MIE 330 Final Exam
1/248
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
249 Terms
Analysis and Design of Work
Responsibility of HR Department
Job Analysis, Work Analysis, and Job Descriptions
Recruitment
the process of seeking applicants for potential employment
recruiting, posting job descriptions, interviewing, testing, coordinating use of temporary employees
Human resource recruitment is any organizational activity that is designed to affect the number of people who apply for vacancies, the type of people who apply for them, and/or the likelihood that those applying for vacancies will accept positions if offered.
Selection
choosing employees
interviewing, testing, coordinating use of temporary employees
Training and Development
Training refers to a planned effort by a company to facilitate learning of job-related competencies, knowledge, skills and behaviors by employees.
Compensation and Benefits
wage and salary administration
incentive pay
insurance
vacation
retirement plans
profit sharing
health and wellness
stock plans
Performance Management
performance measures
preparation and administration of performance appraisals
feedback and coaching
discipline
Employee Relations
attitude surveys
employee handbooks
labor law compliance
relocation and outplacement services
Shared Service Model
refers to a way to organize the HR function that includes centers of expertise and service centers.
Self-Service
is the process of giving employees control of HR transactions.
Outsourcing
refers to the practice of having another company provide services.
Administrative Services
compensation, hiring, staffing.
An emphasis is placed on resource efficiency and service quality.
Business Partner Services
developing effective HR systems and helping implement business plans, talent management.
An emphasis is placed on knowing the business and exercising influence—problem solving, designing effective systems to ensure needed competencies.
Strategic Services
contributing to business strategy based on considerations of human resources.
An emphasis is placed on knowledge of the competition, the market, and business strategies.
Evidence-Based HRM
refers to demonstrating that human resources practices have a positive influence on the company’s bottom line or key stakeholders.
requires the use of data – from financial statements to employee surveys in order to make decisions based upon hard evidence.
Sustainability
refers to the ability of a company to survive and succeed in a dynamic competitive environment.
Social Responsibility
refer to activities that businesses undertake to benefit not just financial outcomes, but social and/or environmental outcomes.
“corporate social responsibility,” “ creating shared value,” and “triple bottom line”
Balanced Scorecard
provides a view of the company from the perspective of internal and external customers, employees and shareholders and is used to:
link HRM activities to company’s business strategy.
Evaluate extent HR is helping meet company’s strategic objectives.
High-Performance work systems and virtual teams
essentially “best-practices” in human resource management.
involve organizing social systems (people) in productive and efficient ways alongside technical systems (written procedures, computer software, etc.).
Important high-performance work practices include:
Work analysis;
Systematic selection/hiring
Extensive training
Pay for performance.
Customer Service and Quality Emphasis
customer-driven excellence includes understanding what the customer wants and anticipating futue needs
Diversity Trends in today’s and tomorrow’s workforce
Diversity includes consideration of a range of different personal backgrounds, including:
Age
Race and ethnicity
Gender
Socioeconomic status
Nationality
Cultural values
The U.S. workforce is becoming increasingly diverse.
To successfully manage a diverse workforce, managers must develop a new set of skills, including:
Communicating effectively
Coaching and developing others
Providing fair and impartial performance feedback
Creating an inclusive work environment.
Trends in Generations of Employees
Healthcare Issues at Work
Characteristics of an Ethical Company
Ethics are the fundamental principles of right and wrong by which employees and companies interact.
Ethical principles include:
The emphasis of mutual benefits;
Employees assuming responsibility for company actions;
Meaningful corporate vision for employees; and
Fairness.
Ethical HR practices involve:
The greatest good for largest number of people
Rights of privacy, due process, consent, and free speech
A code of ethics and other policies.
Sarbanes-Oxley Act
strict set of rules for corporate behavior and sets heavy fines and prison terms for noncompliance
The Global Challenge
The Technology Challenge
Equal Employment Opportunity
general term which describes the government’s efforts to ensure that individuals have an equal chance for employment, regardless of race, color, religion, sex, or national origin.
