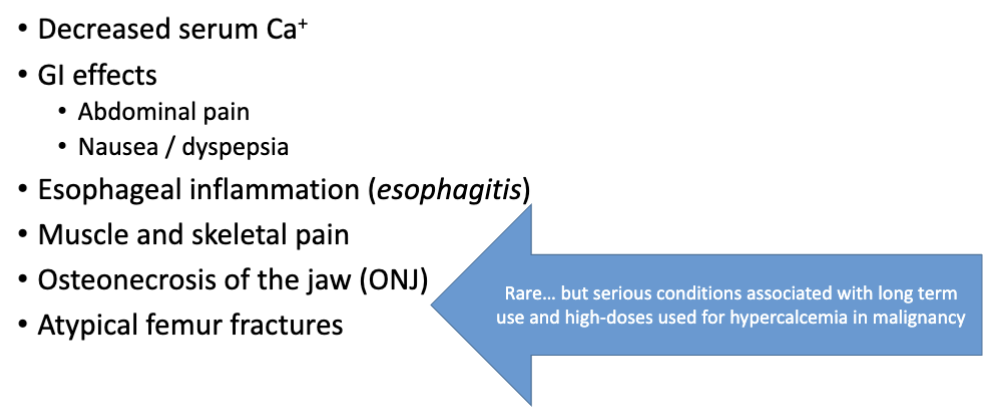
What are the adverse effects with bisphosphonate?
Decreased serum Ca+
GI effects (Abdominal pain, Nausea / dyspepsia)
Esophageal inflammation (esophagitis)
Muscle and skeletal pain
Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ)
Atypical femur fractures
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
What is the RARE adverse effect with bisphosphonate?
Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) (associated with long term use and high-doses used for hypercalcemia in malignancy)
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
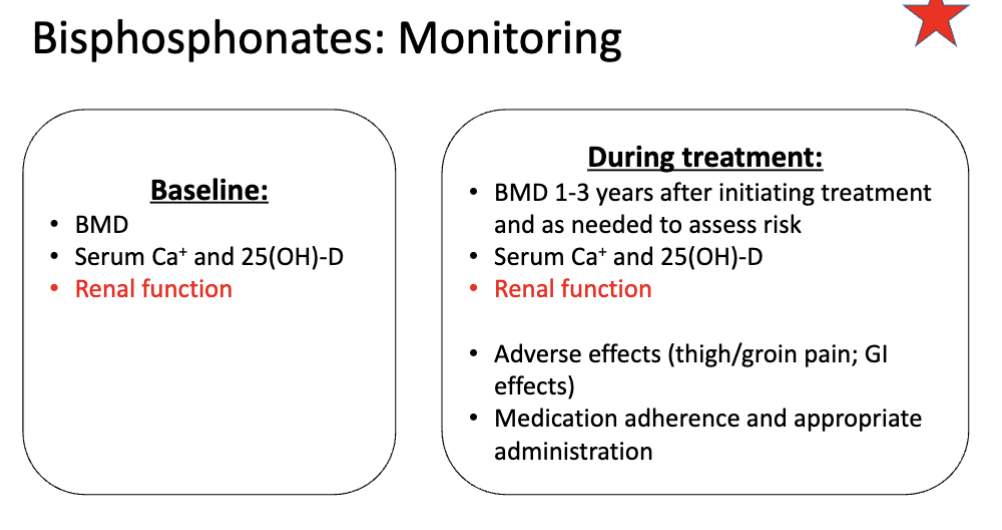
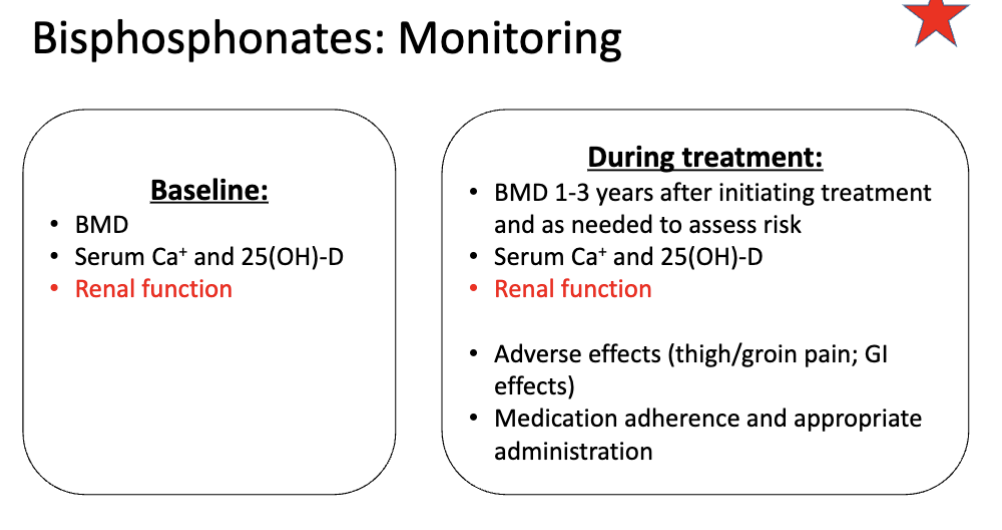
What is the BASELINE monitoring for bisphosphonate?
