Classification and Cladistics
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
taxonomy
scinece of classifying oragnisms into groups.
Groups are called taxa
based on observeable physical traits
once you know the characteristics of known mammals
you know the characteristics of all mammals, even the undiscovered ones
how many species on earth
8.7 million
Taxomy
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Dashing king Philip came over for great soup
Based on cladistsic what does not exist
reptiles
Traditional classification grouped reptiles into a single taxon (Class Reptilia), but this does not correspond to patterns of divergence by evolution.
Cladistics groups organisms into clades, where all members of a clade share a common ancestor. Birds are more closely related to crocodiles and turtles than other reptiles, therefore birds, crocodiles and turtles are classified into a single clade.
paradigm shift
fundamental change in understanding
Taxomy→ cladistics
evolution
change in heretiable characteristics of populations of a species over time
The ideal classification system follows evolutionary relationships, so all the members of a taxonomic group have evolved from
a common ancestor
cladistics
methods of classifying organisms into clades based on shared characteristics
clade
group of organisms or viruses that have all evolved from a common ancestor. Characteristics can be preditced according to cladss classified in
Morphological traits can be used
cladogarms
tree diagramd that organize clades, show probable divergence of species
classifying clades
objective
base sequence, amino acids
DNA, RNA, protein sequences
organisms evolve and diverge, their DNA sequences accumulate mutations. Scientists compare these mutations using sequence alignments to reconstruct evolutionary history
molecular clock
diffrences in base sequence of DNa are the results of proteins
Mutation gradually accumulate over long periods of time at a constant rate so they can be used as a generational clock to see when species diverged from a common ancestor
limits to a molecular clock
generational time- shorter generation time, more opportunity for mutaitons, faster clock
population size- mutaitons are more likely in fixed, small populations resulting in faster molecular clocks
selective pressure-
node
divergince of species from a common ancestor
cladograms are created by grouping oragnisms bu
shared charactersitics
BAse sequence of genes/amino acids
nucleotides sequence
fewer differences, more closly related species are
parsimony analysis
used to select the most probable cladogram, in which observed sequence variation between clades is accounted for with the smallest number of sequence changes.
assumption of parsimony analysis is that a simple hypothesis with a small number of evolutionary changes is more likely to be true than a complex hypothesis.
rapidly evolving cirus
Rapidly evolving viruses can quickly develop resistance to existing drugs and treatment, requiring more research and development of new drugs.
The mutations often produce novel subtypes of the virus, which are no longer recognised by the immune system.
impact the effectiveness of current vaccines, which may no longer confer immunity.
not contained, it can result in epidemics or pandemics.
terminal brance
endpoint representing one group
root
represents theoretical last common ancestor, LUCA
Figwort faimily reclass
orignlally made using morphology, reclassified by cladistics
compared nucleotides sequence of 3 chloroplast genes
Fifty genera were reclassified into the plantain family (Plantaginaceae).
Twelve genera were reclassified into the broomrape family (Orobanchaceae).
Thirteen genera were classified into a new family, lindernia (Linderniaceae)
Two genera were were reclassified into a new family, calceolaria (Calceolariaceae).
Two small families of other plants were reclassified into the figwort family.
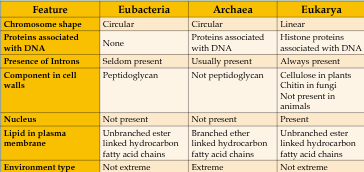
Three Domains
Bacteria
Archaea
Eukaryotes
A and E are more closely related
eurobacteria vs archaea vs eukarya