Chapter 15 disorders
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
1
New cards
Depersonalization
feelings of detachment or unfamiliarty with oneself or aspects of oneself
2
New cards
Derealization
feelings of unfamiliarity or detachment from the world
3
New cards
derealization disorder
a recurring episode of derealization in a disorder
* derealization: feelings of unfamiliarity or detachment from the world
* derealization: feelings of unfamiliarity or detachment from the world
4
New cards
Dissociative fugue
wandering away from home, experience confusion about their identity, or may adopt a new identity
5
New cards
Dysfunction
A characteristics of a disorder: Any impairment, disturbance, or deficiency in behavior.
Ex: Someone with ADHD not being able to concentrate or remember deadlines.
Ex: Someone with ADHD not being able to concentrate or remember deadlines.
6
New cards
Social Deviance / Atypical
A characteristics of a disorder: Behavior that does not follow socially established norms.
Ex: Talking to someone who isn't there, or wearing unusual clothing.
**violation fo cultural norms does not always mean a disorder*
Ex: Talking to someone who isn't there, or wearing unusual clothing.
**violation fo cultural norms does not always mean a disorder*
7
New cards
Comorbidity
Having 2 mental or physical diseases at the same time.
8
New cards
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)
The handbook used by health care professionals in the United States and much of the world as the authoritative guide to the diagnosis of mental disorders.
* International classification of disorders
* Compassionate View of Mental Disorders
* Categories: Anxiety Disorders, Depressive Disorders, and Dissociative Disorders
* Contains overview of disorder, specific symptoms required for diagnosis, prevalence information, and risk factors
* Research purposes
* International classification of disorders
* Compassionate View of Mental Disorders
* Categories: Anxiety Disorders, Depressive Disorders, and Dissociative Disorders
* Contains overview of disorder, specific symptoms required for diagnosis, prevalence information, and risk factors
* Research purposes
9
New cards
Biopsychosocial Model
A model of health that asserts that biology, psychology, and social factors (nature + nurture + thoughts) interact to determine an individual's health.
10
New cards
Diathesis-Stress Model
A diagnostic model that states that a person may be susceptible to having a psychological disorder (nature) which remains unexpressed until triggered by stress (nurture).
* Psychosocial perspective
* Emphasizes learning, stress, faulty/self-defeating thinking patterns, and environmental factors.
* Disorders originate from a combination of biological and psychosocial factors.
* Diathesis- predisposition for a disorder
* Stress- adverse environmental/psychological events
* Psychosocial perspective
* Emphasizes learning, stress, faulty/self-defeating thinking patterns, and environmental factors.
* Disorders originate from a combination of biological and psychosocial factors.
* Diathesis- predisposition for a disorder
* Stress- adverse environmental/psychological events
11
New cards
Specific Phobias
Any of the disorders characterized by extreme and irrational fear of a particular object or situation.
* Acquisition
* Classical Conditioning
* Vicarious Learning/Modeling
* Verbal Transmission
* Acquisition
* Classical Conditioning
* Vicarious Learning/Modeling
* Verbal Transmission
12
New cards
Acrophobia
Fear of heights.
13
New cards
Claustrophobia
An abnormal fear of narrow, enclosed spaces.
14
New cards
Hematophobia
Fear of blood.
15
New cards
Xenophobia
A fear or hatred of foreigners or strangers.
16
New cards
Agoraphobia
An abnormal fear of open or public places.
* Classified as a separate anxiety order
* characterized by intense fear, anxiety, and avoidance of situations in which it might be difficult to escape or receive help if one experiences symptoms of a panic attack
* Classified as a separate anxiety order
* characterized by intense fear, anxiety, and avoidance of situations in which it might be difficult to escape or receive help if one experiences symptoms of a panic attack
17
New cards
Panic Disorder
An anxiety disorder that consists of sudden, overwhelming panic attacks.
* Recurrent and unexpected panic attacks along with at least 1 month of persistent worry about additional panic attacks, consequences of the attacks or changes in behaviour in relation to attacks (avoidance of unfamiliar situations)
* Panic attacks
* Theories
* Abnormal norepinephrine activity in the locus coerulus, __which is responsible for our fight of flight response__
* Conditioning through subtle bodily sensations resembling those normally occurring when one is anxious or frightened
* Cognitive: interpretation of normal body sensations as dangerous or catastrophic, causing panic
* Recurrent and unexpected panic attacks along with at least 1 month of persistent worry about additional panic attacks, consequences of the attacks or changes in behaviour in relation to attacks (avoidance of unfamiliar situations)
* Panic attacks
* Theories
* Abnormal norepinephrine activity in the locus coerulus, __which is responsible for our fight of flight response__
* Conditioning through subtle bodily sensations resembling those normally occurring when one is anxious or frightened
* Cognitive: interpretation of normal body sensations as dangerous or catastrophic, causing panic
18
New cards
Panic Attack
Brief, intense episode of extreme fear characterized by sweating, dizziness, light-headedness, racing heartbeat that have not obvious cause.
* dizziness, lightheadedness, shortness of breath, nausea or abdominal distress, chest pain, palpitation, increased heart rate, hot flashes, chills, fear of losing control/going crazy, fear of dying.
* May be triggered by specific situations
* Reaches peak within 10 minutes
* dizziness, lightheadedness, shortness of breath, nausea or abdominal distress, chest pain, palpitation, increased heart rate, hot flashes, chills, fear of losing control/going crazy, fear of dying.
* May be triggered by specific situations
* Reaches peak within 10 minutes
19
New cards
Night Terror
A sleep disorder characterized by panic attacks during sleep.
20
New cards
Locus Coeruleus
A small area of the brain that seems to be active in the regulation of emotions. Many of its neurons use norepinephrine.
21
New cards
Social Anxiety Disorder
Disorder characterized by an intense fear of social situations.
