NOCTI GA Engineering & Technology Study Guide
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
170 Terms
CAD
computer aided drafting
plot plan
diagram showing everything at the project site at a set scale
floor plan
diagram showing arrangement of rooms and furniture at a set scale
elevation plan
diagram showing the external face of a building showing height at a set scale
foundation plan
diagram showing the plane view of a structure at a set scale
specification sheets
a document describing the specifications a product or property
Brainstorm
A group technique for solving problems, generating ideas, stimulating creative thinking, etc. by unrestrained spontaneous participation in discussion.

Client
A person using the services of a professional person or organization.

Creativity
The ability to make or bring a new concept or idea into existence; marked by the ability or power to create.

Criteria
A means of judging. A standard, rule, or test by which something can be judged.

Constraint
1. A limit to a design process. Constraints may be such things as appearance, funding, space, materials, and human capabilities. 2. A limitation or restriction.
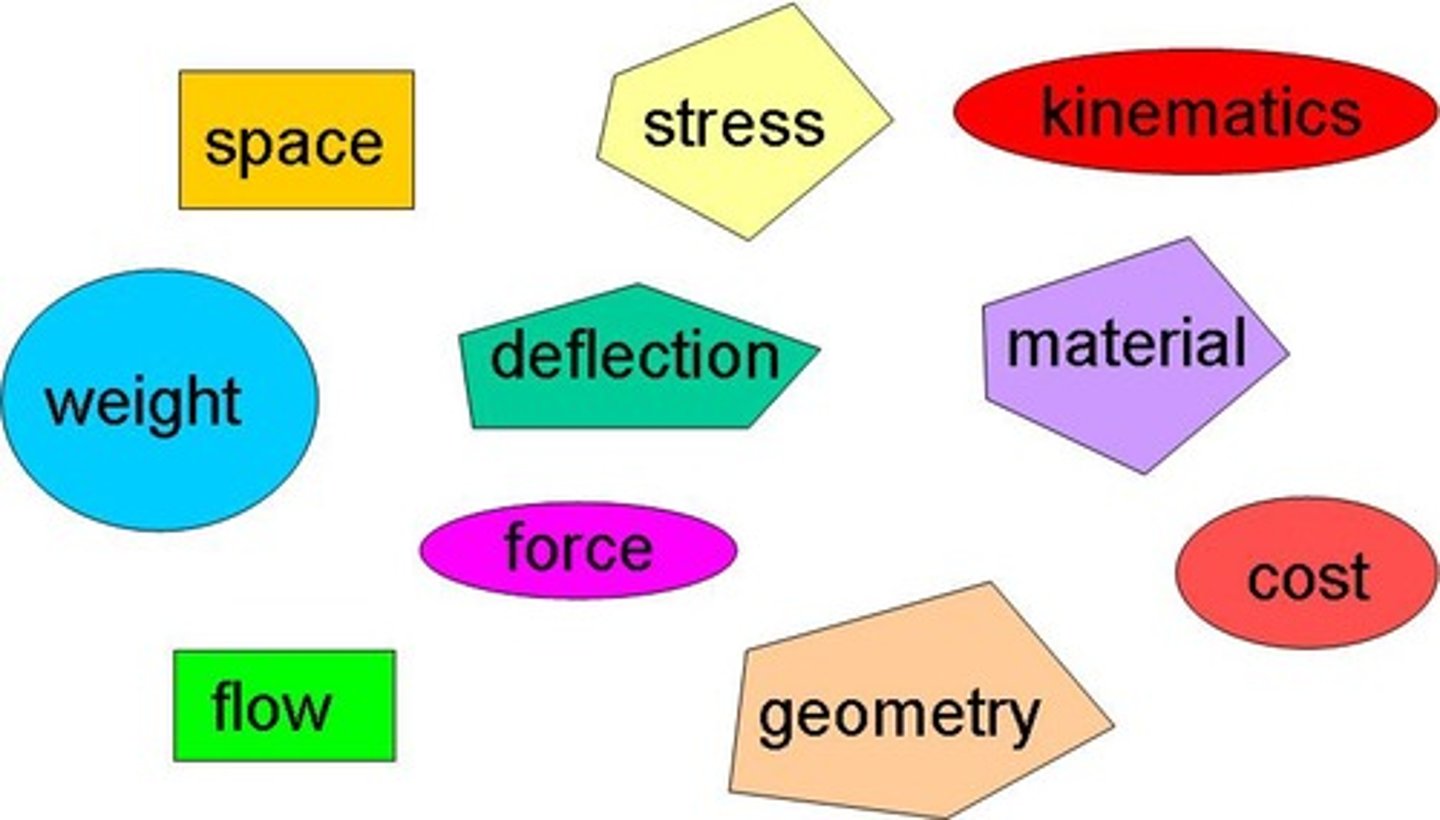
Design
1. An iterative decision-making process that produces plans by which resources are converted into products or systems that meet human needs and wants or solve problems. 2. A plan or drawing produced to show the look and function or workings of something before it is built or made. 3. A decorative pattern.
