Abiotic Factors and Major Biomes Overview
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Abiotic Factors
Non-living components affecting species distribution.
Sunlight
Primary energy source influencing plant growth.
Temperature
Affects metabolic rates and species survival.
Moisture
Essential for hydration and plant growth.
Wind
Influences temperature and moisture distribution.
Seasons
Result from Earth's axial tilt of 23 degrees.
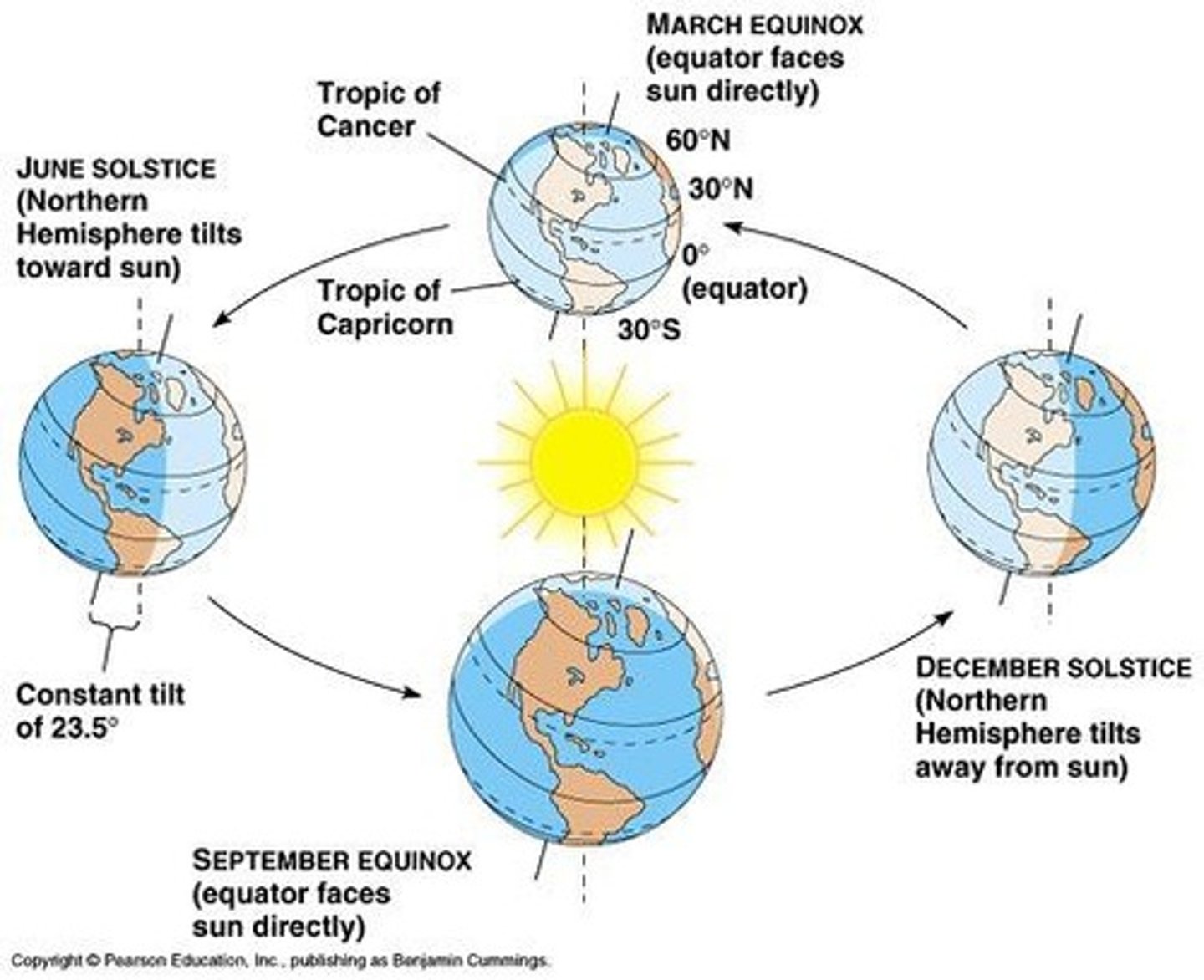
Spring Equinox
Occurs in March; day and night equal.
