5 Etiology and Risk Factors of Periodontal Diseases
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
what term refers to the cause of a disease?
etiology
what term refers to a modifying characteristic that is associated with an increased chance of developing a disease?
risk factor
what are examples of extrinsic risk factors?
plaque, smoking, dental restorations
what are examples of intrinsic risk factors?
genetics, age, gender, race, diabetes, tooth anatomy
what are idiopathic factors?
cause unknown
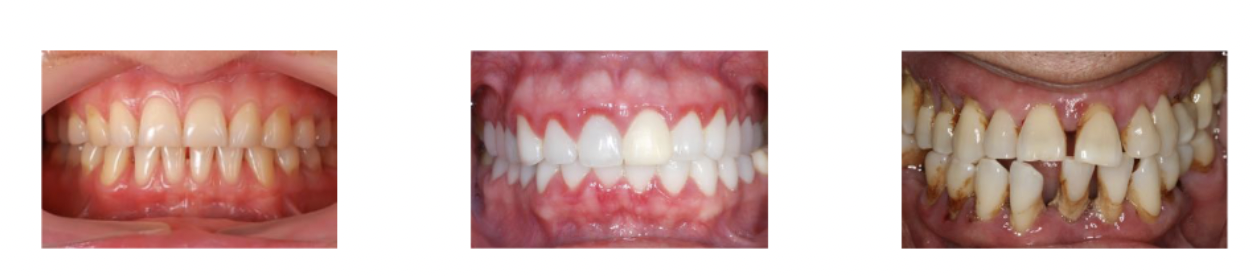
Periodontal inflammation caused by plaque bacteria
For some people only gingivitis develops, for others it progresses to periodontitis. This does not always correspond with the amount of plaque (genetics? idiopathic factors?)
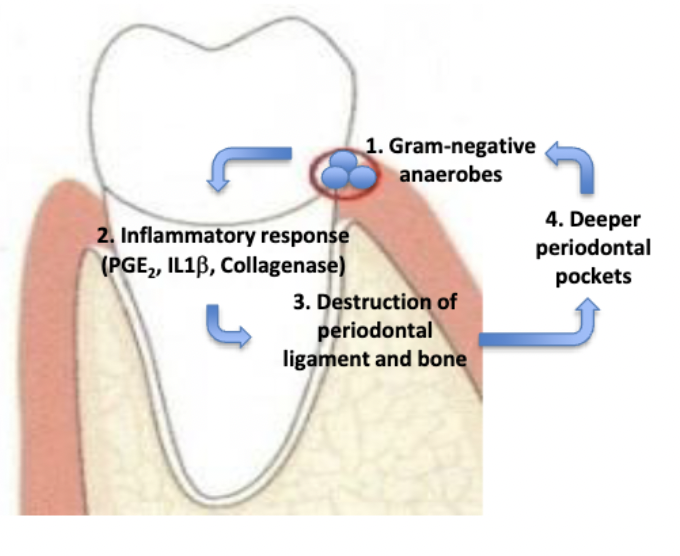
How does bacteria and inflammation cause periodontitis?
Development of deeper pockets create a positive feedback loop
Deeper pockets:
contain more bacteria
contain more Gram-negative anaerobe bacteria
harder to keep clean
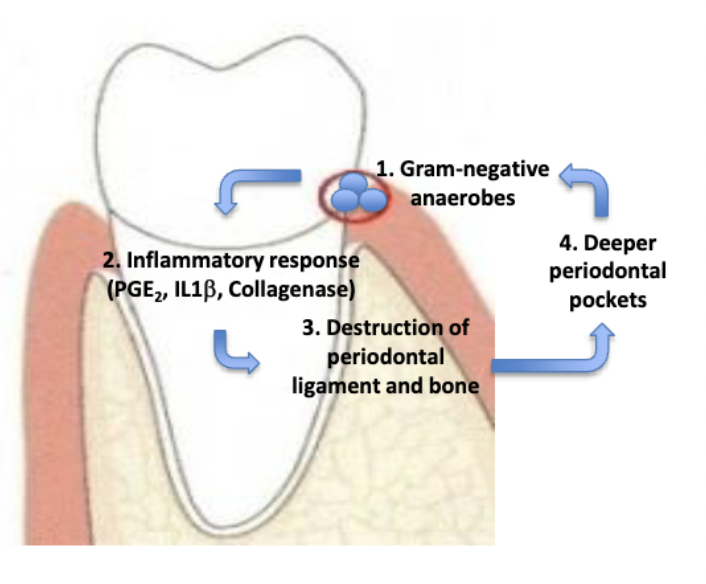
how do deeper pockets create a positive feedback loop?
