IPS1 -A7 - A8 - Phase Diagram and Phase Rule
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Proverbs 16:3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Phase
____-
is a homogeneous, physically distinct, and mechanically separable portion of a system.
It is uniform throughout.
1 phase
2 phase
solution have ___ [how many] phase
suspension have ____ [how many] phase
Phase Diagram
_____ - is a graphical representation of the physical states of a substance under different conditions of temperature and pressure.
Phase Diagram
_____ - is a graphic way to summarize the conditions under which equilibria exist between the different states of matter.
Phase Diagram
____- allows us to predict which phase of a substance is present at any given temperature and pressure.
Molar Heat
Latent Heat is aka ___ ?
Latent Heat / Molar Heat
____-
Heat necessary for 1 mole of a gas, solid, or liquid to change to another phase.
Either gained (absorbed) or lost (released).
Latent Heat / Molar Heat
Without____, no phase transition (phase change)
True
[T/F]
Without latent heat, no phase transition (phase change)
Molar Heat of Fusion (ΔHf)
____-
Heat absorbed to convert 1 mole of solid to liquid
Heat released to convert 1 mole of liquid to solid
Molar Heat of Sublimation (ΔHs)
____-
Heat absorbed to convert 1 mole of solid to gas
Heat released to convert 1 mole of gas to solid
Molar Heat of Vaporization (ΔHv)
____-
Heat absorbed to convert 1 mole of a liquid to gas
Heat released to convert 1 mole of a gas to liquid
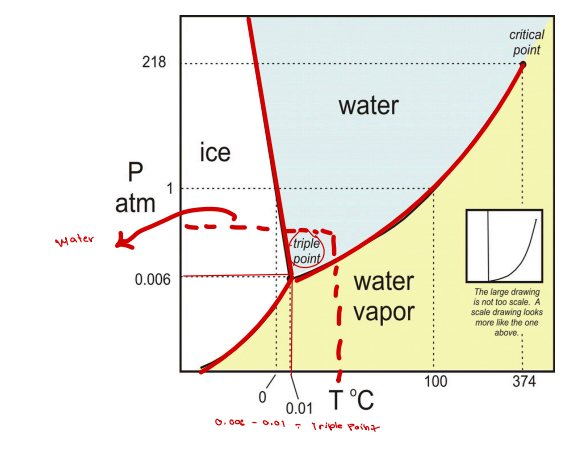
Triple point
____- refers to the temperature and pressure where solid, liquid, and gas phases coexist.
Critical point
____- refers to the Endpoint of the liquid-gas equilibrium curve.
Phase Rule
____-
Used to determine the number of independent variables (temperature, pressure, concentration) that must be set in order to define a system (F).
Formula:
F=(C−P)+2
Gibbs
Phase rule is by ___[who]?
Number of independent variables or degree of freedom (F)
Number of phases that can coexist (P)
Number of components making up the phases (C)
Examples:
• Liquid water + water vapor →F=1
• Liquid hexane + liquid water → F=2
• Liquid ethanol + liquid water → F=3
Gibbs Phase Rule relates to ___[3]
2 phase (immiscible)
hexane + water =____ [how many] phase
Y curve
One Component System shape in graph is ____ curve?
F=2 (P, T must be known)
F=1(P, T must be known)
F=0
One Component System:
1 phase → F = ___
2 phases → F = ___
3 phases → F = ____
Two-Component System
____- is Aka Condensed system
Two-Component System
___- is a System in which vapor phase is ignored and only the solid and/or liquid phases are considered
Liquid–Liquid Phases
Solid–Liquid Phases: Eutectic Mixtures
Types of Two-Component System [2]
b.) Two component system
Liquid–Liquid Phases
Solid–Liquid Phases: Eutectic Mixtures
a.) One component system
b.) Two component system
c.) Three component system
b.) Two component system
Bionodal Curve
Critical solution temperature(upper consolute temperature)
Tie Line
Conjugate phases
a.) One component system
b.) Two component system
c.) Three component system
b.) Solid-Liquid Phases
What phase Eutectic mixture occur ?
a.) Liquid-Liquid Phases
b.) Solid-Liquid Phases
Bionodal Curve
Critical solution temperature (upper consolute temperature)
Tie Line
Conjugate phases
Liquid–Liquid System [4]
Eutectic Mixture
Eutectic point
Eutexia
Solid–Liquid System [3]
U or O curve
Examples:
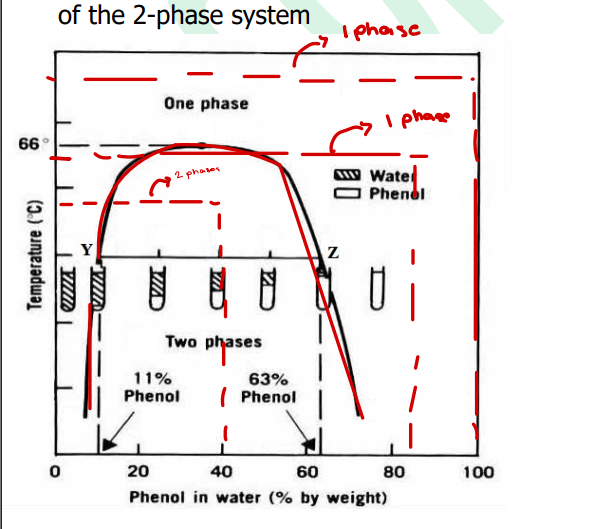
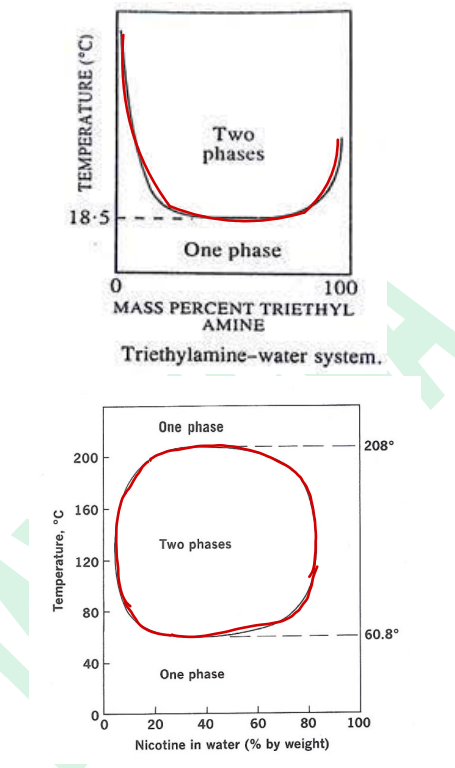
Liquid-Liquid System shape in graph is ___ curve
Binodal curve
____-
is the area within the curve represents a two-phase system
any point beyond it is a single phase
upper consolute temperature
Critical solution temperature is aka ____ ?
