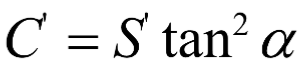2 Properties of Ophthalmic Lenses
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
curvature (R) =
1/r
The smaller circle has (greater/smaller) curvature (R) and a (longer/shorter) radius
greater/shorter
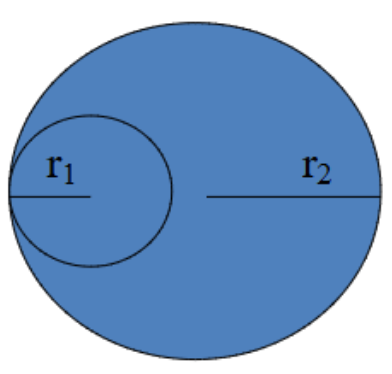
Power =
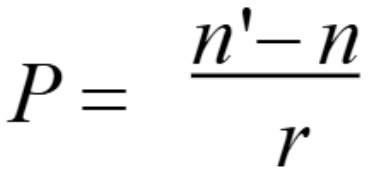
Function of lens clock
measure sagittal depth of lens surface
Sagitta
the distance between a point on the circle and the midpoint of a chord of the circle
Exact sag

What can be calculated with the sagittal depth?
Power of the surface
When is the approximate sag formula used?
when s is small compared to r (as with spectacle lenses)
How does a lens clock work?
Each lens clock is calibrated for a single index of refraction. The center pin moves to directly measure sag (s), and using the separation of outer pins (1/2 of that distance is semi-chord y), surface power is indirectly measured
Lens clock equation
combine surface power and sag depth formula
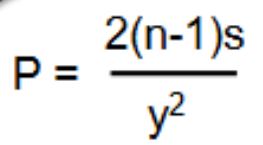
How do you find true surface power with a lens clock for a different n?
solve for r=(n’-n)/P where n’ is lens clock, then plug the true r into original surface power using true index of lens

If lens clock assumes a higher index of refraction than the material, it gives an (over/under)estimate of n and surface power
overestimate
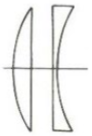
What type of lens form are these?
plano-convex and plano-concave (one flat surface, spherical)
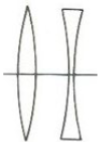
What type of lens are these?
Biconvex and biconcave (spherical)
What is equiconvex and equiconcave?
half of total lens power at each surface
What is a meniscus lens?
convex front surface and concave back surface: we use this, better visual function, reduced aberrations