contain more bacteria
contain more gram-negative anaerobe bacteria
harder to keep clean
No single bacterial strain has been identified as a cause; rather groups of bacteria with varying disease-inducing potential were identified. What are some of the major groups?
• Red complex
• Orange complex
• others
Other yet un-identified bacteria may play significant roles (estimated 600 strains in mouth)
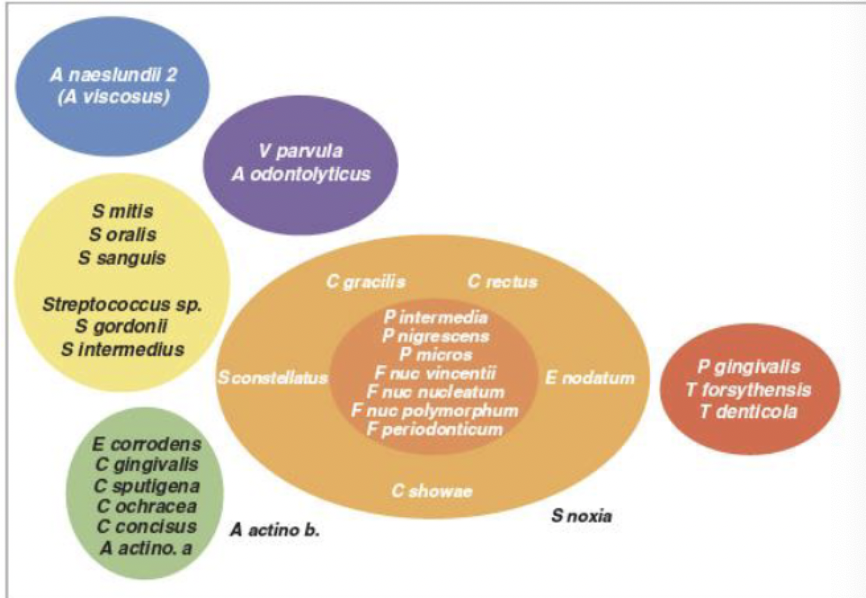
what bacteria make up the red complex?
P. gingivalis
T. forsynthesis
T. denticola
Note that tissue damage is not directly caused by bacteria, but by …?