BMD (bone mineral density)
Serum Ca+ and 25(OH)-D
Renal function (IMPORTANT)
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
What is the monitoring for bisphosphonate DURING treatment?
BMD 1-3 years after initiating treatment then as needed
Serum Ca+ and 25(OH)-D
Renal function (IMPORTANT)
Adverse effects (thigh/groin pain; GI effects)
Medication adherence and appropriate administration (duh)
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
Why is checking renal function both a baseline and continuous monitoring parameter for bisphosphonates?
Not recommended for use below certain CrCl thresholds:
CrCl < 30 → d/c use of risedronate, ibandronate
CrCl < 35 → d/c use of alendronate, zoledronic acid
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
When should denosumab (Prolia) be used?
postmenopausal W + M
Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis
tx bone loss in W/M receiving meds for breast/prostate cancer
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
How is Prolia administered?
q 6 months SQ (HCP needed, only ARM, THIGH, ABDOMEN)
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
What are denosumab’s adverse effects?
HYPOcalcemia
MUST correct b4 tx
skin infections (cellulitis) + skin rash
musculoskeletal pain
flatulence, constipation
ONJ (more common when tx-ing malignant cancer)
Atypical femur fractures
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
What is an important lab to take when monitoring a pt’s initiation with Prolia?
Serum Ca2+ (BASELINE + w/in first 14 days of tx)
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
What are important counseling points with Prolia?
inform PCP of new hip/thigh/groin pain or skin rxns
rapid bone loss once denosumab d/c
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
When would raloxifene (Evista) be considered for use?
Treatment and prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
decr risk for breast cancer (post-menopause)
req 5 year tx duration
NOTE: formulation = oral pill (good for pts who don’t want injections)
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
What is the BBW w/ raloxifene (Evista)?
incr risk of DVT + PE
do NOT use in W w/ hx of VTE
incr risk of death from stroke in W w/ CVD or at risk
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
What are the ADRs w/ raloxifene (Evista)?
hot flashes
PE
leg cramp/muscle spasm
flu-like syndrome/arthralgias
incr TGs in W w/ elevated TG
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
What are important monitoring parameters w/ raloxifene (Evista)?
mammogram / breast exam b4/during tx
lipids
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
When would teriparatide (Forteo) be considered?
post-menopause osteoporosis
MEN
glucocorticoid induced
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
When would abaloparatide (Tymlos) be considered?
post-menopause osteoporosis
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
What is a potential risk with PTH analogs?
risk of osteosarcoma → limit tx use to 18-24 months
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
What are ADEs with PTH analogs teriparatide and abaloparatide?
HYPERcalcemia (4-6 hours after injection)
orthostatic hypotension
N/V, dyspepsia
dizzi, headache
arthralgias, leg cramp, weakness
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
What is an important counseling point with PTH analogs?
sit for first dose to avoid orthostatic hypotension
rotate injection points
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
Calcitonin (Miacalcin) can come in a nasal solution and IM/SQ injection, what is the amount of units delivered in both formulations?
Nasal sln: 200 units/spray
IM/SQ: 100 units/day
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
What are ADE w/ calcitonin?
allergic + hypersensitivity rxns (anaphylaxis)
HYPOcalcemia
nasal irritation / injection site rx
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
When is romosozumab-aqqg (Evenity) considered?
postmenopausal osteoporosis
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
How is romosozumab-aqqg (Evenity) administered?
q month for 12 months by HCP w/ 2 injections per visit
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
What is the BBW w/ romosozumab-aqqg (Evenity)?
may increase risk of MI, stroke, CV death
do not use in pts who have had an MI/stroke w/in preceding year
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
What is an ADE with Evenity that was significant when compared with a placebo?
injection site reactions
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
When is estrogen ± progestin considered? (estrogen-only = Premarin) (E + P = Combipatch)
prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
For W who have not had a hysterectomy, what do they require?
progestin to protect uterine lining
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
What are the BBWs w/ estrogen?
do not use for prevention of CV dz (estrogen incr risk of clots)
incr risk of breast cancer (E+ P)
do not use for prevention of dementia
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
What are ADEs w/ estrogen?
Headache
abdominal pain
weight gain, edema
increase TGs + HDL-C , decr LDL-C
rapid bone loss when d/c
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
What are important monitoring / counseling w/ estrogen ± progestin?
M: risk for breast cancer + CVD b4/during tx
C: W w/ uterus get BOTH E + P
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
When should conjugated estrogens/bazedoxifene (Duavee) considered?
only W W/ UTERUS
prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
Compare pharmacotherapy options for treating osteoporosis
• Use (prevention or treatment of osteoporosis)
• Adverse effects
• Contraindications / Black Box Warnings
• Appropriate administration
What are the BBWs w/ estrogens/bazedoxifene (Duavee)?
do not use for prevention of CVD
do not use for prevention of dementia
Special consideration: do not use in pts w/ hx of VTE
Provide appropriate counseling (including administration directions and adverse effects) for osteoporosis medications
What medications are associated with osteoporosis? (red bolded)
Depo-medroxyprogesterone
thiazolidinediones (TZD)
SGLT2-i
glucocorticoids (≥ 5 mg/d prednisone* for ≥ 3 months)
Thyroid hormone (in excess)
GnRH agonists/antagonists

Provide appropriate counseling (including administration directions and adverse effects) for osteoporosis medications