ULTIMATE AP BIO VOCABULARY SET (UNITS 1-9)
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Polarity
A lack of electrical symmetry in a molecule. Charge differences on opposite ends of a structure.
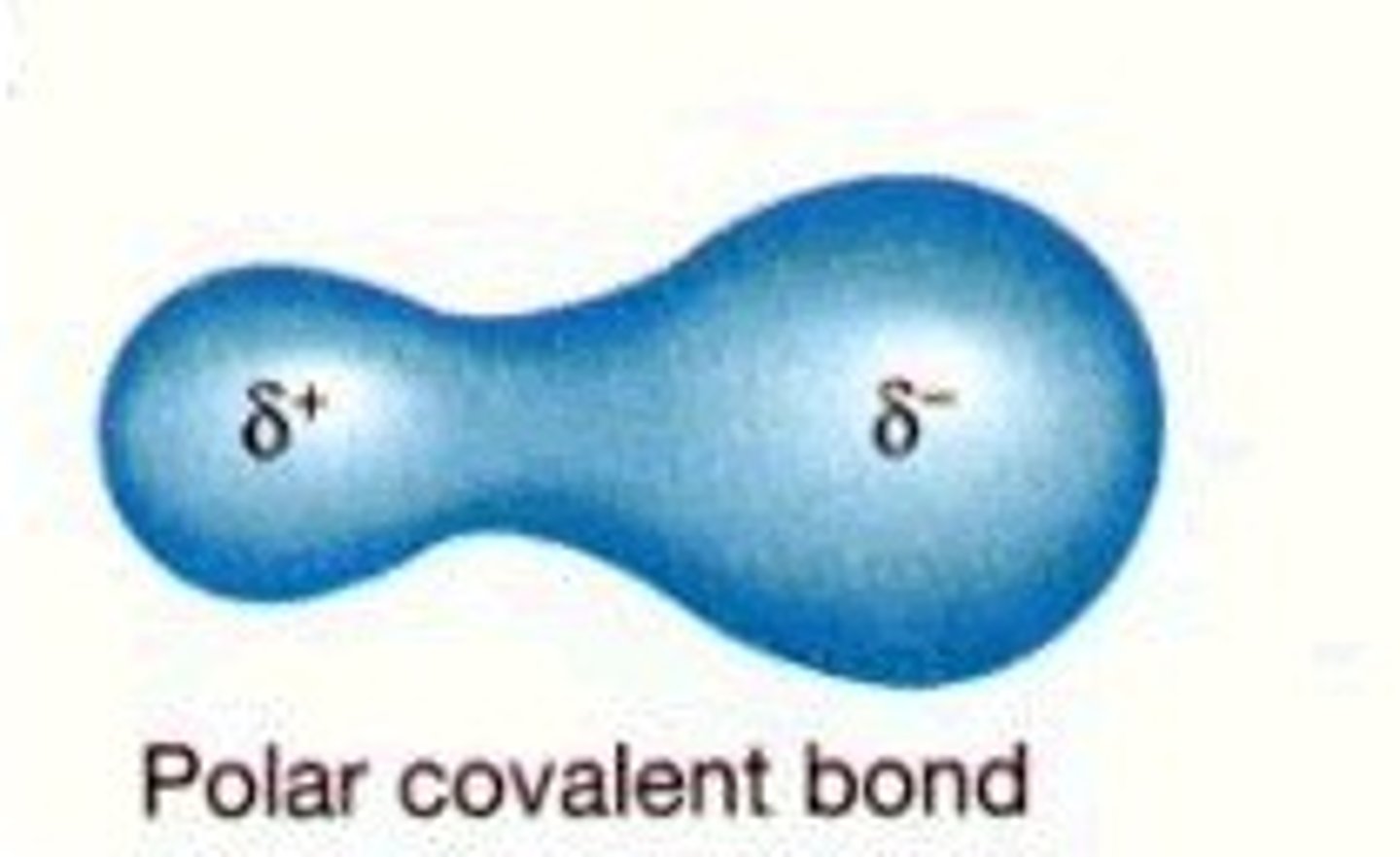
Which atom has a higher electronegativity: hydrogen or oxygen?
Oxygen

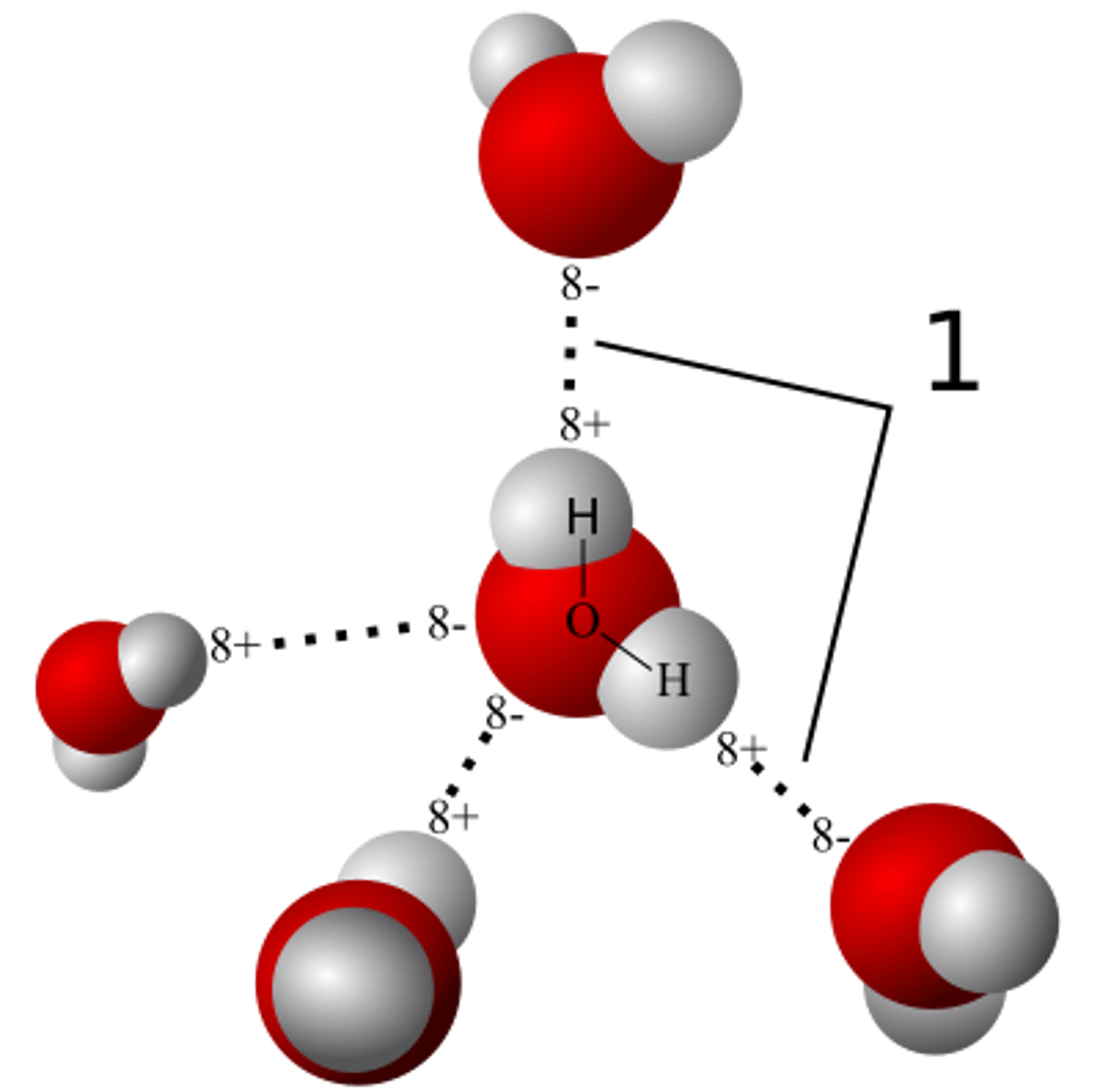
Hydrogen bond
weak attraction between a hydrogen atom and another atom
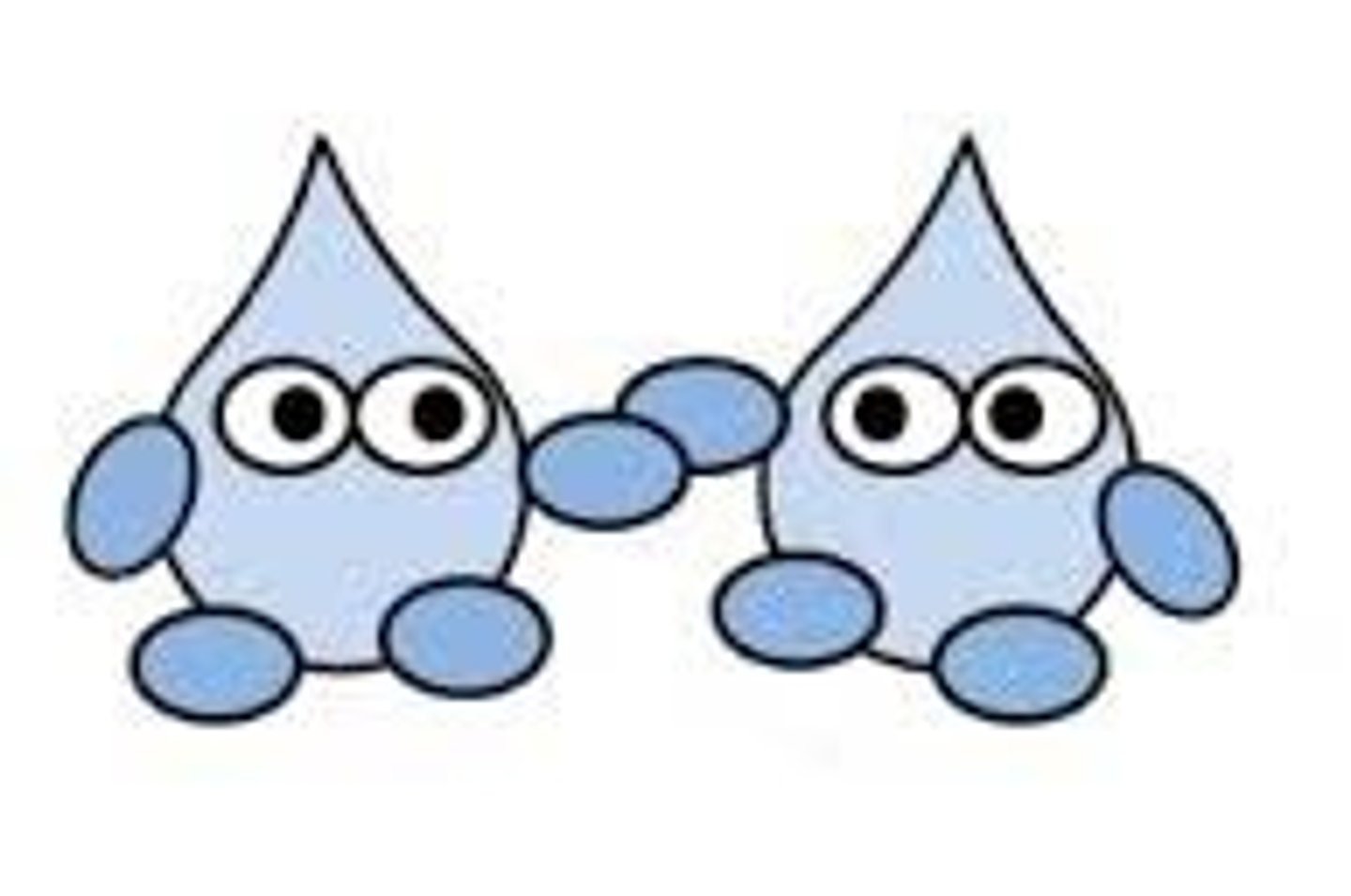
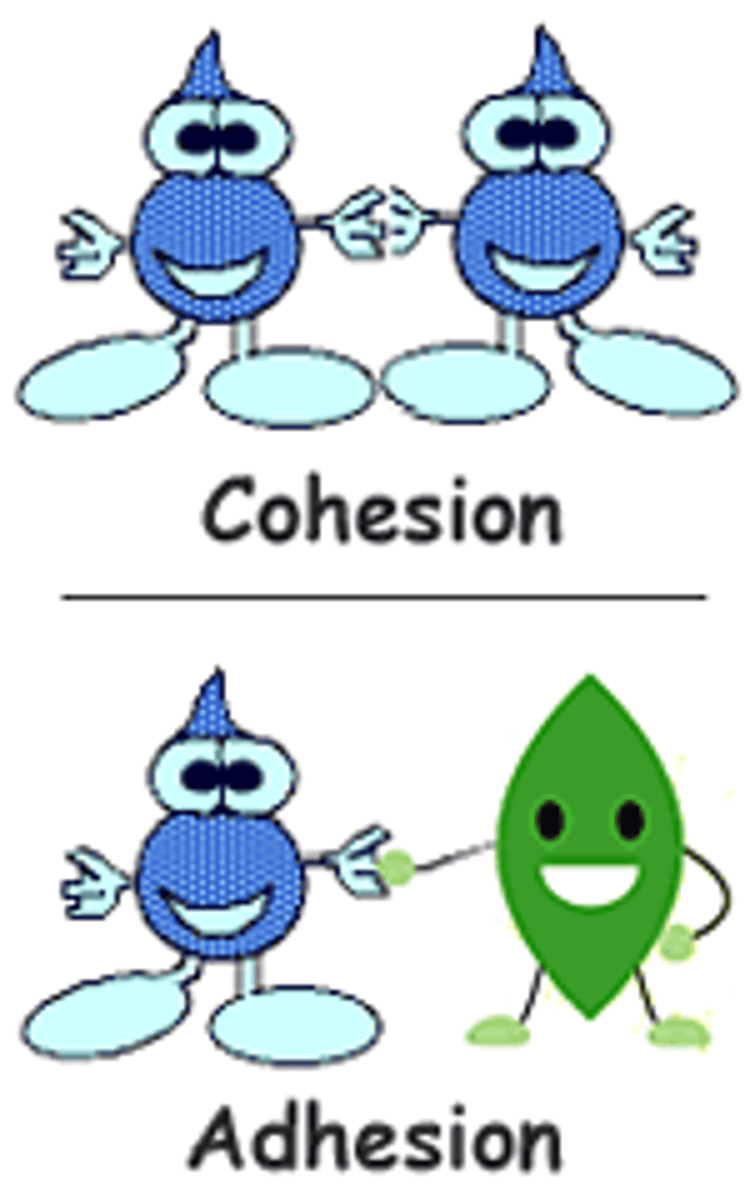
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
High Specific Heat
A property of water. Water can absorb lots of heat before changing temperature

Water is typically called a...
Universal solvent

Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
Surface tension
A measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid

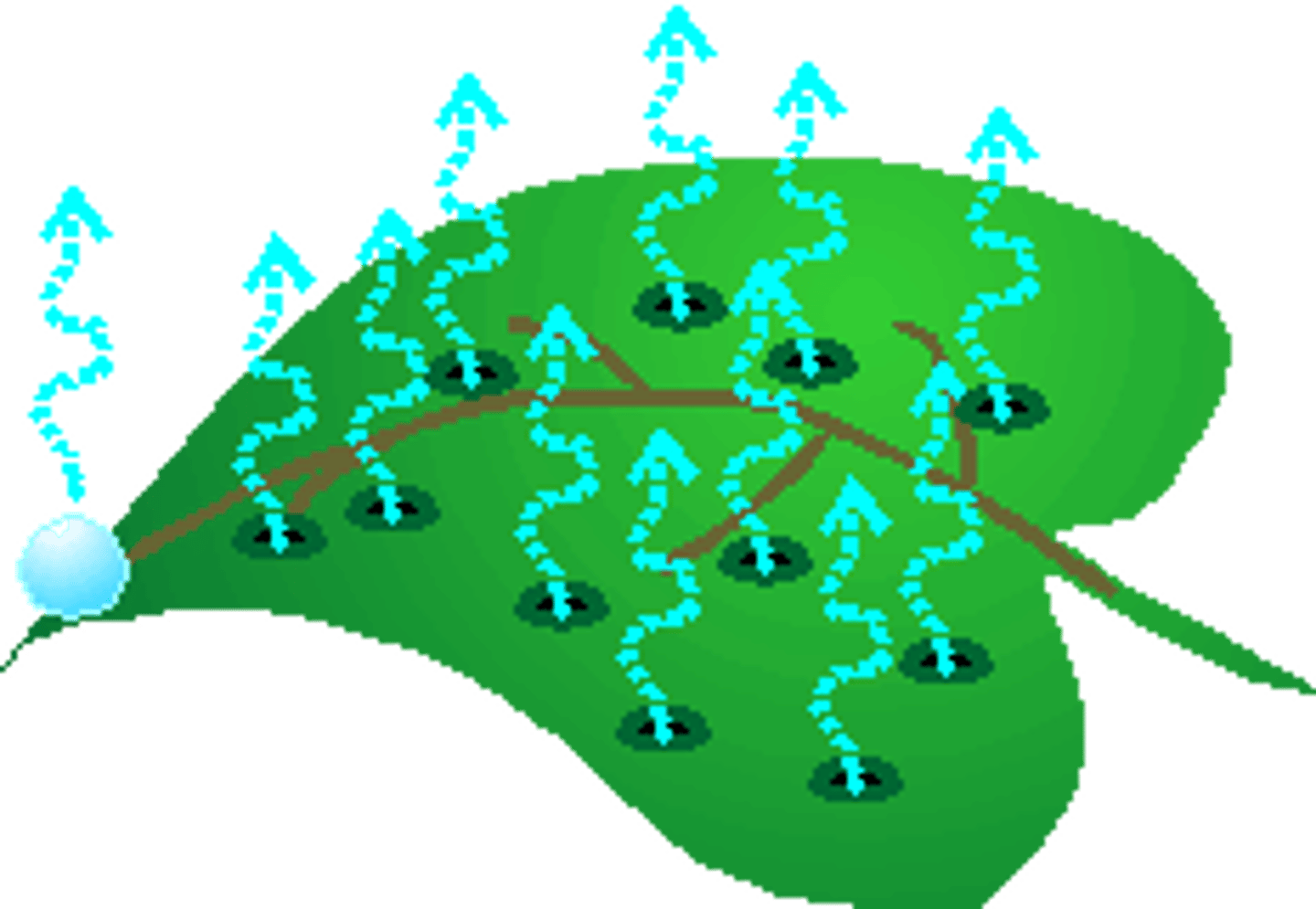
Plant transpiration
Water that is released to the atmosphere as vapor from pores on a leaf's underside after being absorbed by the roots and used through the plant.
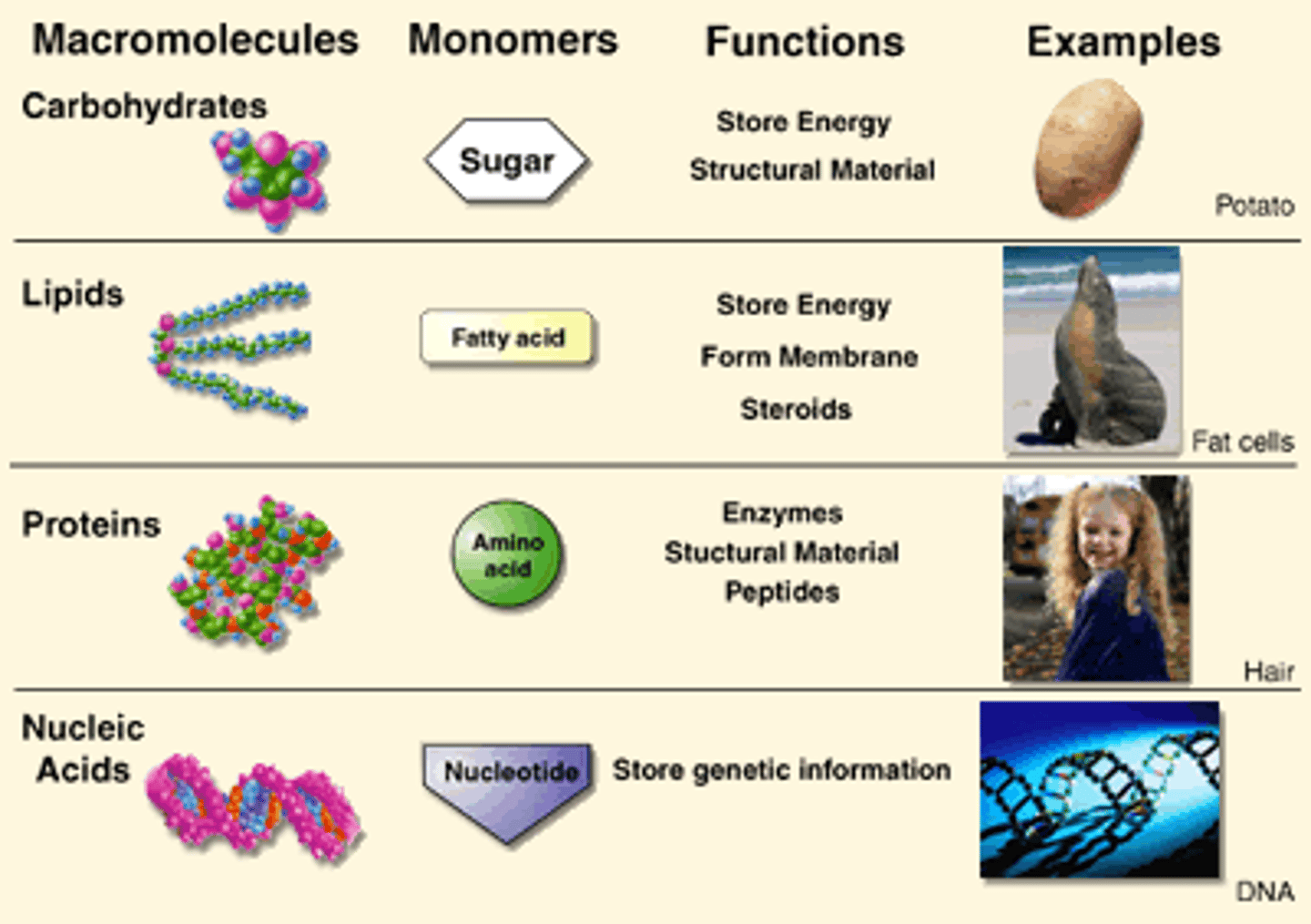
Macromolecules
A very large organic molecule composed of many smaller molecules

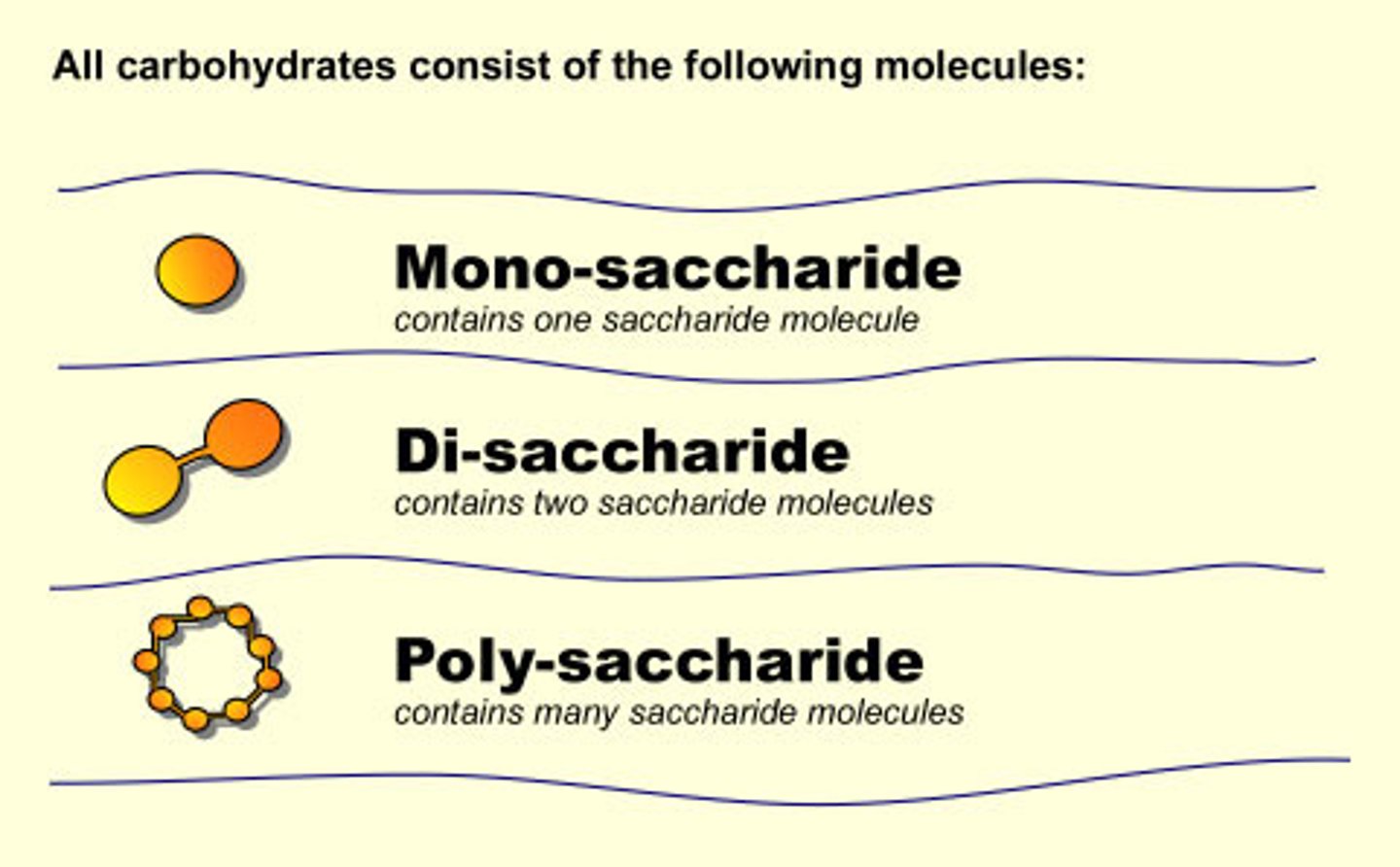
Carbohydrates
the starches and sugars present in foods
Lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.

Proteins
Nutrients the body uses to build and maintain its cells and tissues

Nucleic Acids
DNA and RNA
Monomers
building blocks of polymers
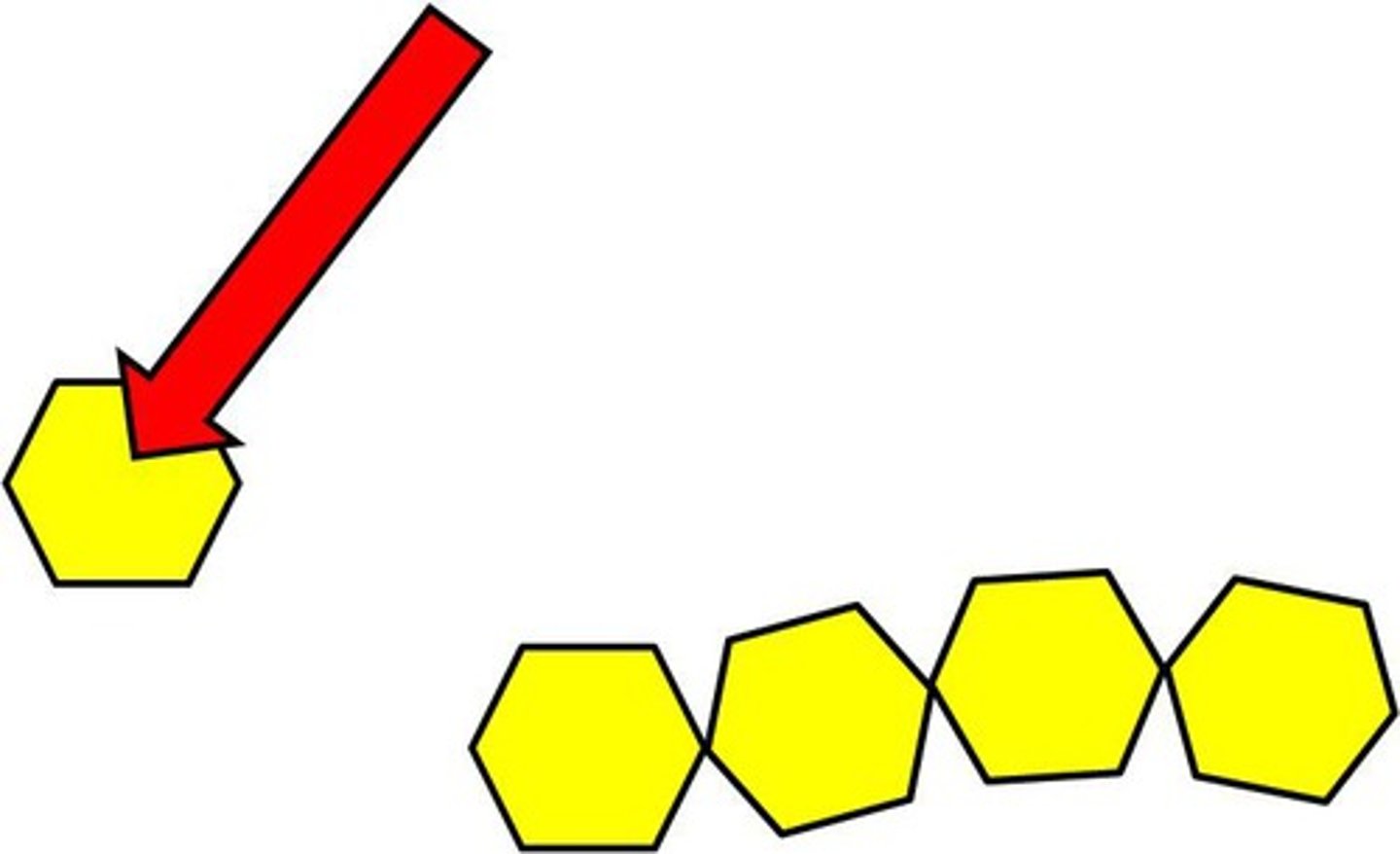
Monomers of Macromolecules
Carbohydrates - monosaccharides.
Lipids - glycerol and fatty acids.
Nucleic acids - nucleotides.
Proteins - amino acids.
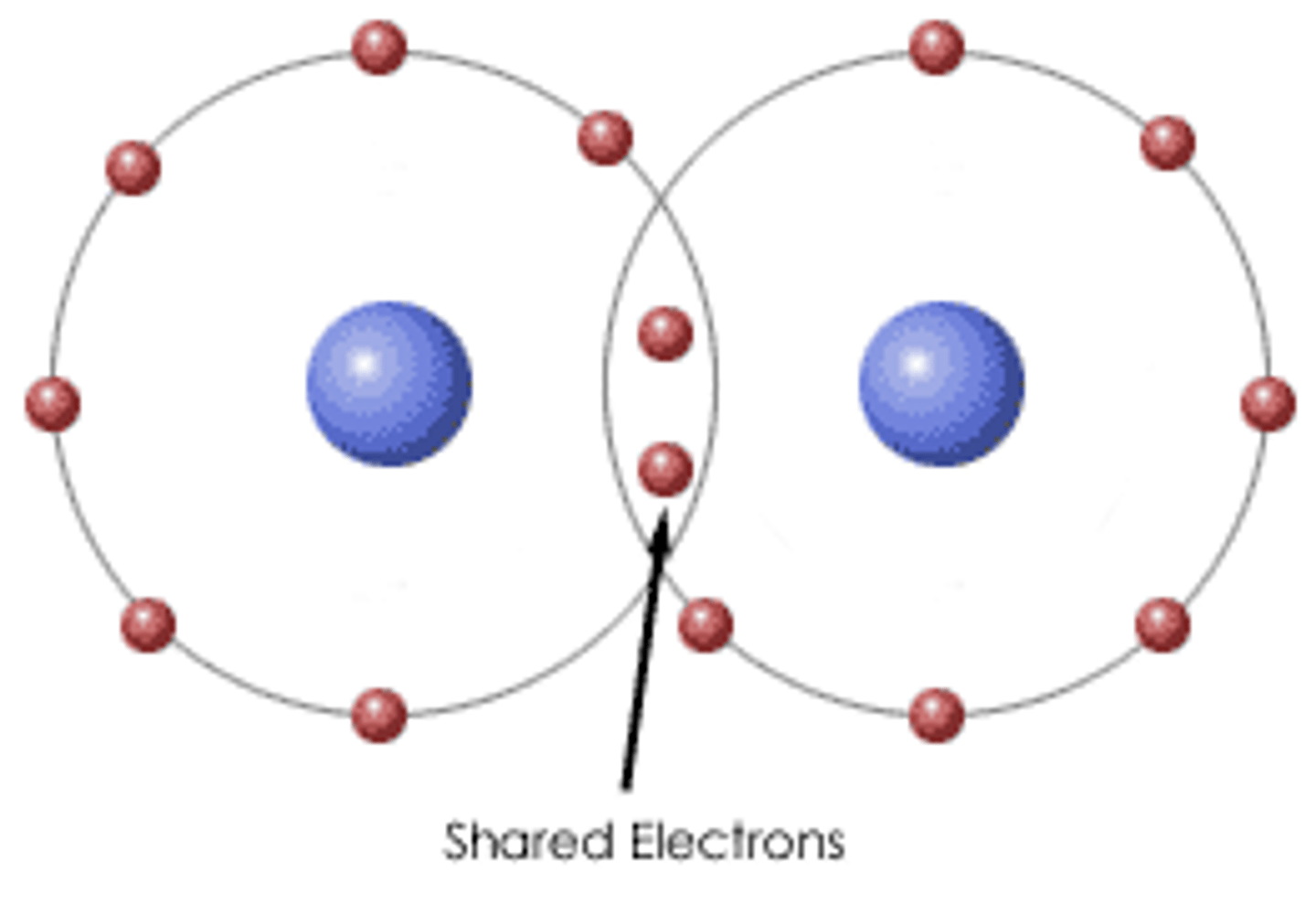
Covalent bond
A chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
Dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule.
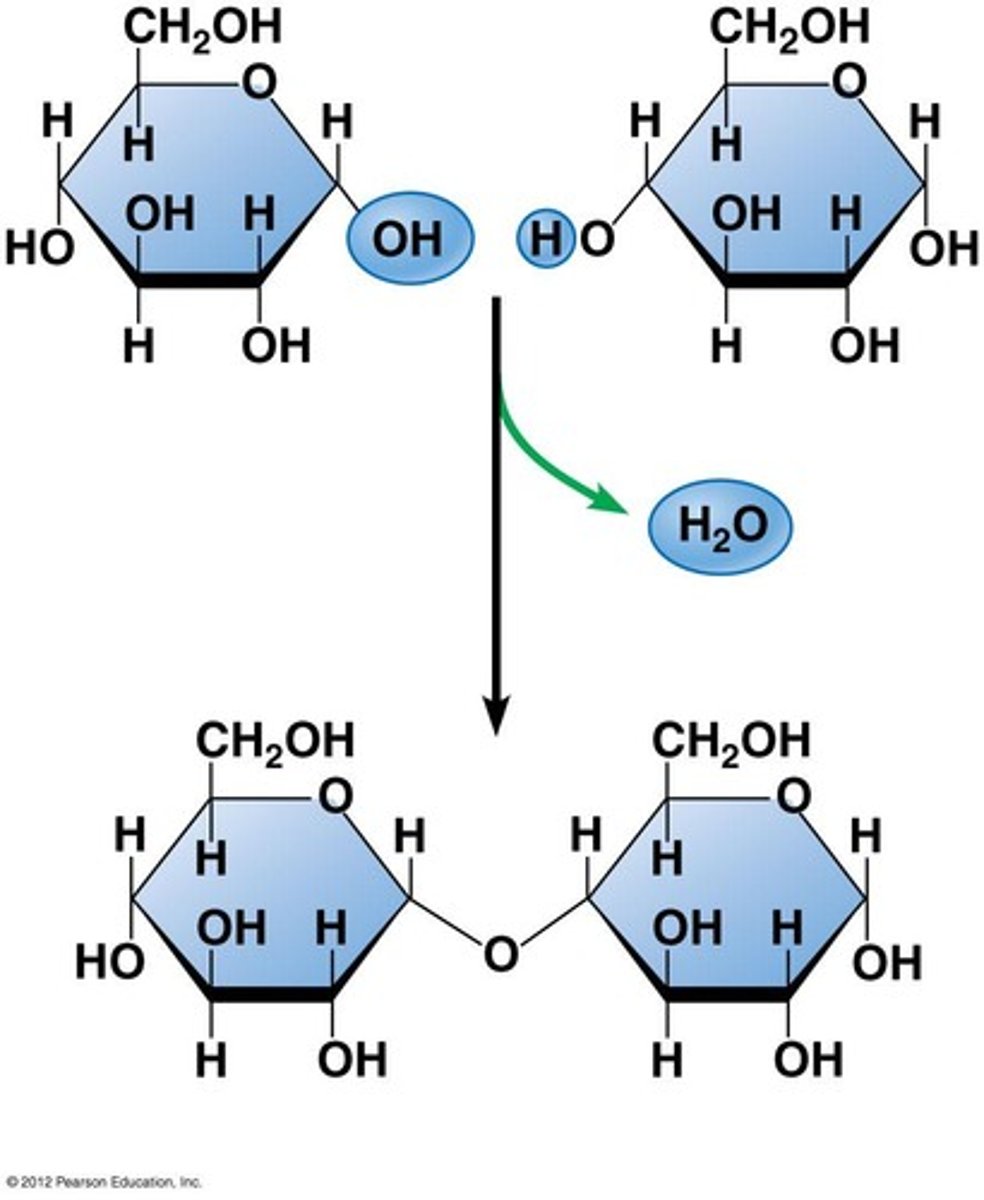
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
Membrane-bound organelles
Only eukaryotic cells have
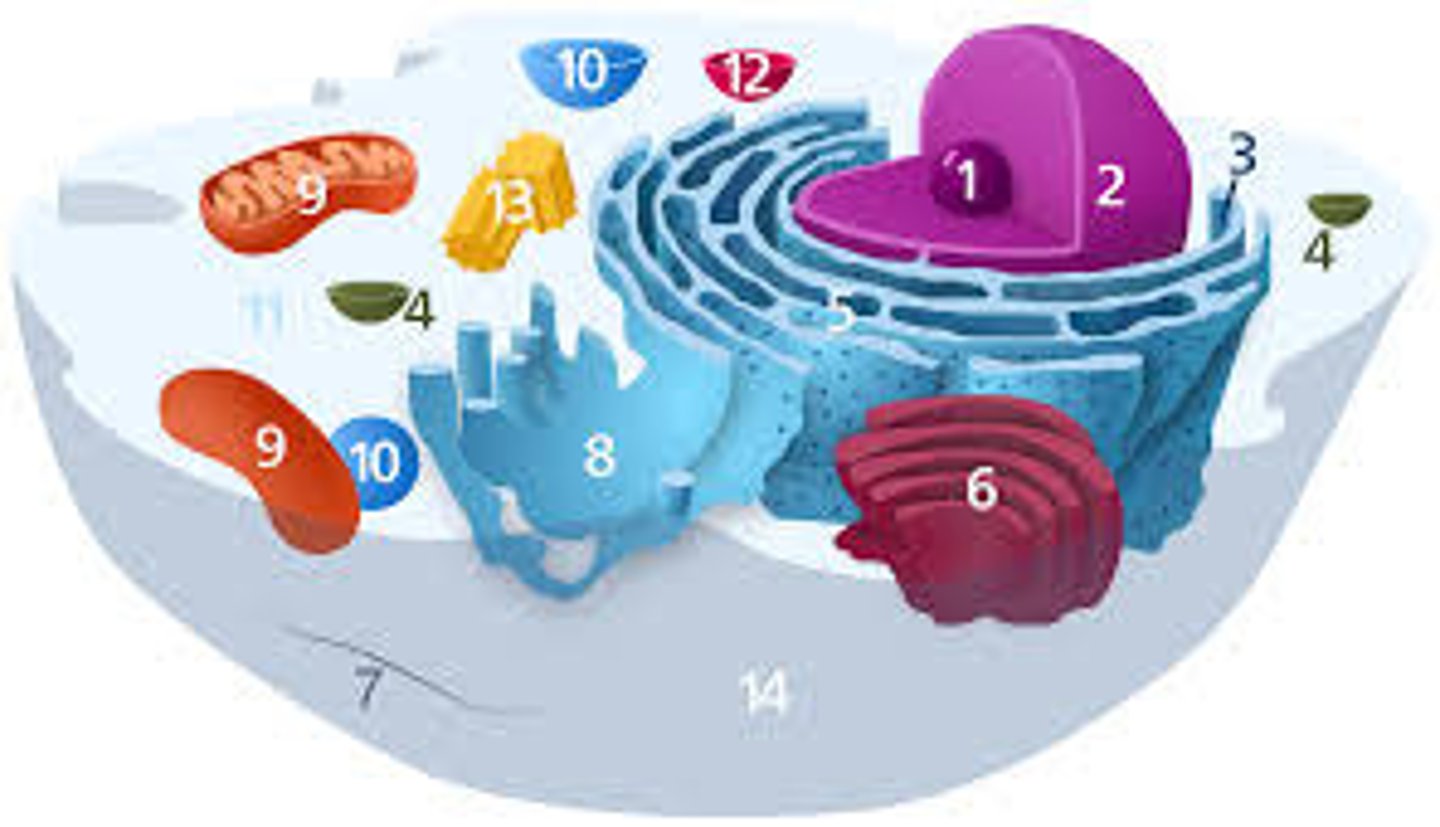
Non-membrane-bound organelles
ribosomes, cytoskeleton, centrosome, proteasomes
Mitochondrian
cell organelle that releases energy from stored food molecules: "powerhouse of the cell"