the body’s immune response to the bacteria
Periodontal attachment loss leads to:
• Periodontal pocket formation
• Gingival recession
• Root exposure
• Bone loss
• Tooth loosening
• Tooth loss
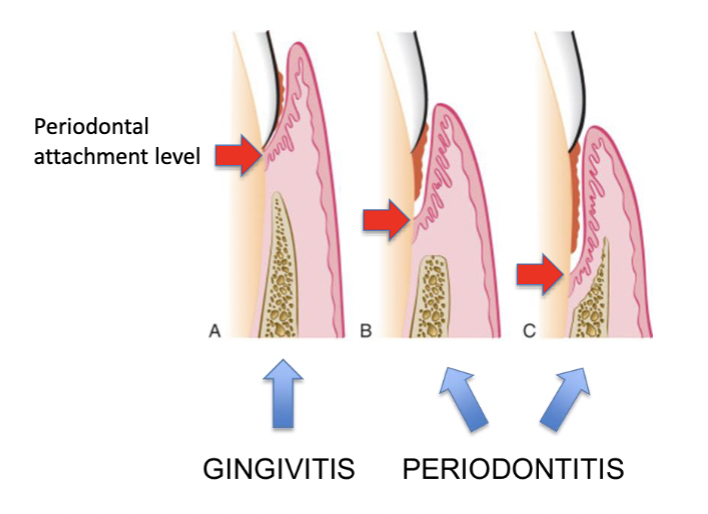
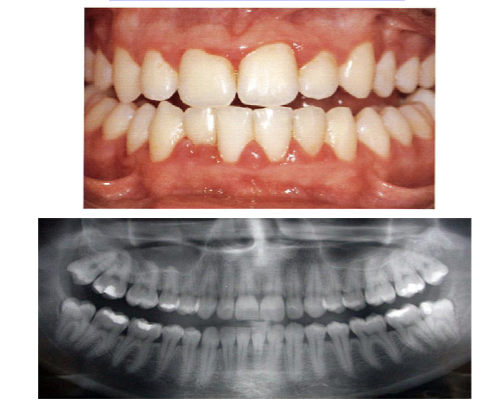
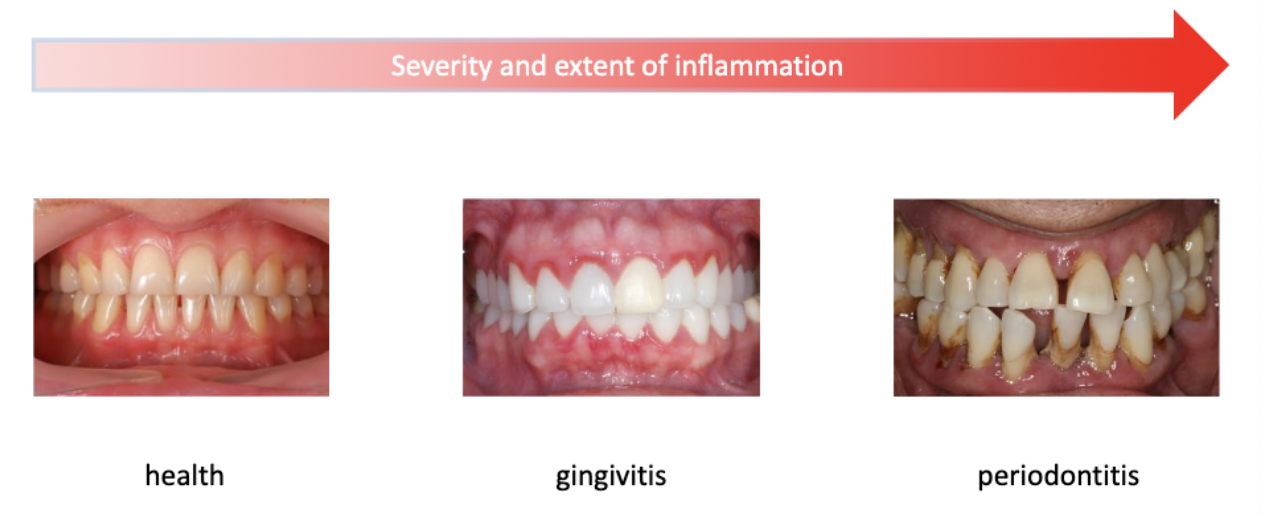
inflammation only, no attachment loss, no bone loss
gingivits
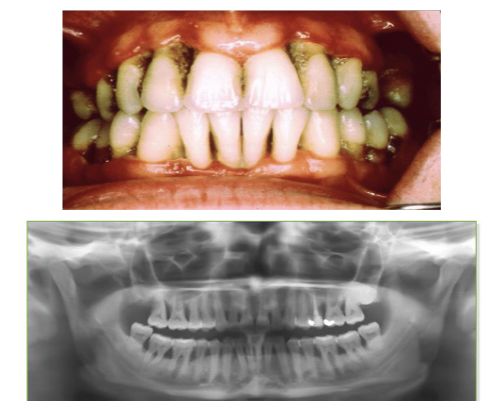
inflammation, attachment loss and bone loss
periodontitis
what is the co-existence of two organisms, which may be beneficial to one or the other?
