ESS - Topic 1.2 Systems
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Define each term below, explain it, and outline at least one specific example
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
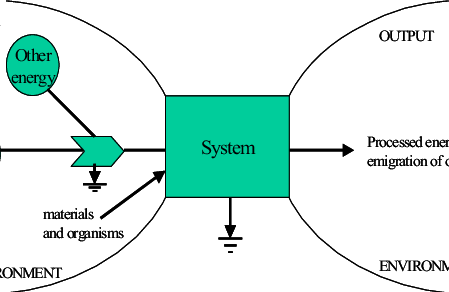
System
Any set of interactions or parts organized to create a functional whole with a purpose.
Systems Approach
Exploring connection between the parts of a system to understand the whole.
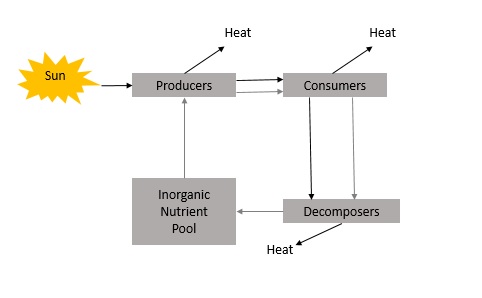
Storages
An accumulation of material, energy, or information into or out of a storage in a system.
Flows
The movement of mater, energy or information into or out of a storage in a system.
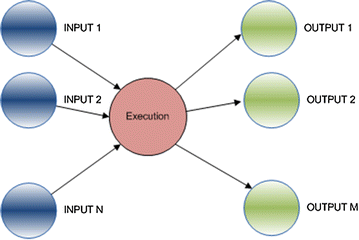
Inputs
Things going into a system that can be counted or accumulated
Outputs
Things going out of a system that can be counted or accumulated
Transfers
A change in location of energy or matter, without any change in its state or form
Transformations