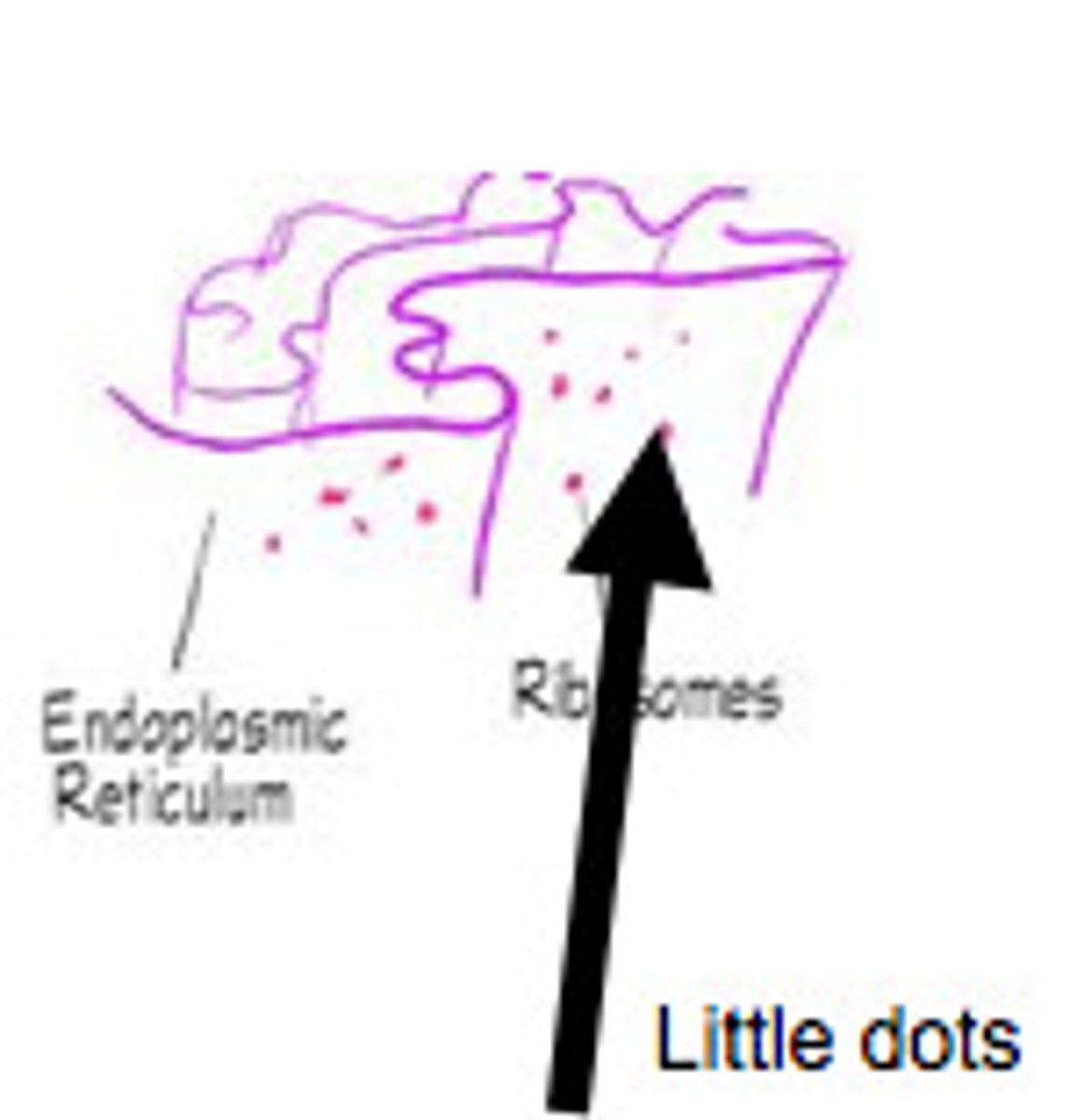
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Studded with ribosomes, transports materials through the cell and produces proteins
Smooth ER
Makes lipids
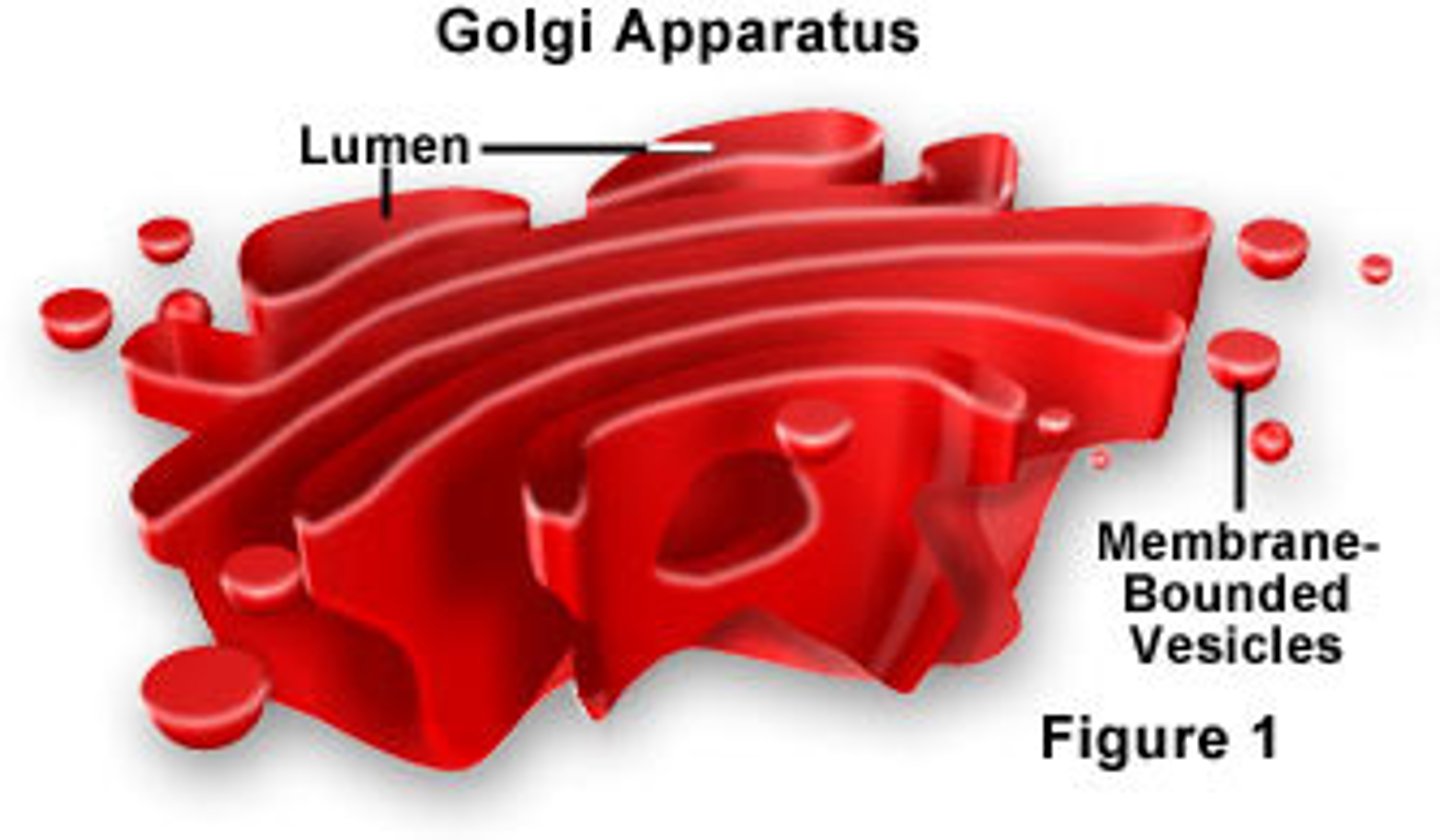
Golgi Apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell
Lysosome
An organelle containing digestive enzymes
Vacuole
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
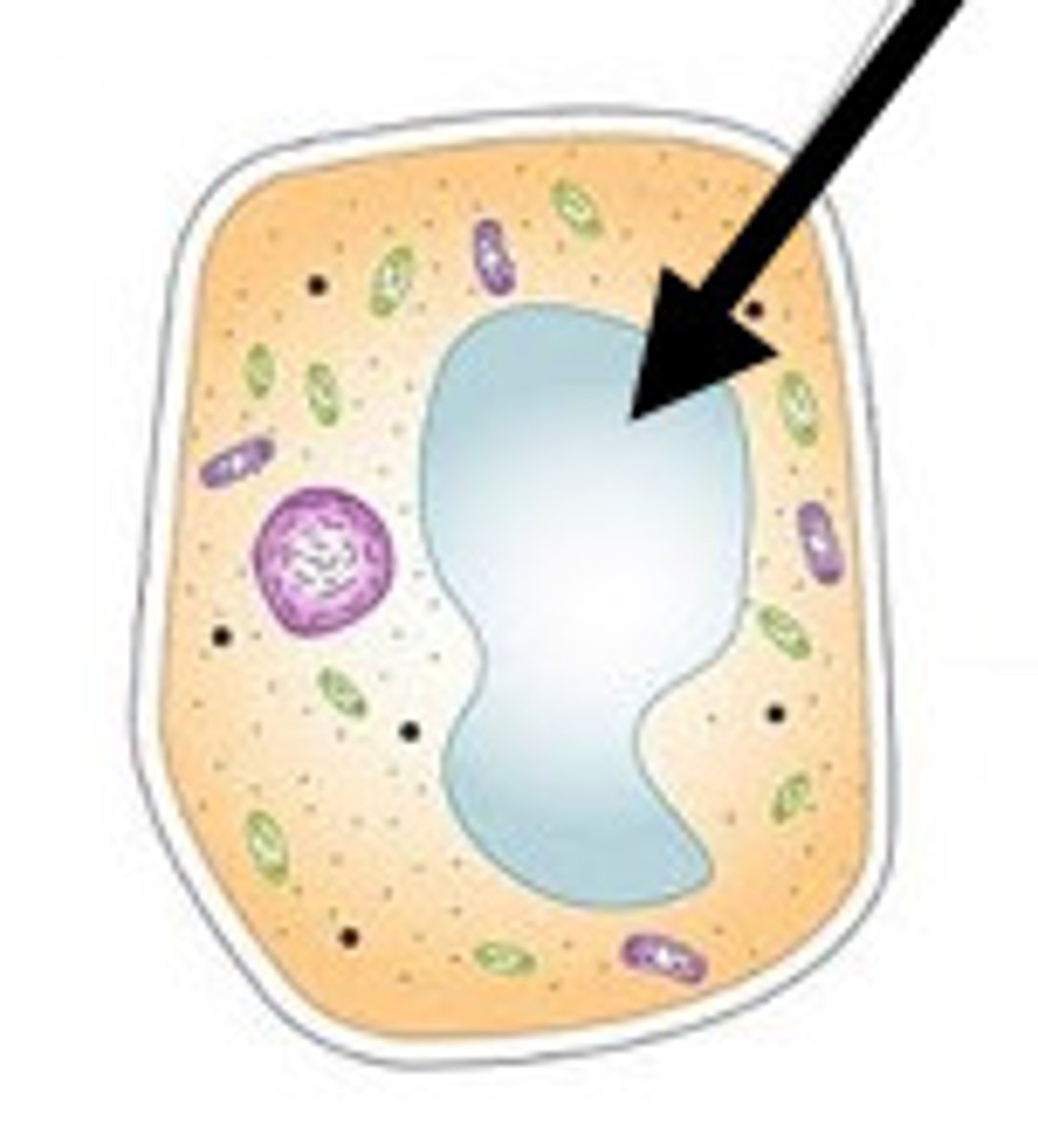
Ribosome
site of protein synthesis
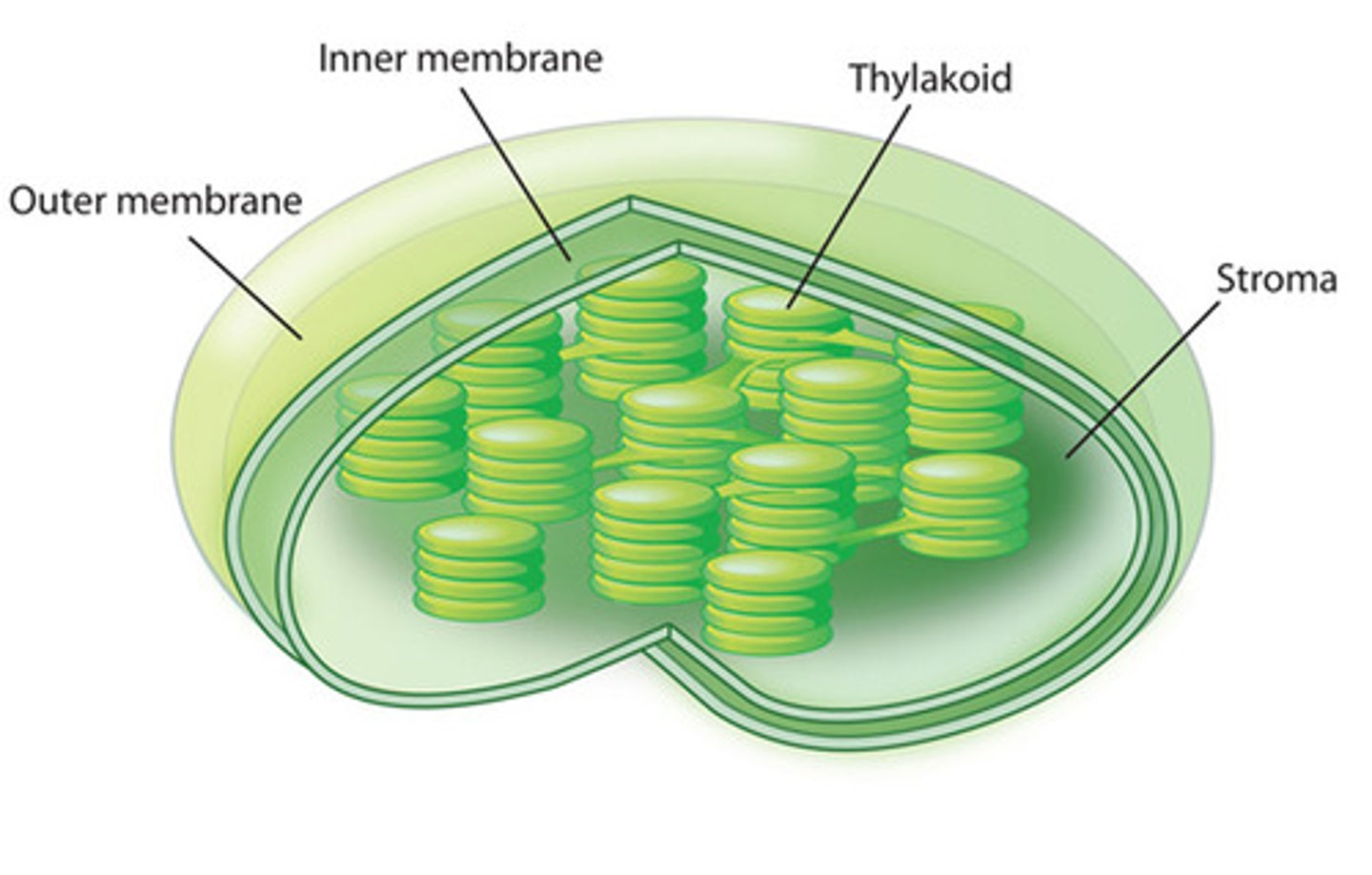
Chloroplasts
Capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell
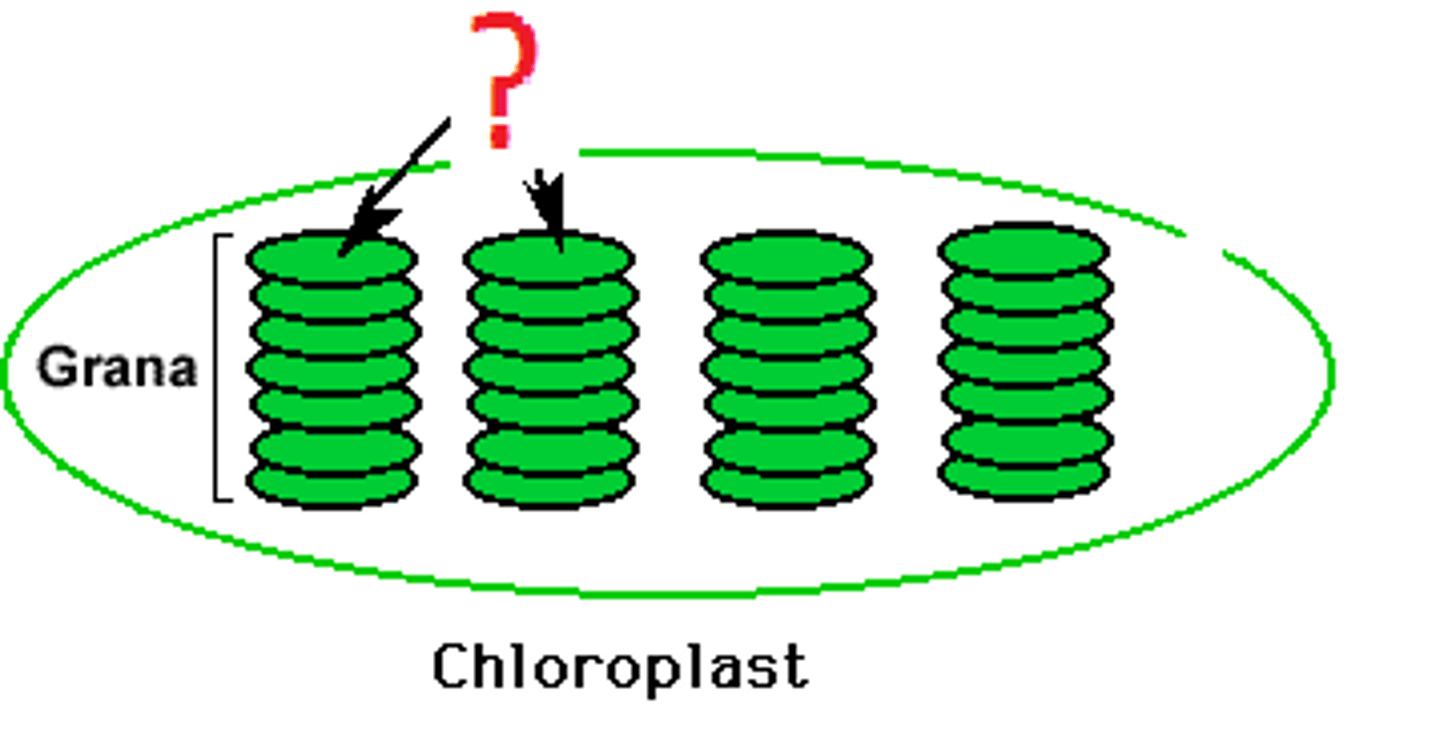
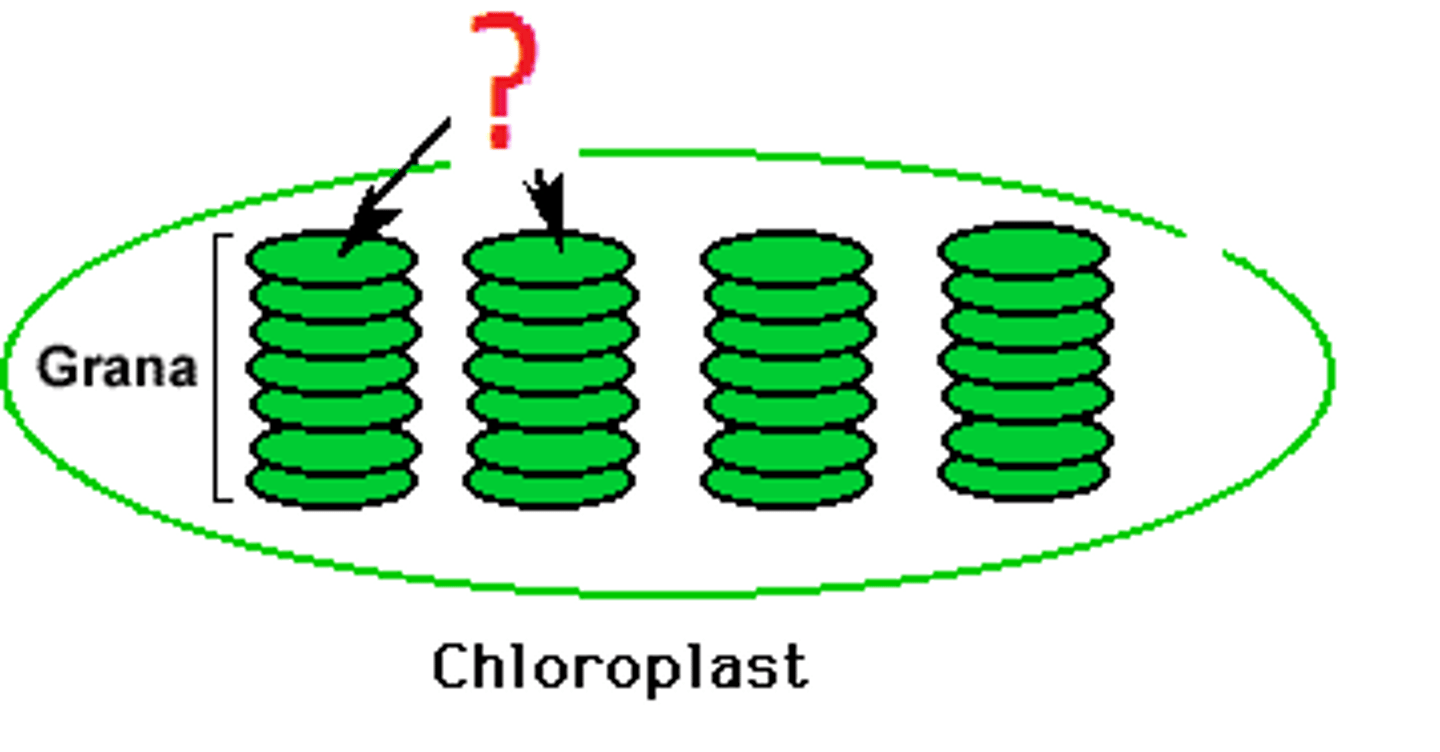
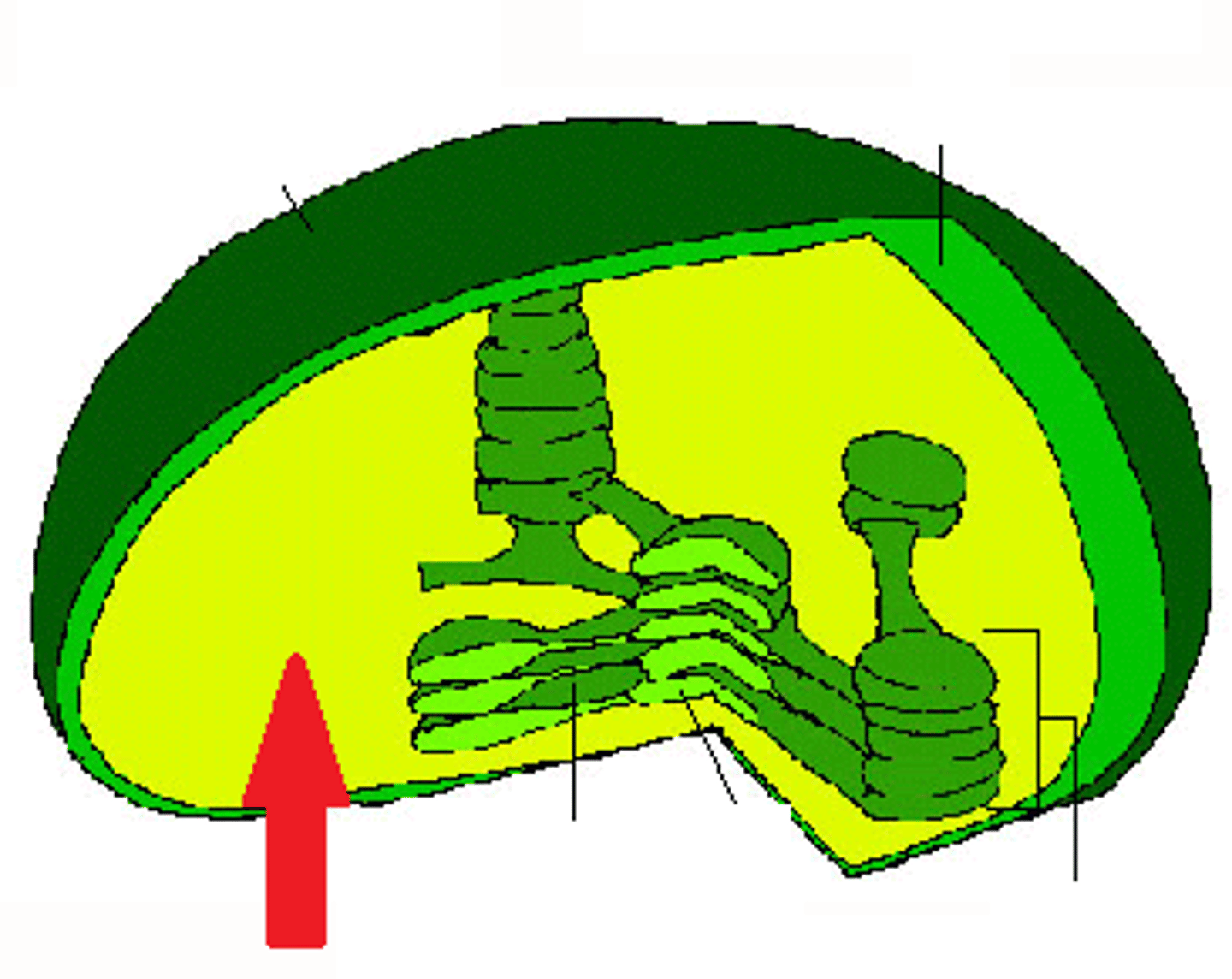
Thylakoid membranes (grana)
Site of light-dependent reactions in chloroplasts.
Chlorophyll
A green pigment found in the chloroplasts of plants, algae, and some bacteria