symbiosis
what is an example of symbiosis?
biofilm in healthy mouth
what is an imbalance of bacteria and the host?
dysbiosis
dysbiosis in periodontal sulcus leads to a disproportionate immune response to periodontal bacteria causes tissue injury and bone loss
what are major risk factors for periodontitis?
smoking
diabetes
what are minor risk factors for periodontitis?
• Genetics
• Age
• Gender
• Race
• Obesity
• Poor nutrition
• Alcohol consumption
• Medication
• Dental restorations
• Occlusal trauma
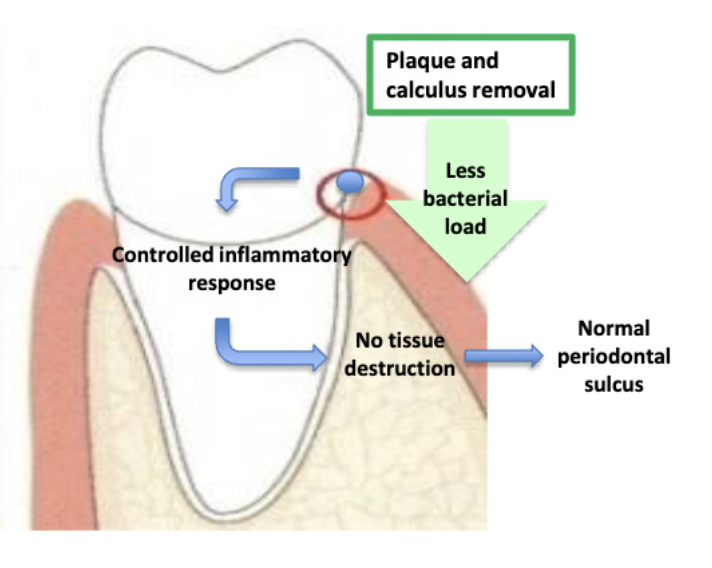
plaque and calculus can be removed by…? why is removal so important?
brushing
flossing
prophylaxis
Decreasing bacterial load disrupts positive feedback loop
describe the positive feedback loop created by development of deeper pockets in periodontitis/
When smokers and non-smokers with comparable plaque levels are compared, smokers have:
– Fewer teeth
– Deeper periodontal pockets
– More supragingival calculus
– More attachment loss
– More bone loss
– Less gingival bleeding on probing
epidemiological studies have found smokers are at greater relative risk of…/
periodontal attachment lost
severe bone loss

what are 3 proposed mechanisms of how smoking negatively effects the periodontium?
impaired immune response
increased prevalence of periodontal pathogens
impaired healing
how does smoking impair immune response?
– Neutrophil chemotaxis and phagocytosis
– Decreased IgG antibody production
– Decreased B-helper lymphocyte numbers
how does smoking impair healing?
– Altered fibroblast attachment and function
– Negative local effects on cytokine and growth factor production
– Poor response to periodontal therapy
what’s a normal fasting blood glucose level?
<100 mg/dL
what’s a hyperglycemic fasting glucose level?
>126 mg/dL
what’s a hyperglycemic casual (non-fasting) glucose level?
>200 mg/dL
what’s a normal HbA1c level? (normal glycated hemoglobin)
what’s the therapeutic target level?
normal: <5.7%
therapeutic target: <6.5%
how does diabetes damage tissues?
vascular changes
altered host immune response
alteration in CT metabolism
there a plethora of chronic complications that pts with diabetes are at a higher relative risk of developing including…?