3 types of cylindrical toric designs
Plano cyl (rarely used, one surface flat, other cylindrical)
Toric (usually used now, one surface toric, other spherical)
Bi-toric lens (both surfaces toric, used in RGPs and some eikonic)
What are the types of toric lenses?
Minus cylinder lens form (spherical front +, toric - back) - nearly all single vision spectacle lenses are designed this way
Plus cyl lens form (toric front +, spherical back -)
What factors help us decide what powers of the front and back surface for a given lens?
Maximize optical quality (reduce aberrations)
Cosmetic appearance (steeper surface = less attractive)
Types of lens blanks
Rough blank: neither side ground or polished
Semi-finished Blank: one surface ground and polished
Uncut Lens (most common): both surfaces ground and polished, lens has not been edged to fit the frame
Base Curve (BC) def for spherical, plus cyl, and minus cyl lenses
Surface power of lens
for spherical lenses, front surface power
for plus cyl, flatter front surface meridian
for minus cyl, front spherical curve/surface power
Cross curve
the steeper meridian on plus cyl lens (where front surface is toric)
flatter is called base curve
Corrected Curve Lenses (aka best-form lenses)
Appropriate selection of base curve to minimize oblique astigmatism aberrations and curvature of image aberrations
Compromise of thinness and image quality (thicker=better image quality)
Which aberration is most important to minimize in a corrected curve lens?
oblique astigmatism
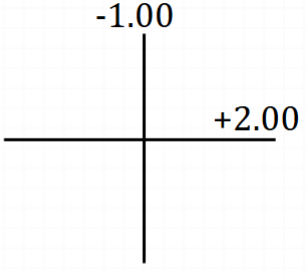
Use crosses to describe to make this Rx
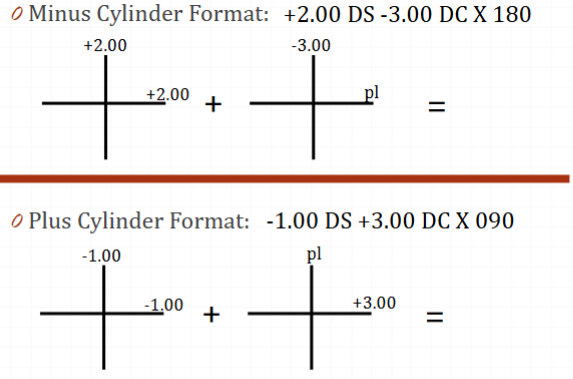
T or F, the lens form (plus and minus cyl) is determined by the Rx format (plus and minus cyl)
F, we almost always use minus cyl lens form (minus on back surface), gives us better optical quality
3 steps for cylinder transposition
add sph and cyl power = new sph power
flip cyl sign
rotate cyl axis 90 degrees (+90 if <90, subtract if >90)
When writing Rx, how many digits should be used for the powers? axis?
2 decimal places (+2.00); 3 (x005)
When writing Rx, what range should the axis be within?
001-180
Crossed cylinder form
Plus cyl ground on front surface
Minus on back surface
Axes 90 degrees apart
This is a bitoric lens, as both surfaces are toric
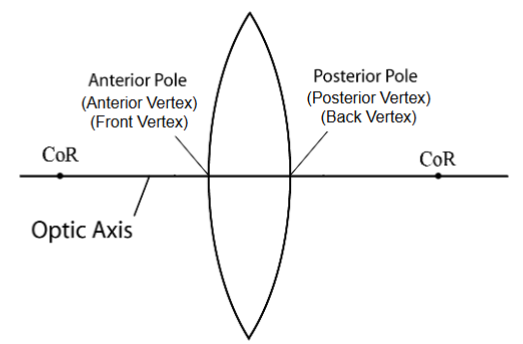
Optic axis
line connecting centers of curvature of 2 lens surfaces
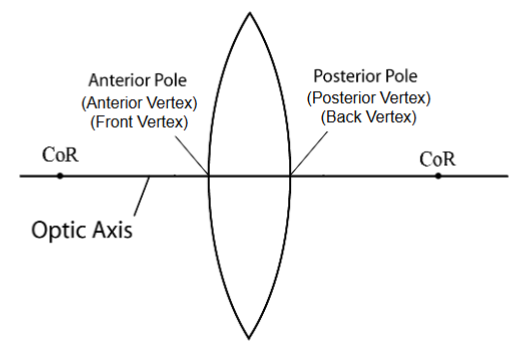
Lens poles
points (vertices) on front and back surface of lens that intersect optic axis
for a spherical lens, parallel rays of light from a distant object incident onto a spherical __ lens, forming a point image at the __ focal plane
convex; secondary
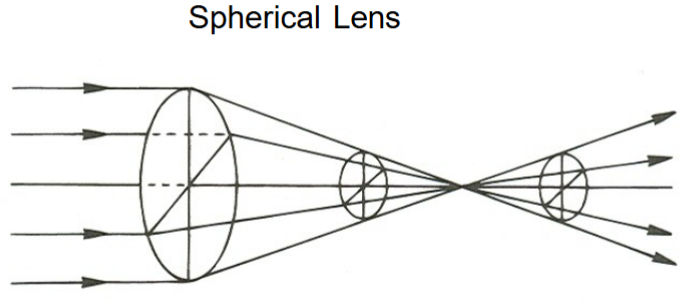
Where is a blur circle formed at any distance behind the lens?
Everywhere besides the secondary focal plane
Size of blur circle dependent on
distance of secondary focal plane
size of lens aperture
For sphero-cylindrical lenses, the dioptric midpoint is aka
circle of least confusion
The spherical equivalent of lens determines the
location of the COLC
How do we cut the cyl (astigmatism) but keep the SE?
Cut cyl
add ½ the cut power to sphere power (if cut 0.5 D, add 0.25 sph)
The SE can be considered a special case where
all cyl is removed (OG sph + cyl/2 = adjusted sphere)
What equation to calculate oblique power in cylindrical lens (power in meridian that is not 90 or 180)?
provided!
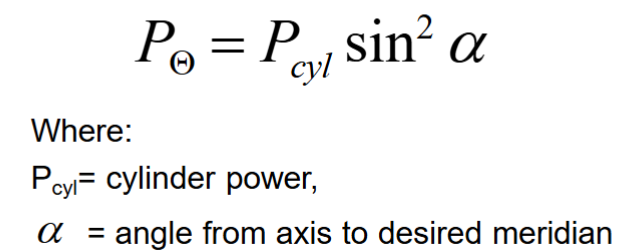
What equation to find approximate power of toric lens (has sph and cyl components) in an oblique meridian
not provided, juts add sphere power to equation for just cyl lens
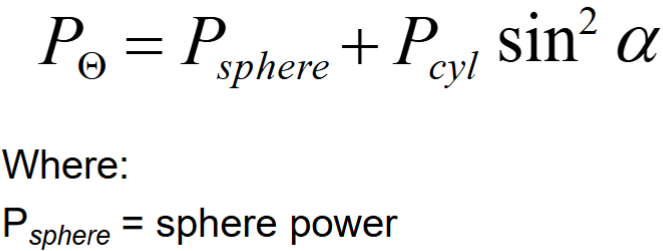
3 methods to find resulting power of obliquely crossed cylinders
Vector analysis
Mathematical
Polar Coordinates
Tilting a lens causes incident light to enter the lens __, resulting in change in what power(s)?
obliquely, change in both spherical and cylinder power —> alters power of lens
What type of tilt is is when the bottom of the lens is closer to the face than the top?
Pantoscopic tilt (opposite of retroscopic or negative pantascopic)
What type of tilt is it when the temporal aspect of the lens is closer to the face than the medial aspect is?
Faceform (opposite is negative faceform)
Tiltilng a lens induces more or less sphere power?
more
How does tilting a lens change the cylinder power?
increases it with same sign as sphere
The cyl axis induced with tilt is (parallel or perpendicular) to axis of rotation of lens
parallel (pantascopic induces 180 cyl, faceform induces 90 cyl)
What equation gets you the induced sph of a tilted lens?
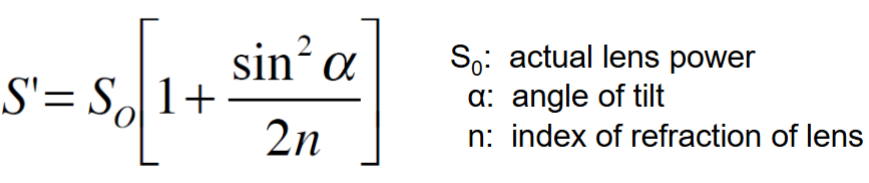
What equation gets you the induced cyl of a tilted lens?