* treatment that could lessen the chance of negative social outcomes: safety behaviors
* treatment that could lessen the chance of negative social outcomes: safety behaviors
22
New cards
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
An anxiety disorder in which a person is continually tense, apprehensive, and in a state of anxiety for 6 months or longer with no specific cause.
* State of continuous persistent and excessive anxiety/worry about everyday things
* Anxiety must not be part of another disorder and they must exhibit symptoms more days than not in a 6 month period to receive diagnosis
* State of continuous persistent and excessive anxiety/worry about everyday things
* Anxiety must not be part of another disorder and they must exhibit symptoms more days than not in a 6 month period to receive diagnosis
23
New cards
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
A disorder characterized by unwanted repetitive thoughts (obsessions) and/or actions (compulsions).
* Experience intrusive and unwanted thoughts and urges (obsessive) and/or need to engage in repeated physical or mental acts (compulsive)
* __Obsessive thoughts__: unwanted, distressing, unintentional
* __Compulsions__: repetitive and ritualistic acts used to lessen the distress triggered from obsessions or reduce the likelihood of a feared event
\
* Causes of OCD
* Genetic factors
* A brain region called the orbitofrontal region of the brain is said to play a critical part in causing OCD. It is involved with learning and decision making.
* OCD circuit: consists of several interconnected regions that influence both the emotional value of stimuli as well as the selection of both behavioral and cognitive responses.
* Also shows heightened activity when provoked, suggesting that abnormalities in this region of the brain could be a cause for OCD.
* Experience intrusive and unwanted thoughts and urges (obsessive) and/or need to engage in repeated physical or mental acts (compulsive)
* __Obsessive thoughts__: unwanted, distressing, unintentional
* __Compulsions__: repetitive and ritualistic acts used to lessen the distress triggered from obsessions or reduce the likelihood of a feared event
\
* Causes of OCD
* Genetic factors
* A brain region called the orbitofrontal region of the brain is said to play a critical part in causing OCD. It is involved with learning and decision making.
* OCD circuit: consists of several interconnected regions that influence both the emotional value of stimuli as well as the selection of both behavioral and cognitive responses.
* Also shows heightened activity when provoked, suggesting that abnormalities in this region of the brain could be a cause for OCD.
24
New cards
Body Dysmorphic Disorder
A disorder characterized by the unrealistic perception of physical flaws and a desire to change one's appearance.
25
New cards
Hoarding Disorder
A disorder characterized by persistent difficulty discarding or parting with possessions, regardless of their actual value.
26
New cards
Trichotillomania (Hair Pulling)
A disorder in which the person compulsively pulls at his or her hair, from the scalp, eyebrows, and other body areas.
27
New cards
Obsession
A persistent, unwanted thought or idea that keeps recurring.
28
New cards
Compulsion
Uncontrollable urge to perform an act repeatedly.
Ex: Knock on a door, avoid stepping on sidewalk cracks, wash hands, etc.
Ex: Knock on a door, avoid stepping on sidewalk cracks, wash hands, etc.
29
New cards
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
An anxiety disorder characterized by haunting memories, nightmares, social withdrawal, jumpy anxiety, and/or insomnia that lingers for weeks or months after a traumatic experience.
\
* Caused by exposure to, witnessing or experiencing extreme trauma that include serious injury, threatened death, or sexual assault.
* Symptoms include
* Distressing and intrusive memories of the trauma
* __*Flashbacks*__, which is a state that can last for a few seconds to a few days during which the person relives their trauma and acts as if it were happening at that moment.
* Persistent negative emotions
* Avoidance of stimuli associated with the event
* Feelings of detachment from others, prone to outbursts, and jumpiness
* Risk factors include
* Trauma experienced, greater trauma severity, lack of immediate social support, and subsequent life stress.
* Development and Support
* Social support has been shown to decrease the likelihood of PTSD
* Classical Conditioning may be a cause for the development and maintaining of symptoms
* Traumatic experience causes extreme fear and anxiety
* Conditioned stimuli include cognitive, emotional, physiological, and environmental cues
* Traumatic reminders induce extreme fear and anxiety
* Cognitive factors:
* Cruicial: Disturbances in memory of the event and negative appraisal of the event and its aftermath
* Some people may not encode the memory correctly, leading to only bits and fragments of the trauma being encoded. This leads to the inability to see the event in context and meaning .
* Fragments stand out and may trigger the person
* Negative appraisal may lead to dysfunctional behaviour
\
* Caused by exposure to, witnessing or experiencing extreme trauma that include serious injury, threatened death, or sexual assault.
* Symptoms include
* Distressing and intrusive memories of the trauma
* __*Flashbacks*__, which is a state that can last for a few seconds to a few days during which the person relives their trauma and acts as if it were happening at that moment.
* Persistent negative emotions
* Avoidance of stimuli associated with the event
* Feelings of detachment from others, prone to outbursts, and jumpiness
* Risk factors include
* Trauma experienced, greater trauma severity, lack of immediate social support, and subsequent life stress.
* Development and Support
* Social support has been shown to decrease the likelihood of PTSD
* Classical Conditioning may be a cause for the development and maintaining of symptoms
* Traumatic experience causes extreme fear and anxiety
* Conditioned stimuli include cognitive, emotional, physiological, and environmental cues
* Traumatic reminders induce extreme fear and anxiety
* Cognitive factors:
* Cruicial: Disturbances in memory of the event and negative appraisal of the event and its aftermath
* Some people may not encode the memory correctly, leading to only bits and fragments of the trauma being encoded. This leads to the inability to see the event in context and meaning .
* Fragments stand out and may trigger the person
* Negative appraisal may lead to dysfunctional behaviour
30
New cards
Flashback
In people suffering from PTSD, the feeling of reliving a traumatic experience.
31
New cards
Adjustment Disorder
A disorder characterized by unhealthy, emotionally overreactions to a change in life.
32
New cards
Major Depressive Disorder
A mood disorder in which a person feels sad and hopeless for weeks or months.