• Retinopathy (rr: 25x)
• Glomerulosclerosis (rr: 17x)
• Cardiovascular complications (rr: 2-4x)
• Neuropathy
• Impaired wound healing
• Periodontal disease (rr: 2.3x)
how do vascular changes caused by diabetes damage tissues?
Vascular changes leading to diabetic microangiopathy, resulting in kidney failure, retinopathy, atherosclerosis and impaired wound healing
how does diabetes alter host immune response?
• impairment of neutrophil adherence, chemotaxis and phagocytosis that impairs bacterial killing
• Hyper-responsiveness of monocytes and macrophages resulting in increased pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediators
how does diabetes altering connective tissue metabolism damage tissue?
uncouple the resorptive and formative responses and impair bone remodeling
what national societies have released statements regarding the association between diabetes and periodontal disease?
American Academy of Periodontology
Diabetes increases the risk of periodontal diseases, and biologically plausible mechanism have been demonstrated in abundance
American Diabetes Association:
Research shows that there is an increased prevalence of gum diseases among those with diabetes, adding serious gum disease to the list of other complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
what role do genetics play in periodontal disease?
NOT A MAJOR COMPONENT BUT
Family (twin) studies indicate that early onset forms of periodontitis such as localized aggressive periodontal disease may be partially inherited. Inherited leukocyte deficiency may play a role.
For chronic periodontal disease twin studies indicate some genetic component; however environmental factors appear more powerful
Estimates for hereditability of periodontitis are:
38% (twin studies)
15% (other family studies)
7% (genome-wide association studies, GWAS)
Kornman et al. reported a specific genotype of the ___________ that was associated with severity of periodontitis in non-smokers, and distinguished individuals with severe periodontitis from those with mild disease
polymorphic IL-1 gene cluster
Pro-inflammatory cytokines such as ______ are key regulators of the host response to microbial infection during periodontal pathogenesis
interleukin-1 (IL-1) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-ALPHA)
IL-1 is a major modulator of extracellular matrix catabolism and bone resorption
Therefore, increased production of IL-1 may result in greater periodontal tissue destruction (i.e. alveolar bone, extracellular matrix)
Prevalence and severity of periodontitis increases/decreases with age
increases
is periodontitis an inevitable consequence of aging?
NO.
There are many older individuals without periodontitis
The “age effect” is likely due to cumulative effect of prolonged exposure to true risk factors (wear ‘n’ tear)
gingival recession, not pocket depth is responsible for increased
attachment loss with aging
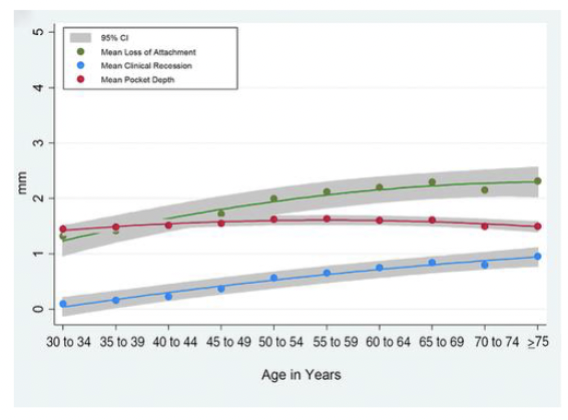
what is the relationships between gender and prevalence of periodontitis?
• No clear difference between male and female in susceptibility to periodontitis
• Oral hygiene and health care utilization is better in females, resulting in better observed periodontal status
• On the other hand females may retain teeth longer, resulting in more remaining teeth with periodontitis
what is the relationships between race and prevalence of periodontitis?
• In the US, Mexican-Americans and Non-Hispanic blacks show higher prevalence of periodontitis
• However no consistent pattern shown worldwide
• Socio-economic status and access to care may be important confounding factor
what is an important confounding factor that may cause a perceived association between race and prevalence of periodontitis?