Design Brief
A written plan that identifies a problem to be solved, its criteria, and its constraints. Encourage thinking of all aspects of a problem before attempting a solution.

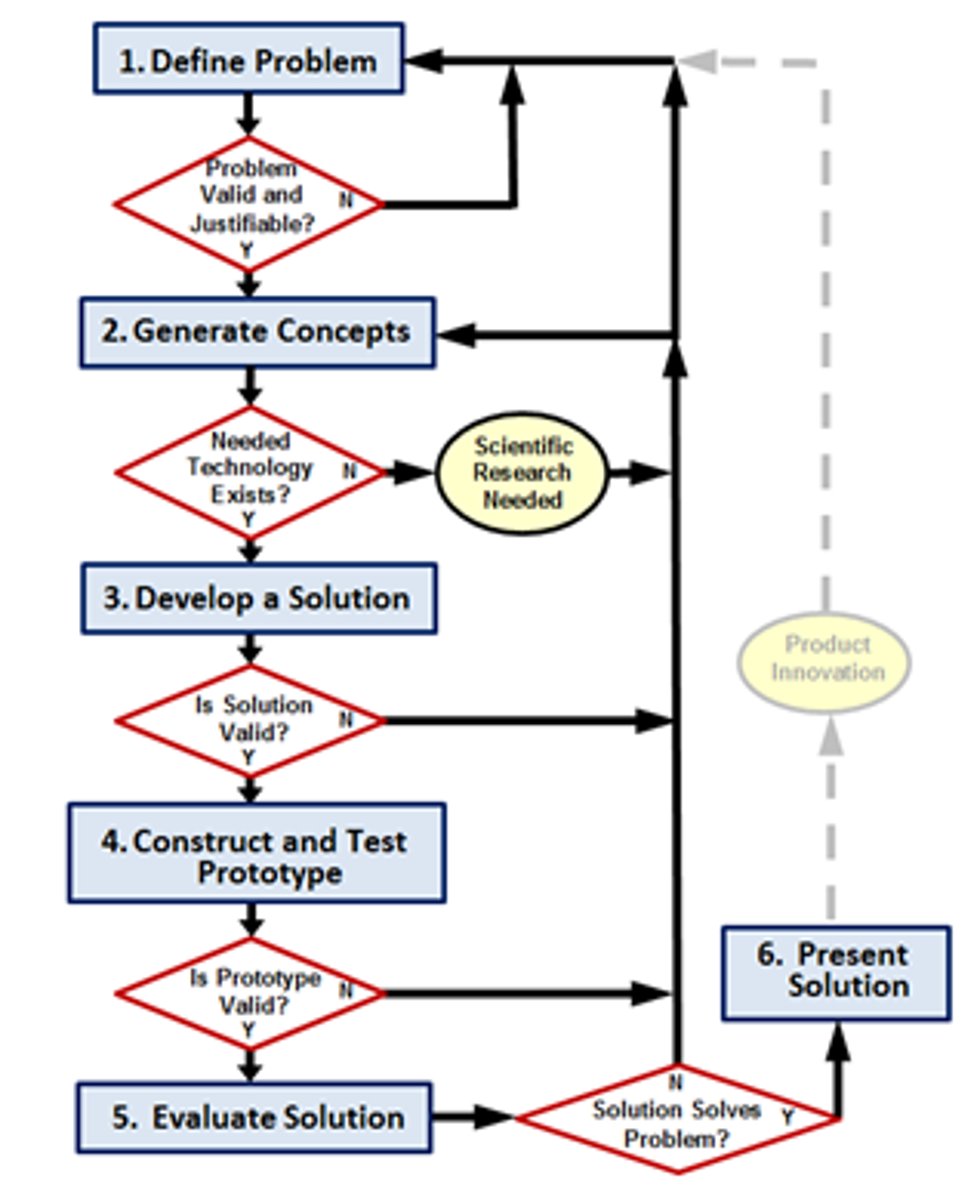
Design Process
A systematic problem-solving strategy, with criteria and constraints, used to develop many possible solutions to solve a problem or satisfy human needs and wants and to winnow (narrow) down the possible solutions to one final choice.