\
* Depressed mood most of the day, nearly every day, loss of interest/pleasure in activities one used to enjoy.
* Episodic: symptoms are present at their full magnitude for a certain period of time before gradually abating.
* Diagnosis requires at least 5 symptoms for 2 weeks that cause significant distress or impair normal functioning, and that are not caused by a substance or medical condition.
* Symptoms:
* Significant weight loss/gain when not dieting, or a decrease/increase in appetite
* Difficulty falling asleep or sleeping too much
* Psychomotor agitation: jumpy, fidgeting, or psychomotor \[r word\]: slow movement, talking softly or very little and often in a monotone.
* fatigue/loss of energy
* Feelings of guilt or worthlessness
* Concentration difficulties and indecisiveness
* Suicidal ideation
\
* Depressed mood most of the day, nearly every day, loss of interest/pleasure in activities one used to enjoy.
* Episodic: symptoms are present at their full magnitude for a certain period of time before gradually abating.
* Diagnosis requires at least 5 symptoms for 2 weeks that cause significant distress or impair normal functioning, and that are not caused by a substance or medical condition.
* Symptoms:
* Significant weight loss/gain when not dieting, or a decrease/increase in appetite
* Difficulty falling asleep or sleeping too much
* Psychomotor agitation: jumpy, fidgeting, or psychomotor \[r word\]: slow movement, talking softly or very little and often in a monotone.
* fatigue/loss of energy
* Feelings of guilt or worthlessness
* Concentration difficulties and indecisiveness
* Suicidal ideation
33
New cards
Persistent Depressive Disorder (Dysthymia)
Mood disorder involving a persistently depressed mood for at least 2 years, with no absence of symptoms for more than 2 months.
34
New cards
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
A mood disorder caused by the body's reaction to low levels of sunlight in the winter months.
35
New cards
Bipolar Disorder / Manic Depression
A mood disorder in which the person alternates between the hopelessness and lethargy of depression and the overexcited state of mania.
\
* Often Expereinces mood states that alternate between depression and mania.
* Mania symptoms
* Distinct and abnormal and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood and abnormally and persistently increased activity or energy lasting at least one week
* Lasts most of the day for the manic period
* Euphoric mood or hostile mood
* Easilty distracted, talkative, flight of ideas, taking on several tasks at once
* Show little to no need for sleep
* Engagement in pleasurable but harmful activities like shopping sprees, foolish investments or reckless driving
* Reckless behaviours may be illegal, antisocial or dangerous
* Subtype:
* rapid cycling characterized by four manic or a combination of four manic and depressive episodes within a year
\
* Often Expereinces mood states that alternate between depression and mania.
* Mania symptoms
* Distinct and abnormal and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood and abnormally and persistently increased activity or energy lasting at least one week
* Lasts most of the day for the manic period
* Euphoric mood or hostile mood
* Easilty distracted, talkative, flight of ideas, taking on several tasks at once
* Show little to no need for sleep
* Engagement in pleasurable but harmful activities like shopping sprees, foolish investments or reckless driving
* Reckless behaviours may be illegal, antisocial or dangerous
* Subtype:
* rapid cycling characterized by four manic or a combination of four manic and depressive episodes within a year
36
New cards
Mania
A mood disorder marked by a hyperactive, wildly optimistic state in which a person feels invincible and has little sense of consequences.
37
New cards
Flight of Ideas
Symptom of mania that involves an abruptly switching in conversation from one topic to another.
38
New cards
Delusions, Hallucinations, Disorganized Thinking/Speech, Disorganized Motor Movements, Negative Symptoms
Five Symptoms Associated with Schizophrenia
39
New cards
Delusions
False beliefs held by a person who refuses to accept evidence of their falseness. Ex: Believing someone is out to get you, believing you can fly, etc.
40
New cards
Paranoid Delusions
Delusions characterized by beliefs that others are out to harm them
41
New cards
Grandiose Delusions
Delusions involving beliefs that one holds special power, unique knowledge, or is extremely important
42
New cards
Somatic Delusions
Delusions involving beliefs that one's body is changing in an unusual way, such as growing a third arm
43
New cards
Hallucinations
Perceiving things that are not there, such as hearing voices.
* in schizophrenia: the most common hallucination is auditory
* visual hallucinations are more commonly linked withh substance use diorder and withdrawal
* tactile and olfactory hallucinations are rare
* in schizophrenia: the most common hallucination is auditory
* visual hallucinations are more commonly linked withh substance use diorder and withdrawal
* tactile and olfactory hallucinations are rare
44
New cards
Disorganized Thinking/Speech
A severe disruption of verbal communication in which ideas shift rapidly and incoherently from one to another unrelated topic.
45
New cards
Disorganized Motor Behavior
Highly unusual behaviors and movements, repeated and purposeless movements, and displaying odd facial expressions and gestures.
* includes catatonic
* includes catatonic
46
New cards
Negative Symptoms
Schizophrenic symptoms that involve behavioral deficits, such as flattened emotions, social withdrawal, apathy, impaired attention, and poverty of speech.
* includes avolition, alogia, asociality, anhedonia
* includes avolition, alogia, asociality, anhedonia
47
New cards
Alogia
reduced speaking
* type of negative symptom in schizophrenia
* type of negative symptom in schizophrenia
48
New cards
avolition
lack of motivation to engage in meaningful and self-initiated activties, such as taking bath
* a type of negative symptom in schizophrenia
* a type of negative symptom in schizophrenia
49
New cards
asociality
social withdrawal or lack of interest in interactions with others
* a type of negative symptom in schizophrenia
* a type of negative symptom in schizophrenia
50
New cards
Anhedonia
lack of pleasure
* a type of negative ymptom in schizophrenia
* a type of negative ymptom in schizophrenia
51
New cards
Schizophrenia
A psychological disorder characterized by delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, disorganized motor movements, and/or diminished, inappropriate emotional expression.