Socio-economic status and access to care
The overall odd ratio of having periodontal disease in obese or overweight individuals is ___
2.13
how might poor nutrition be a minor risk factor for periodontitis?
The negative association between plasma vitamin C levels and periodontal attachment loss suggests that vitamin C deficiency may contribute to the severity of periodontal breakdown (scurvy)
how might alcohol be a minor risk factor for periodontitis?
Alcohol consumption may be associated with increased severity of attachment loss in a dose-dependent fashion. (Counfounder?
what types of medications are minor risk factors for periodontitis?
Anticonvulsants, beta-blockers and immunosuppressants can cause gingival hyperplasia
what blood disease pose a minor risk factor for periodontitis?
Acute leukemias (AML, ALL): enlargement, bleeding, ulcerations
Neutropenia, agranulocytosis: ulcerations, attachment loss
Anemia: hemorrhage, mucosal atrophy
what are some local contributing factors that lay contribute to periodontitis?
• Overhanging / defective restorations
• Open contacts / food impaction
• Subgingival calculus deposits
• Brushing trauma (non-carious cervical lesions, NCCL)
• Tooth position (gingival recession)
• Local tooth related anatomy
• Occlusal trauma
Alveolar bone loss was found greater around what type of restorative margins and restorations?
overhanging and defective
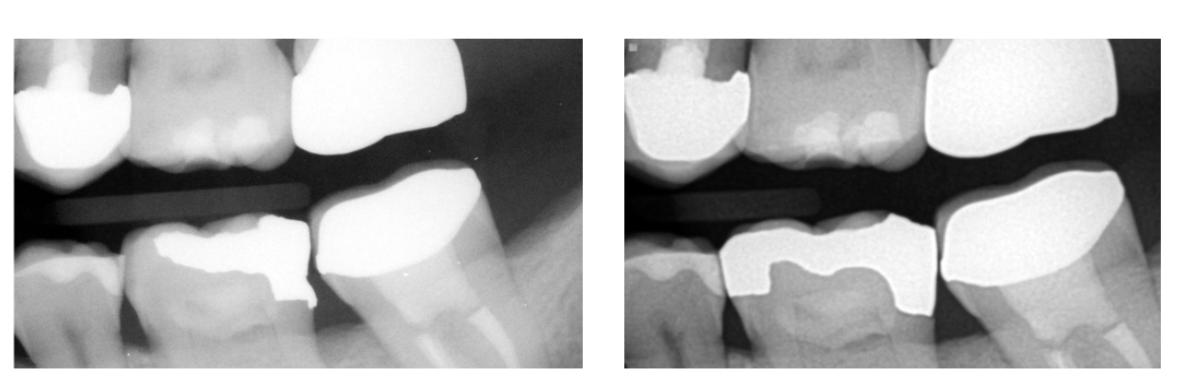
what type of interproximal contacts in class II restorations were found to be associated with less alveolar bone height.
Open (Role of food impaction?)