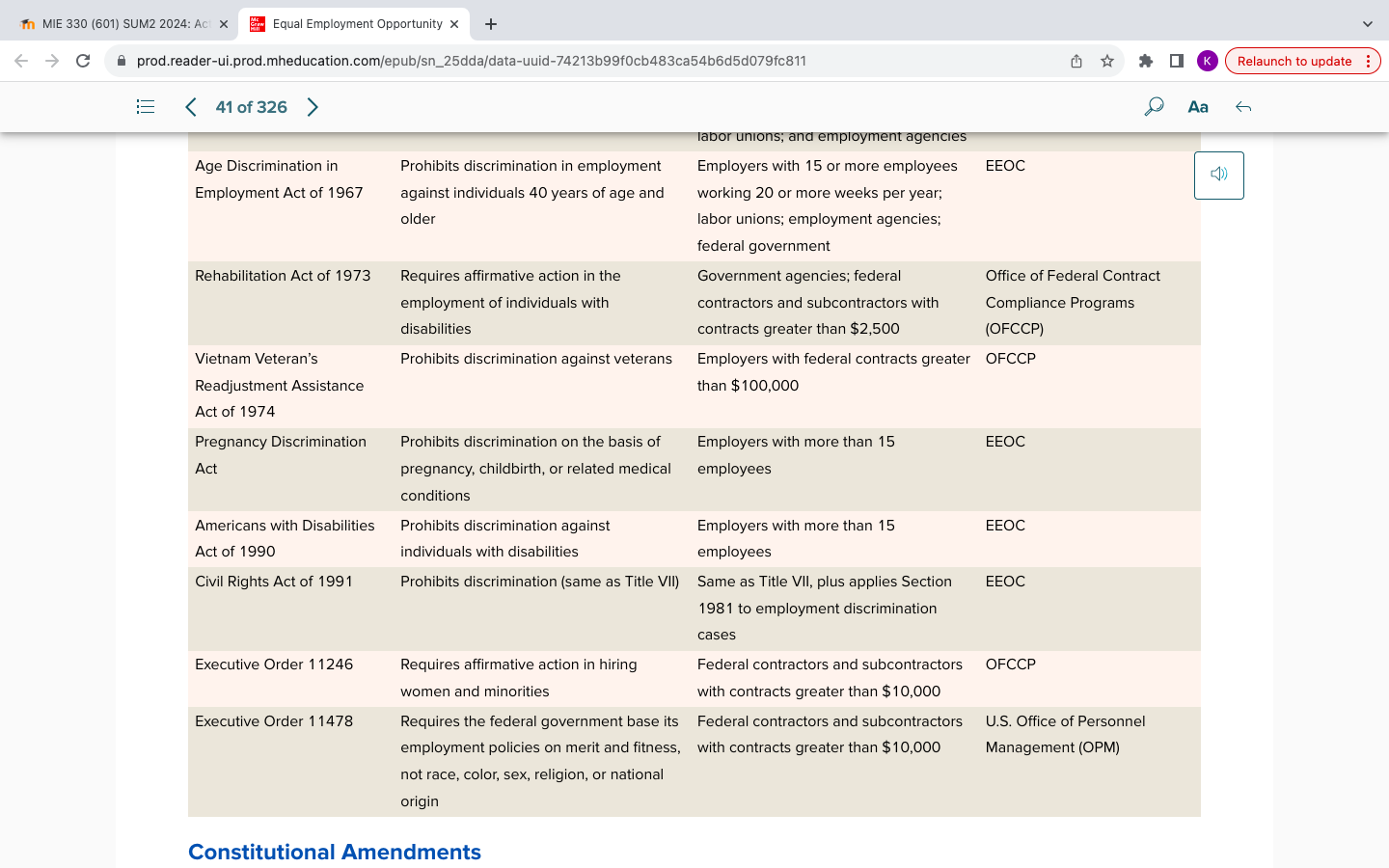
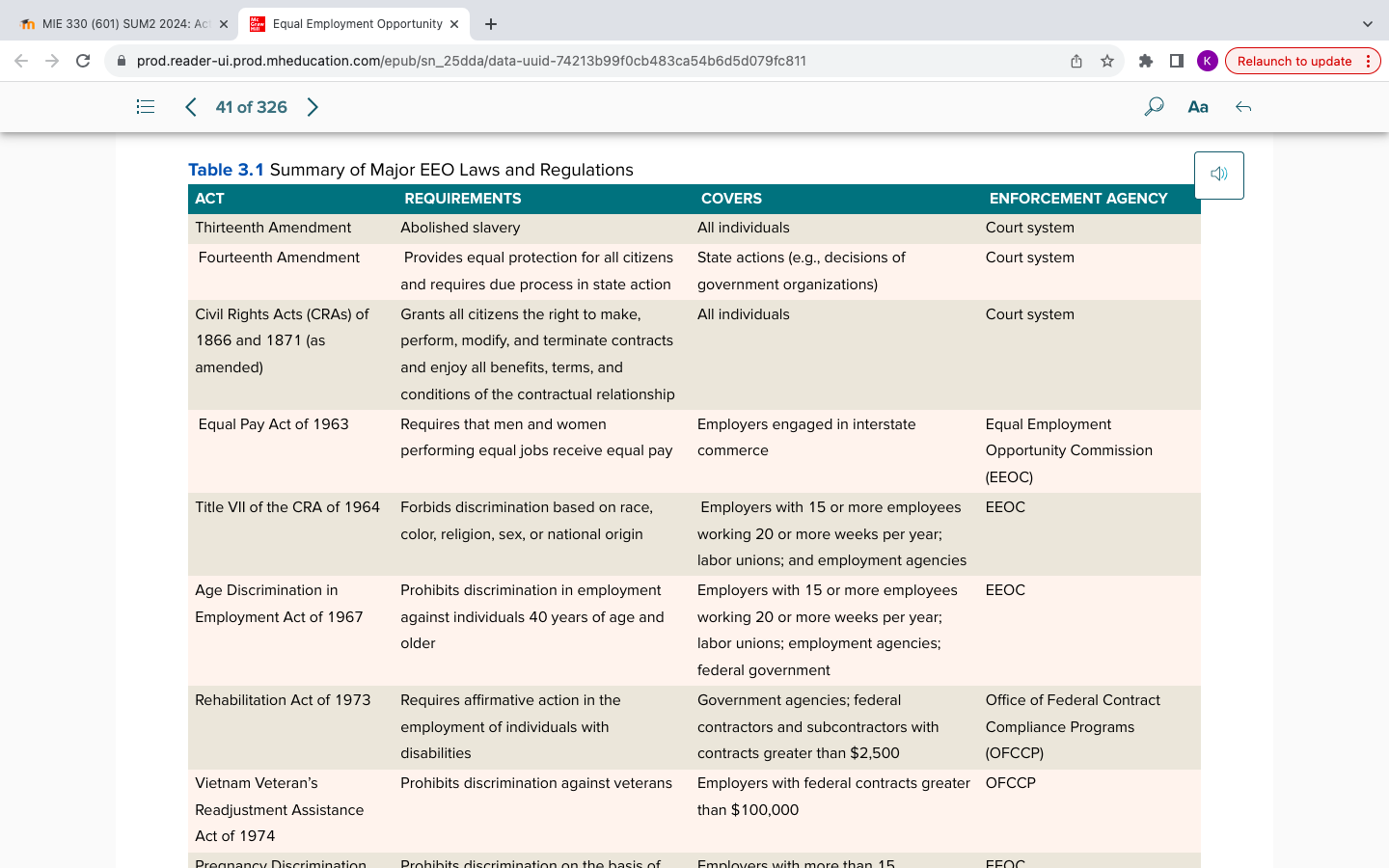
Laws, Regulations, and Enforcement Agencies (Table 3.1)
Disparate Treatment
exists when individuals in similar situations are treated differently based upon their race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age, or disability status.
Disparate treatment is often intended.
Proof of Disparate Treatment:
Plaintiff belongs to a protected group
Plaintiff applied for and was qualified for the job
Plaintiff was rejected
Disparate Impact
occurs when an employment practice thought to be neutral disproportionately excludes a protected group from employment opportunities.
Disparate impact is often unintended.
Proof of Disparate Impact:
Four-fifths rule (80%)
standard deviation rule.
Reasonable Accommodation
places a special obligation on an employer to affirmatively do something to accomodate an individual’s disability or religion
this theory is violated when an employer fails to make reasonable accommodation
Affirmative Action
originally conceived as a way of taking extra effort to attract and retain employees from underrepresented ethnic and racial groups
resorted to quota-like hiring
Quid Pro Quo
occurs when some type of benefit or punishment is made contingent upon the employee submitting to sexual advances.
Hostile Work environment
occurs when someone's behavior in the workplace creates an environment that makes it difficult for someone of a particular sex to work.
Standard Deviation Rule
uses actual probability distributions to determine adverse impact
uses the difference between expected representation or hiring rates for visible minorities and the actual representation to determine whether the difference between these two values is greater than would occur by chance
4/5ths Rule
80% rule or the "adverse impact" rule, is a principle used in employment discrimination law to determine if a selection process is discriminatory.