\
* **Causes**
* **Genetic basis**
* Studies from research on twins, relatives, and adoptees showed that __schizophrenia had a genetic factor__, and children having a high risk for schizophrenia genetically and being raised in a disturbed household had increased risk of having it
* **Neurotransmitters**
* **Dopamine hypothesis:** during studies that showed an increase in dopamine caused schizophrenia-like symptoms and medications that blocked dopamine reduced the symptoms, this theory suggests that too much dopamine/dopamine receptors play a part
* **Brain Anatomy**
* Large ventricles, which means less brain mass in other areas, suggesting that schizophrenia may be caused by lack of brain tissue
* **Events during Pregancy**
* Catching influenza, mother’s stress, and obstetric complications may all increase the risk of developing schizophrenia
* **Marijuana**
* Those with schizophrenia are more likely to use marijuana, and it is a risk factor
* *Warning signs include unusual thought content, paranoia, delusions, odd communication, problems in school/work and a decrease in social functioning*
\
* **Causes**
* **Genetic basis**
* Studies from research on twins, relatives, and adoptees showed that __schizophrenia had a genetic factor__, and children having a high risk for schizophrenia genetically and being raised in a disturbed household had increased risk of having it
* **Neurotransmitters**
* **Dopamine hypothesis:** during studies that showed an increase in dopamine caused schizophrenia-like symptoms and medications that blocked dopamine reduced the symptoms, this theory suggests that too much dopamine/dopamine receptors play a part
* **Brain Anatomy**
* Large ventricles, which means less brain mass in other areas, suggesting that schizophrenia may be caused by lack of brain tissue
* **Events during Pregancy**
* Catching influenza, mother’s stress, and obstetric complications may all increase the risk of developing schizophrenia
* **Marijuana**
* Those with schizophrenia are more likely to use marijuana, and it is a risk factor
* *Warning signs include unusual thought content, paranoia, delusions, odd communication, problems in school/work and a decrease in social functioning*
52
New cards
Dopamine Hypothesis of Schizophrenia
Theory that schizophrenia results from excess activity at dopamine synapses in certain brain areas.
* during studies that showed an increase in dopamine caused schizophrenia-like symptoms and medications that blocked dopamine reduced the symptoms, this theory suggests that too much dopamine/dopamine receptors play a part
* during studies that showed an increase in dopamine caused schizophrenia-like symptoms and medications that blocked dopamine reduced the symptoms, this theory suggests that too much dopamine/dopamine receptors play a part
53
New cards
Dissociative Amnesia
Disorder characterized by the sudden inability to recall important personal information, usually of a traumatic or stressful nature.
* Inability to recall important person information , usually following a traumatic or very stressful experience, such as combat, natural disasters or sexual violence
* Dissociative fugue
* Inability to recall important person information , usually following a traumatic or very stressful experience, such as combat, natural disasters or sexual violence
* Dissociative fugue
54
New cards
Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID)
A rare disorder in which a person exhibits two or more distinct and alternating personalities. Formerly called multiple personality disorder.
* Two or more distinct personalities
* Memory gaps when another identity is in charge
* Some may hear voices
* Two or more distinct personalities
* Memory gaps when another identity is in charge
* Some may hear voices
55
New cards
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
A disorder characterized by restlessness, inattentiveness, and impulsivity.
* Symptoms include hyperactivity, impulsiveness, lack of attention span, forgetting, disorganization, easily distracted, and failure to follow instructions.
* Thought to be caused by genetic factors, more specifically genes associated with the regulation of dopamine
* Symptoms include hyperactivity, impulsiveness, lack of attention span, forgetting, disorganization, easily distracted, and failure to follow instructions.
* Thought to be caused by genetic factors, more specifically genes associated with the regulation of dopamine
56
New cards
Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD)
Disorder in which a person is unable to focus and is easily distracted.
57
New cards
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
A disorder characterized by deficits in social relatedness and communication skills that are often accompanied by repetitive, ritualistic behavior.
\
* Symptoms include deficits in social interaction and communication, as well as repetitive patterns of behavior or interest
* Isolated, may not recognized social cues or facial expressions, inability to speak, only able to speak one-word phrases, repetitive movements (stimming), great distress in changes in routine
* Hyperfixation
* Spectrum: those with autism can display their symptoms in many ways and in different magnitudes
* There is no link of autism with the MMR vaccine
* Autism is a genetic, environmental, and/or biological factors
\
* Symptoms include deficits in social interaction and communication, as well as repetitive patterns of behavior or interest
* Isolated, may not recognized social cues or facial expressions, inability to speak, only able to speak one-word phrases, repetitive movements (stimming), great distress in changes in routine
* Hyperfixation
* Spectrum: those with autism can display their symptoms in many ways and in different magnitudes
* There is no link of autism with the MMR vaccine
* Autism is a genetic, environmental, and/or biological factors
58
New cards
Specific Learning Disabilities (SLD)
Disorders in which students have normal cognitive functioning and the ability to learn some skills and strategies quickly, but have great difficulty learning other skills and strategies.
59
New cards
Tourette's Disorder/Syndrome
A neurological disorder beginning in childhood that involves stereotypical, repetitive motor movements (tics). These are often accompanied by multiple vocal outbursts such grunting. It is about three times more prevalent in boys than in girls.
60
New cards
Parkinson's Disease
A progressive disease that destroys brain cells and is identified by muscular tremors, slowing of movement, and partial facial paralysis. Most common in older people.