Move in energy and matter, but in the process there is a change in the chemical nature, state, or in energy
Open System
A system that exchanges both matter and energy with its external environment
Closed System
Exchanges energy with the external environment but NOT matter

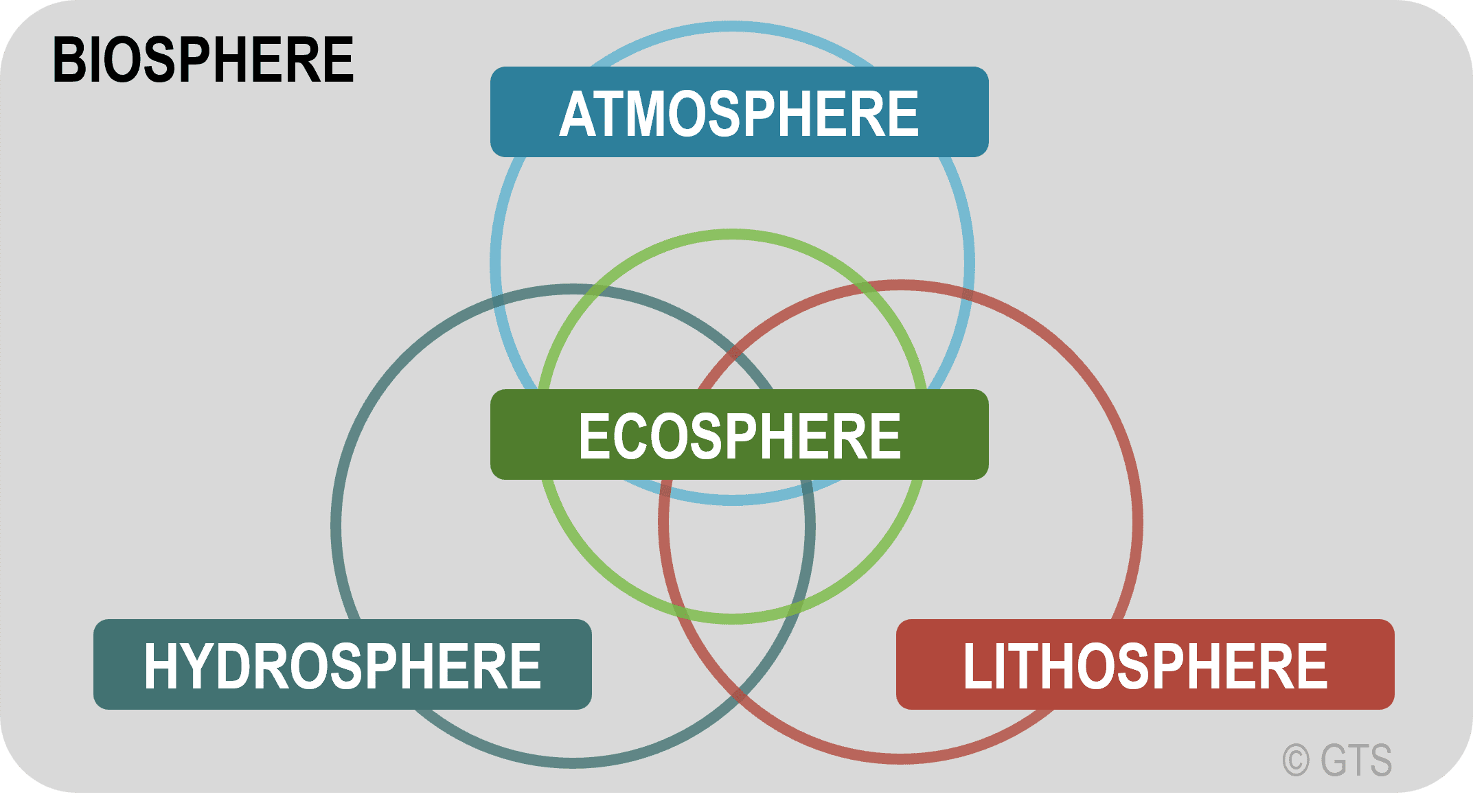
Biosphere
All of Earth’s organisms, including humans
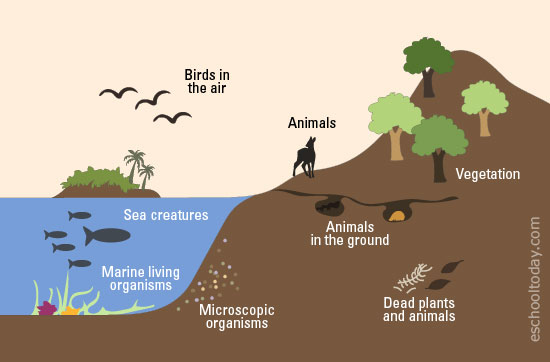
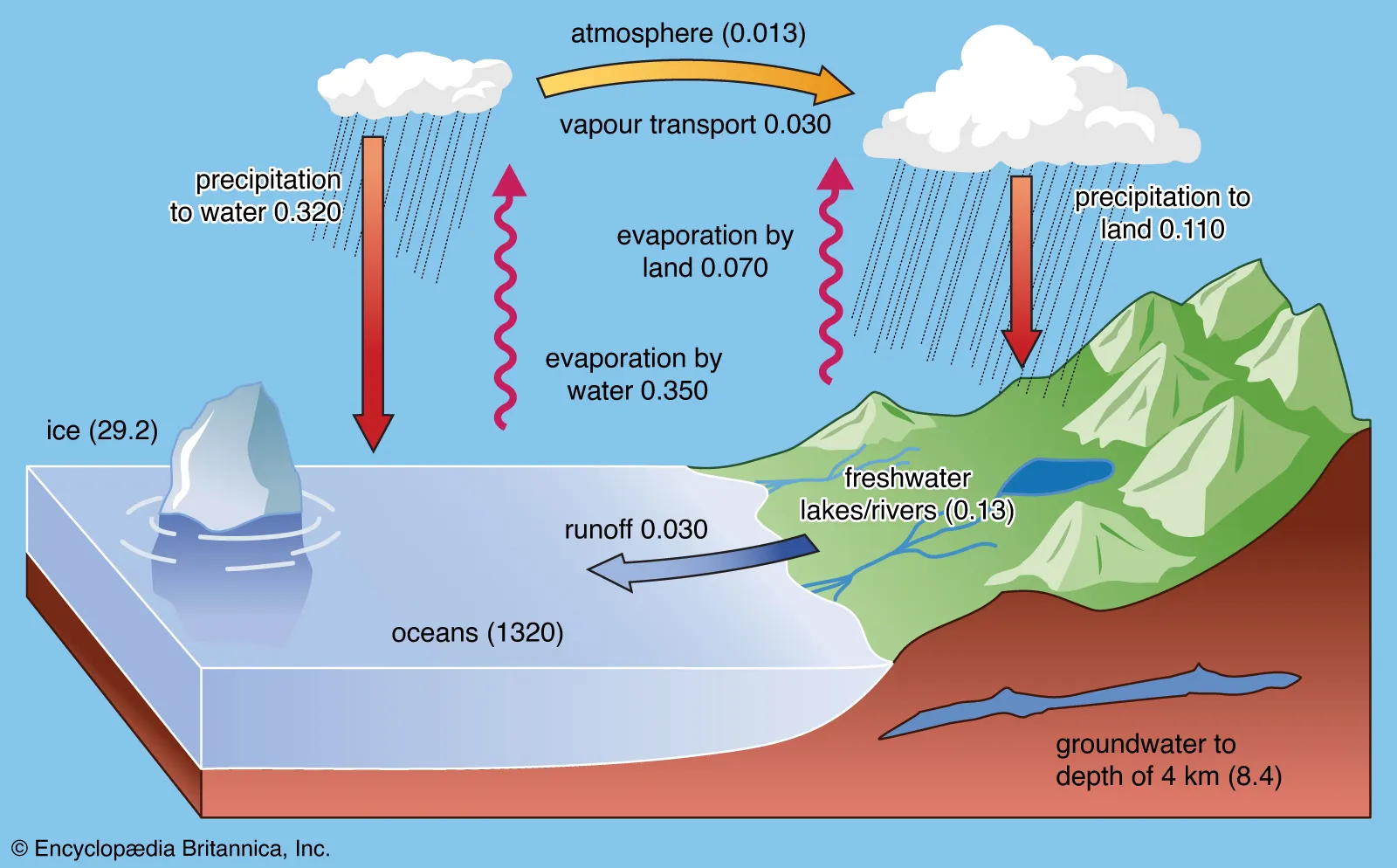
Hydrosphere
Liquid ocean, inland bodies of water ground water