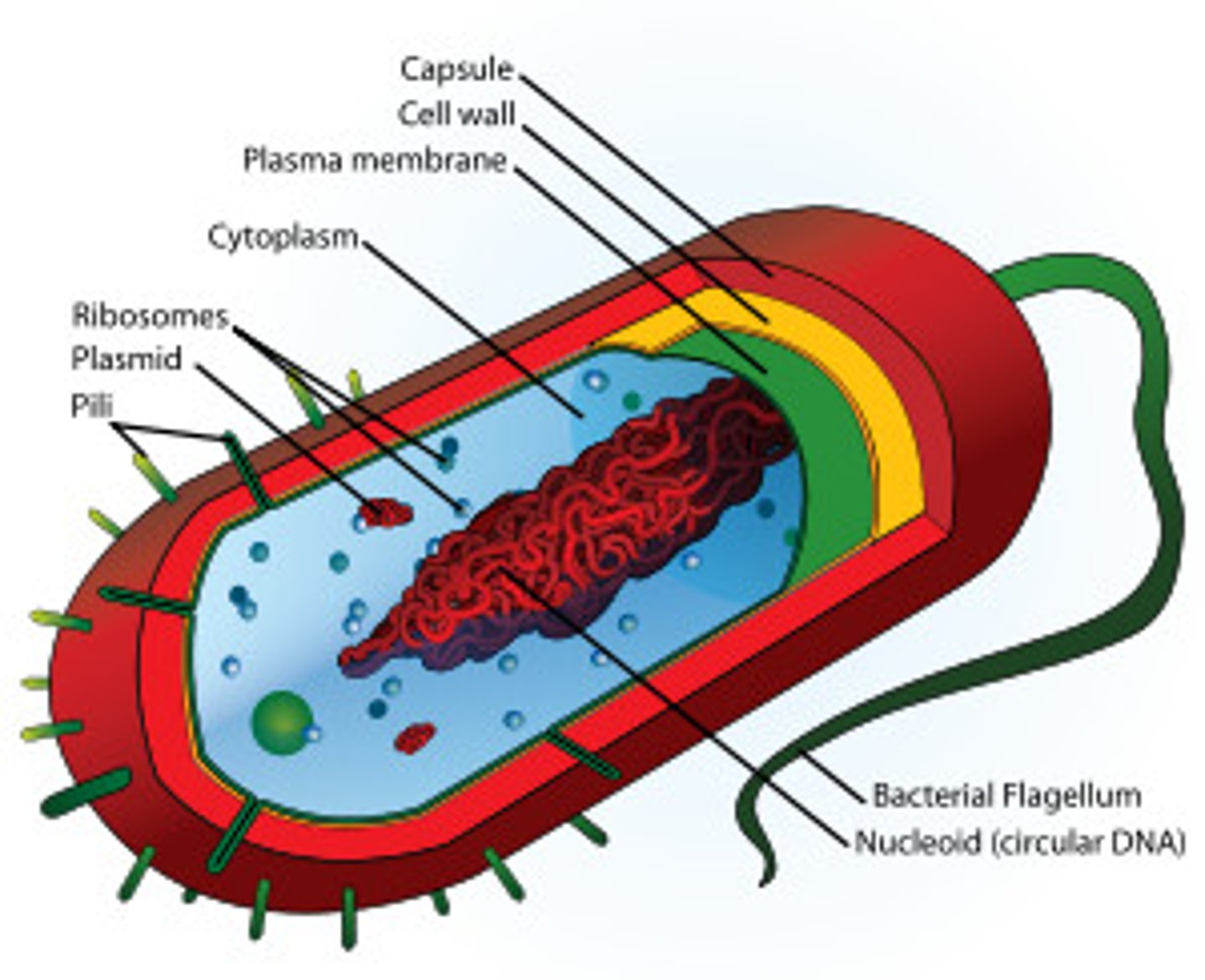
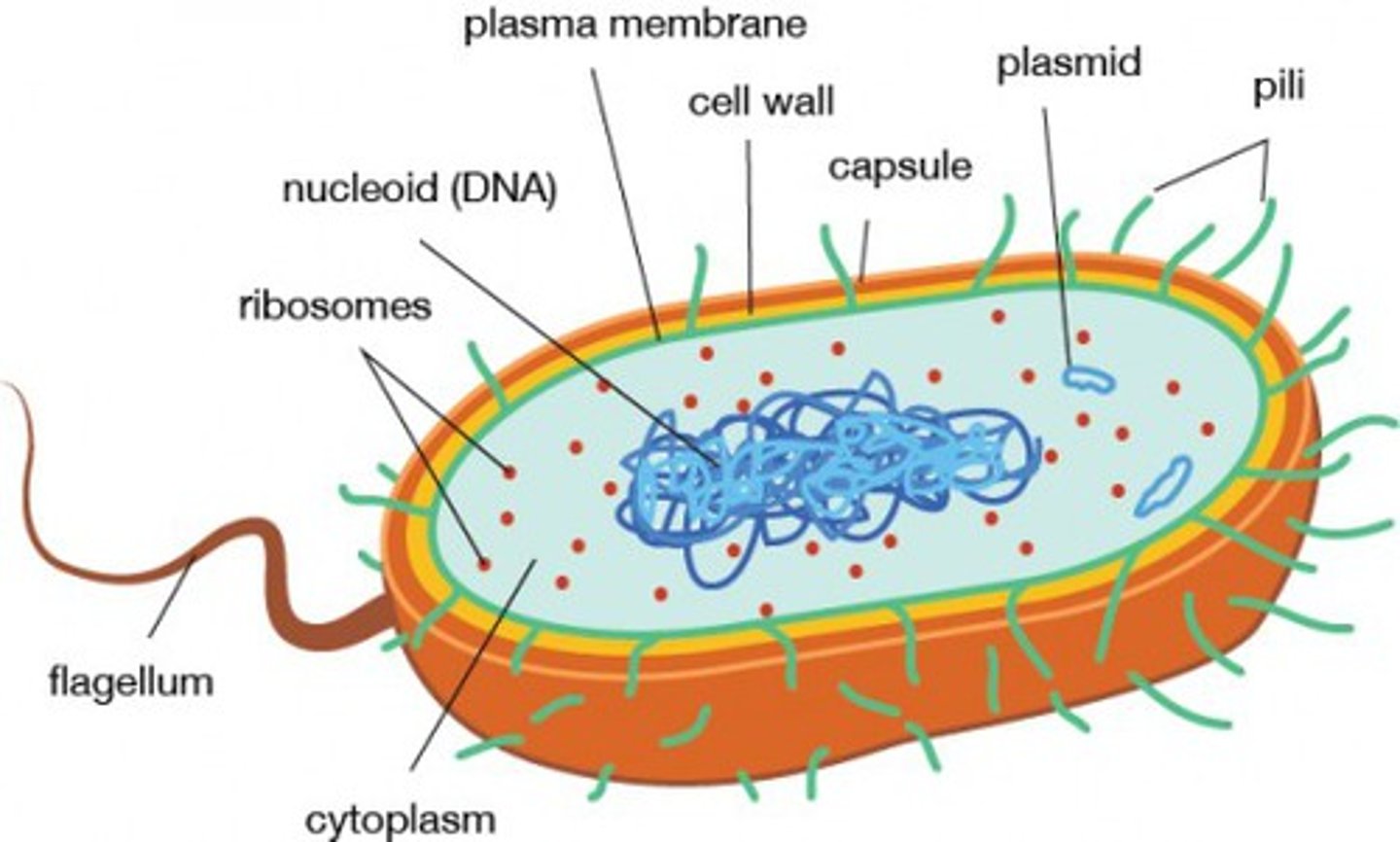
Prokaryotic cells
do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles
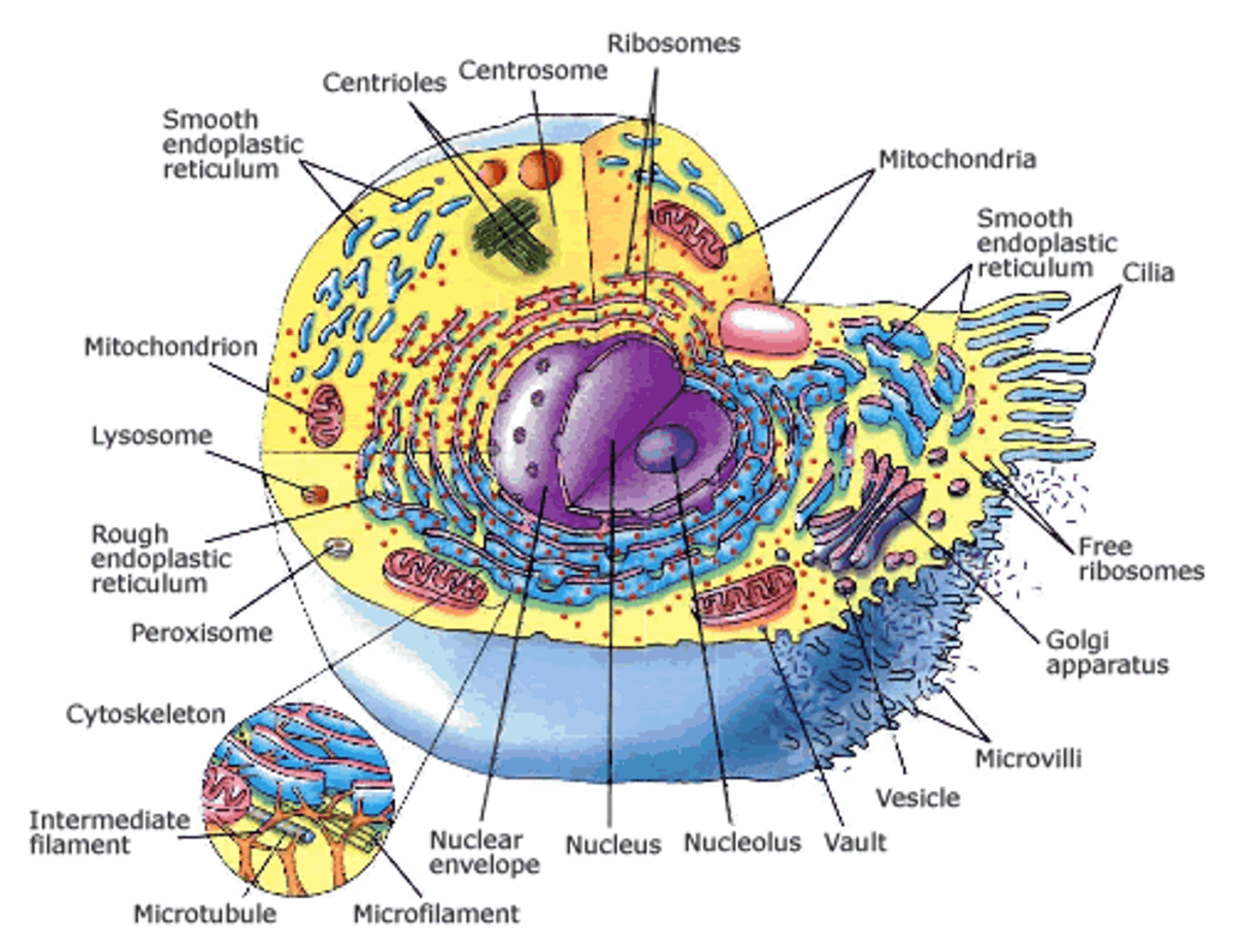
Eukaryotic cells
Contain a nucleus and other organelles that are bound by membranes.
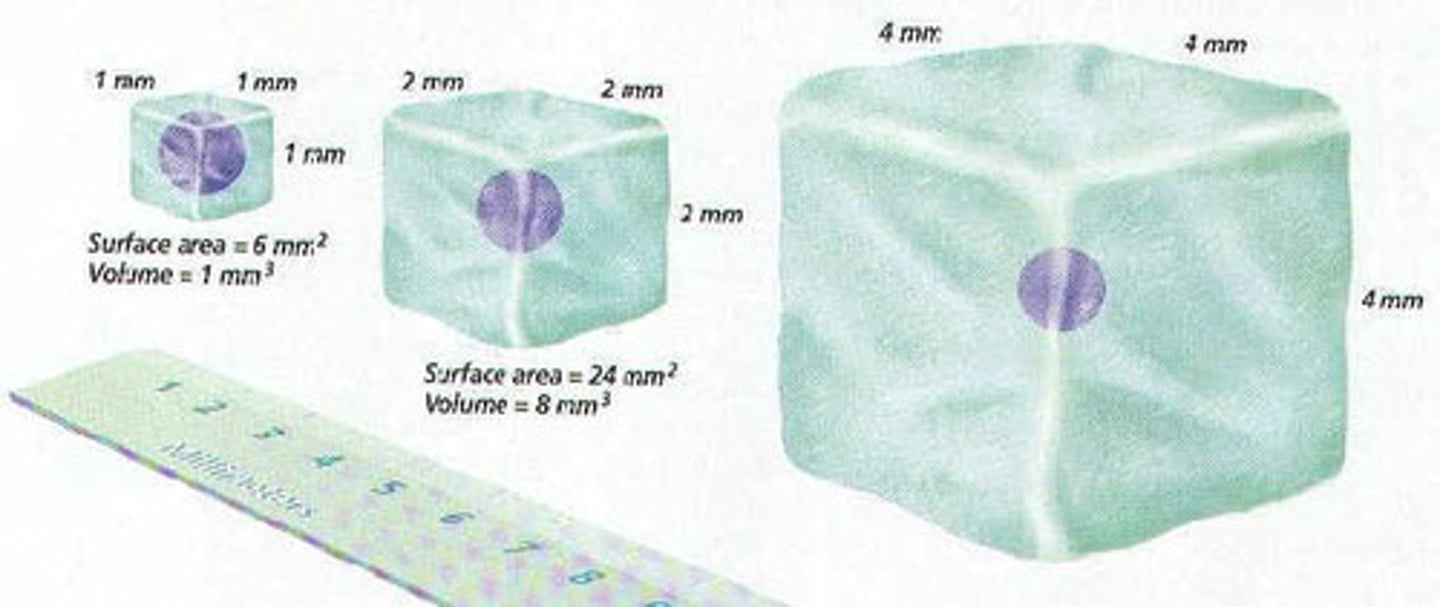
Cell surface area to volume ratio
As a cell's size increases, its volume increases much more rapidly than its surface area
Cell surface area formula
SA = 4πr²
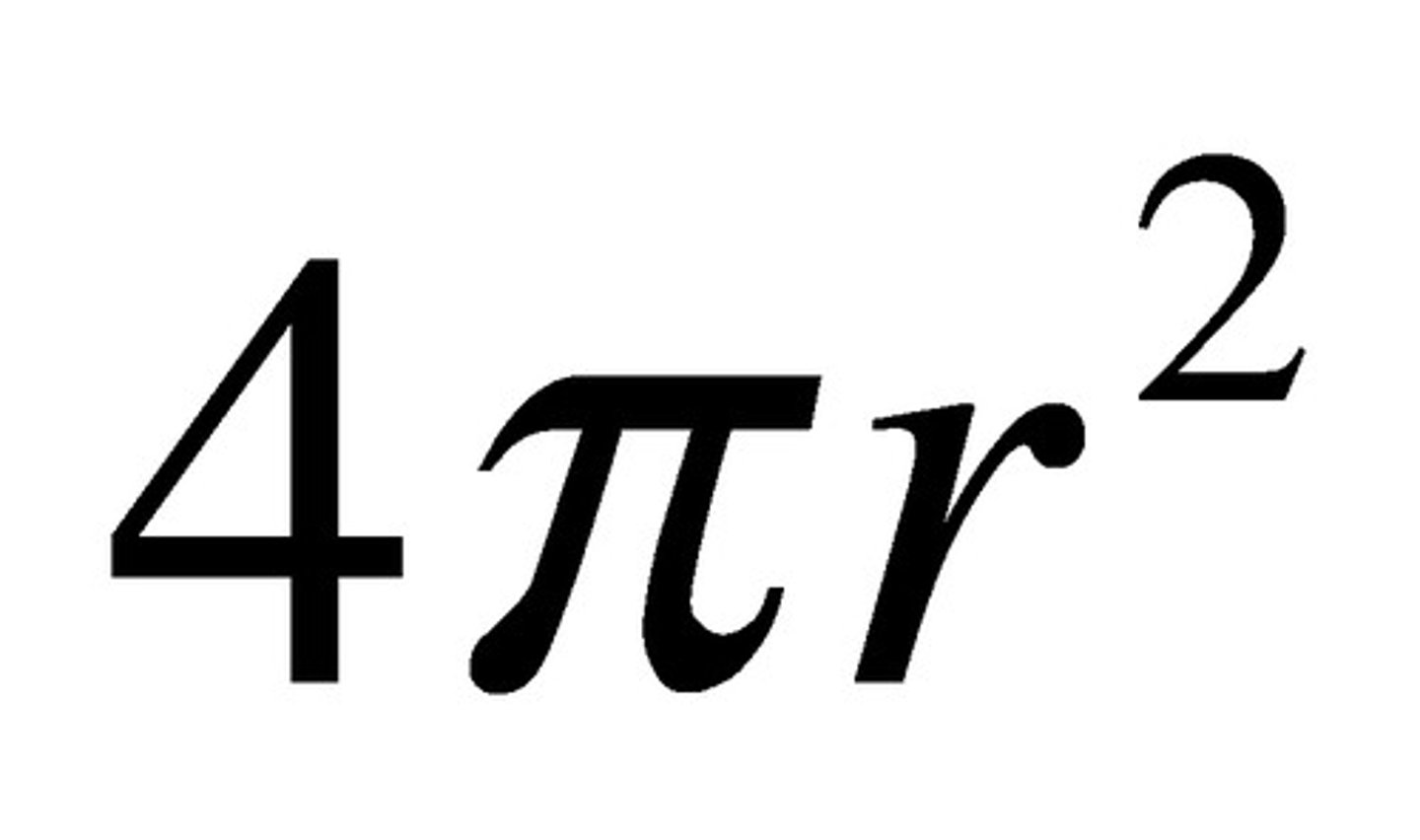
Cell volume formula
V = (4/3)πr³
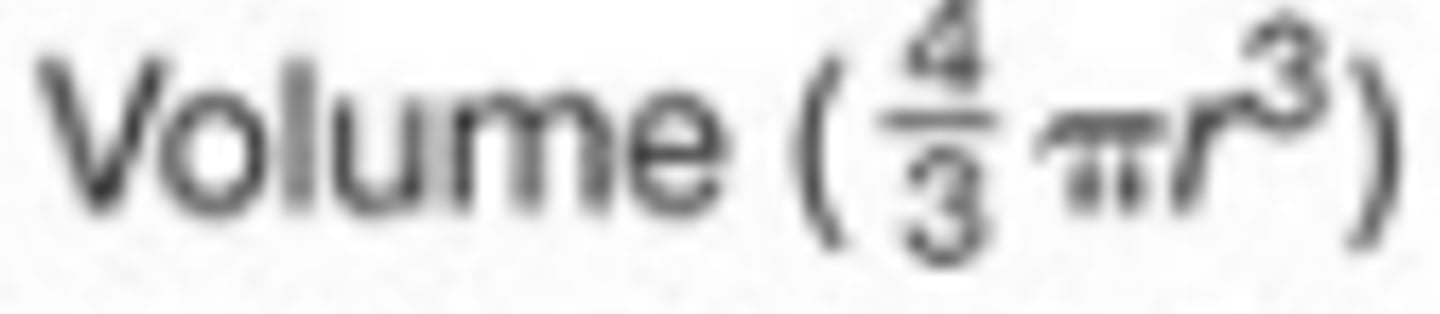
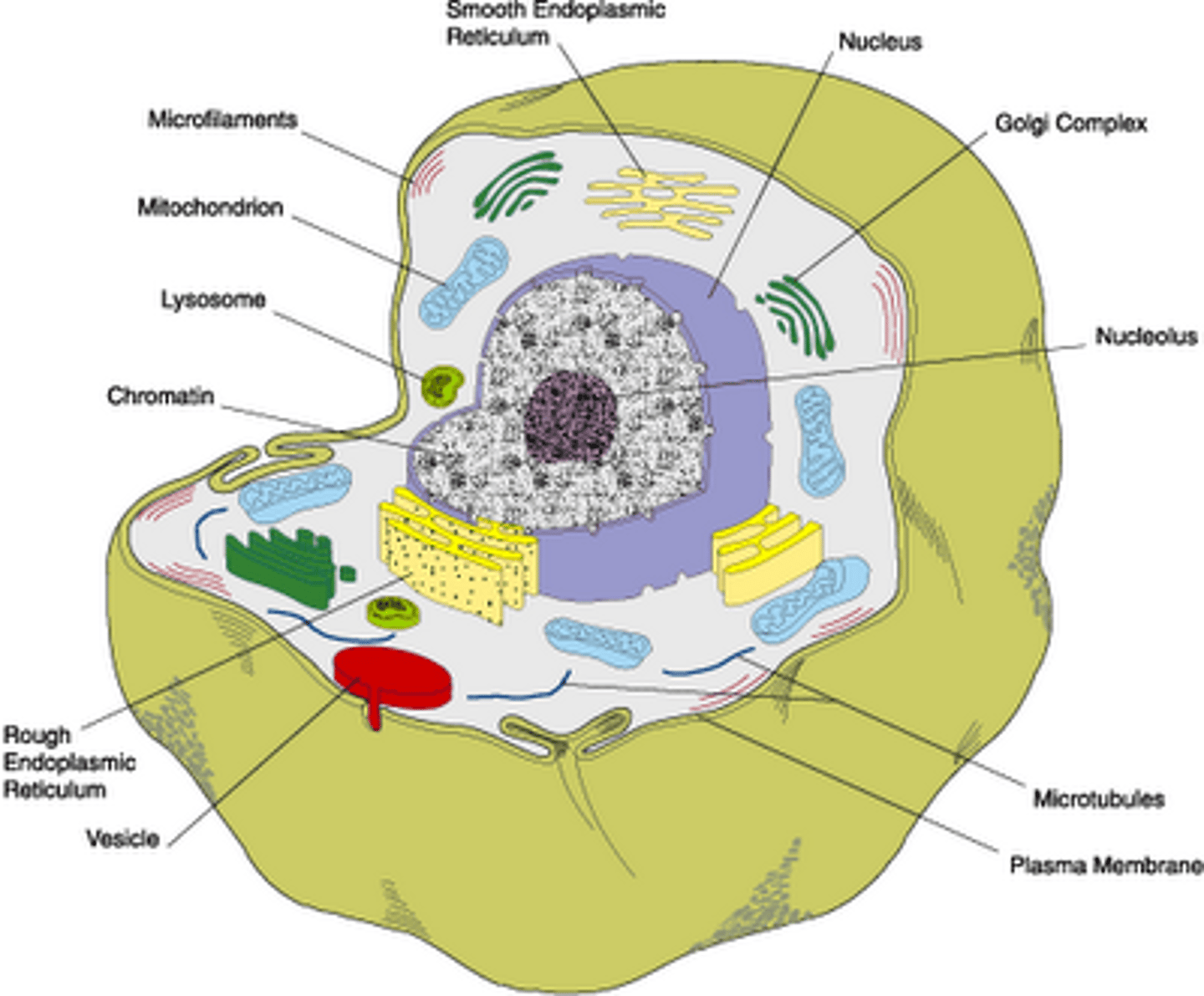
Compartmentalization
Membrane-bound organelles allow different parts of the cell to perform different functions at the same time
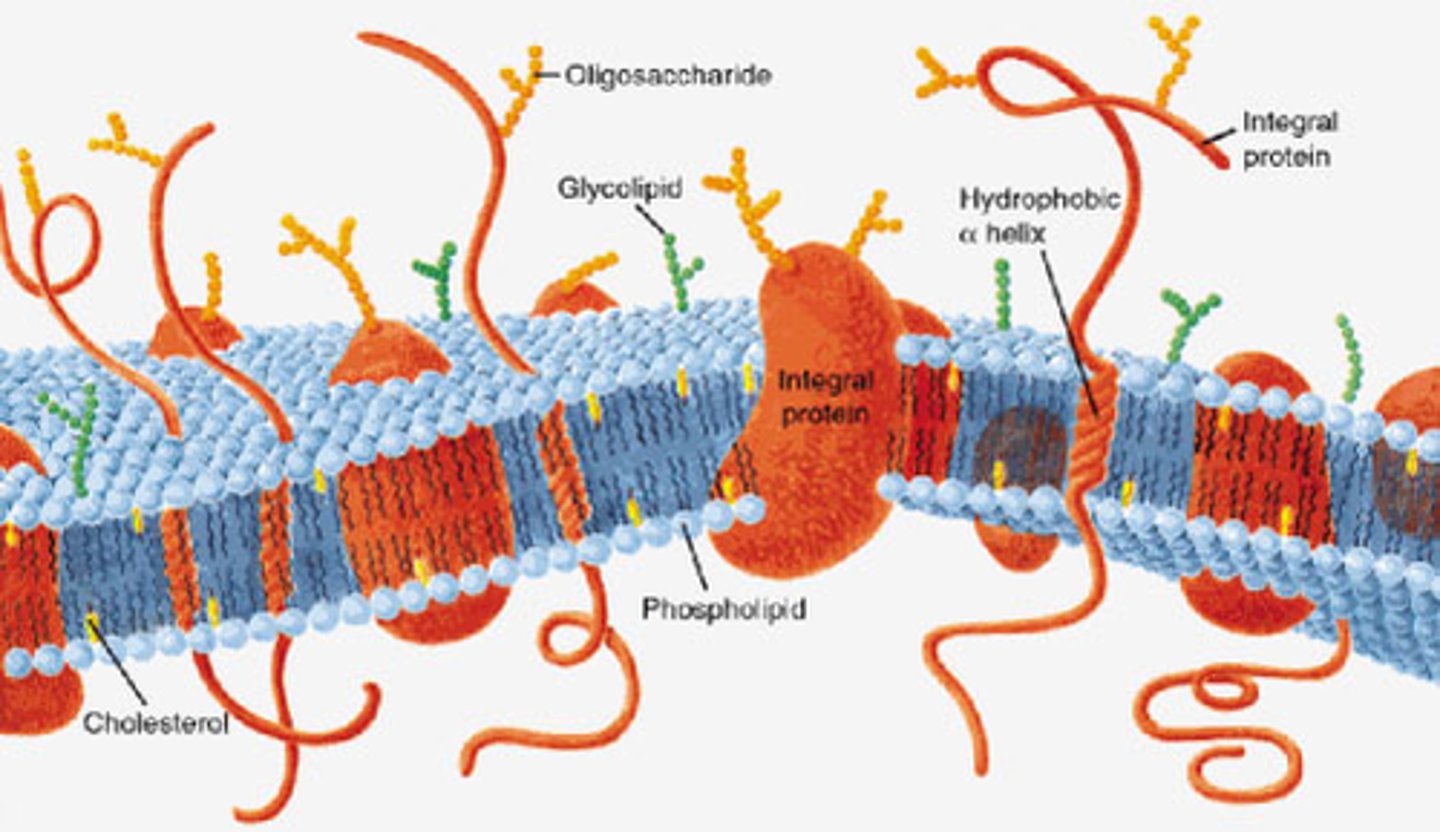
Plasma membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
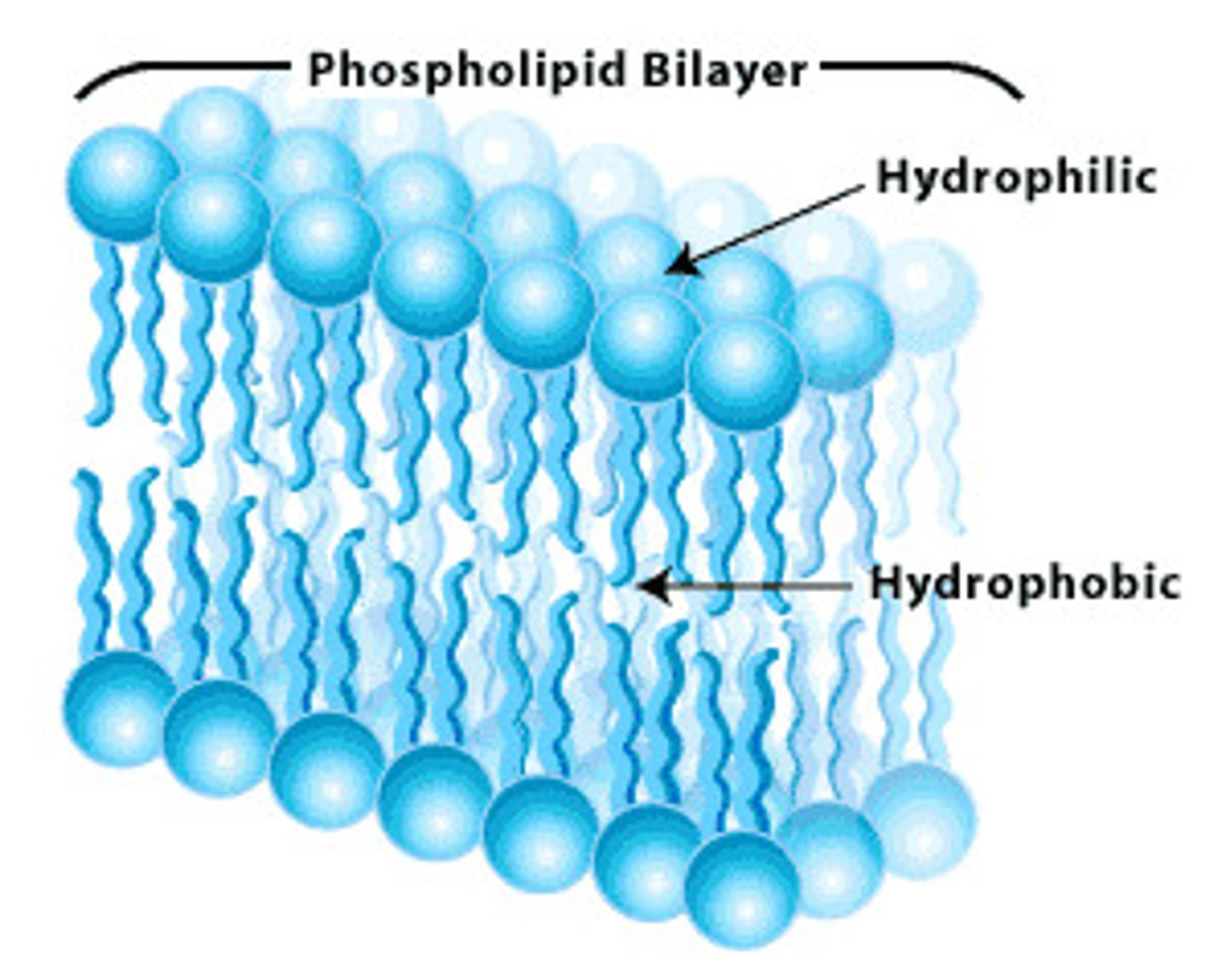
Phospholipids
A molecule that is a constituent of the inner bilayer of biological membranes, having a polar, hydrophilic head and a nonpolar, hydrophobic tail.
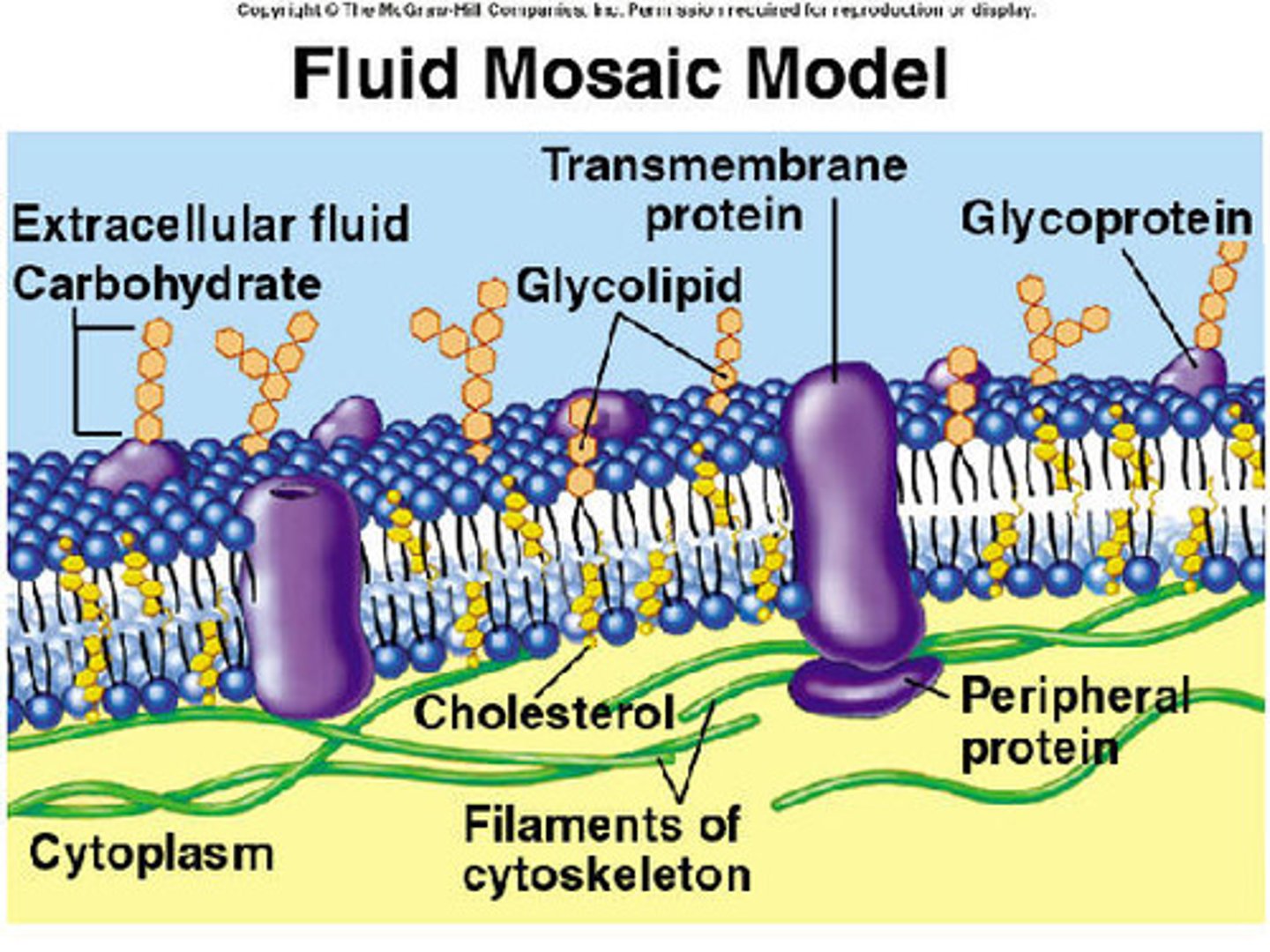
Fluid mosaic model
model that describes the arrangement and movement of the molecules that make up a cell membrane (proteins, cholesterol, glycoproteins, glycolipids, embedded in the bilayer)
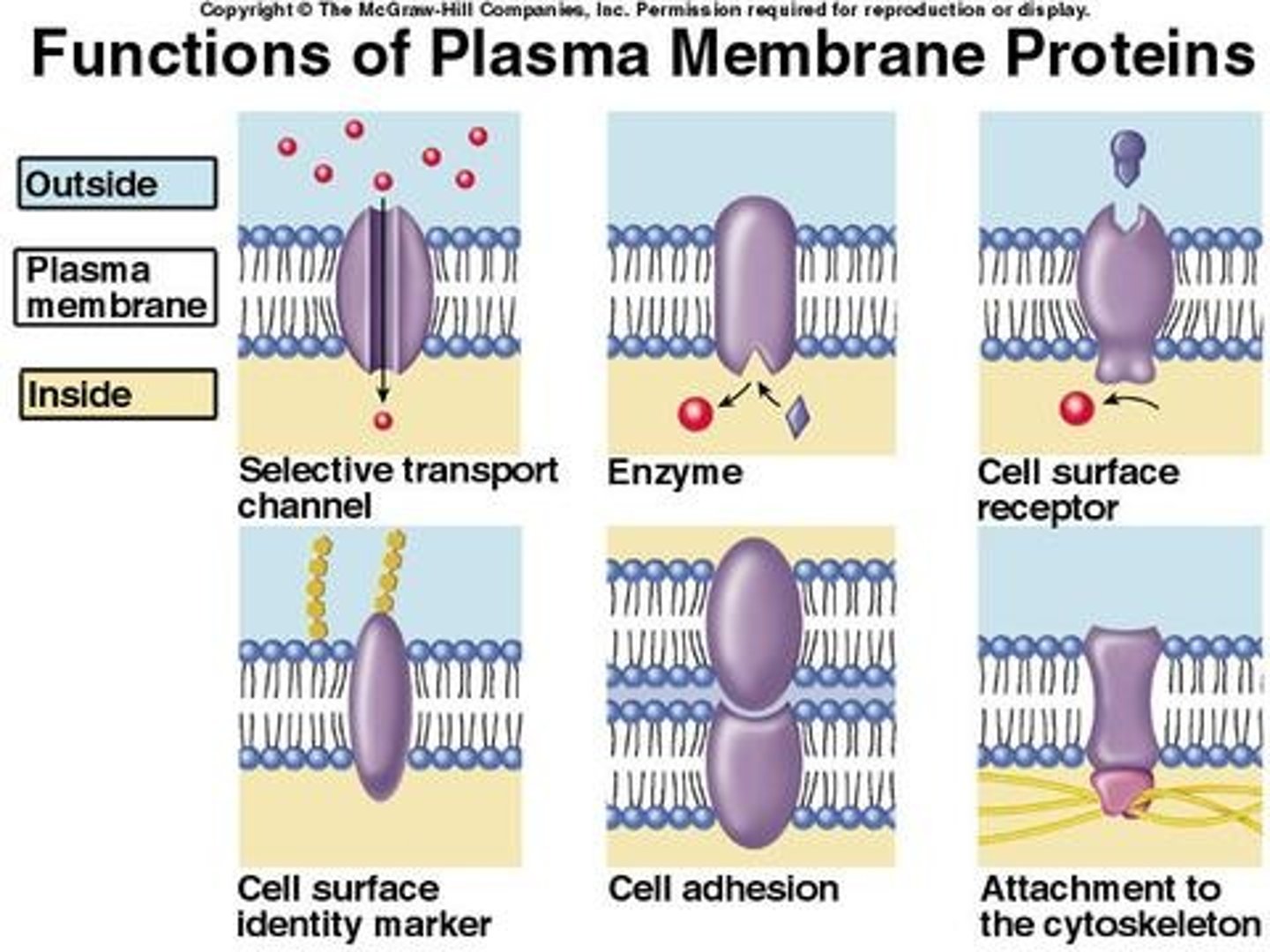
Functions of membrane proteins
transport, enzymatic activity, signal transduction, cell-cell recognition, intercellular joining, attachment to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix
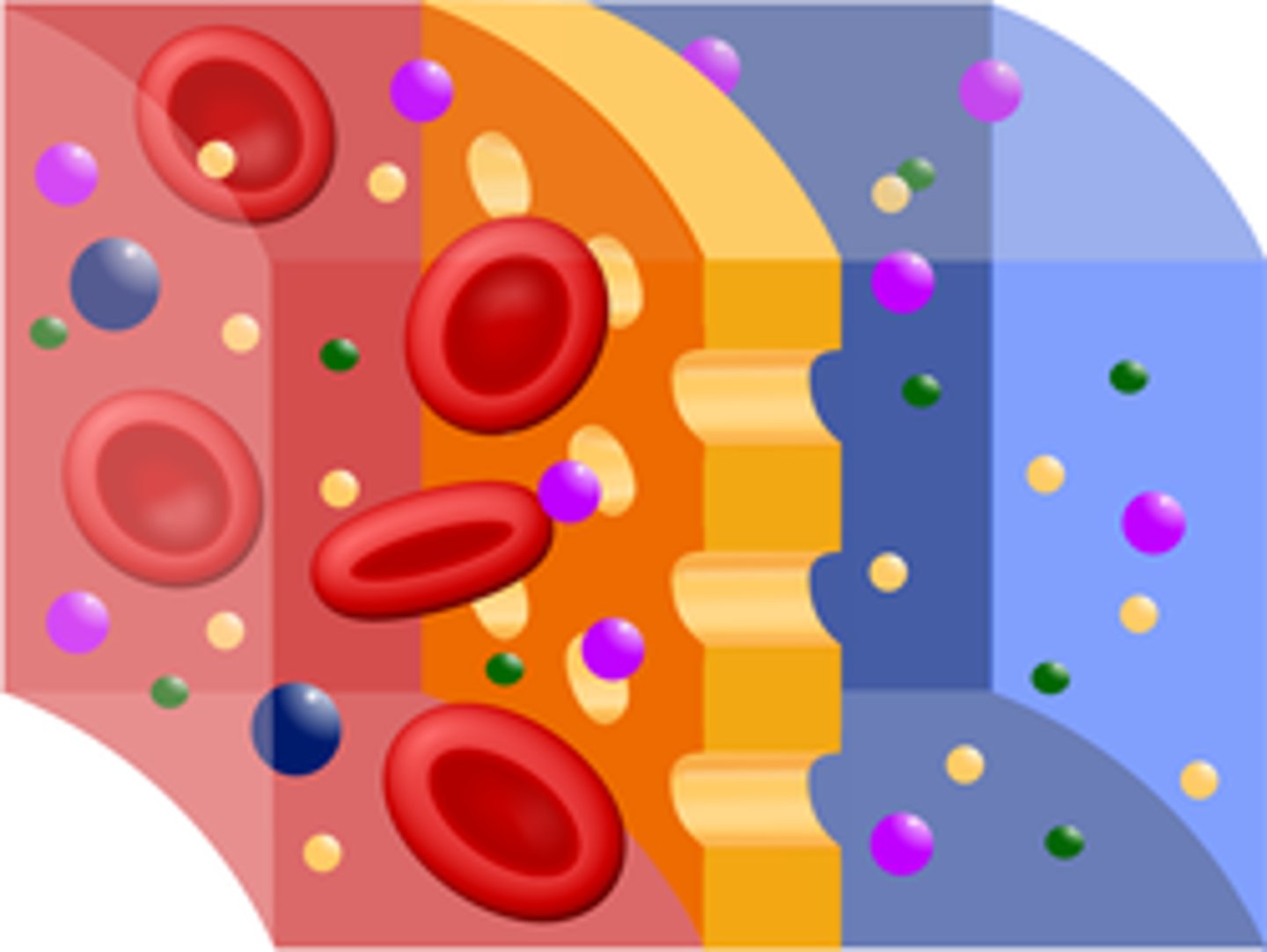
Selective permeability
A property of a plasma membrane that allows some substances to cross more easily than others.
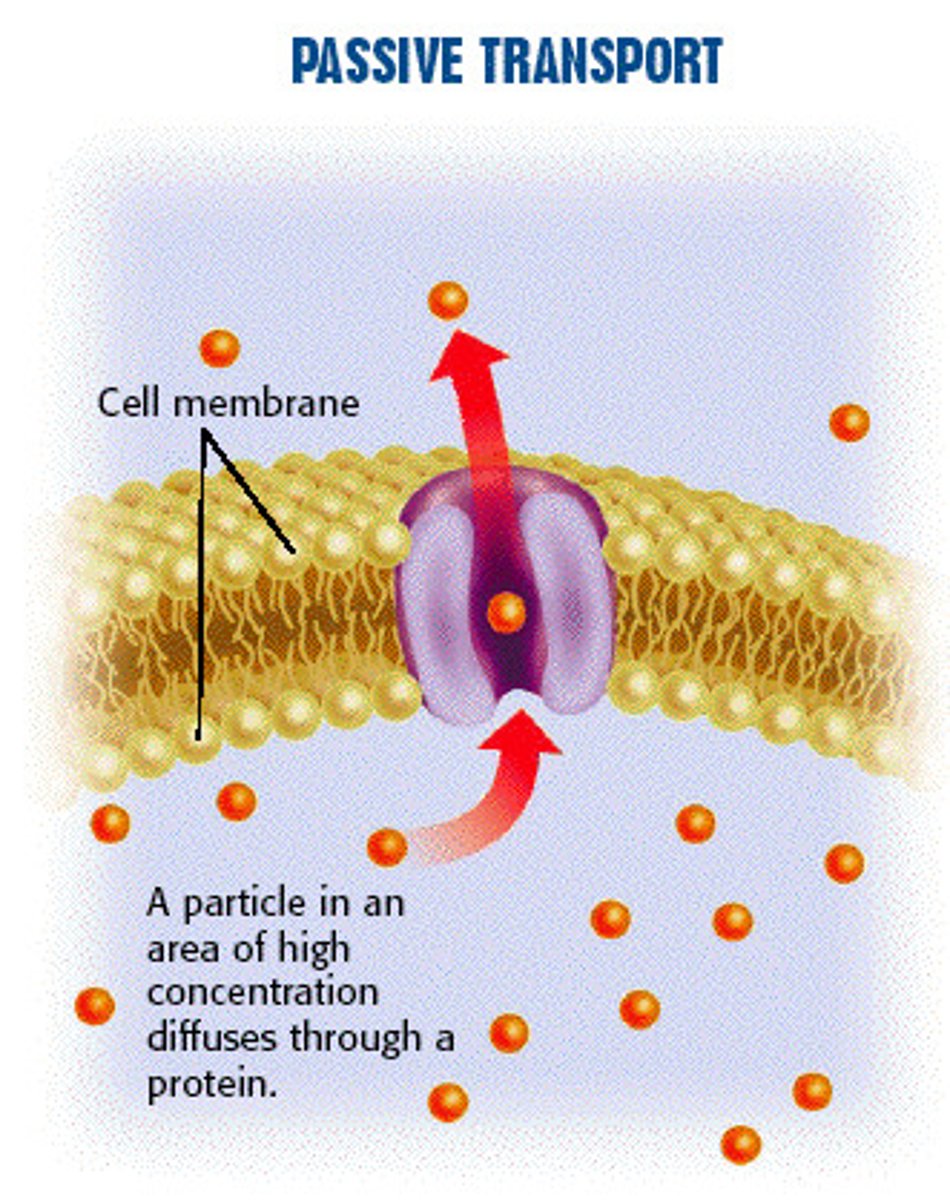
Passive transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell
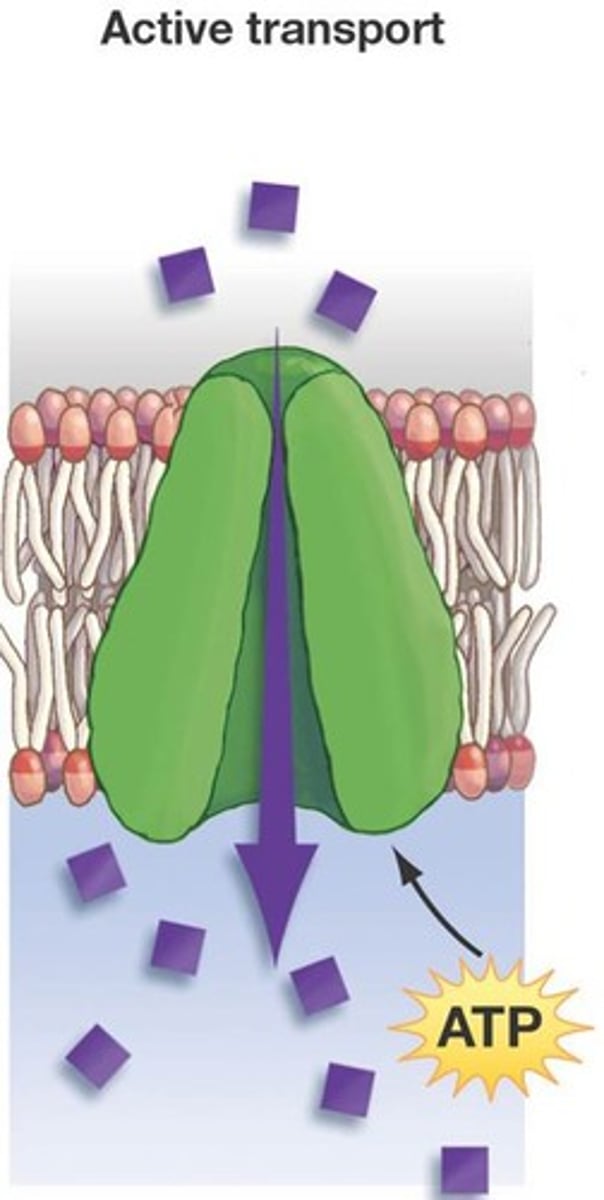
Active Transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
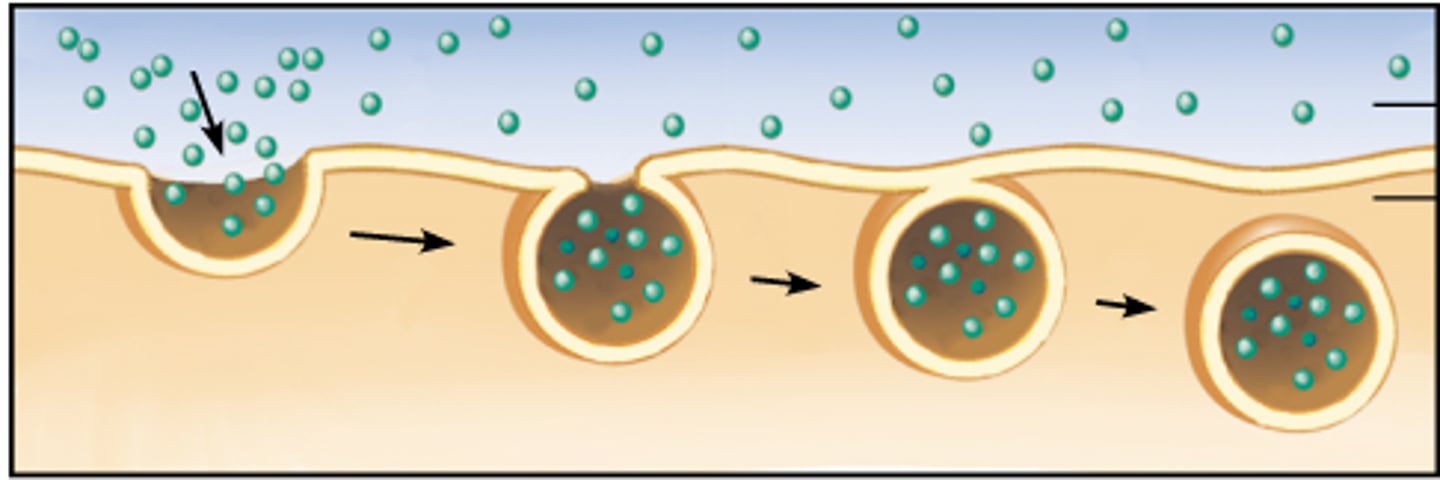
Endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
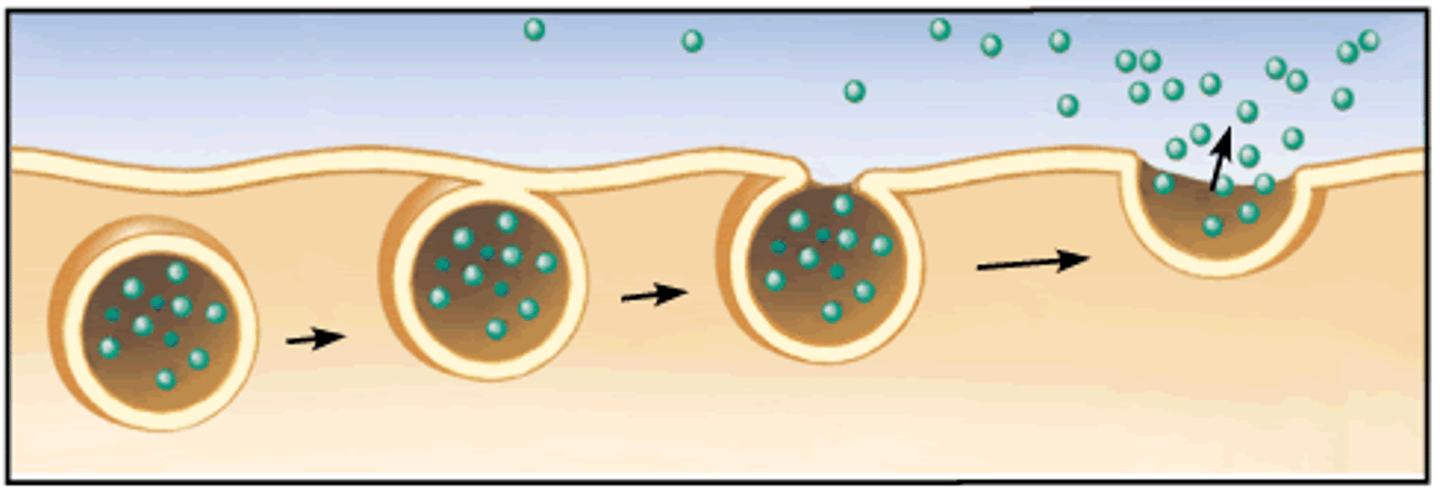
Exocytosis
Process by which a cell releases large amounts of material
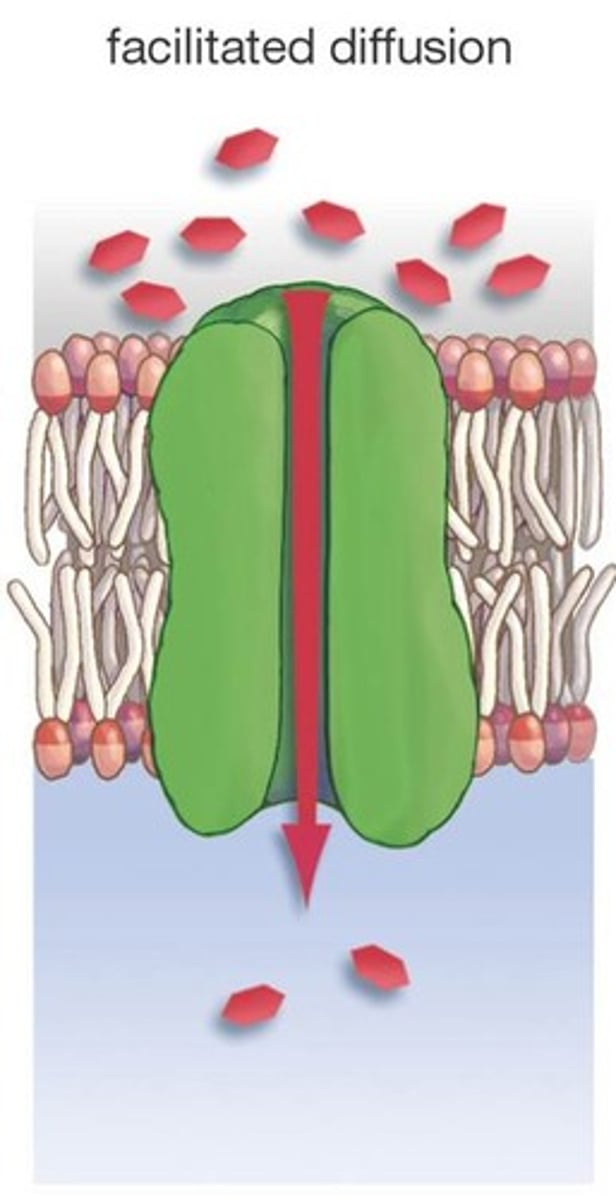
Facilitated Diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels
Channel proteins
provide corridors that allow a specific molecule or ion to cross the membrane
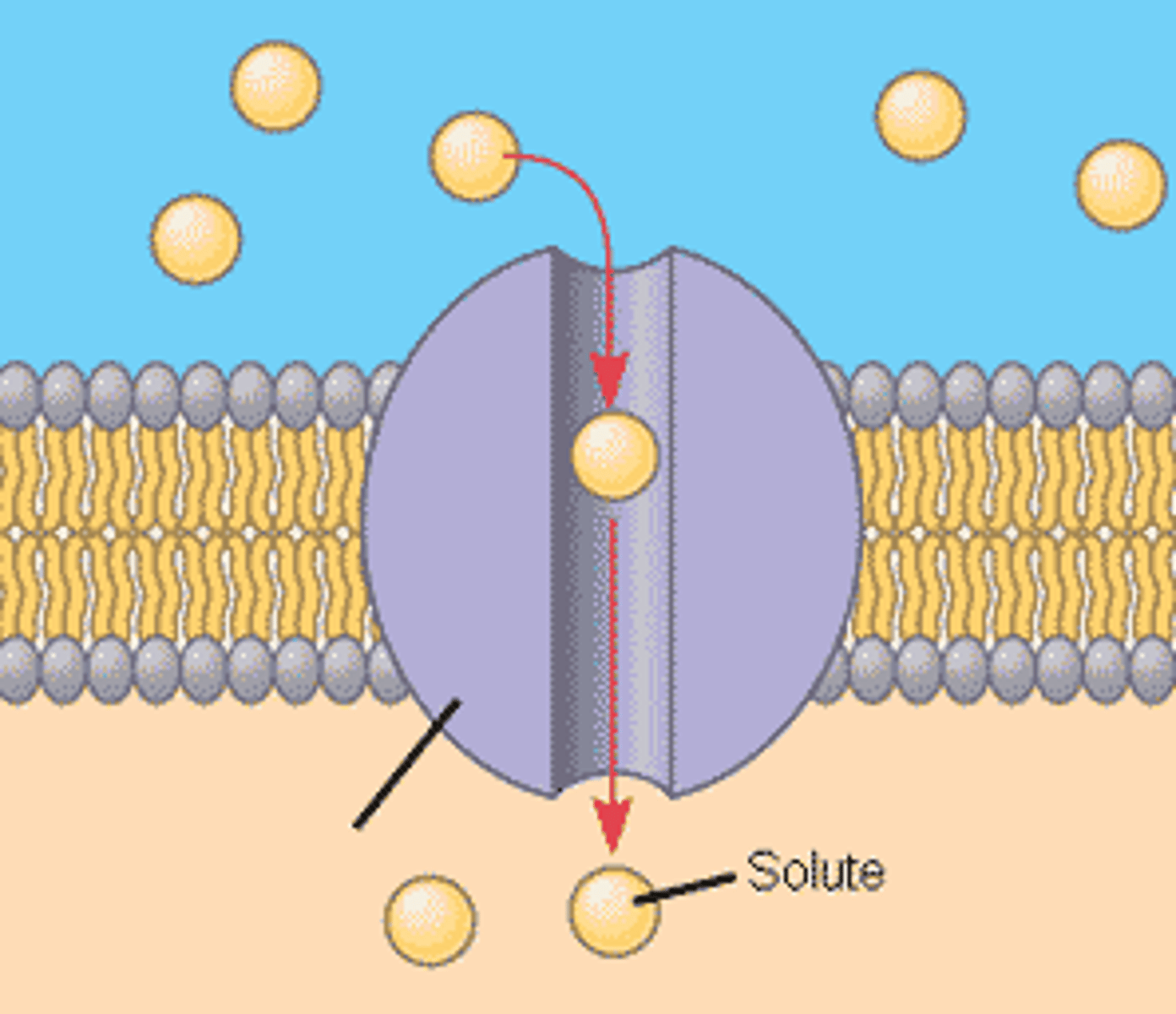
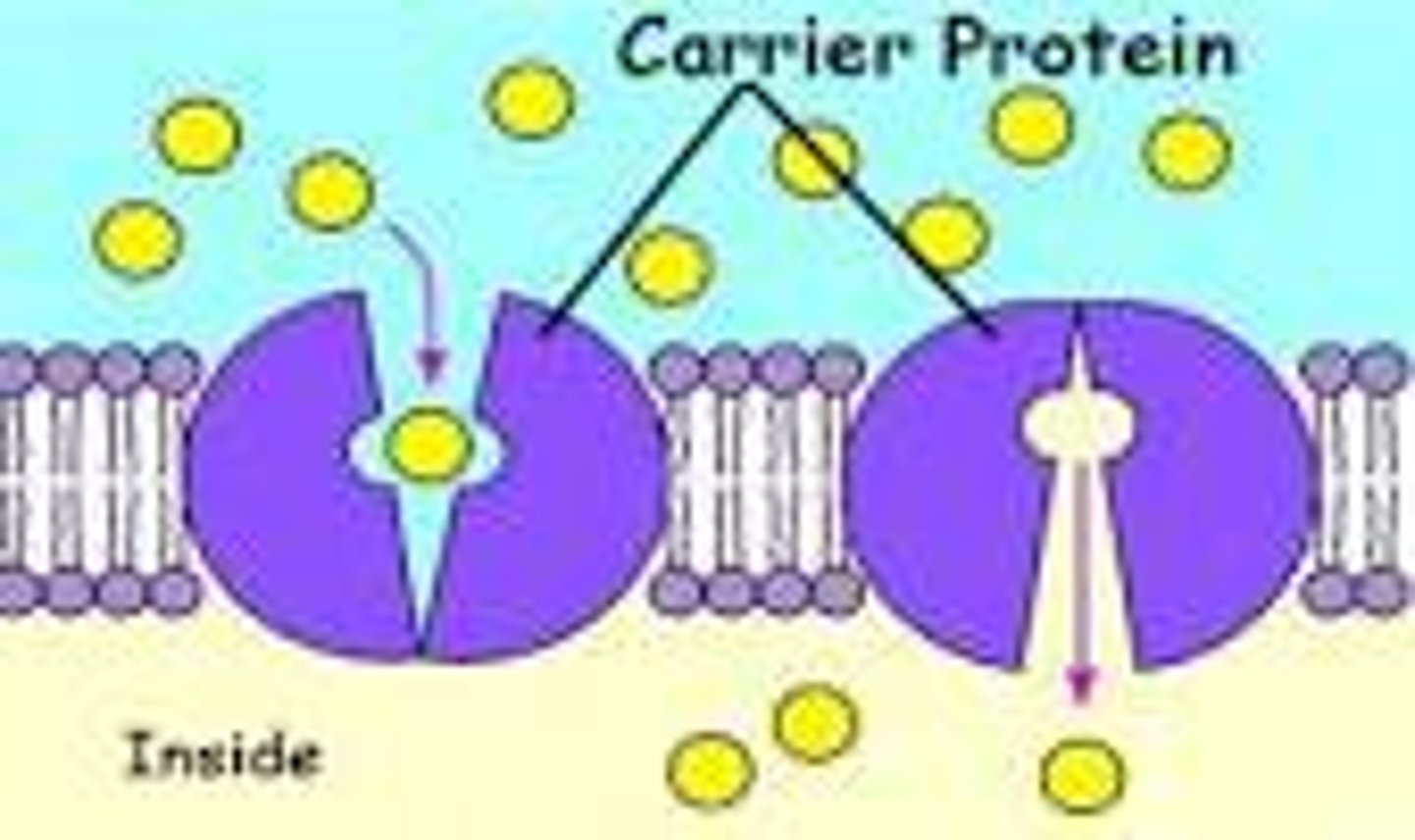
Carrier proteins
a protein that transports substances across a cell membrane
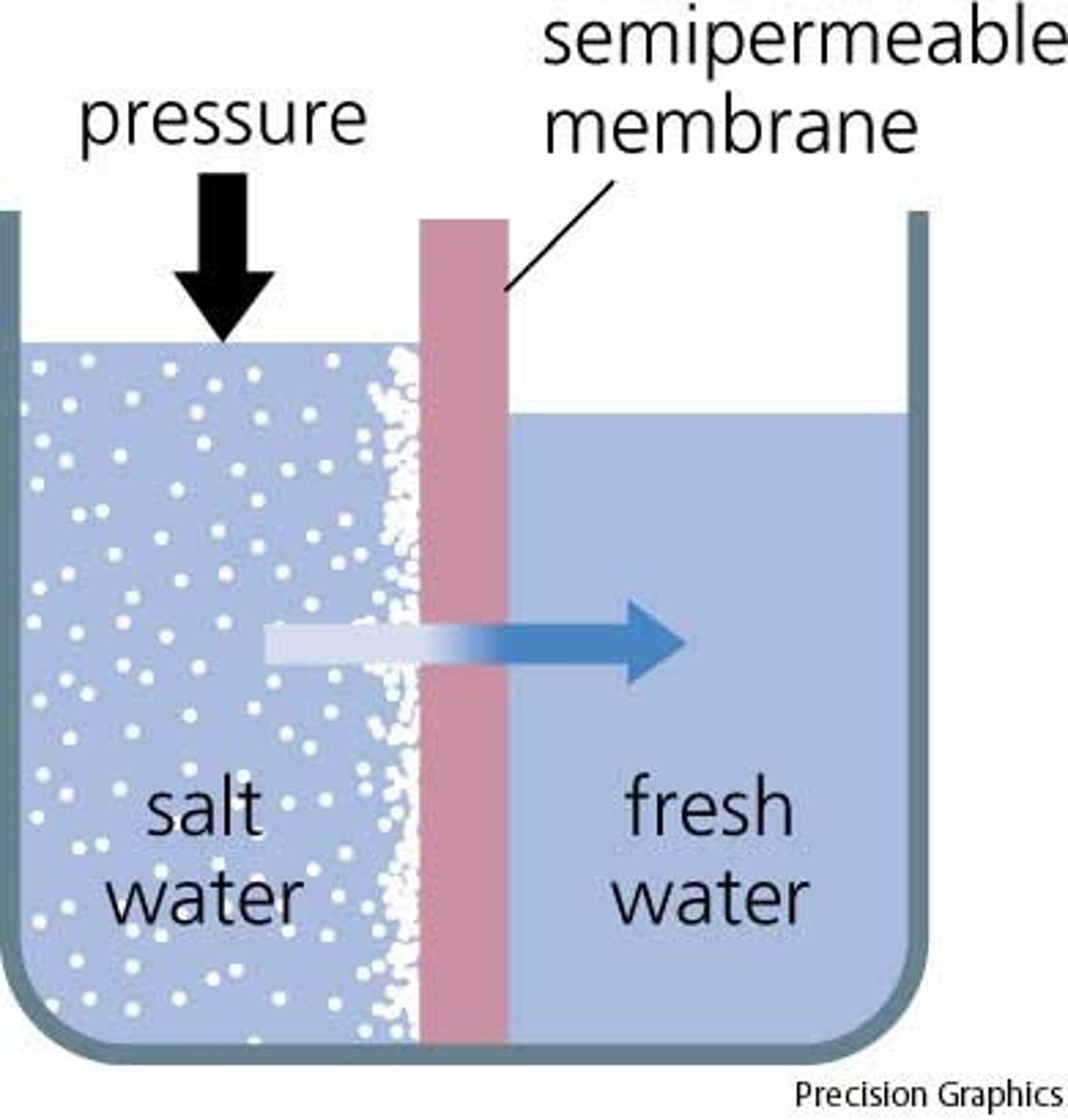
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane, from an area of high water potential (low solute concentration) to low water potential (high solute concentration)
Tonicity
the ability of a surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water
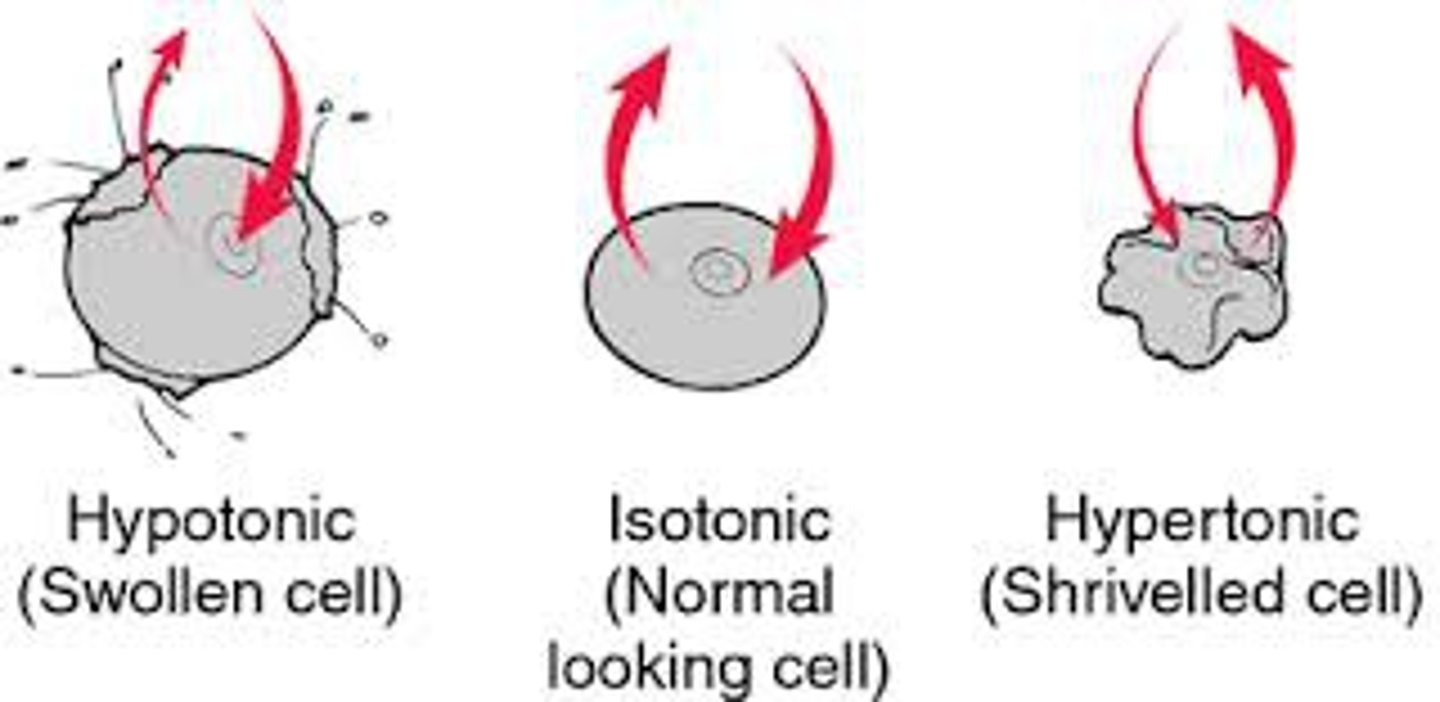
Hypotonic
lower solute concentration than cell, water moves into cell and causes to swell (excessive swelling can lead to lysis in animal cells)
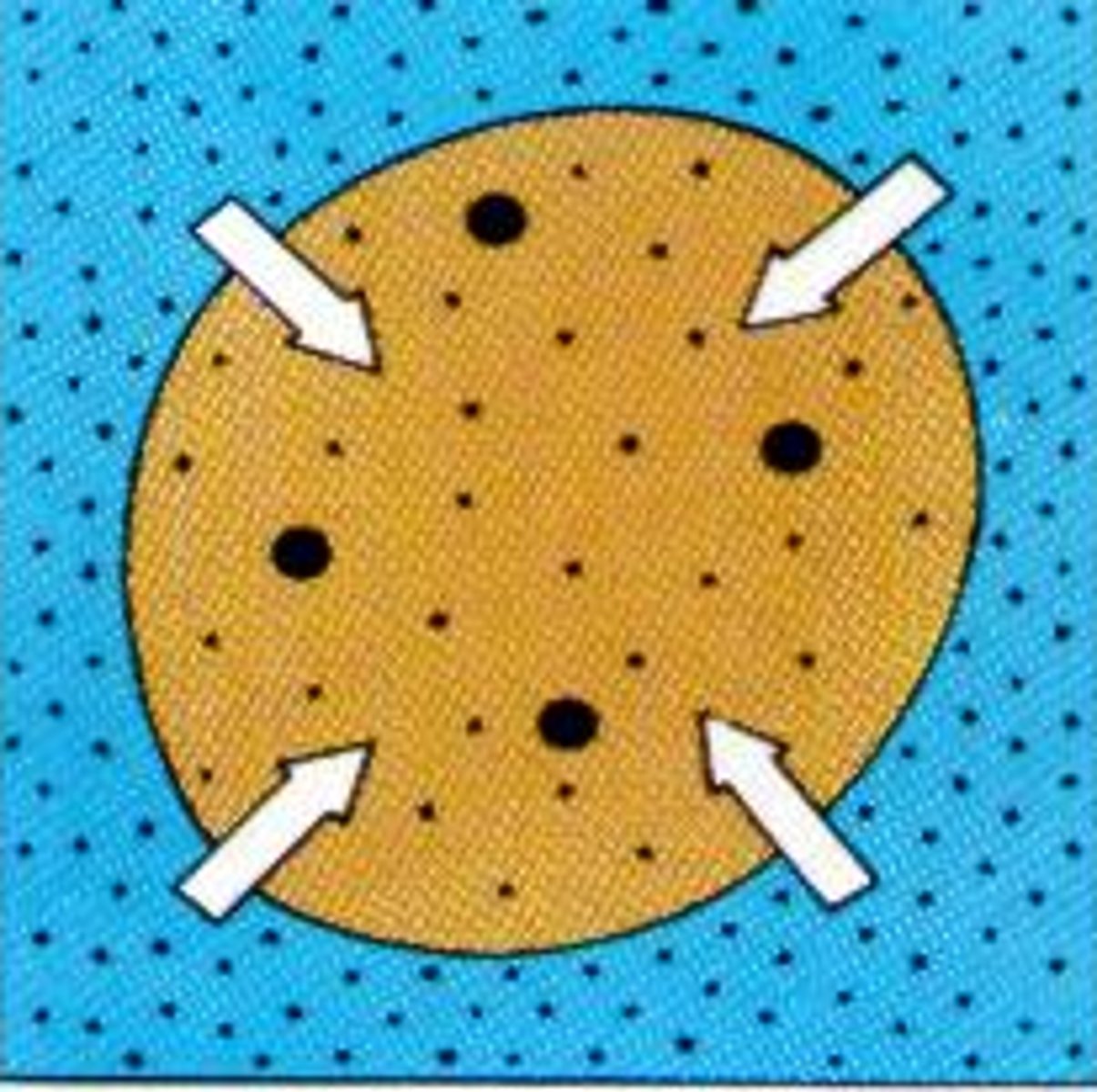
Hypertonic
higher solute concentration than cell leads to cell shrink because of loss of water (leads to plasmolysis in plant cells)
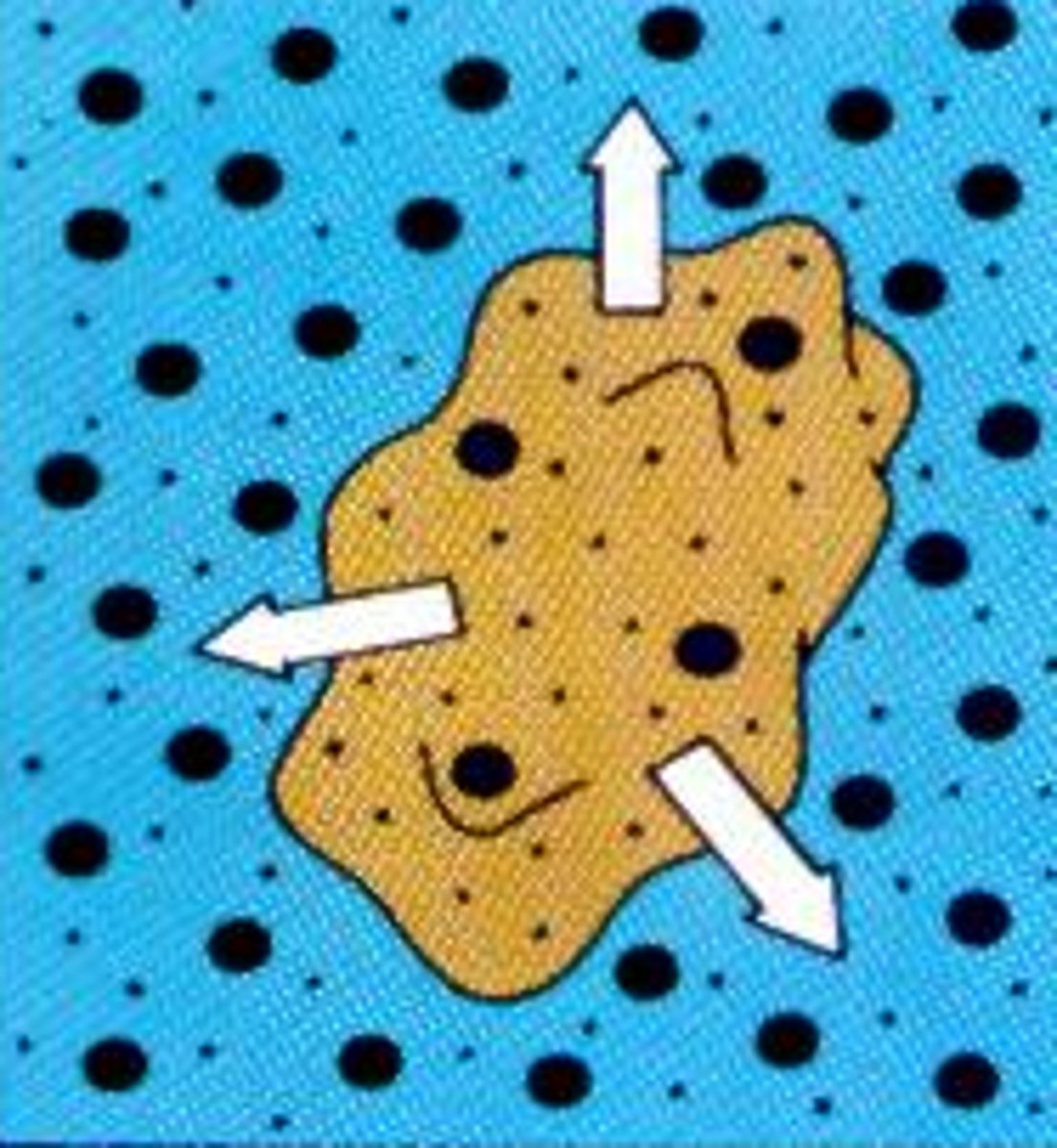