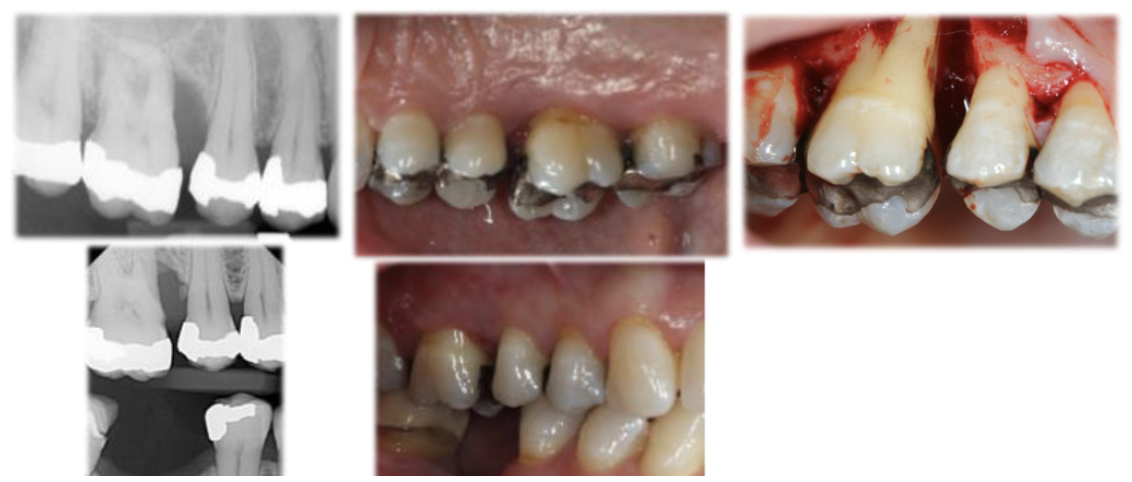
_________is always covered with a non-mineralized layer of plaque. The non-mineralized plaque on the calculus surface is the principal irritant, but the underlying calcified portion may be a significant contributing factor.
Subgingival calculus
how is subgingival calculus deposits a local contributing factor to periodontits?
subgingival calculus is always covered with a non-mineralized layer of plaque. The non-mineralized plaque on the calculus surface is the principal irritant, but the underlying calcified portion may be a significant contributing factor.
what type of lesion is frequently seen as horizontal non-carious v-shaped grooves along the gingival margin. Most likely caused by …? It can cause…?
Non-carious cervical lesions (NCCL)
traumatic brushing
gingival recession and root sensitivity
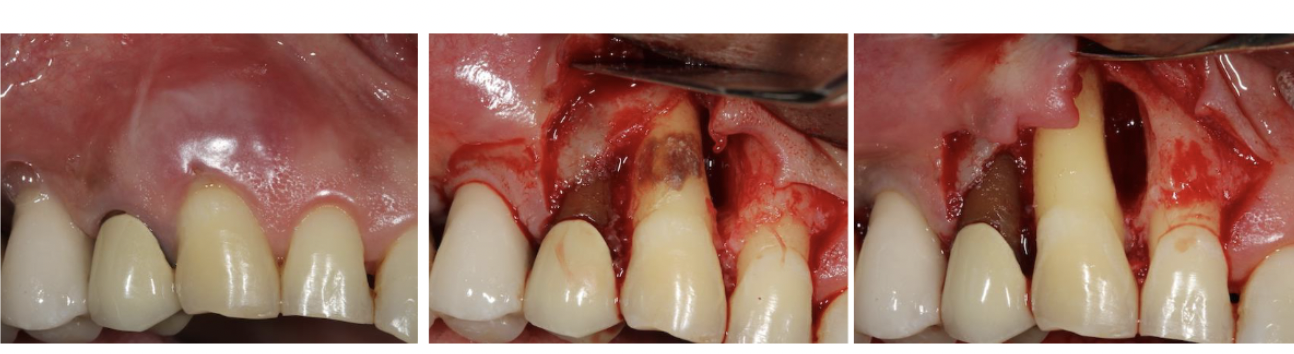
how is brushing trauma a local contributing factor to periodontal disease?
Non-carious cervical lesions (NCCL) is frequently seen as horizontal non-carious v-shaped grooves along the gingival margin. Most likely caused by traumatic brushing. It can cause gingival recession and root sensitivity
how is tooth position a local contributing factor to periodontal disease?