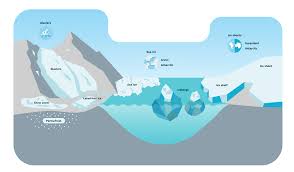
Cryosphere
All frozen water
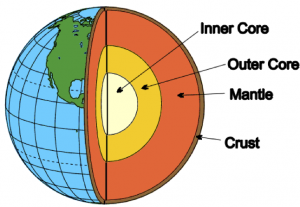
Geosphere
The Earth’s core, mantle, crust, and soils
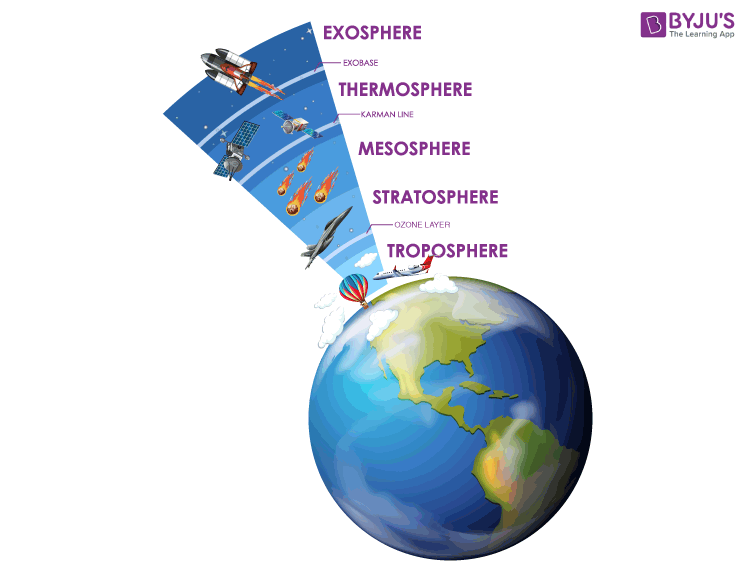
Atmosphere
The gases and particles that surround the Earth
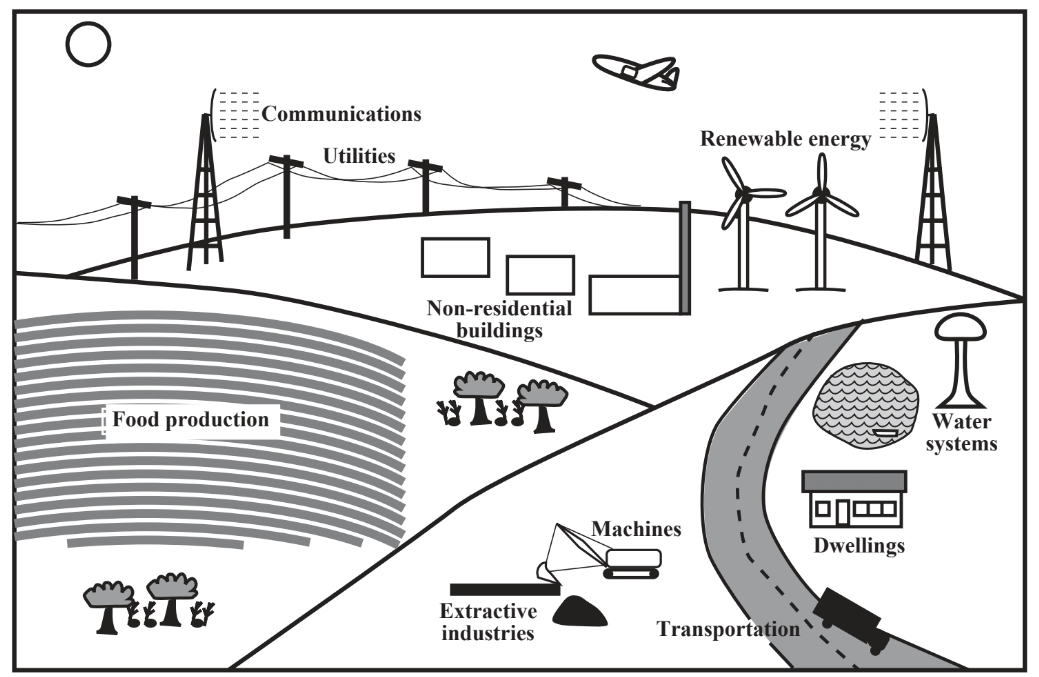
Anthroposphere
Human impact on Earth, including culture, technology, built environment, etc.
Gaia Hypothesis
All living organisms form a complex system that maintains conditions suitable for life.