Design Statement
A part of a design brief that challenges the designer, describes what a design solution should do without describing how to solve the problem, and identifies the degree to which the solution must be executed.

Designer
A person who designs any of a variety of things. This usually implies the task of creating drawings or in some ways uses visual cues to organize his or her work.

Engineer
A person who is trained in and uses technological and scientific knowledge to solve practical problems.

Engineering Notebook
A book in which an engineer will formally document, in chronological order, all of his/her work that is associated with a specific design project.

Innovation
An improvement of an existing technological product, system, or method of doing something.
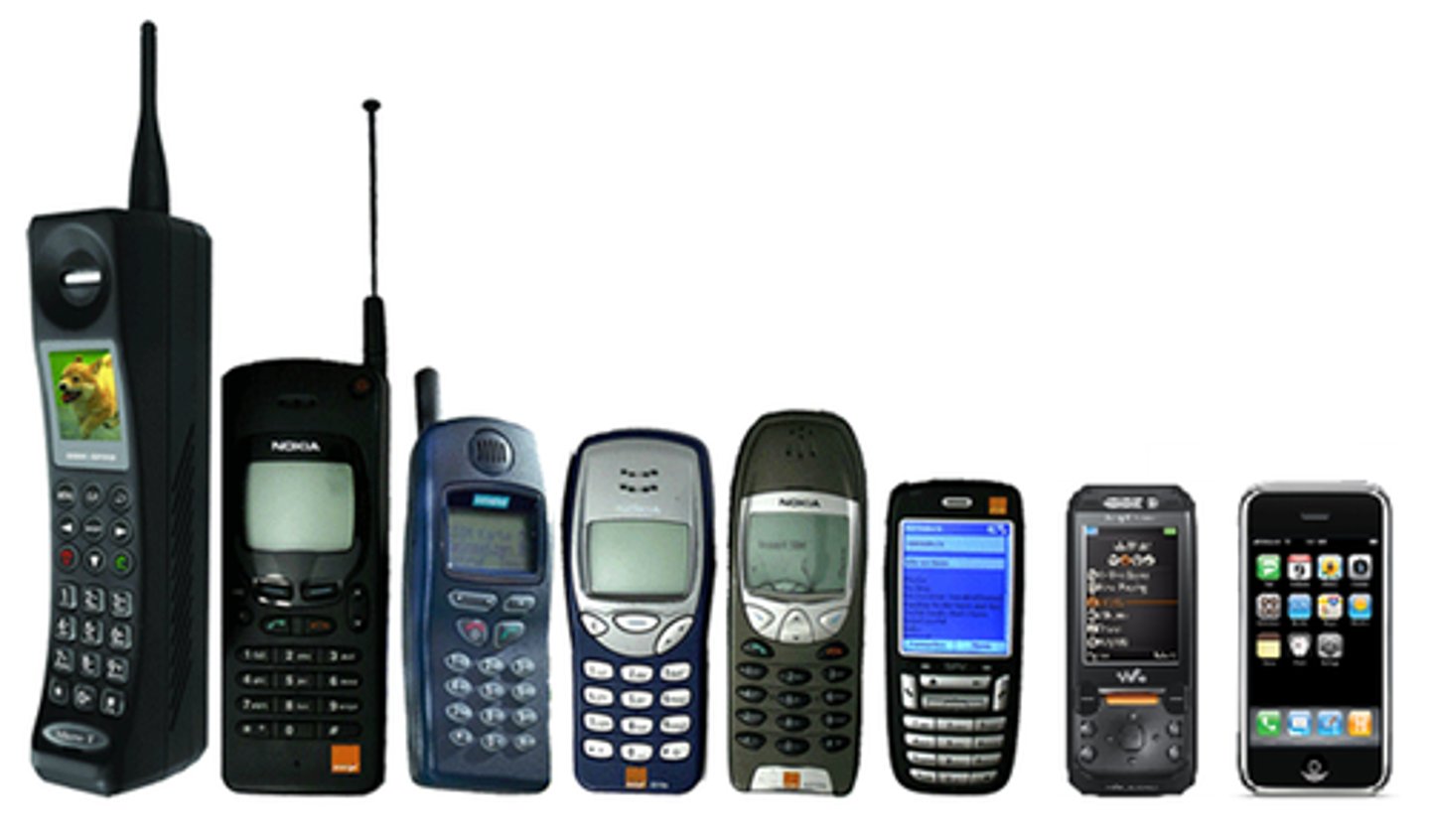

Invention
A new product, system, or process that has never existed before, created by study and experimentation.