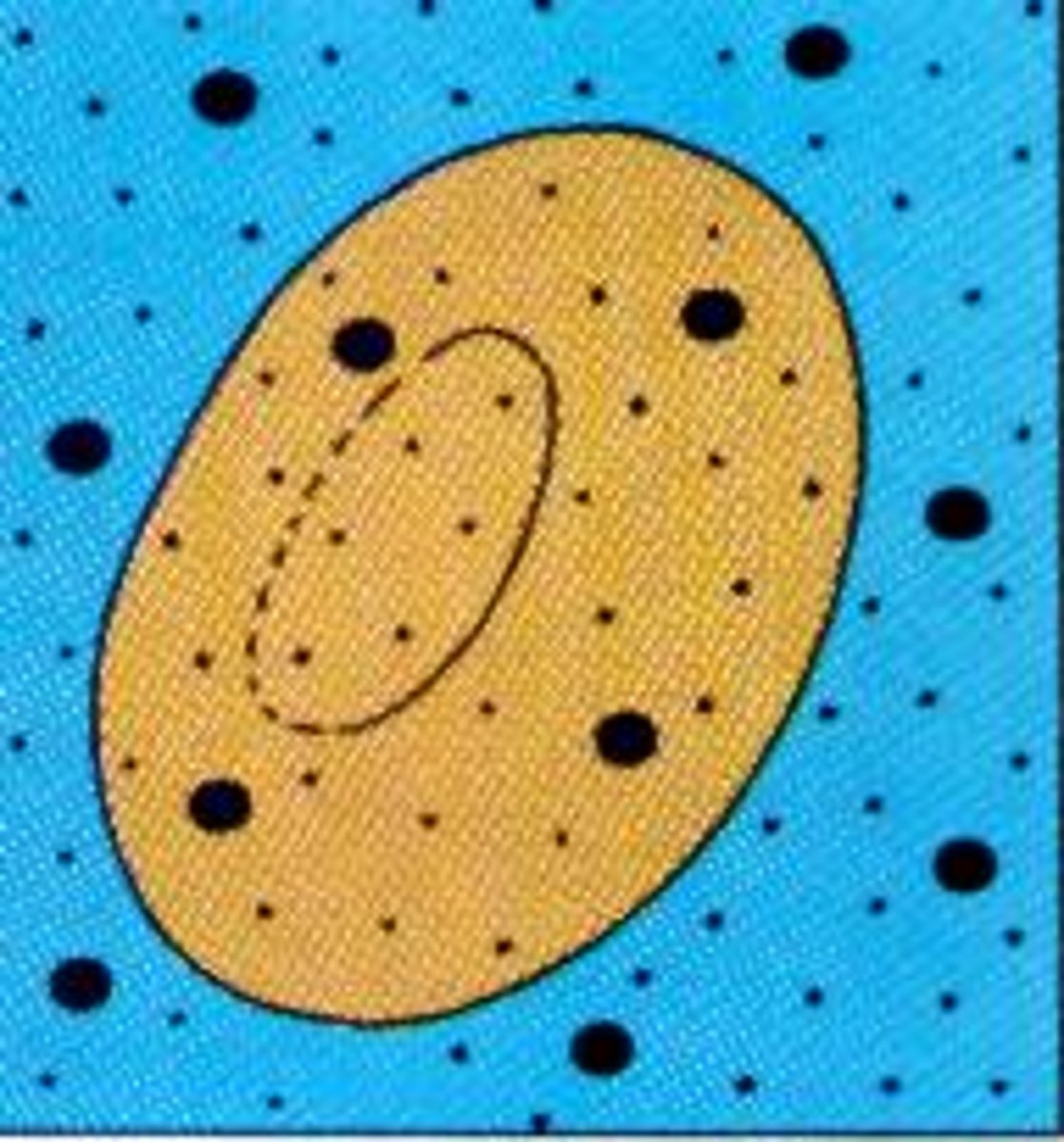
Isotonic
when the concentration of two solutions is the same
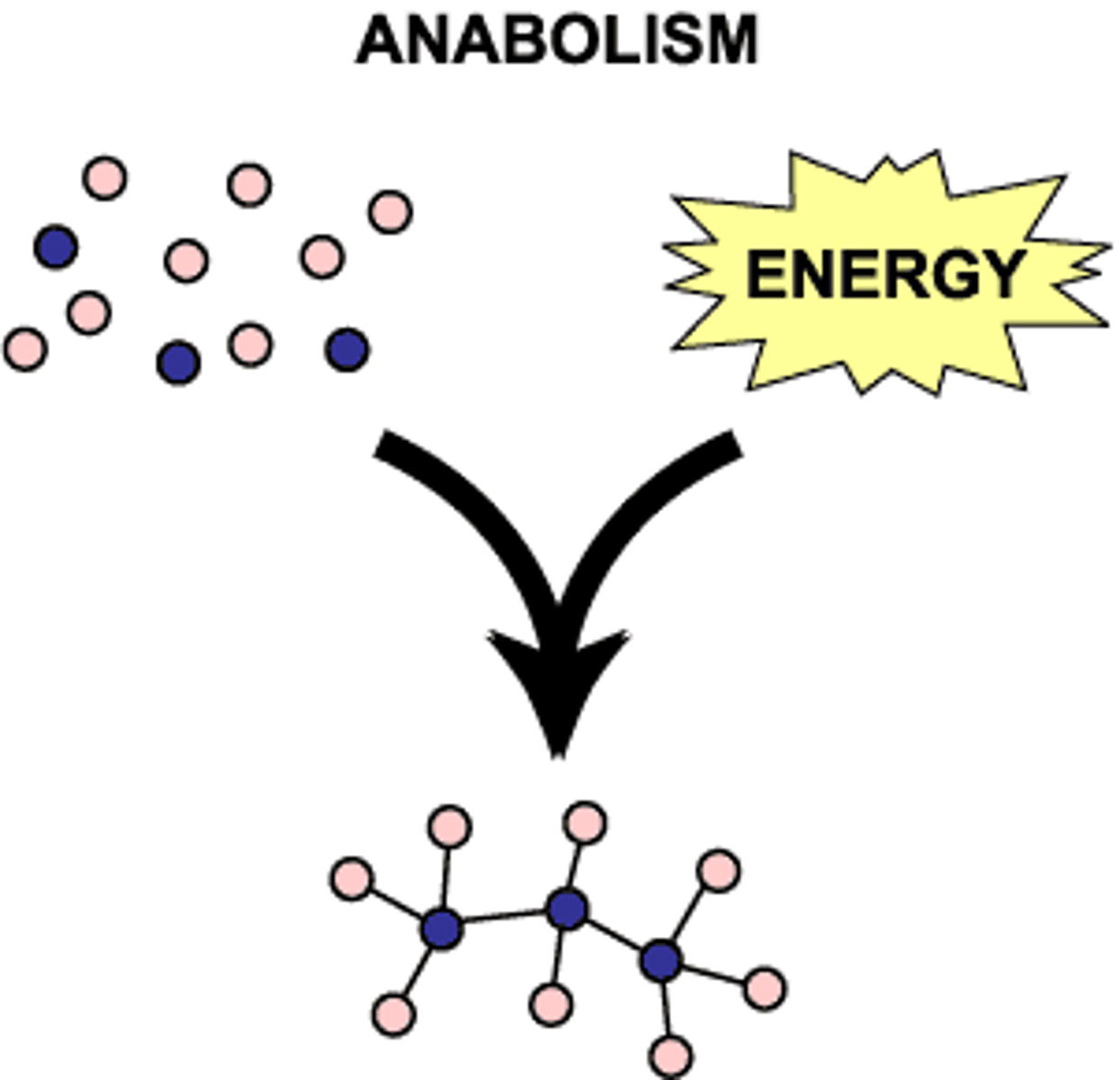
Anabolism
Metabolic pathways that construct molecules, requiring energy.
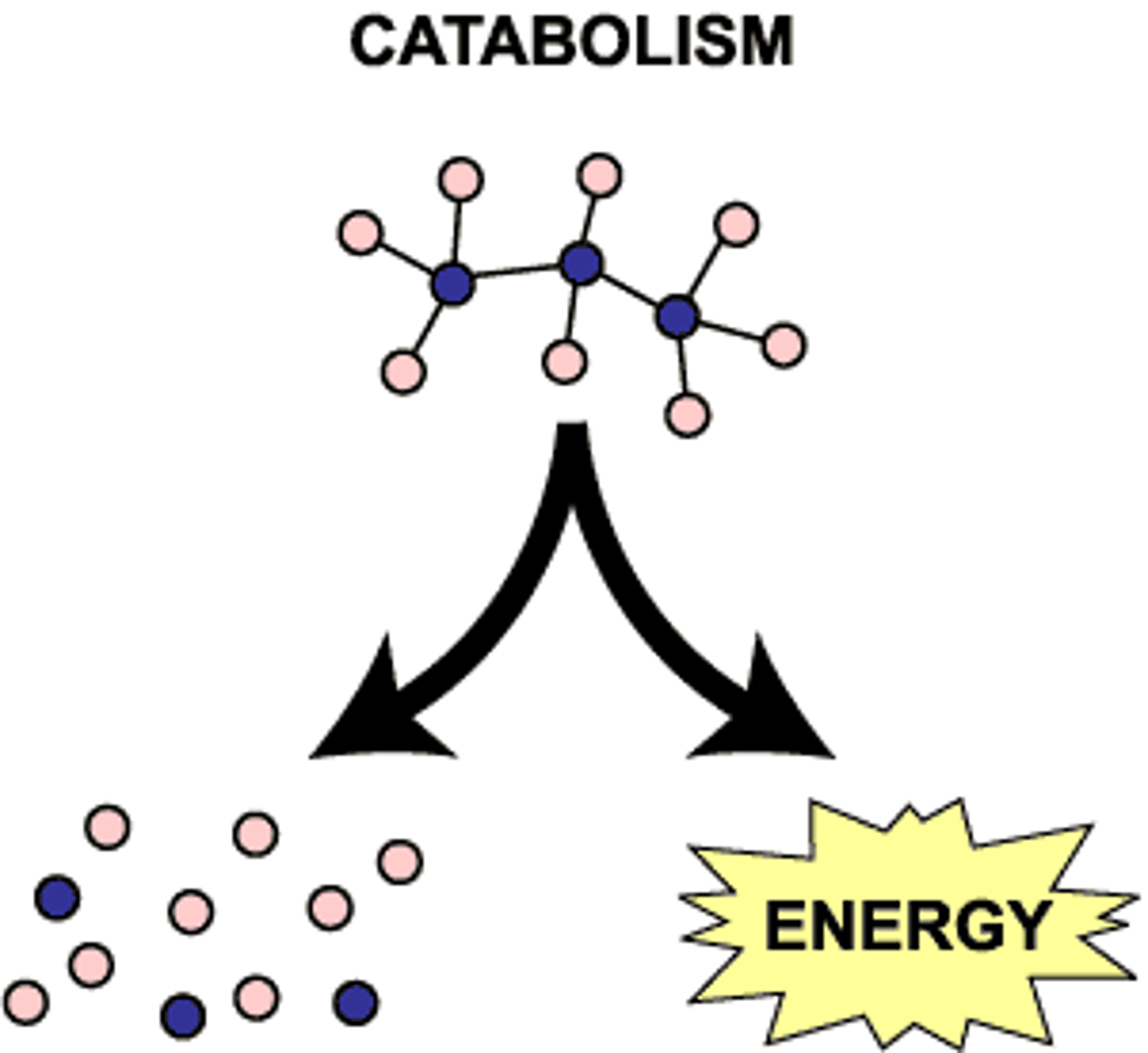
Catabolism
Metabolic pathways that break down molecules, releasing energy.
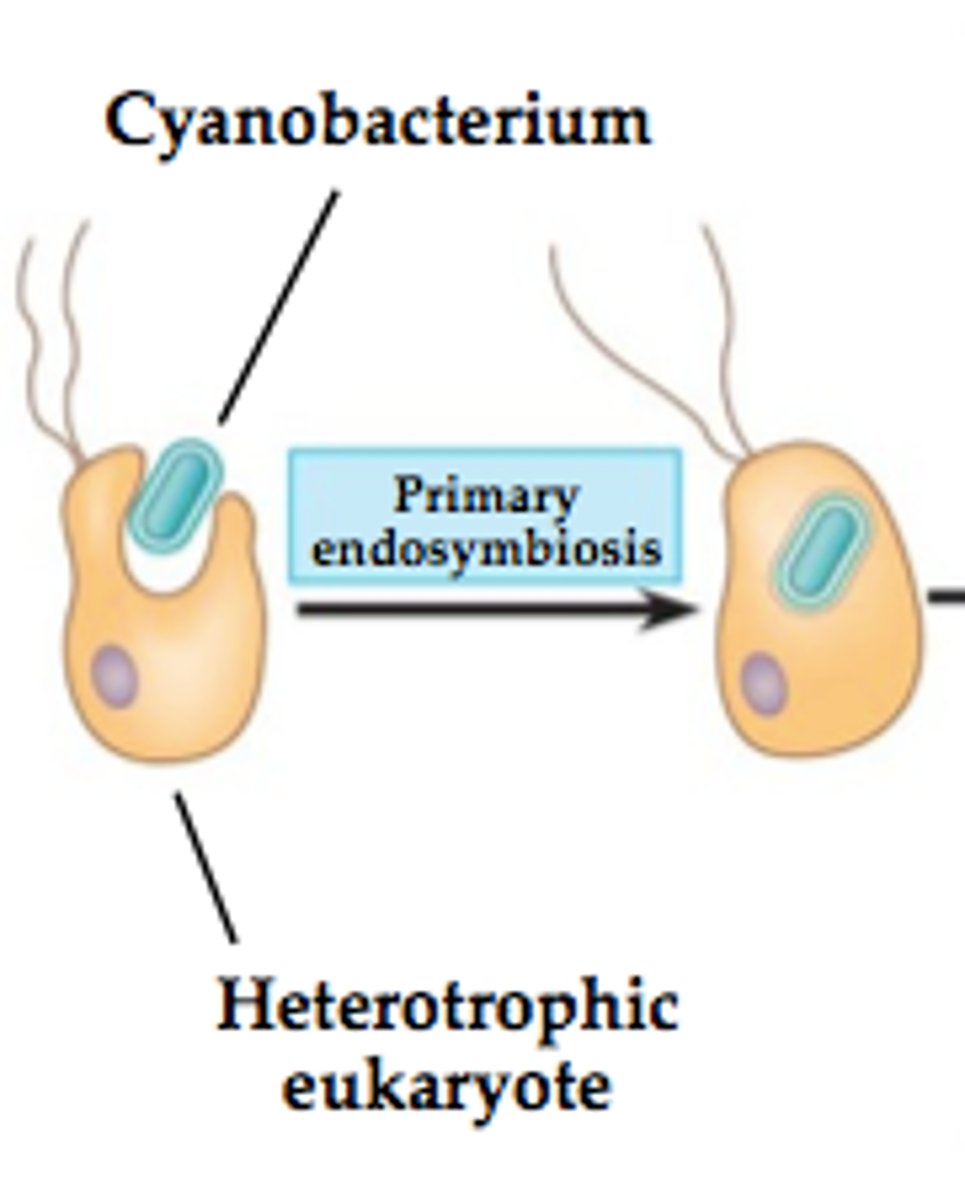
Endosymbiotic Theory
theory that eukaryotic cells formed from a symbiosis among several different prokaryotic organisms
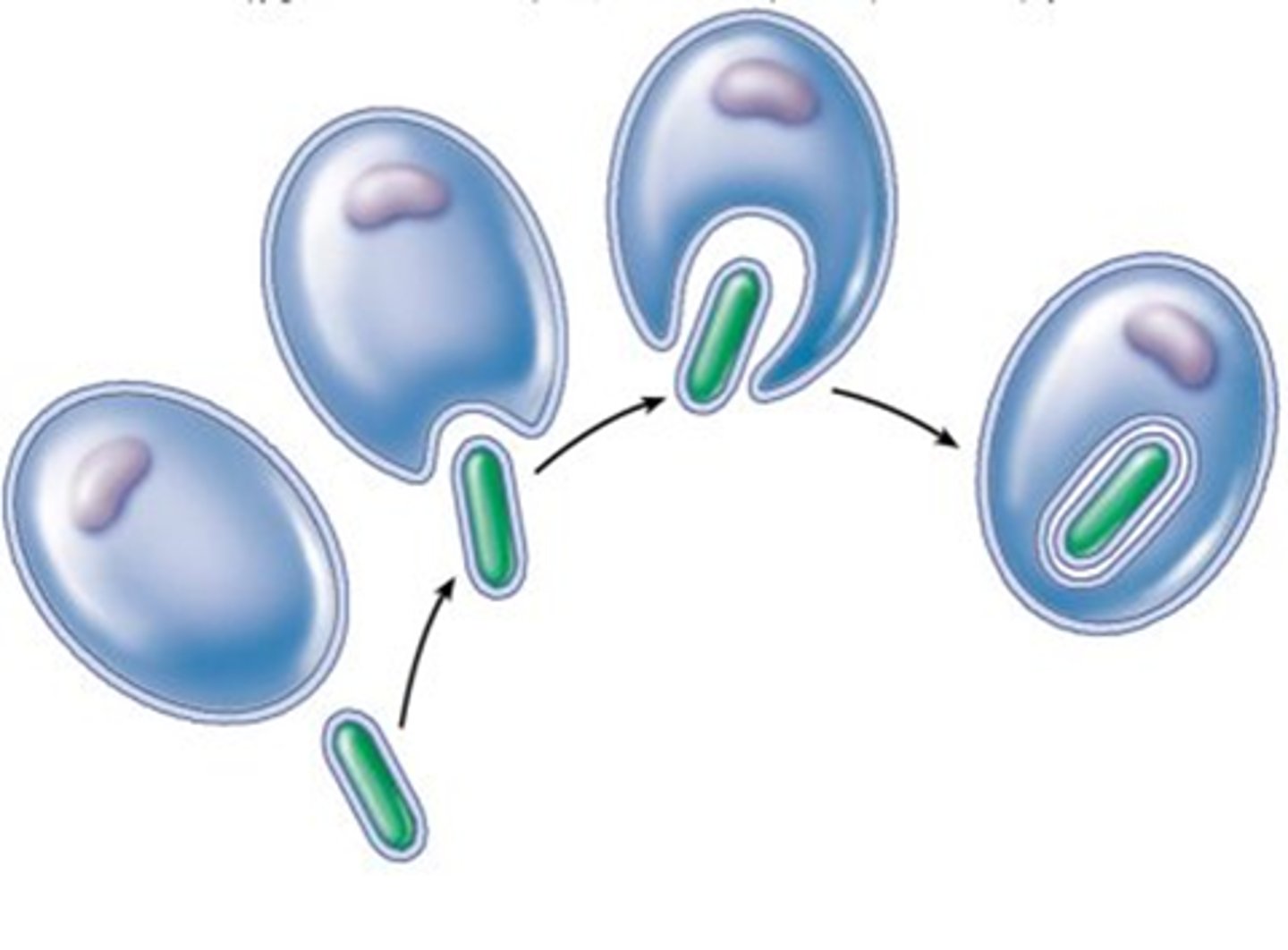
Endosymbiosis
A theorized process in which early eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes.
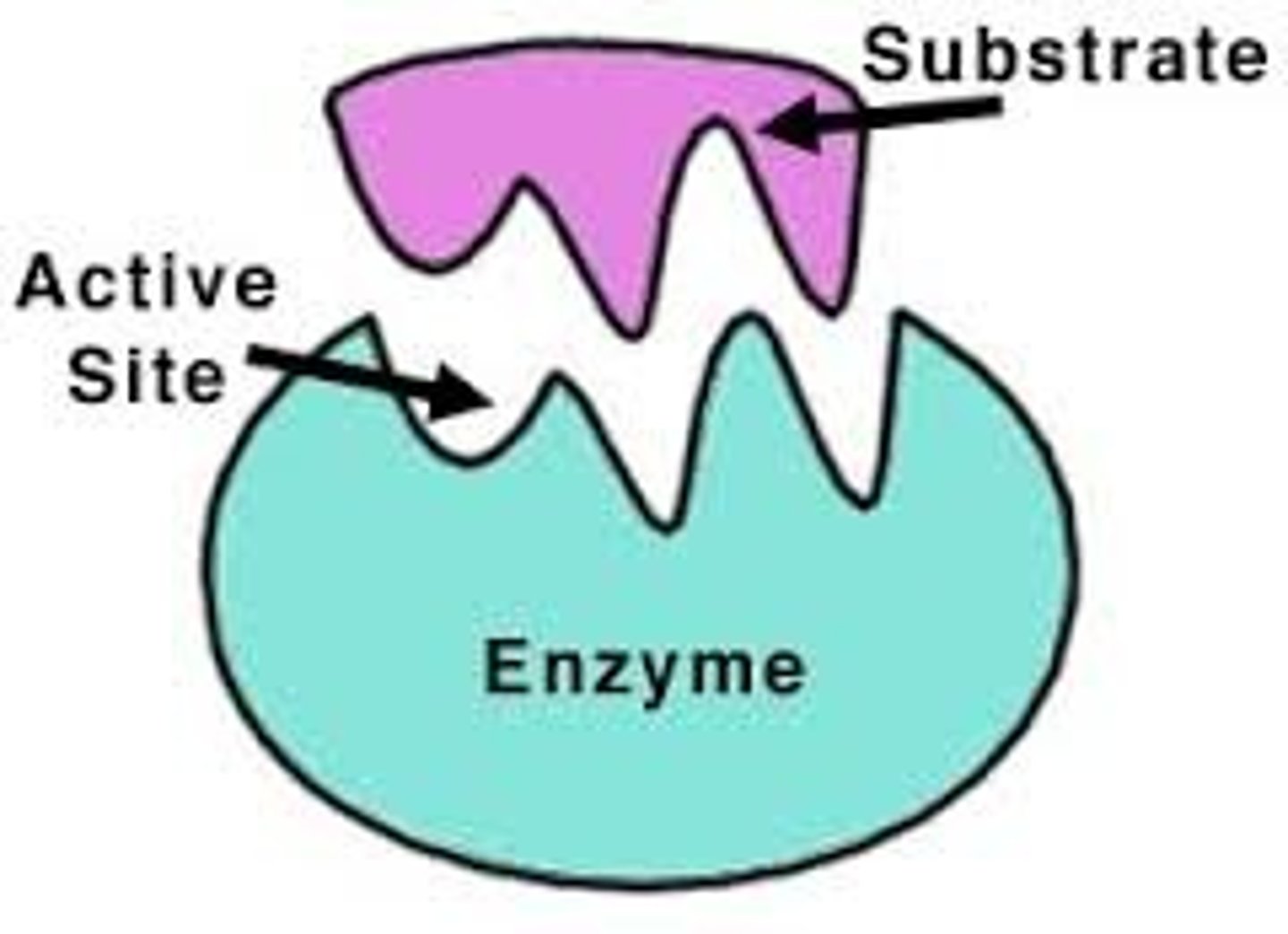
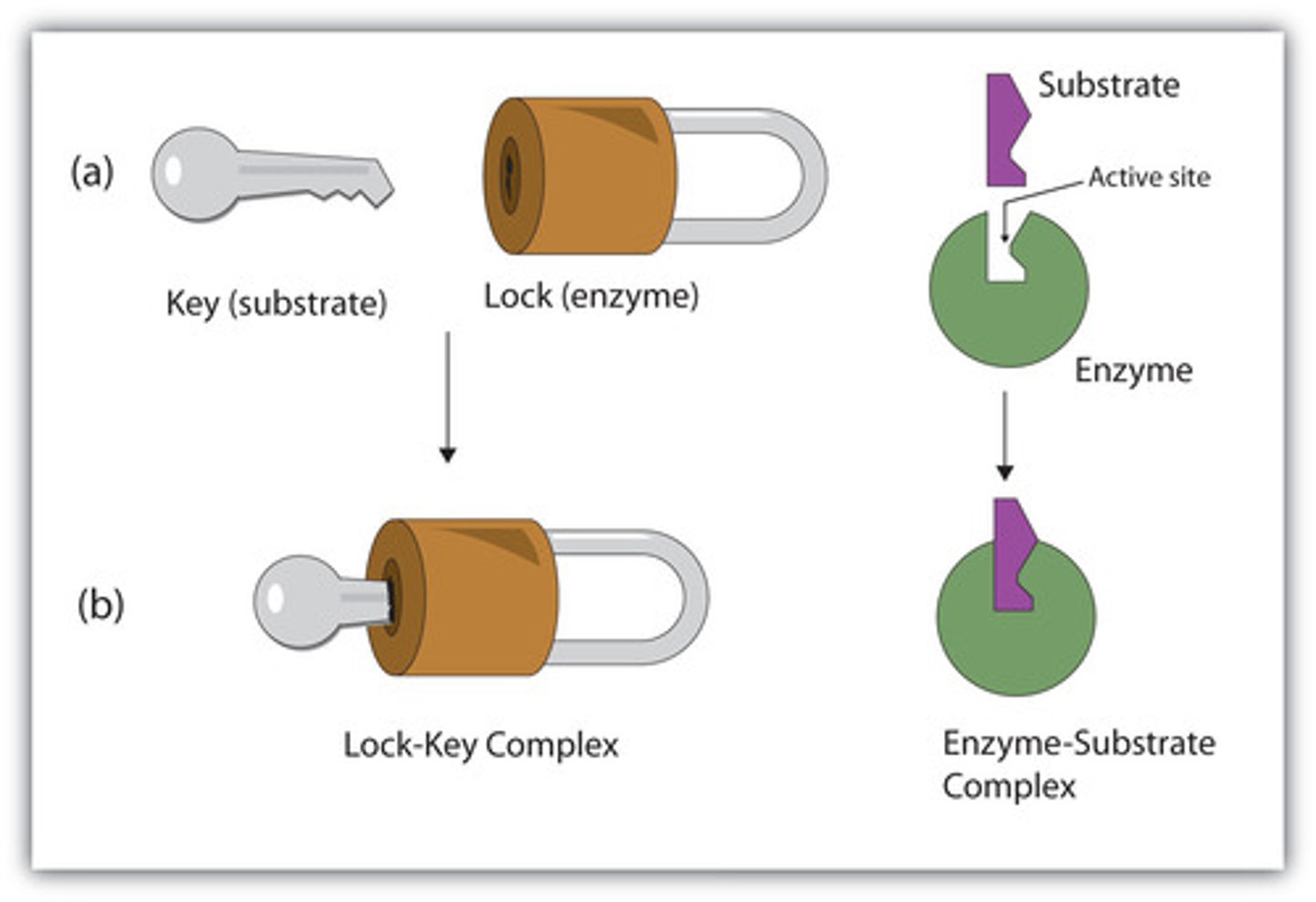
Enzyme
A type of protein that speeds up a chemical reaction in a living thing (catalyst)
Specificity
Choosing the right types of activities to improve a given element of fitness
Primary Structure
sequence of amino acids
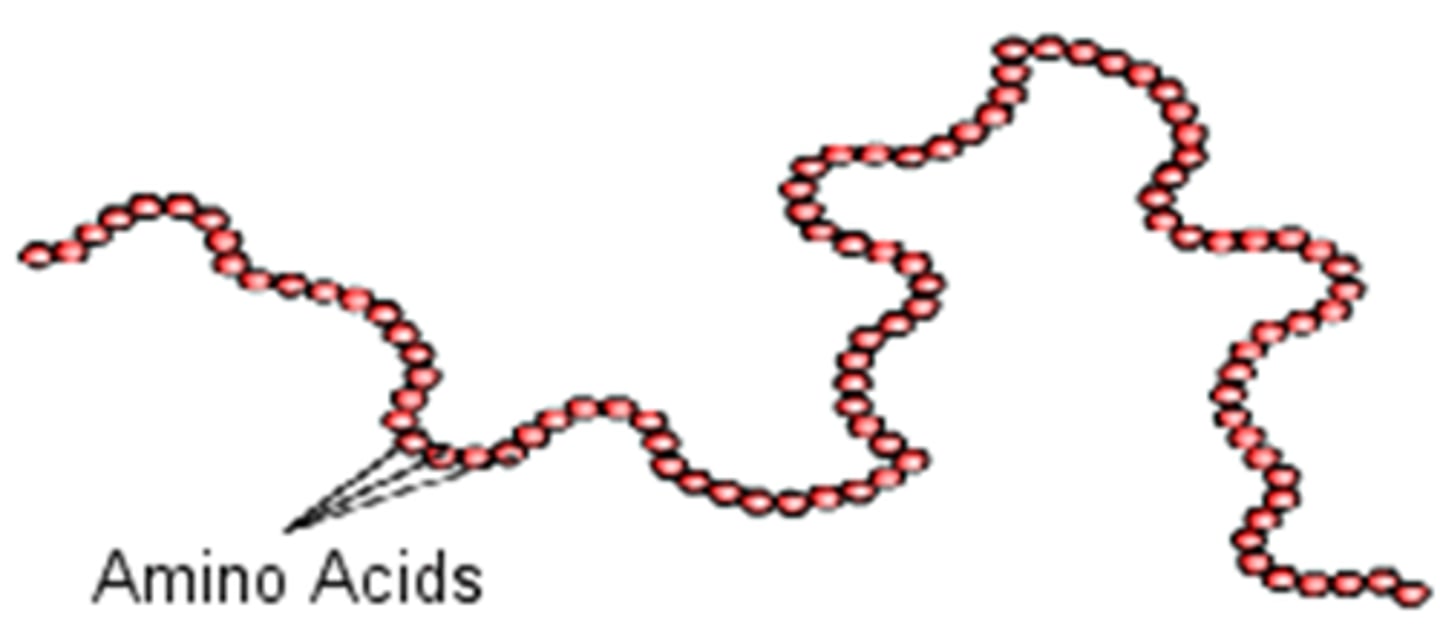