61
New cards
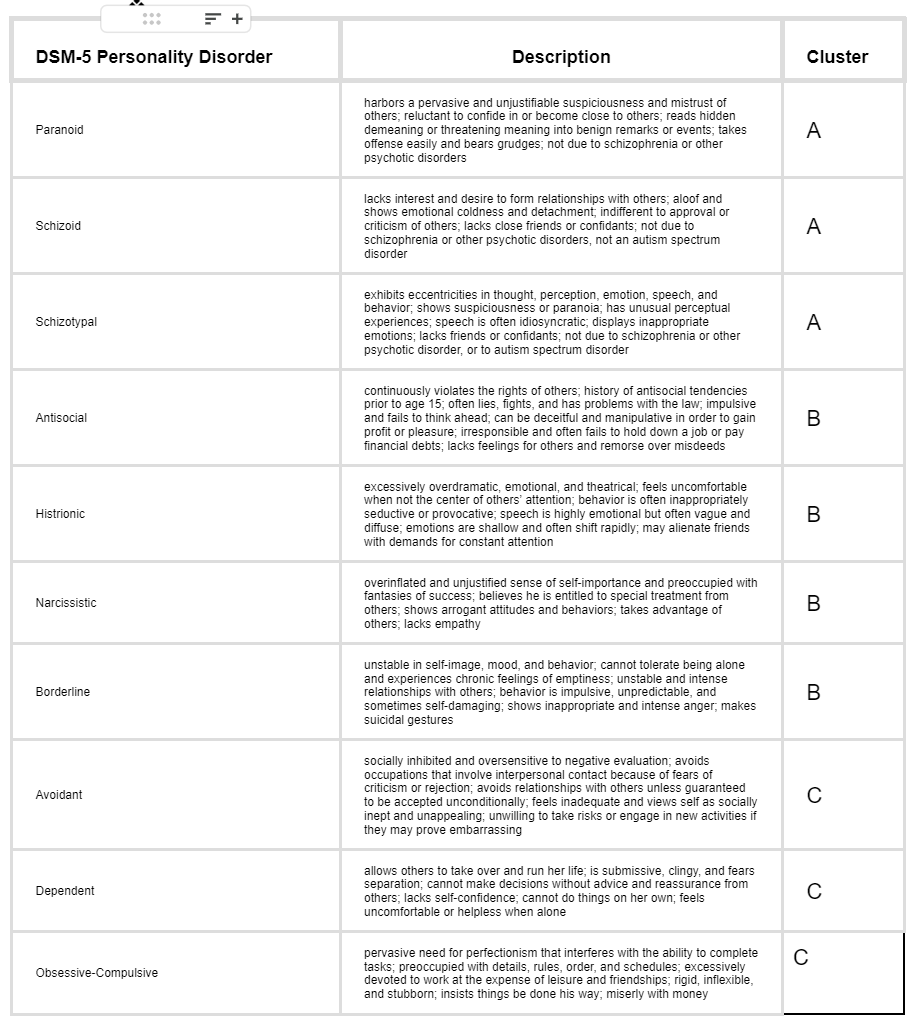
Personality Disorders: Cluster A
Cluster of personality disorders that involve behavior that seems unusual and eccentric to others.
\
mnemonic:
a. **weird**
1. accusatory: paranoid (suspicious)
2. aloof: schizoid (voluntary social withdrawal)
3. awkward (schizoid + magical thinking)
b. **wild**
1. bad: antisocial (>/=18 years with a history of Conduct Disorder, Sociopath and Manipulative)
2. borderline: borderline (unstable and afraid of abandonment)
3. flamBoyant: histrionic (attention-seeking and excesion emotionality)
4. best: narcissistic (grandiosity, reacts to criticisms)
c. **worried**
1. Cowardly: Avoidant (Seeks social relationship but avoids social situation; hypersensitive to rejection)
2. Compulsive: Obsessive-compulsive (Inflexible but inefficient)
* Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder: Ego-syntonic (happy with how they are)
* Obsessive-compulsive disorder: Ego-dystoni (wishes they could stop)
3. Clingy: Dependent (Submissive)
\
mnemonic:
a. **weird**
1. accusatory: paranoid (suspicious)
2. aloof: schizoid (voluntary social withdrawal)
3. awkward (schizoid + magical thinking)
b. **wild**
1. bad: antisocial (>/=18 years with a history of Conduct Disorder, Sociopath and Manipulative)
2. borderline: borderline (unstable and afraid of abandonment)
3. flamBoyant: histrionic (attention-seeking and excesion emotionality)
4. best: narcissistic (grandiosity, reacts to criticisms)
c. **worried**
1. Cowardly: Avoidant (Seeks social relationship but avoids social situation; hypersensitive to rejection)
2. Compulsive: Obsessive-compulsive (Inflexible but inefficient)
* Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder: Ego-syntonic (happy with how they are)
* Obsessive-compulsive disorder: Ego-dystoni (wishes they could stop)
3. Clingy: Dependent (Submissive)
62
New cards
Paranoid Personality Disorder
A personality disorder marked by a pattern of distrust and suspiciousness of others.
* cluster A personality disorder
* cluster A personality disorder
63
New cards
Schizoid Personality Disorder
A personality disorder characterized by persistent avoidance of social relationships and little expression of emotion.
* cluster A personality disorder
* cluster A personality disorder
64
New cards
Schizotypal Personality Disorder
A personality disorder involving a discomfort with, and reduced capacity for, close relationships, as well as cognitive or perceptual distortions and eccentricities of behavior.