Summer Solstice
Occurs in June; longest day of year.
Fall Equinox
Occurs in September; day and night equal.
Winter Solstice
Occurs in December; shortest day of year.
Tropical Circulation Cells
Warm air rises at the equator.
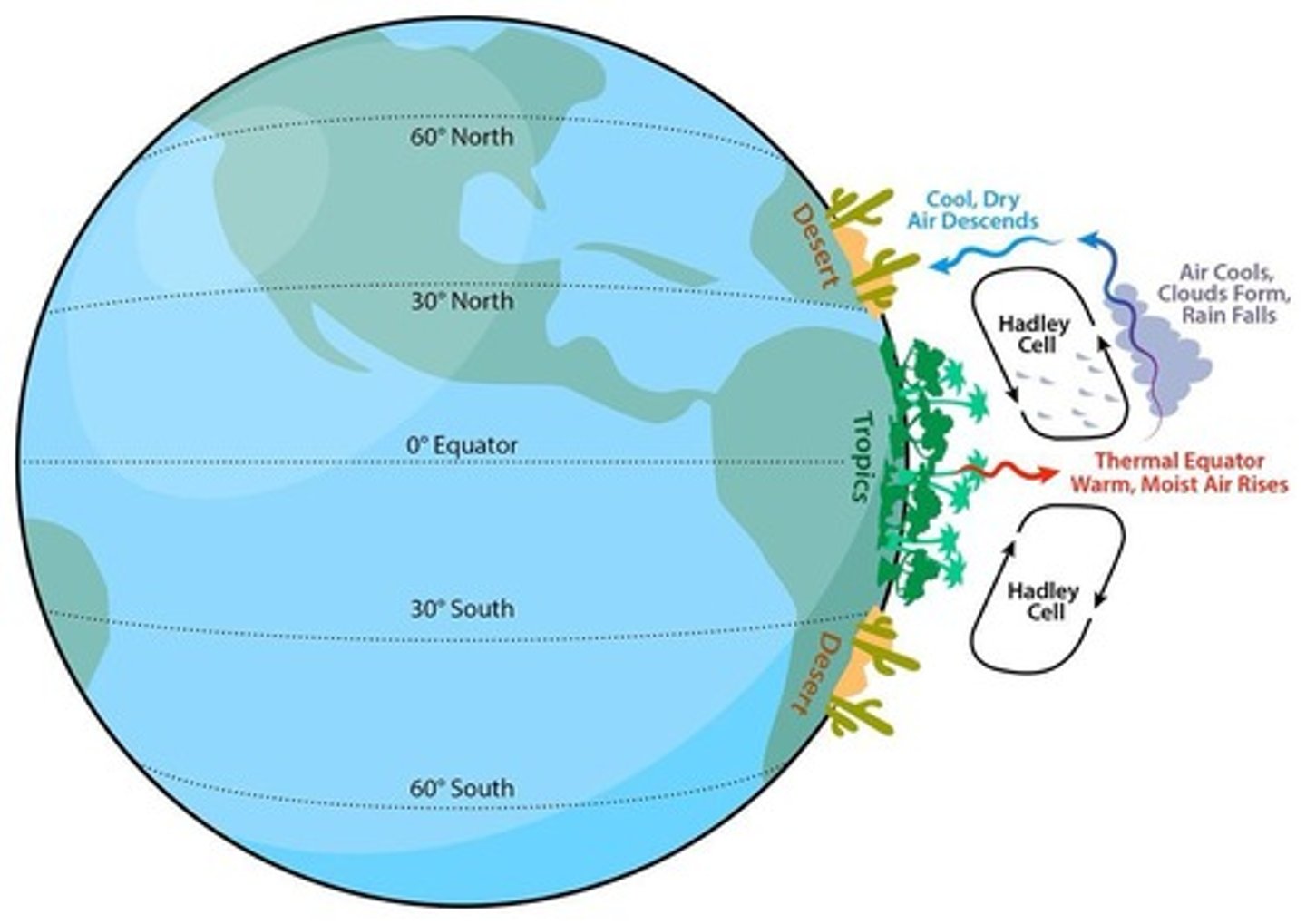
Temperate Circulation Cells
Air circulation patterns in temperate zones.