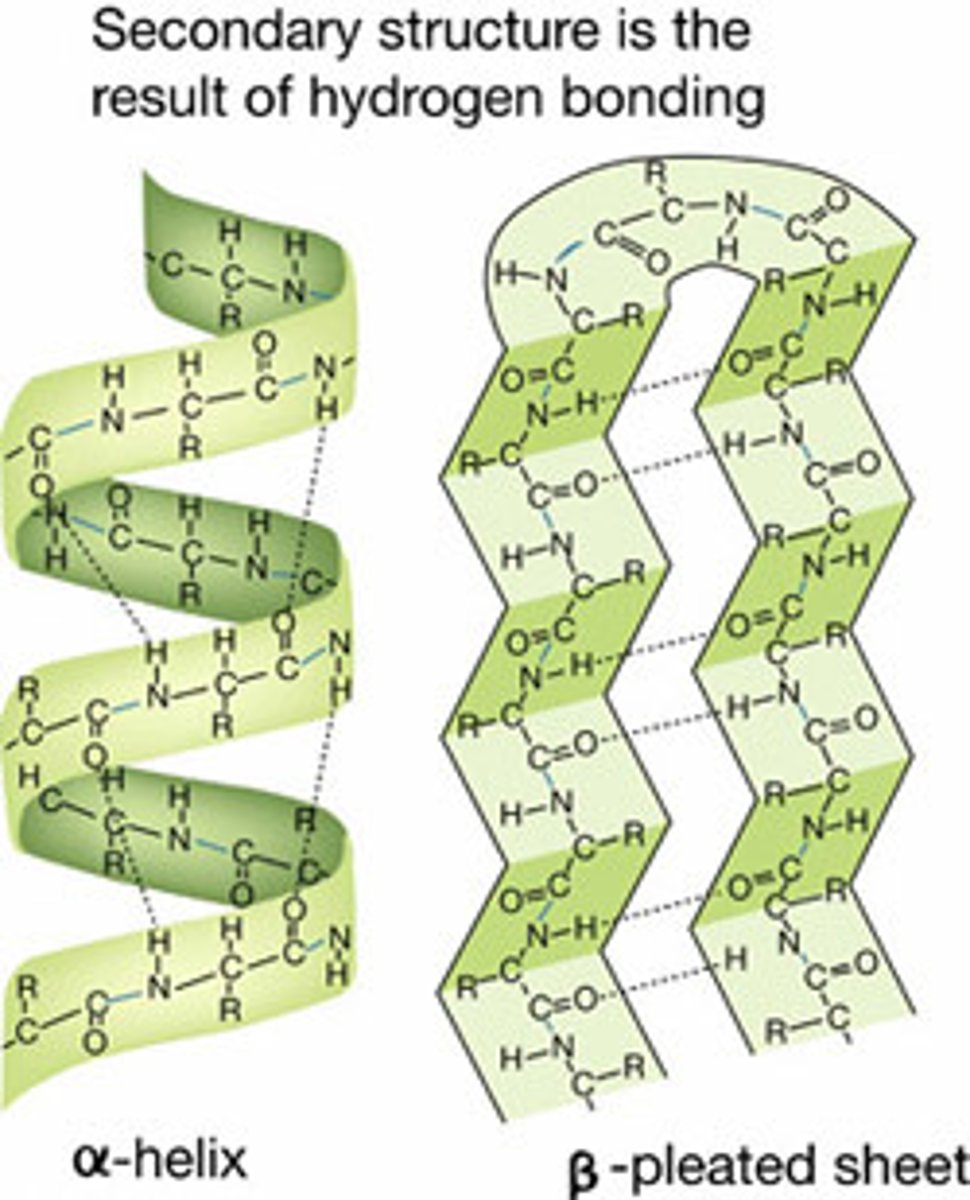
Secondary Structure
The regular local patterns of coils or folds of a polypeptide chain.
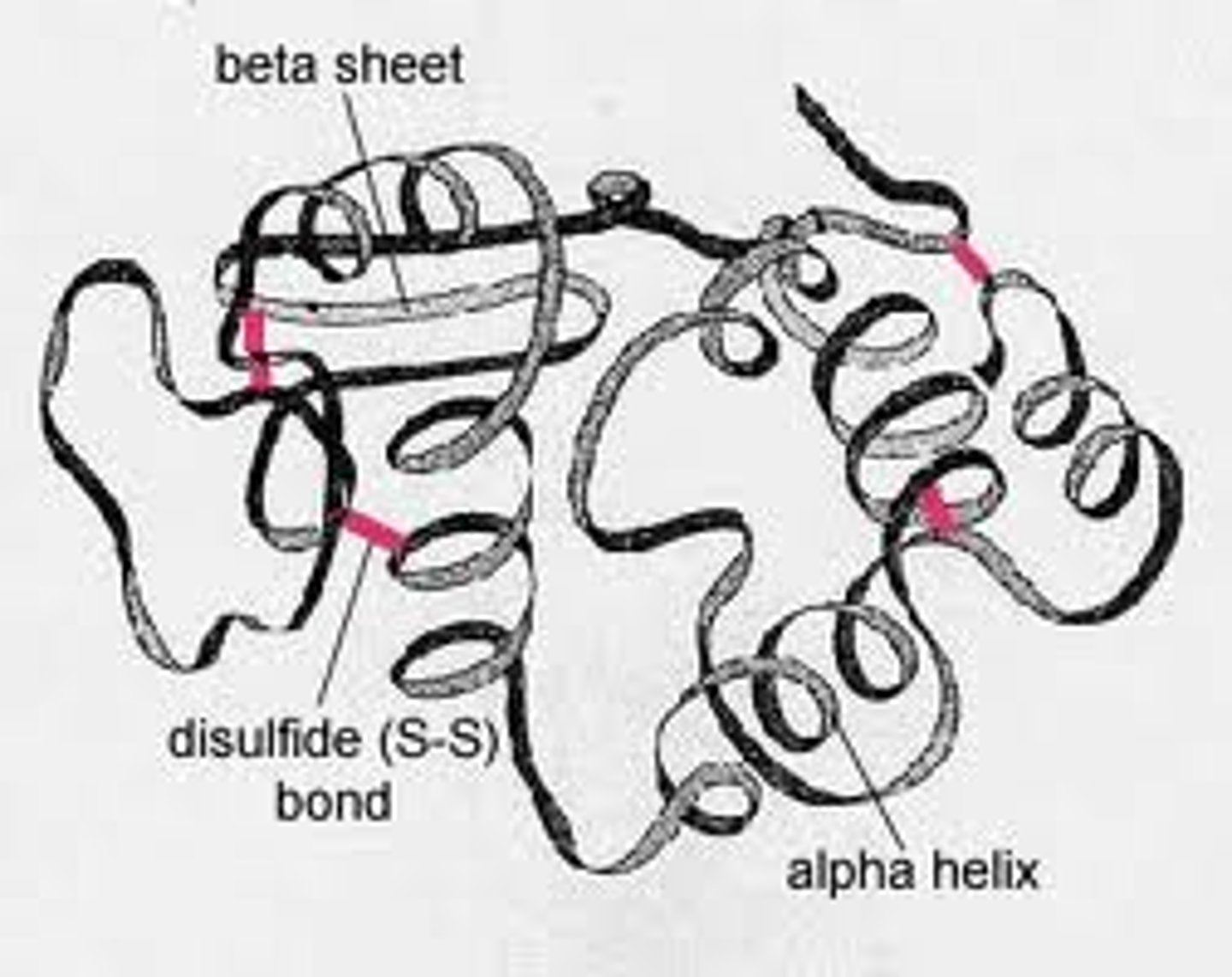
Tertiary Structure
Three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain.
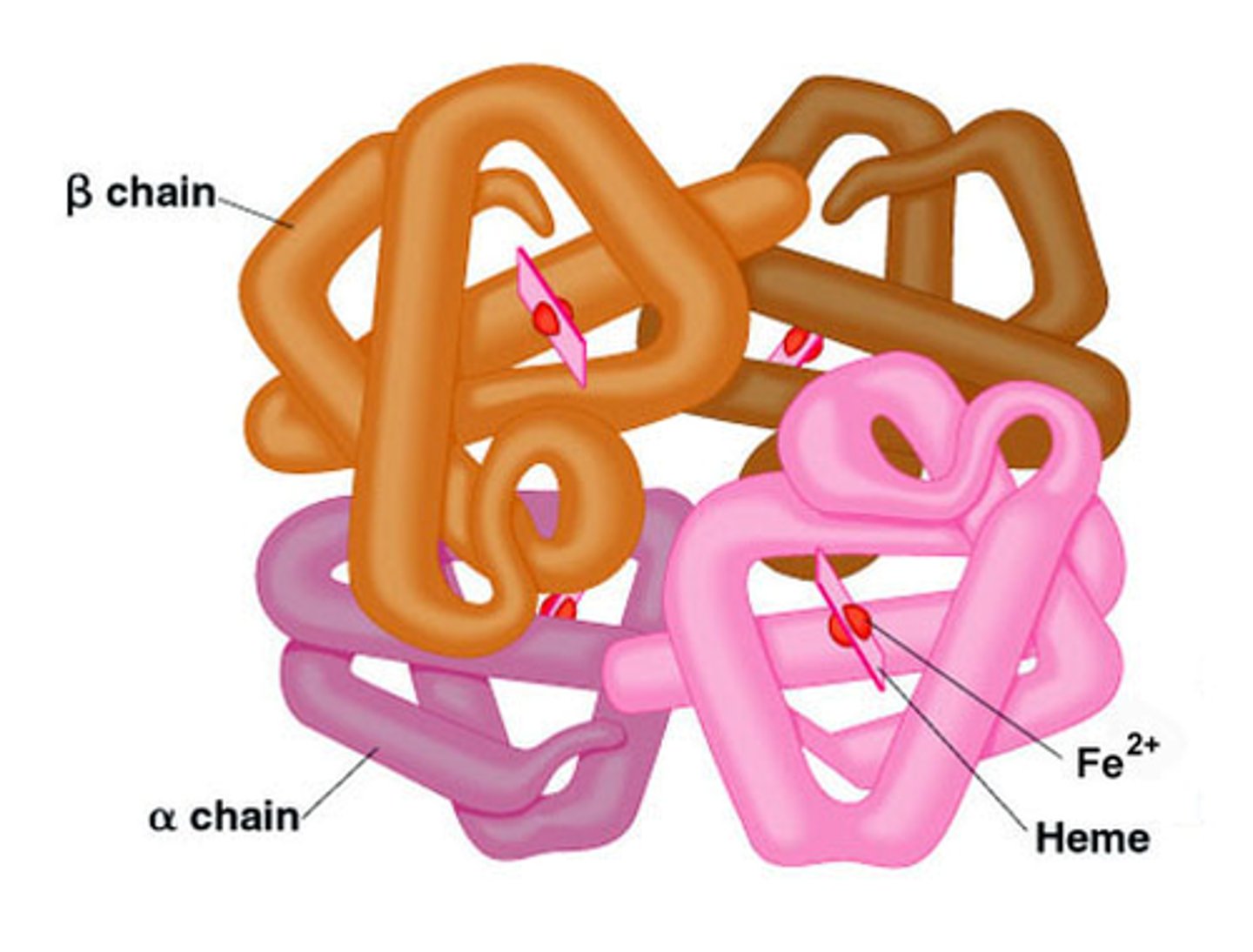
Quaternary Structure
The shape resulting from the association of two or more polypeptide subunits.
Catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction (enzyme) by lowering activation energy