Labially positioned tooth (inherited/acquired through orthodontic movement)
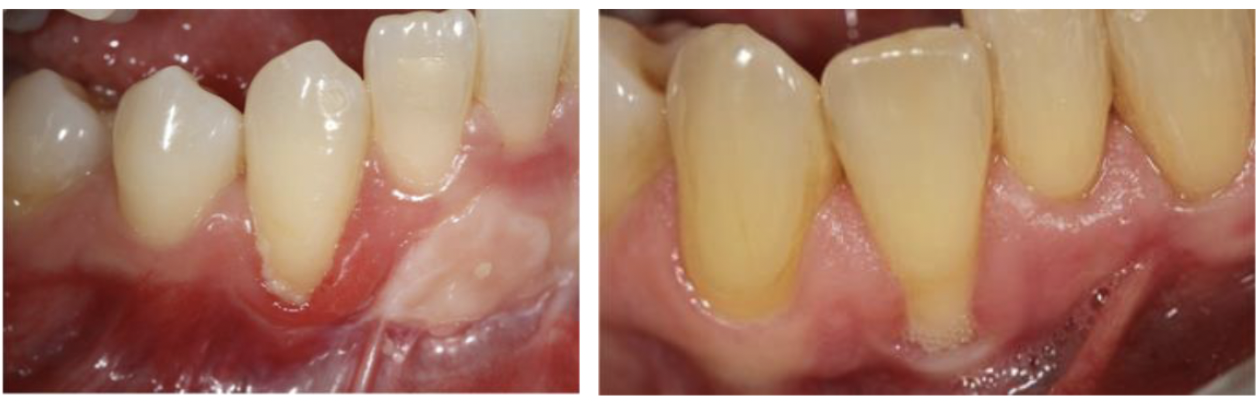
does occlusal trauma cause periodontitis?
Occlusal trauma (bruxism, premature occlusal contact, crossbite, attrition, wear facets) alone do not cause periodontitis.
When combined with periodontal inflammation, occlusal trauma may accelerate attachment loss and development of vertical bone loss
how is cervical enamel project a local contributing factor for periodontitis?
Enamel projections may be removed because connective tissue attachment is not possible on enamel, and the projections may created a pathway for the ingress of bacteria that will have detrimental effect on periodontal health
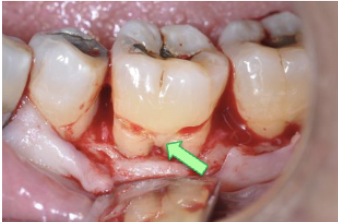
how are radical grooves a local contributing factor for periodontitis?
Enamel-covered groove on the root resulting in deep probing, food impaction
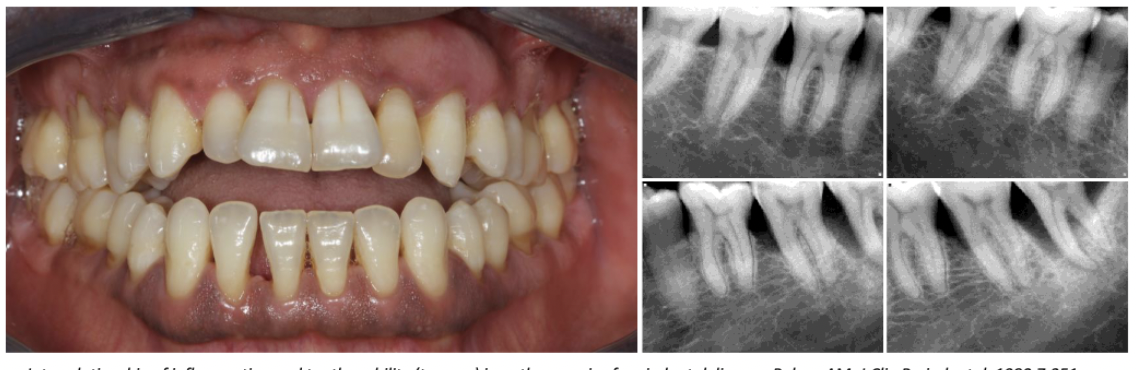
what types of tooth anatomy may be local contributing factors for periodontitis?
cervical enamel projection
radical groove