Prevailing Winds
Dominant wind patterns affecting climate.
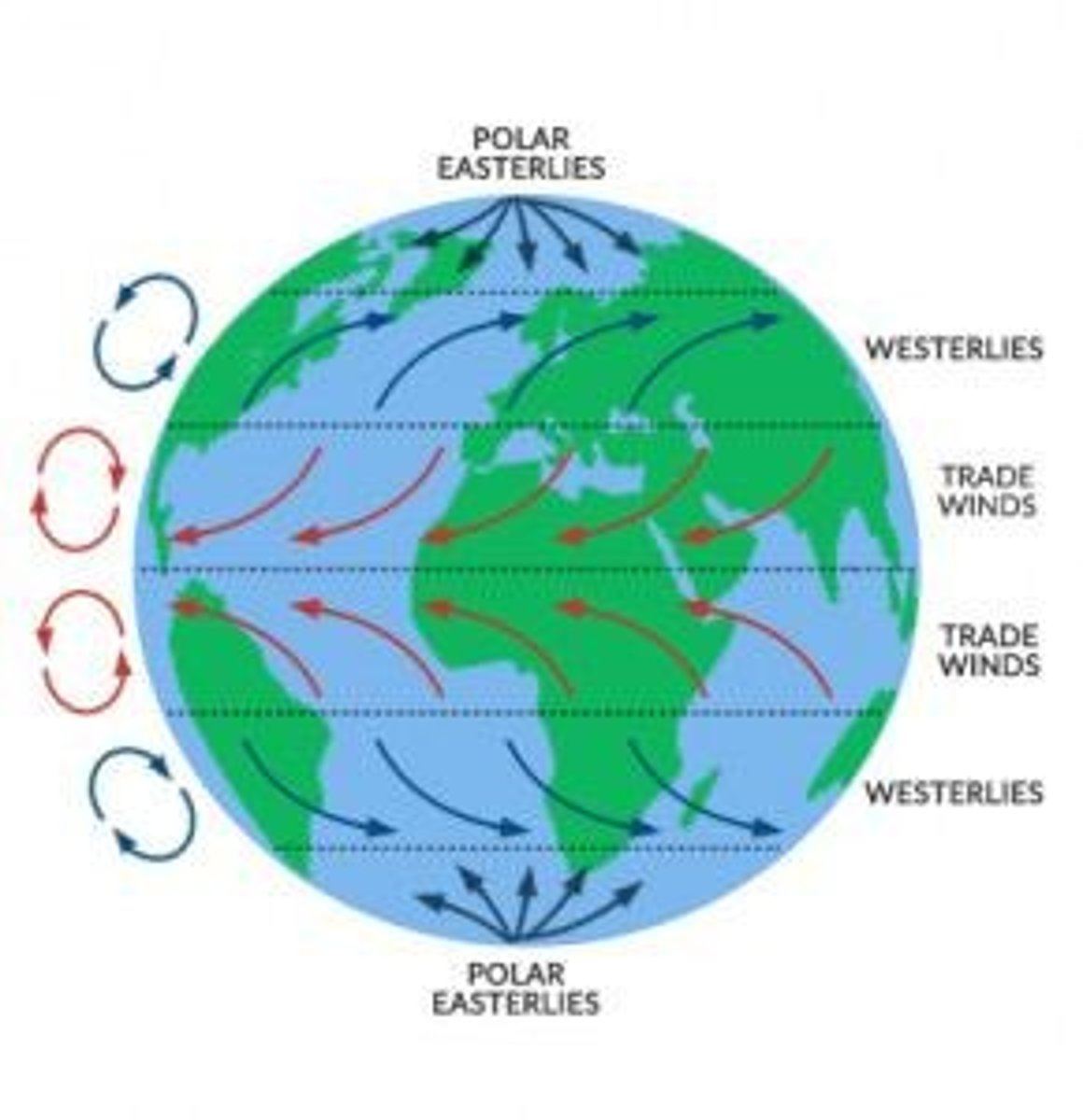
Coriolis Effect
Curvature of air and water movement.