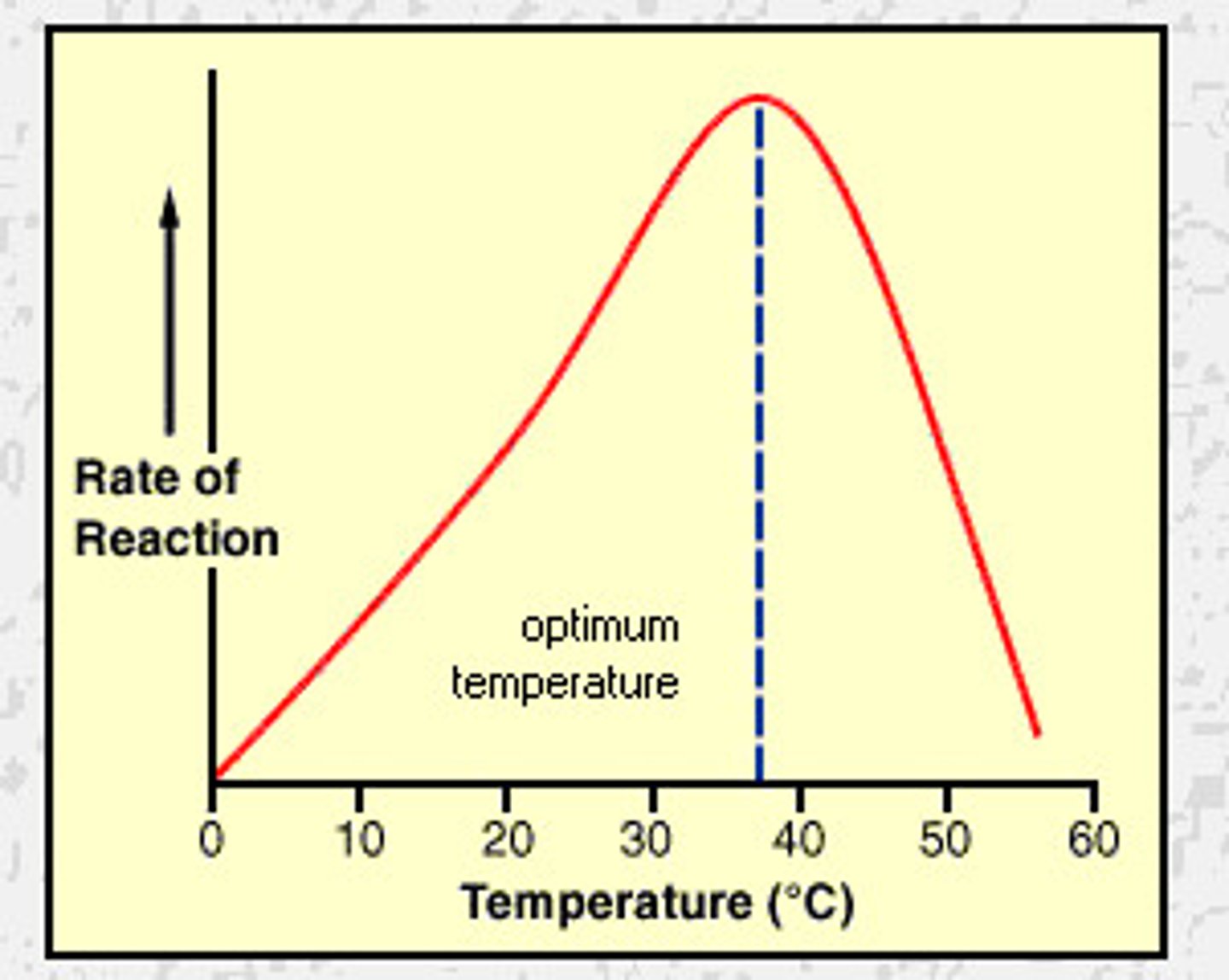
Factors affecting enzymes
enzyme concentration; substrate concentration; temperatures ;pH
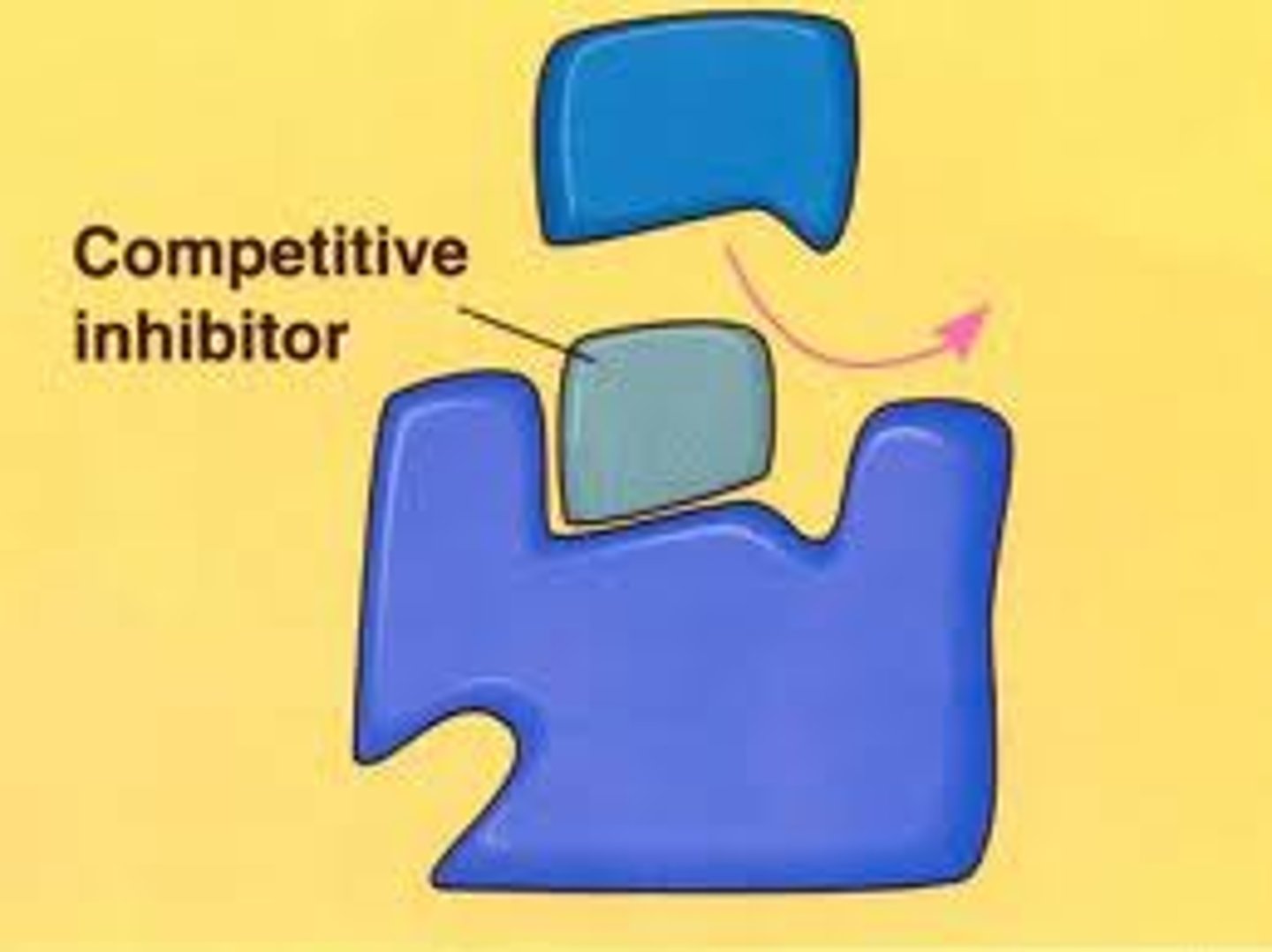
Inhibitor
A substance that slows down or stops a chemical reaction

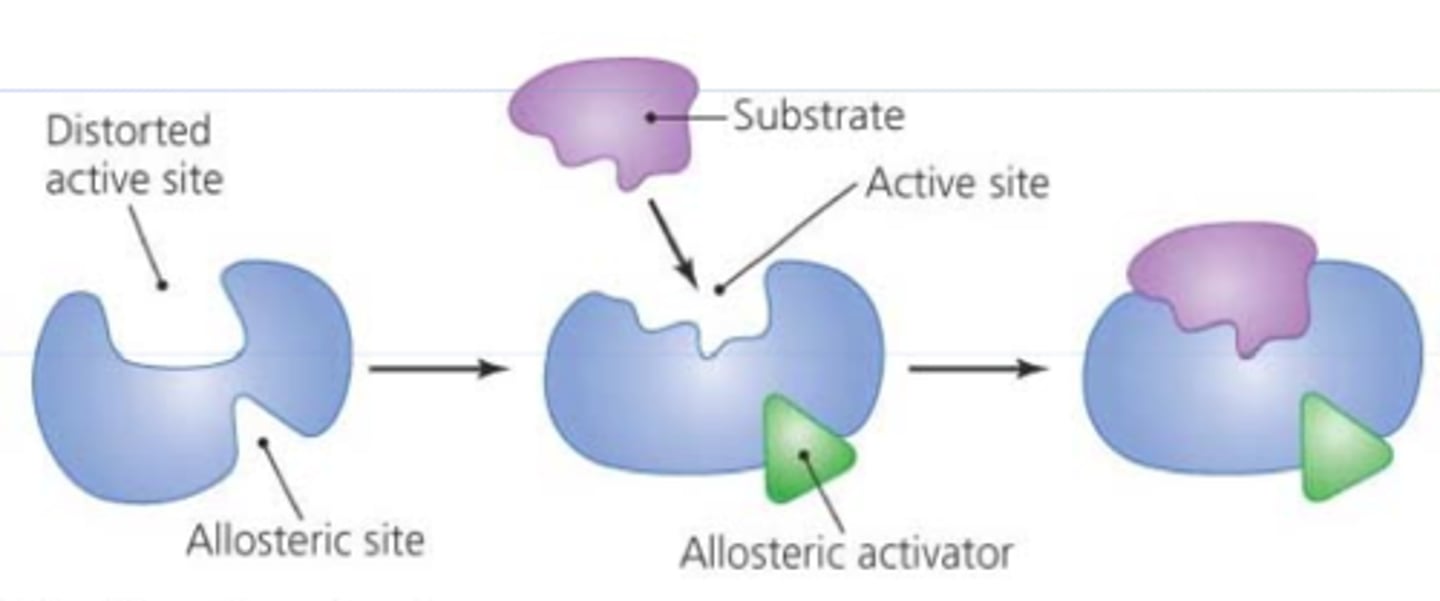
Activator
A protein that binds to DNA and stimulates transcription of a specific gene.
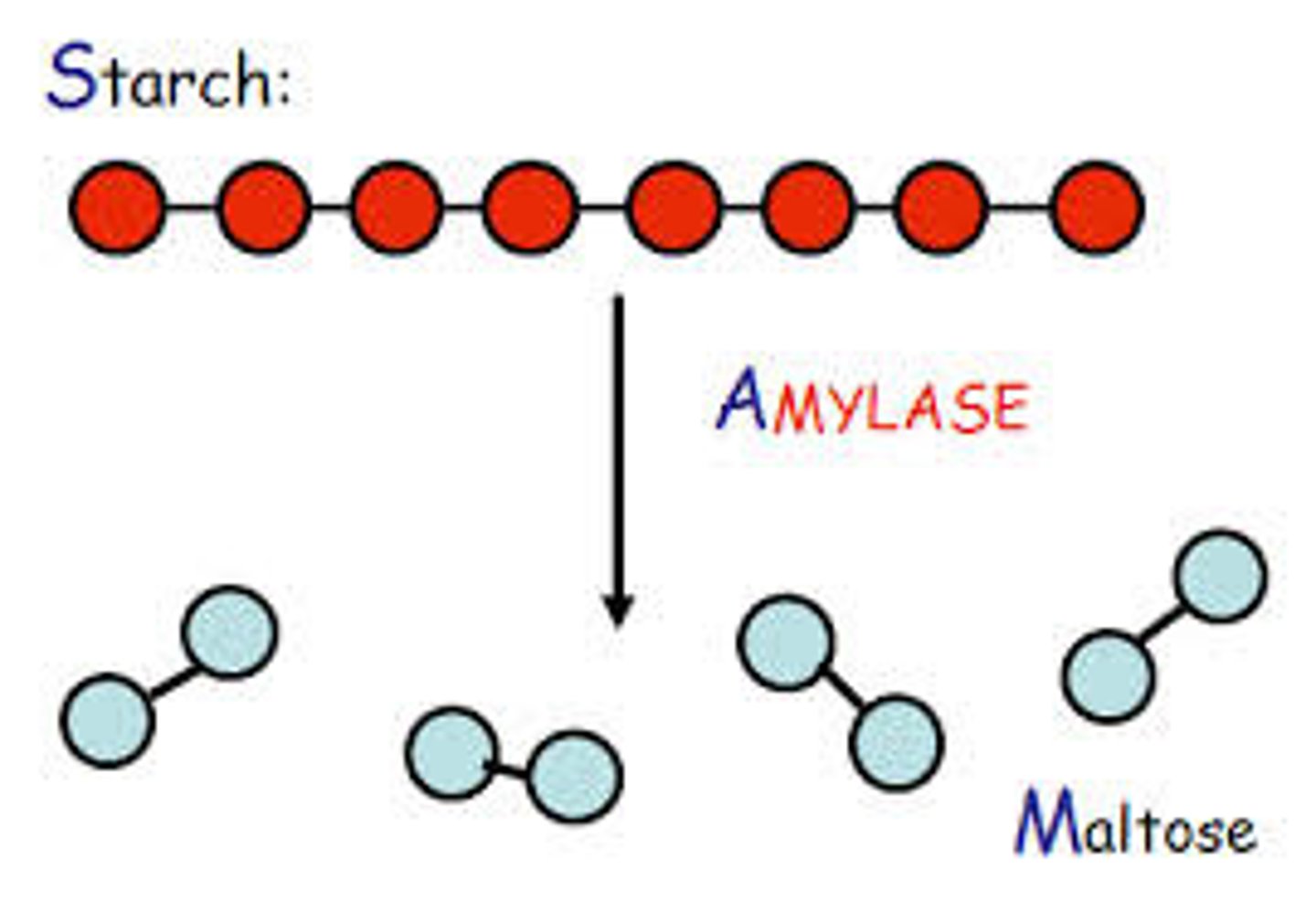
Digestion enzymes
Chemicals that change certain kinds of food into a form that can be used by the body (amylase, lipase, proteases)
World applications of enzymes
Industrial, biotechnological, and environmental
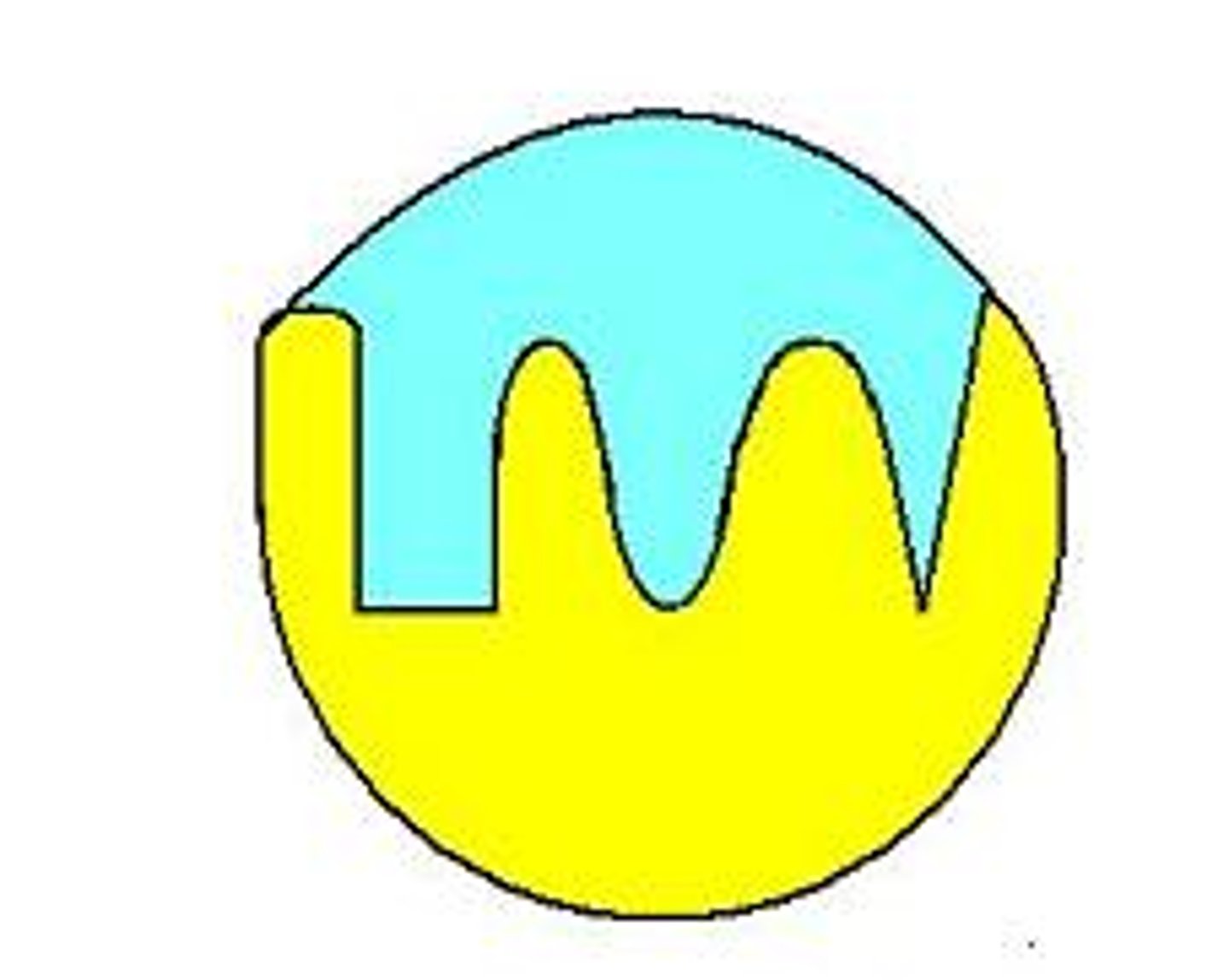

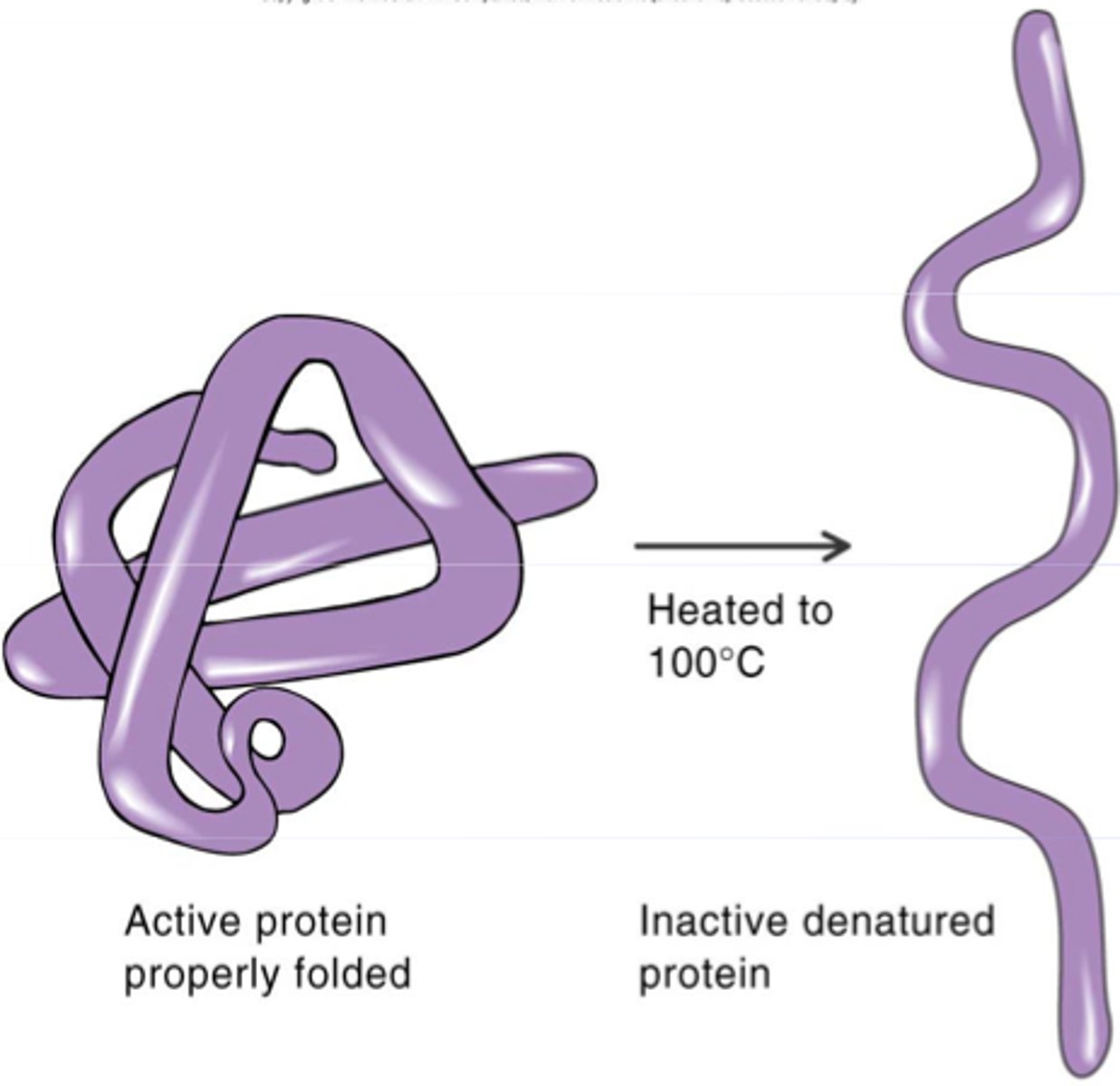
Denaturation
loss of normal shape of a protein due to heat or other factor
Optimal range temperature
37 degrees C/98.6 degrees F
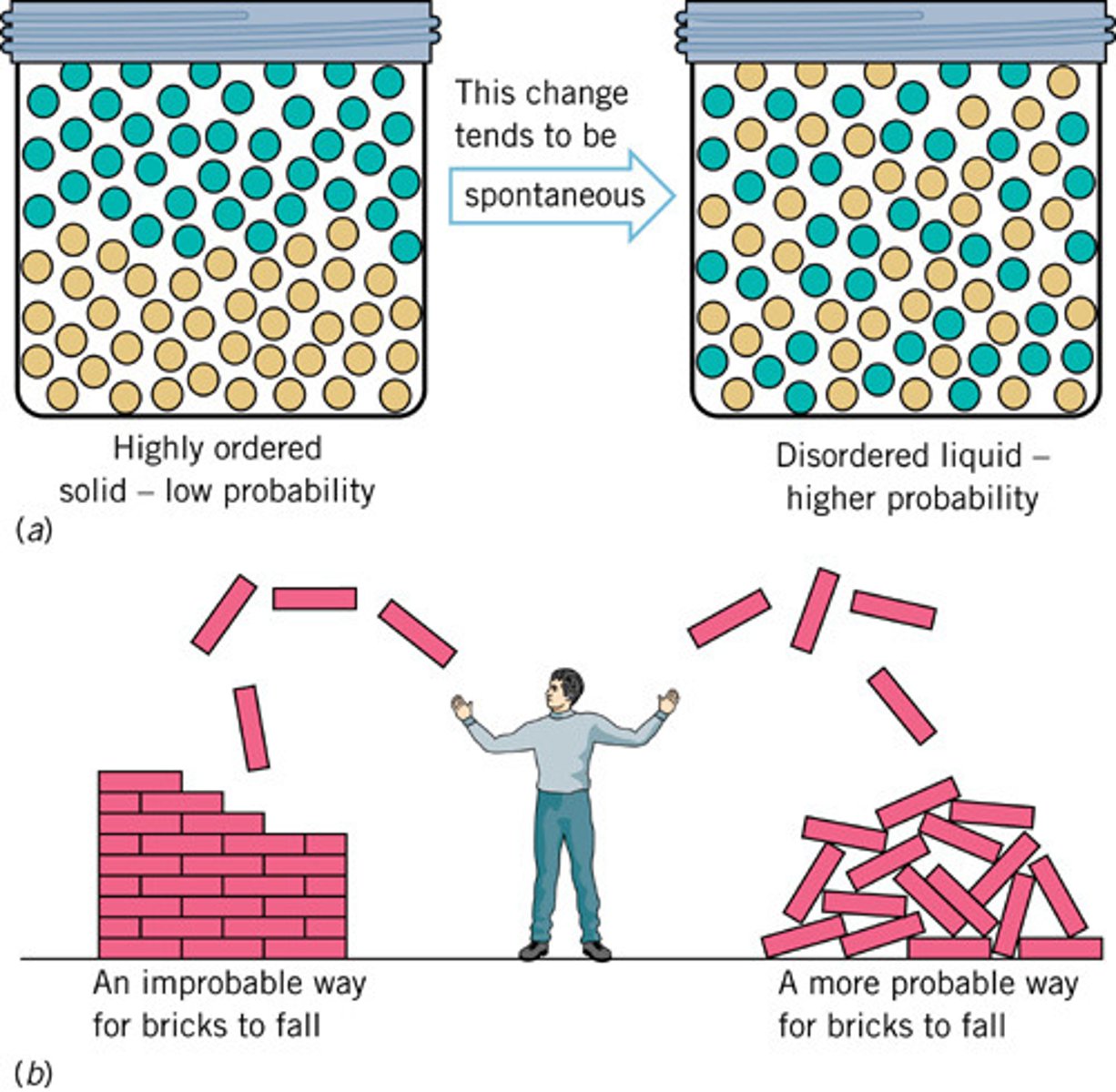
2nd law of Thermodynamics
Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe.
Coupled reactions
pairs of chemical reactions in which some of the energy released from the breakdown of one compound is used to create a bond in the formation of another compound