It states that if the selection rate for a particular group is less than 80% of the selection rate for the group with the highest selection rate, then the selection process is considered discriminatory.
Occupational Safety and Health Act and Administration
authorizes the federal government to establish and enforce occupational safety and health standards for all places of employment engaging in interstate commerce.
Under OSHA, employees have the right to:
Request an inspection.
Have a representative present at an inspection.
Have dangerous substances identified.
Be promptly informed about exposure to hazards and be given access to accurate records regarding exposures.
Have employer violations posted at the work-site.
Strategic Management
is a process to address the organization’s competitive challenges by integrating goals, policies and action sequences into a cohesive whole.
Strategic Human Resource Management: is the pattern of planned HR activities and deployments intended to enable an organization to achieve its goals.
Role of HRM in Strategy Formulation (linkages)
Strategies to create a competitive advantage come in two basic forms:
Overall cost leadership – that is, producing the lowest cost products or services;
Differentiation strategy – this is, creating the perception that products or services are different from others in the industry.
Porter also discusses five forces that shape strategy:
Rivalry among existing competitors
Bargaining power of suppliers;
Threat of substitute products or services;
Bargaining power of buyers.
Threat of new entrants;
SHRM Process Model
A pattern of planned human resource deployments and activities intended to enable an organization to achieve its goals.
Formulation, Implementation
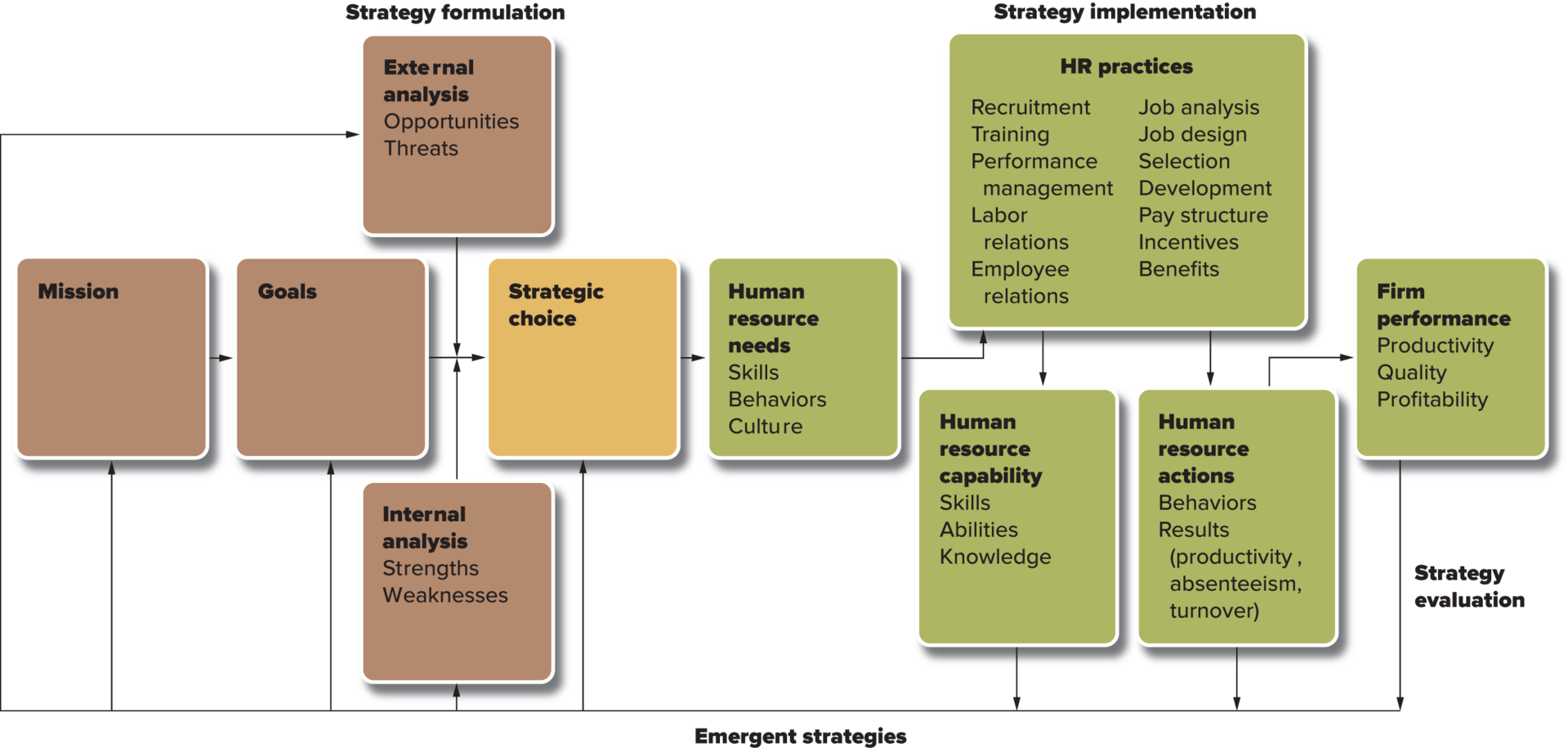
Strategy Formulation
The process of deciding on a strategic direction by defining a company’s mission and goals, its external opportunities and threats, and its internal strengths and weaknesses.