Deserts
Regions with less than 50 cm rainfall annually.
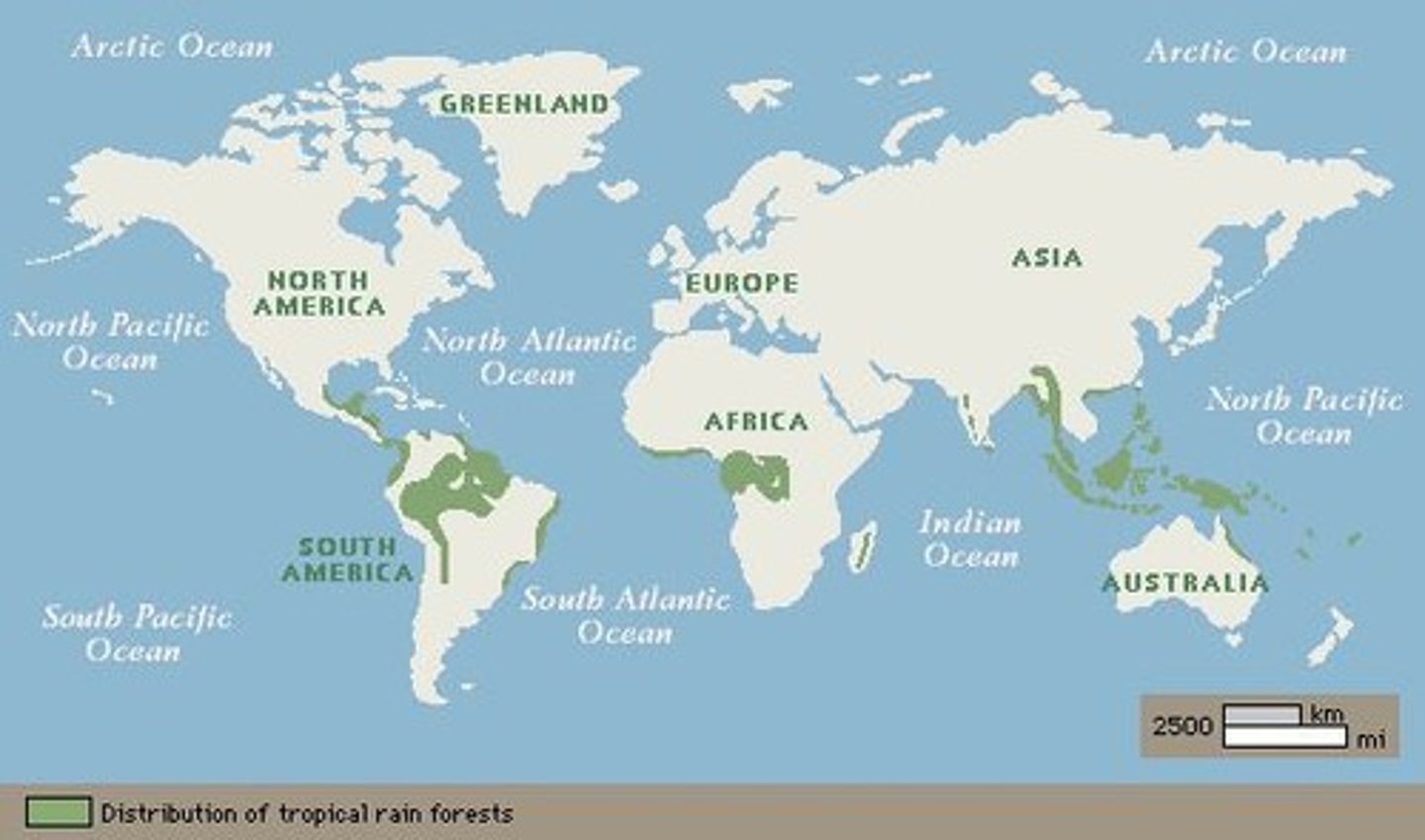
Rainforests
High biodiversity biome with over 200 cm rain.