Negative Feedback Loop
The output of a storage/ system returns as an input in a way that reverses the operation of the same processes
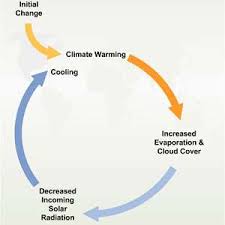
Positive Feedback Loop
The output of a storage/ system returns as an input in a way that amplifies change disestablishing the system and driving it away from its equilibrium
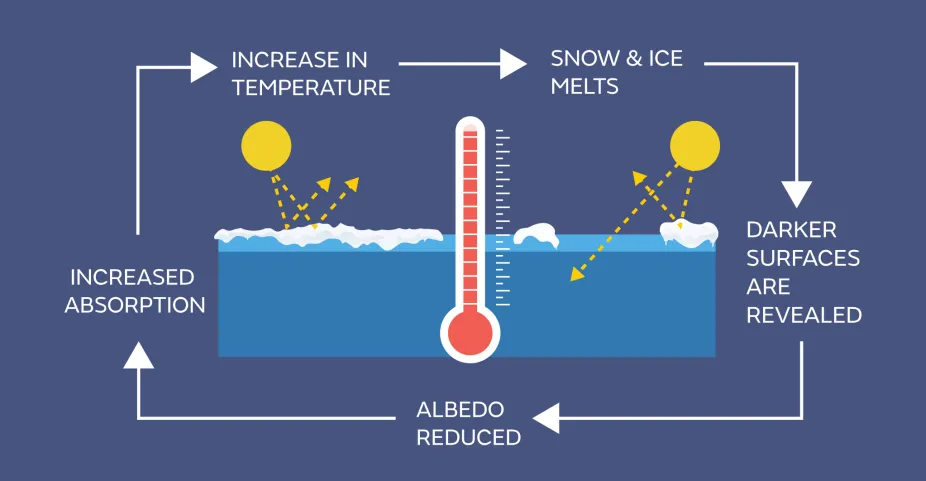
Steady-State Equilibrium
A situation, mainly in open systems, where there are continuous inputs and outputs of energy or matter that may result in short-term changes and imbalances