Mission
a statement of the organizations reason for being
usually specifies the customers served, the needs satisfied, and the values received by the customers, and technology used
often accompanied by a mission statement
Goals
What an organization hopes to achieve in the medium- to long-term future.
SWOT Analysis
strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats
Strategy Implementation
The process of devising structures and allocating resources to enact the strategy a company has chosen.
Overall Cost Leadership
according to Porter, focuses on becoming the lowest cost producer in an industry
achieved by constructing efficient large-scale facilities by reducing costs through capitalizing on the experience curve, and by controlling overhead costs and costs in areas such as research and development, service, sales force, and advertising
Differentiation Strategy
attempts to create the impression that a the company’s product or service is different from the of others in the industry
can come from creating a brand image, from tech, from offering unique features or customer service
if a company succeeds in differentiating its product, it will achieve above-average returns, and the differentiation may protect it from price sensitivity
Forces that shape strategy (Porter)
Rivalry among existing competitors;
Threat of new entrants;
Bargaining power of suppliers;
Threat of substitute products or services;
Bargaining power of buyers.
Cascio (2009)
Work-Flow design
the process of analyzing the tasks necessary for the production of a product or service, prior to allocating and assigning these tasks to a particular job category or person.
In a work-flow design, consideration is made of:
Inputs;
Resources;
Human capital;
Work activities;
Outputs.
Work-Unit activity analysis
Work analysis
also known as job analysis) is the process of getting detailed information about the work that is assigned to individuals or groups in an organization.
Work analysis has been called the building block of everything that the personnel department does.
Indeed, the following human resource practices rely upon a detailed understanding of work:
Work redesign;
Recruitment;
Selection;
Training;
Performance appraisal;
Job evaluation.
Centralization
dimension of organizational structure
Departmentalization
dimension of organization structure
Functional Structure
employs a functional departmentalization scheme with high levels of centralization.
Divisional Structure
employs a workflow departmentalization and low levels of centralization.
Job Description
list of the tasks, duties, and responsibilities (TDRs) that a job entails.
Job Specification
a list of the knowledge, skills, abilities, and other characteristics (KSAOs) that an individual must have to perform the job.
Occupational Information Network (O*NET)
uses common language that generalizes across jobs to describe the abilities, work styles, work activities, and work context required for various occupations that are more broadly defined
Dictionary of Occupational Titles
1930’s
DOT no longer served its purpose
abandoned for ONET
link demand for skills and the supply of skills in the US workforce
Position Analysis Questionnaire
standardized job analysis questionnaire containing 194 items
represents work behavior, conditions, and job characteristics
6 Sections:
Information Input (where and how a worker gets info)
Mental Processes (reasoning, decision-making, planning)
Work Output (physical activities, tools, devices)
Relationships with other Persons
Other Characteristics
Mechanistic Approach
this approach has its roots in classical industrial engineering and focuses on designing jobs around the concepts of task specialization, skill simplification, and repetition.
Motivational Approach
the job characteristics model which emphasizes the importance of motivation job characteristics, including: skill variety, task identity, task significance, autonomy, and feedback.
Forecasting
he attempts to determine the supply of and demand for various types of human resources to predict areas within the organization where there will be future labor shortages or surpluses.
Determine Labor Demand
Derived from product/service demanded;
External in nature.
Determine Labor Supply
Internal movements caused by transfers, promotions, turnover, retirements, etc.
Leading Indicator
An objective measure that accurately predicts future labor demand.
Transitional Matrix
identify employee movements in different job categories over time.