Boreal Forest
Cold forest biome with evergreen conifers.
Tundra
Cold biome with permafrost and low diversity.
Grasslands
Biomes dominated by grasses, seasonal rainfall.
Latitude
Distance from equator affecting climate and biomes.
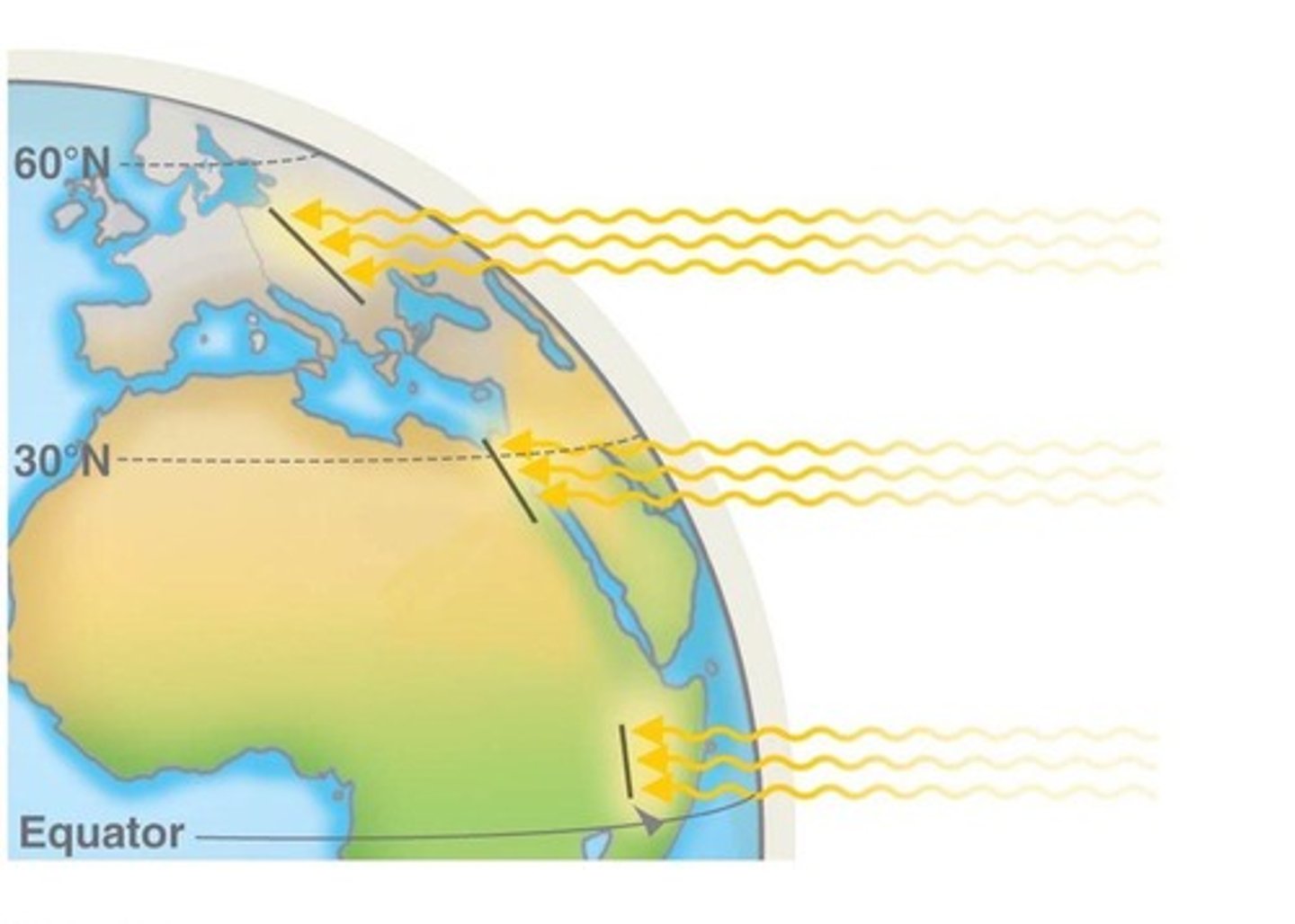
Nearby Oceans
Influence local climate and precipitation patterns.