* cluster A personality disorder
* cluster A personality disorder
65
New cards
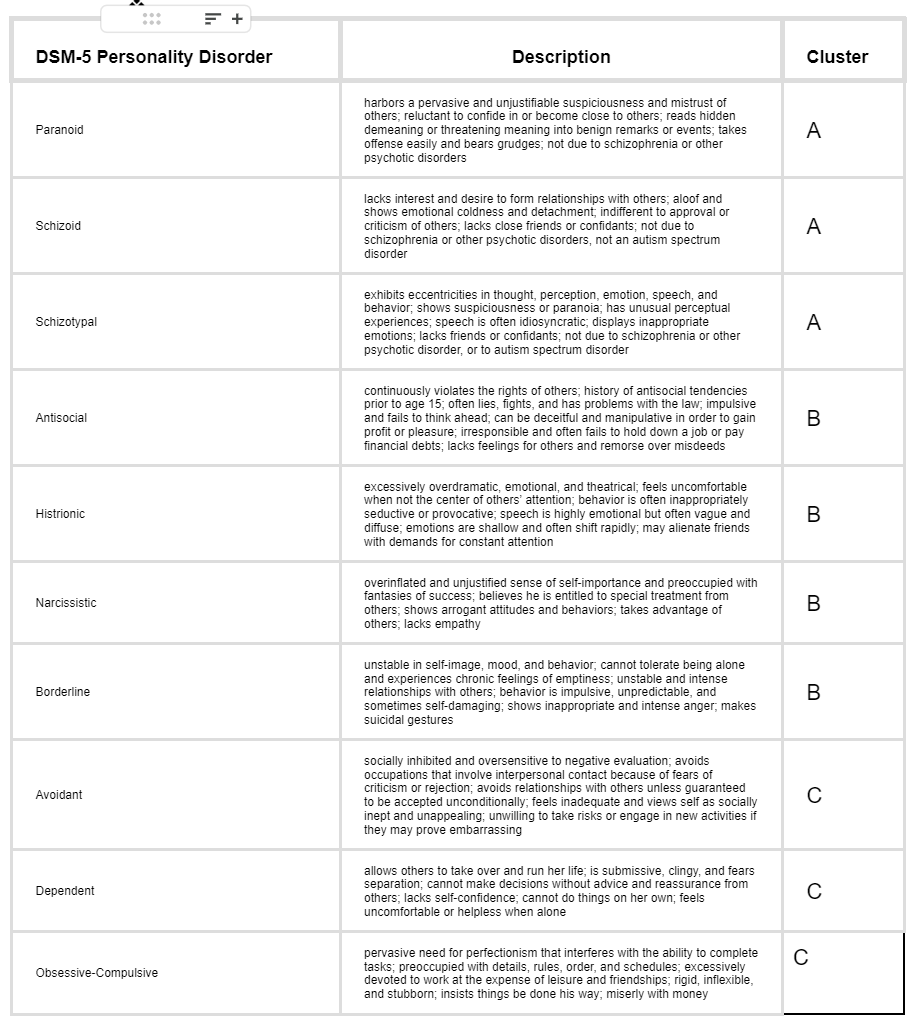
Personality Disorders: Cluster B
Cluster of personality disorders that feature emotional, dramatic, or erratic behaviors.
\
mnemonic:
a. **weird**
b. **wild**
c. **worried**
\
mnemonic:
a. **weird**
b. **wild**
c. **worried**
66
New cards
Antisocial Personality Disorder
A personality disorder in which the person (usually a man) exhibits a lack of conscience for wrongdoing, even toward friends and family members. May be aggressive and ruthless or a clever con artist.
* cluster B personality disorder
* Diagnosis requires 18 years of age
* Seemingly no moral compass
* Lack of empathy, impulsive, and reckless, irritable and aggressive
* Sense of over self-importance, arrogance
* cluster B personality disorder
* Diagnosis requires 18 years of age
* Seemingly no moral compass
* Lack of empathy, impulsive, and reckless, irritable and aggressive
* Sense of over self-importance, arrogance
67
New cards
Borderline Personality Disorder
A personality disorder characterized by lack of stability in interpersonal relationships, self-image, and emotion; impulsivity; angry outbursts; intense fear of abandonment; recurring suicidal gestures.
* cluster B personality disorder
* Instability in interpersonal relationships, mood and self image. Impulsive
* Cannot tolerate being alone
* Instability is view of self can cause changes in personal attitudes, interests, career plans, and choice of friends
* Causes: genetic, some characteristics seem to be heritable, those with borderline personality disorder also report higher childhood physical, emotional and sexual abuse, so the environment is also crucial.
* cluster B personality disorder
* Instability in interpersonal relationships, mood and self image. Impulsive
* Cannot tolerate being alone
* Instability is view of self can cause changes in personal attitudes, interests, career plans, and choice of friends
* Causes: genetic, some characteristics seem to be heritable, those with borderline personality disorder also report higher childhood physical, emotional and sexual abuse, so the environment is also crucial.
68
New cards
Histrionic Personality Disorder
A personality disorder characterized by excessive emotionality and preoccupation with being the center of attention, emotional shallowness, and overly dramatic behavior.
* cluster B personality disorder
* cluster B personality disorder
69
New cards
Narcissistic Personality Disorder
A personality disorder characterized by exaggerated ideas of self-importance and achievements, preoccupation with fantasies of success, and arrogance.