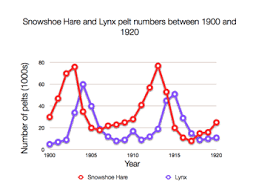
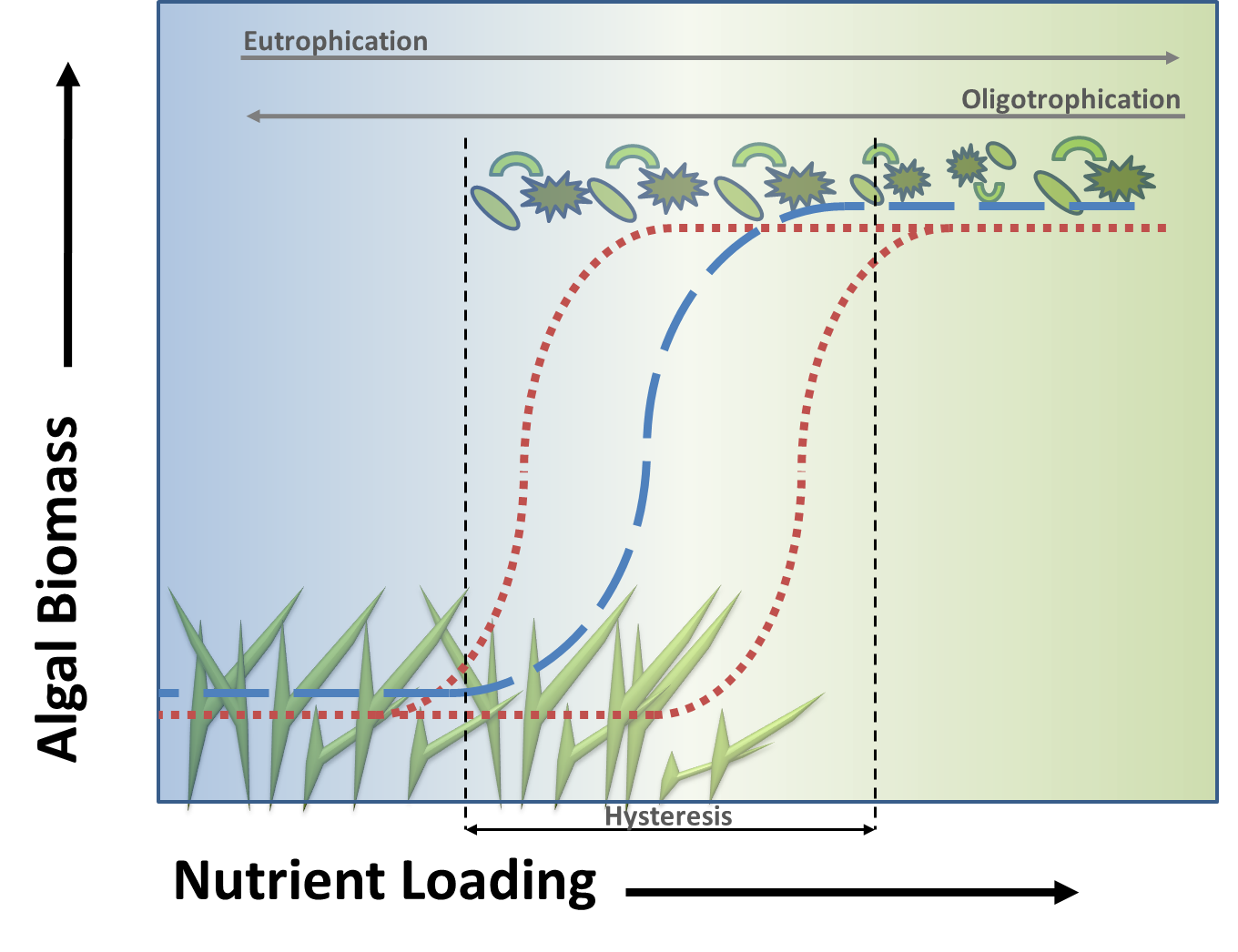
Tipping Point
The minimum amount of change that will cause destabilization within a system leading to a new equilibrium state
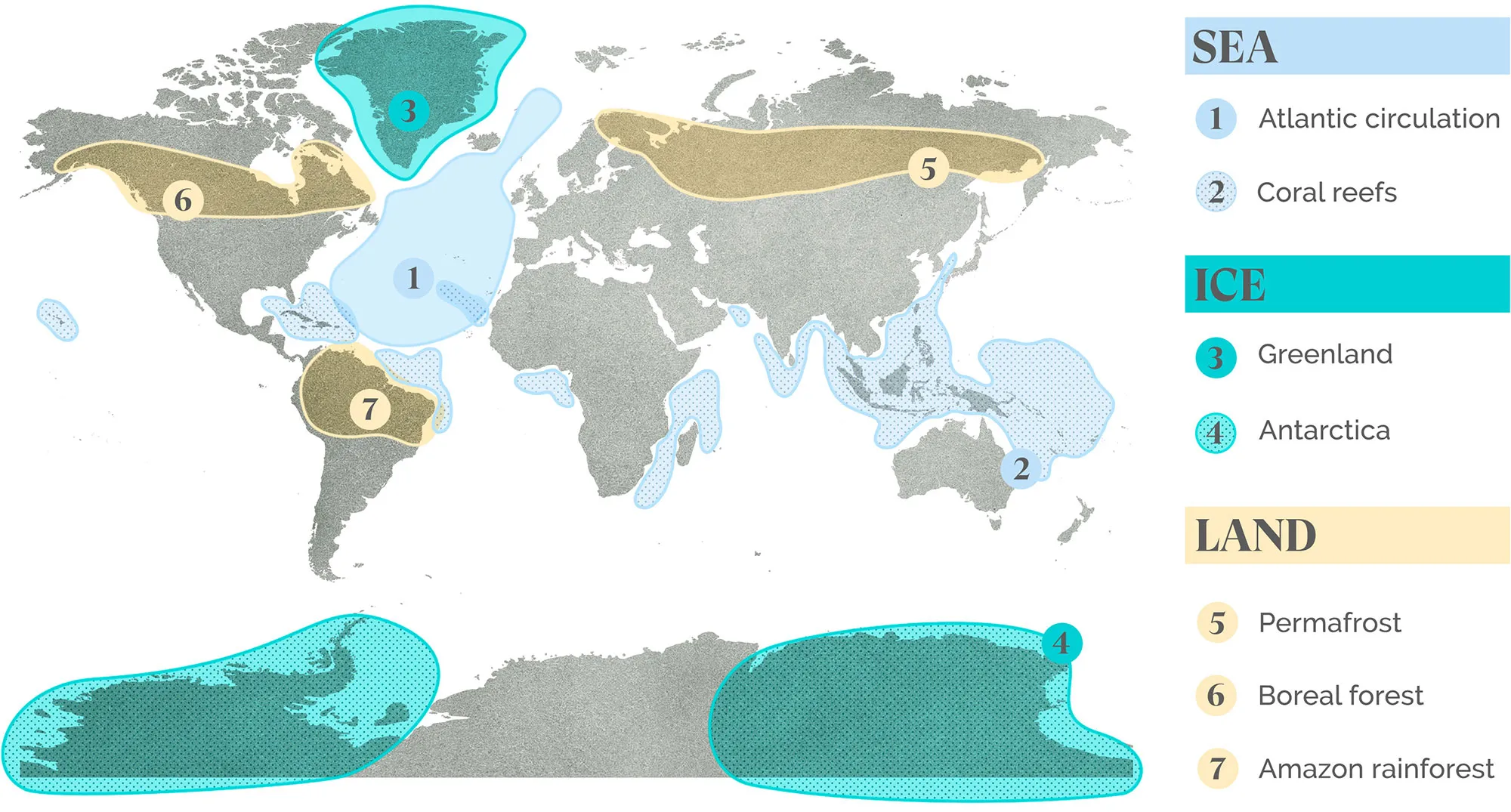
Model
A simplified representation of structures, relationships, or processes
Emergent Properties
Characteristics of a system that appear when the individual system parts interact; the parts themselves do not have the characteristics
