CH #13: Services
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Importance of Service
Adding a service to product increases the value of the product
Service as a Product (Productization)
Attempts to treat service as product by:
Standardizing services into modularized products
Creating a name/logo/identity for the service
Purpose of Productization
To capture more brand equity
To reduce costs and increase margin
To maintain consistent performance
Product as a Service (Servicization)
You should consider “something” as a service if:
Your product is one time purchase good (software)
Your product is expensive to purchase for many
Your product requires maintenance and after-services frequently
Services are Intangible
No physical presence, we can’t see it or touch it
Brand association is low
It is difficult to convey the benefits of services.
Therefore, offer cues to help customers experience and perceived their service more positively, waiting rooms with large TVs, beverages, and comfortable chairs
Memory aids (logos, tagline) are more important for service
Word of Mouth
With the rise of social media, the rate at which information move has increased exponentially
Consumers are consistently asked to provide rating of everything
Marketers of services must manage their digital reputation emphasizing positive experience
More important for services than for hard goods
Service are Perishable, and cannot be Inventorized
Service cannot be inspected the same as inventory checking for a physical product
we cannot hold inventory for fluctuation for demand
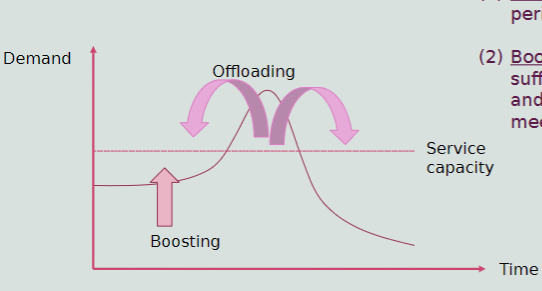
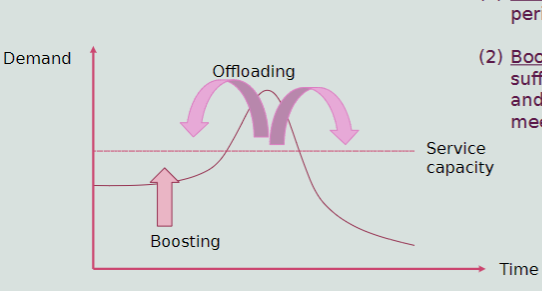
Planning for Demand Fluctuations
Offload Demand
Boost low-period demand
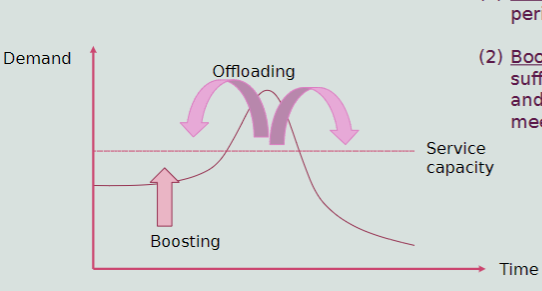
Offload Demand
Method to stall work flow during peak periods/times of the day
I.E. Customer are more willing to wait to sit down to dinner at 9:30 PM instead of 8 PM if they are provided a comfortable bar and lounge area to socialize while waiting
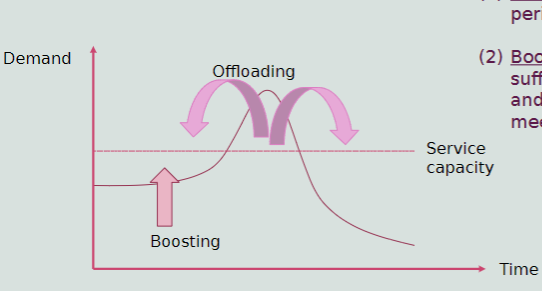
Boost Low-Period Demand
To increase productive to support the fixed and labor costs necessary to meet peak demand, occurs in “slower” periods/time of the day
I.E. A resturant may offer a 5 PM dinner special or happy hour to generate increased revenue during a common slow period
Service Gaps
When delivery of a service fails to meet customer expectations
Providing Great Service: Service Gap Model
Knowledge gap
Standards gap
The delivery gap
The communication gap
Knowledge Gap
Exist when management misunderstands customer expectation for service quality
Important early step in providing good service is knowing what customers want
Ongoing marketing research is needed to understand customers’ changing expectations of service quality
Zone Tolerance
Define service quality dimensions
Ask question about each service quality dimension about
Desired level of service
Expected level of service
The importance
Customers’ perceptions of how well our service performs an how well a competitive service performs
Service Quality Dimensions
Reliability
Responsiveness
Assurance
Empathy
Tangibles
Reliability
The ability to perform the service dependably and accurately

Responsiveness
The willingness to help customers and provide prompt service

Assurance
The knowledge of and courtesy by employees and their ability to convey trust and confidence

Empathy
The caring, individualized attention provided to customers

Tangibles
The appearance of physical facilities, equipment, personnel, and communication materials

Ways to Understand Customer Expectations
Ask customers how they liked the service
Collect complaints and analyze them
Put managers on the frontline occasionally
Standard Gap
Exist when the service standards differ from customer expectations for service quality
By setting appropriate service standards, training employees, and measuring service performance, firms can close this gap
Delivery Gap
Where customer directly interact with the service providers
Can be reduced when employees are empowered to spontaneously act in the customers’ and the firm’s best interest when problems or crises arises
Communication Gap
Promise only what you can deliver, communicate service expectations
I.E. An advertisement may lure a customer into a service situation once, but if the service doesn’t deliver ton the promise, the customer will be dissatisfied and never return
Service Recovery
When service providers fail to meet customer expectations, the best course of action is to attempt to make amends with the customers and learn from the experience:
By doing this, it can increase customer satisfaction and positive word of mouth
Qualities of Good Service Recovery
Listening to the customers and involving them in service recovery
Finding a fair solution
Resolving problems quickly