Critical solution temperature (upper consolute temperature)
____- is the temperature beyond which every proportion of A & B will exist as 1-phase.
Critical solution temperature (upper consolute temperature)
____- is the maximum temperature to obtain a one-phase system
Tie Line
___- is the line from which a system separates into phases of constant composition
Tie Line
____- is used to approximate the proportions of components A & B existing at a particular temperature
Conjugate phases
____- are phases of constant composition that separate when a mixture is prepared within the boundary of the two-phase system
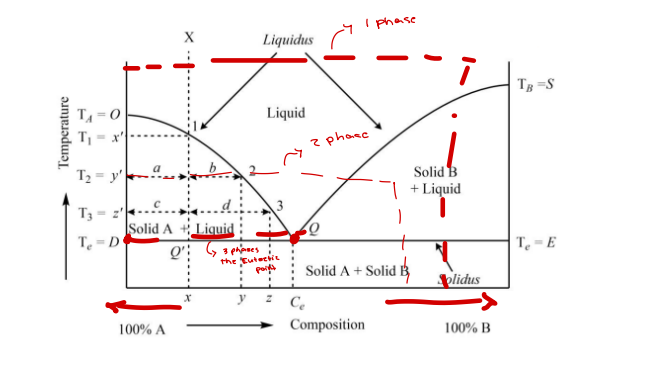
M curve
Solid–Liquid System shape in graph is ____ curve
Eutectic Mixture
____- is the composition of two or more compounds that exhibits a melting temperature lower than that of any other mixture of the compounds
MPA+B < MPA or MPA+B < MPB
Eutectic point
____- is the point at which the liquid and solid phases have the same composition and co-exist
Eutexia
____- is a phenomenon of lowering the melting point due to combinations of components
EMLA (Eutectic Mixture of Local Anesthetics)
____- is the most common application of eutexia in pharmacy
lidocaine + prilocaine
EMLA (Eutectic Mixture of Local Anesthetics) contains ___ [2]
EMLA (Eutectic Mixture of Local Anesthetics)
lidocaine + prilocaine = ____ [kind of mixture] ?
Thymol – Salol
Camphor – Menthol
Lidocaine – Prilocaine (→ basis of EMLA cream)
Example of Eutectic Mixtures [3]
hahhahah
EXPLAIN MO LNG
Triangle
Three-Component System shape in graph is a ___?
b.) Two component system
Eutectic Mixture , Eutexia , and Eutectic Point is a under
a.) One component system
b.) Two component system
c.) Three component system
c.) Three component system
Ternary system is under
a.) One component system
b.) Two component system
c.) Three component system
Ternary system
____ - is a system consisting of 3 components existing in phase equilibrium
c.) Three component system
[TYPE OF COMPONENT SYSTEM]
Temperature and pressure are both made constant
a.) One component system
b.) Two component system
c.) Three component system
c.) Three component system
Consists of two liquids that are partially miscible to each other and the third component acts as co- solvent which has the affinity to both immiscible layers
a.) One component system
b.) Two component system
c.) Three component system
c.) Three component system
Apex - 100% of each component
Base - opposite of apex; 0% of each
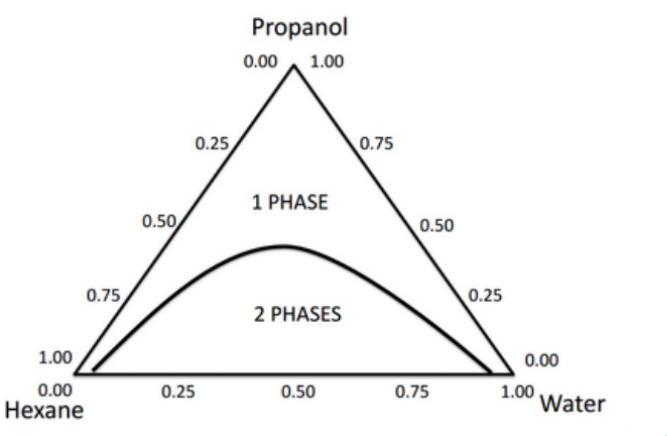
a.) One component system
b.) Two component system
c.) Three component system
Apex
[Apex / Base] ___ - 100% of each component
Base
[Apex / Base] ___ - opposite of apex; 0% of each component