Resilience
A system’s ability to recover after a disturbance by avoiding tipping points and staying stable due to a balance of positive and negative feedback loops
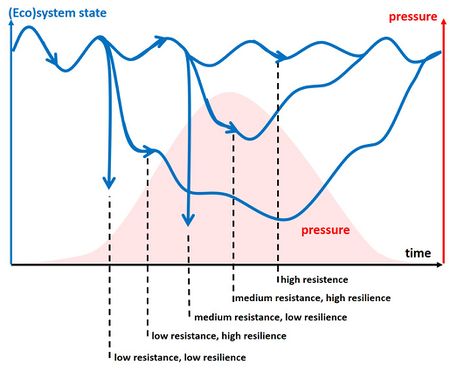
Regime Shifts
A large, persistent change in an ecosystem’s structure and function, moving it from one stable state to another
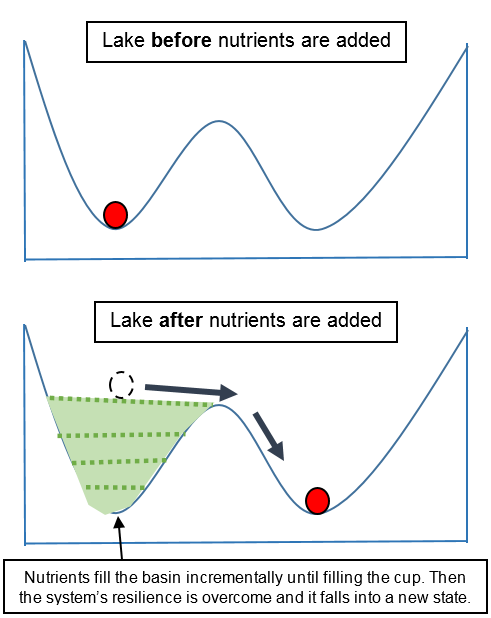
Alternative Stable States
Two or more distinct, non-transitory conditions that an ecosystem can exist in, even under the same external environmental conditions.