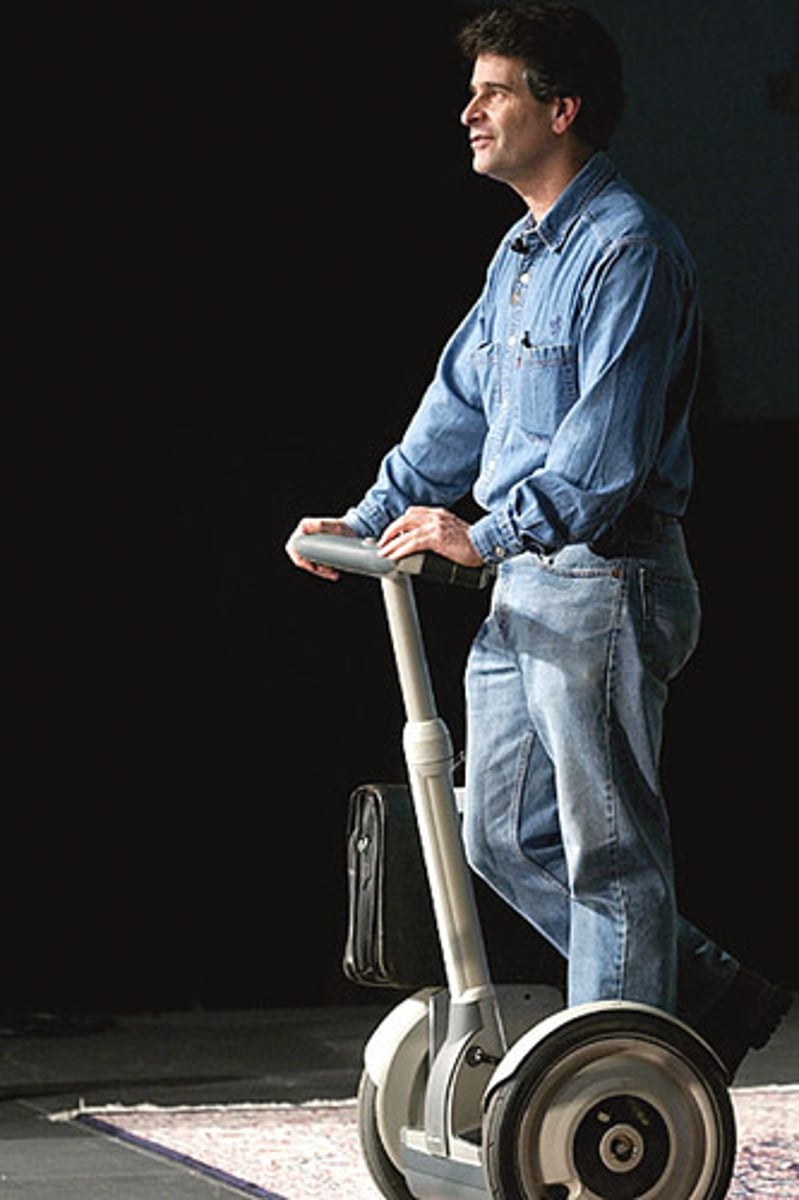

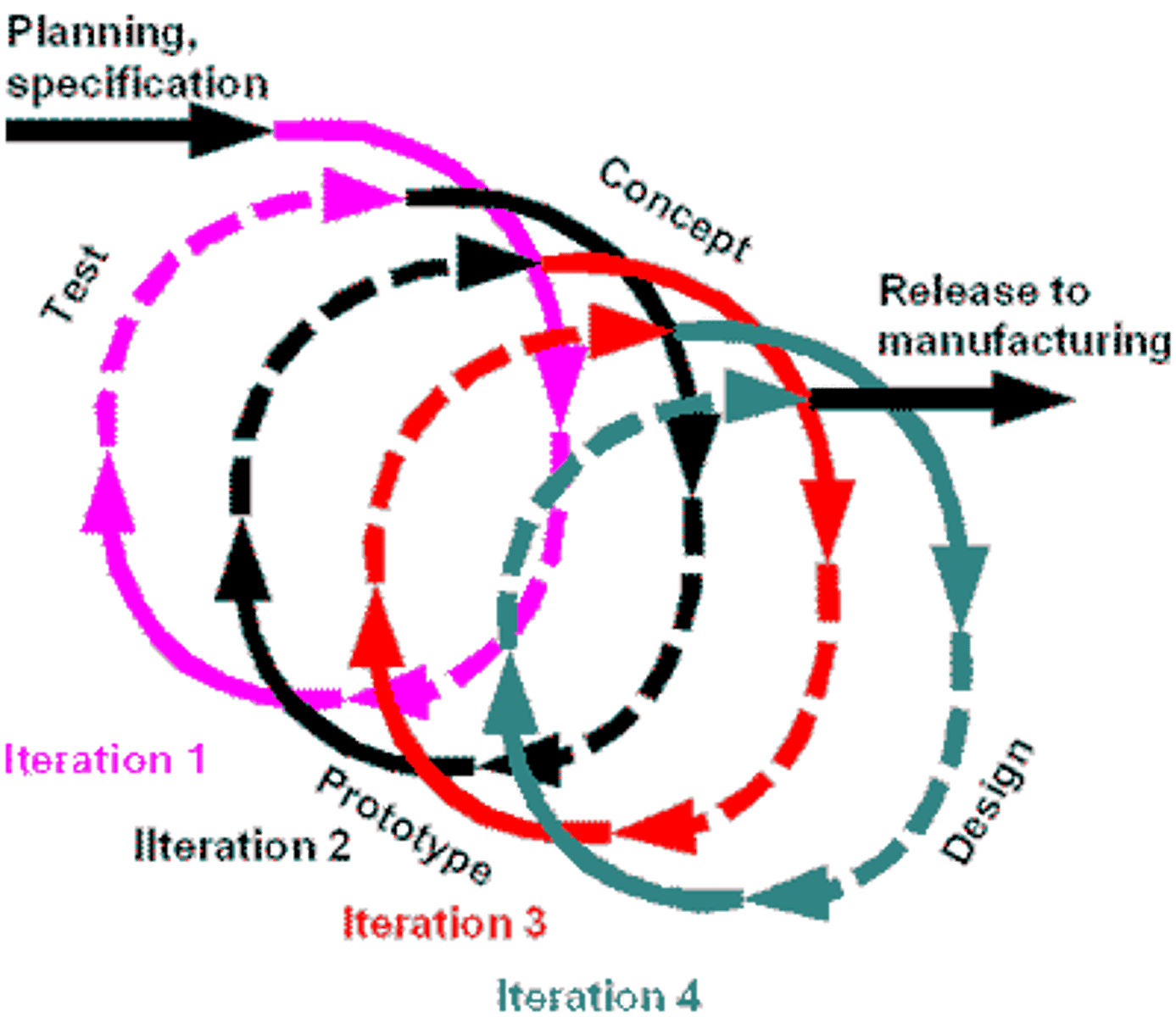
Iterative
A process that repeats a series of steps over and over until the desired outcome is obtained.
Valid
Well-founded on evidence and corresponds accurately to the real world.

open-looped
a system that has to have input each time the system is used
feedback
fourth step of a system
closed-looped
a system that has feedback
process
second step of a system
output
third step of a system
subsystem
smaller systems intergrated into a larger system
What are some important resources for engineering and technology?
People,Energy, Capital(Money), Information,Tools, Machines, Materials, and Time
What is a system?
a set or group of parts that all work together, all of them include input, a process and an output
What is a subsystem
a system that operates as part of another system
What does constraint mean?
a limit, such as appearance, budget, space, materials, or human capital in the design process.