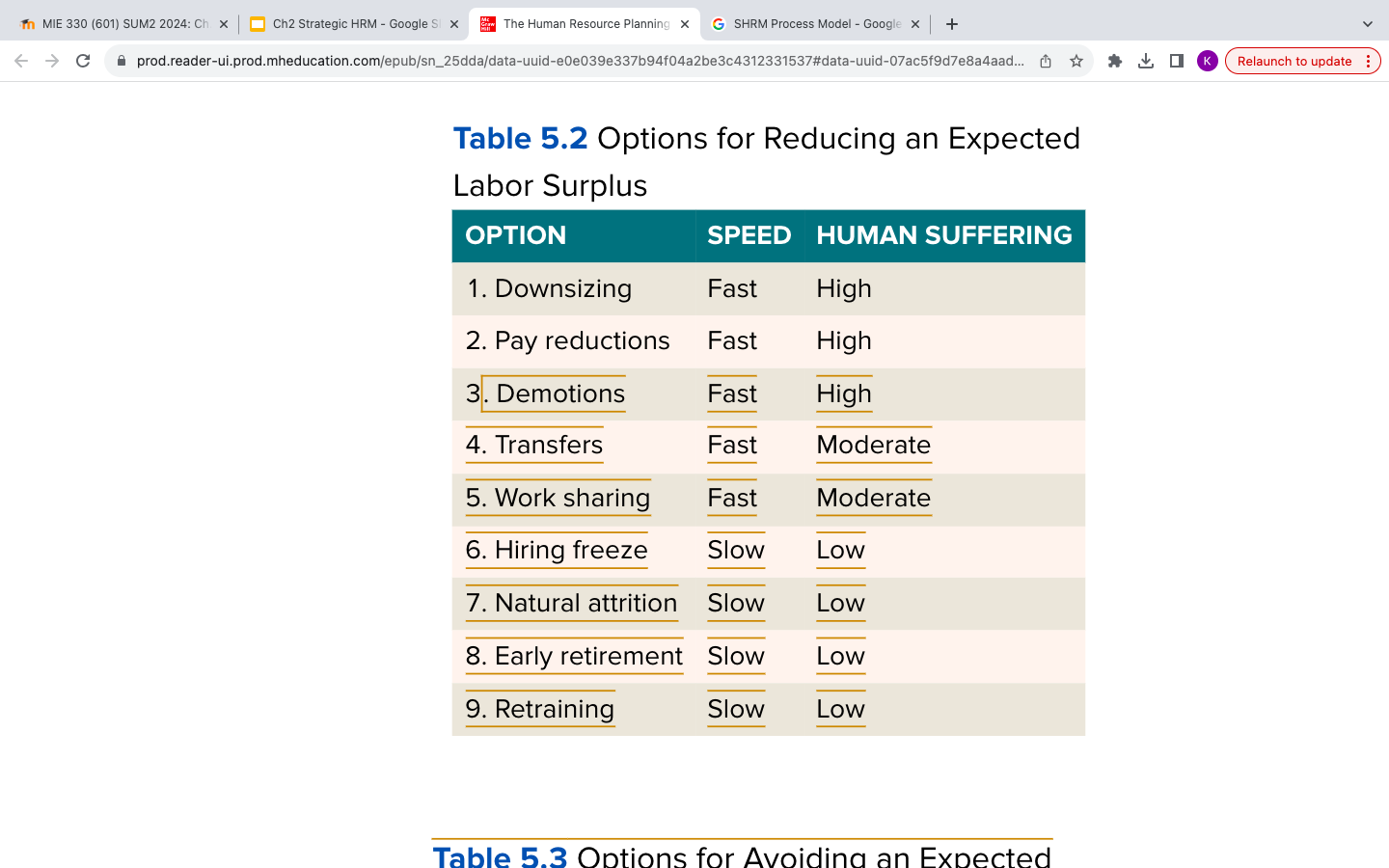
Options for Surplus (5.2)
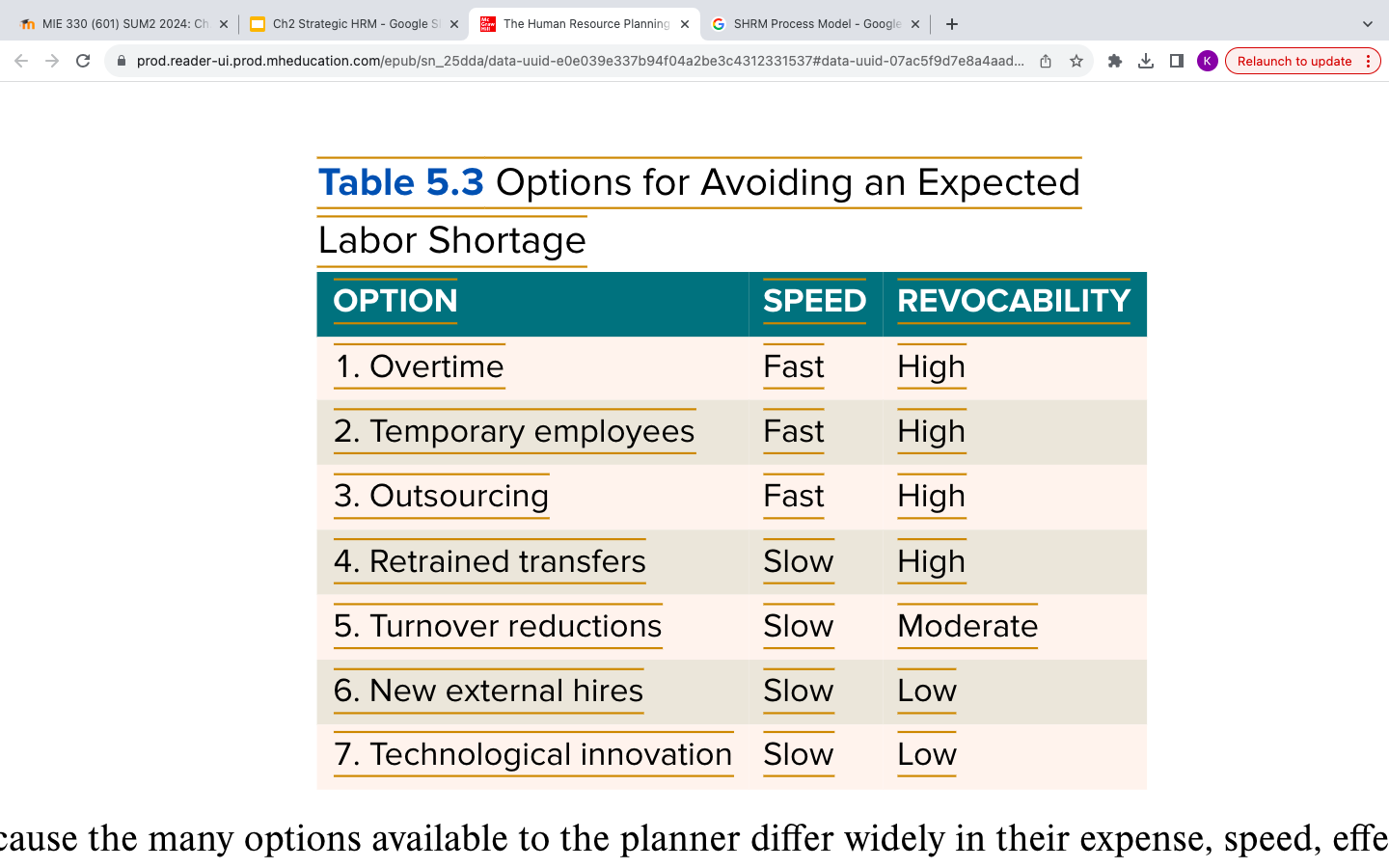
Options for Shortages (5.3)
Downsizing
fast speed but high human suffering
The planned elimination of large numbers of personnel, designed to enhance organizational effectiveness.
Outsourcing
fast speed and high revocability
An organization’s use of an outside organization for a broad set of services.
Offshoring
A special case of outsourcing, in which the jobs that move leave one country and go to another.
Workforce Utilization Review
A comparison of the proportion of workers in protected subgroups with the proportion that each subgroup represents in the relevant labor market.
Job Choice (5.4)
Recruitment Policies
Internal versus external recruiting—A decision must be made on whether to recruit from within or outside the organization.
Extrinsic and intrinsic rewards—Lead‑the‑market pay strategy is a policy of paying higher than current market wages.
Employment‑at‑will policies state that either party in the employment relationship can terminate that relationship at anytime, regardless of cause.
Due process policies formally lay out the steps an employee can take to appeal a termination decision.
Image advertising promotes an organization as a good place to work in general and may be particularly important for organizations in highly competitive labor markets that perceive themselves as having a bad image.