* cluster B personality disorder
* cluster B personality disorder
70
New cards
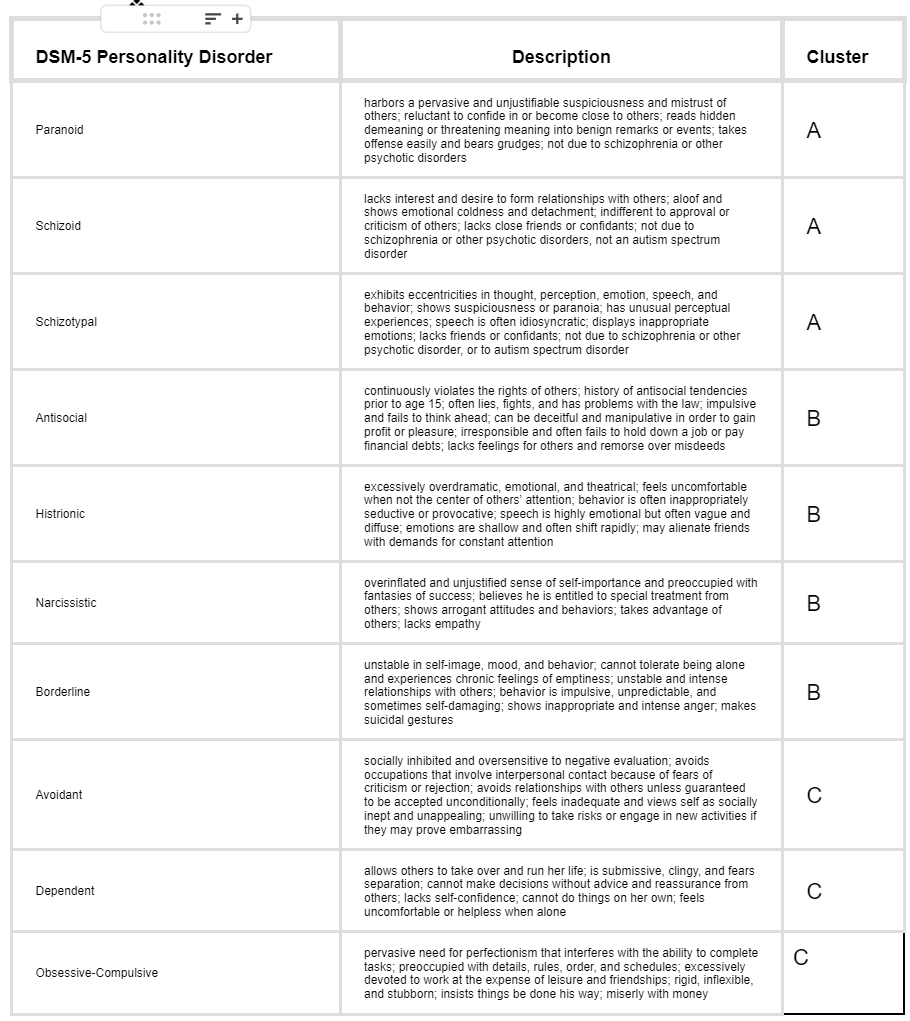
Personality Disorders: Cluster C
Cluster of personality disorders that are based on anxiety and/or fear.
\
mnemonic:
a. **weird**
b. **wild**
c. **worried**
\
mnemonic:
a. **weird**
b. **wild**
c. **worried**
71
New cards
Avoidant Personality Disorder
A personality disorder characterized by consistent discomfort and restraint in social situations, overwhelming feelings of inadequacy, and extreme sensitivity to negative evaluation.
* cluster C
* cluster C
72
New cards
depersonalization disorder
Recuring episodes of depersonalization, which is the feelings of detachment or unfamiliarity or detachment from the world
73
New cards
Dependent Personality Disorder
A personality disorder characterized by a pattern of clinging and obedience, fear of separation, and an ongoing need to be taken care of.
* cluster C
* cluster C
74
New cards
Obsessive-Compulsive Personality Disorder
A personality disorder characterized by preoccupation with orderliness, perfection, and control
75
New cards
psychological diorders
Exhibiting atypical, distressful, dysfunctional, or dangerous behaviors thoughts and inner experiences could be used to conceptualize someone as having a psychological disorder
* APA Definition:
* Significant disturbances in thoughts feelings and beahviour
* The disturbances reflect some kind of biological, psychological, or developmental dysfunction
* Stress/disability in one’s life
* Disturbances do not reflect expected/culturally approved responses to an event
* APA Definition:
* Significant disturbances in thoughts feelings and beahviour
* The disturbances reflect some kind of biological, psychological, or developmental dysfunction
* Stress/disability in one’s life
* Disturbances do not reflect expected/culturally approved responses to an event
76
New cards
Psychopathology
study of psychological disorders
* includes etiology
* includes etiology
77
New cards
Etiology
study of causes for psychological disorders
78
New cards
Dysfunctional
internal mechanism breaks down
* Must be harmful in order to be characterized as a disorder
* Must be harmful in order to be characterized as a disorder
79
New cards
International classification of disorders
Categories and criteria similar to DSM
* Used in clinical settings and to measure prevalence of diseases and general health of populations
* Used in clinical settings and to measure prevalence of diseases and general health of populations
80
New cards
Compassionate View of Mental Disorders
A view that states that psychological disorders are just more extreme inner experiences and behaviour
* People are more than their disorders.
* People are more than their disorders.
81
New cards
Supernatural perspective
a POV that viewed psychological disorders as an attribute to a force beyond scientific understanding
* Often mental illnesses were attributed to dark spirits or witchcraft
* Often mental illnesses were attributed to dark spirits or witchcraft
82
New cards
Biological Perspectives
A perspective that states that there is a link with psychological disorders with biological factors such as genetics, brain abnormalities, and chemical imbalances
* Genetics, brain abnormalities, neurotransmitters and hormones may all play a role in causing psychological disorders
* Genetics, brain abnormalities, neurotransmitters and hormones may all play a role in causing psychological disorders
83
New cards
diathesis
predisposition for a disorder
84
New cards
Anxiety disorders
a disorder characterized by persistent and excessive anxiety/worrying
* Anxiety vs Fear
* Fear is an instanteous reaction to a threat, while anxiety involves apprehension, avoidance and cautiousness regarding a potential threat
* Anxiety vs Fear
* Fear is an instanteous reaction to a threat, while anxiety involves apprehension, avoidance and cautiousness regarding a potential threat
85
New cards
Safety Behaviours
mental or physical acts that reduce anxiety by reducing the chances of negative social outcomes
* Avoiding eye contact, rehearsing sentences before speaking, talking only briefly, avoiding talking about oneself, assuming roles with little social interaction, asking people many questions to avoid focus on oneself, selecting a position to avoid contact with others, wearing bland neutral colors to avoid attention, and avoiding substances or activities that may worsen symptoms
* Avoiding eye contact, rehearsing sentences before speaking, talking only briefly, avoiding talking about oneself, assuming roles with little social interaction, asking people many questions to avoid focus on oneself, selecting a position to avoid contact with others, wearing bland neutral colors to avoid attention, and avoiding substances or activities that may worsen symptoms
86
New cards
mood disorder
a disorder is charactertized by disturbances in mood and emotion.