ISO
International Standards Organization
ANSI
American National Standards Institute
Drawing to scale
when objects are drawn at a reduced or enlarged size
Multiview drawing
another term for orthographic projection
Third-angle projection
the system in which the top view of a drawing is placed above the front view
CAD (Computer Aided Design)
The use of a computer to assist in the process of designing a part, circuit, building, etc.
Fabricate
Construct or manufacture an industrial product.
Mockup
A model devised to expose its parts for study, training or testing.
Model
A visual, mathematical, or three-dimensional representation in detail of an object or design, often smaller than the original. A model is often used to test ideas, make changes to a design, and to learn more about what would happen to a similar, real object.
Engineering
The profession which the knowledge of the mathematical and natural sciences, gained by study, experience, and practice, is applied with judgement to develop ways to use, economically, the materials and forces of nature for the benefit of mankind.
Systems Model
input -> process -> output -> feedback
7 resources of input
time, energy, tools, materials, people, capital, information
input
information, ideas, and activities that we need to provide to determine what you want to accomplish
process
The conversion of ideas or activities through the use of machines, resources and labor into useful products
output
What the system produces.
feedback
the part of a system that measures and controls the outcome of a system
types of outputs
expected, unexpected, desirable, undesirable
EDP: Step 1
Define the problem
EDP: Step 2
Brainstorm, research
EDP: Step 3
Brainstorm-develop solutions
EDP: Step 4
Choose the best solution
EDP: Step 5
Create a prototype
EDP: Step 6
Evaluate the solution
EDP: Step 7
Communicate the design
EDP: Step 8
Refine the Design
Who is an Engineer?
a person who designs products, structures, or systems to improve people's lives
What is Engineering?
it is the process of designing solutions
Who is an Engineer Technologist?
these people work out the production details and design the system for manufacturing a product