Metabolic pathway
A series of chemical reactions that either builds a complex molecule or breaks down a complex molecule into simpler compounds.
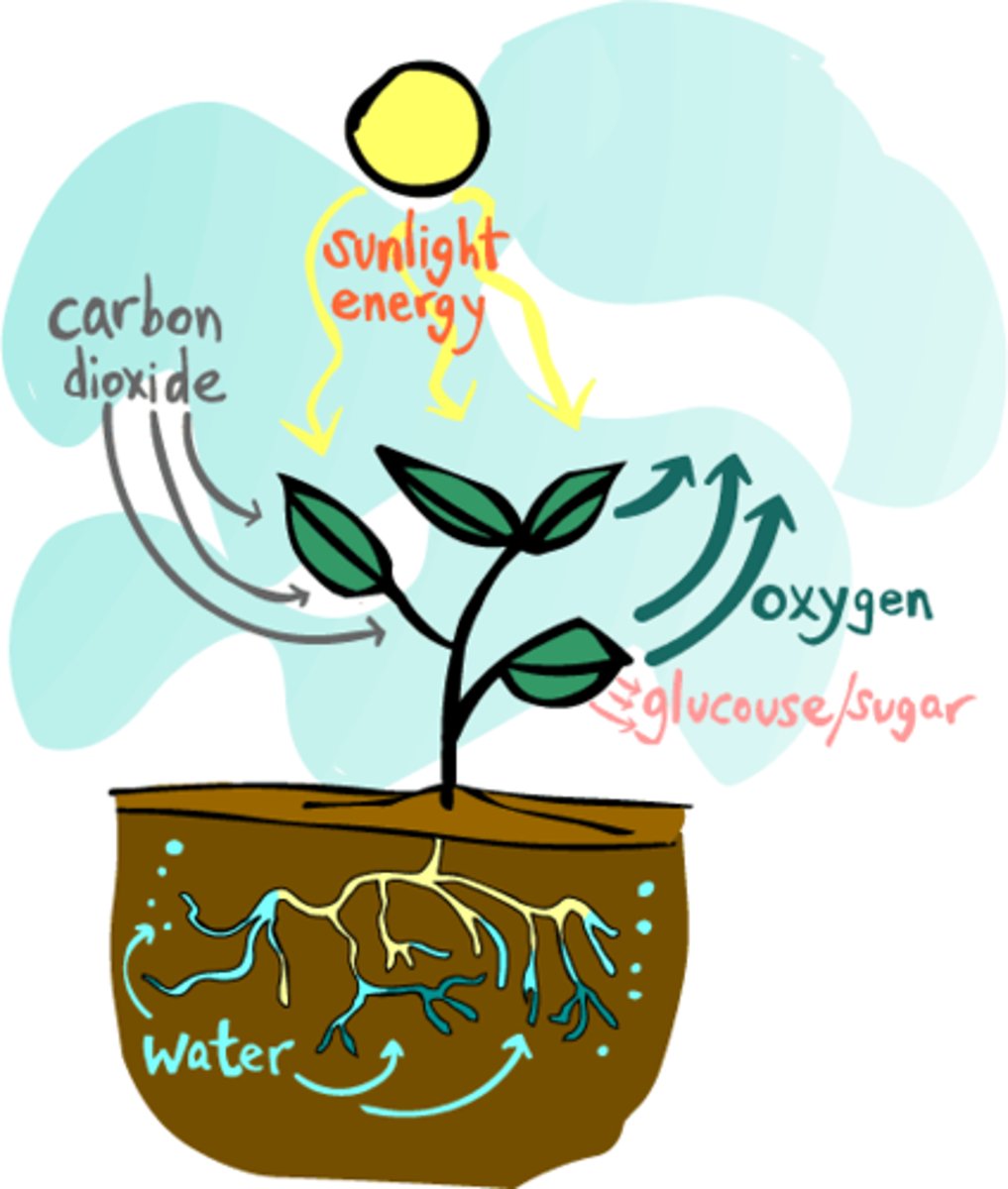
Photosynthesis
Conversion of light energy from the sun into chemical energy.
reactants: carbon dioxide, water, light energy
products: glucose and oxygen
Thylakoids
A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy to chemical energy. (Grana are stacks of thylakoids)
Stroma
fluid portion of the chloroplast; outside of the thylakoids
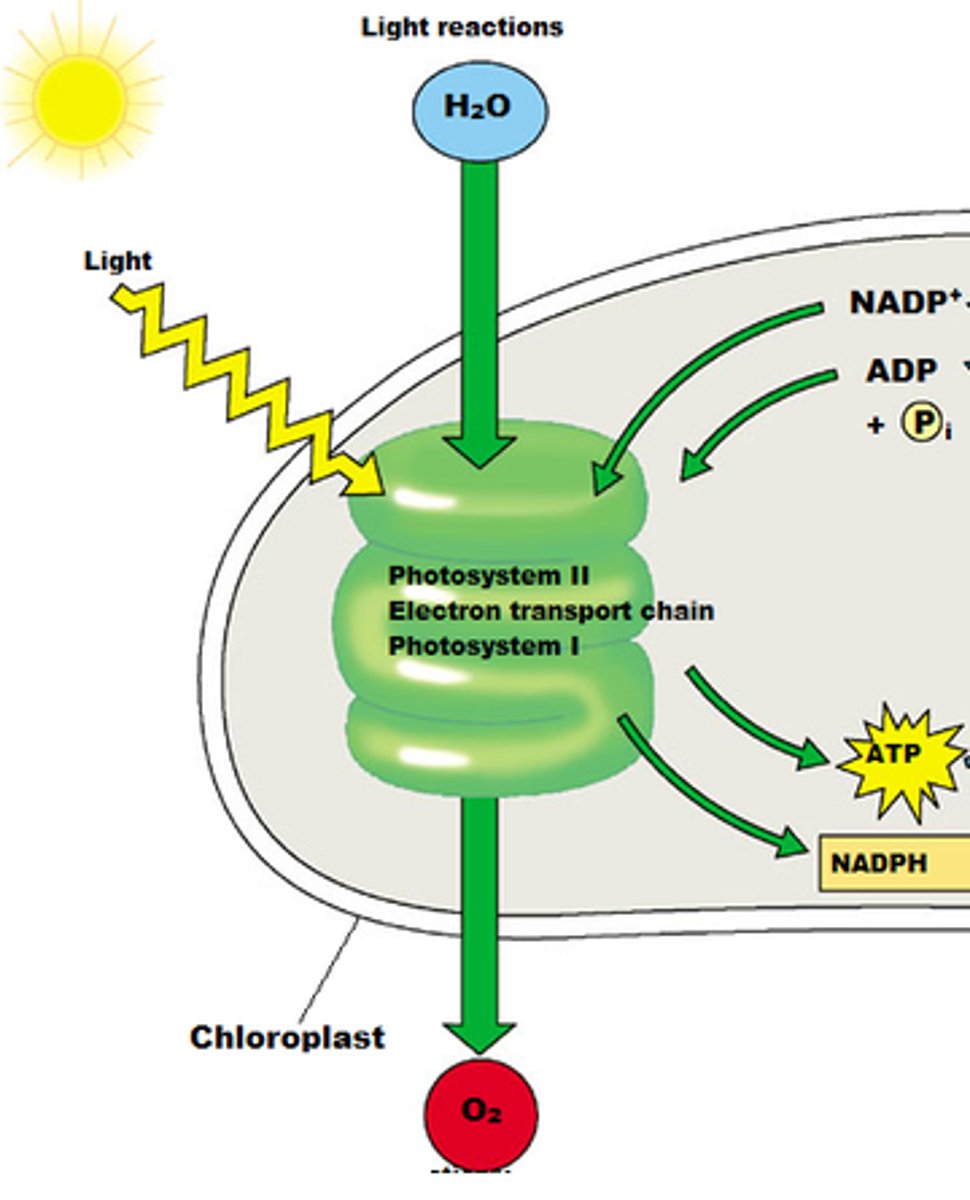
Light dependent reactions
reactions of photosynthesis that use energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH, occurs in thylakoid
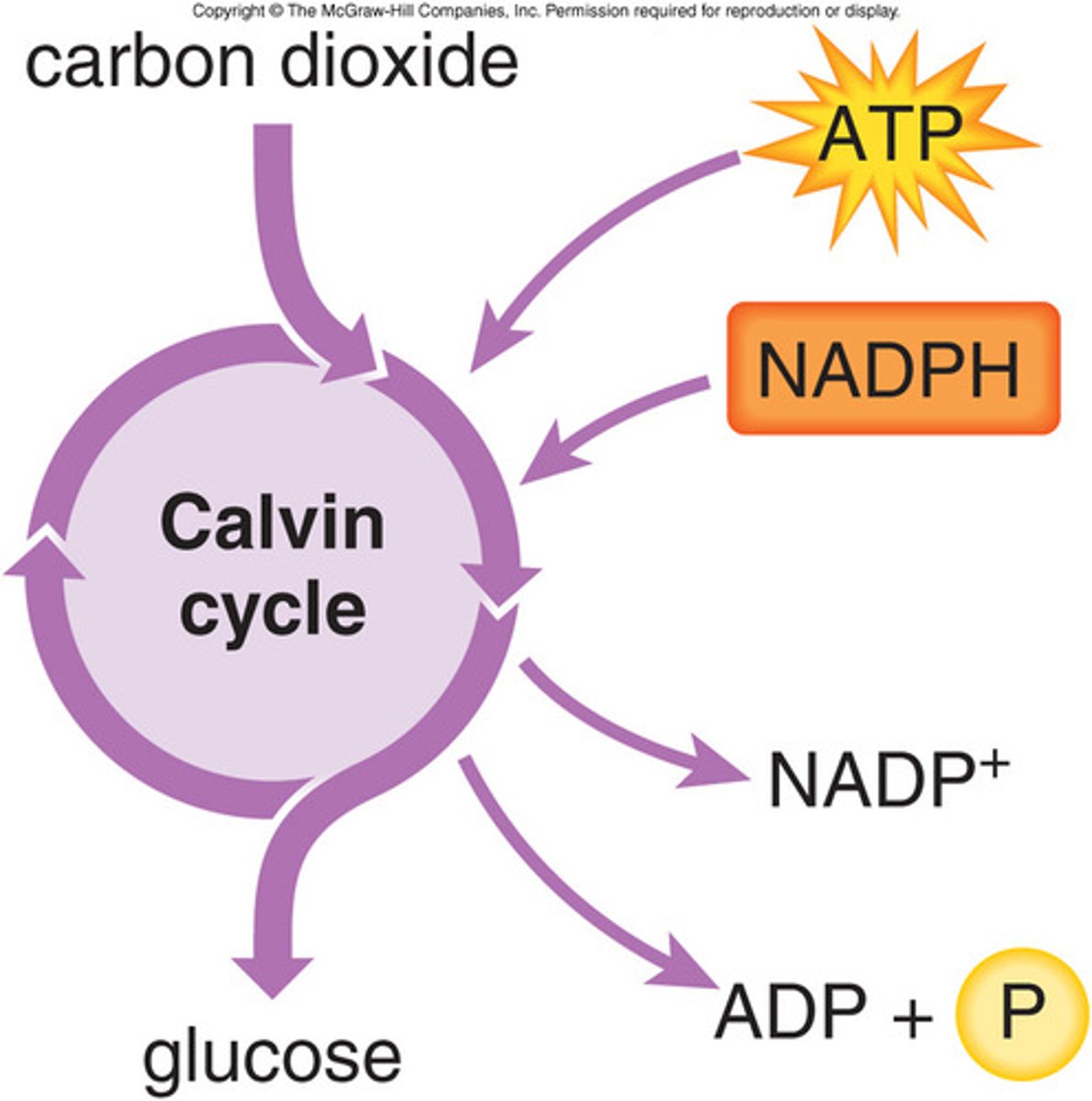
Calvin Cycle (Light independent)
reactions of photosynthesis in which energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build high-energy compounds such as sugars, occurs in stroma
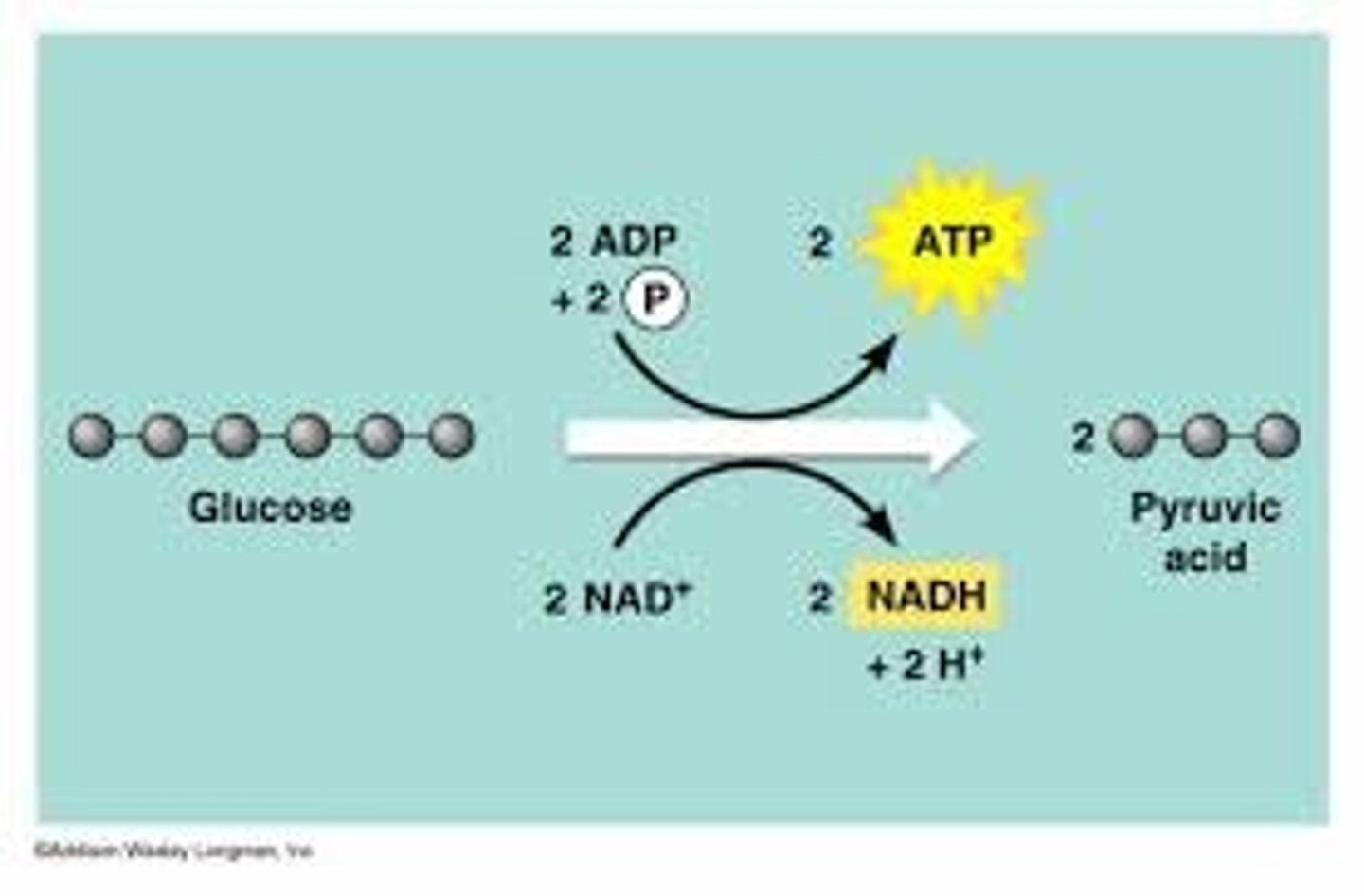
Cellular Respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen
reactants: glucose and oxygen
products: carbon dioxide, water, ATP