* Often depression, but may also be mania/elation
* Fluctuations in mood are extreme, distort their outlook on life, and impair their ability to function
* DSM Categories
* Depressive; depression is main feature. Depression is persistent and intense sadness. Feelings of discouragement and hopelessness may also occur.
* Loss in interest in activities, less hunger/sex drive
* A broad spectrum of symtoms that range in severity
* Bipolar and related disorders: often have mania as a main feature. Mania is intense feelings of agitation and elation.
* Biological basis
* Strong genetic predisposition
* Diathesis-Stress Model & MDD
* Stressful life events can lead to depression, as well as numerous biological factors
* Traumatic childhoods increase risk of development
* Alteration in a gene that is in involved in the regulation of serotonin may also be a factor
* Cognitive Theories about Depression
* Triggered by negative thoughts, interpretations, self evaluations, and expectations
* Aaron Beck: Depression prone people have a mental predisposition to think about things in a negative way
* Themes of loss, failure, rejection, worthlessness, inadequacy
* May result from childhood experiences
* Hopelessness Theory: particular style of negative thinking leads to hopelessness
* Hopelessness is defined as the expectation that negative things will occur or that desired outcomes will not occur.
* Assumes that hopelessness stems from a tendency to believe that negative life events as being stable and global.
* Stable: unable to chance
* Global: affects everything
* Third theory focuses on rumination and how people’s thoughts on their depression can increase the duration and risk
* Rumination: the passive and repetitive thinking about one’s depression and dweling on it rather than distracting oneself or trying to actively treat it
* Suicide
* Often depression, but may also be mania/elation
* Fluctuations in mood are extreme, distort their outlook on life, and impair their ability to function
* DSM Categories
* Depressive; depression is main feature. Depression is persistent and intense sadness. Feelings of discouragement and hopelessness may also occur.
* Loss in interest in activities, less hunger/sex drive
* A broad spectrum of symtoms that range in severity
* Bipolar and related disorders: often have mania as a main feature. Mania is intense feelings of agitation and elation.
* Biological basis
* Strong genetic predisposition
* Diathesis-Stress Model & MDD
* Stressful life events can lead to depression, as well as numerous biological factors
* Traumatic childhoods increase risk of development
* Alteration in a gene that is in involved in the regulation of serotonin may also be a factor
* Cognitive Theories about Depression
* Triggered by negative thoughts, interpretations, self evaluations, and expectations
* Aaron Beck: Depression prone people have a mental predisposition to think about things in a negative way
* Themes of loss, failure, rejection, worthlessness, inadequacy
* May result from childhood experiences
* Hopelessness Theory: particular style of negative thinking leads to hopelessness
* Hopelessness is defined as the expectation that negative things will occur or that desired outcomes will not occur.
* Assumes that hopelessness stems from a tendency to believe that negative life events as being stable and global.
* Stable: unable to chance
* Global: affects everything
* Third theory focuses on rumination and how people’s thoughts on their depression can increase the duration and risk
* Rumination: the passive and repetitive thinking about one’s depression and dweling on it rather than distracting oneself or trying to actively treat it
* Suicide
87
New cards
Episodic
symptoms are present at their full magnitude for a certain period of time before gradually abating
* major depresive disorder is usually handled as episodic, ut many live with it as chronic
* major depresive disorder is usually handled as episodic, ut many live with it as chronic
88
New cards
Peripartum onset/postpartum
a type of depression experienced by women during pregnancy or up to 4 weeks after giving birth
89
New cards
aaron beck
the person who stated that Depression prone people have a mental predisposition to think about things in a negative way
* Themes of loss, failure, rejection, worthlessness, inadequacy
* May result from childhood experiences
* Themes of loss, failure, rejection, worthlessness, inadequacy
* May result from childhood experiences
90
New cards
Hopelessness Theory
the theory that claims that a particular style of negative thinking leads to hopelessness
* Hopelessness is defined as the expectation that negative things will occur or that desired outcomes will not occur.
* Assumes that hopelessness stems from a tendency to believe that negative life events as being stable and global.
* Stable: unable to chance
* Global: affects everything
* Hopelessness is defined as the expectation that negative things will occur or that desired outcomes will not occur.
* Assumes that hopelessness stems from a tendency to believe that negative life events as being stable and global.
* Stable: unable to chance
* Global: affects everything
91
New cards
rumination
the passive and repetitive thinking about one’s depression and dweling on it rather than distracting oneself or trying to actively treat it
* this is associated with a theory taht focuse on rumination adn how people’s throught on their depresion can increase the duration and risk
* this is associated with a theory taht focuse on rumination adn how people’s throught on their depresion can increase the duration and risk
92
New cards
suicide
death as a result of injurious behaviour with the intention of death
93
New cards
thought insertion
a type of deluion that the person believes that one’s thought are being placed inside their head
94
New cards
Thought withdrawal
a type of delusion that the person believes that one’s thoughts are being removed
95
New cards
Catatonic
decreased reactivity to the environment
* also a disorder that disrupts a person’s awareness of the world around them
* included in disorganized/abonrmal motor behavior
* also a disorder that disrupts a person’s awareness of the world around them
* included in disorganized/abonrmal motor behavior
96
New cards
flat affect
a lack of emotional responsiveness
* may be elated or depressed, but otehrs cant tell
* may be uncaring and unresposnive, but you still feel an emotion
\*there is a diconnect between emotions and how you express them
* may be elated or depressed, but otehrs cant tell
* may be uncaring and unresposnive, but you still feel an emotion
\*there is a diconnect between emotions and how you express them
97
New cards
inappropriate affect
Display of emotions that are unsuited to the situation; a symptom of schizophrenia.
98
New cards
cland associations
rhythmic/rhyming patterns associated with psychotic speech
99
New cards
neologisms
Made-up words that typically have only meaning to the individual who uses them.
100
New cards
The Cognitive Triad
Aaron Beck, Depression comes from people having unreasonably negative ideas about themselves, their world, and their future.