Employment-at-will-Policies
Policies stating that either an employer or an employee can terminate the employment relationship at any time, regardless of cause.
Due Process Policies
Policies by which a company formally lays out the steps an employee can take to appeal a termination decision.
Direct Applications
People who apply for a job vacancy without prompting from the organization.
Referrals
People who are prompted to apply for a job by someone within the organization.
Recruiter’s Functional Areas, Traits, and Realism
Recruiters: Recruiters may have more impact depending on a number of factors.
1. Recruiter’s functional area—The recruiter is likely to be perceived as more credible if he or she is from the same functional area the recruit is being considered for.
2. Recruiter‘s traits—Critical traits appear to be warmth and “informativeness.”
3. Recruiter's realism—Deceiving candidates about the negative elements of a job may increase later turnover.
Reliability
The degree to which a measure of physical or cognitive abilities, or traits, is free from random error.
If a measure of a stable characteristic is reliable, the score a person receives will be consistent over time and over different contexts.
Reliability is a necessary but not sufficient characteristic of a good measuring device.
Major types:
Correlation coefficient;
Test-retest reliability.
Validity
The extent to which a performance measure assesses all the relevant –and only the relevant- aspects of job performance.
Criterion-Related Validation
a substantial correlation between test scores and job-performance scores
Predictive validity;
Concurrent validity.
Predictive Validation
A criterion-related validity study that seeks to establish an empirical relationship between applicants’ test scores and their eventual performance on the job.
Concurrent Validation
A criterion-related validity study in which a test is administered to all the people currently in a job and then incumbents’ scores are correlated with existing measures of their performance on the job.
Content Validation
the items, questions, or problems posed by a test are a representative sample of the kinds of situations or problems that may occur on the job.
A test-validation strategy performed by demonstrating that the items, questions, or problems posed by a test are a representative sample of the kinds of situations or problems that occur on the job.
Generalizability
the degree to which the validity of a selection method established in one context extends to other contexts.
Utility
The degree to which the information provided by selection methods enhances the effectiveness of selecting personnel in real organizations.
Utility is impacted by reliability, validity, and generalizability.
Legality
All selection methods must conform to existing laws and legal precedents
The Civil Rights Act of 1991 (an extension of the Civil Rights Act of 1964) protects individuals from discrimination based on race, color, sex, religion, and national origin with respect to hiring as well as compensation and working conditions. The 1991 CRA:
Defines employers' obligation to establish the business necessity of any neutral‑appearing selection method that has adverse impact on protected groups;
Allows for juries to hear discrimination complaints;
Prohibits the granting of preferential treatment to minority groups.
Situational Interview
An interview procedure where applicants are confronted with specific issues, questions, or problems that are likely to arise on the job.
defined as a dialogue initiated by one or more persons to gather information and evaluate the qualifications of an applicant for employment.
It is the most widely used selection method, although research suggests it can unreliable, low in validity, and biased against a number of groups.
The utility of an interview can be increased by the following suggestions
Interviews should be structured, standardized, and focused on accomplishing a small number of goals oriented to skills and behaviors that are observable.
Interviewers should plan to come out of each interview with a quantitative rating.
Interviewers should also have a structured note-taking system that will aid recall when it comes to satisfying the ratings.
Cognitive Ability Tests
differentiate individuals based on their mental rather than physical capacities.
One of the major drawbacks to these tests is that they typically have adverse impacts on some minority groups.
Verbal Comprehension
refers to a person’s capacity to understand and use written and spoken language.
Quantitative Ability
concerns the speed and accuracy at which one can solve arithmetic problems.
Reasoning Ability
refers to a person’s capacity to invent solutions to many diverse problems.
Personality Inventories
categorize individuals relative to what they can do, personality measures tend to categorize individuals by what they are like.
Common dimensions assessed are extroversion, adjustment (also called emotional stability), agreeableness, conscientiousness, and inquisitiveness (also called openness to experience).
Work Sample Tests
attempt to simulate the job in a pre-hiring context to observe how the applicant performs.
Assessment Center
Honesty Testing
attempts to assess the likelihood that employees will steal.
Formal Training
refers to training and development programs, courses and events that are developed and organized by the company.
Informal Learning
refers to learning that is learner initiated, involves action and doing, is motivated by intent to develop, and does not occur in a formal setting.
Continuous Learning
a learning system that requires employees to understand the entire work process and expects them to acquire new skills, apply them on the job, and share what they have learned with other employees.