Glycolysis
the breakdown of glucose by enzymes, releasing energy and pyruvic acid.
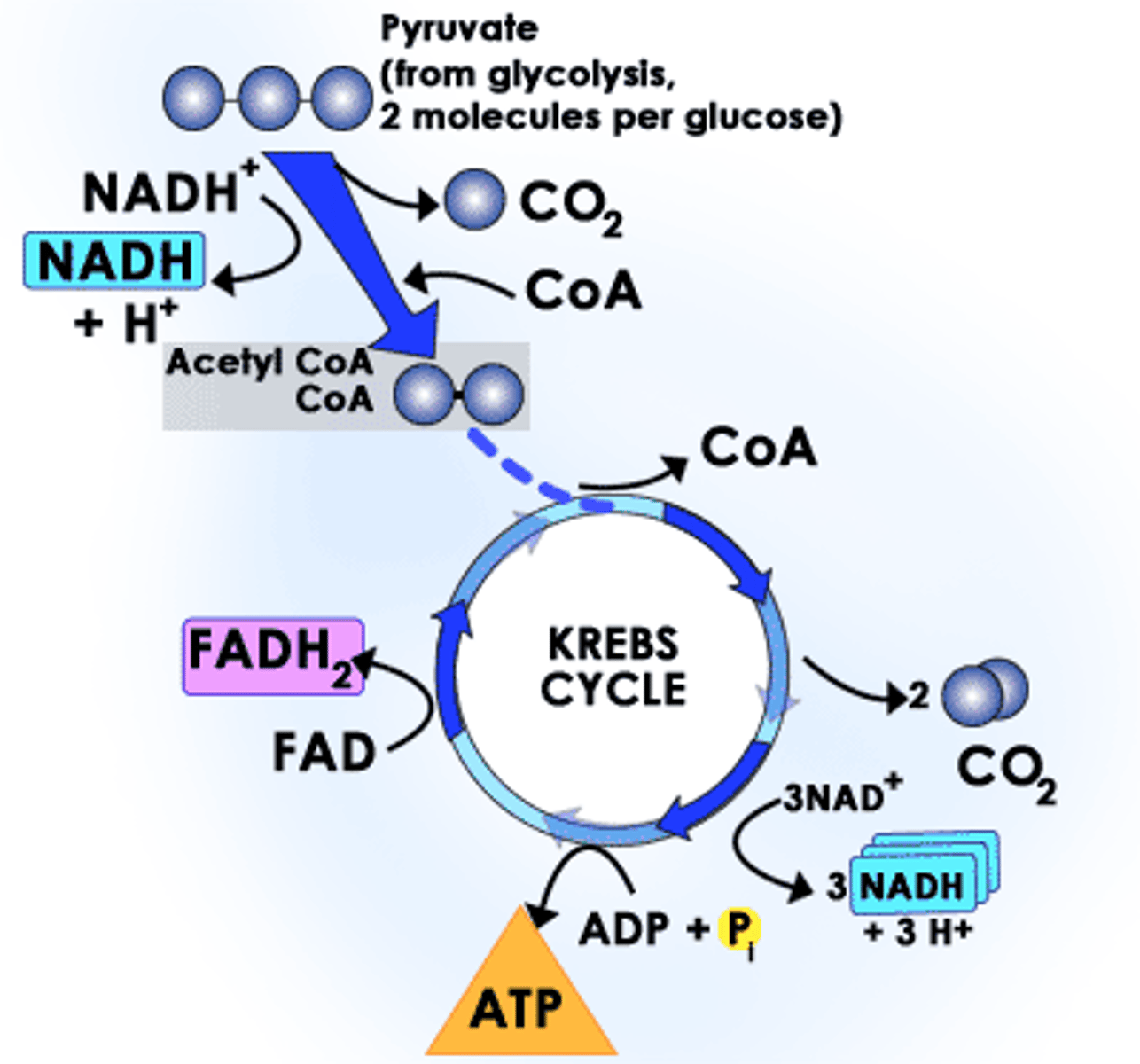
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
second stage of cellular respiration, in which pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions
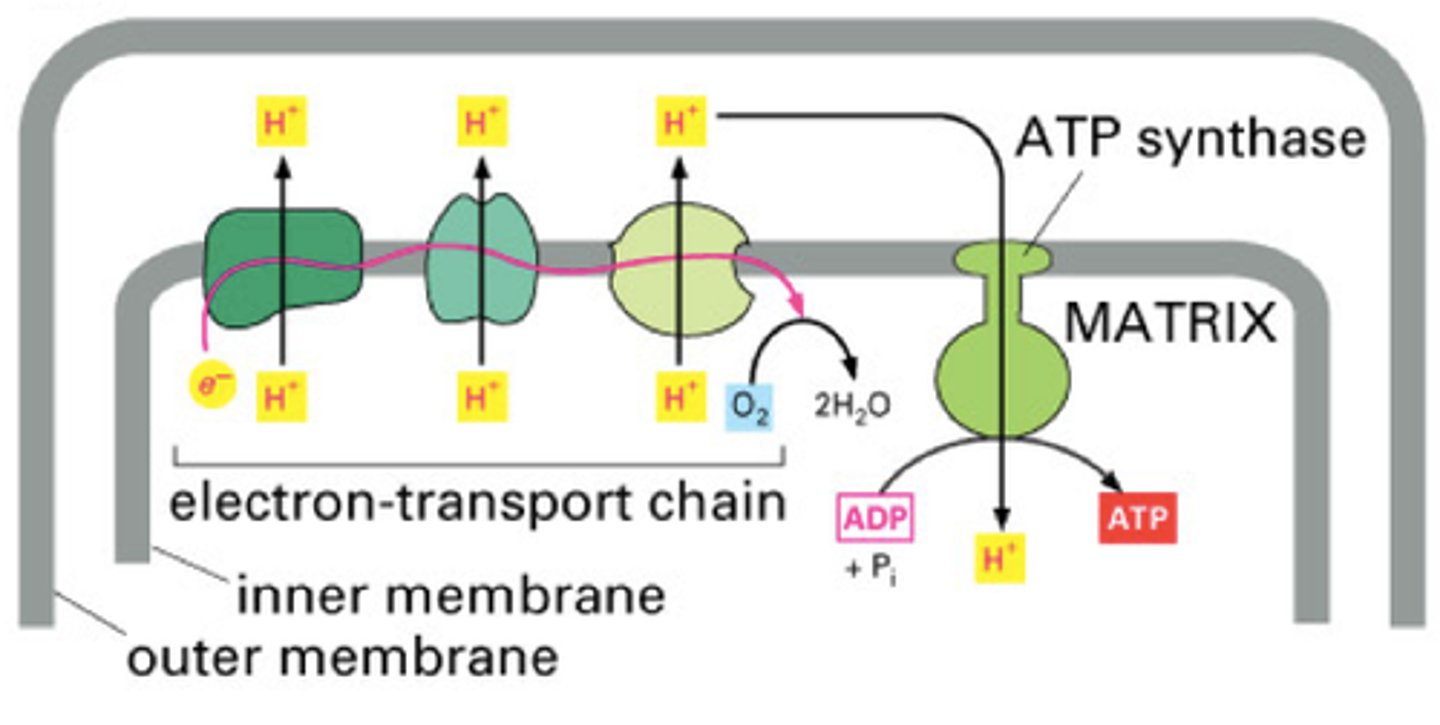
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
series of electron carrier proteins that shuttle high-energy electrons during ATP-generating reactions
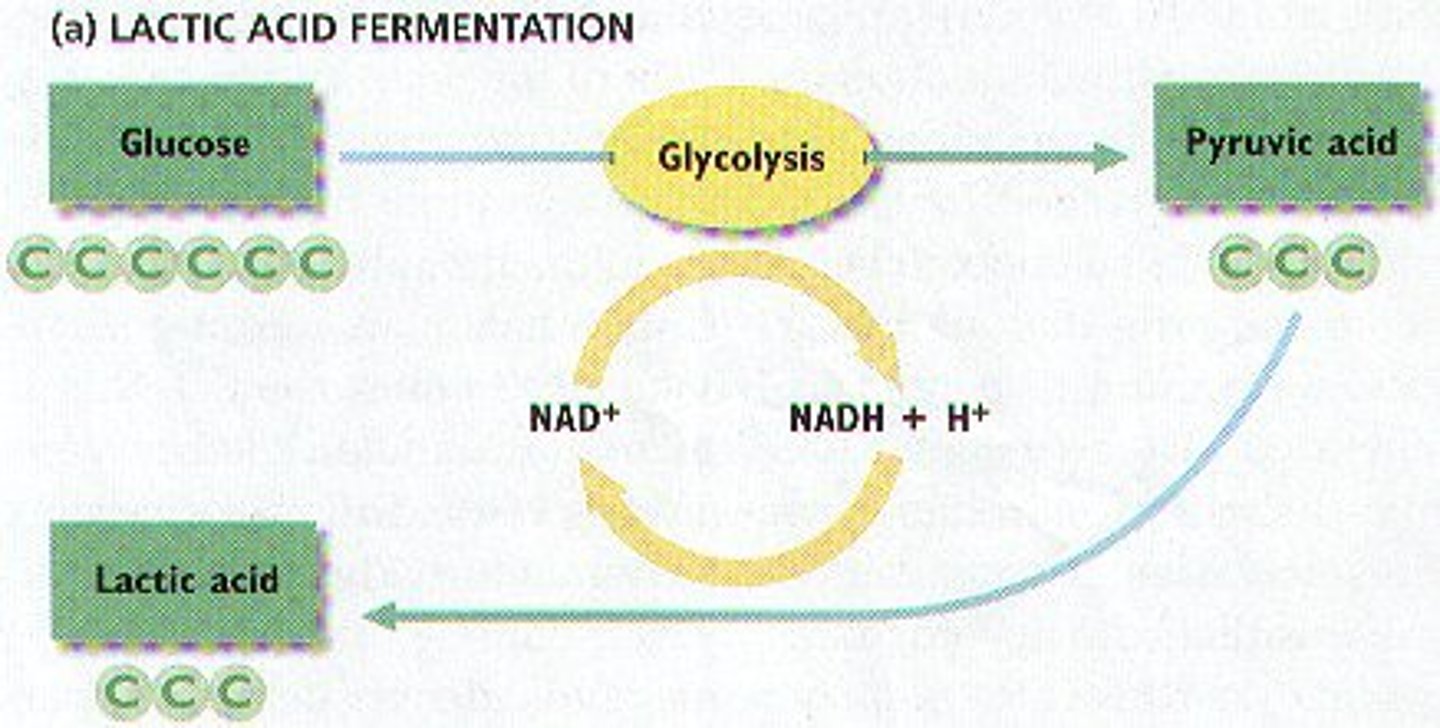
Fermentation
Process by which cells release energy in the absence of oxygen (Lactic acid + alcoholic)
Cell homeostasis
Maintaining a constant internal environment
Molecular variation
variation within the molecules of a cell
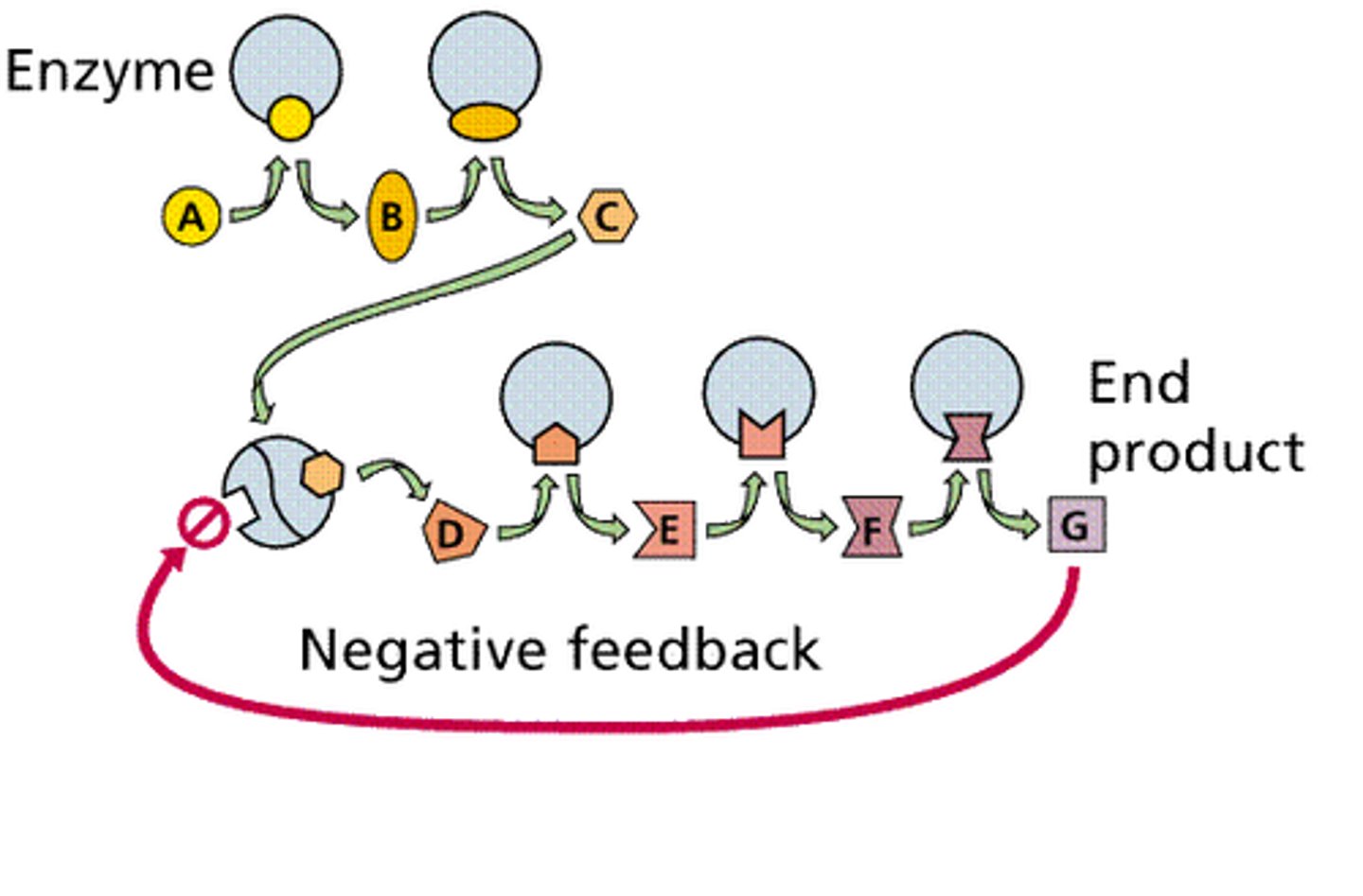
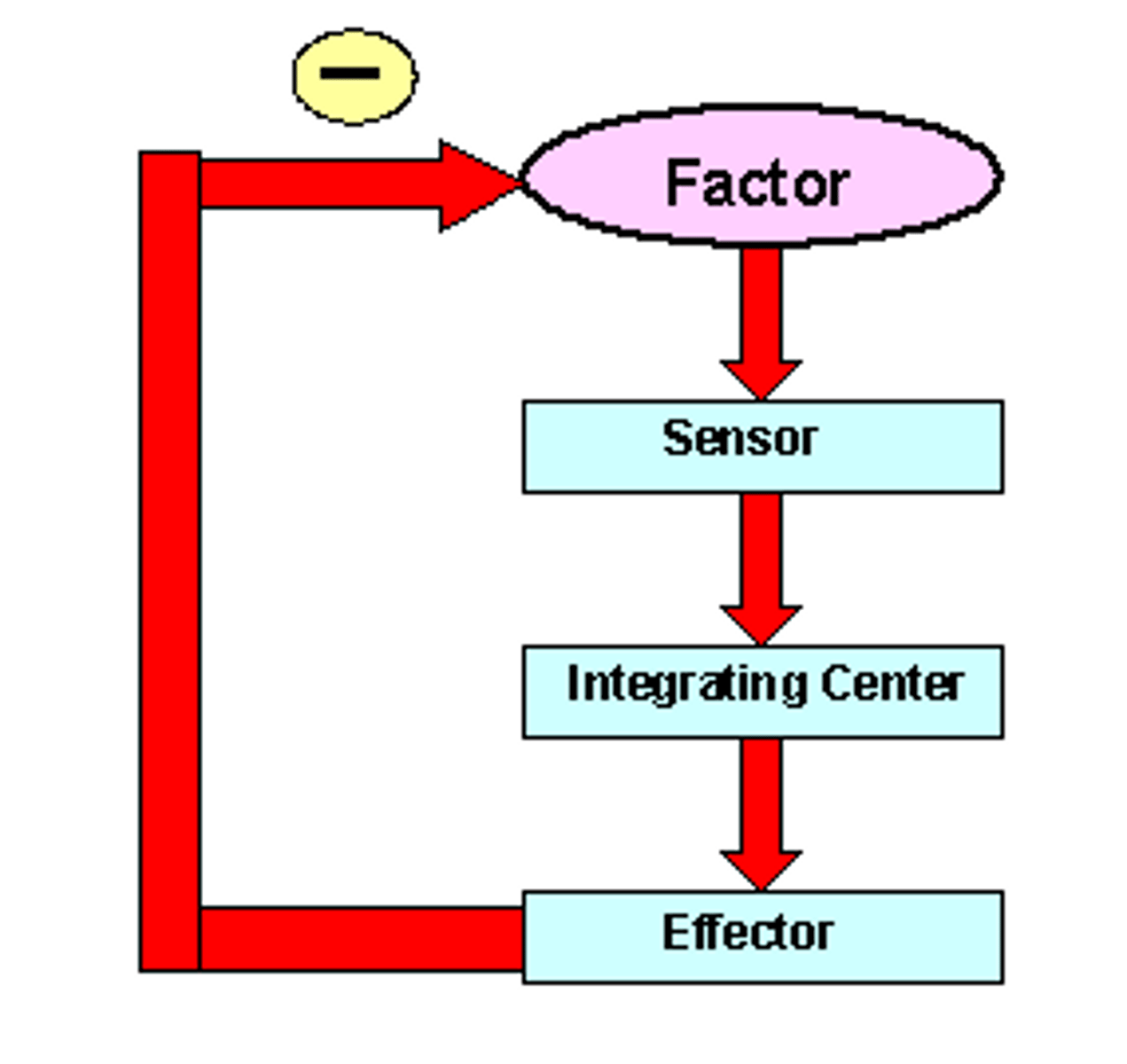
Negative feedback
A primary mechanism of homeostasis, whereby a change in a physiological variable that is being monitored triggers a response that counteracts the initial fluctuation.
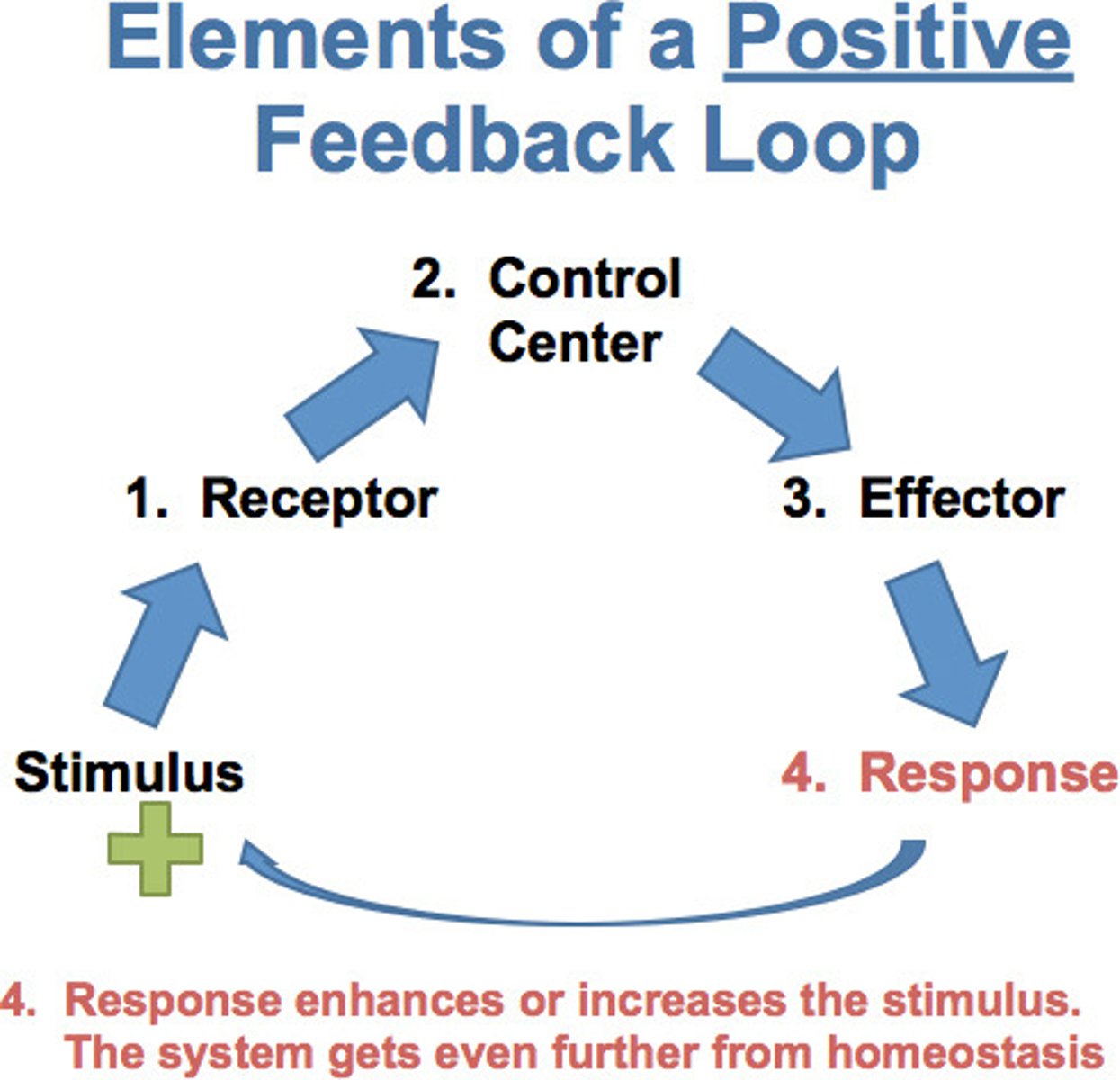
Positive feedback
A type of regulation that responds to a change in conditions by initiating responses that will amplify the change. Takes organism away from a steady state.
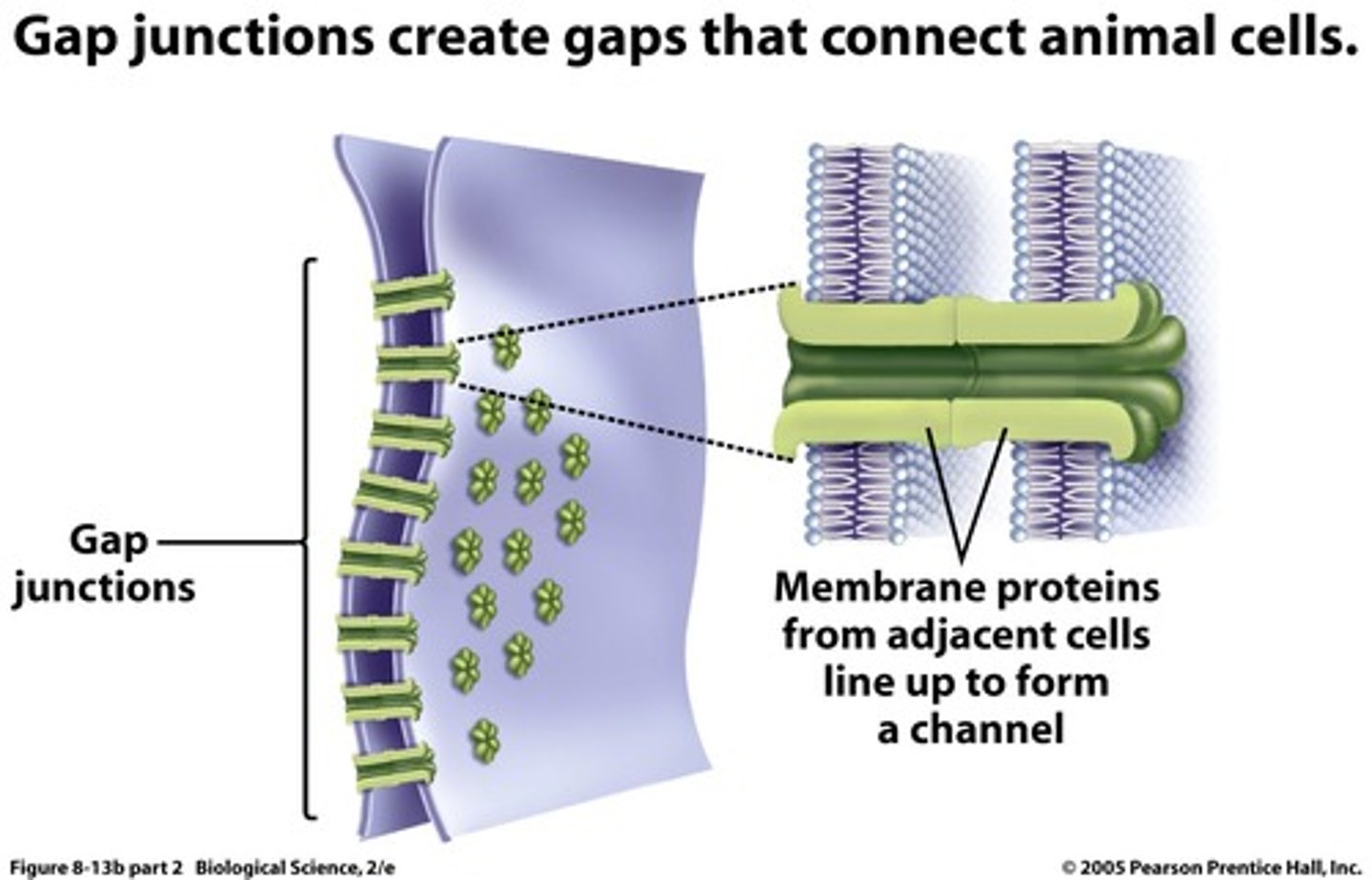
gap junctions + plasmodesmata
small molecules pass directly from one cell to a directly adjacent one: channels that directly connect the cytoplasm of adjacent cells, rapid pass through of ions + signaling molecules
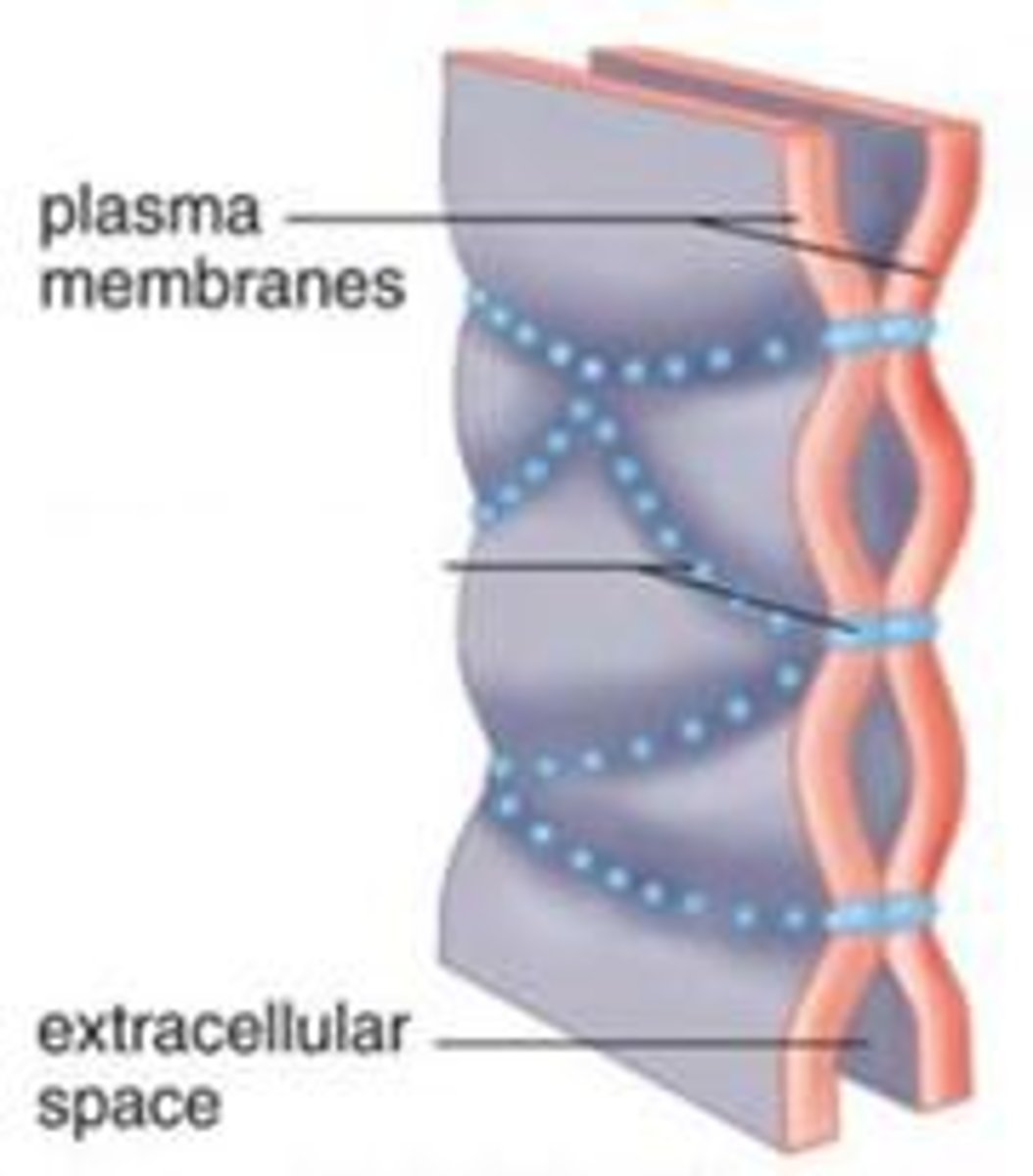
Tight junctions
Membranes of neighboring cells are pressed together, preventing leakage of extracellular fluid
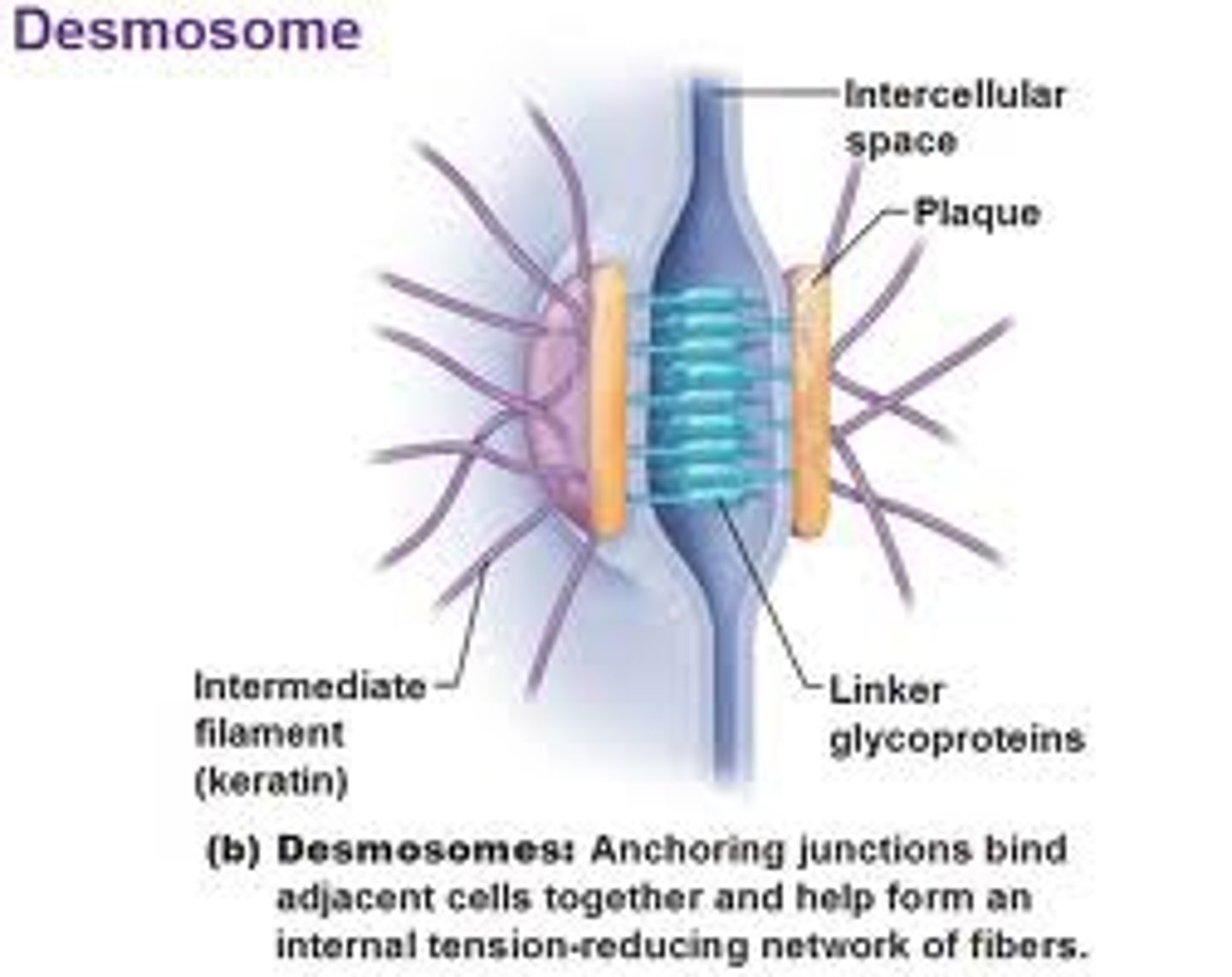
Desmosomes
Anchoring junctions that prevent cells from being pulled apart
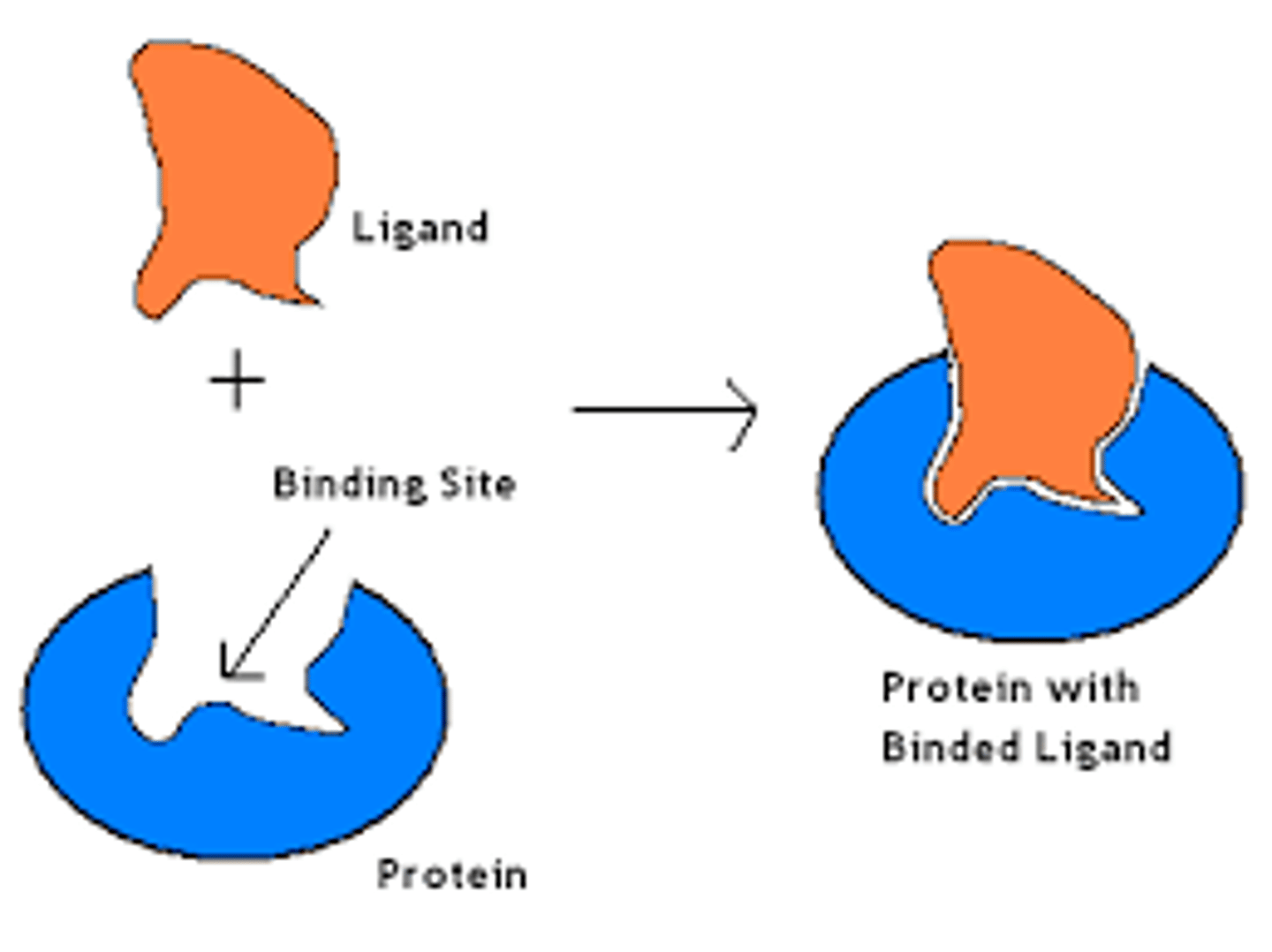
Ligands
A molecule that binds specifically to a receptor site of another molecule.
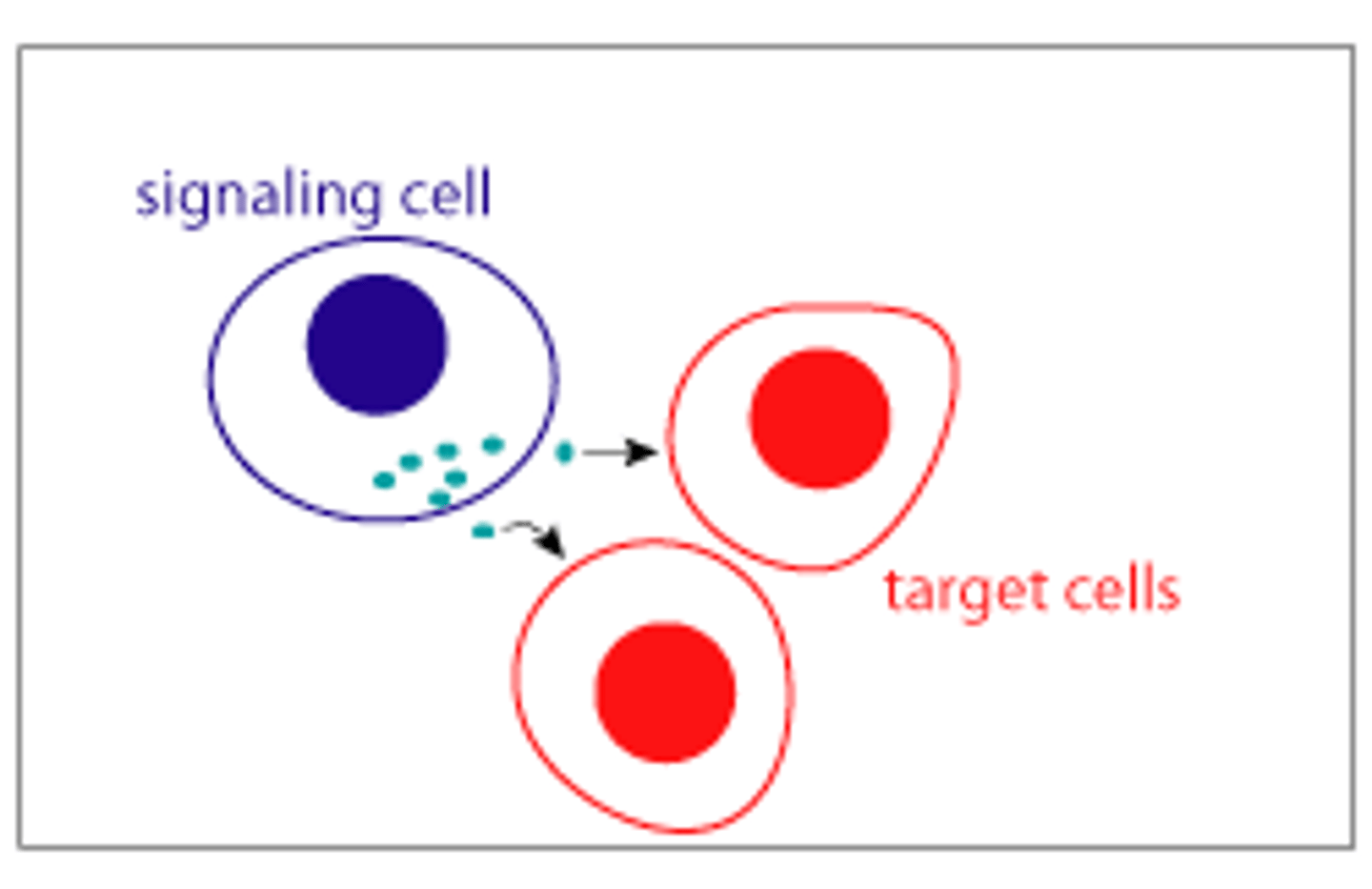
Paracrine signaling
Signal released from a cell has an effect on neighboring cells.
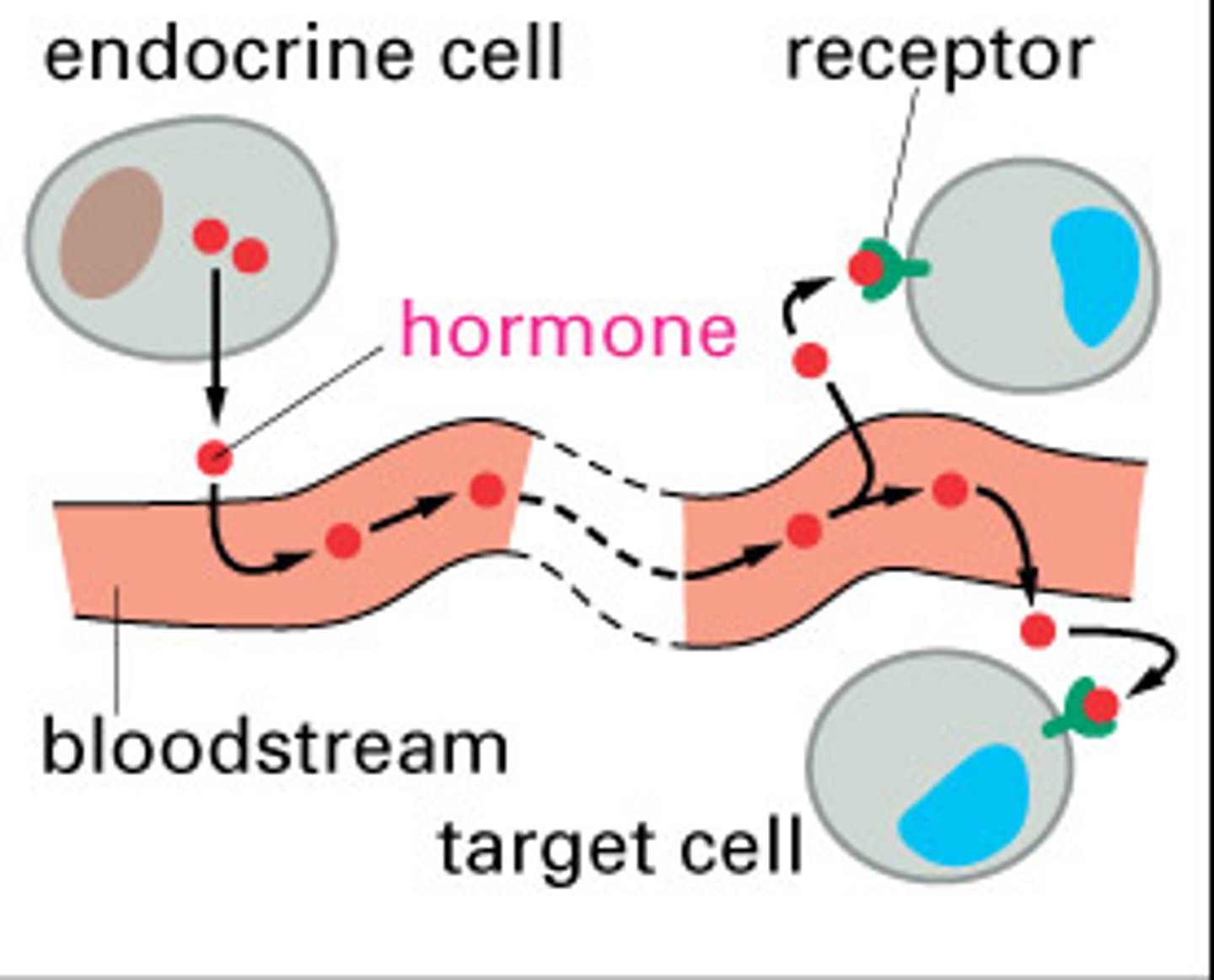
Endocrine signaling
Specialized cells release hormone molecules into vessels of the circulatory system, by which they travel to target cells in other parts of the body.
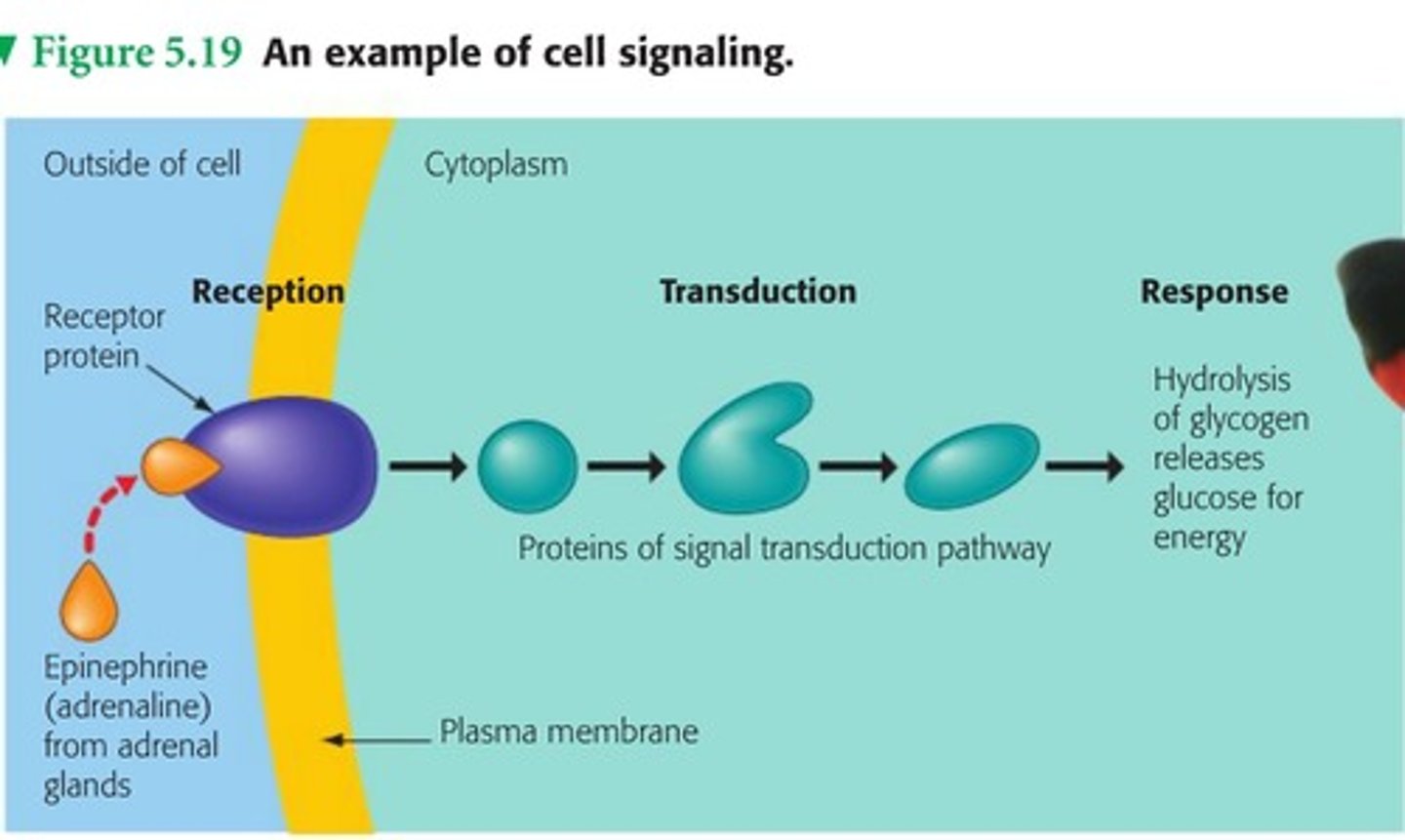
Signal transduction
A series of molecular changes that converts a signal on a target cell's surface to a specific response inside the cell.
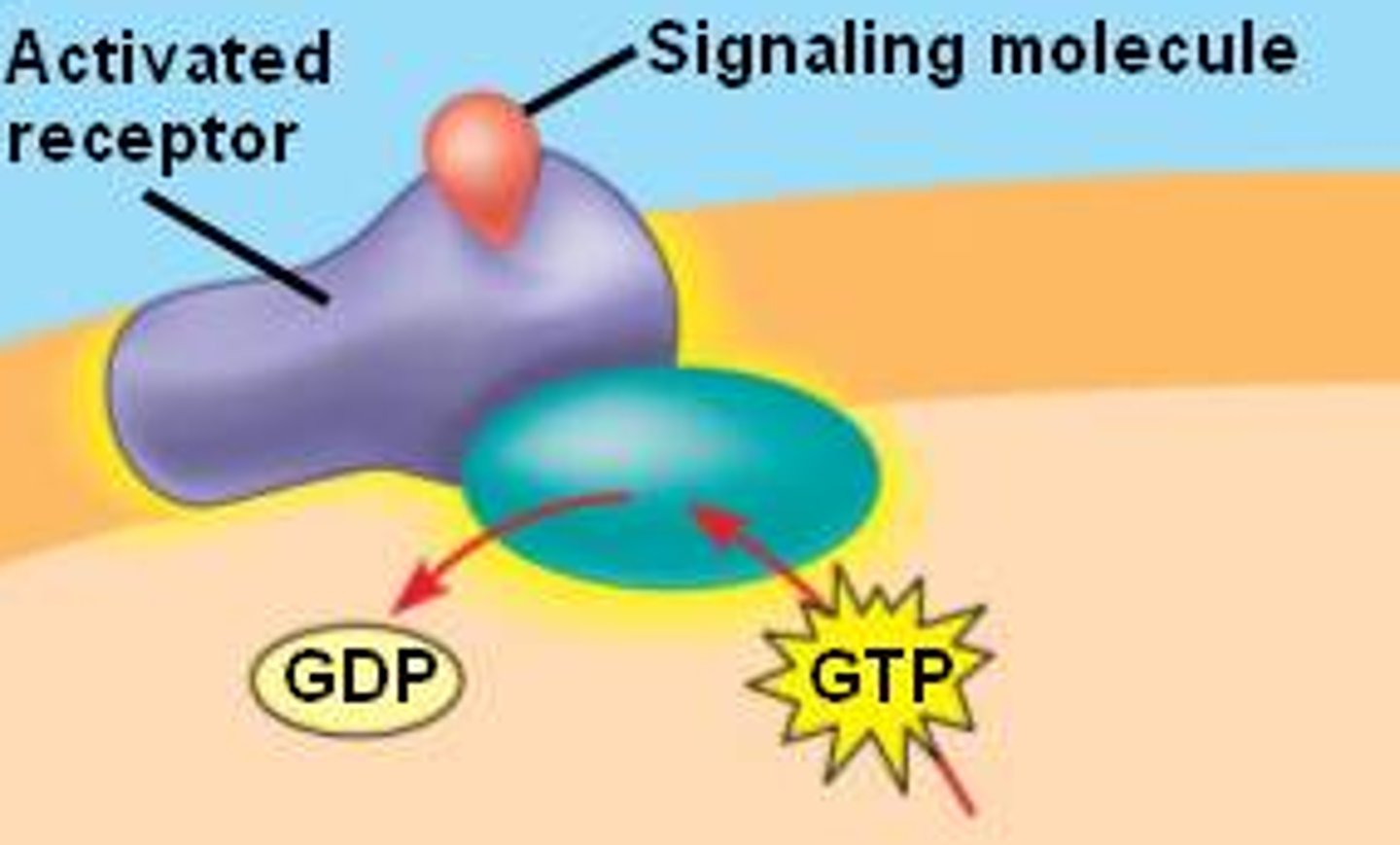
Receptors
Special structures that allow living organisms to sense the conditions of their internal or external environment.
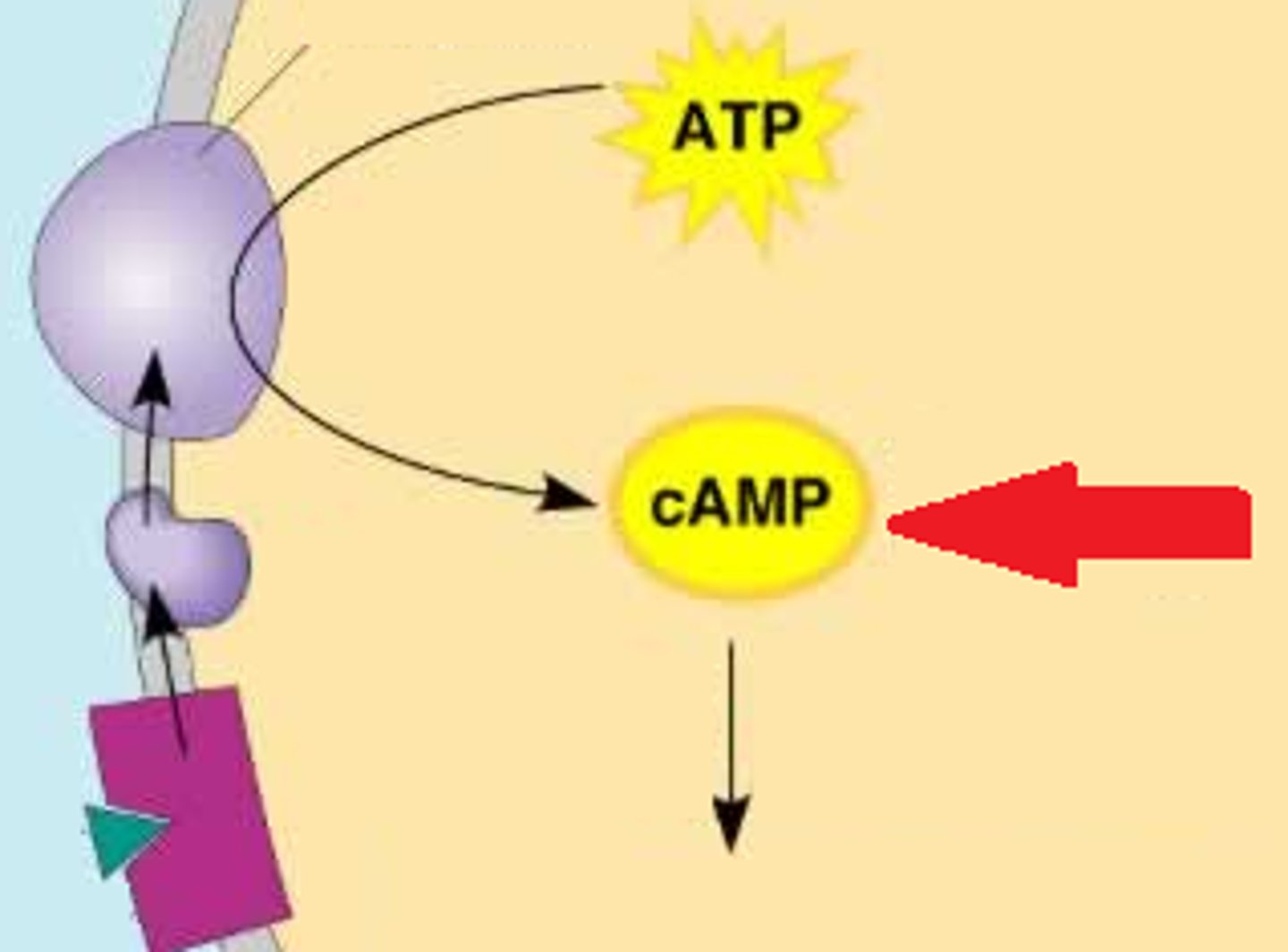
Second messengers
Small, non-protein water soluble molecules or ions that send messages throughout the cells by diffusion.
The Cell cycle
series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide
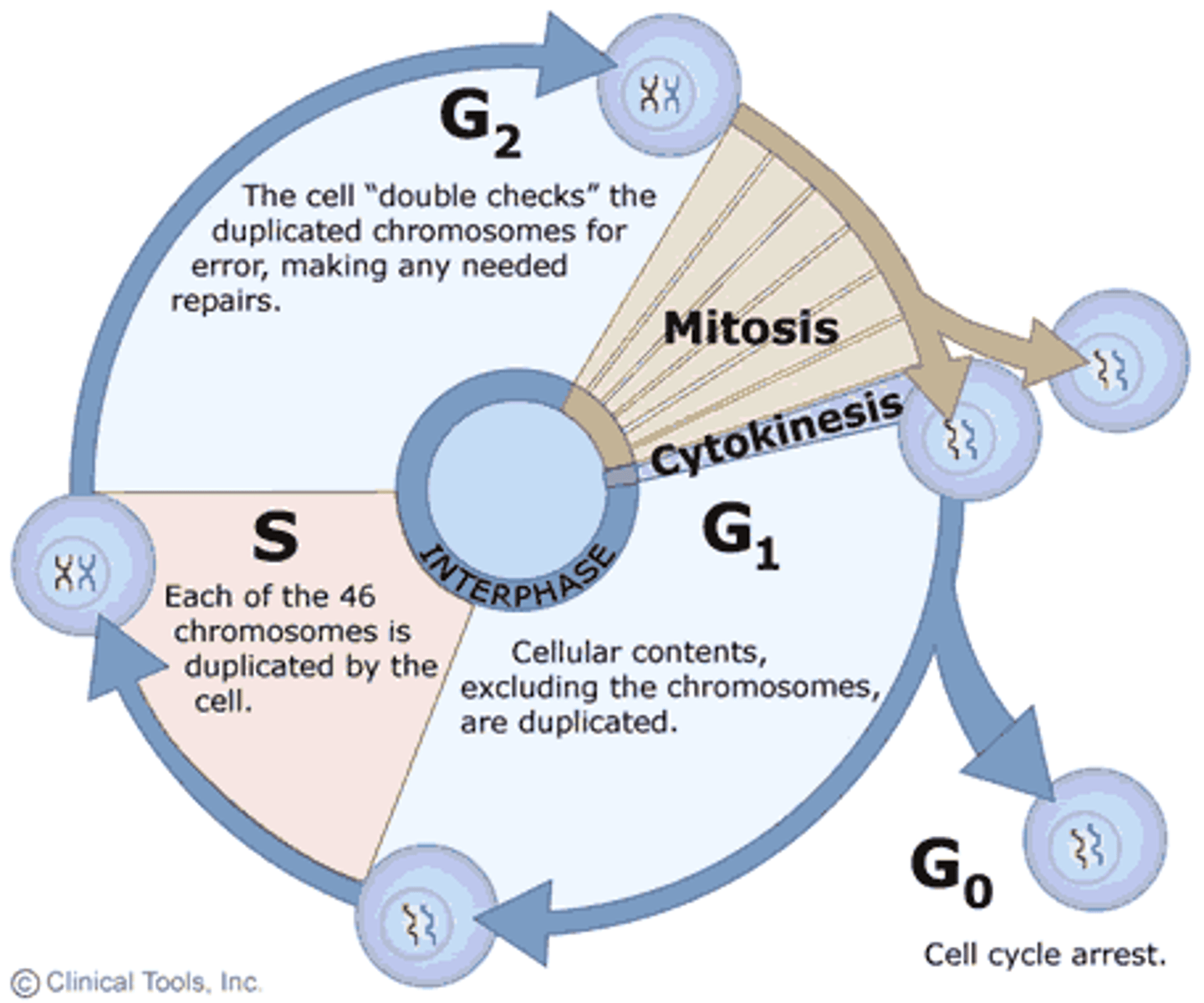
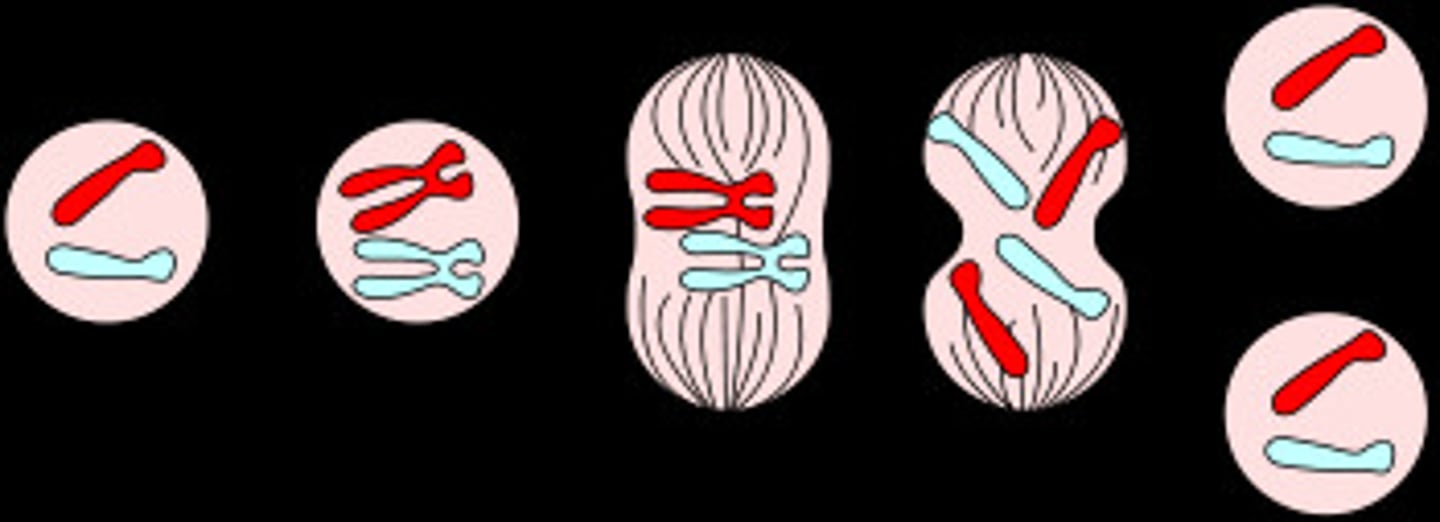
Mitosis
part of eukaryotic cell division during which the cell nucleus divides