model
an object, usually built to scale, that communicates information and represents a larger object
design brief
a written plan that identifies the problem to be solved, its criteria, and its constriants. It is used to encourage thinking about all aspects of the problem before attempting a solution
engineer
a person who is trained in and use technological and scientific knowledge to solve practical problems
evolution
a gradual development
Environmental Engineering
Solve environmental problems related to pollution, water use, materials and energy use, waste treatment, etc.
Electronic Engineering
Design, develop, and test small electronic systems, such as appliances, telephones, surgical devices, etc.
Electrical Engineering
Design, develop, and test the manufacture of electrical equipment and large-scale electrical systems.
Computer Hardware Engineering
Research, design, develop, and test computer systems and computer-related equipment.
Civil Engineering
Plan the design, construction, and maintenance of various civil structures.
Chemical Engineering
Address issues related to chemical production, transformation of raw materials, and chemical use.
Biomedical Engineering
Devise procedures and devices to improve medical conditions.
Agricultural Engineering
Create technology to advance food, biological, irrigation, and machinery systems.
Aerospace Engineering
Design, develop, and test aircraft and spacecraft ranging from rockets and spacecraft to gliders and small passenger aircraft.
What is a constraint?
A constraint is what holds parts together according to certain boundaries.
mock-up
a rough model made of cardboard or other materials
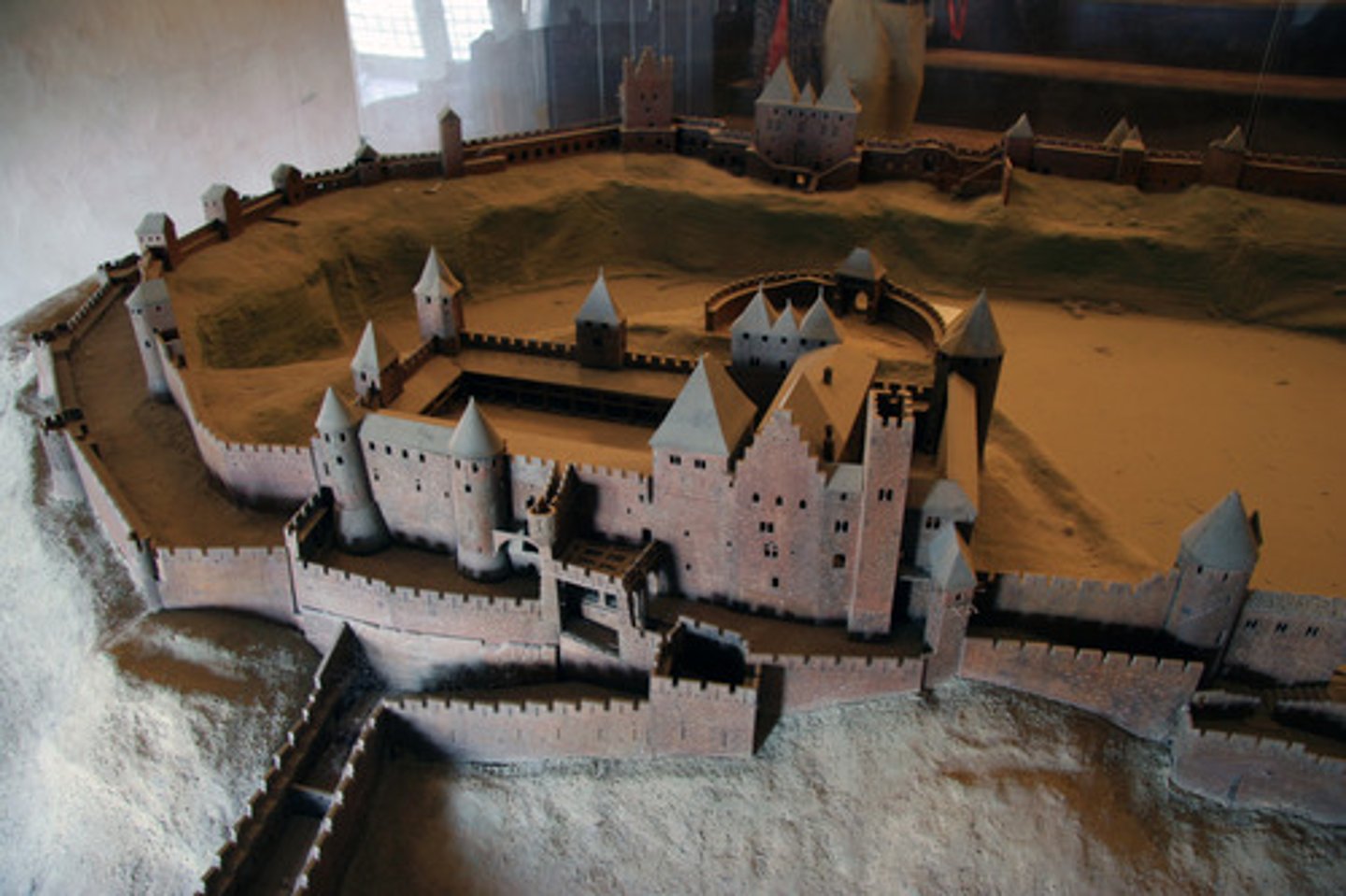

prototype
a model made of the actual materials that can be used
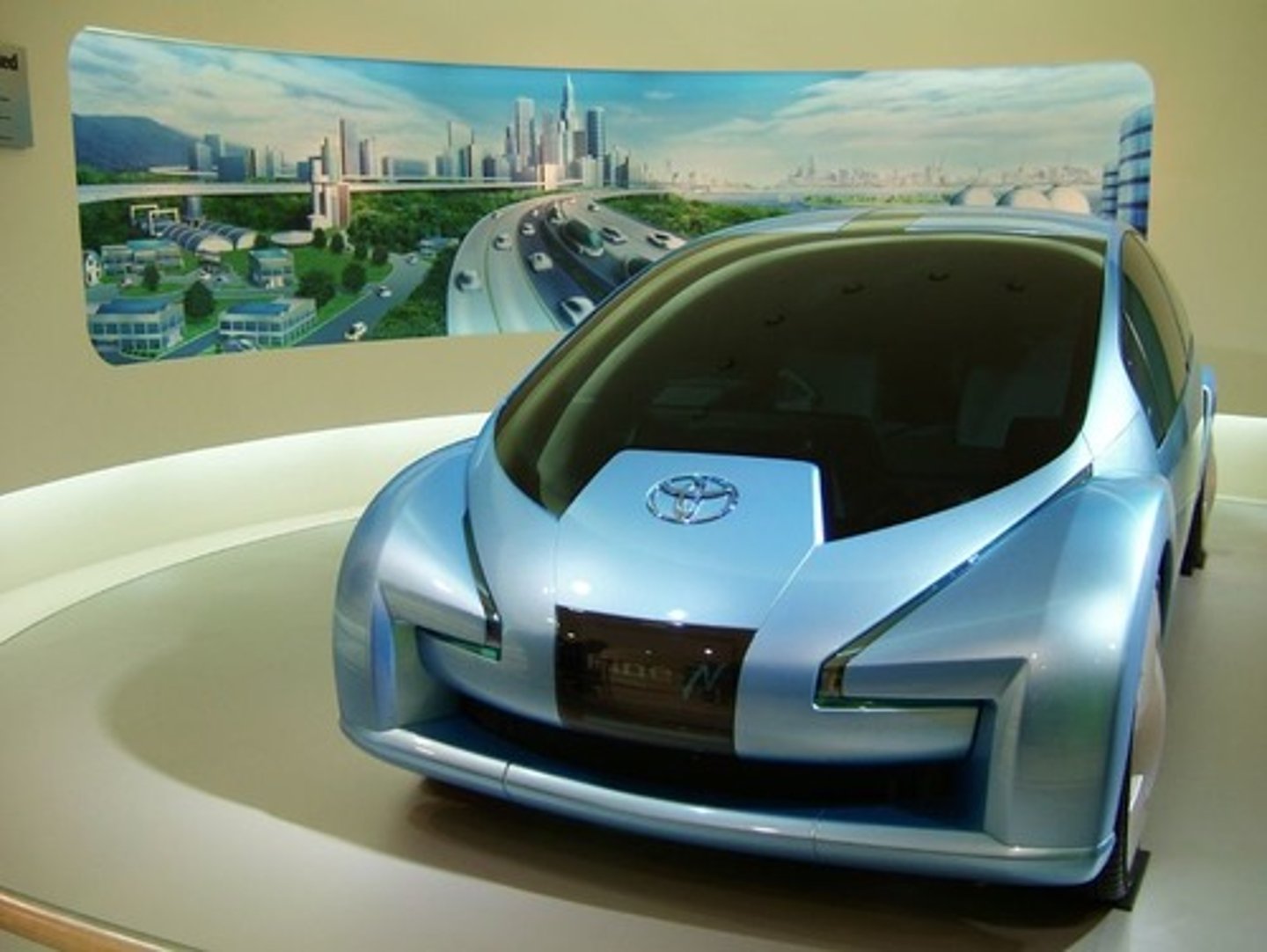

TECHNOLOGY
processes and knowledge that can be used to extend human abilities as well as satisfy human needs and wants.
TEAM
a group of people working together to accomplish a common goal.
Design
A plan or drawing produced to show the look and function or workings of something before it is built or made or a decorative pattern.
Design Brief
