Equlibrium - CHemistry
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
1
New cards
Kc > 1
Kc >>1
Kc >>1
Product favoured →
Very strongly product favoured ( Very little reactants remain)
Very strongly product favoured ( Very little reactants remain)
2
New cards
Kc < 1
Kc <
Kc <
Reactant Favoured
3
New cards
Partial Pressure
Individual Gas Pressure within gas mixture
4
New cards
Le Chateliers Principle
If Eq system is subjected to a change, the system will adjust itself to partially oppose effect of that change
5
New cards
Factors affecting Eq position
Temp
Concentration
Pressure
Concentration
Pressure
6
New cards
Adding Reactant (Conc.)
Formation of more products (Net FR)
Eq shifts →
Eq shifts →
7
New cards
Adding Product (Conc.)
Formation of more Reactants (Net RR)
Eq shifts
Eq shifts
8
New cards
Removing product (Conc.)
Favours formation of products
9
New cards
Removing Reactants (Conc.)
Favours Formation of Reactants
10
New cards
Increasing pressure
Shifts to side with LESS particles
11
New cards
Decreasing Pressure
Shifts to side with MORE particles
12
New cards
Raising Temp
Favours Endothermic Reaction
Kc Decreases
Kc Decreases
13
New cards
Lowering Temp
Favours Exothermic Reactions
Kc Increases
Kc Increases
14
New cards
Why Kc changes only to Temp
For concentration increasing one thing shifts Eq to counteract by producing more of the other.
Increasing temp depends on Exo or Endo. Increasing or Decreasing causes no shift in opposite direction to counteract so there will be wither more R or P causing Kc to change.
Increasing temp depends on Exo or Endo. Increasing or Decreasing causes no shift in opposite direction to counteract so there will be wither more R or P causing Kc to change.
15
New cards
Adding water
Dilutes everything
One with most ions Dilutes the most
One with most ions Dilutes the most
16
New cards
Haber Process
N2 + 3H2 = 2NH (-92kJ)
17
New cards
Eq Yield
Amount of Product Present at Eq
18
New cards
Meaning of Eq Constant
How far forward reaction proceeds before Eq is establishes and the Eq yield
19
New cards
Ocean Acidification Reactions
\
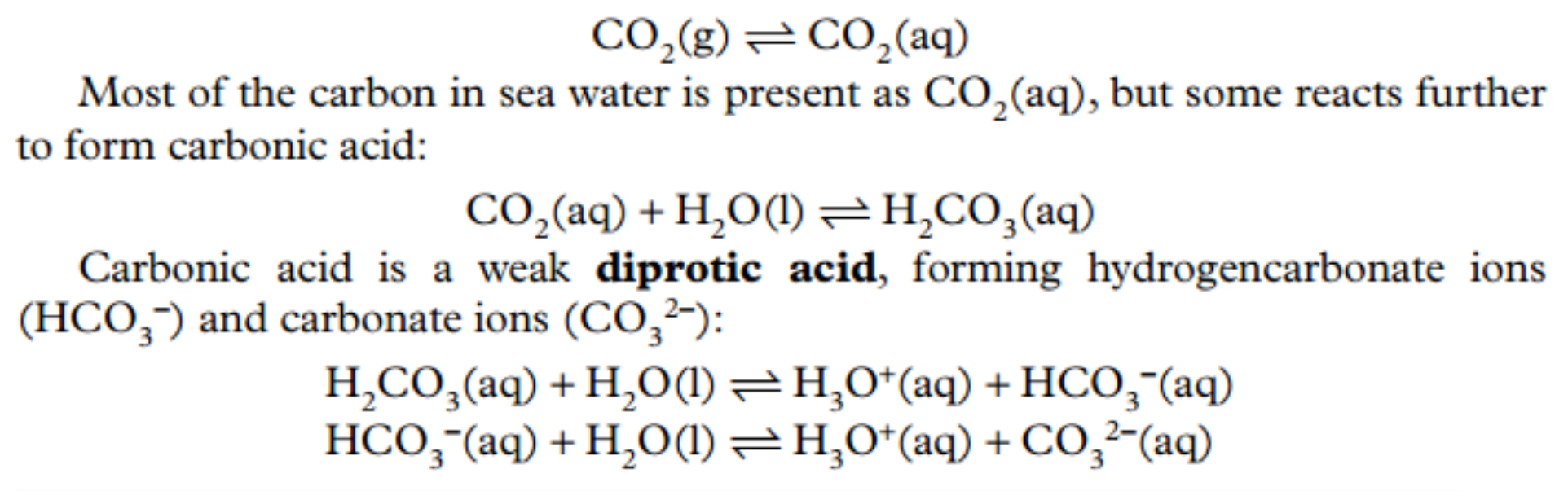
20
New cards
Ocean Acidification
As CO2(aq) increases (H)+ ions increases
pH decreases and solid CaCO3 starts to dissolve
pH decreases and solid CaCO3 starts to dissolve
21
New cards
Buffer Solutions
Are able to resist change in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added
22
New cards
Buffer Solutions are made of:
Weak Acid + Conjugate Base
Weak Base + Conjugate Acid
Weak Base + Conjugate Acid
23
New cards
Adding Acid to Buffer
Conjugate base combines with H3O+ to maintain stable pH
24
New cards
Adding Base to Buffer
Conjugate acid combines with OH= to maintain stable pH
25
New cards
Buffer Capacity
Measure of effectiveness of a buffer solution to resist a change in pH when strong acid or base is added
26
New cards
Buffer Capacity is greatest when:
* High conc. of weak acid and its conjugate base
* Conc. of acid and conjugate base are equal
* Conc. of acid and conjugate base are equal