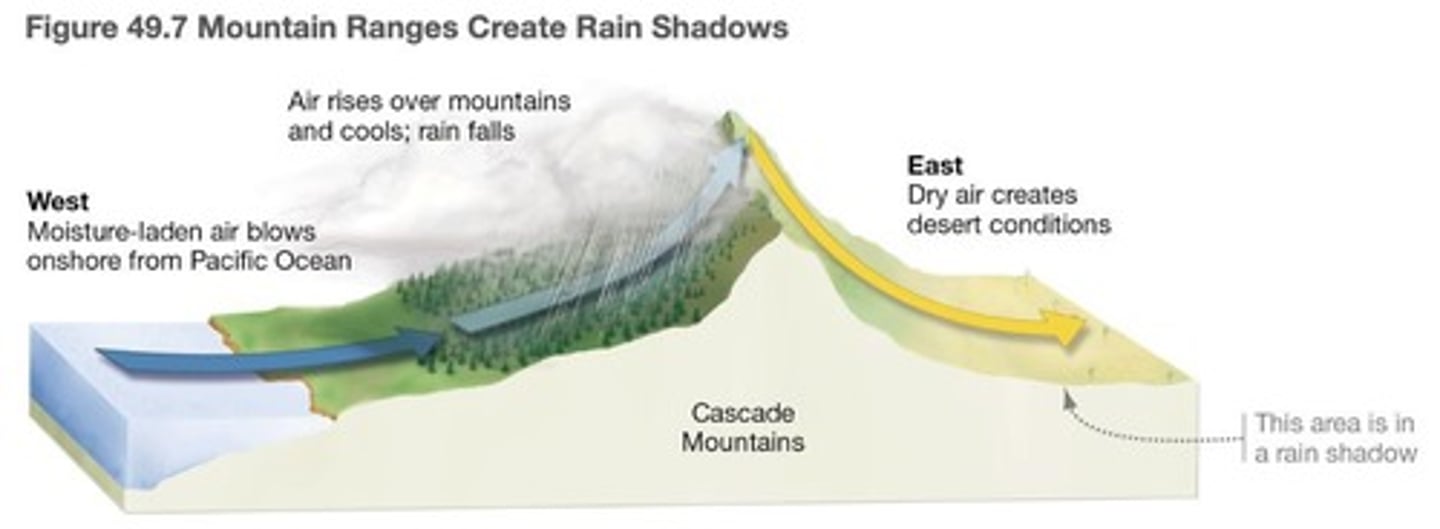
Nearby Mountains
Affect precipitation through orographic lift.
Plant Adaptations
Features enabling survival in specific biomes.
Animal Adaptations
Traits aiding survival in specific environments.
Nutrient Poor Soil
Common in rainforests, limits plant growth.
Permafrost
Permanently frozen subsoil in tundra regions.
Biodiversity
Variety of life forms in a biome.
Evapotranspiration
Water loss from soil and plants.
Climate Change
Long-term alteration of temperature and weather patterns.