A written plan that identifies a problem to be solved, its criteria, and its constraints.
Design Process
A systematic problem-solving strategy, with criteria and constraints, used to develop many possible solutions to solve a problem or satisfy human needs and wants and to narrow down the possible solutions to one final choice.
Engineering Notebook
A book in which an engineer will formally document, in chronological order, all of his/her work that is associated with a specific design project.
Innovation
An improvement of an existing technological product, system, or method of doing something.
Invention
A new product, system, or process that has never existed before, created by study and experimentation.
Product
A tangible artifact produced by means of either human or mechanical work, or by biological or chemical process.
Research
The systematic study of materials and sources in order to establish facts and reach new conclusions.
Assess
To thoroughly and methodically analyze accomplishment against specific goals and criteria.
Creativity
The ability to make or bring a new concept or idea into existence; marked by the ability or power to create.
Criteria
A standard, rule, or test by which something can be judged.
Problem Identification
The recognition of an unwelcome or harmful matter needing to be dealt with.
Prototype
A full-scale working model used to test a design concept by making actual observations and necessary adjustments.
Assess
To thoroughly and methodically analyze accomplishment against specific goals and criteria
Creativity
The ability to make or bring a new concept or idea into existence; marked by the ability or power to create
Criteria
A means of judging. A standard, rule, or test by which something can be judged
Constraint
1. A limit to a design process. Constraints may be such things as appearance, funding, space, materials, and human capabilities. 2. A limitation or restriction
ABET
Accreditation Board for Engineering & Technology
ANSI
American National Standards Institute
ISO
International Standards Organization - International Organization for Standardization
EIA
Electronic Industries Alliance
IEEE
Institute of Electrical & Electronics Engineers